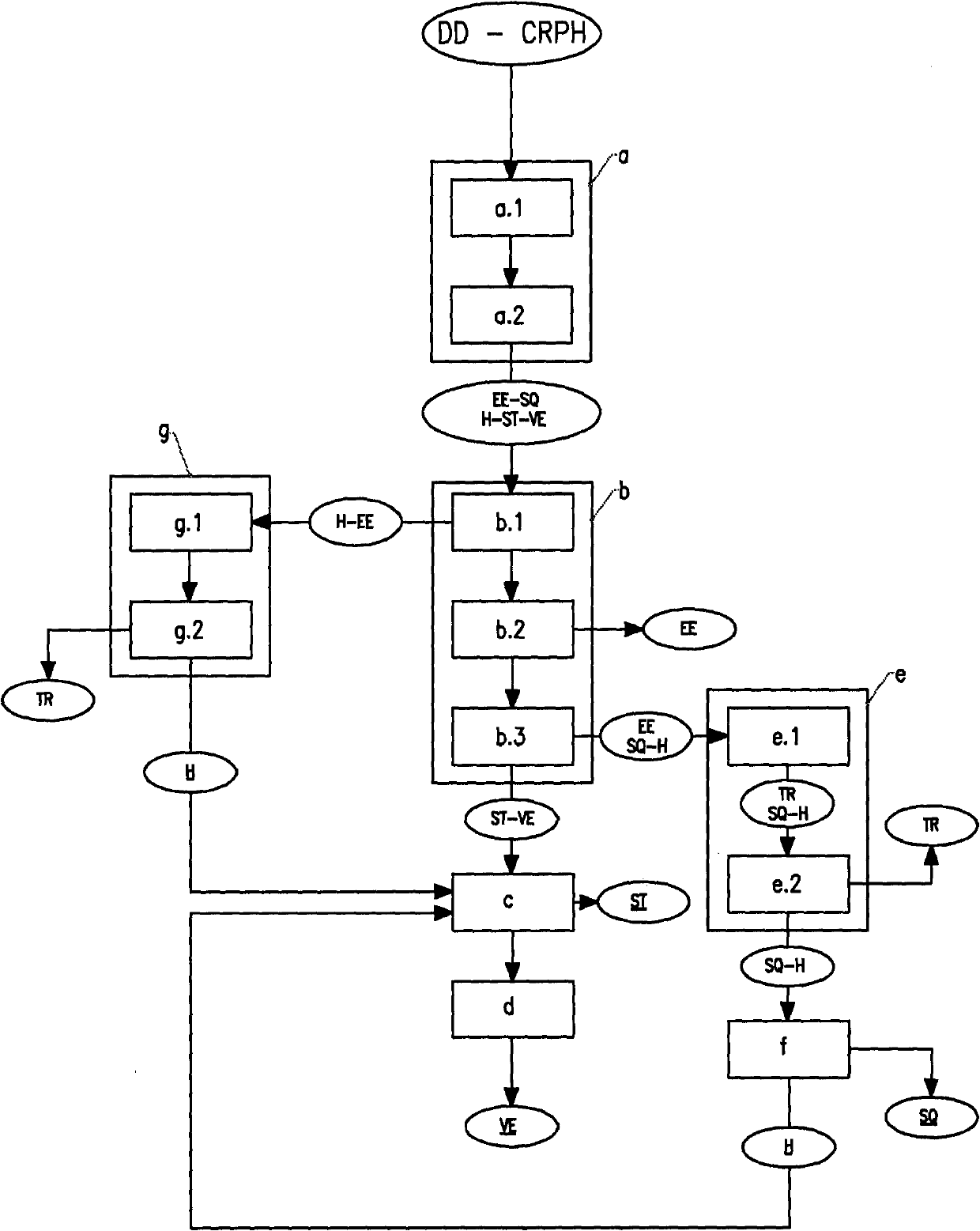
Process for the extraction of squalene, sterols and vitamin e contained in condensates of physical refining and/or in distillates of deodorization of plant oils
A technology of deodorization distillate and physical refining, applied in the fields of sterols, vitamin E and squalene
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0106] Example 1 - Esterification of a deodorized distillate of sunflower oil with bioethanol - step a).
[0107] In a 5 liter round bottom flask, DD 1.000 g of oleic sunflower oil (tournesol oléique) is introduced, which has the following composition:
[0108] Saponifiable fraction: free fatty acid: 38%, triglyceride: 25.8%, fatty acid ester: 7%;
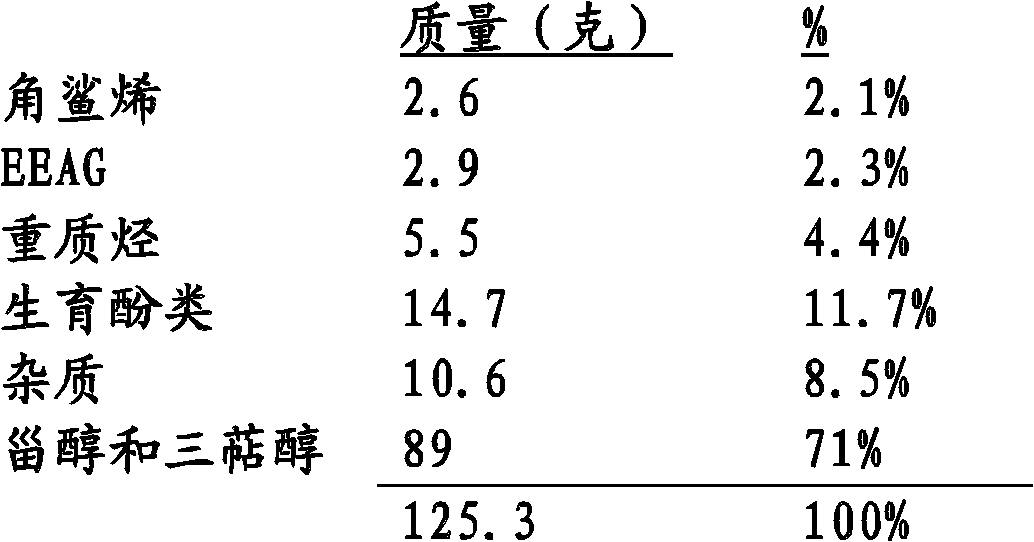
[0109] • Unsaponifiable fraction: 29.2%. The unsaponifiable fraction consisted of 38.6% sterols and triterpene alcohols, 19.9% squalene, 6.5% vitamin E, 29.8% non-squalene hydrocarbons, 5.2% unidentified products and impurities.
[0110]The condensate was mixed with 620 g of absolute ethanol, ie ethanol in a 10-fold molar excess relative to the fatty acid. 1 g of concentrated sulfuric acid was added, ie 0.1% relative to the mass of the condensate added. The stirred round bottom flask was purged several times with nitrogen and then heated to 90°C. The reaction was carried out under reflux of ethanol for 4 hours. After cooling...
Embodiment 2
[0111] Example 2 - Esterification of sunflower oil DD with bioethanol - step a).
[0112] The same sunflower oil DD 500 g as in Example 1 was introduced into a 1 liter autoclave. The condensate was mixed with 154.9 g of anhydrous bioethanol, ie a 5-fold molar excess of ethanol / fatty acid. 0.5 g of concentrated sulfuric acid was added, ie 0.1% relative to the mass of the condensate added. After purging several times with nitrogen, the reactor was gradually heated to 90° C. with stirring within 1 hour, a pressure of 2.5 bar was achieved. After cooling the reactor, the reaction medium is neutralized with 0.5 N sodium ethoxide solution by stirring for 30 minutes. The ethanol was then distilled at atmospheric pressure and then at the end of the distillation at a vacuum of 50 mbar and a temperature of 100° C. to remove the water of esterification. An anhydrous product with an acid number of 0.8 is obtained without isomerization of the squalene.
Embodiment 3
[0113] Example 3 - Ethanolysis of sunflower oil DD esterified with bioethanol - step a).
[0114] In a 5-liter round-bottomed flask, 1.000 g of the esterification product of Example 1, containing 25.8% of triglycerides and 11.2% of sterols in esterified form, corresponding to 1 mole of ester, were introduced. Add 20 moles of anhydrous bioethanol (20-fold molar excess), that is, 920 grams of bioethanol, in which 1% by weight of sodium is pre-dissolved, so as to generate sodium alkoxide in situ. The round bottom flask was then heated at 80° C. for 2 hours under reflux of ethanol with stirring. The sodium present in the form of sodium ethoxide was then neutralized by 0.5N sulfuric acid solution. The ethanol was distilled first at atmospheric pressure and then at a reduced pressure of 50 mbar. Sodium sulfate formed during neutralization was removed by washing with water. All glycerides, as well as pre-existing steroids, have been converted to ethyl esters, which results in effi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| flash point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flash point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com