Methods of treating non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (nash) using cysteamine products
A steatohepatitis, non-alcoholic technology, applied in the direction of medical preparations containing active ingredients, non-central analgesics, botanical equipment and methods, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0096] Enteric coated cysteamine preparation
[0097] International Publication No. WO 2007 / 089670 describes the administration of cysteamine to patients with cystinosis using a nasoenteric tube to determine the effectiveness of enteral administration for improvement in patients with cystinosis. WO 2007 / 089670 shows that enteral administration of cysteamine increases the rate of cysteamine absorption and increases plasma cysteamine levels. Enteral administration also reduces cystine levels within leukocytes. These results indicate that enteral administration of cysteamine is more effective than oral administration of cysteamine.
[0098] For more effective and easier administration, an enteric-coated formulation of cysteamine (Cystagon-EC) was established. Capsules (Mylan Laboratories Inc., PA, USA) were enteric coated using a Wurster coating unit model 600 with a 4 / 6" chamber. The coating material was Eudragit L30D-55 (Rohm GmbH & Co KG, Darmstadt, Germany ) and the EC co...
Embodiment 2
[0102] Administration of cysteamine to patients with fatty liver disease
[0103] Administration of cysteamine has been shown to reduce cystinosis symptoms by reducing levels of damaging cystine. To determine the role of cysteamine on fibrosis causing liver damage in patients with NASH, an open-label, nonrandomized pilot study of enteric-coated cysteamine in 12 children and adolescents with nonalcoholic fatty disease was conducted. Research.
[0104] Patients with a definitive diagnosis of NASH who had undergone lifestyle changes (such as diet and exercise) for at least 3 months were included in the study. Complete medical history and physical examination. Symptom scores designed for acid-digestive disease and previously used in children taking cysteamine were used. Blood was drawn for liver function tests, including liver transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, and gamma-GT. Blood was also drawn for complete blood count, ESR, CRP, fasting insulin and fasting lipid...
Embodiment 3
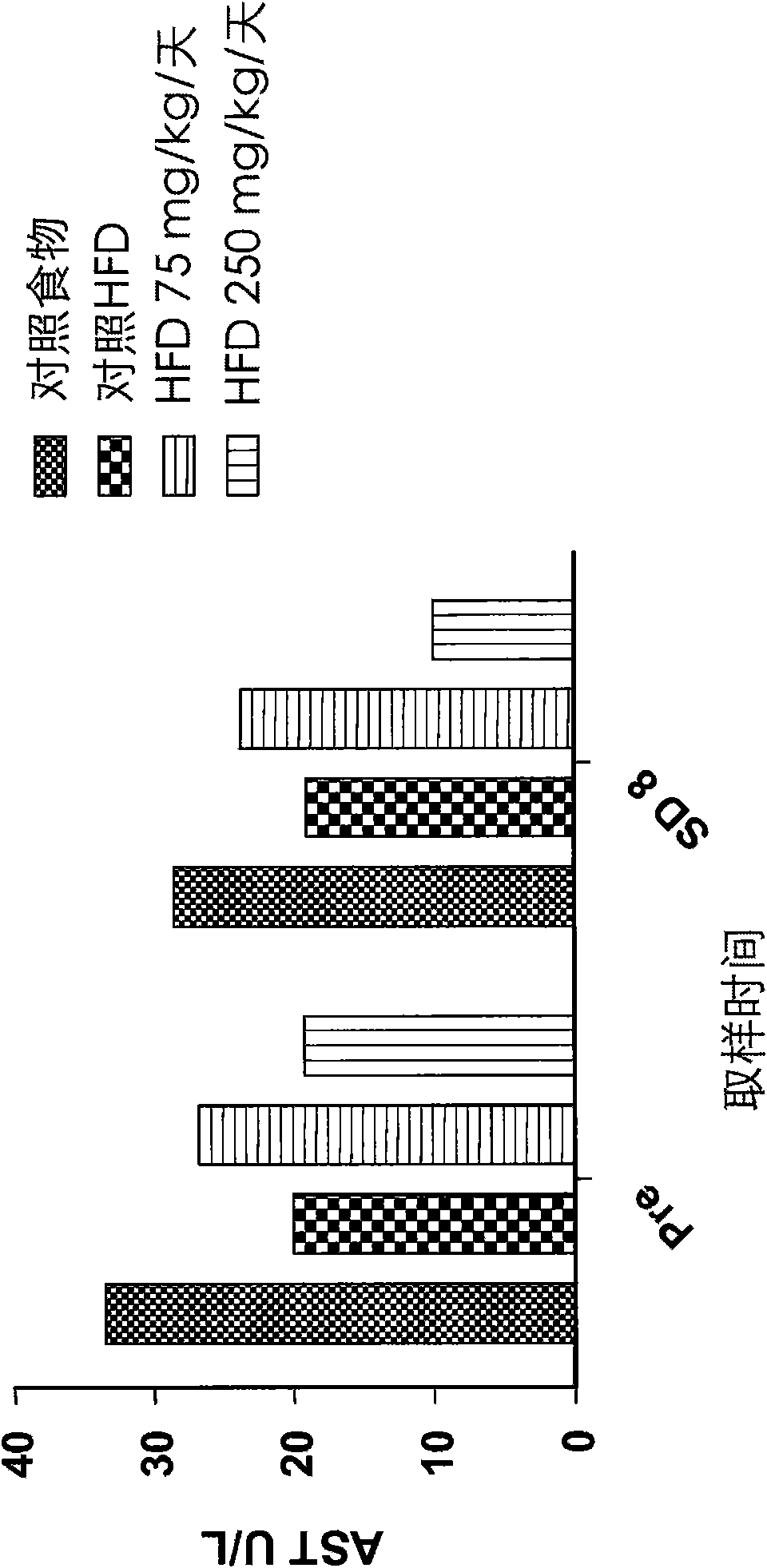
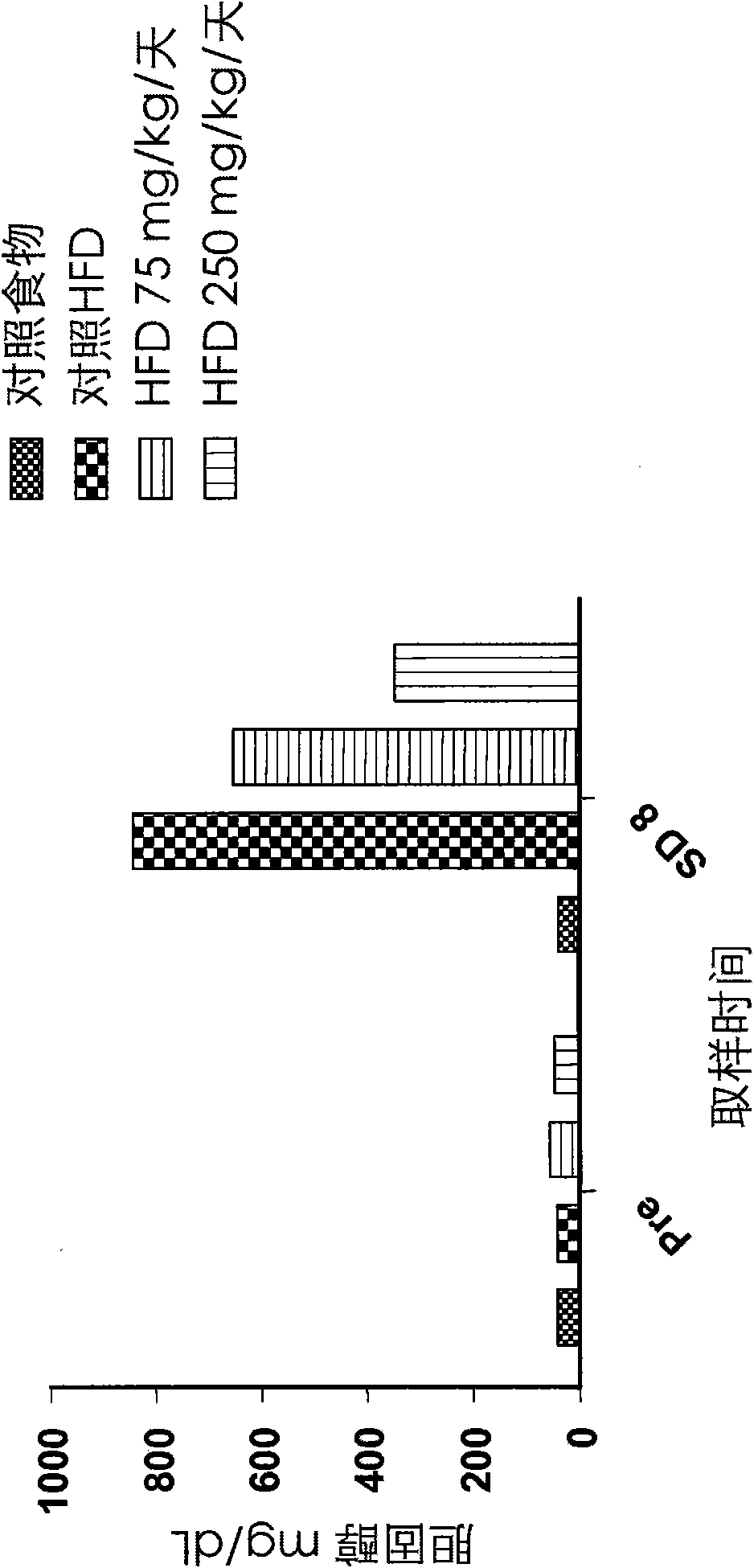
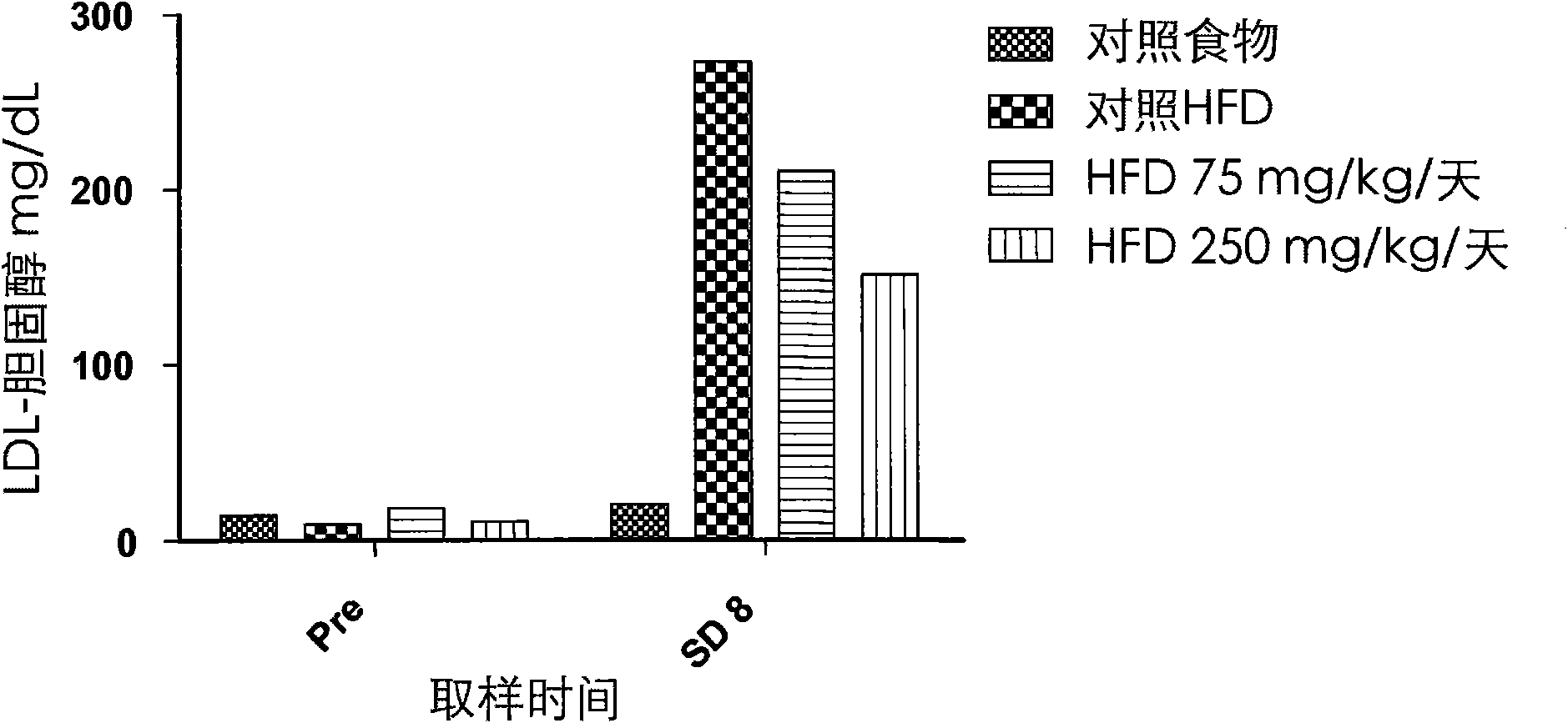
[0110] Effects on cysteamine preparations were assessed in a dietary animal model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) as described by Otogawa et al., Am. J. Pathol., 170(3):967-980 (2007). Male New Zealand white rabbits were fed a high fat diet (HFD) containing 20% corn oil and 1.25% cholesterol to induce the clinical and histological features of NAFLD and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). A pilot study of 7 days duration was conducted with cysteamine bitartrate administered intraperitoneally (IP) on an every 8 hour schedule (Q8H) at two dose levels, 75 or 250 mg / kg / day. Longer studies of the 8-week duration phase delivered cysteamine bitartrate in drinking water at 25, 75, or 250 mg / kg / day.
[0111] As discussed in further detail below, data from two studies showed that cysteamine treatment improved liver transaminase (aspartate aminotransferase or AST) levels compared to HFD-treated controls. Elevated AST is considered to be one of the best markers of liver inf...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com