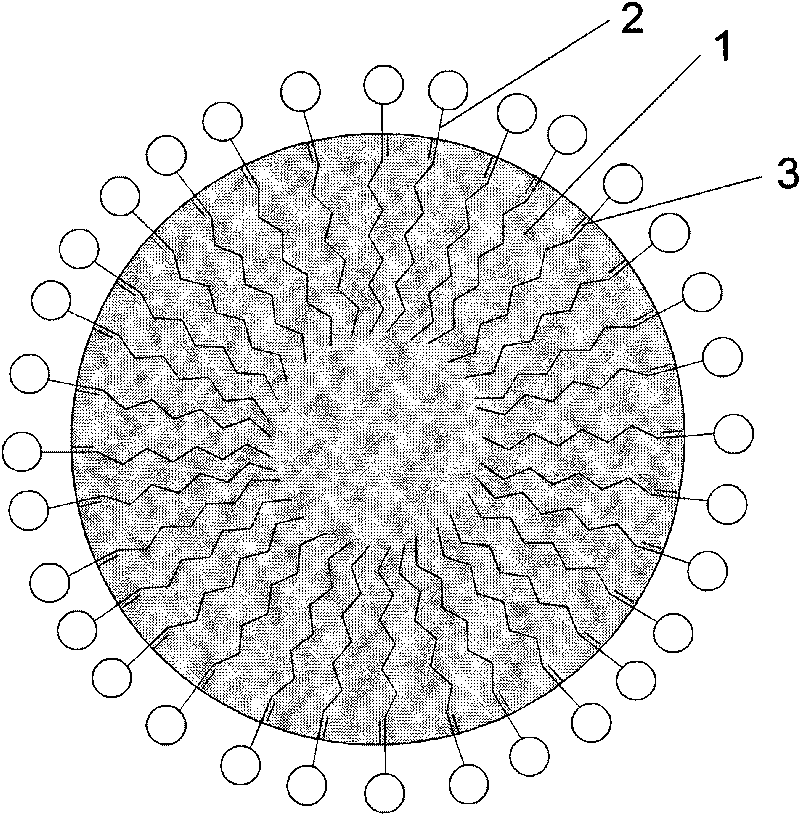
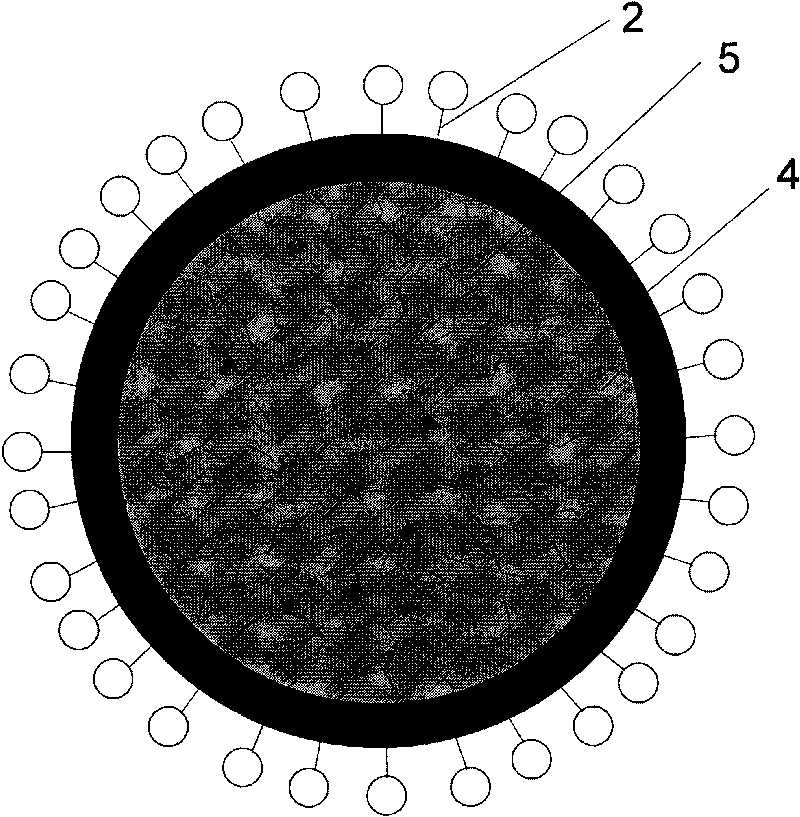
Preparation method of phase-change material microcapsule
A phase change material and microcapsule technology, applied in the field of preparation of phase change material microcapsules, can solve the problems of low encapsulation yield, easy leakage, difficult reaction, etc., and achieves easy control of reaction speed, high encapsulation yield, Density-enhancing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0035] Specifically, the processing steps of the preparation method of the present invention include:
[0036] (1) Preparation of oil phase
[0037] 10-60 parts by weight of phase change material, 5-10 parts of lipophilic vinyl radical monomer, 0.1-5 parts of hydrophilic vinyl radical monomer, 0.1-5 parts of Oil-soluble monomers are mixed. If an oil-soluble initiator is used, 0.05 to 1 part of the oil-soluble initiator is added, dissolved and heated to a temperature above the phase change point of the phase change material to obtain an oil phase;
[0038] (2) Preparation of water phase
[0039] Dissolve 0.1-5 parts of functional surfactant in 100-500 parts of water, and heat to the temperature above the phase transition point of the phase change material. If a water-soluble initiator is used, then 0.05-1 part of water-soluble initiator agent is added to obtain the aqueous phase;
[0040] (3) Preparation of emulsion
[0041] The oil phase is added to the water phase at a te...
Embodiment 1
[0051] (1) Preparation of the oil phase: the phase transition point of 13g is mixed with the phase change material of 24°C and the methyl methacrylate of 3.7g, the methacrylic acid of 1.9g and the benzoyl peroxide of 0.2g, heated to At 45°C, an oil phase is formed after dissolution;
[0052] (2) Preparation of the water phase: dissolving 2 g of the functional surfactant sodium oleate in 100 g of distilled water and heating to 45° C. to form the water phase;
[0053] (3) Preparation of emulsion: place the water phase on a high-speed shear emulsifier and adjust the rotating speed to 1600 rpm, slowly add the oil phase, and emulsify for 15 minutes to form a stable emulsion;
[0054] (4) Preparation of phase-change material microcapsules: under nitrogen protection, adding a reflux device and a stirring speed of 500 rpm, the emulsion is gradually warmed up to 75°C and kept for 4.5 hours, then the heating is stopped, cooled to room temperature, the mixture is filtered, Washing with ...
Embodiment 2
[0058] (1) Preparation of the oil phase: 10.0 g of phase change materials with a phase transition temperature of 24° C., 5.712 g of styrene, 0.5085 g of methacrylic acid, 0.2401 g of butylene glycol diacrylate and 0.3019 g of diacrylate Mix nitrogen diisobutyronitrile, heat to 55°C, and form an oil phase after dissolving;
[0059] (2) Preparation of the water phase: 4 g of methacryloxyethyl dodecyl dimethyl ammonium bromide was dissolved in 200 g of distilled water, and heated to 55° C. after dissolving to form a water phase;
[0060] (3) Preparation of emulsion: Mix the oil phase with the water phase, stir at low speed and pre-emulsify for 10 minutes, keep the temperature at 55°C and emulsify in an ultrasonic emulsifier for 5 minutes to form a stable emulsion;
[0061] (4) Preparation of phase change material microcapsules: Under nitrogen protection, add reflux device and at a stirring speed of 300 rpm, the emulsion is gradually warmed up to 75°C and kept for 3 hours, stop th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com