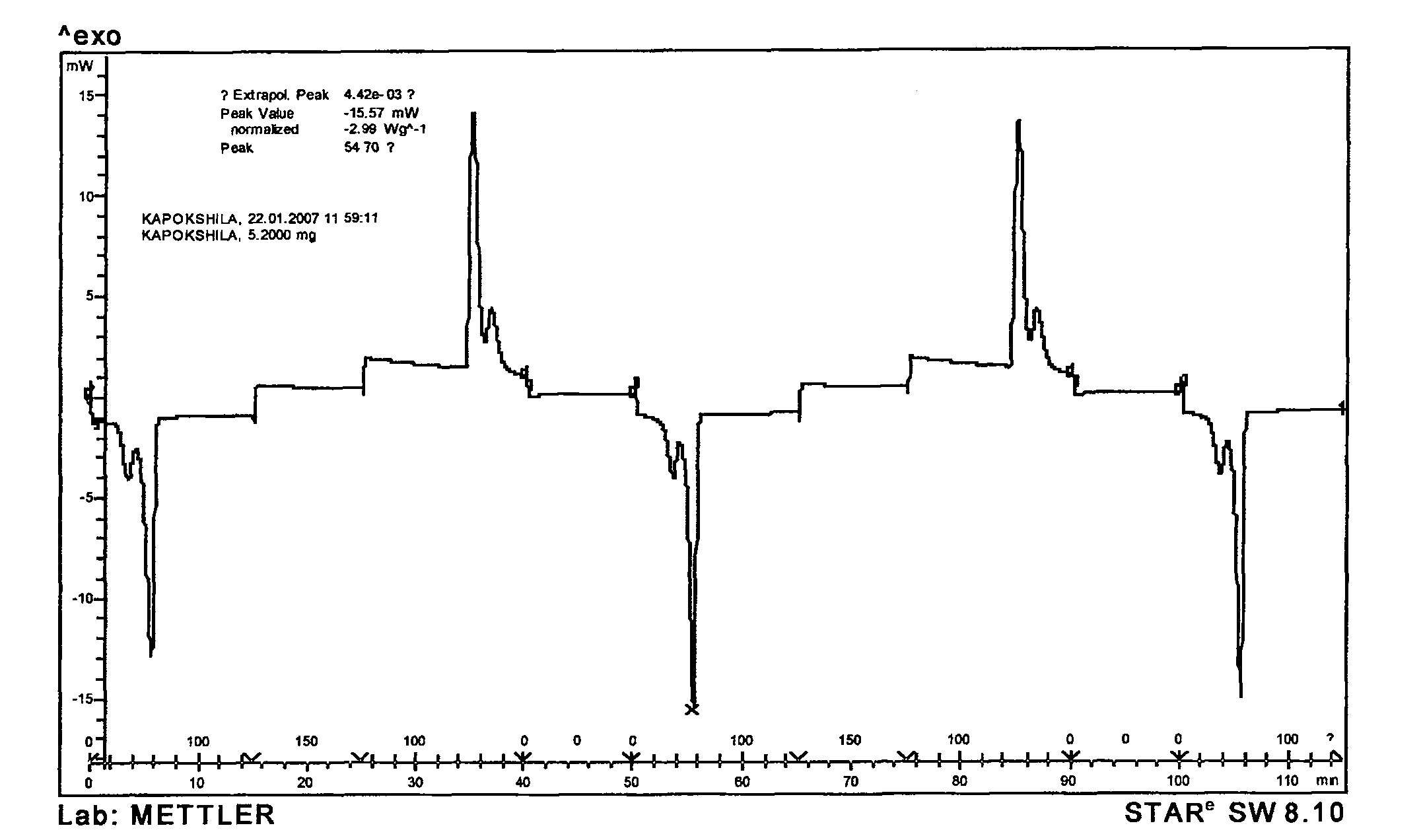
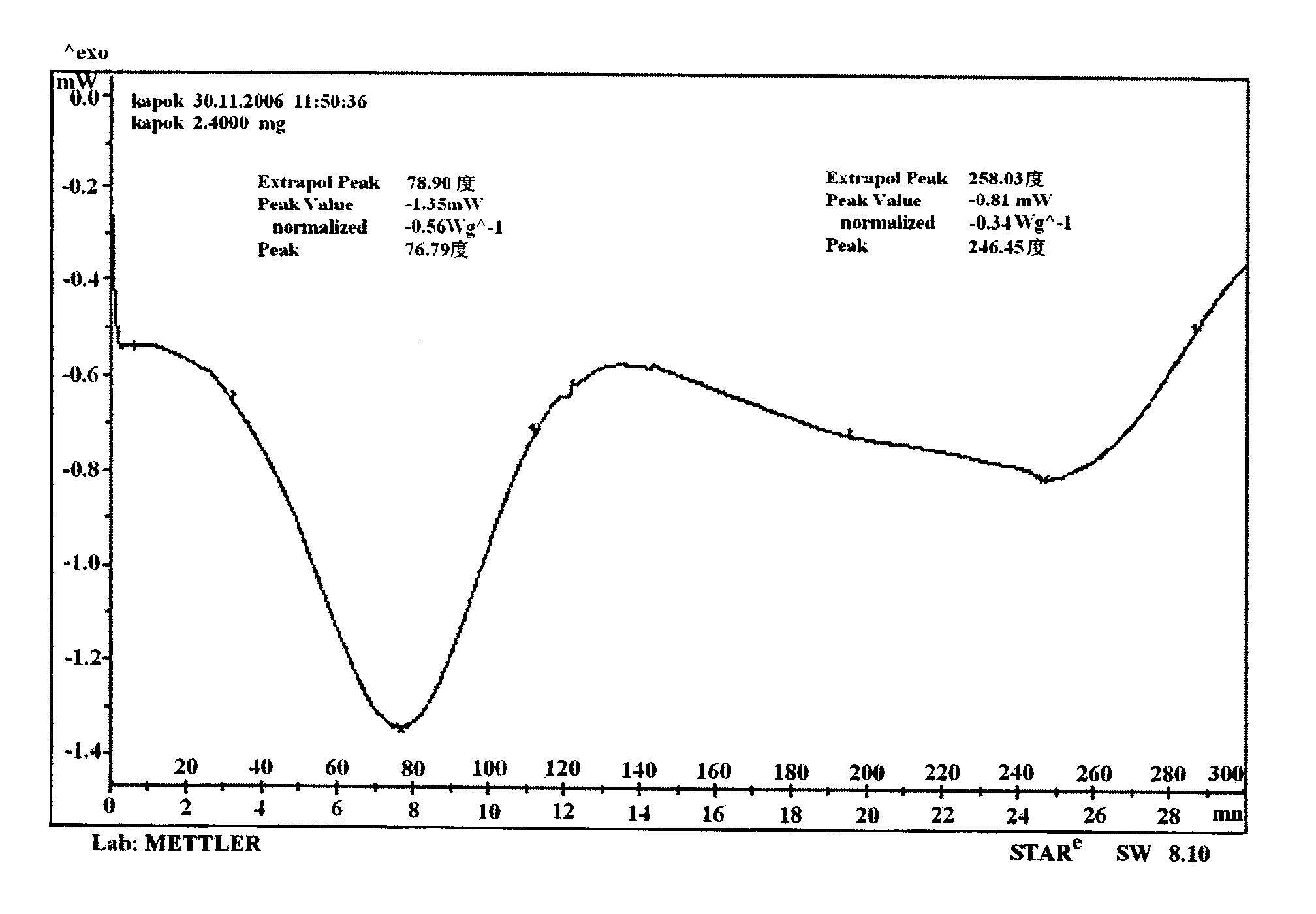
Phase-change material of natural kawo fiber pipe encapsulation and encapsulation method thereof
A composite phase change material and phase change material technology, applied in the field of encapsulating phase change materials, can solve the problems of limited material selection, high cost, small latent heat of phase change, etc., and achieve good chemical stability, stable energy output, thermal and chemical stability. The effect of stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] (1) Liquefaction of core material
[0045] Heating the organic phase change material paraffin to a melting point above 60°C to obtain a liquid paraffin phase change material;
[0046] (2) Capillary adsorption of natural kapok fiber tubes to liquid phase change materials
[0047] The natural kapok fiber tube is dispersed in the liquid phase change material in step (1), soaked to balance the capillary absorption, and the fiber tube is filled with the liquid phase change material. Then, the fiber tube is pulled out, and the phase change material adsorbed between the fibers is squeezed out, while the remaining fiber is still filled with the liquid phase change material;
[0048] (3) Curing of phase change materials
[0049] Lowering the temperature of the system in step (2) to below 60°C of the phase change point of the phase change material to solidify the paraffin wax of the phase change material;
[0050] (4) Seal the wall and end of the fiber tube filled with phase c...
Embodiment 2
[0053] (1) Liquefaction of core material
[0054] Dissolving the organic phase change material pentaerythritol (PE) into ethanol to obtain a liquid pentaerythritol (PE) solution phase change material;
[0055] (2) Capillary adsorption of natural kapok fiber tubes to liquid phase change materials
[0056] The natural kapok fiber tube is dispersed in the liquid phase change material obtained in step (1), soaked to balance the capillary absorption, and the fiber tube is filled with the liquid phase change material. Then, the fiber tube is pulled out, and the phase change material adsorbed between the fibers is squeezed out, while the remaining fiber is still filled with the liquid phase change material;
[0057] (3) Curing of phase change materials
[0058] The ethanol of the phase change material containing the ethanol solvent obtained in step (2) is volatilized, and the phase change material pentaerythritol (PE) solution is concentrated and solidified;
[0059] (4) Seal the ...
Embodiment 3
[0062] (1) Liquefaction of core material
[0063] Inorganic phase change material CaCl 2 ·6H 2 O dissolved in deionized water to obtain liquid CaCl 2 ·6H 2 O solution phase change material;
[0064] (2) Capillary adsorption of natural kapok fiber tubes to liquid phase change materials
[0065] The natural kapok fiber tube is dispersed in the liquid phase change material in step (1), soaked to balance the capillary absorption, and the fiber tube is filled with the liquid phase change material. Then, the fiber tube is pulled out, and the phase change material adsorbed between the fibers is squeezed out, while the inside of the retained fiber is still filled with the liquid phase change material.
[0066] (3) Curing of phase change materials
[0067] The deionized water of the phase change material containing the deionized water solvent that step (2) obtains is volatilized, and the phase change material CaCl 2 ·6H 2 O solution is concentrated and solidified;
[0068] (4)...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com