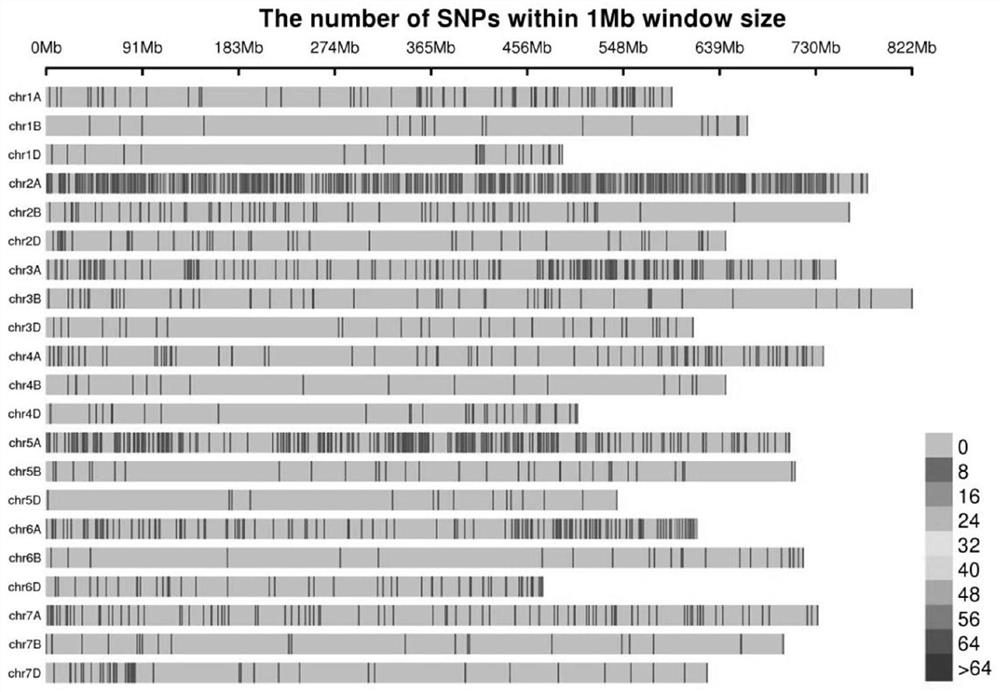
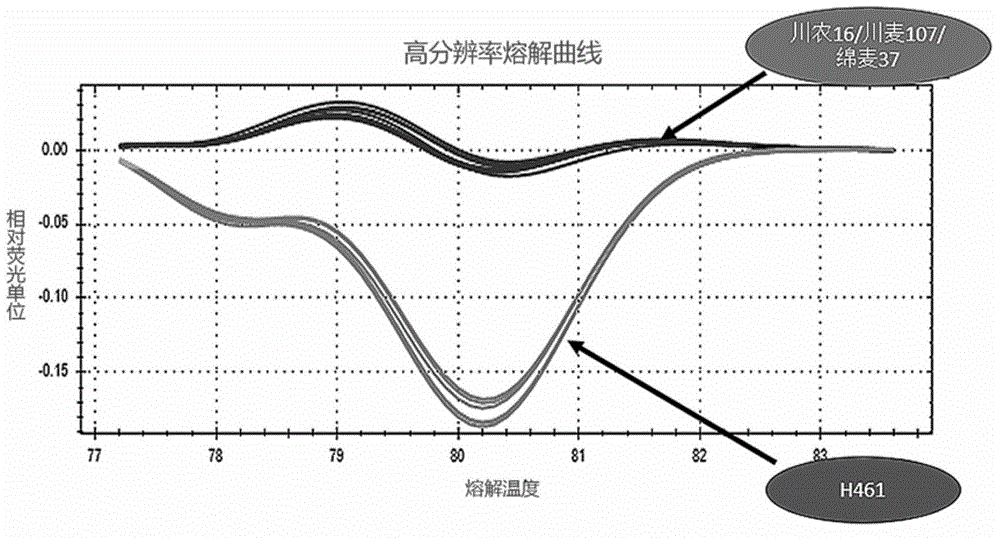
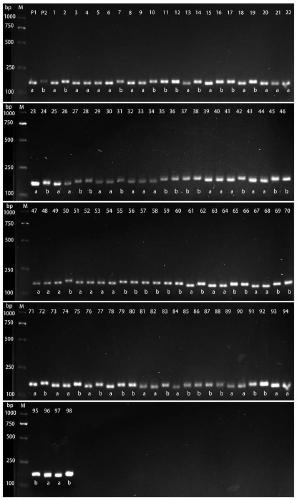
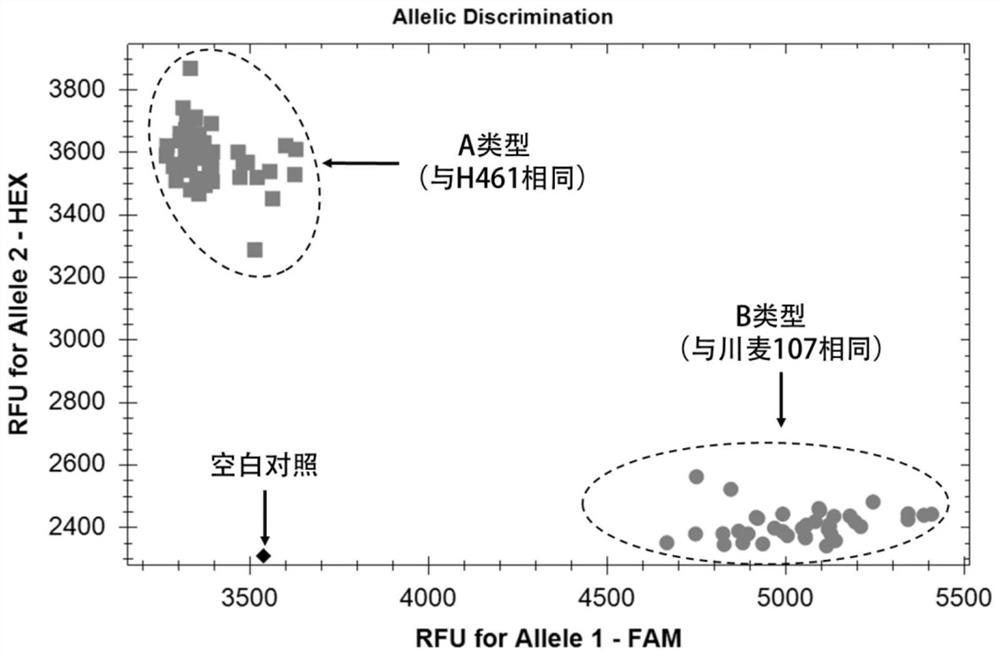
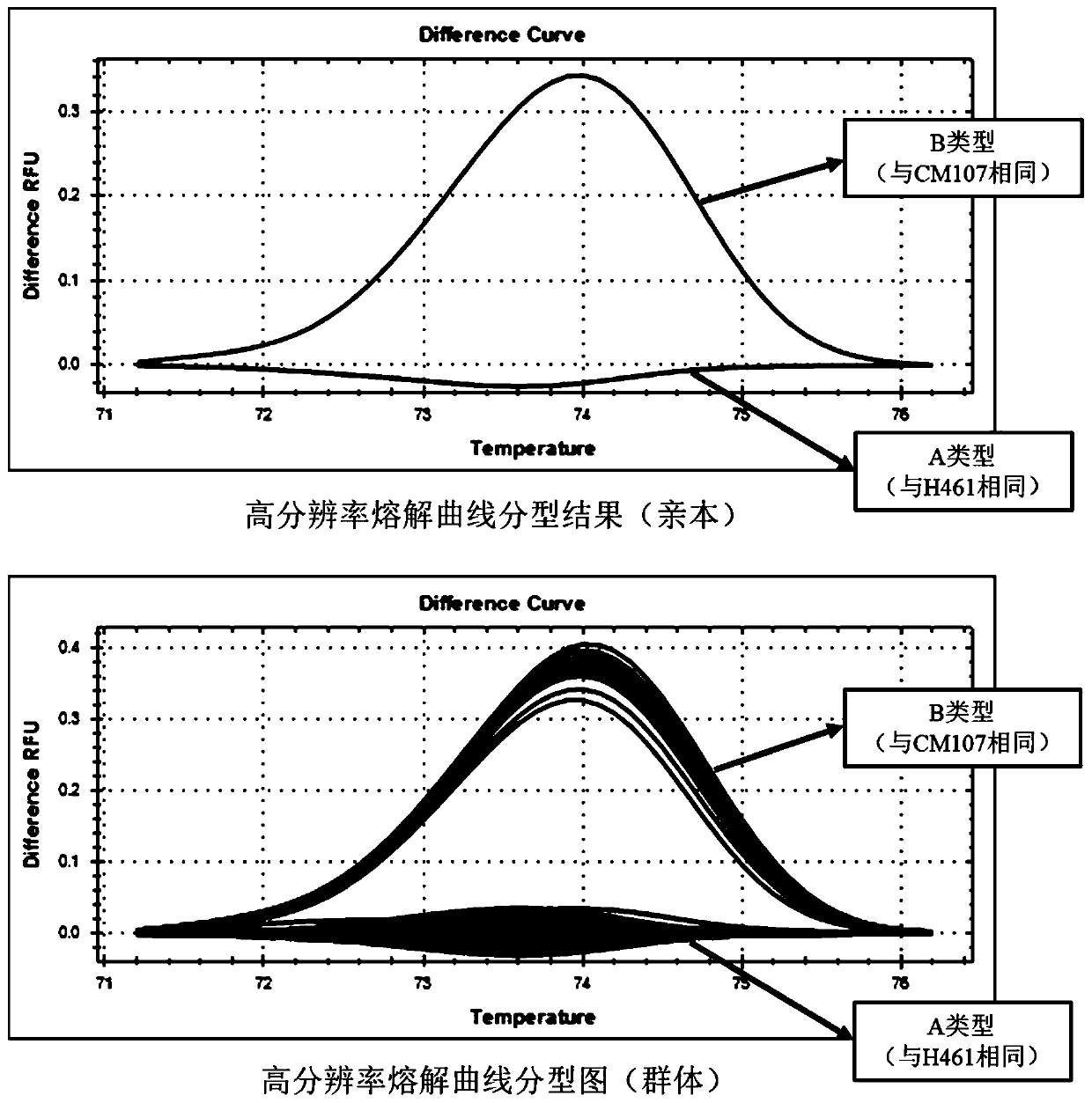
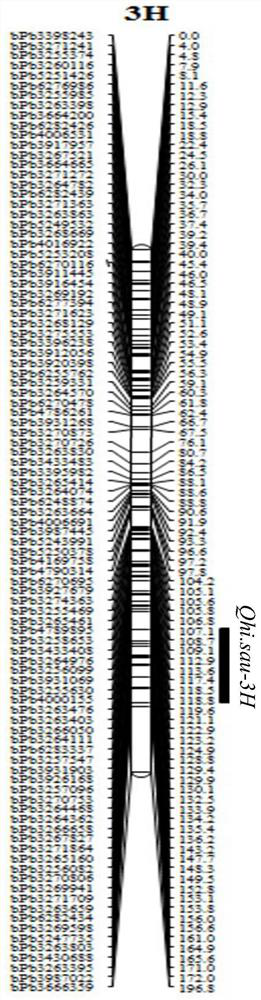
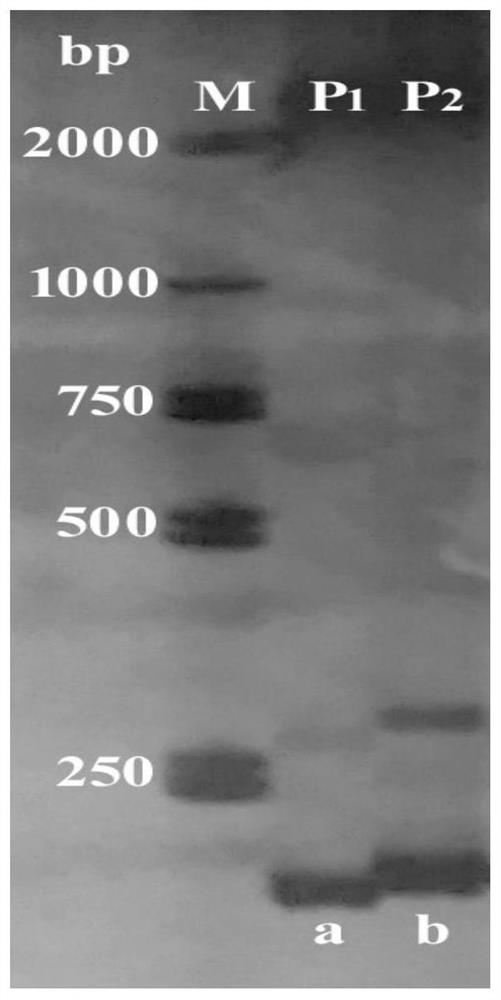
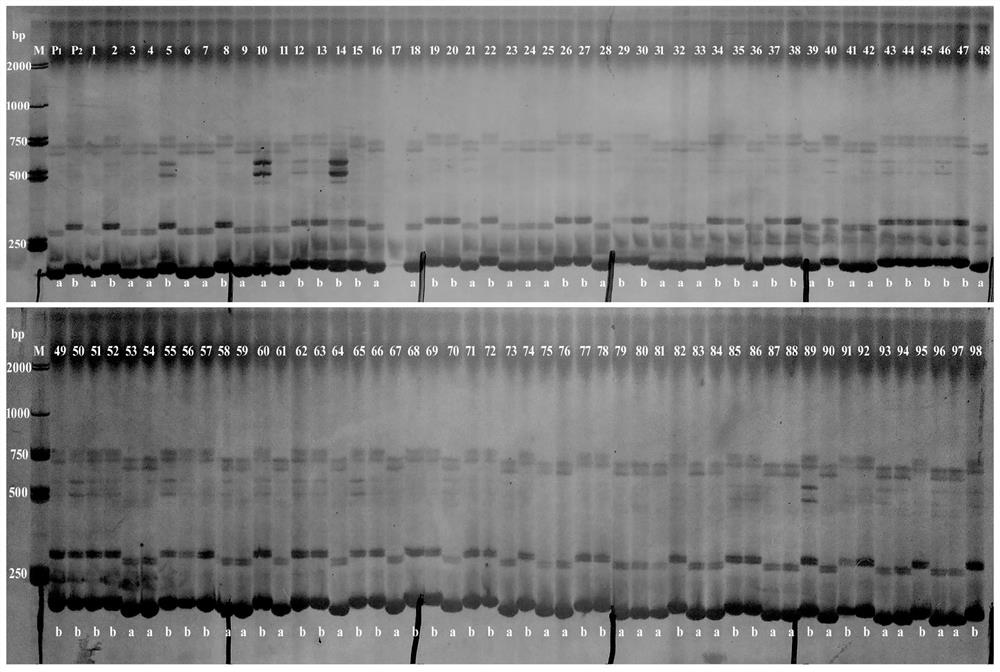
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39results about How to "Easy to expand and stable" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
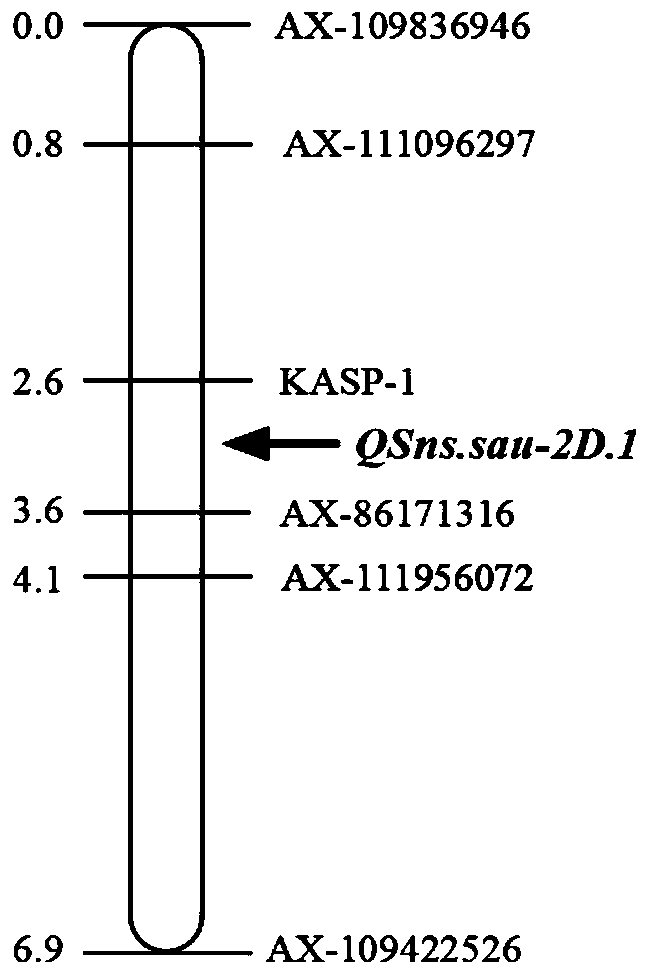
Wheat spikelet number QTL linked SNP molecular marker and application thereof
ActiveCN109825621AImprove use valueImprove selection identification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceMolecular breeding
The invention discloses a wheat spikelet number QTL linked SNP molecular marker and application thereof. The SNP molecular marker KASP-1 is located on the short arm of a 2D chromosome of the RefSeqv1.0 genome version, and the 100 bp sequence before and after is shown as SEQ ID NO.46, the polymorphism is C / T and can be obtained by primer amplification shown in SEQ ID NO.1-3. The molecular marker can accurately track the wheat spikelet number QTL QSns.sau-2D.1 to predict the wheat spikelet number and facilitate molecular breeding. The invention also discloses a method for identifying the wheat spikelet number QTL QSns.sau-2D.1 molecular marker. By means of the method, the wheat spikelet number prediction accuracy can be enhanced, so as to quickly screen out wheat varieties or lines with increased spikelet number for breeding, and the breeding process of the wheat high yield varieties can be accelerated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
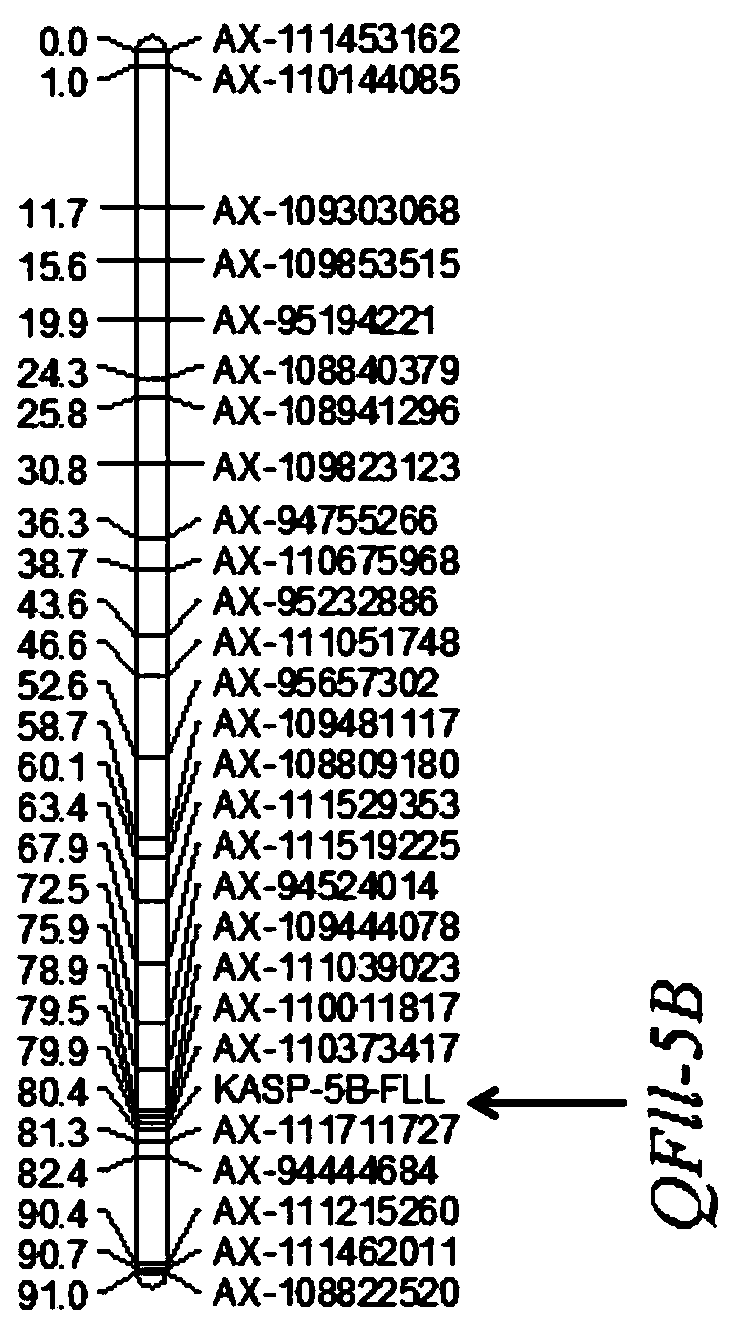
Triticum aestivum L. flag leaf length quantitative trait locus (QTL) linked molecular marker and application thereof
ActiveCN110499387AHigh linkageImprove use valueMicrobiological testing/measurementAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyLong arm
The invention relates to the field of triticum aestivum L. molecular breeding, and particularly discloses a triticum aestivum L. flag leaf length quantitative trait locus (QTL) linked molecular markerand application thereof. The single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) molecular marker linked with triticum aestivum L. flag leaf length QTL QFll-5B is provided and located on a 5B chromosome long arm ofa RefSeqv1.0 genome edition, and is the 51st of a sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.31, polymorphism is C / T, and the SNP molecular marker can be obtained by amplification of a primer shown in a nucleotidesequence such as SEQ ID NO.1-3. The SNP molecular marker can accurately trace the triticum aestivum L. flag leaf length QTL QFll-5B, and predict the flag leaf length characteristics of triticum aestivum L., and molecular design breeding is convenient. The invention further discloses a method for identifying the molecular marker. The prediction accuracy of the flag leaf length can be enhanced by using the method, so that varieties or strains of the triticum aestivum L. with increased the flag leaf length are conveniently and rapidly screened for breeding, and the breeding progress of the varieties of the triticum aestivum L. with a high yield can be greatly accelerated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
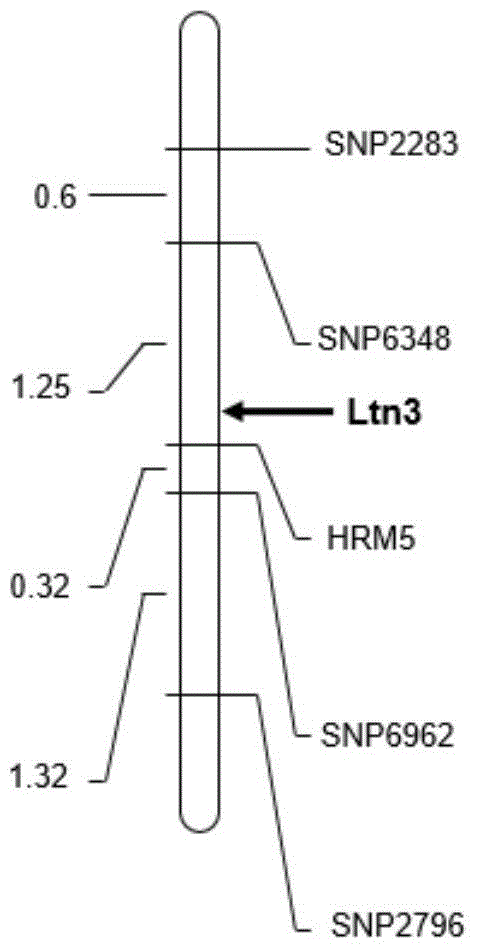
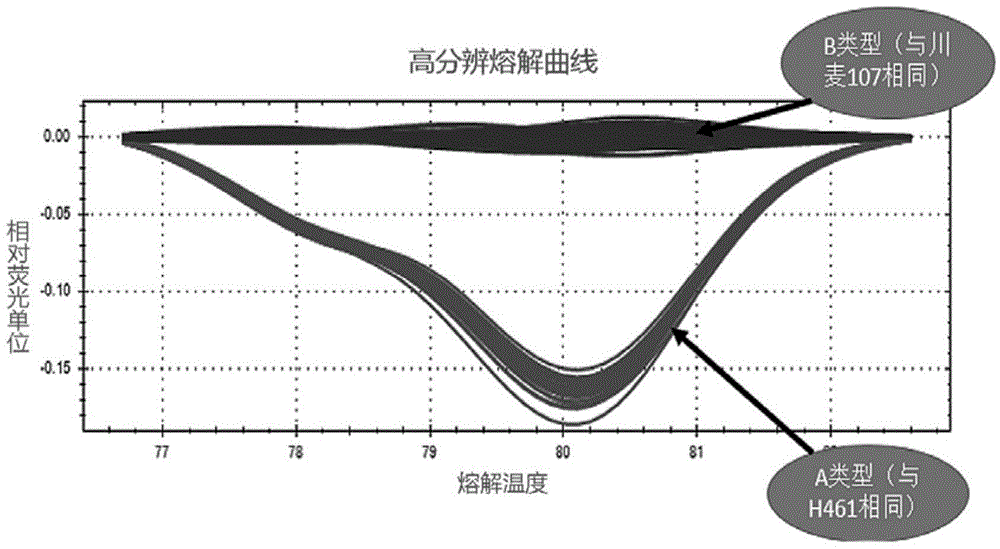
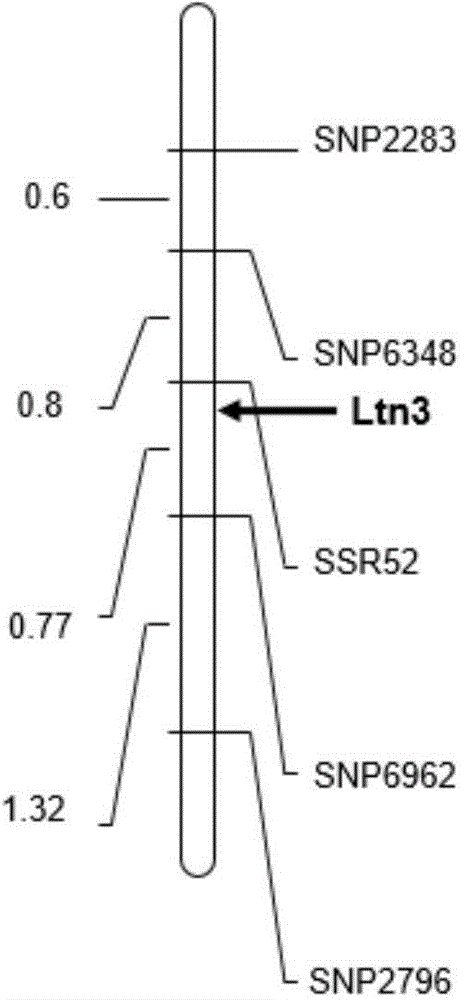
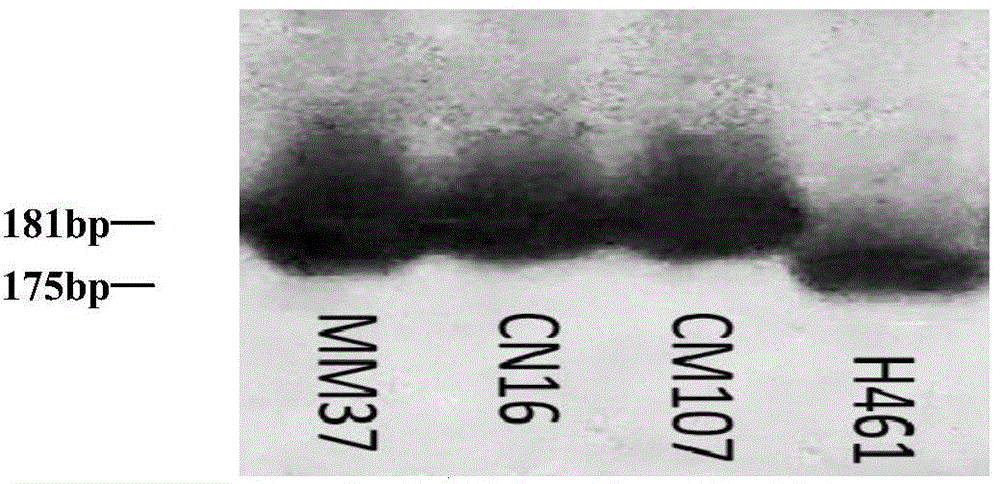
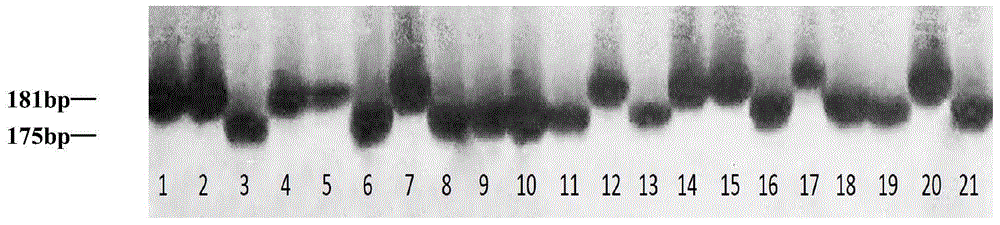
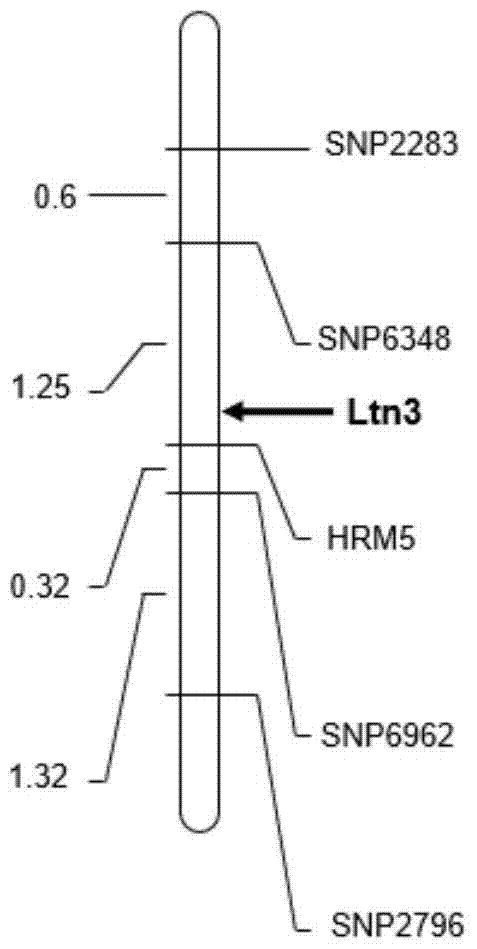
Molecular marker HRM5 of wheat few-tillering gene Ltn3 and application thereof
InactiveCN104818271AImprove selection identification efficiencyImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyTriticeae
The invention discloses a molecular marker HRM5 which is closely linked with wheat few-tillering gene Ltn3, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the molecular marker HRM5 is represented as the SEQ ID No.1. Genetic distance between the molecular marker and the wheat few-tillering gene Ltn3 is 0.35 cM. A test result proves that the molecular marker can accurately trace the wheat few-tillering gene and predict tillering characters of wheat, thereby further carrying molecular-designing breeding conveniently. The invention also discloses a method of identifying the molecular marker of the wheat few-tillering gene Ltn3. By means of the method, accuracy of tillering prediction can be increased, success rate of specific plant type breeding can be increased, and achievement of an object of increasing per unit area yield of wheat is accelerated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
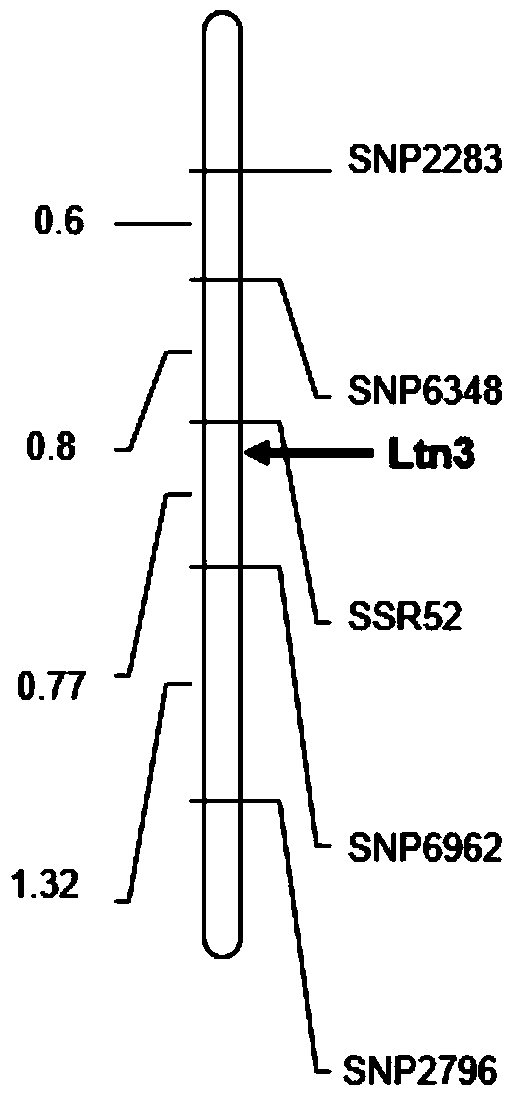
Molecular marker SSR52 of wheat few-tillering gene Ltn3 and application thereof
InactiveCN104818272AImprove use valueEfficient and accurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyTriticeae
The invention discloses a molecular marker SSR52 which is closely linked with wheat few-tillering gene Ltn3, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the molecular marker SSR52 is represented as the SEQ ID No.1. Genetic distance between the molecular marker and the wheat few-tillering gene Ltn3 is 0.3 cM. A test result proves that the molecular marker can accurately trace the wheat few-tillering gene and predict tillering characters of wheat, thereby further carrying molecular-designing breeding conveniently. The invention also discloses a method of identifying the molecular marker of the wheat few-tillering gene Ltn3. By means of the method, accuracy of tillering prediction can be increased, success rate of specific plant type breeding can be increased, and achievement of an object of increasing per unit area yield of wheat is accelerated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
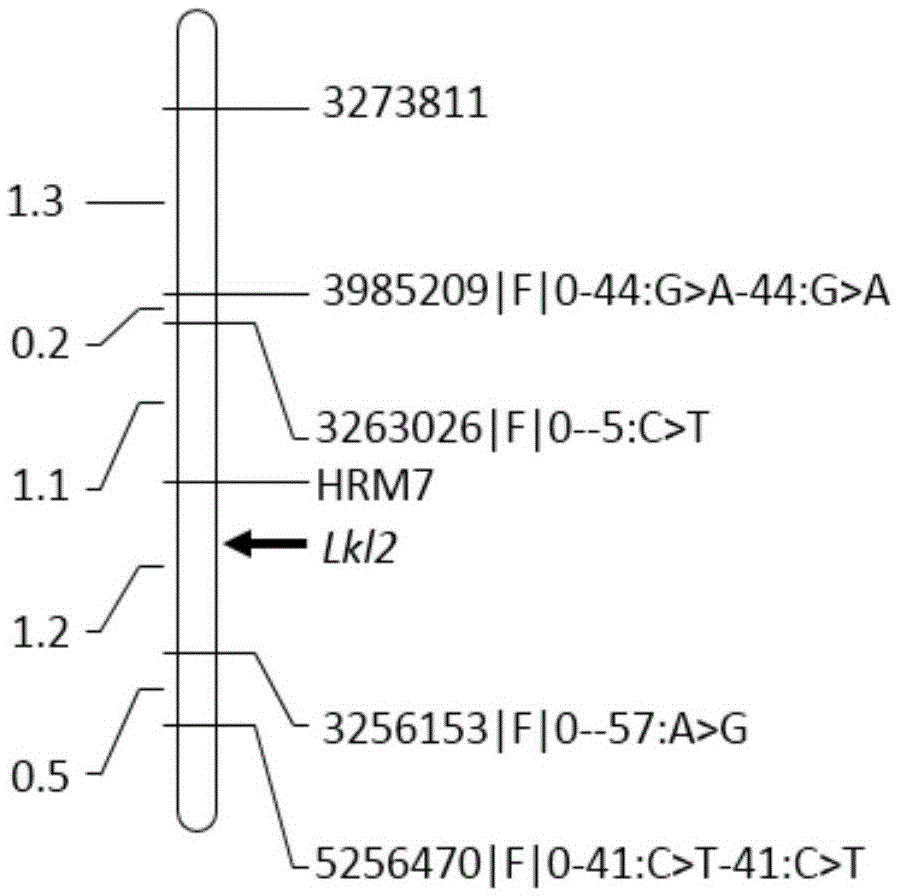
Molecular marker HRM7 of barley grain length gene LkI2 and application of molecular marker
InactiveCN105524994AImprove selection identification efficiencyImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceMolecular breeding
The invention relates to the field of barley molecular breeding, and in particular discloses a molecular marker HRM7 of barley grain length gene LkI2 and application of the molecular marker. The nucleotide sequence of the molecular marker HRM7, which is closely linked with the barley grain length gene LkI2, is as shown in SEQ ID No.1. Upon detection and analysis, the molecular marker can accurately track the barley grain length gene and predict the grain length traits of the barley, so as to facilitate molecular designing and breeding. The invention also discloses a method for identifying the molecular marker of the barley grain length gene LkI2; by virtue of the method provided by the invention, the accuracy of grain length prediction is enhanced, so that barley varieties or lines having enhanced grain length QTL can be conveniently and rapidly screened out; and the process of selecting high-yield barley varieties can be greatly accelerated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
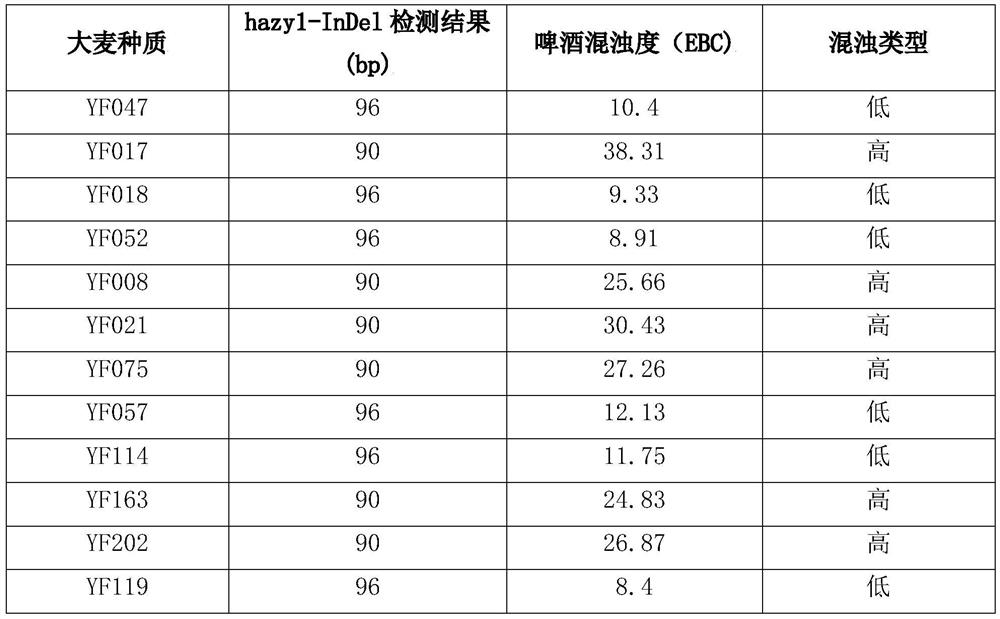
InDel molecular marker related to barley beer turbid character and application thereof
InactiveCN111690764AImprove identification efficiencyEfficient and accurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideHordeum vulgare
The invention discloses an InDel molecular marker related to barley beer turbid characters and application thereof. The InDel molecular marker is designed based on a segment of 6bp deletion existing at 70bp downstream of an initial site ATG of a barley beer turbid gene hazy1 coding region. The method is used for identifying the beer turbidity character of barley. A nucleotide sequence of a codingregion of the barley beer turbid gene hazy1 is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1; the 6 bp deleted nucleotide sequence is CCGCTG. The invention discloses the InDel molecular marker closely linked with the barleybeer turbid character QTL for the first time, and the molecular marker is a codominant marker, is accurate and efficient in detection and convenient and stable in amplification, can be used for molecular marker-assisted selection, and improves the identification efficiency of barley varieties with different turbid characteristics.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Molecular marker for increasing barley harvest index QTL site under low phosphor condition and application thereof
ActiveCN107746895AIncrease harvest indexImprove use valueMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention provides a molecular marker for increasing barley harvest index QTL site under low phosphor condition and an application thereof. The molecular marker is Hvc316, a nucleotide sequence isshown as SEQ ID No:1, the molecular marker is positioned on barley 3H chromosome, and can accurately track the site for increasing a barley harvest index QTL under low phosphor condition, predicts the harvest index characteristic of the barley under the low phosphor condition, and is convenient for molecular design breeding with nutrient efficient utilization. The invention also provides the application of the molecular marker Hvc316 in barley high-yield nutrient efficient breeding. A method provided in the invention is capable of enhancing the accuracy of prediction of the barley harvest index under low phosphor condition, and is convenient for rapidly screening the barley variety or lines used for breeding for increasing the barley harvest index QTL under low phosphor condition, so thata seed selection process of the barley high-yield high-efficiency variety can be greatly accelerated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Molecular marker for efficient utilization of QTL site by barley phosphorus and application of marker
InactiveCN109913579AImprove use valueImprove utilization efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural sciencePhosphorus utilization
The invention discloses a molecular marker for efficient utilization of a QTL site by barley phosphorus and an application of the marker. The molecular marker is Hvc630, a nucleotide sequence of the marker is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 and is positioned on a barley 3H chromosome, and thus the marker can accurately track the QTL site efficiently utilized by the barley phosphorus, predict barley phosphorus utilization efficiency characteristics, and further facilitate molecular design breeding for nutrient efficient utilization. The invention further provides the application of the molecular marker Hvc630 in barley breeding with high-yield high-efficiency nutrients. By using the method, the accuracy of barley phosphorus utilization efficiency prediction can be enhanced, and barley varieties or strains with QTL for improving barley phosphorus utilization efficiency can be rapidly screened for breeding, so that the breeding process of high-yield high-efficiency barley varieties can be greatly accelerated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
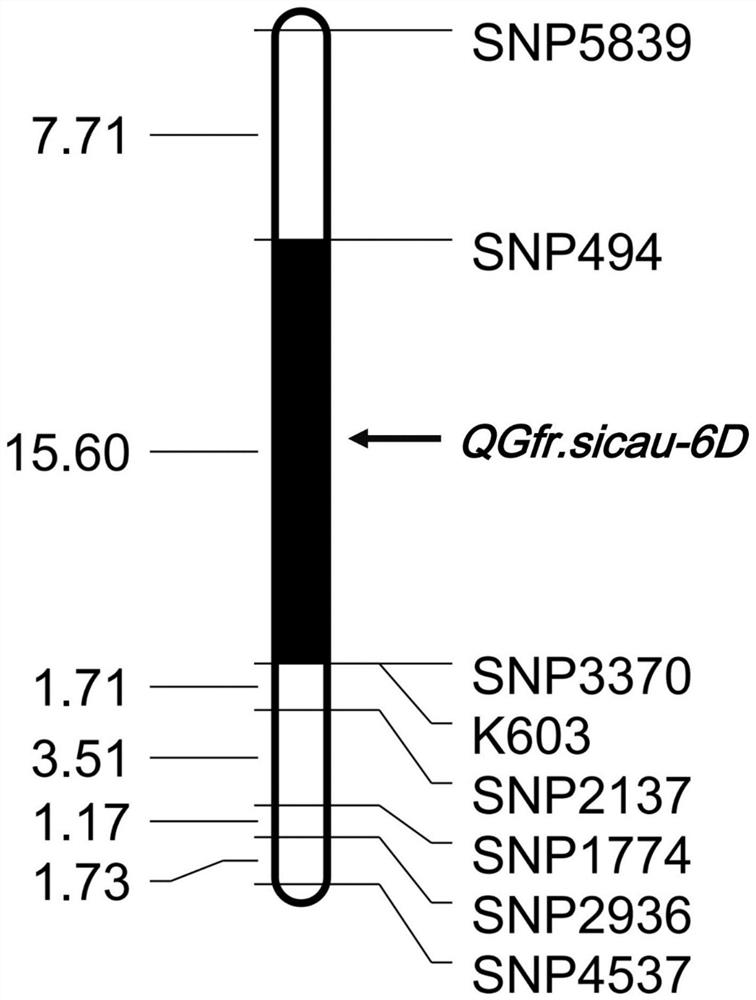
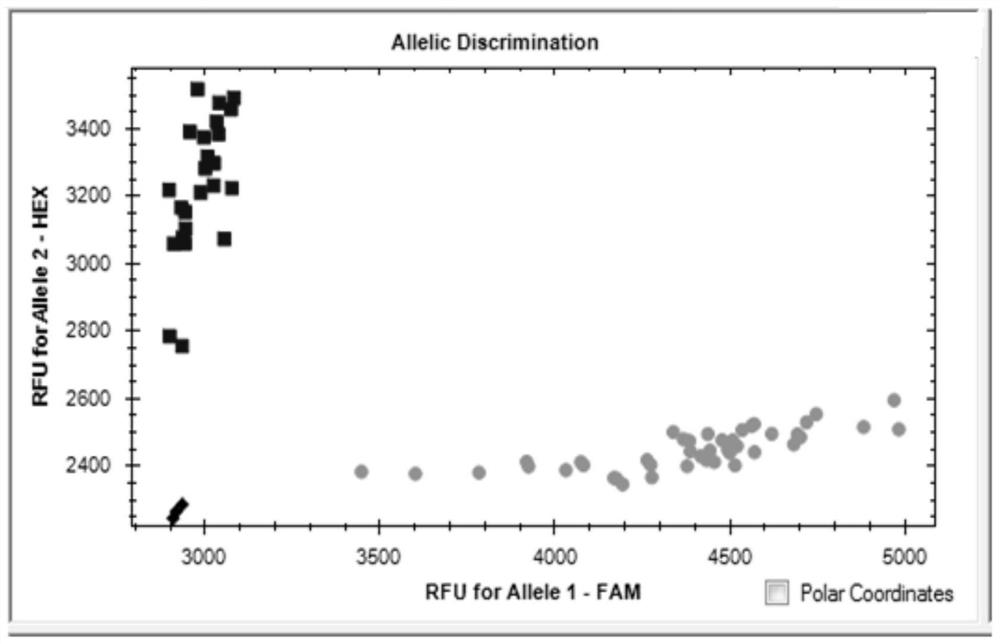
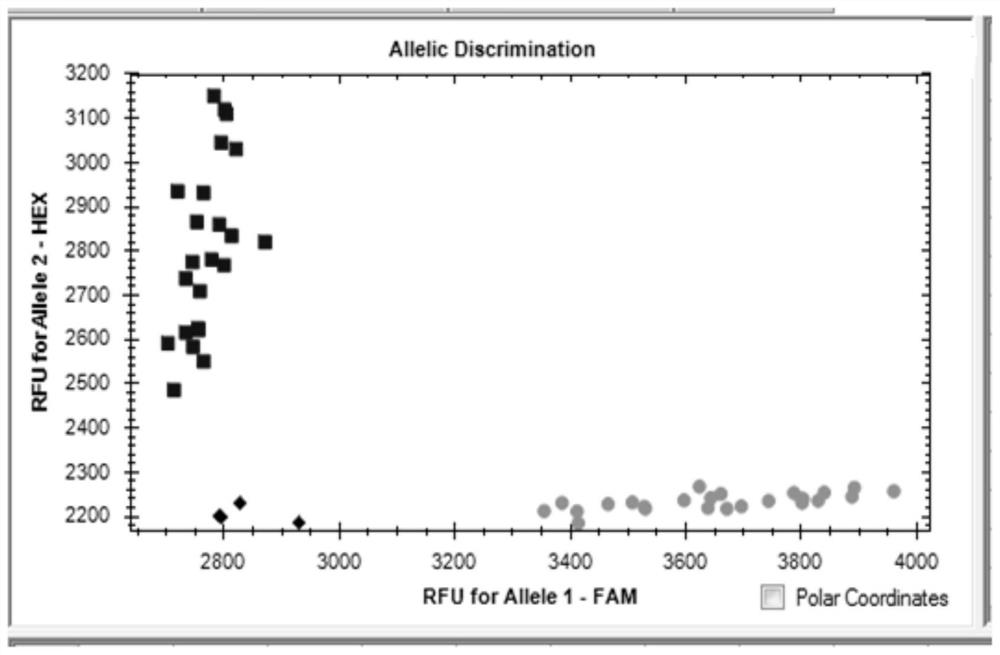
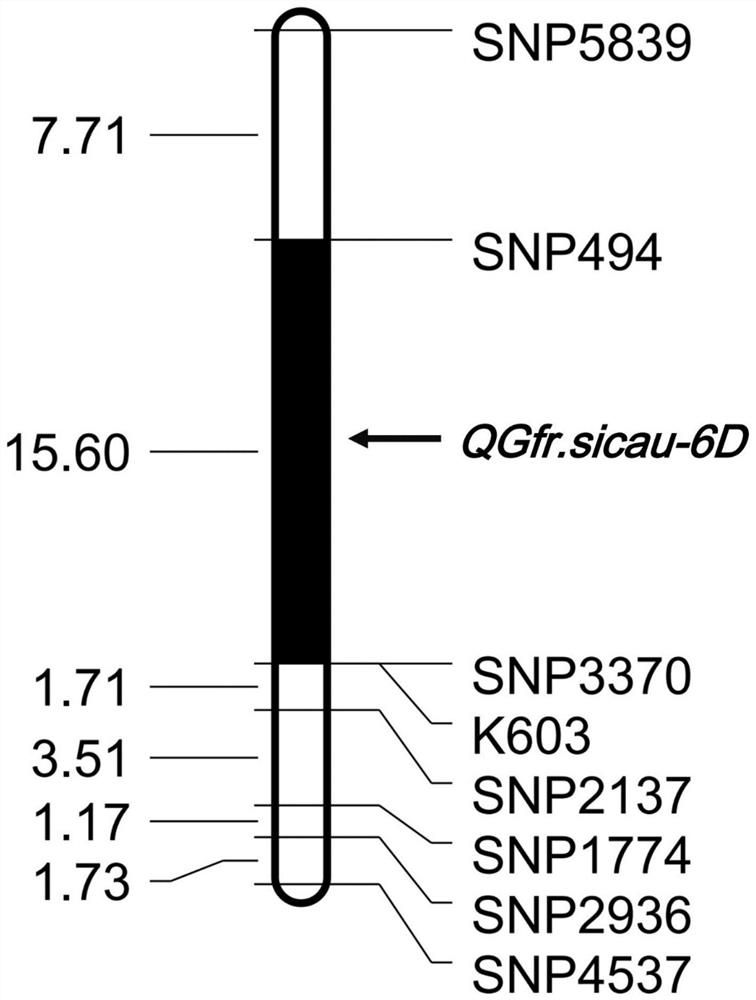
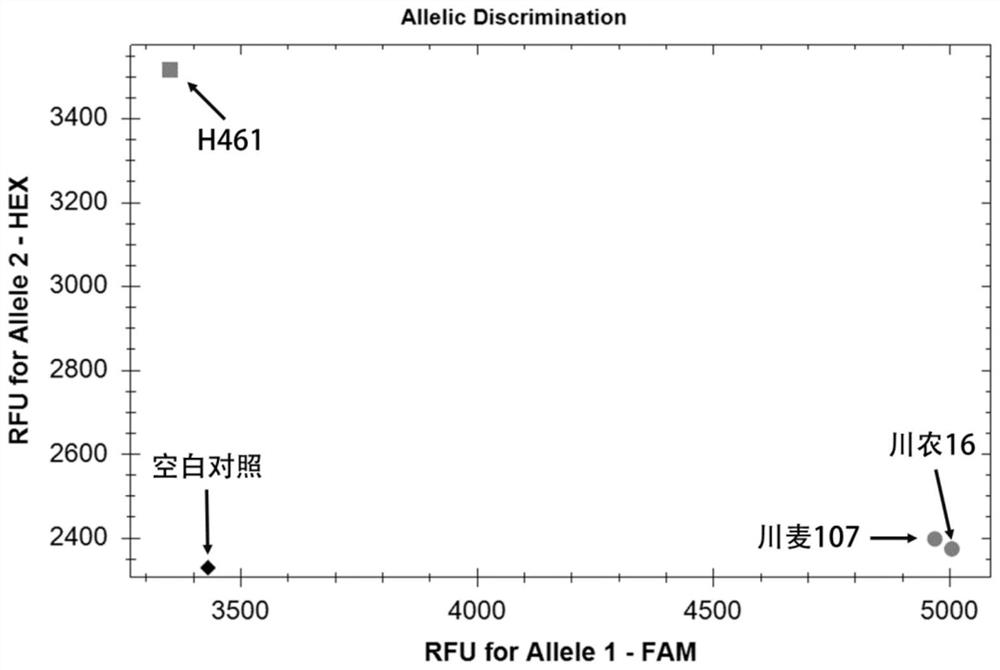
Molecular marker closely linked to wheat grain filling rate QTL QGfr.sicau-6D and application of molecular marker
ActiveCN111647677AIncreased grout rateImprove selection identification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention provides a molecular marker closely linked to the wheat grain filling rate QTL QGfr.sicau-6D. The molecular marker is K603, and the nucleotide sequence of the molecular marker is as shown by SEQ ID NO.1. The molecular marker K603 is closely linked to the wheat grain filling rate QTL. Detection analysis shows that the molecular marker can be used for accurately tracking the wheat grain filling rate QTL and predicting the wheat grain filling rate characteristics to further provide convenience for molecular design breeding. Through detection, the molecular marker K603 can enhance the accuracy of the wheat grain filling rate prediction, so that the wheat varieties or strains with the grain filling rate increasing QTL can be fast screened for breeding, and the breeding progress ofthe wheat high-yield varieties can be greatly accelerated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
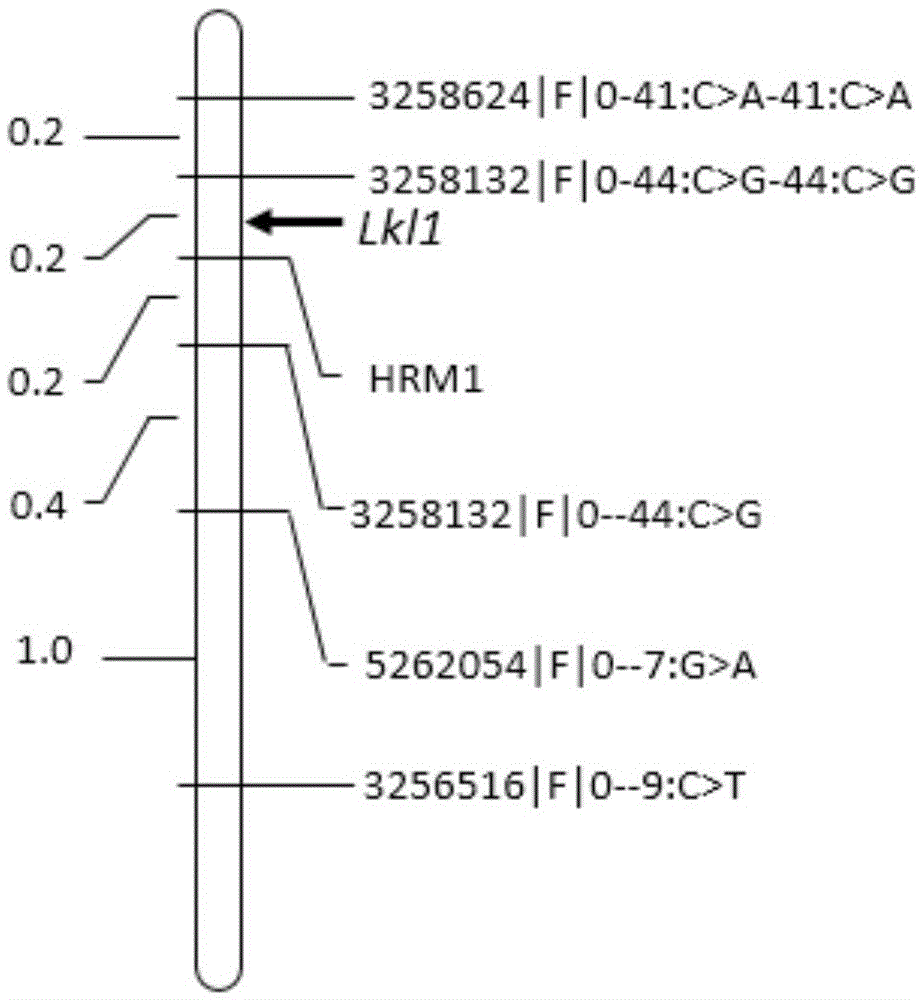
Molecular marker HRM1 of barley grain length gene LkI1 and application of molecular marker
InactiveCN105524993AImprove accuracyImprove selection identification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionMolecular breedingAgricultural science
The invention relates to the field of barley molecular breeding, and in particular discloses a molecular marker HRM1 of barley grain length gene LkI1 and application of the molecular marker. The nucleotide sequence of the molecular marker HRM1, which is closely linked with the barley grain length gene LkI1, is as shown in SEQ ID No.1. Upon detection and analysis, the molecular marker can accurately track the barley grain length gene and predict the grain length traits of the barley, so as to facilitate molecular designing and breeding. The invention also discloses a method for identifying the molecular marker of the barley grain length gene LkI1; by virtue of the method provided by the invention, the accuracy of grain length prediction is enhanced, so that barley varieties or lines having enhanced grain length QTL can be conveniently and rapidly screened out; and the process of selecting high-yield barley varieties can be greatly accelerated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
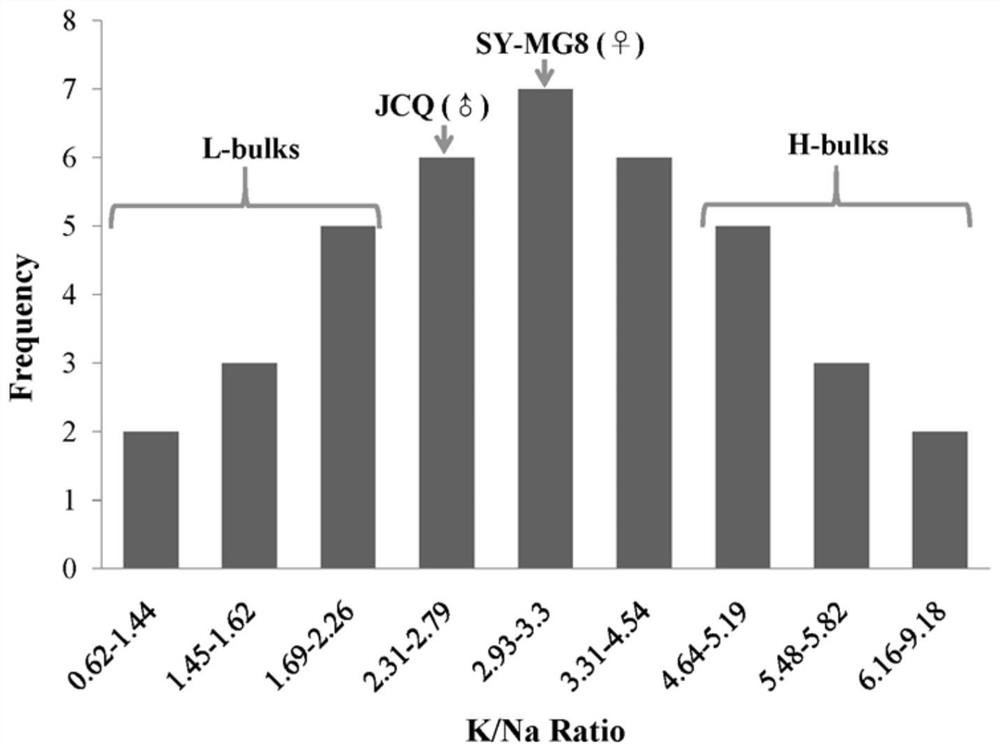
SNP molecular markers linked with rice sodium and potassium ion absorption QTL and application thereof
PendingCN111733278AImprove purposeHigh linkageMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyMolecular breeding
The invention relates to the field of genetic breeding, and particularly relates to SNP molecular markers linked with rice sodium and potassium ion absorption QTL qK / Na-3-1, primers and application. The SNP molecular markers RS (36172492) and RS (36174628) are located on a Chr3 chromosome short arm of an IRGSP-1.0 genome version, the sequences are shown as SEQ ID NO. 1 and SEQ ID NO. 2, the polymorphisms are (T / G) (G / -), (A / -), and the SNP molecular markers can be obtained by amplifying the primers shown as SEQ ID NO. 3 and SEQ ID NO. 5. The molecular markers can accurately track the rice sodium and potassium ion absorption QTL qK / Na-3-1 and predict the potential salt tolerance characteristic of rice, and then molecular breeding is facilitated. The invention further discloses a method foridentifying the rice sodium and potassium ion absorption QTL qK / Na-3-1 molecular markers. By means of the method, the accuracy of sodium and potassium ion absorption prediction can be enhanced, so that rice varieties or strains with potential enhanced rice salt tolerance are quickly screened out for breeding, and the breeding process of the rice varieties with potential salt tolerance can be greatly accelerated.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A molecular marker ssr52 of wheat oligo-tiller gene ltn3 and its application
InactiveCN104818272BImprove use valueEfficient and accurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceType specific
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
A molecular marker hrm5 of wheat oligo-tiller gene ltn3 and its application
InactiveCN104818271BImprove use valueEfficient and accurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a molecular marker HRM5 closely linked with the wheat oligo-tiller gene Ltn3, the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID No.1, and the genetic distance between the molecular marker and the wheat oligo-tiller gene Ltn3 is 0.35cM. Detection and analysis show that the molecular marker can accurately track the wheat oligo-tiller gene, predict the tiller characteristics of wheat, and facilitate molecular design breeding. The invention also discloses a method for identifying the molecular marker of the wheat oligo-tiller gene Ltn3. The method provided by the invention can enhance the accuracy of tiller prediction, improve the success rate of specific plant type breeding, and accelerate the realization of the goal of increasing wheat yield per unit area .
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
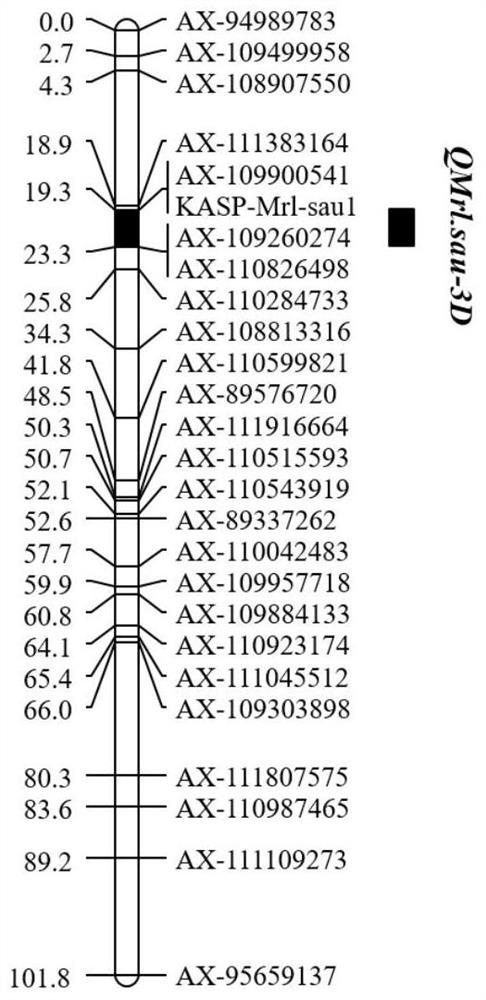
Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) molecular marker linked with maximum root length QTL QMrl.sau-3D of wheat and application of SNP molecular marker
ActiveCN114807429AClosely linkedIncreased root lengthMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationLong root lengthNucleotide
The invention discloses a wheat maximum root length QTLQMrl.sau-3D linked SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) molecular marker and application thereof, and relates to the field of wheat molecular genetic breeding. The SNP molecular marker and QMrl.sau-3D are co-localized on a 3D chromosome long arm of a wheat genome, the nucleotide sequence of the SNP molecular marker is shown as SEQ ID NO.16, and C / T mutation exists at the 36bp position of the SNP molecular marker. The SNP molecular marker KASP-Mrl-sau1 is closely linked with the maximum root length QTLQMrl.sau-3D of wheat, the maximum root length QTLQMrl.sau-3D of wheat can be accurately tracked, the maximum root length characteristic of wheat can be predicted, the selection and identification efficiency of the maximum root length of wheat can be remarkably improved, wheat varieties or strains with the long root length can be rapidly screened out, and the application prospect is wide. The process of wheat molecular genetic breeding is accelerated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
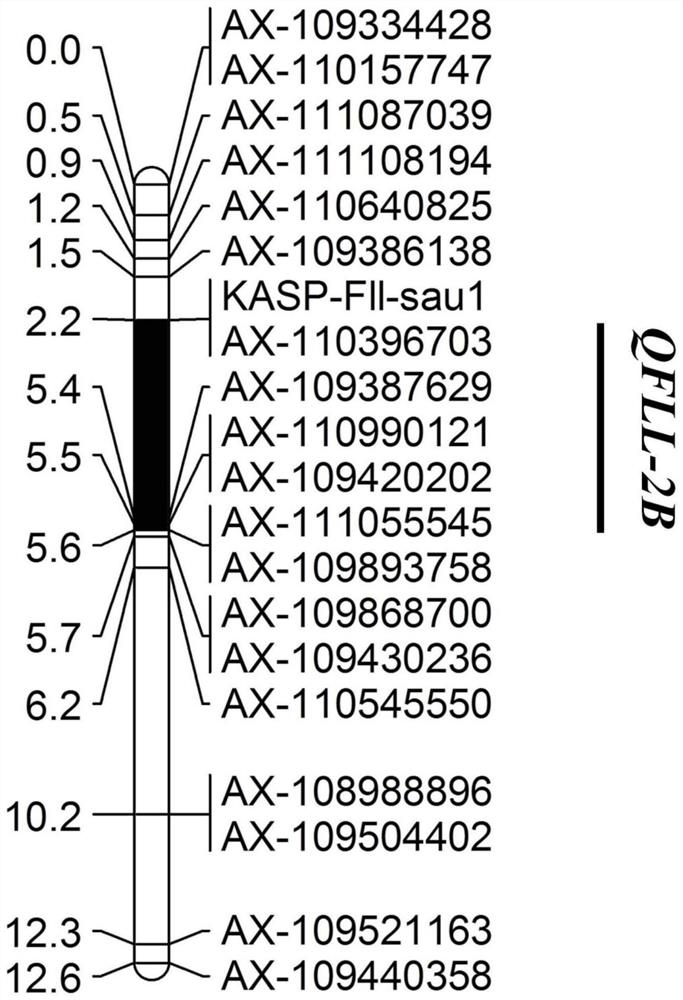
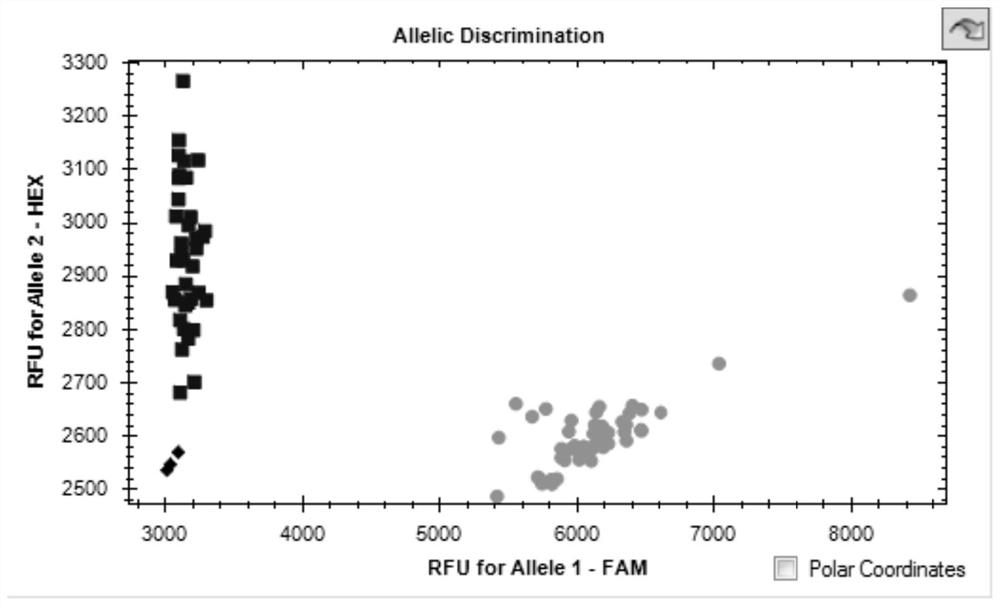
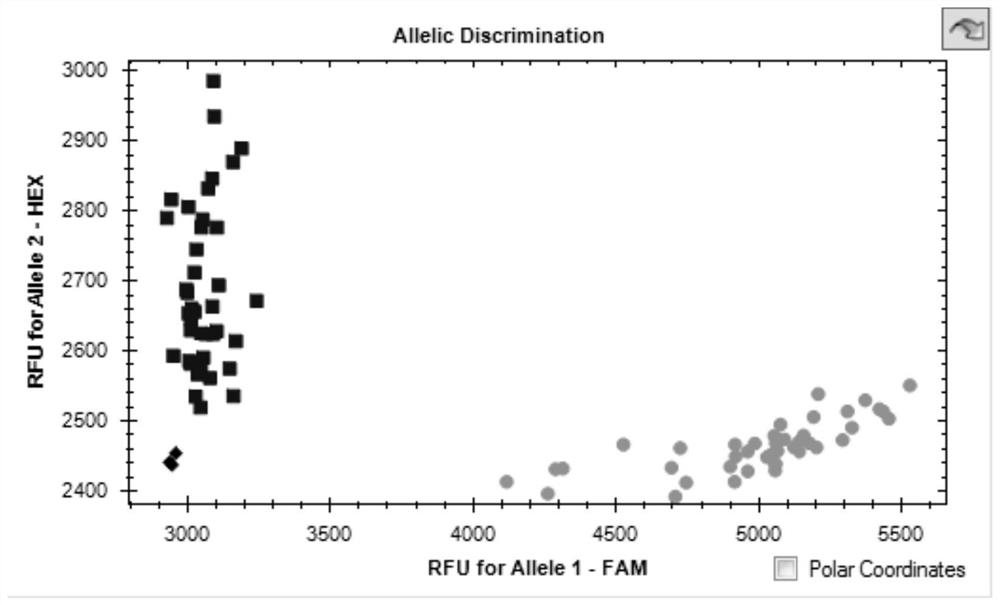
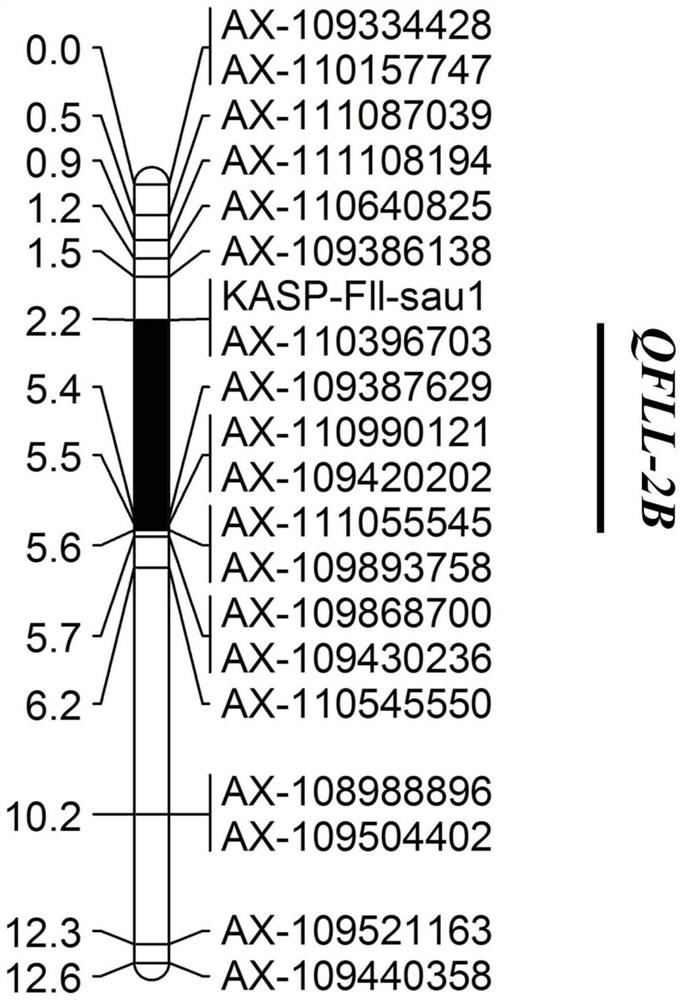
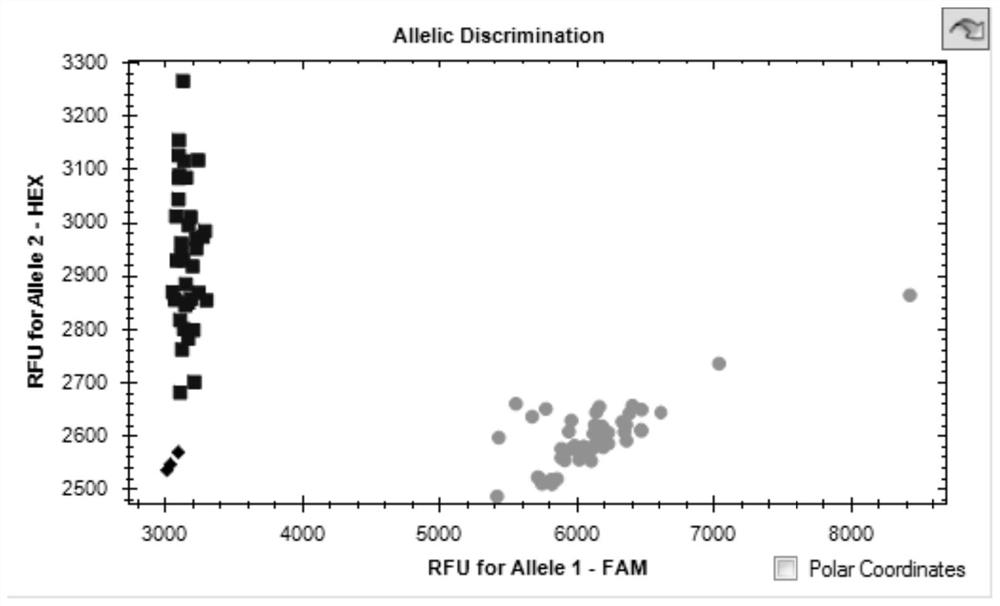
KASP molecular marker linked to wheat flag leaf length QTL QFll-2B and application thereof
ActiveCN111893207AConvenient Assisted BreedingHigh linkageMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyMolecular breeding
The invention discloses a KASP molecular marker linked to wheat flag leaf length QTL QFll-2B and application thereof. The molecular marker is located on the long arm of chromosome 2B of a RefSeqv1.0 genome. The detection and analysis show that the molecular marker can accurately track the wheat flag leaf length QTL QFll-2B, predict wheat flag leaf length characteristics, and then facilitate molecular breeding. The invention also discloses a method for identifying the molecular marker of the wheat flag leaf length QTL QFll-2B, and the method provided by the invention can be used to enhance theaccuracy of predicting the flag leaf length, and can screen wheat varieties or lines with longer flag leaves more quickly for wheat breeding, greatly accelerating the process of wheat breeding.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
A KASP molecular marker linked to wheat flag leaf long qtl QFll-2B and its application
ActiveCN111893207BImprove use valueEfficient and accurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyMolecular breeding
The invention discloses a KASP molecular marker linked with wheat flag leaf long QTL QFll‑2B and an application thereof. The molecular marker is located on the long arm of chromosome 2B of the RefSeqv1.0 genome. Detection and analysis show that the molecular marker can accurately track the wheat flag leaf length QTL QFll-2B, predict the flag leaf length characteristics of wheat, and facilitate molecular breeding. The invention also discloses a method for identifying the molecular marker of the wheat flag leaf length QTL QFll-2B. The method provided by the invention can enhance the accuracy of the prediction of the flag leaf length, and can more quickly screen out those with longer flag leaves. Wheat varieties or strains are used for breeding, which greatly speeds up the process of wheat breeding.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
A SNP Molecular Marker Linked to Wheat Grain Length QTL and Its Application
ActiveCN112593007BImprove use valueImprove selection identification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyNucleotide
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
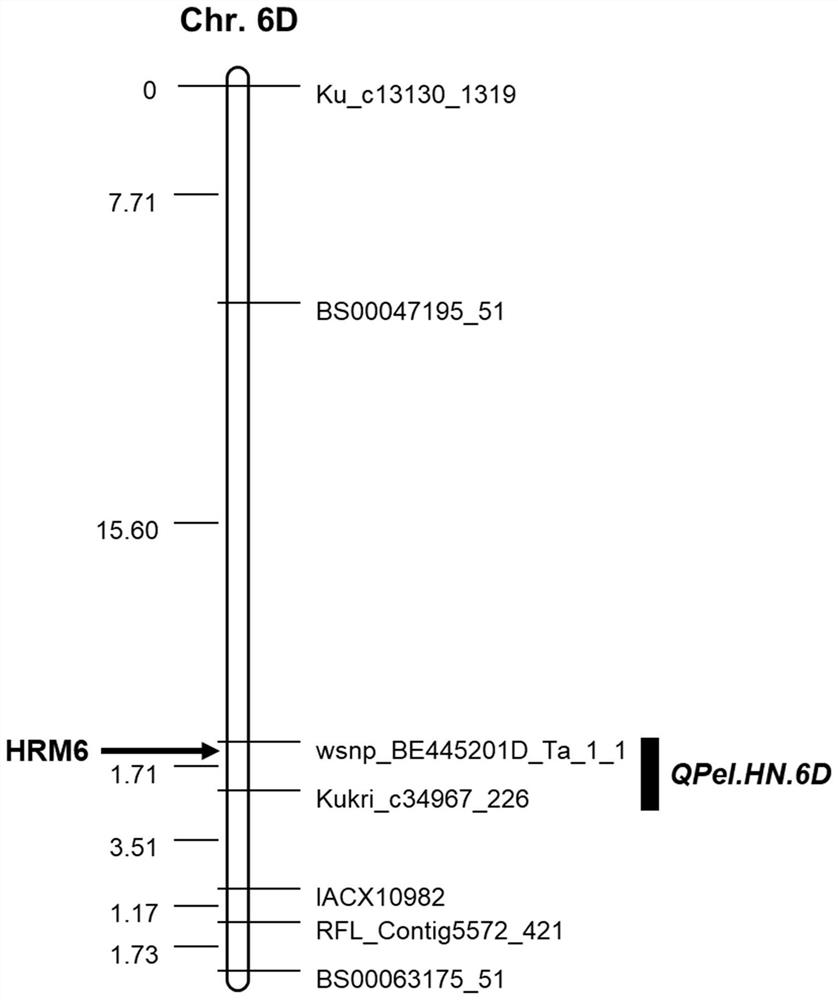
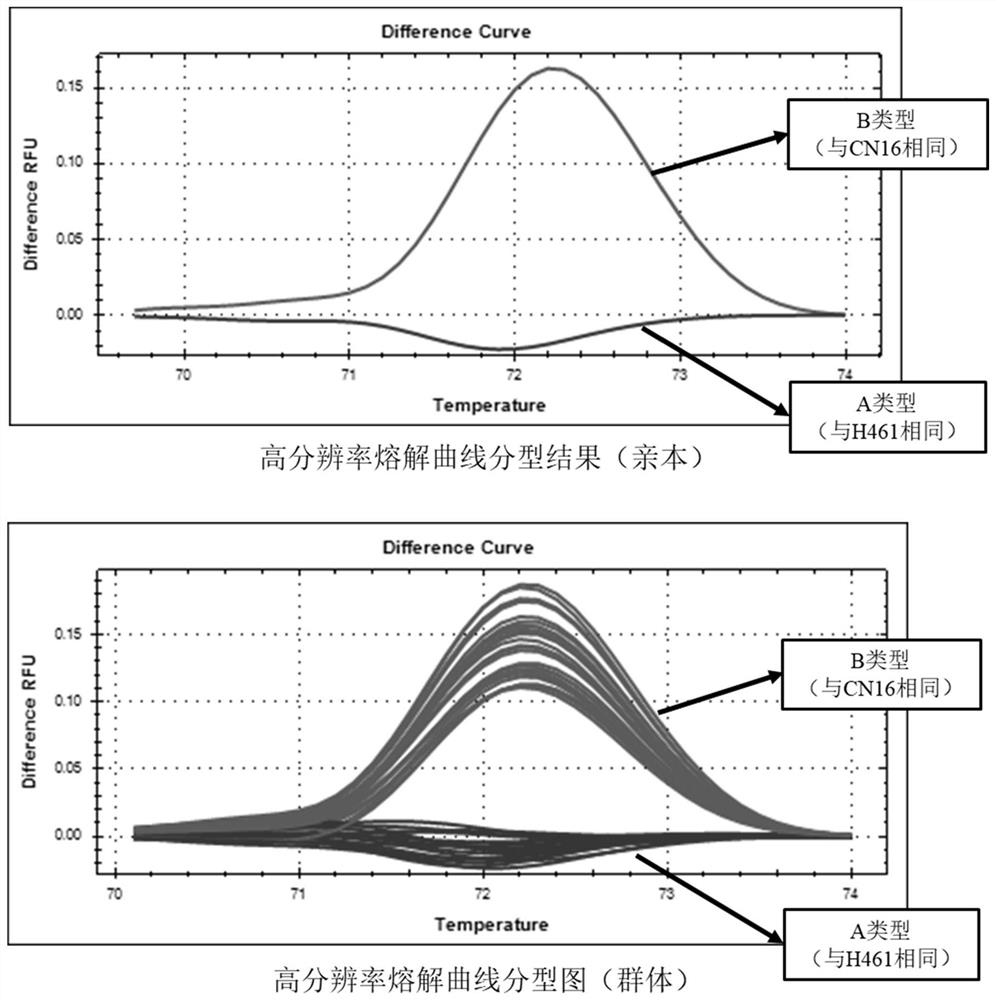
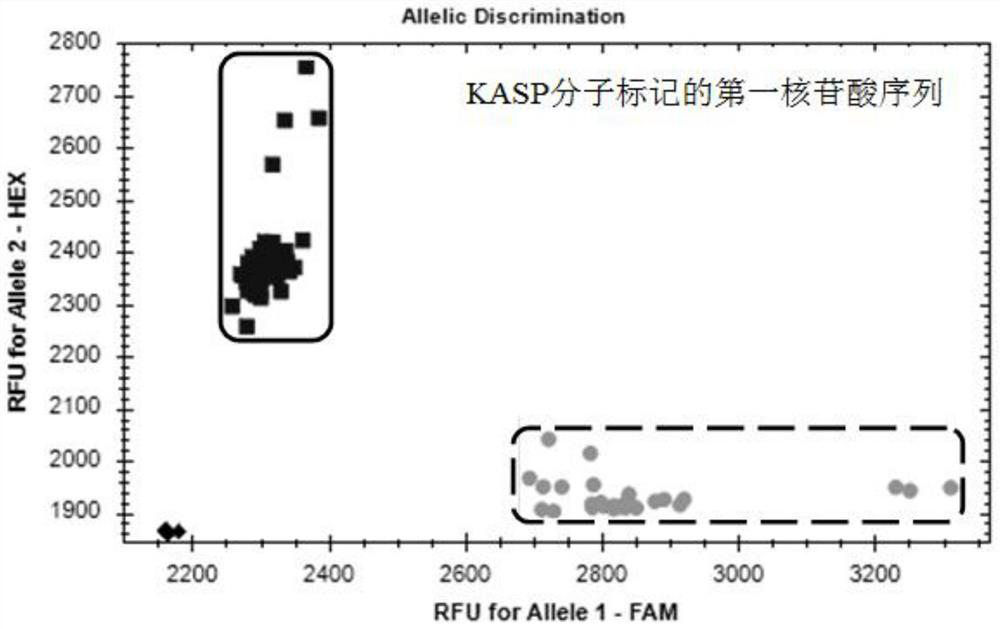
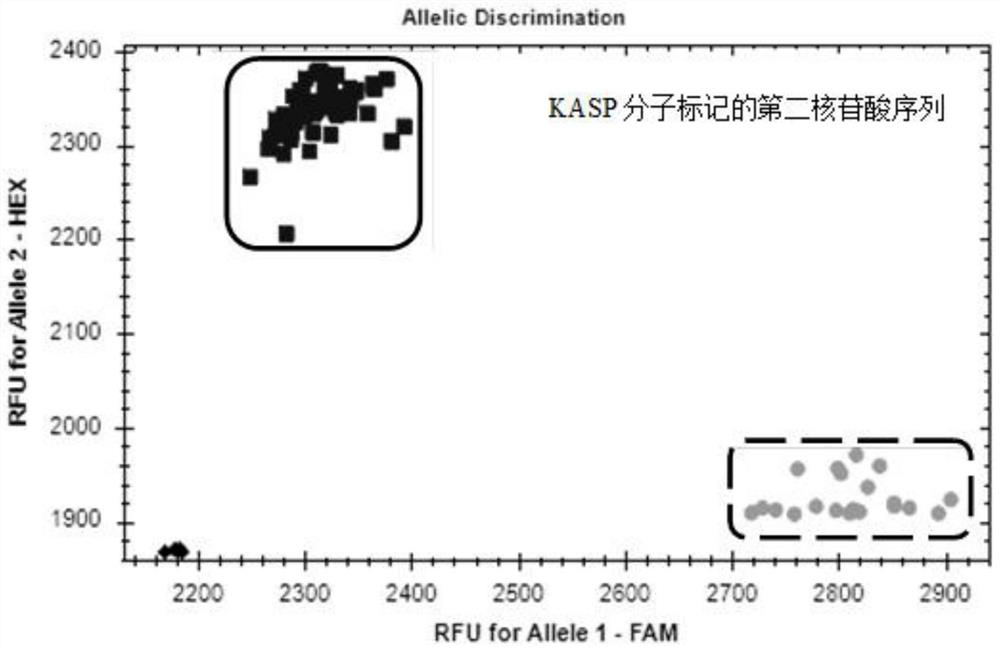
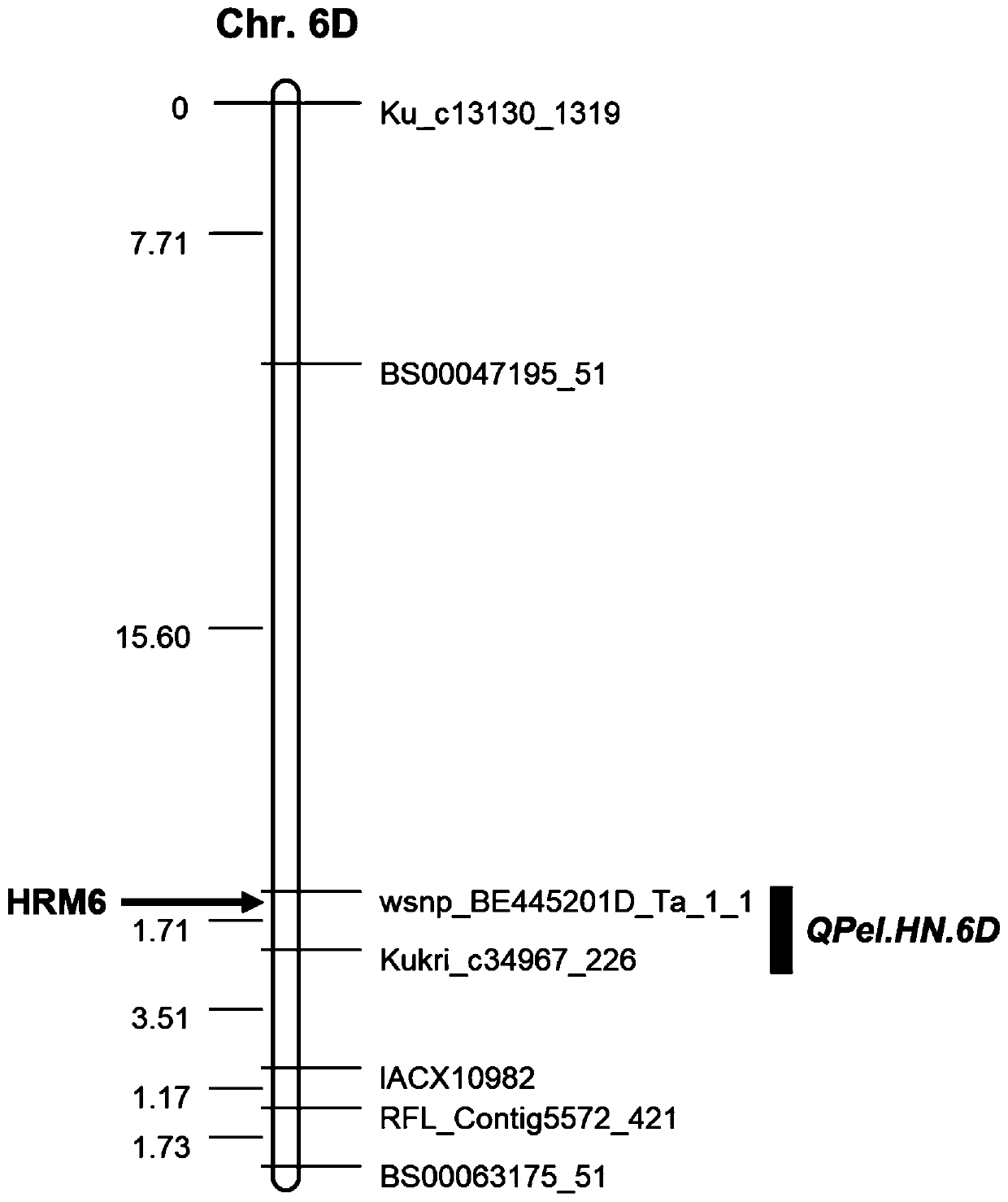
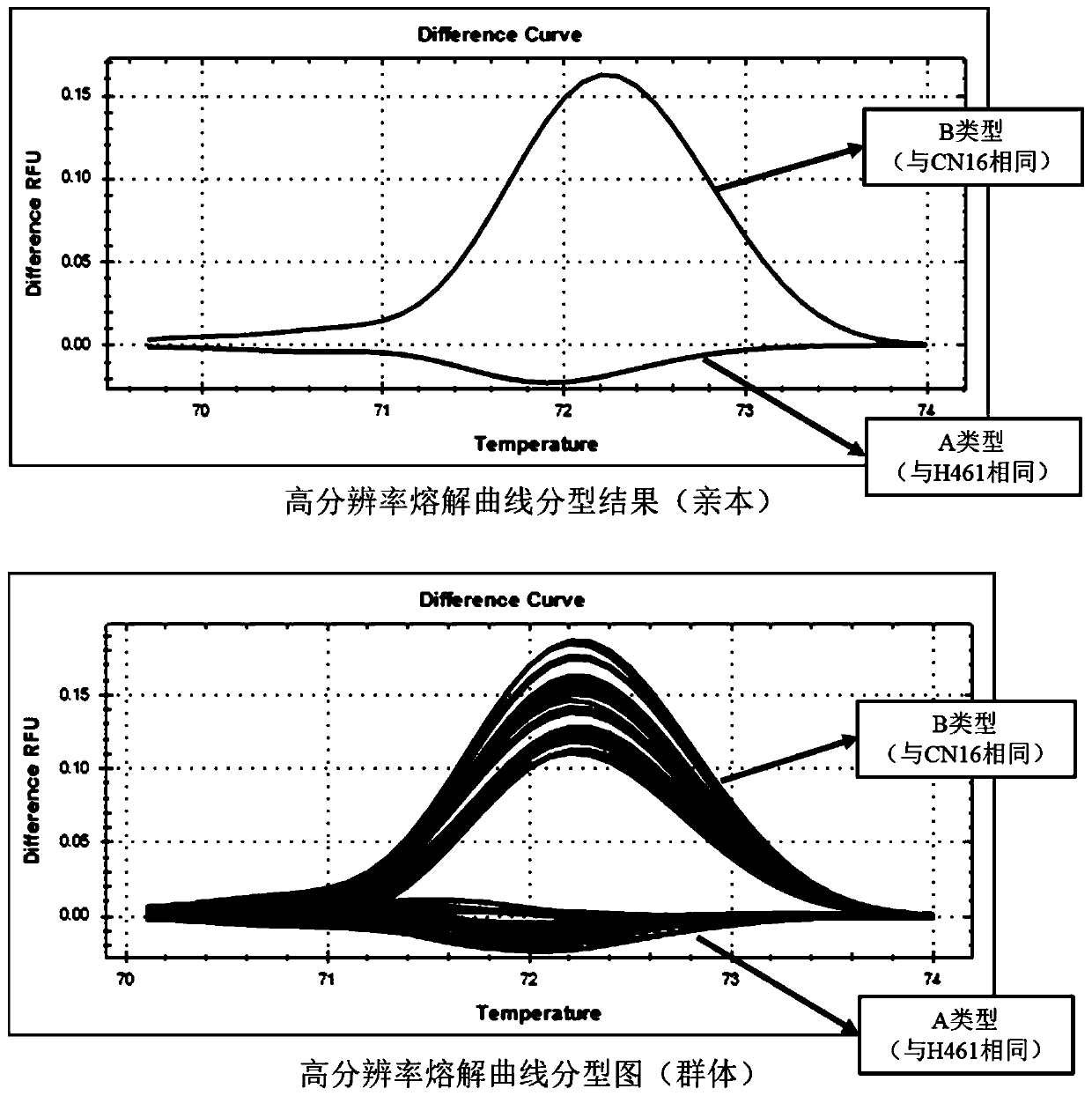
A Molecular Marker Closely Linked to Wheat Ear Extraction qtl QPel.HN.6D and Its Application
ActiveCN110106274BDrawout reductionEasy to expand and stableMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideGenetics
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular biology, in particular to a molecular marker closely linked to wheat ear extraction QTL QPel.HN.6D and its application. The present invention provides a molecular marker closely linked to wheat ear extraction QTL QPel.HN.6D, the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; molecular marker HRM6 is located at the end of wheat ear extraction QTL QPel.HN.6D Within the confidence interval, the two co-localized on wheat chromosome 6D. The molecular marker can accurately track the wheat panicle withdrawal QTL QPel.HN.6D, predict the characteristics of wheat panicle withdrawal, facilitate molecular design and breeding, and enhance the accuracy of ear withdrawal prediction, so as to quickly screen out QTLs with reduced panicle withdrawal Wheat varieties or strains are used for breeding, which can greatly speed up the breeding process of high-yielding wheat varieties with ideal plant types.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
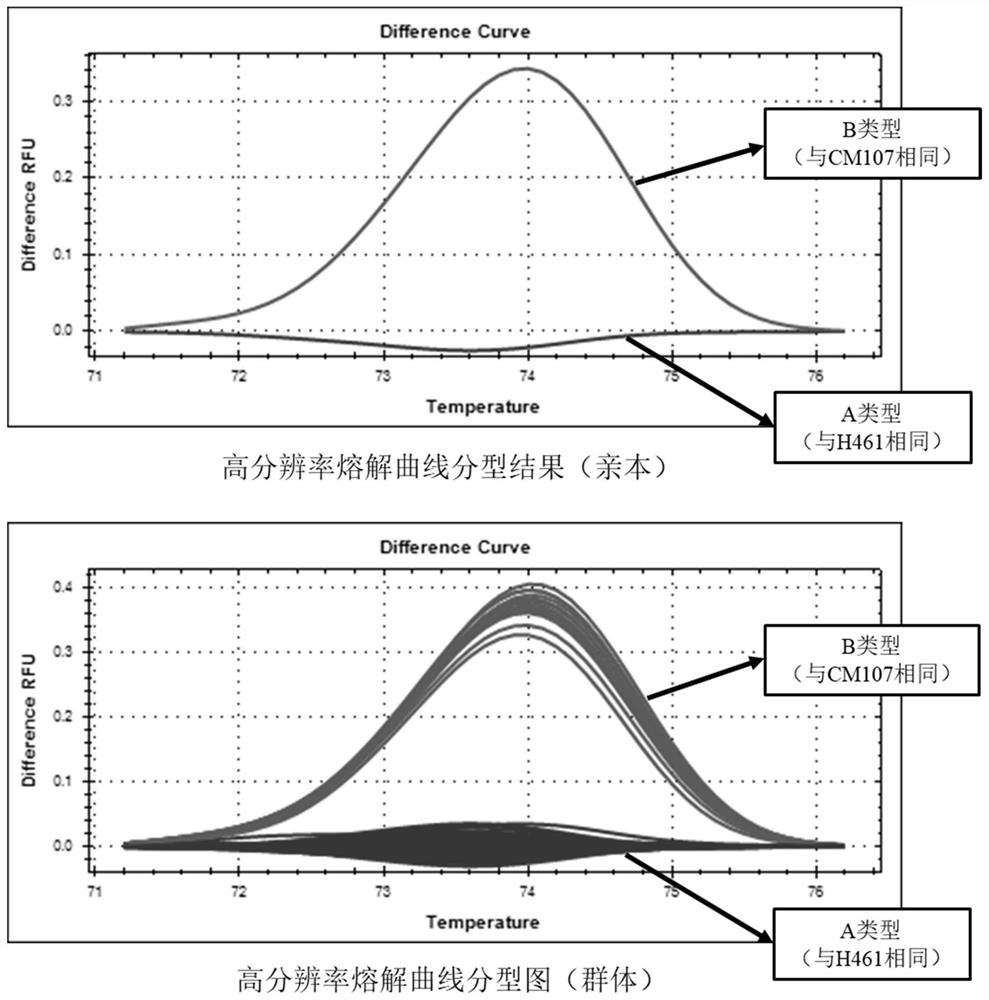
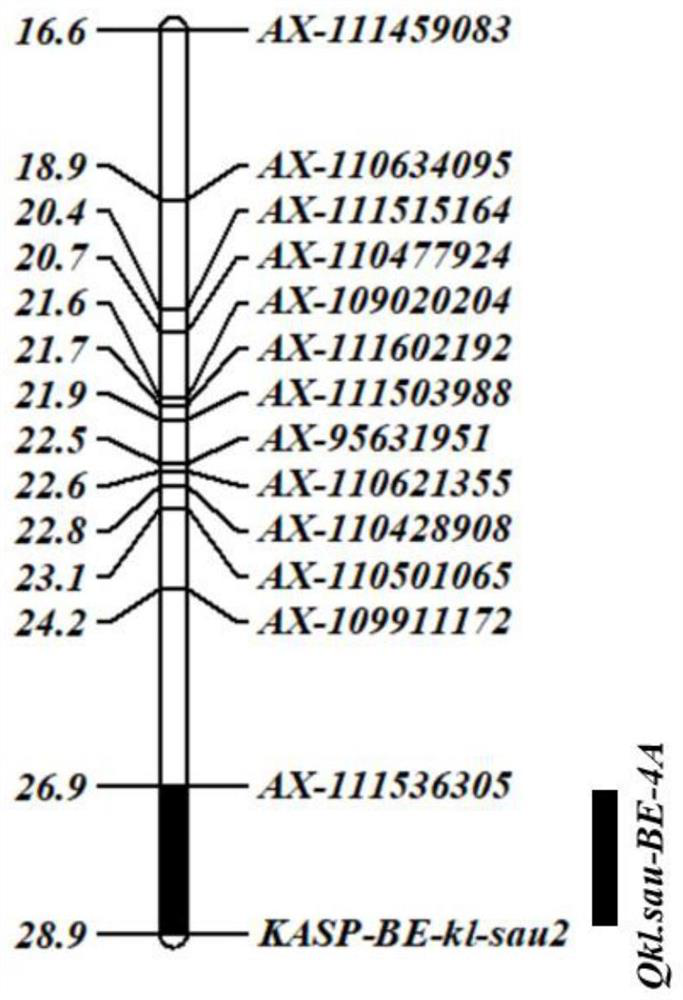
SNP molecular marker kasp-be-kl-sau2 linked to wheat grain length major QTL and its application
ActiveCN113801957BIncrease in grain lengthImprove use valueMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenetics
The invention discloses a SNP molecular marker KASP-BE-kl-sau2 linked with the main effect QTL of wheat grain length and its application, belonging to the field of crop molecular genetics and breeding. The molecular marker KASP‑BE‑kl‑sau2 polymorphism is C / T, KASP‑BE‑kl‑sau2 co-localizes with wheat grain length QTL Qkl.sau‑BE‑4A on the short arm of wheat chromosome 4A, and is located Within the Qkl.sau‑BE‑4A interval. The molecular marker KASP-BE-kl-sau2 disclosed by the present invention is extremely significantly correlated with the grain length QTLQkl.sau-BE-4A, presents the characteristics of closely linked markers, has high accuracy for molecular marker-assisted selection, and can accurately predict wheat grain length Traits play an important role in improving wheat yield and efficiently screening high-quality wheat varieties with longer grain length, and are also conducive to improving the efficiency of wheat breeding.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Molecular markers closely linked to wheat grain filling rate qtl QGfr.sicau-6D and its application
ActiveCN111647677BIncreased grout rateImprove selection identification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
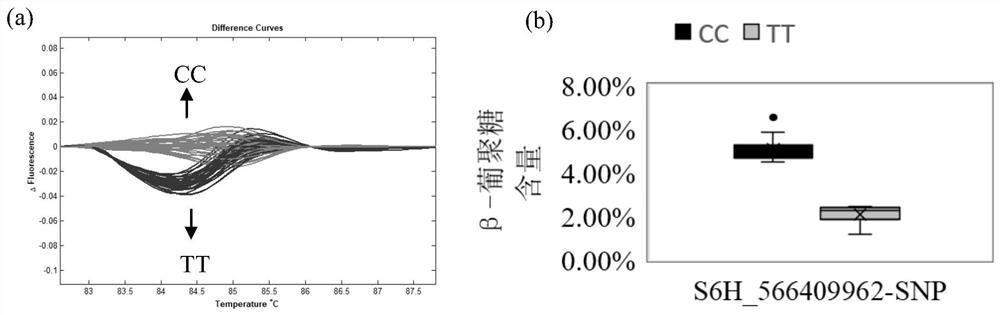
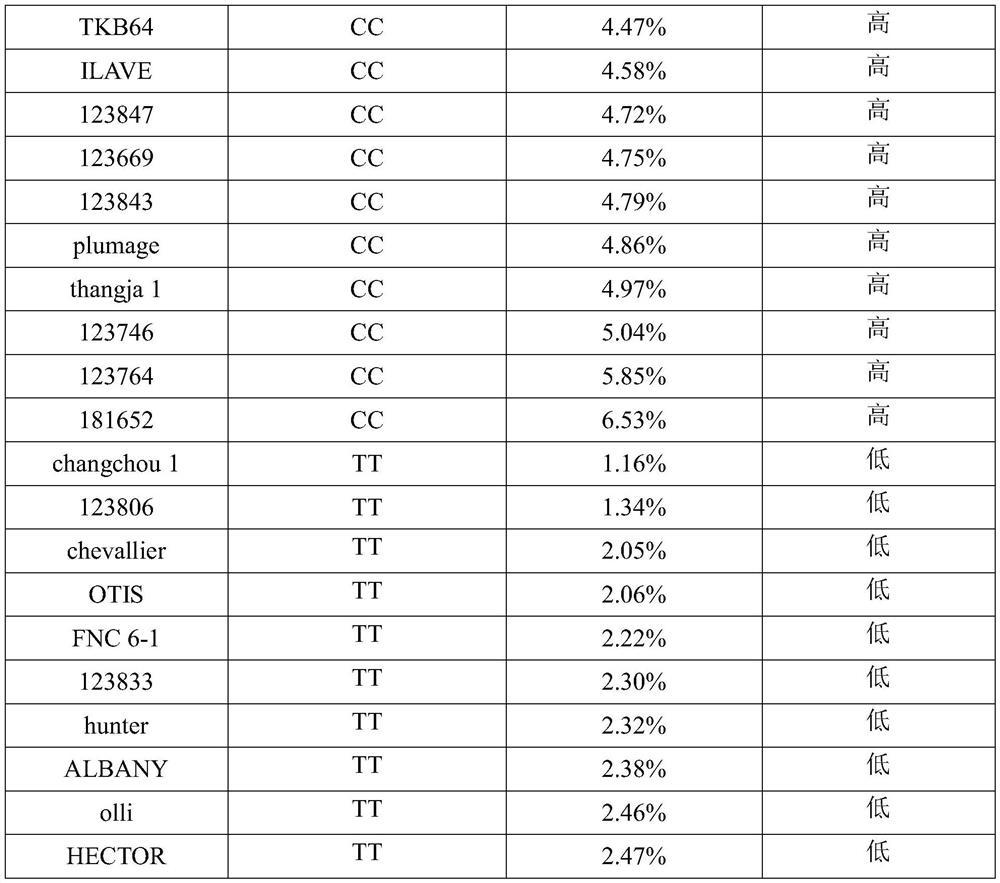
SNP molecular markers related to barley grain β-glucan content and their application
ActiveCN111705156BImprove identification efficiencyImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyHordeum vulgare
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
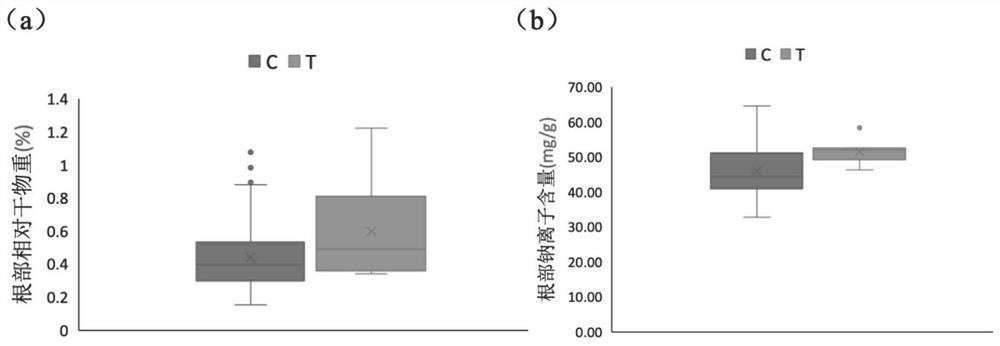
SNP molecular marker and application thereof
PendingCN113462804AImprove identification efficiencyEfficient and accurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyHordeum vulgare
The invention discloses an SNP molecular marker and application thereof. The locus of the SNP molecular marker is located at the 527797394th basic group of a barley chromosome I; the SNP base difference is C or T. According to the invention, an SNP locus with an improvement effect on salt tolerance is identified through whole-genome association analysis of relative dry matter weight and sodium content of roots under barley salt stress. The invention discloses an SNP molecular marker which is obviously associated with the relative dry matter weight and the sodium ion content of the root under the stress of barley salt, and the molecular marker is accurate and efficient in detection and convenient and stable in amplification. The SNP molecular marker can be used for molecular marker-assisted selection, and the identification efficiency of different salt-tolerant barley varieties is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
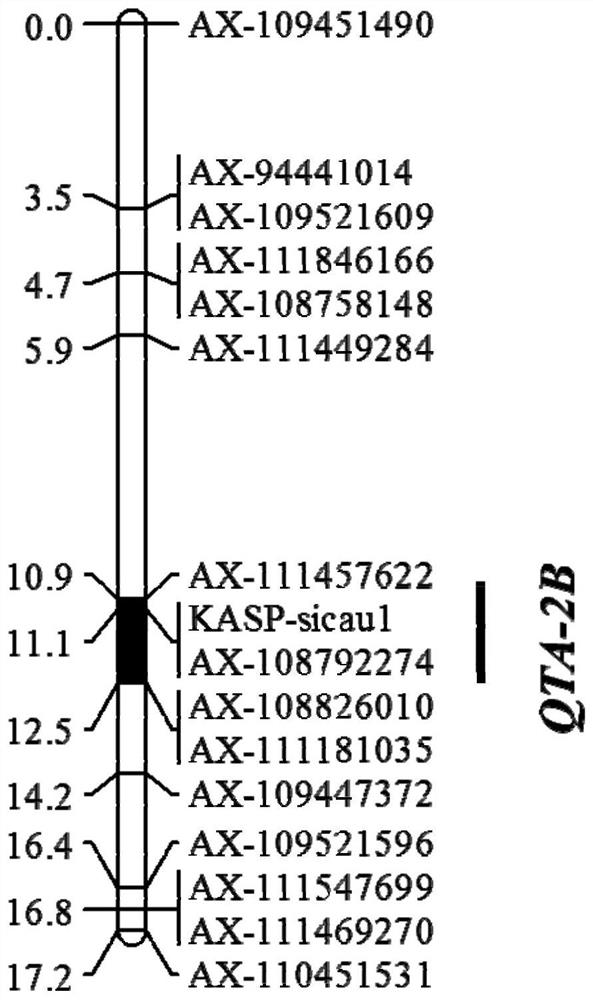
Molecular markers linked to qtl QTA-2B linked to tiller angle in wheat and its application
ActiveCN111763759BTiller angle increasedImprove use valueMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationGeneticsMolecular marker
The invention discloses a wheat tiller angle QTL QTA‑2B linked molecular marker and its application. The KASP‑sicau1 molecular marker is a SNP molecular marker, and the polymorphism is A / G. It co-localizes with wheat tiller angle QTL QTA‑2B on the long arm of wheat chromosome 2B, and is located in the QTL QTA‑2B interval. The molecular marker KASP-sicau1 disclosed in the present invention is extremely significantly correlated with the tiller angle QTL QTA-2B, presents the characteristics of closely linked markers, has high accuracy for molecular marker-assisted selection, and can significantly improve wheat varieties with larger tiller angles adapted to different environments The selection and identification efficiency is high, and the success rate is high.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
KASP molecular marker linked with wheat stripe rust resistant QTL and application
ActiveCN113897457AImprove selection identification efficiencyEfficient and accurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationNucleotideGenetics
The invention belongs to the technical field of crop molecular genetic breeding, and discloses a KASP molecular marker linked with wheat stripe rust resistance QTL and application. The nucleotide sequence of the KASP molecular marker comprises a first nucleotide sequence and a second nucleotide sequence; and the first nucleotide sequence is SEQ ID NO: 1, and the second nucleotide sequence is SEQ ID NO: 2. The molecular marker linked with wheat stripe rust resistance QTL and located on a wheat 2A chromosome is a flanking marker of a stripe rust resistance site QYr.sicau-2AS on a short arm of the wheat 2A chromosome, and the linkage degree is high. The marker can be used for detecting the stripe rust resistance site QYr.sicau-2AS on the wheat 2A chromosome, plants with the loci are rapidly screened, and then the wheat disease resistance breeding efficiency is improved.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Molecular marker closely linked with wheat heading degree QTL QPel.HN.6D and application thereof
ActiveCN110106274AImprove the efficiency of design breedingPredicted Withdrawal CharacteristicsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceStatistical Confidence
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular biology, in particular to a molecular marker closely linked with the wheat heading degree QTL QPel.HN.6D and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the molecular marker closely linked with the wheat heading degree QTL QPel.HN.6D is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The molecular marker HRM6 is in the confidence interval of the wheat headingdegree QTL QPel.HN.6D, and the molecular marker and the wheat heading degree QTL QPel.HN.6D are both positioned on a wheat 6D chromosome. The molecular marker can accurately track the wheat heading degree QTL QPel.HN.6D, predict the characteristics of the wheat heading degree, facilitate molecular design breeding, enhance the prediction accuracy of the heading degree so as to quickly screen out wheat varieties or strains capable of reducing the heading degree QTL for breeding, and greatly accelerate the breeding process of high-yield wheat varieties which are identical in plant type.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
A molecular marker and application of qtl loci for improving barley harvest index under low phosphorus conditions
ActiveCN107746895BIncrease harvest indexImprove use valueMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention provides a molecular marker for increasing barley harvest index QTL site under low phosphor condition and an application thereof. The molecular marker is Hvc316, a nucleotide sequence isshown as SEQ ID No:1, the molecular marker is positioned on barley 3H chromosome, and can accurately track the site for increasing a barley harvest index QTL under low phosphor condition, predicts the harvest index characteristic of the barley under the low phosphor condition, and is convenient for molecular design breeding with nutrient efficient utilization. The invention also provides the application of the molecular marker Hvc316 in barley high-yield nutrient efficient breeding. A method provided in the invention is capable of enhancing the accuracy of prediction of the barley harvest index under low phosphor condition, and is convenient for rapidly screening the barley variety or lines used for breeding for increasing the barley harvest index QTL under low phosphor condition, so thata seed selection process of the barley high-yield high-efficiency variety can be greatly accelerated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Molecular marker closely linked to wheat grain filling rate qtl QGfr.sicau-7D.1 and its application
ActiveCN111471790BIncreased grout rateImprove selection identification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention provides a molecular marker closely linked to the wheat grain filling rate QTL QGfr.sicau-7D.1, the molecular marker is KASP705, and its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO. 1; the molecular marker KASP705 is associated with the wheat grain The filling rate QTLs are tightly linked. Detection and analysis showed that the molecular marker could accurately track the QTL of the grain filling rate of wheat, predict the grain filling rate characteristics of wheat, and then facilitate molecular design breeding. The detection molecular marker KASP705 can enhance the accuracy of wheat grain filling rate prediction, so as to quickly screen wheat varieties or lines with QTL increasing grain filling rate for breeding, which can greatly speed up the breeding process of high-yielding wheat varieties.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
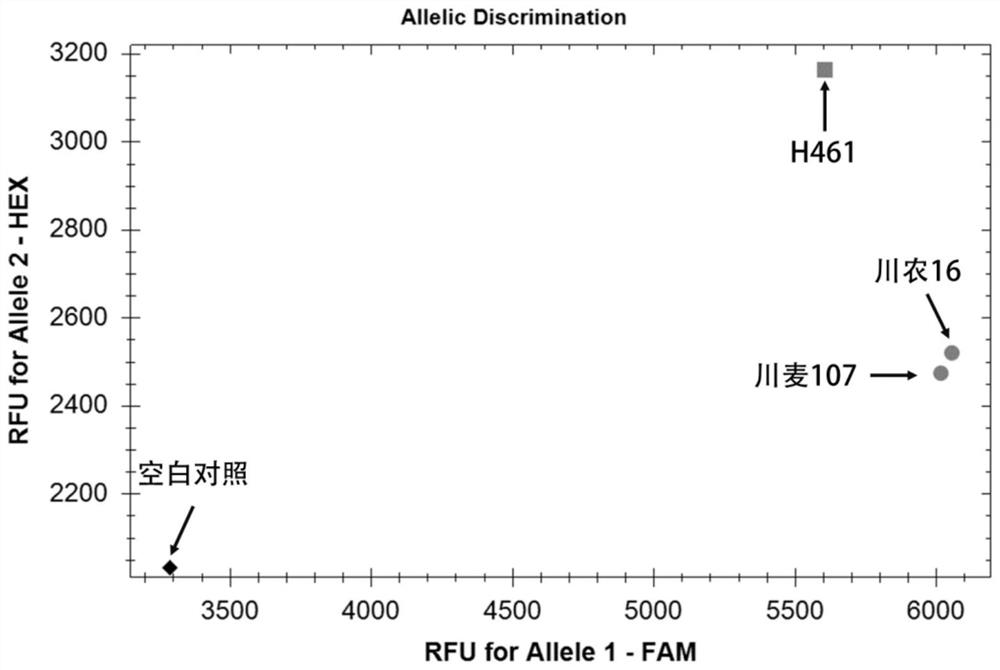
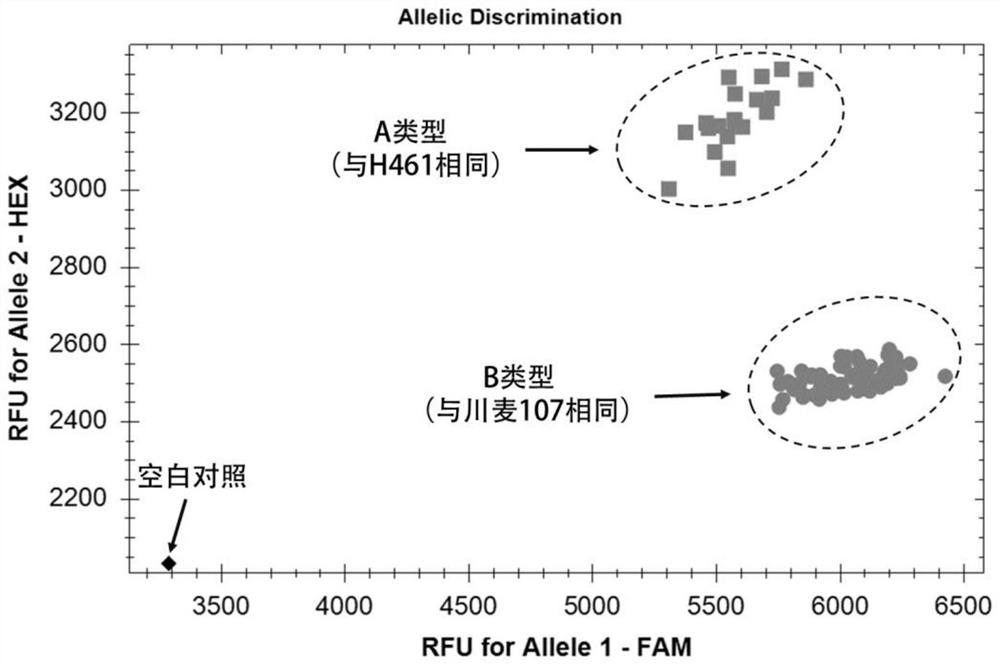
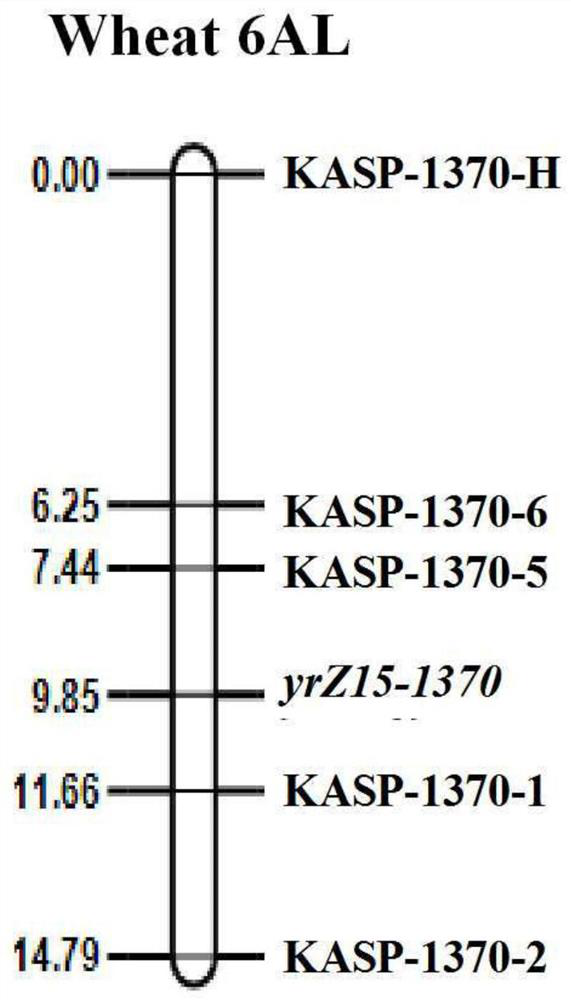
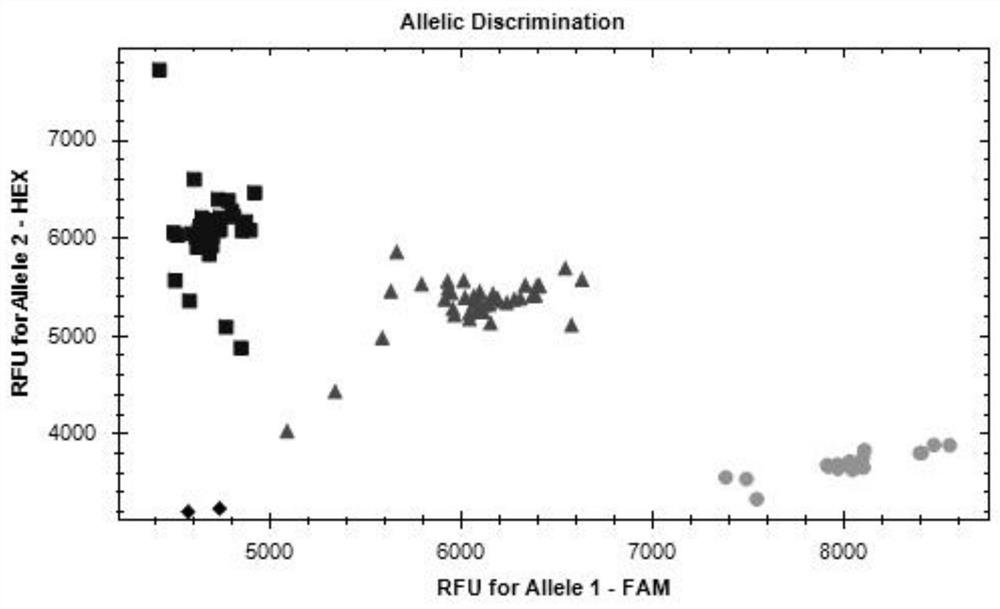
A wheat stripe rust resistance gene yrz15-1370 and its molecular marker and application
ActiveCN112481275BHigh linkageConvenient Assisted BreedingMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyStripe rust
The invention discloses a wheat stripe rust resistance gene yrZ15-1370 and its molecular marker and application. The wheat stripe rust resistance gene yrZ15‑1370 is located on the long arm of wheat chromosome 6A, and its physical location is 601.47Mb‑603.30Mb in the RefSeqv1.0 genome version. The SNP site of the molecular marker is located in the yrZ15-1370 interval, the polymorphism is A / G, and the molecular marker can accurately track the wheat stripe rust resistance gene yrZ15-1370. The present invention also discloses a primer set for identifying the wheat stripe rust resistance gene yrZ15-1370, using the primer set provided by the present invention can quickly screen out wheat varieties or strains with the wheat stripe rust resistance gene yrZ15-1370 for breeding, It can greatly speed up the breeding process of wheat disease-resistant varieties.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
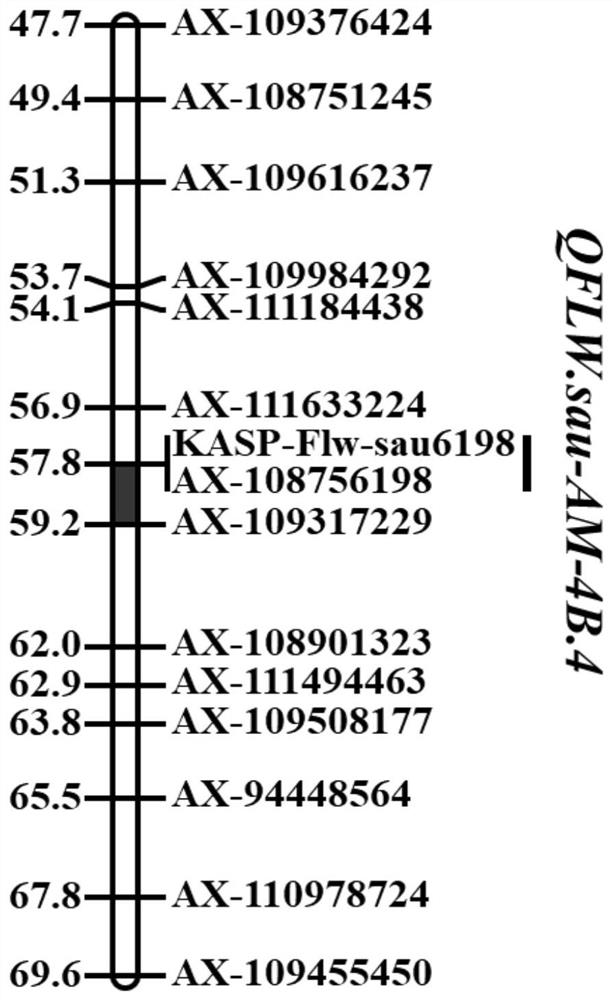
Kasp-flw-sau6198 Molecular Marker Linked to the Major QTL of Wheat Flag Leaf Width and Its Application
ActiveCN113817862BWide increaseImprove use valueMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenetic stock
The invention discloses a KASP-Flw-sau6198 molecular marker linked with the main effect QTL of wheat flag leaf width and its application, belonging to the fields of molecular biology and crop genetics and breeding. The molecular marker is a SNP molecular marker, and the polymorphism is A / G, which co-localizes with the wheat flag leaf width QTL QFLW.sau-AM-4B.4 on the long arm of the tetraploid wheat chromosome 4B, and is located in the QTL QFLW .sau‑AM‑4B.4 range. After detection and analysis, it is shown that the molecular marker can accurately track the flag leaf width QTLQFLW.sau‑AM‑4B.4 of wheat, and predict the flag leaf width characteristics of wheat, which is conducive to more rapid screening of wheat varieties or lines with wider flag leaves For breeding, greatly speed up the process of wheat breeding.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
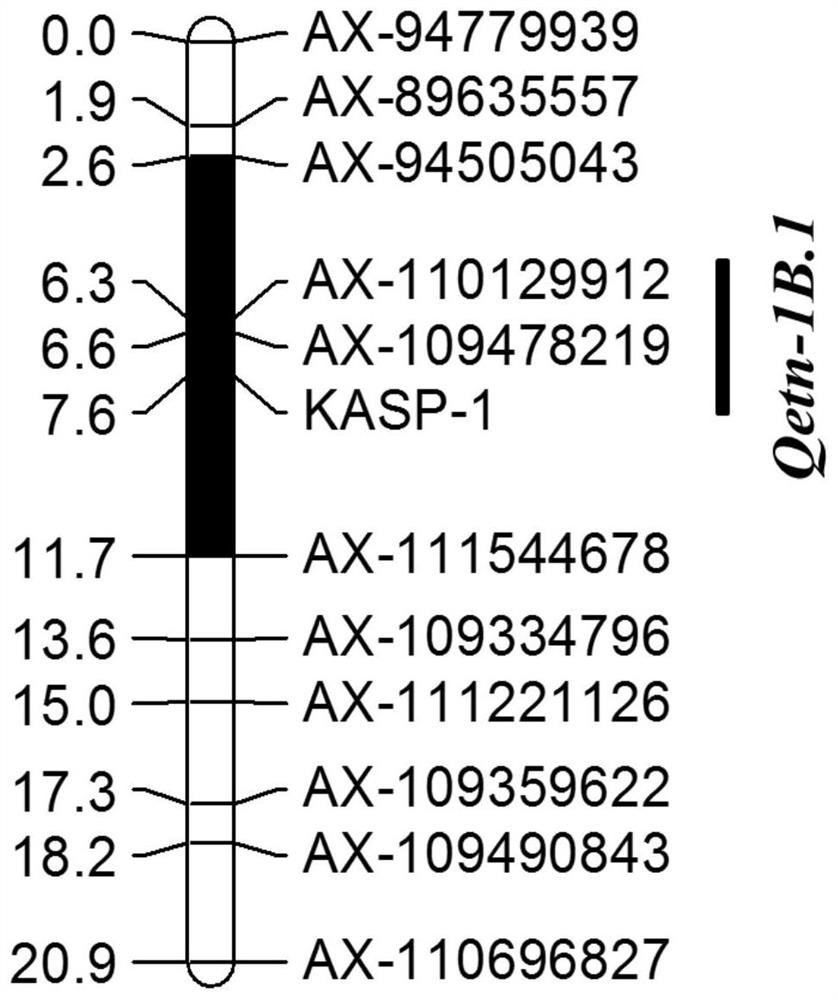
Qtl-linked Molecular Markers for Wheat Effective Tiller Number and Its Application
ActiveCN110904261BImprove use valueImprove selection identification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a molecular marker linked to QTL for effective tiller number in wheat and its application. The wheat effective tiller number QTL is QTL Qetn-1B.1, the molecular marker is named KASP-1, and its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1-3. Detection and analysis showed that the molecular marker could accurately track the wheat effective tiller number QTL Qetn‑1B.1, predict the effective tiller number characteristics of wheat, and facilitate molecular design breeding. The invention also discloses a method for identifying the molecular markers of wheat effective tiller number QTL Qetn-1B.1. The method provided by the invention can enhance the accuracy of prediction of effective tiller number, so as to quickly screen out the QTLs with increased effective tiller number. A large number of wheat varieties or lines are used for breeding, which can greatly speed up the process of breeding high-yield varieties of wheat.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com