Method for detecting protein content
A protein content and detection method technology, applied in the field of protein content detection, can solve the problems of the influence of the absorbance value of protein samples, inconvenient protein content determination, poor tolerance of surfactants, etc., and achieves low measurement cost, high speed and good repeatability. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
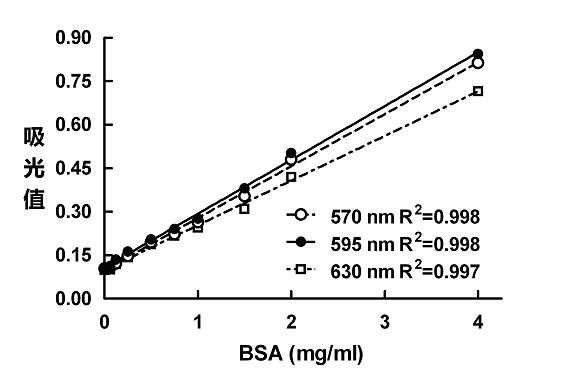
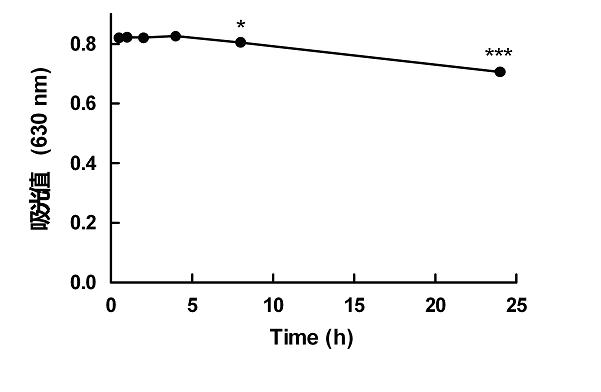
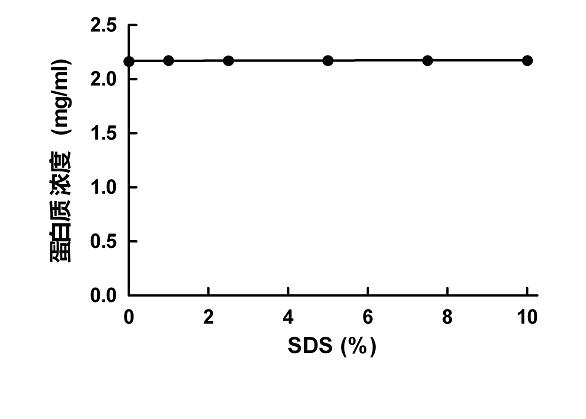
[0050] [Example 1] BSA standard curve and chromogenic product stability experiment with wavelengths of 570, 595 and 630 nm
[0051] 1) Preparation of standard samples
[0052] Weigh bovine serum albumin (BSA) and dissolve it in distilled water to adjust the final concentration to 4 mg / mL, which is the prepared standard sample.
[0053] 2) Reagent preparation
[0054] Reagent ①:
[0055] Sodium carbonate 1.89 mol / L
[0056] Sodium hydroxide 1.00 mol / L
[0057] Reagent ②:
[0060] SDS 2.5%
[0061] When preparing, it is necessary to mix sodium tartrate and copper sulfate first and then add SDS.
[0062] When in use, reagent ① and reagent ② are mixed at a ratio of 50 / 1 and prepared for immediate use.
[0063] Reagent ③:
[0064] Dilute the 2 N Folinol solution, then adjust the pH to 1, and finally make it 10 times the volume.
[0065] 3) Preparation of protein concentration st...
Embodiment 2
[0070] [Example 2] Determination of protein content in mammalian cells under surfactant interference
[0071] 1) Preparation of standard samples
[0072] Weigh bovine serum albumin (BSA) and dissolve it in distilled water to adjust the final concentration to 4 mg / mL, which is the prepared standard sample.
[0073] 2) Reagent preparation
[0074] Reagent ①
[0075] Sodium carbonate 1.89 mol / L
[0076] Sodium hydroxide 1.00 mol / L
[0077] Reagent ②
[0078] Sodium tartrate 0.25 %
[0079] Copper sulfate 0.125 %
[0080] SDS 2.5%
[0081] When preparing, it is necessary to mix sodium tartrate and copper sulfate first and then add SDS.
[0082] When in use, reagent ① and reagent ② are mixed at a ratio of 50 / 1 and prepared for immediate use.
[0083] Reagent ③
[0084] Dilute the 2 N Folinol solution, then adjust the pH to 1, and finally make it 10 times the volume.
[0085] 3) Mammalian cell culture and cell protein extraction
[0086] will be 1.0X10 6 Human pr...
Embodiment 3
[0097] [Example 3] Determination of mammalian cell protein content under reducing agent interference
[0098] 1) Preparation of standard samples
[0099] Weigh bovine serum albumin (BSA) and dissolve it in distilled water to adjust the final concentration to 4 mg / mL, which is the prepared standard sample.
[0100] 2) Reagent preparation
[0101] Reagent ①
[0102] Sodium carbonate 1.89 mol / L
[0103] Sodium hydroxide 1.00 mol / L
[0104] Reagent ②
[0105] Sodium tartrate 0.25 %
[0106] Copper sulfate 0.125 %
[0107] SDS 2.5%
[0108] When preparing, it is necessary to mix sodium tartrate and copper sulfate first and then add SDS.
[0109] When in use, reagent ① and reagent ② are mixed at a ratio of 50 / 1 and prepared for immediate use.
[0110] Reagent ③
[0111] Dilute the 2 N Folinol solution, then adjust the pH to 1, and finally make it 10 times the volume.
[0112] 3) Mammalian cell culture and whole protein extraction
[0113] will be 1.0X10 6 Human prostate ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com