System for purifying and recycling electroplating/chemical plating wastewater on line
An electroless plating and wastewater technology, which is applied in metallurgical wastewater treatment, dispersed particle separation, separation methods, etc., can solve problems such as wastewater treatment that is difficult to meet in practice, and achieve the effects of reducing burden, optimizing application parameters, and simplifying steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
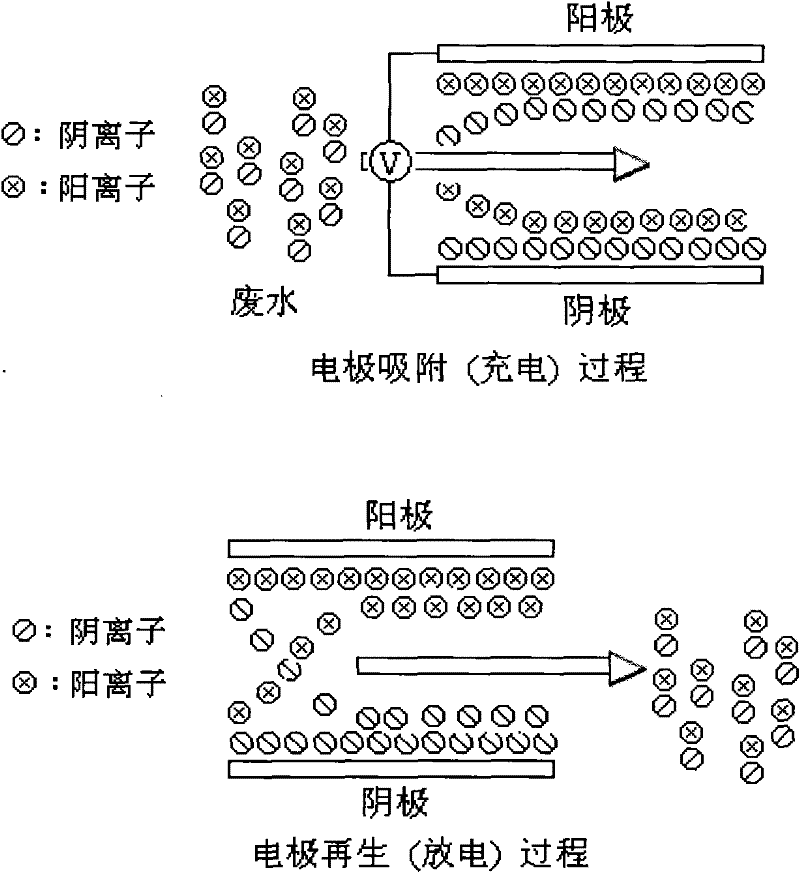
[0033] Plate capacitive deionization device:
[0034]Activated carbon fibers are selected as the electrode material for ion electrosorption, with a thickness of 3 mm and a specific surface area of 1100 square meters per gram; expanded graphite plates with a thickness of 1 mm are used as collectors.
[0035] Cut 10 pieces of activated carbon fibers of 50 cm x 50 cm, and cut 10 pieces of graphite plates of 50 cm x 50 cm. The area of each electrode layer is 2500 square centimeters, and the distance between electrode pairs is 0.5 cm.
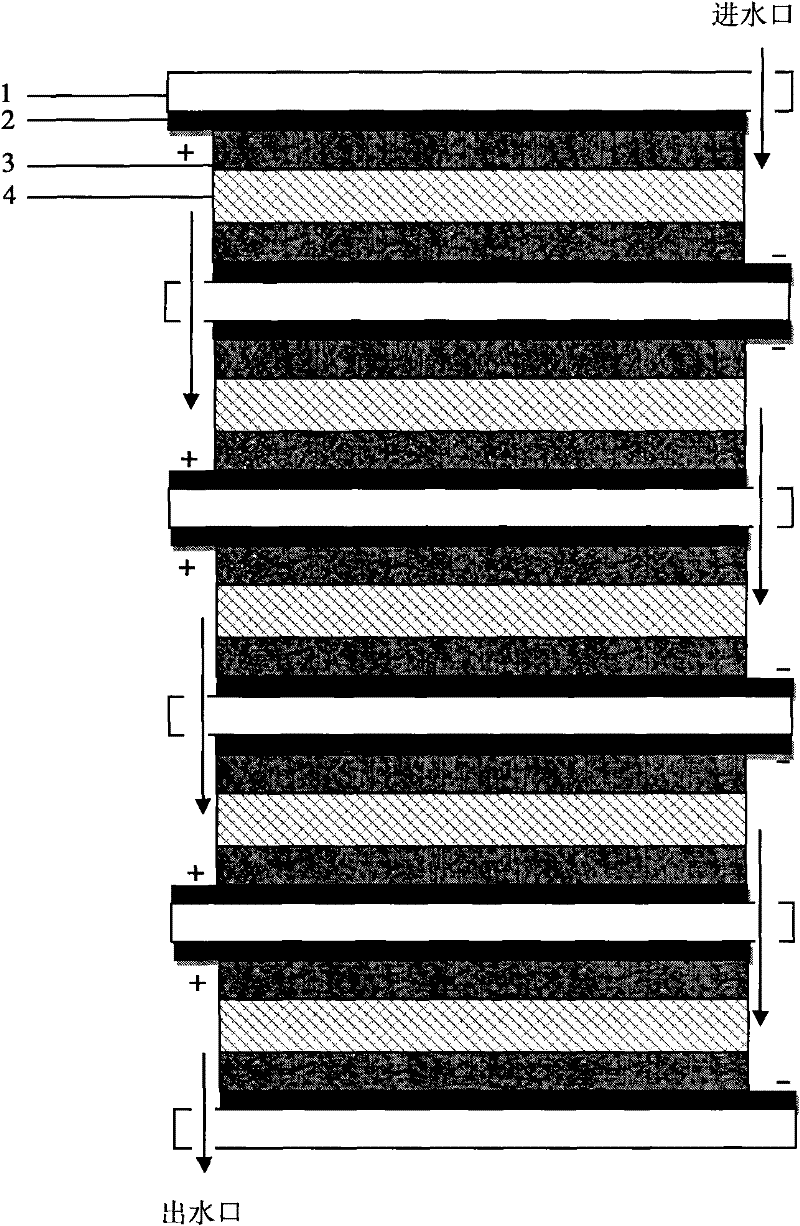
[0036] Assemble the CDI device electrode group consisting of 5 electrode pairs. The assembly sequence of the components is: the lower compression plate, and 5 sets of graphite plate-activated carbon fiber-insulated porous separator-activated carbon fiber-graphite plate are arranged in the middle. The space is separated by a support plate, and finally the upper compression plate is installed.
Embodiment 2
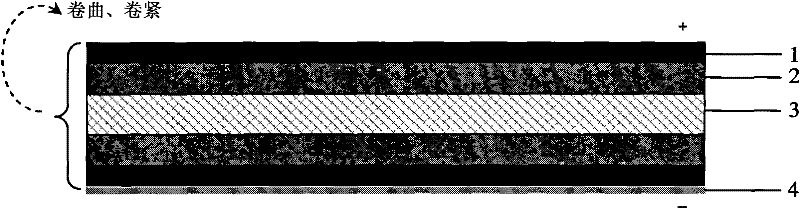
[0038] Roll type capacitive deionization device:
[0039] Activated carbon fiber is selected as the ion electroadsorption electrode material, with a thickness of 3 mm and a specific surface area of 1100 square meters per gram. A 1 mm thick expanded graphite plate was used as the collector.
[0040] Cutting Cut out 2 pieces of activated carbon fibers of 50 cm x 100 cm, and cut 2 pieces of graphite plates of 50 cm x 100 cm.
[0041] Lay up the strip-shaped graphite plate, activated carbon fiber, insulating porous separator, activated carbon fiber, graphite plate, and polyethylene plastic film in sequence, leaving one end of the graphite plate higher than the activated carbon fiber as a conductive ear. Then roll it tightly to form a cylinder with an appropriate diameter, install it in a cylindrical container and seal it, leaving the conductive ear of the graphite plate, and the liquid enters at one end and exits at the other end.
Embodiment 3
[0043] The plate-type CDI apparatus of Example 1 was used to place in a water washing apparatus with a capacity of 100 liters, and a parallel electrosorption test was performed on the nickel-plating washing water.
[0044] The metal ion content in the nickel-plating washing water is 300ppm, the COD value is 1100, and the water inlet flow rate is 4 liters / minute. Assuming that the concentration of nickel ions in the effluent reaches 100ppm, the results of the treatment capacity of electroplating water per square meter of electrode pairs at operating voltages of 2, 10, and 20 volts are listed in Table 1. The concentration of metal ions and COD in the effluent were detected by atomic absorption spectrometry and potassium dichromate oxidation method, respectively.
[0045] Table 1: Effect of CDI device on purified washing water under different operating voltages
[0046]
[0047] It can be seen from the data in Table 1 that when other technical parameters remain unchanged, the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com