DNA electrochemical sensor and preparation method thereof
An electrochemical and sensor technology, applied in the field of deoxyribonucleic acid electrochemical sensor and its preparation, can solve the problems of inability to realize SNP detection and insufficient detection sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
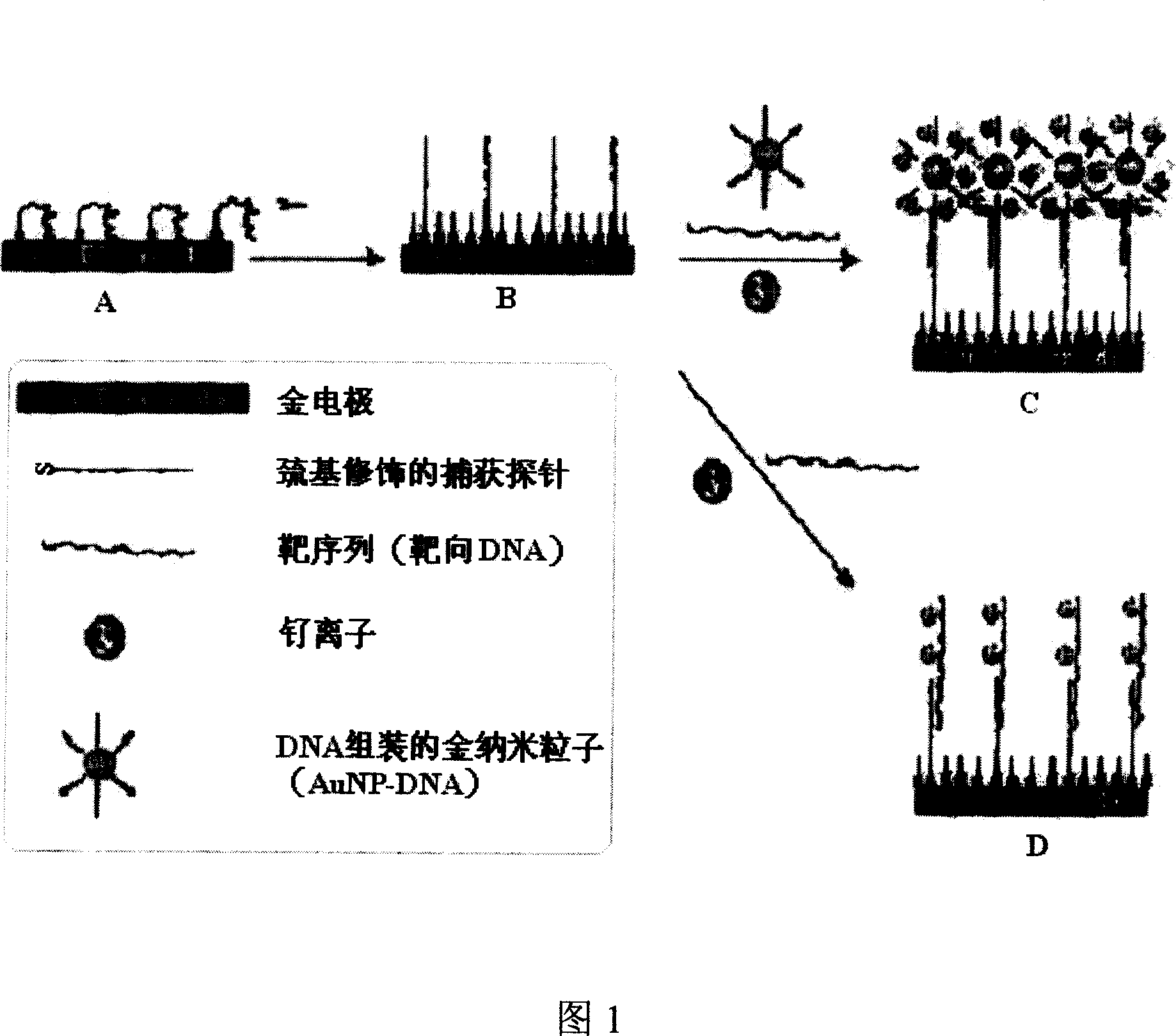
[0038] As shown in Figure 1, steps A, B, and C are used to prepare the DNA electrochemical sensor of the present invention.
[0039] (1) Electrode pretreatment and assembly of capture probe DNA
[0040] Firstly, the gold electrode was polished with alumina abrasive suspension on a grinding cloth, then ultrasonically cleaned in ethanol and MilliQ water respectively, and finally the electrode was cleaned electrochemically to remove residual impurities. After blowing dry with nitrogen, add 0.2 μM thiol-modified oligonucleotide probe assembly solution [pH7.2 phosphate buffer (PBS), where the NaCl concentration is 0.1M] dropwise on the electrode, and let it stand at room temperature for about 60 Minutes, and then soak in 2mM mercaptohexanol aqueous solution for about 2 hours, take it out and rinse it with MilliQ water.
[0041] (2) hybridization
[0042] First mix the DNA of the target sequence with the AuNP-DNA solution (AuNP diameter is 20 nanometers), pre-hybridize at 25°C for...
Embodiment 2
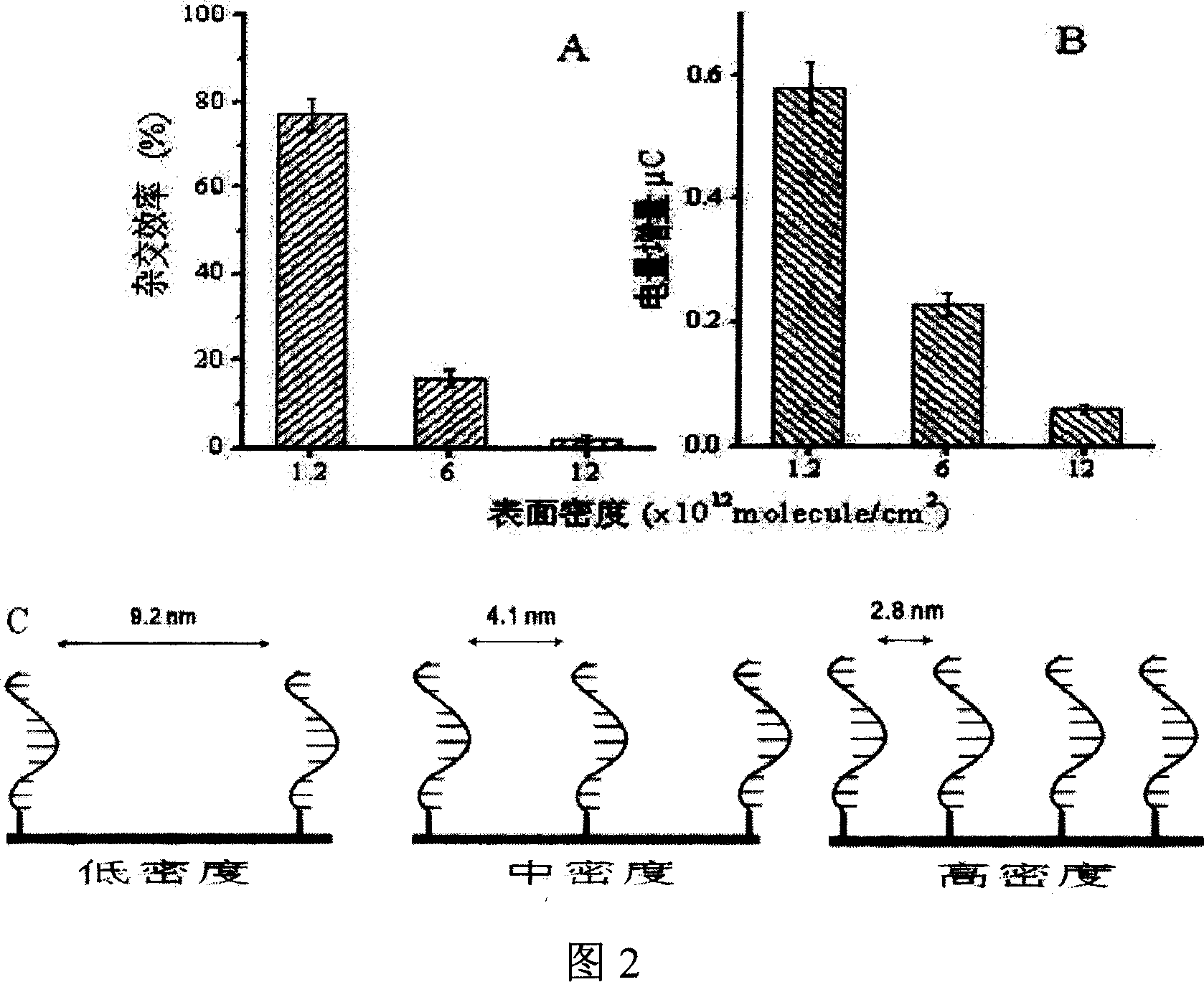
[0050] (1) Assembly of capture probe DNA on gold electrode surface
[0051] A PBS solution of sulfhydryl-modified capture probes at pH 7.4 was added dropwise on a clean and dry gold electrode, and assembled at room temperature for 60 minutes. Among them, by changing the concentration of the capture probe in the assembly solution to 0.2, 2.0, 5.0 μM and the concentration of NaCl to 0.1M, 1.0M, 1.0M respectively, DNA modified electrodes with different densities were assembled, divided into high (1.2×10 13 molecule / cm 2 ), Medium (6.0×10 12 molecule / cm 2 ), low (1.2×10 12 molecule / cm 2 ) three densities (as shown in Figure 2 C), and then soaked in 1mM mercaptohexanol aqueous solution for 3 hours, rinsed with MilliQ water after taking it out.
[0052] (2) hybridization
[0053] Mix target sequence DNA with AuNP-DNA solution (AuNP diameter is 20 nm), and pre-hybridize at 37° C. for 30 minutes. The rest is the same as in Example 1.
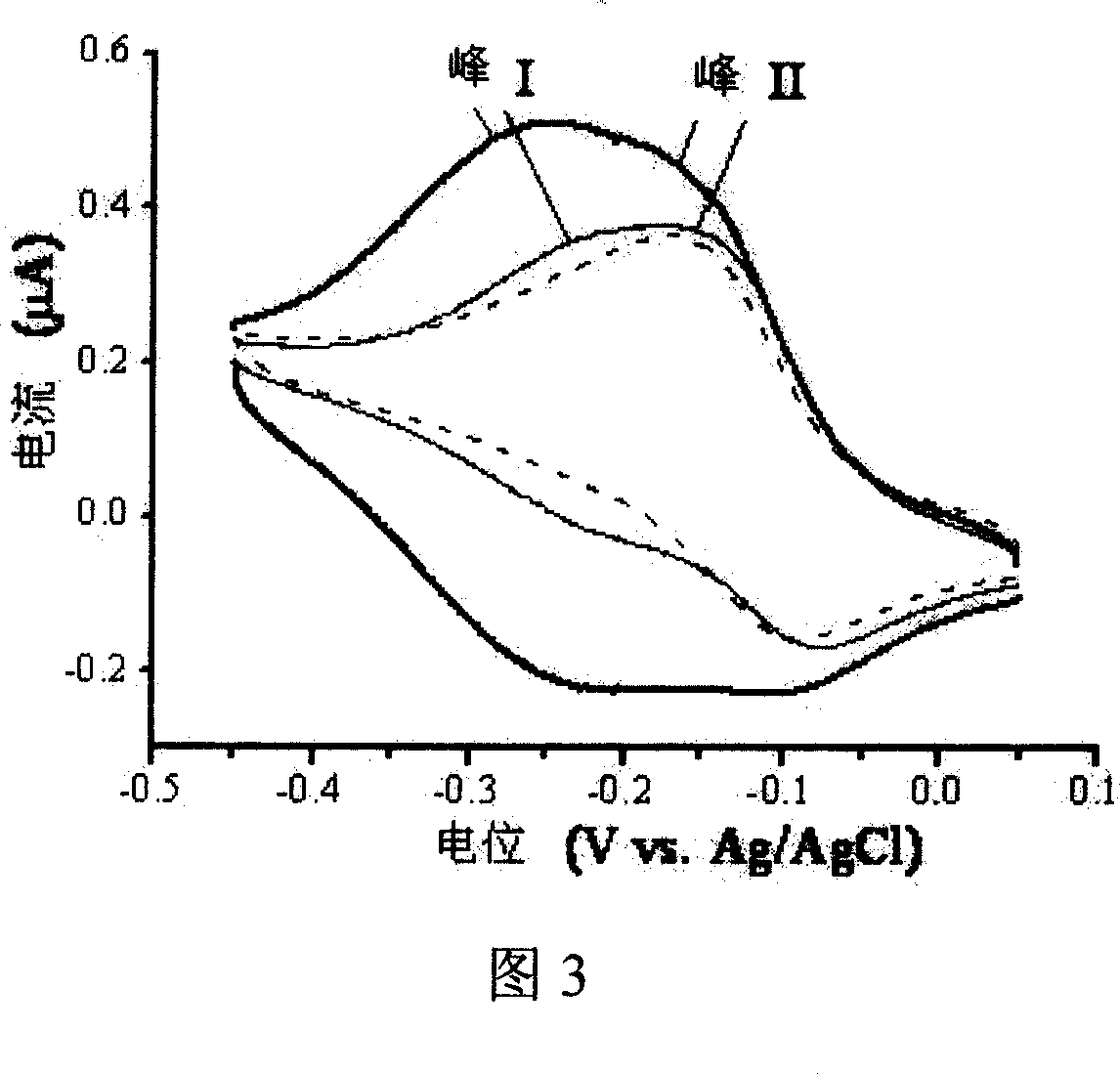
[0054] (3) Electrochemical detection
[0...
Embodiment 3
[0060] The pH of the capture probe solution is 7.8, assembled for 30 minutes, and then soaked in 1mM mercaptohexanol aqueous solution for 4 hours; using gold nanoparticles with a diameter of 10 nm, the gold electrode modified with the capture probe DNA is immersed in the prehybridization solution at room temperature hybridization for 2 hours; the electrochemical indicator is cobalt ion (Co 2+ ), the remainder is the same as in Example 1, indicating the occurrence of the hybridization reaction by the change in the electric quantity of cobalt ions on the electrode surface before and after the hybridization. Using this method to determine the gene sequence containing 38 bases, the linear concentration range is 0.5 pmol L -1 ~10pmol·L -1 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com