Improved combination structure and combining method of baseplate and heat dissipating structure
A heat dissipation structure and substrate technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, electrical solid devices, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as difficult welding, and achieve the effect of improving the overall heat transfer coefficient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Example 1: Ceramic Substrate
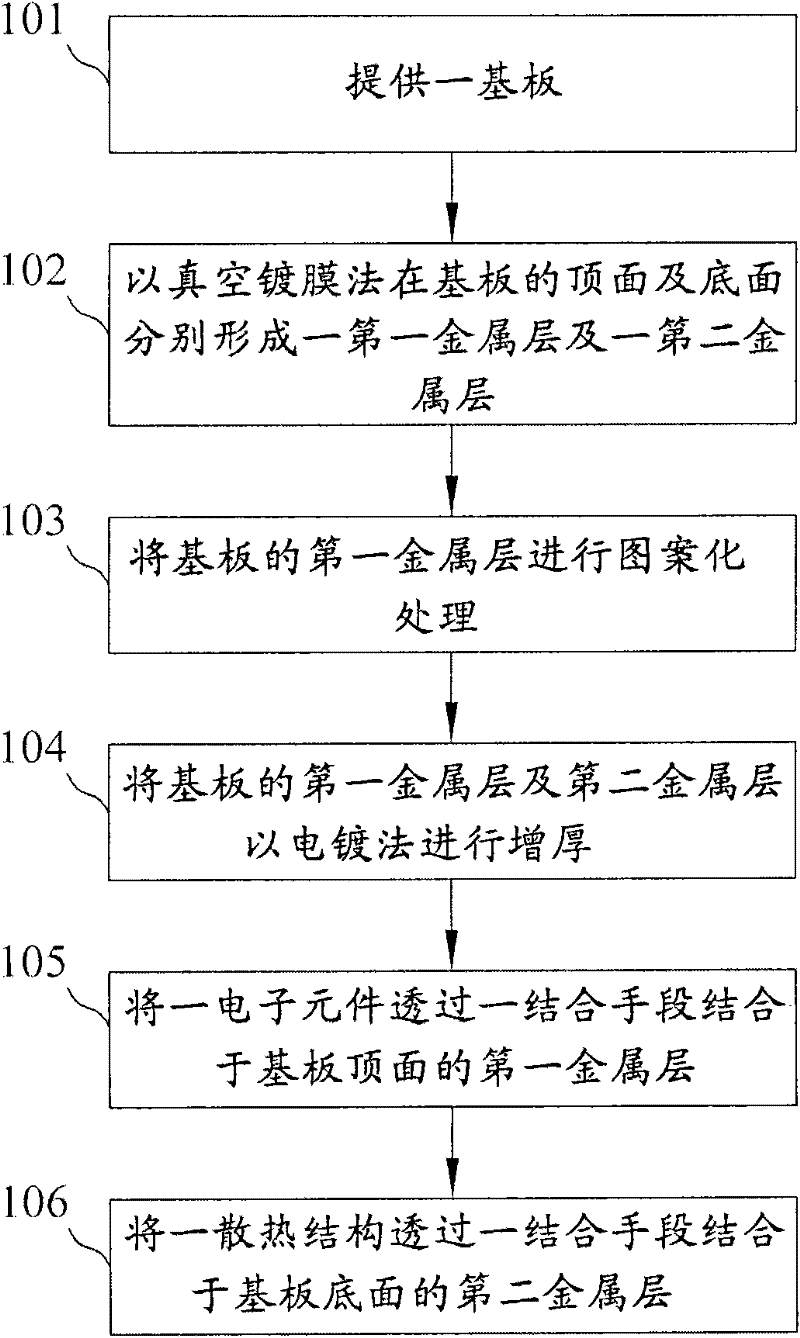
[0053] see figure 1 , is a flow block diagram showing the combination method of the substrate and the heat dissipation structure in this embodiment. and can also refer to Figure 2A ~ Figure 2F , is a diagram showing the various steps. The method of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
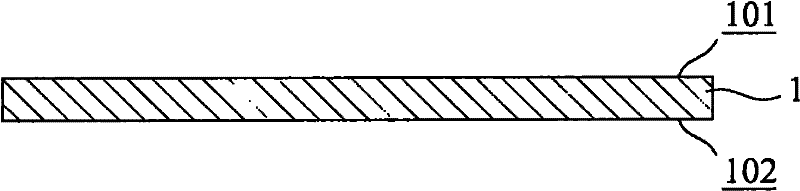
[0054] A substrate 1 is provided (step 101). The substrate 1 in this embodiment is a ceramic substrate, for example, it can be a commonly used ceramic substrate such as an alumina substrate, an aluminum nitride substrate, a silicon carbide substrate or a beryllium oxide substrate (see Figure 2A ).
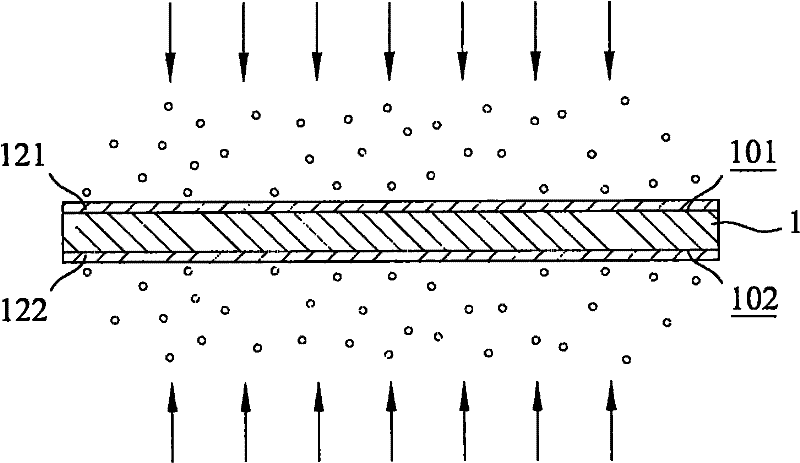
[0055] A first metal layer 121 and a second metal layer 122 are respectively formed on the top surface 101 and the bottom surface 102 of the substrate 1 by a vacuum coating method (step 102 ). The vacuum coating method in this step can include traditional vacuum sputtering, low-temperature vacuum sputtering, batch vacuum sputtering and c...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Embodiment 2: Aluminum substrate (1)
[0062] see image 3, is a flow block diagram showing the combination method of the substrate and the heat dissipation structure in this embodiment. and can also refer to Figure 4A ~ Figure 4F , is a diagram showing the various steps. The method of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0063] A substrate 2 is provided (step 201). The substrate 2 in this embodiment is an aluminum substrate, because aluminum has high thermal conductivity and good heat dissipation, it can effectively export internal heat (see Figure 4A ).
[0064] A first metal layer 211 and a second metal layer 212 are respectively formed on the top surface 201 and the bottom surface 202 of the substrate 2 by vacuum coating (step 202 ). Same as the first embodiment, the vacuum coating method in this step can include traditional vacuum sputtering, low-temperature vacuum sputtering, batch vacuum sputtering and continuous vacuum sputtering, etc....
Embodiment 3
[0070] Embodiment 3: Aluminum substrate (2)
[0071] see Figure 5 , is a flow block diagram showing the combination method of the substrate and the heat dissipation structure in this embodiment. and can also refer to Figure 5 A~ Figure 5 F, is a schematic diagram showing the various steps. Since this embodiment is another embodiment using an aluminum substrate, the details of its implementation steps are mostly similar to those of the second embodiment, and the similarities will not be repeated, and only the key points will be described. The method of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0072] A substrate 3 is provided (step 301). With embodiment 2, the substrate 3 in the present embodiment is an aluminum substrate (see Figure 5 A).
[0073] Form an insulating layer 322 at a predetermined position on the top surface 301 of the substrate 3 (step 302), see Figure 5 b.
[0074] Partially form a first metal layer 311 and a second metal layer 312 a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com