Halogenohydrin dehalogenation enzyme and encoding gene and vector and bacterial strain and application
A halohydrin dehalogenase, gene technology, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve the problems of poor self-degradation ability, carcinogenicity, high mutagenesis of xenobiotic halides
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] The total genomic DNA of Agromyces sp. CCTCC No: M 2012299 was extracted with a rapid nucleic acid extractor, and PCR was performed under the action of primer 1 (ATGMGNATCGCCCTCGTGACTC) and primer 2 (TTAGGGCAGATAGCC ACCG) using the genomic DNA as a template Amplify.
[0048] The amount of each component in the PCR reaction system (total volume 100 μL): 10×Pfu DNA Polymerase Buffer 10 μL (Mg 2+ ), 0.5 μL of 10 mM dNTP mixture (2.5 mM each of dATP, dCTP, dGTP, and dTTP), 0.5 μL of each cloning primer 1 and primer 2 at a concentration of 50 μM, 1 μL of genomic DNA, 1 μL of Pfu Taq DNA Polymerase, and 86.5 μL of nucleic acid-free water.
[0049] Using Biorad’s PCR instrument, the PCR reaction conditions were: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 3 minutes, then entering into a temperature cycle of 94°C for 30 s, 60°C for 30 s, and 72°C for 1.5 min, a total of 30 cycles, and finally extending at 72°C for 10 min, with a termination temperature of 8 ℃.
[0050] Take 10 μL of the PCR...
Embodiment 2
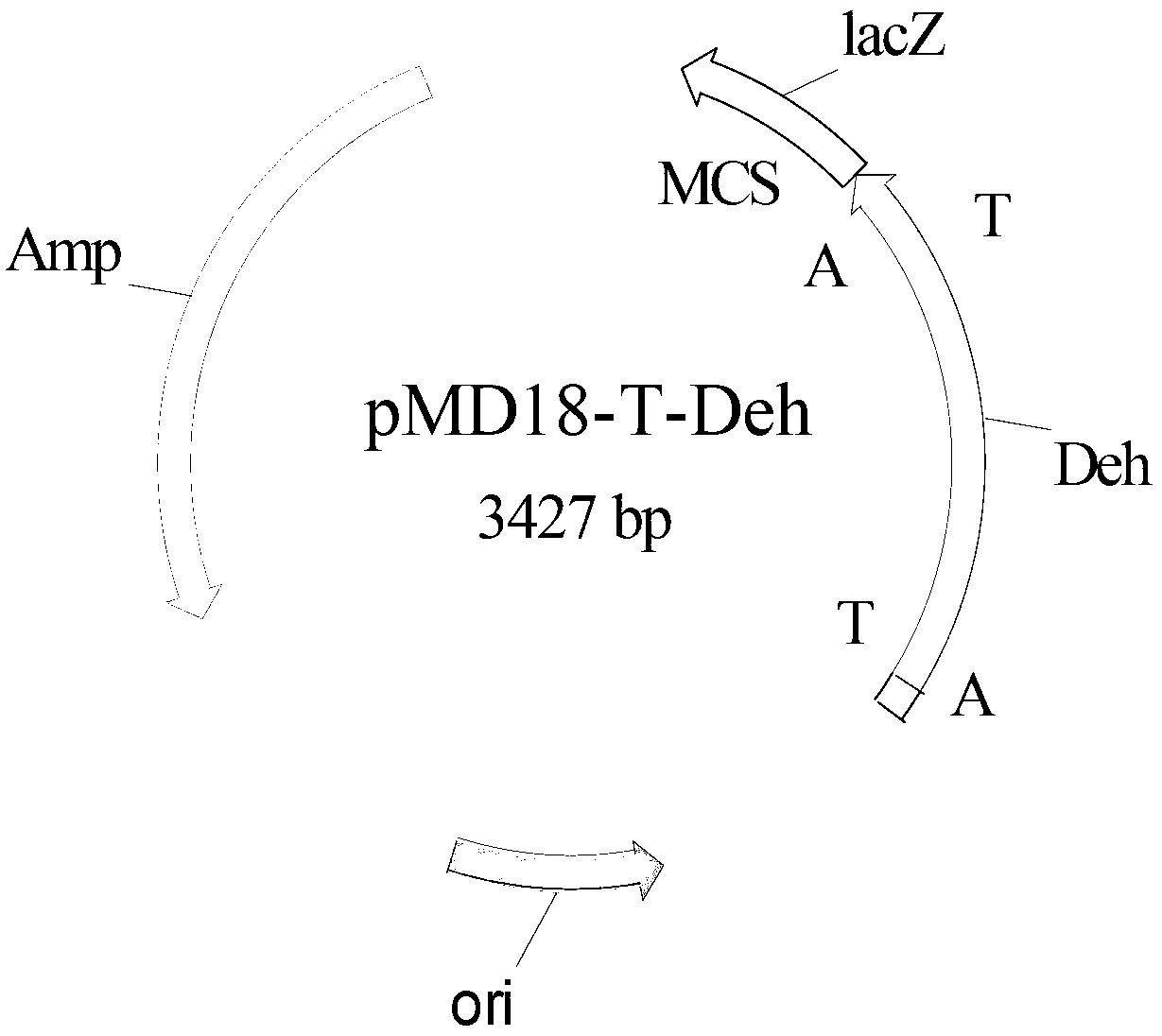
[0052] Design primer 3 according to embodiment 1 analysis result (CGC CATATG CGCATCGCCCTC GTGACTC) and Primer 4 (CCG CTCGAG TTAGGGCAGATAGCCACCG), and NdeI and XhoI restriction enzyme sites were introduced into primer 3 and primer 4, respectively. Initiated by primer 4 and primer 4, high-fidelity Pfu DNA polymerase (fermentas) was used to amplify to obtain a 735bp halohydrin dehalogenase gene fragment (SEQ ID NO: 1), which was sequenced using Nde I and Treat the amplified fragment with XhoI restriction endonuclease (fermentas), and use T4 DNA ligase (TaKaRa) to connect the fragment with the commercial vector pET28b treated with the same restriction endonuclease to construct the expression vector pET28b - Deh. The constructed intracellular expression vector pET28b-Deh was electrotransformed into Escherichia coli BL21 (Invitrogen), plated and cultured overnight at 37°C, and clones were randomly selected to extract plasmids for enzyme digestion identification. The identificatio...
Embodiment 3
[0054] The recombinant Escherichia coli BL21 / pET28b-Deh containing the intracellular expression recombinant plasmid pET28b-Deh after verification in Example 2 was cultured with LB liquid medium containing 50 μg / ml kanamycin resistance for 12 hours, and then treated with 1% The inoculum amount (v / v) was inoculated into fresh LB liquid medium containing 50 μg / ml kanamycin resistance, and cultivated to the cell concentration OD 600 About 0.6, then add IPTG with a final concentration of 0.5mM to the LB liquid medium, induce culture for 10 hours, centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes at 4°C, and collect the bacterial cells containing the recombinant halohydrin dehalogenase.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com