Relieved tooth and preparation method thereof
A technology of shovel teeth and mass percentage, applied in the field of shovel teeth for loaders and their preparation, can solve the problems of complex smelting process, unsatisfactory wear resistance of materials, and high cost of raw materials and heat treatment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
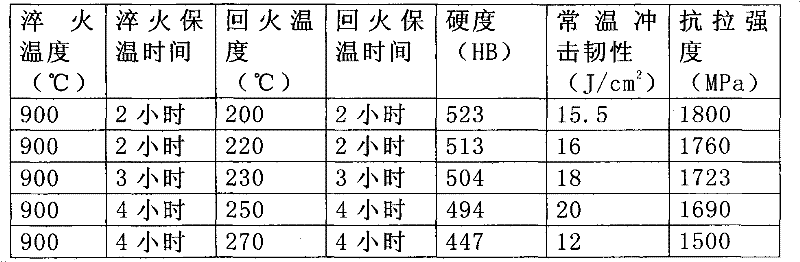
[0012] The composition and mass percentage of the shovel teeth in this embodiment are: C: 0.29%, Mn: 0.90%, Si: 0.8%, Cr: 1.40%, B: 0.001%, Al: 0.02%, and the balance is Fe. At the same time, due to the adverse effects of S and P elements on the mechanical properties of the shovel teeth, it is necessary to ensure that the mass percentage of the S element is less than or equal to 0.025%, and the mass percentage of the P element is less than or equal to 0.025%.
[0013] As the basic element of alloy steel, C element forms carbides with Fe and Mn, which improves the hardness and wear resistance of steel, and plays an important role in solid solution strengthening.
[0014] Although Mn element is an element that promotes the formation of austenite in alloy steel, the content of Mn element is usually higher, above 10%. However, under the premise of ensuring the austenite structure, with the decrease of the content of Mn element, although the stability of austenite decreases, the pr...
Embodiment 2
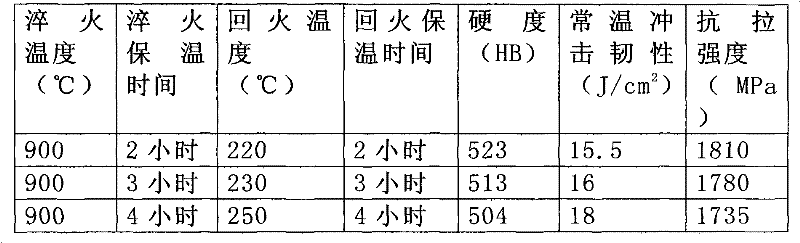
[0027] The composition and mass percentage of the shovel teeth in this embodiment are: C: 0.31%, Mn: 1.2%, Si: 1.0%, Cr: 1.50%, B: 0.003%, Al: 0.03%, and the balance is Fe. At the same time, due to the adverse effects of S and P elements on the mechanical properties of the shovel teeth, it is necessary to ensure that the mass percentage of the S element is less than or equal to 0.025%, and the mass percentage of the P element is less than or equal to 0.025%.
[0028] In this embodiment, the shovel teeth go through a casting process and a heat treatment process. The heat treatment process adopts the same process conditions as in Example 1, that is, quenching after heating up to 900 ° C and tempering at 220 ° C to 250 ° C after holding for 2-4 hours Temper at low temperature, and keep warm for 2-4 hours after tempering. Test its mechanical properties as shown in Table 2:
[0029] Table 2
[0030]
[0031] After adopting the ratio of this embodiment, the mechanical propertie...
Embodiment 3
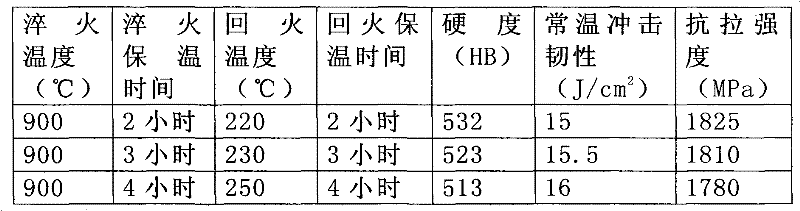
[0033] The composition and mass percentage of the shovel teeth in this embodiment are: C: 0.33%, Mn: 1.40%, Si: 1.20%, Cr: 1.70%, B: 0.005%, Al: 0.06%, and the balance is Fe. At the same time, due to the adverse effects of S and P elements on the mechanical properties of the shovel teeth, it is necessary to ensure that the mass percentage of the S element is less than or equal to 0.025%, and the mass percentage of the P element is less than or equal to 0.025%.
[0034] In this embodiment, the shovel teeth go through a casting process and a heat treatment process. The heat treatment process adopts the same process conditions as in Example 1, that is, quenching after heating up to 900 ° C and tempering at 220 ° C to 250 ° C after holding for 2-4 hours Temper at low temperature, and keep warm for 2-4 hours after tempering. Test its mechanical properties as shown in Table 3:
[0035] table 3
[0036]
[0037] After adopting the ratio of this embodiment, the mechanical propert...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com