A method for photocatalytic purification of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid in water under simulated sunlight
A technology of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid and sunlight, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve the problems that PFOS degradation is difficult to play a role, photocatalytic oxidation is difficult to reduce PFOS, etc., and achieves high-efficiency photocatalytic activity, low cost of raw materials, and simple preparation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0031] Wherein the preparation step of photocatalyst comprises:
[0032] 1) dissolving sodium vanadate, bismuth nitrate pentahydrate and a nonionic surfactant as a dispersant in deionized water to form a turbid composite sol;
[0033] 2) The composite sol obtained in step 1) was left to stand for 3 hours, then transferred to a synthetic kettle with a polytetrafluoroethylene liner, crystallized at 160°C for 24 hours, and the precipitate was taken out, washed with deionized water for 3 times drying at room temperature to obtain catalyst precursor particles;
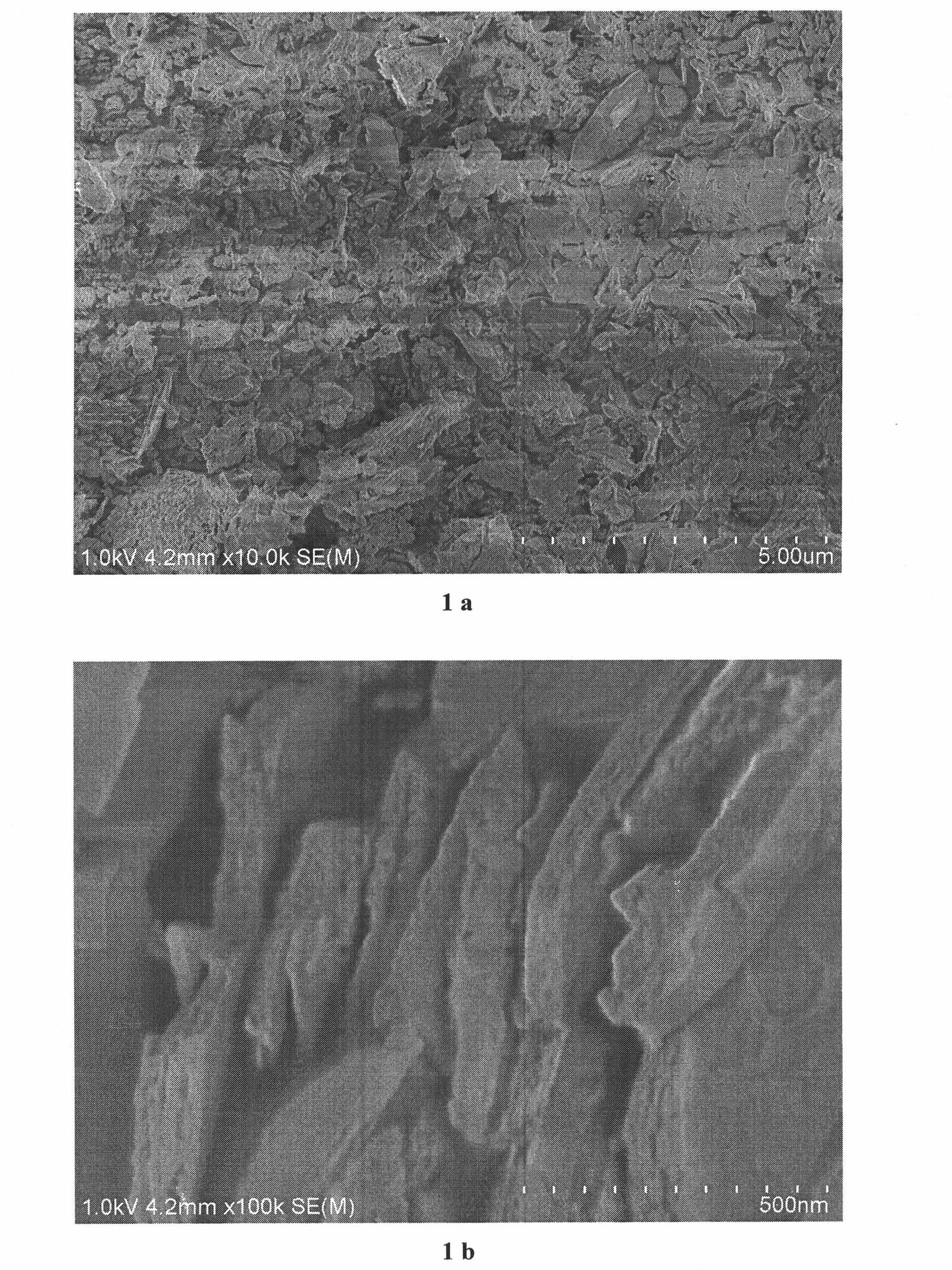
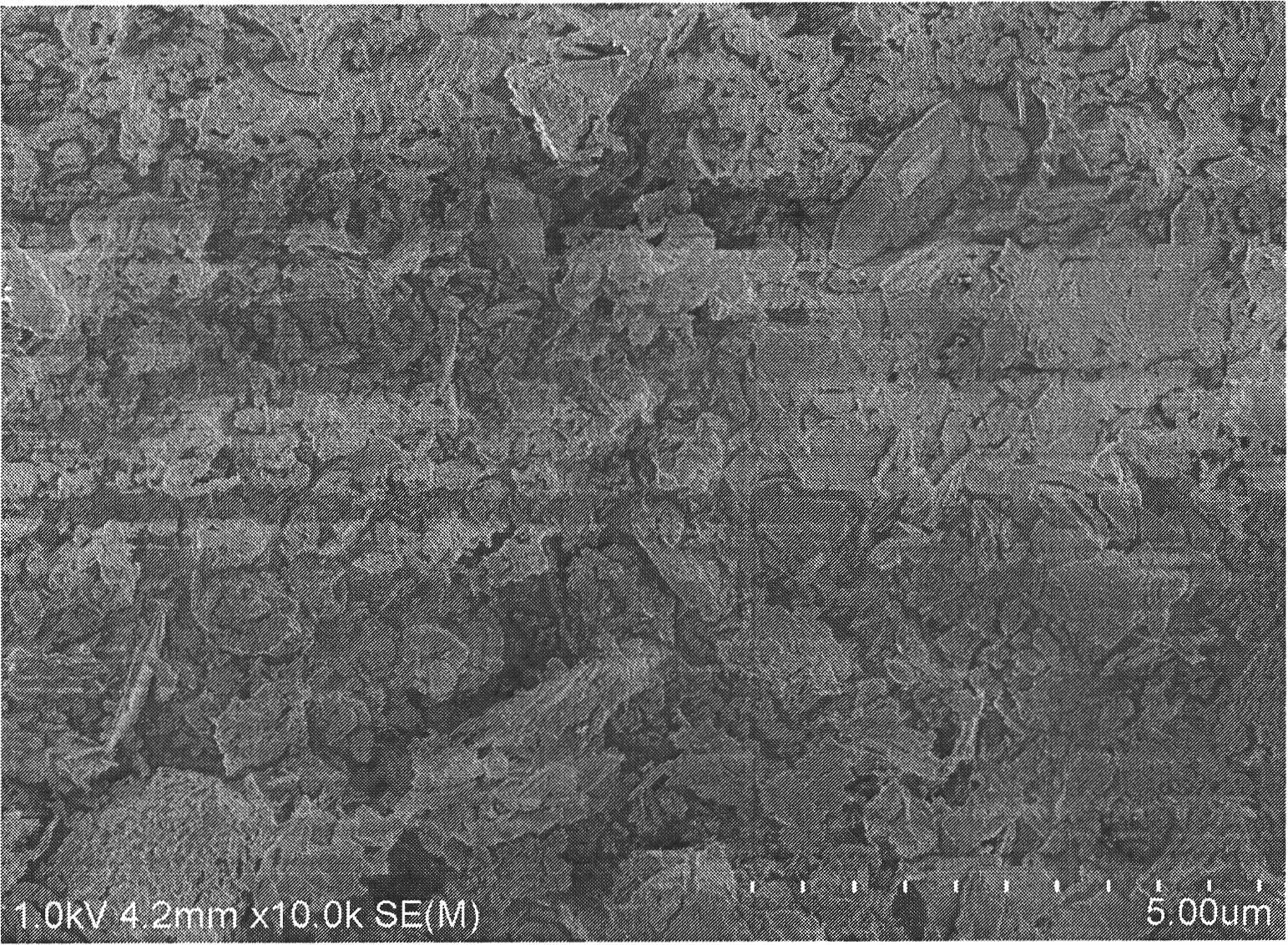
[0034] 3) Calcining the catalyst precursor particles obtained in step 2) in an air atmosphere at 550° C. for 5 hours to prepare vanadium-doped bismuth oxide particles, which are ground for later use;
[0035] The steps of using photocatalyst to catalytically degrade perfluorooctane sulfonic acid in water under simulated sunlight include:
[0036] a) 100 milliliters of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid aqueous solution with a co...
Embodiment 1
[0046] Weigh 1.61 g of nonionic surfactant F127 and dissolve it in 28.8 ml of deionized water, stir continuously until completely dissolved, then slowly add 41.2 g of bismuth nitrate pentahydrate and 1.84 g of sodium vanadate, and vigorously stir to form a composite sol. After the composite sol was left standing for 3 hours, it was transferred to a synthesis kettle lined with polytetrafluoroethylene, and crystallized at 160°C for 24 hours. After washing three times, drying at room temperature (25° C.), catalyst precursor particles can be obtained. The obtained precursor particles were calcined in an air atmosphere at 550° C. for 5 hours to prepare vanadium-doped bismuth oxide visible light catalyst particles, which were ground in a mortar and placed in a desiccator for later use.
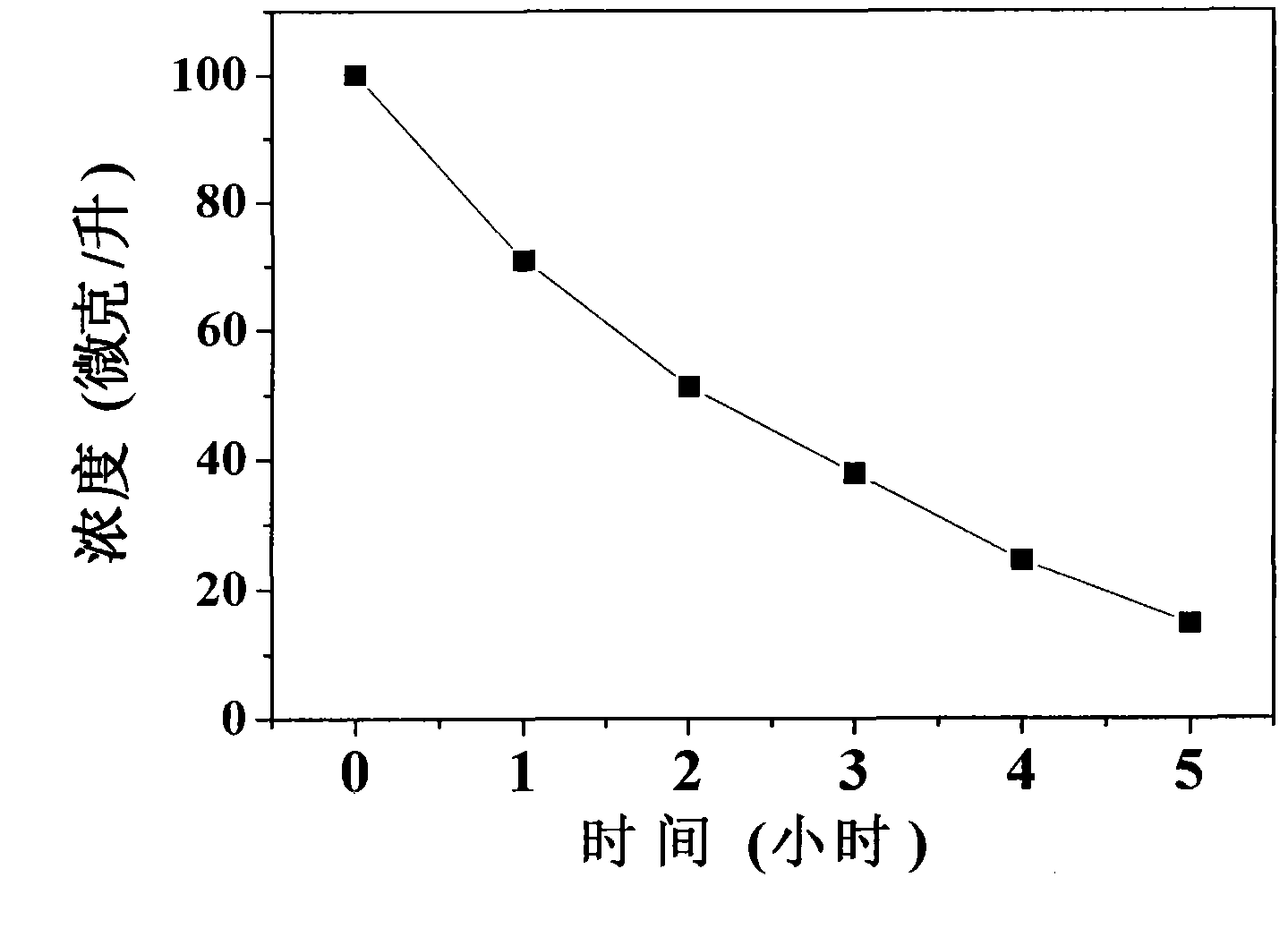
[0047] Measure 100 ml of PFOS solution with a concentration of 100 μg / L and place it in a 150 ml polypropylene beaker, and add 50 mg of vanadium-doped bismuth oxide visible light catalyst. The mixe...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The preparation steps of the photocatalyst are the same as in Example 1.
[0050] 100 ml of PFOS solution with a concentration of 10 μg / L was measured and placed in a 150 ml polypropylene beaker, and 20 mg of vanadium-doped bismuth oxide visible light catalyst was added. The mixed system was placed on a magnetic stirrer to start stirring (600 rpm), and kept away from light for 30 minutes to achieve the adsorption-desorption equilibrium of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid on the catalyst surface. Then move into the simulated solar photocatalytic activity evaluation reactor, turn on the xenon lamp light source (LITC175W 300W, Philips, Netherlands) to react at 30°C and 600 rpm, take samples regularly and use the liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry system to analyze the PFOS was determined (UltiMate3000, Dionex, USA, equipped with AB API3200 mass spectrometer). The method can remove 89% of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid in water within 5 hours.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com