Construction method of genetic engineering strains for improving quantity of soybean nodules
The technology of a genetically engineered strain and a construction method is applied in the field of constructing genetically engineered strains, which can solve the problems of small increase in soybean yield of soybean plants, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0012] Specific embodiment one: the construction method of the genetically engineered bacterial strain that this embodiment improves soybean nodulation quantity, carries out according to the following steps:
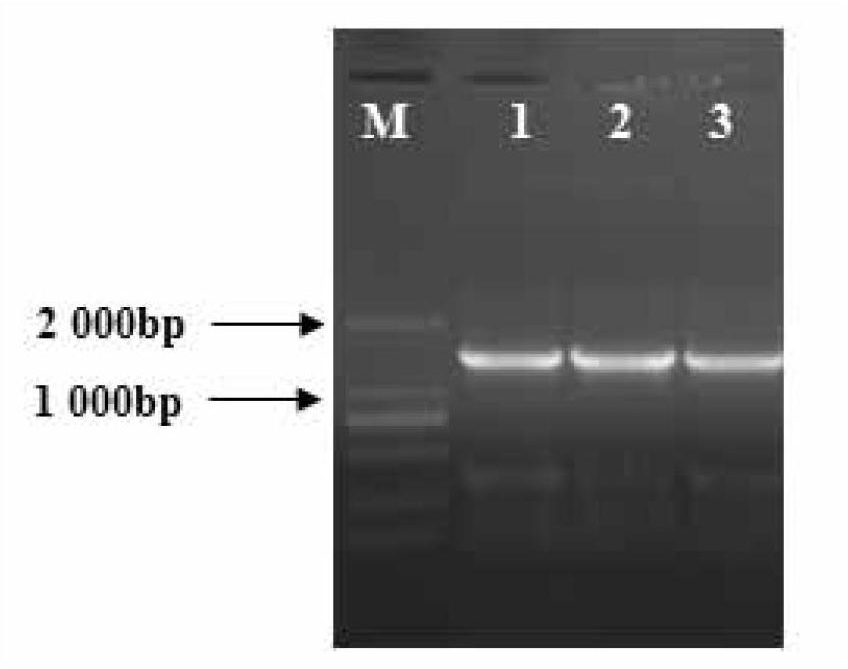
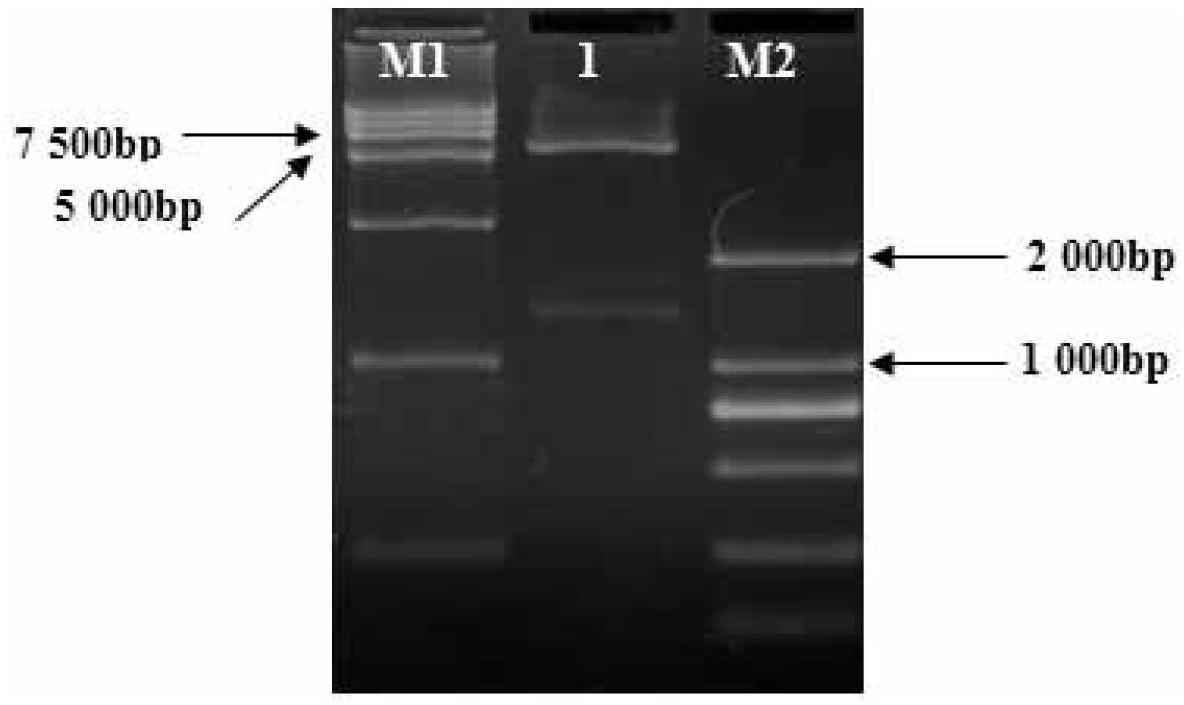
[0013] 1. Activate and expand the culture of S. fischeri 15067, and then extract the genomic DNA of S. The amplified product was obtained, and the amplified product was detected by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, and then purified by a gel recovery kit to obtain the target gene dctA; 3. Sequencing and identification of the target gene dctA; 4. The target gene dctA and recombinant plasmid vector pET-P lac Carry out double enzyme digestion with NdeI and BamHI respectively, and digest the target gene dctA and the vector pET-P after digestion lac Ligated to obtain the recombinant vector pET-P lac -dctA; 5. Using the recombinant vector pET-P lac -dctA is used as a template for PCR amplification to construct P lac -dctA-T7 fragment, then P lac - The dctA-T7 fragment and t...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0045] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the reaction system of PCR amplification in step 2 is as follows:
[0046]
[0047] PCR amplification conditions were: denaturation at 94°C for 5 min, denaturation at 94°C for 30 s, annealing at 54°C for 30 s, extension at 72°C for 90 s, a total of 35 cycles, extension at 72°C for 7 min, and incubation at 4°C. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0048] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the double-enzyme digestion reaction system of the target gene dctA in step four is as follows:
[0049]
[0050] Enzyme digestion reaction conditions: keep warm in a water bath at 37°C for 3 hours. Others are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com