Mixed powder alloy with high melting point particles or fibers and low melting point particles as well as method for preparing same
A mixed powder, high melting point technology, applied in the field of powder metallurgy materials, can solve problems such as the collapse of porous particles and the interconnection of network fiber structures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
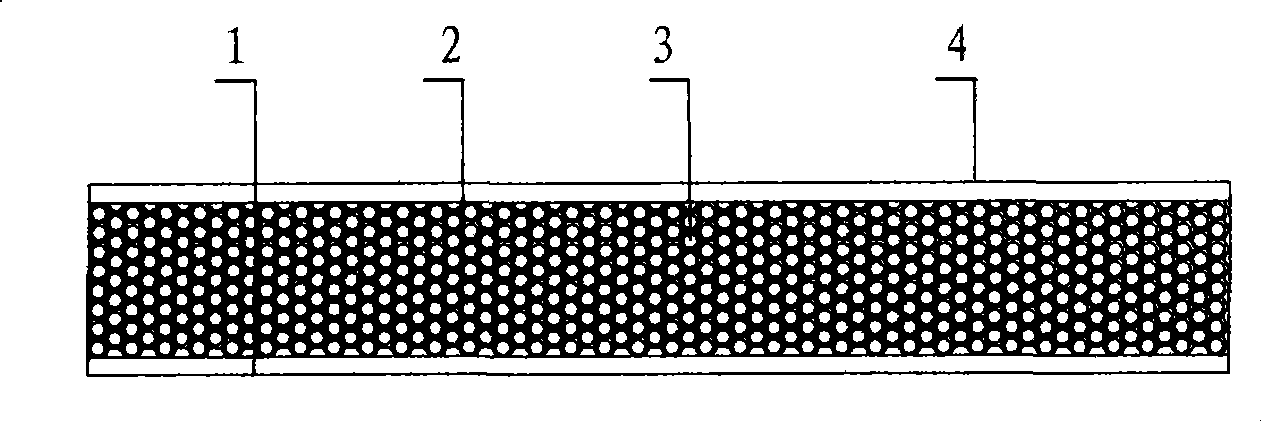
[0049] A structural diagram of a thermal insulation wallboard filled with expanded perlite particles figure 1 as shown, figure 2 It is the manufacturing structure diagram of the thermal insulation wallboard filled with expanded perlite particles, of which: 1 is the PVDF panel, 2 is the expanded perlite particle after filling, 3 is the PP resin mesh skeleton, 4 is the PP panel, 5 is the metal sleeve mold, 6 is Metal gland, 7 is the metal bottom plate, 8 is the mold cavity, 9 is expanded perlite particles, 10 is toluenesulfonamide (TSS or TSSC) foaming powder, 11 is the core PP resin particles, 12 is PP resin Particles, 13 are PVDF resin particles. The porous thermal insulation wallboard is composed of PVDF panel 1 and PP panel 4 and core PP porous resin network skeleton 3 wrapped with expanded perlite particles 4 .
[0050] The manufacturing process of the thermal insulation wallboard is as follows: the expanded perlite particles 9 are evenly mixed with 1% silane coupling ag...
Embodiment 2
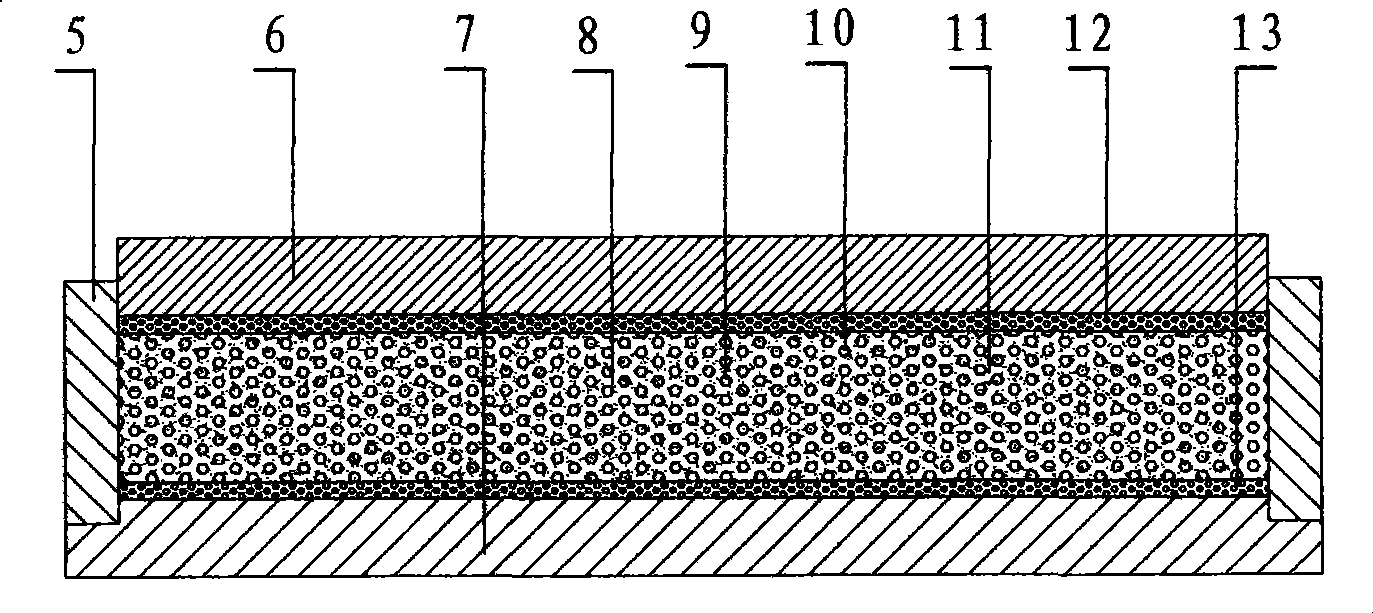
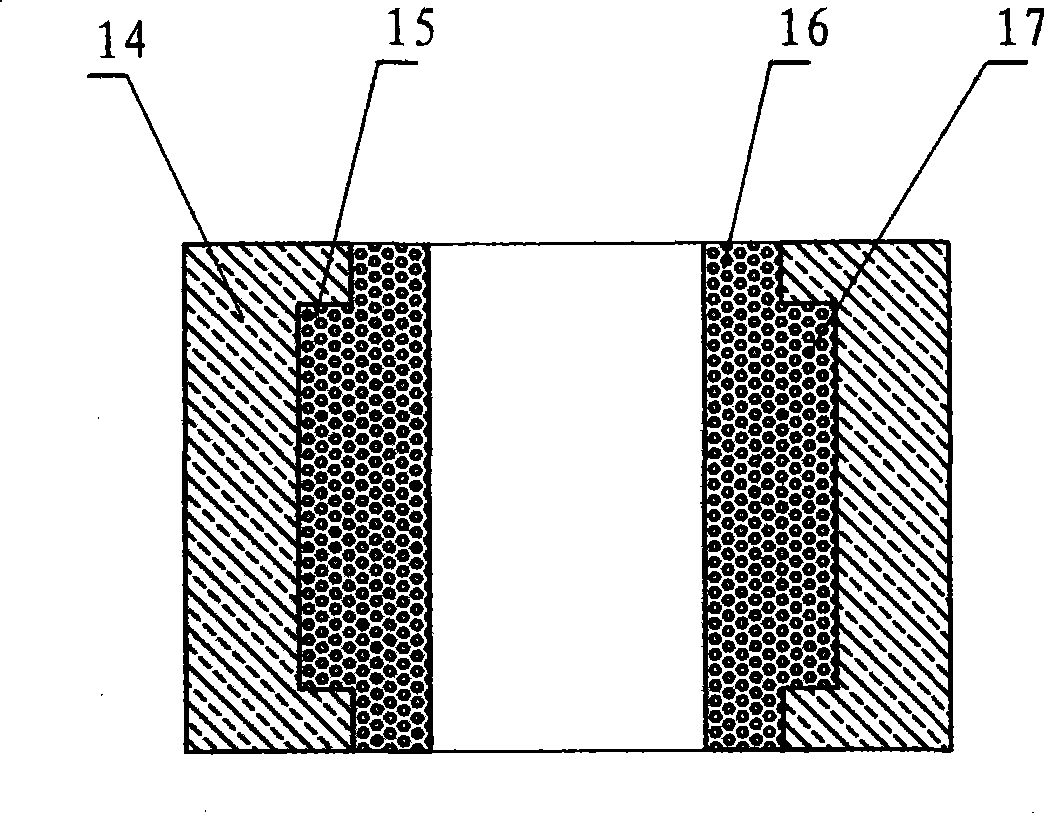
[0053] A copper-tin polyimide alloy bearing structure diagram as shown image 3 as shown, Figure 4 It is the flow chart of the manufacture of copper-tin polyimide particles, Figure 5 is the structural diagram of the manufacturing process of the copper-tin polyimide alloy bearing pad, in which: 14 is the steel jacket, its function is to keep the bearing with sufficient strength without deformation; The imide composite material is inlaid in the steel jacket groove to prevent the copper-tin polyimide composite material from falling off, 16 is the polyimide mesh skeleton, 17 is the copper-tin alloy particle, and the copper-tin alloy particle 17 is wrapped in polyimide In the mesh skeleton 16 pores, 18 is a polyimide particle, 19 is a heater, 20 is a mold base, 21 is a mold upper cover, 22 is a central axis, and 23 is a pressure ring of copper-tin-polyimide mixed particles. First, the coupling agent with a weight ratio of 1% of the CuSn particles is sprayed into the 2500-mesh C...
Embodiment 3
[0056] The manufacturing structure diagram of a corrosion-resistant propeller Figure 6 As shown, wherein: 24 is the metal propeller core, 25 is the positioning shaft under the propeller core, and 26 is TiO 2Particles, 27 are epoxy resin particles, 28 are carbon fibers or hybrid fibers, 29 are models, 30 are fixed sleeves, and 31 are vibrators. First, 5% TiO2 particles 26 are mixed with epoxy resin particles 27 and 10% carbon fibers or hybrid fibers to manufacture epoxy resin mixture particles containing TiO2 particles 26 and carbon fibers or hybrid fibers, and the metal propeller core 24 is placed on the model 29 Among them, the upper part is fixed with a fixed sleeve 30, and the lower part is fixed with the positioning shaft 25 under the propeller core, leaving a gap of 5-50mm between the model and the metal propeller core, and the epoxy resin mixed particles containing TiO2 and carbon fiber or hybrid fiber are placed along the model and Metal propeller core gap filling, wh...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com