Method for reducing metal secondary electron yield by utilizing regular array structure
A technology of secondary electron emission and array structure, which is applied in the direction of microstructure technology, microstructure device, and manufacturing microstructure device, etc. It can solve the problem of deterioration of electromagnetic wave transmission characteristics of microwave devices, increase of microwave loss, and failure of device or system performance indicators to meet requirements etc. to achieve the effect of reducing the secondary electron emission coefficient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
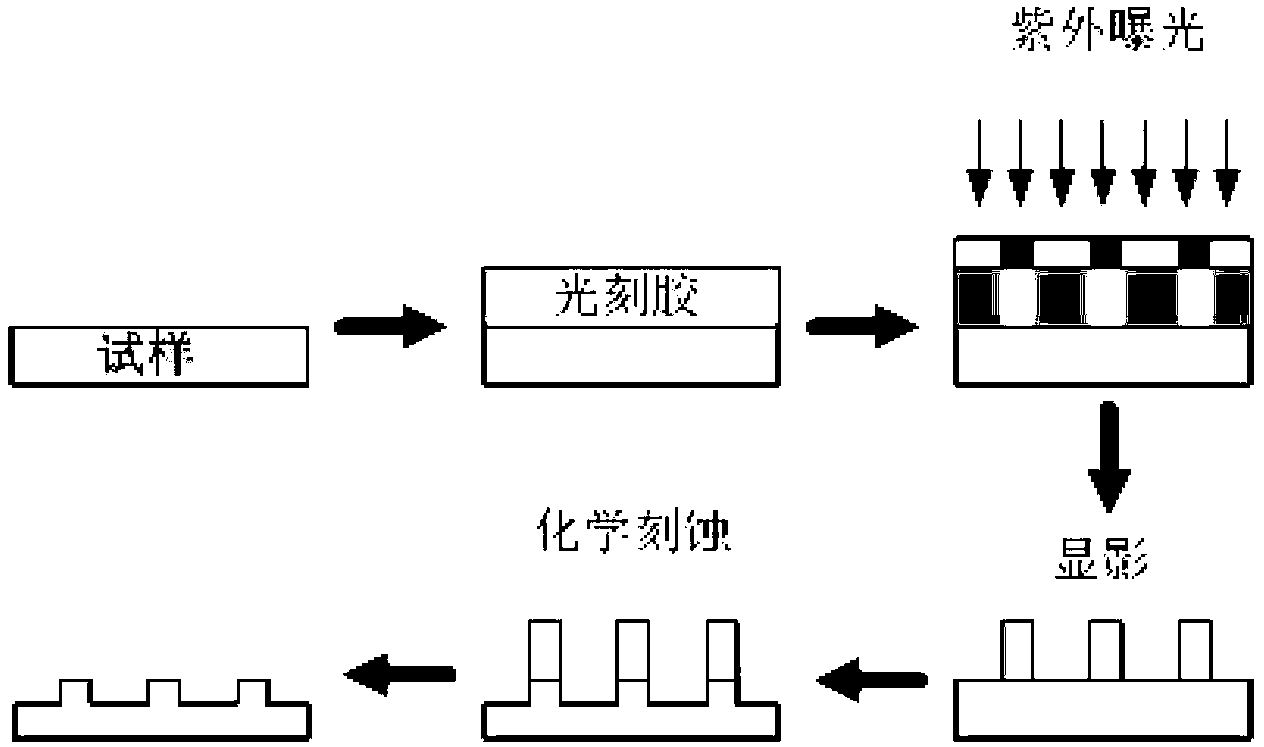
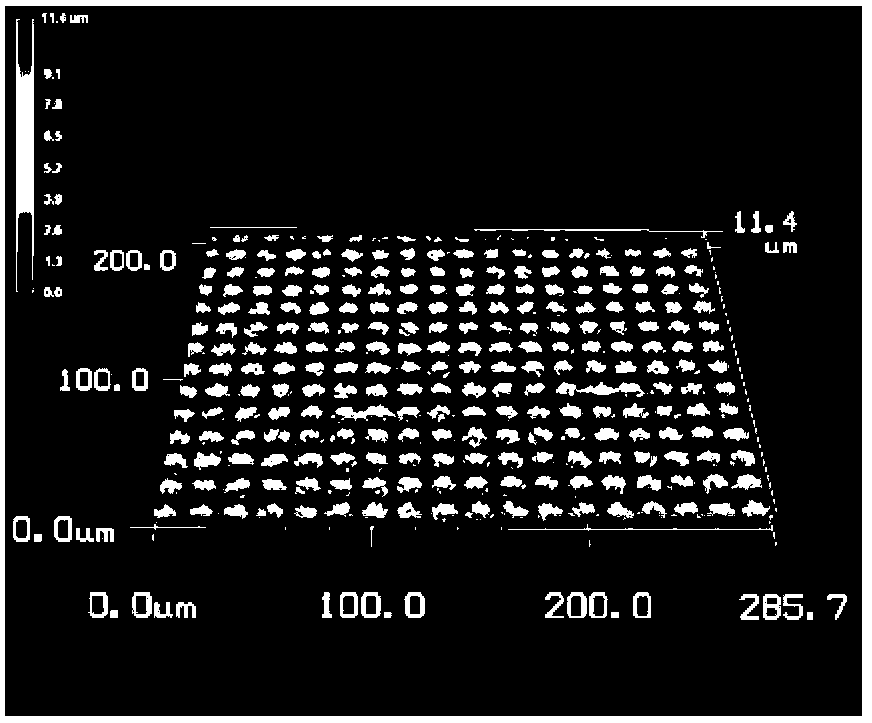
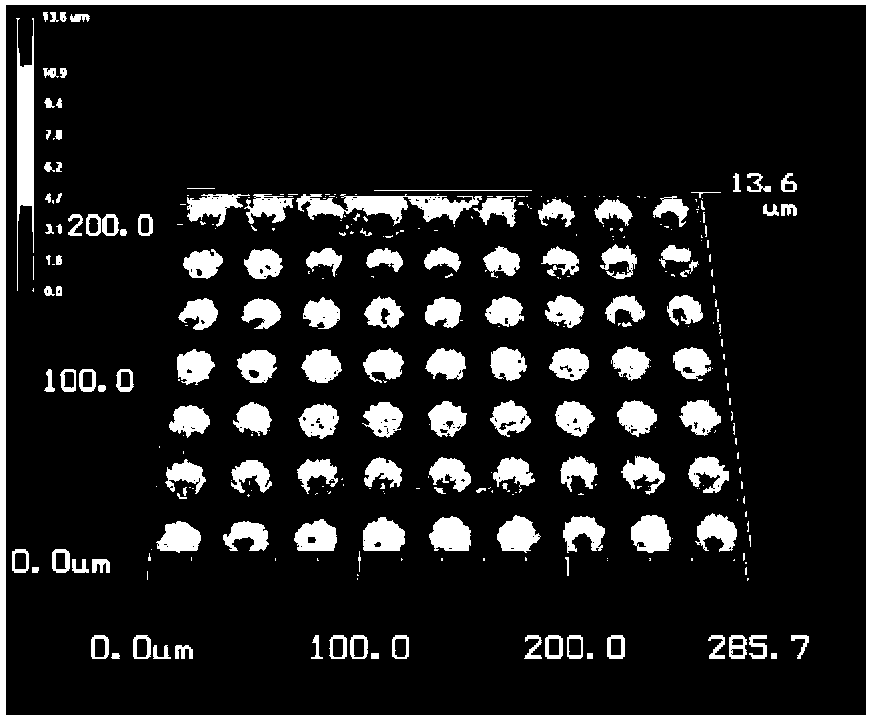
[0035] The process of a typical micron-scale array structure on a metal surface is as follows: figure 1 shown.
[0036] This patent proposes a method for effectively suppressing the secondary electron emission coefficient of the metal surface. This method uses a typical semiconductor photolithography process to prepare micron-scale array structures on the surface of common metals, thereby achieving the purpose of suppressing SEY. The method mainly includes the following processing steps: Ultrasonic cleaning of the metal sample to be treated with absolute ethanol and deionized water to remove surface contamination; spin coating of the sample at a certain rotation speed (according to the required array pattern and mask Plate parameters determine whether to use positive photoresist or negative photoresist); bake the sample after coating at a certain temperature for a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com