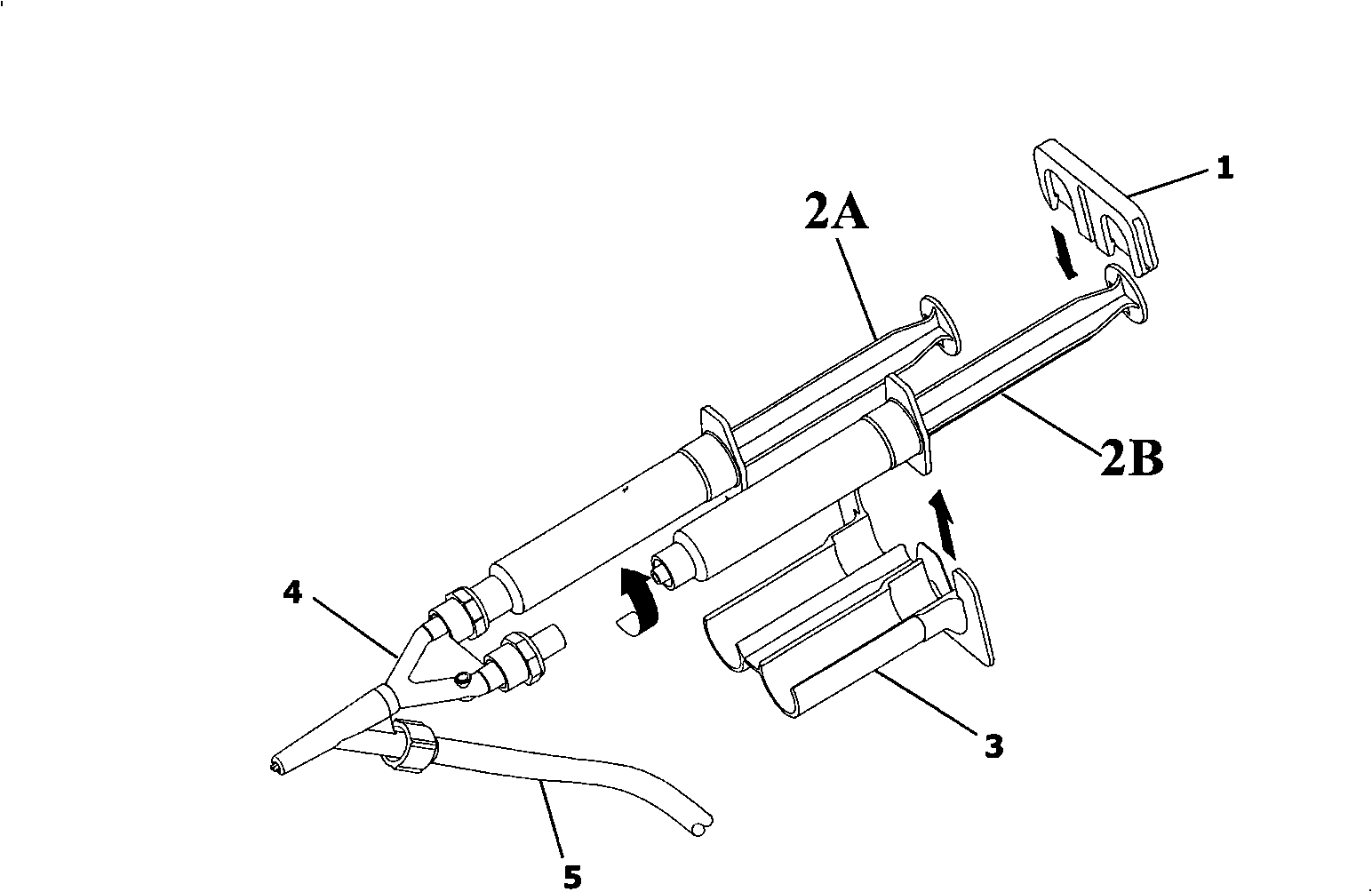
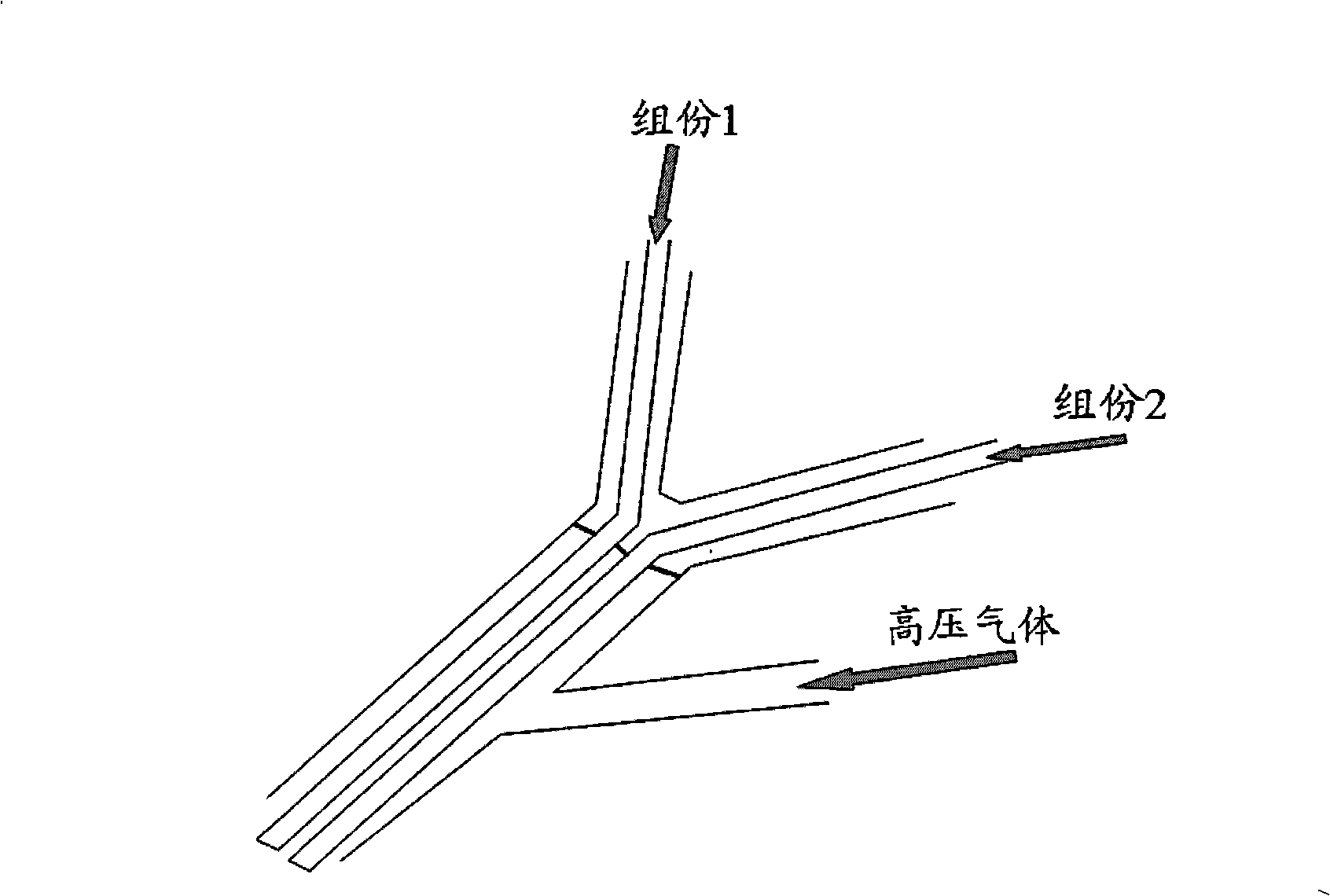
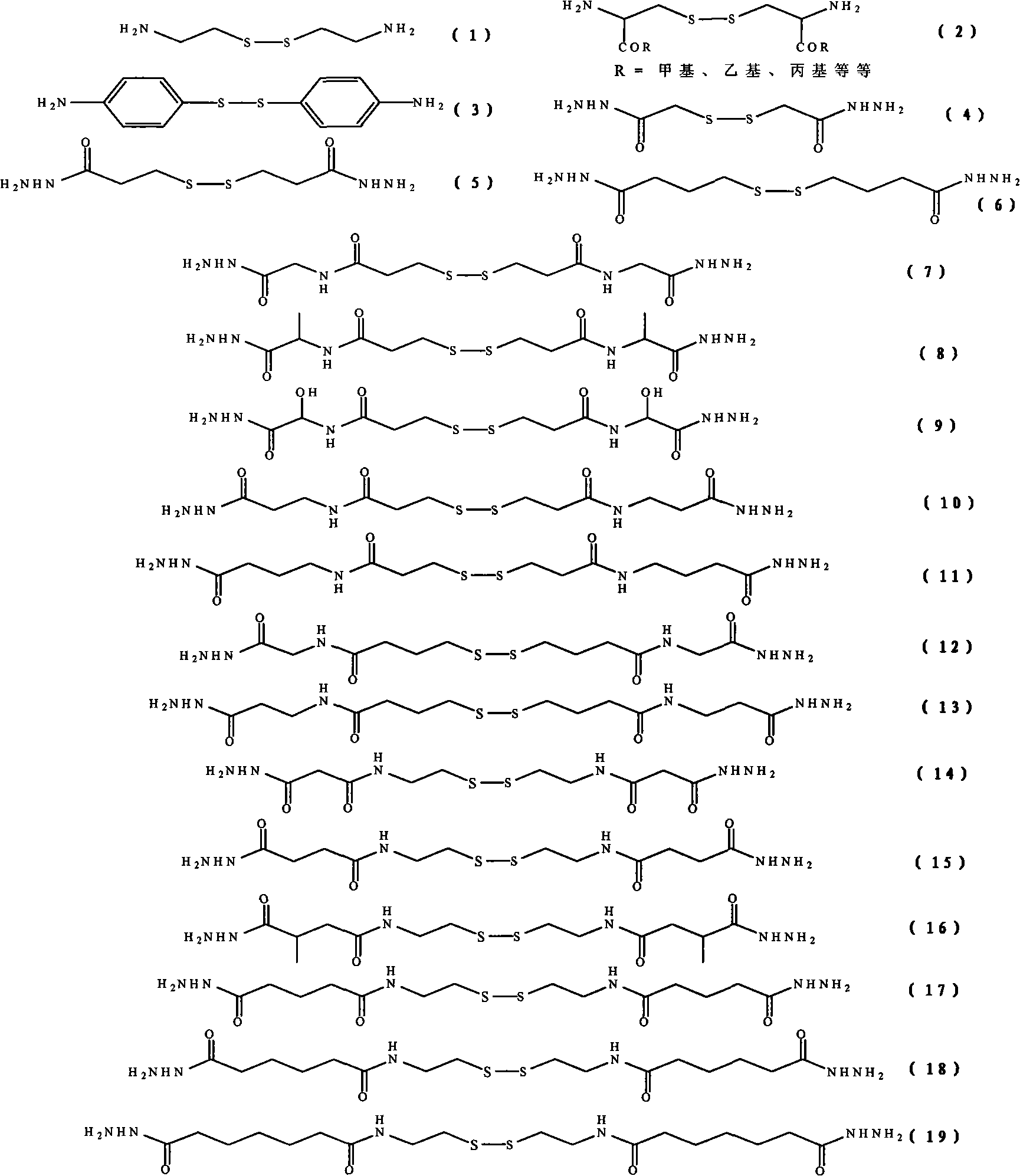
Biocompatible quick-gelatinizing hydrogels and method for preparing spray thereof
A biocompatible and hydrogel technology, which is applied in the preparation of biocompatible fast-gelling hydrogels and the preparation of biocompatible fast-gelling hydrogel sprays, can solve the problem of expensive and easy to lose activity. , inconvenient to use, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0112] Embodiment 1 Preparation of thiol-modified hyaluronic acid (HA-DTPH)
[0113] Prepared by the method reported by Shu et al. (Shu et al., Biomacromolecules, 3, 1304, 2002).
[0114] Dissolve 20 grams of sodium hyaluronate (molecular weight about 1.5 million) in 2 liters of distilled water, add concentrated hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH value of the solution to about 0.5, and then degrade it in a shaker at 37 degrees Celsius and 150 rpm for 24 hours. Dialysis, purification, freeze-drying to obtain low molecular weight hyaluronic acid (weight average molecular weight 246,000, number average molecular weight 120,000).
[0115] 20 grams of the above low molecular weight hyaluronic acid was dissolved in 2 liters of distilled water. Add 23.8 g of dithiodimalonohydrazide (prepared according to the method disclosed in Biomacromolecules, 3, 1304, 2002 by Shu et al.) to the above solution, and stir to dissolve. Then the pH value of the solution was adjusted to 4.75 with 0.1...
Embodiment 2
[0118] Example 2 Preparation of mercapto-reactive biocompatible cross-linking agent
[0119] Polyethylene glycol diacrylate, polyethylene glycol di(meth)acrylate, polyethylene glycol diacrylamide and polyethylene glycol di(meth)acrylamide are prepared by corresponding polyethylene glycol (molecular weight 3,400 or 10,000, Sigma-Aldrich, U.S.) and polyethylene glycol diamine (molecular weight 3400, Nektar Therapeutics, U.S.) preparation, multiarm (4 arms and 8 arms) polyethylene glycol diacrylate and polyethylene glycol Di(meth)acrylates were prepared from the corresponding multi-armed polyethylene glycols (molecular weight 10,000). The general process of its preparation is that polyethylene glycol or polyethylene glycol diamine reacts with acryloyl chloride or methacryloyl chloride under the action of triethylamine, and the product can be obtained after purification. For the detailed process, see Shu et al., Biomaterials, 25, 1339, 2004.
[0120] Replace the corresponding ac...
Embodiment 3
[0121] Example 3 Preparation of Biocompatible Rapid Gelation Hydrogel
[0122] The HA-DTPH solution (2.0% w / v, pH 5.0) prepared in Example 1 was thawed at room temperature for use. Polyethylene glycol diacrylate (molecular weight 3400, Nektar Therapeutics, USA) was dissolved in 0.3 mol / L sodium phosphate / sodium carbonate buffer to obtain a 2.0% w / v solution (pH 9.6), which was sterilized by filtration for use. Under electromagnetic stirring, the above-mentioned solution (5 milliliters) was quickly added into another solution (5 milliliters), and the stirring was continued for 3 seconds, then the stirring was stopped. The pH value of the reactive mixture was about 9.4, and the mixed solution lost its The fluidity forms a gel.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com