Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
500results about "Semi-structured data retrieval" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Content Metadata Directory Services
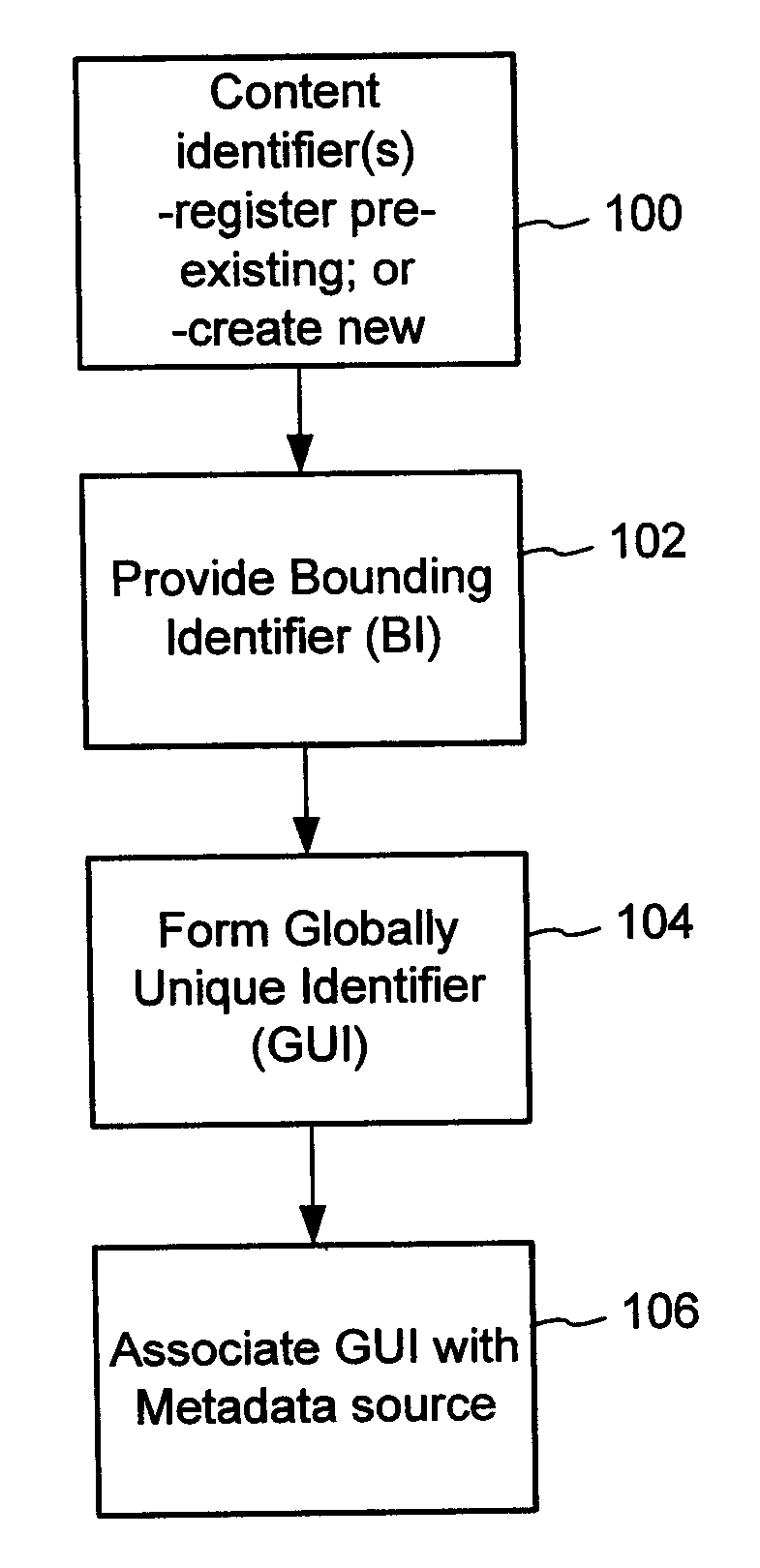
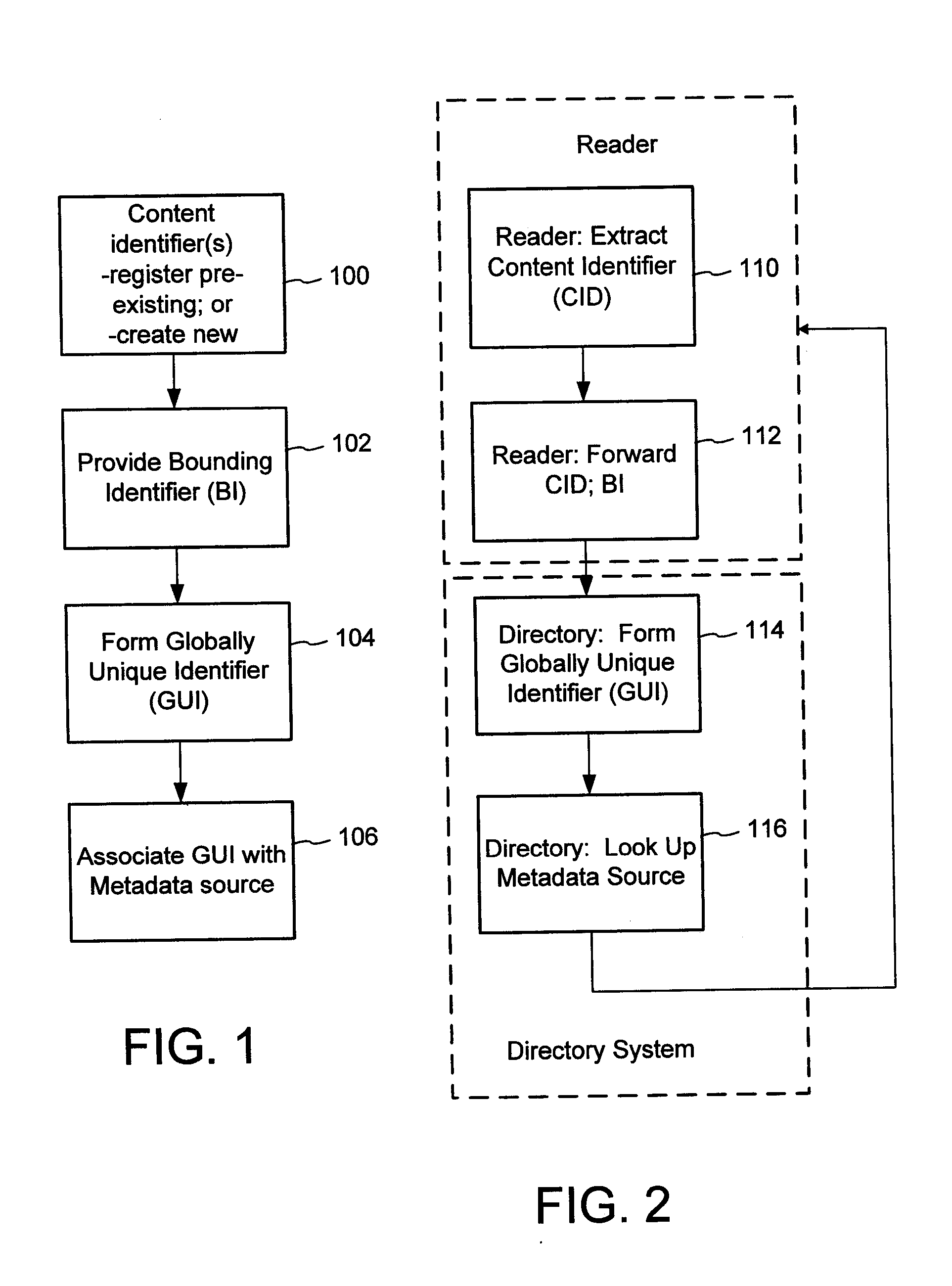
ActiveUS20070156726A1Improve interoperabilityIncrease the number ofMultimedia data indexingDigital data processing detailsContent IdentifierSystems management
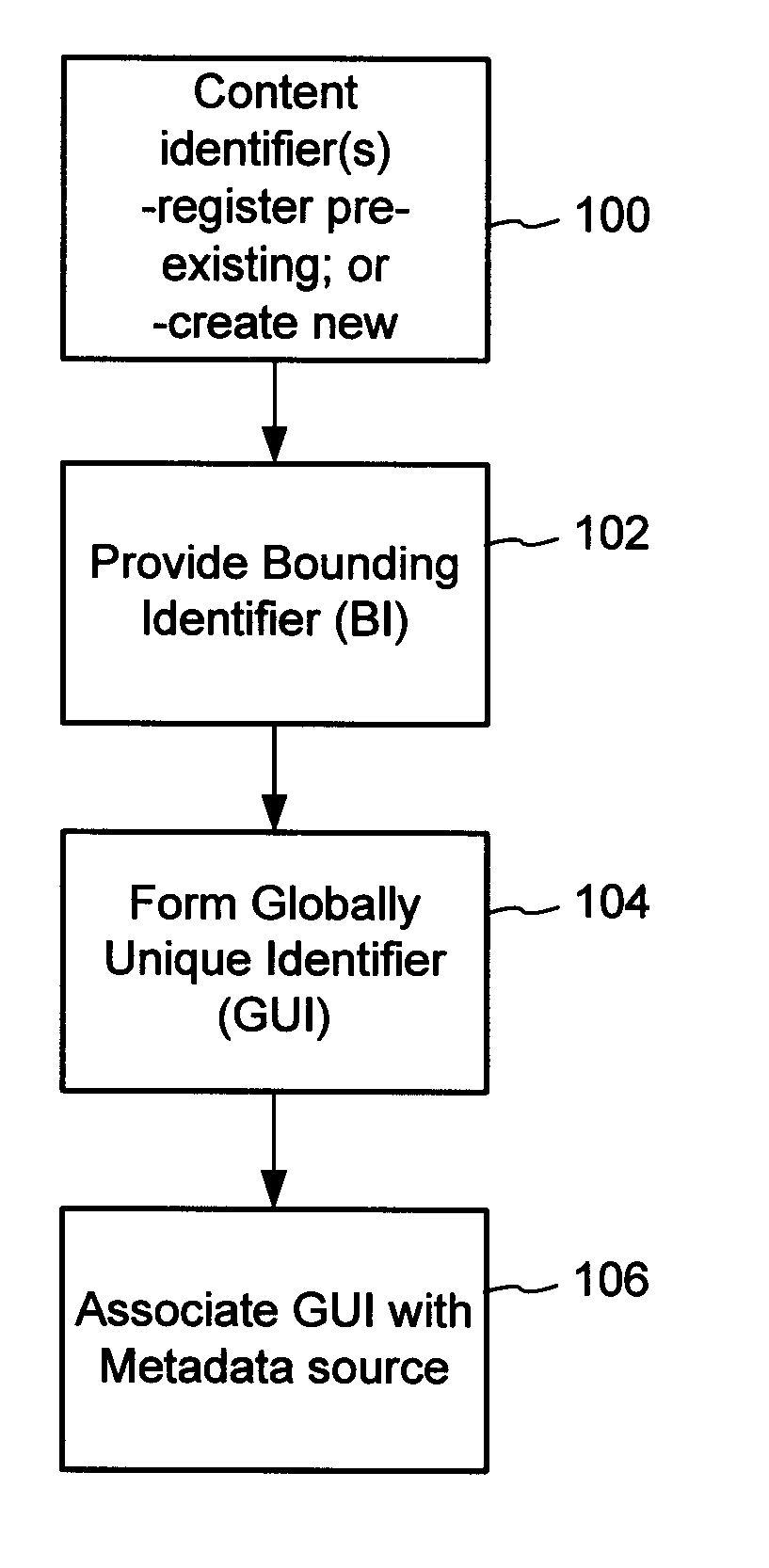
The content metadata directory system connects consumers of identified content to managed metadata databases and other digital resources. The system manages links between identifiers in content objects and metadata sources. It supports a variety of different type of content identifiers and allows for overlap among different content identification schemes. One method of associating a content object with metadata uses a combination of a content identifier and a bounding identifier to enable handling of disparate sets of content identifiers for content objects with potentially conflicting content identifiers. The method receives a content identifier for a content object from among a set of content identifiers and provides a unique bounding identifier for the set of content identifiers. This unique bounding identifier is used in combination with the content identifier to form a globally unique identifier for the content object. This globally unique identifier is associated with a metadata source, which enables routing of a user to the metadata source.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
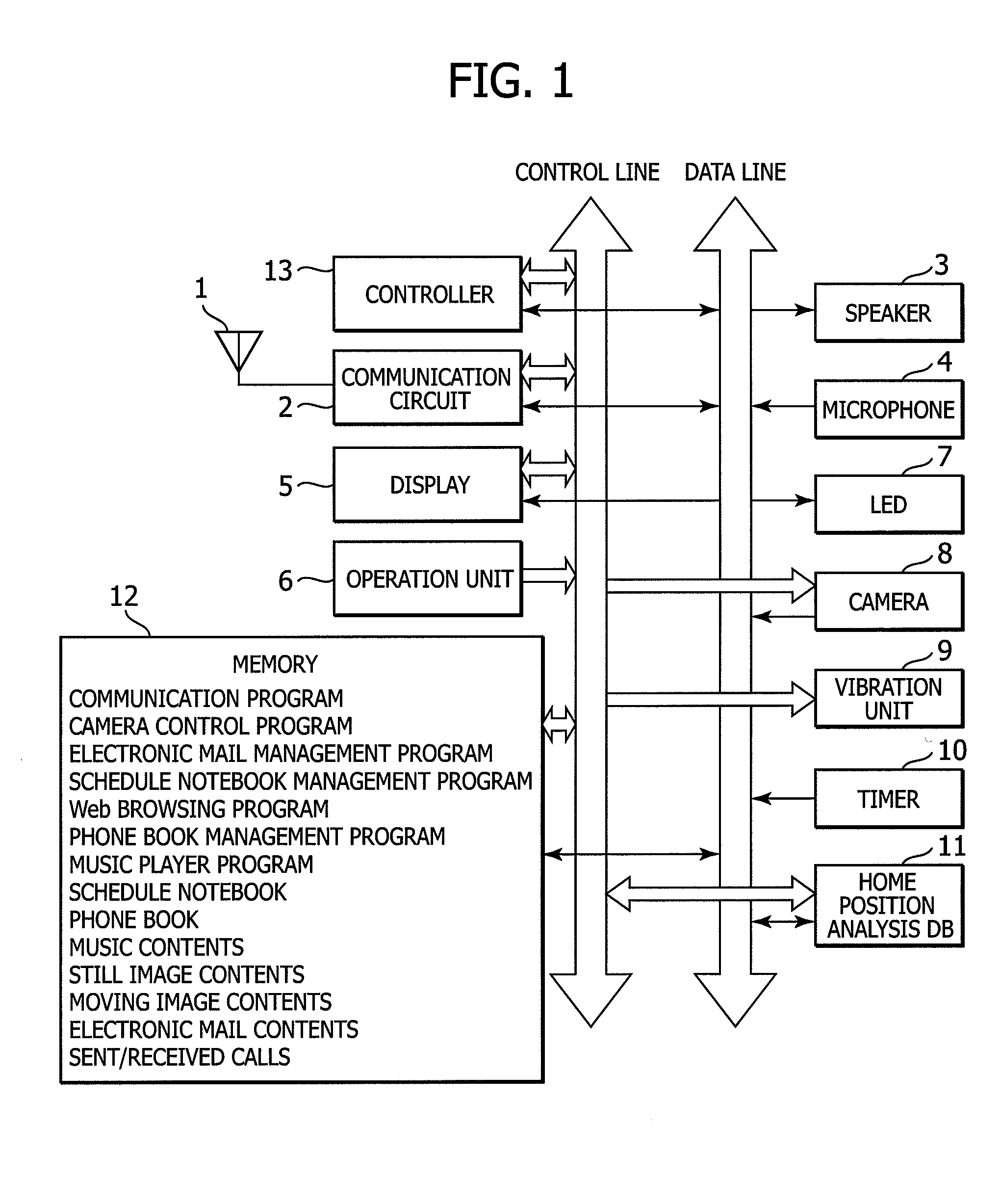
Display controller, display control method, display control program, and portable terminal device
InactiveUS20080256446A1Semi-structured data retrievalTransmissionTerminal equipmentUniform resource locator
Owner:SONY MOBILE COMM INC
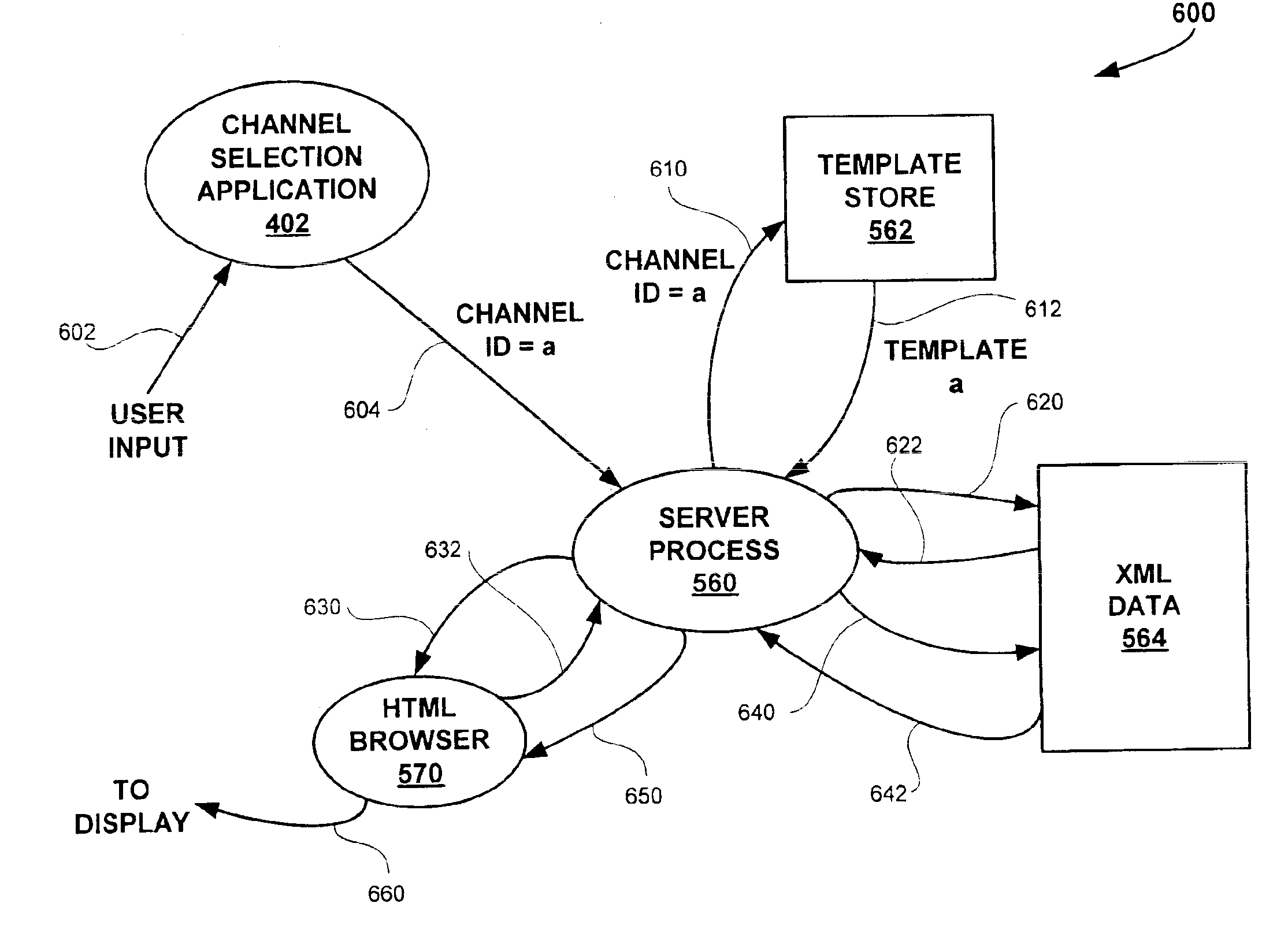
Method and apparatus for sharing common data objects among multiple applications in a client device
InactiveUS6934740B1Readily apparentData processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsObject basedSoftware architecture
Disclosed is software architecture and method for sharing data objects among multiple applications in a client device. The architecture includes a server process in the client device for processing a template, such as a SHTML template for the Extended Markup Language (XML), based on a template identifier value received from a user application. Each of multiple applications has a template. Each template identifies a series of objects identified by tag values, such as XML entities, that are to be incorporated into a display page. A database of objects, such as a database of XML entities identified by tag values, is maintained that contains data objects for the applications. An update process periodically establishes a communication link with a remote server and requests download of a data document containing content data corresponding to at least a portion of several of the templates. The data document is parsed into the database of objects based on the structure of the data document, which generally conforms to a data type definition. When the server process processes different templates that reference the same data object, it will retrieve the data object from the database. Each template may then be rendered into a page of output data for display to a user. The architecture and method according to the present invention thus permit data objects to be shared by multiple applications and to be automatically updated. Each time a data object is updated, the data will be current for each user application that references the data object.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
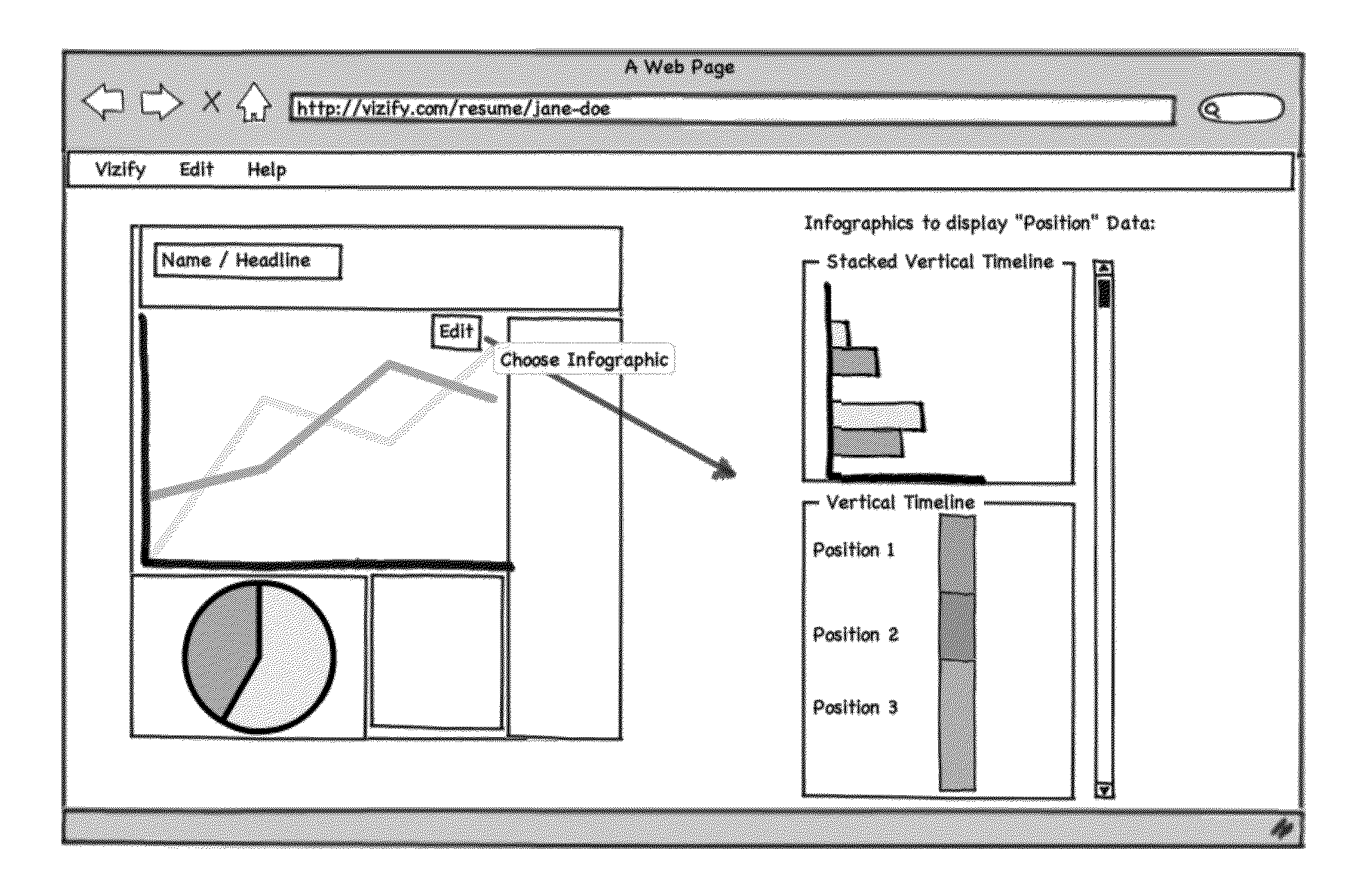
Automated presentation of information using infographics
In one embodiment, a method for creating one or more infographics, comprising: receiving and storing data associated with an individual or an entity, in a format according to a schema that includes at least two properties associated with the individual or entity; reading at least a portion of the data; determining which of the at least two properties in the schema do not have corresponding read data associated with the individual or entity; based on that determination, selecting an infographic definition from among a plurality of infographic definitions defining the appearance of at least a portion of an infographic; generating one or more infographics based on (i) the at least a portion of the data and (ii) the selected infographic definition; and providing the one or more generated infographics to an output device.
Owner:YAHOO ASSETS LLC
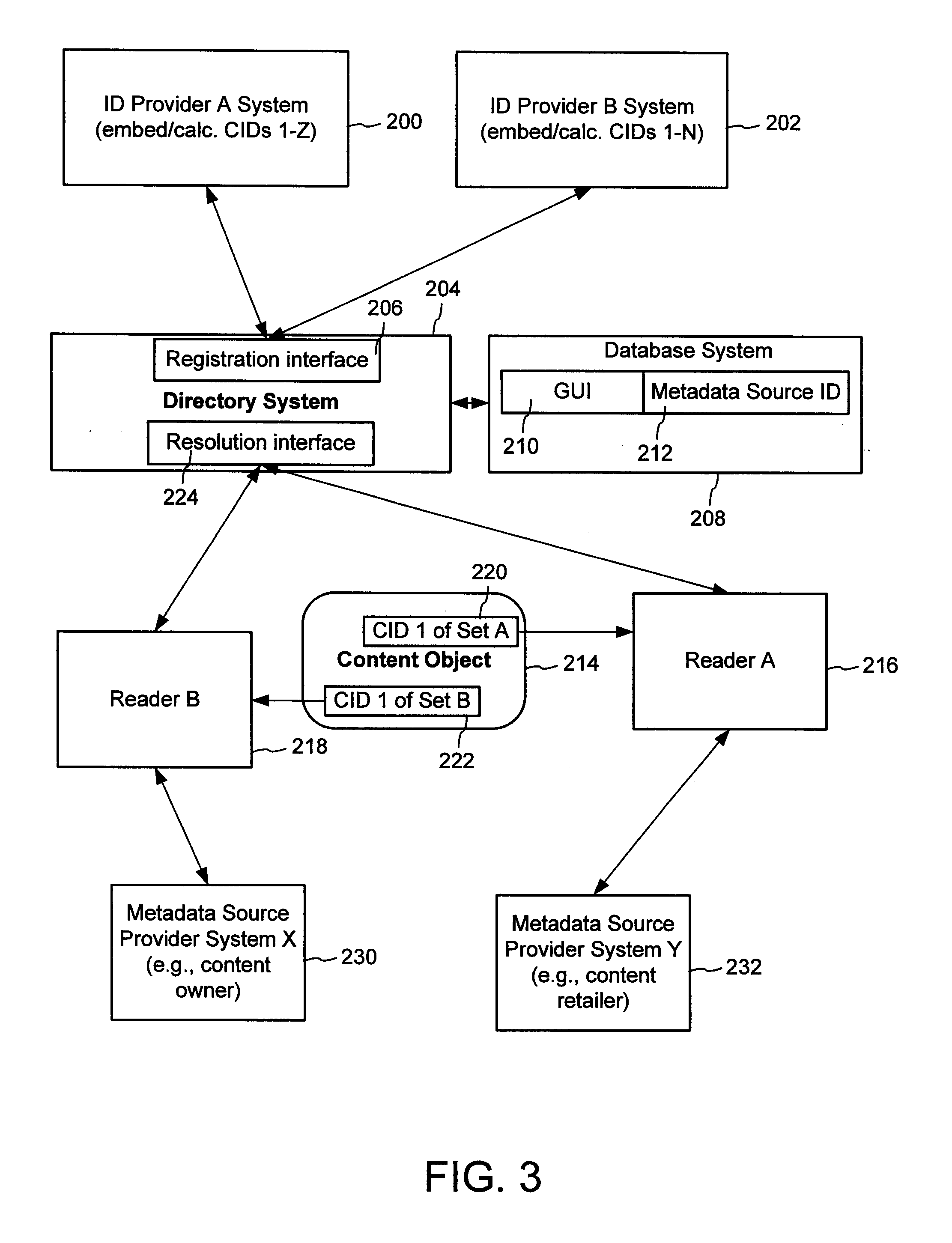
Content Metadata Directory Services
ActiveUS20070192352A1Increase the number ofComplicate to identifyMultimedia data indexingDigital data processing detailsContent IdentifierWeb site
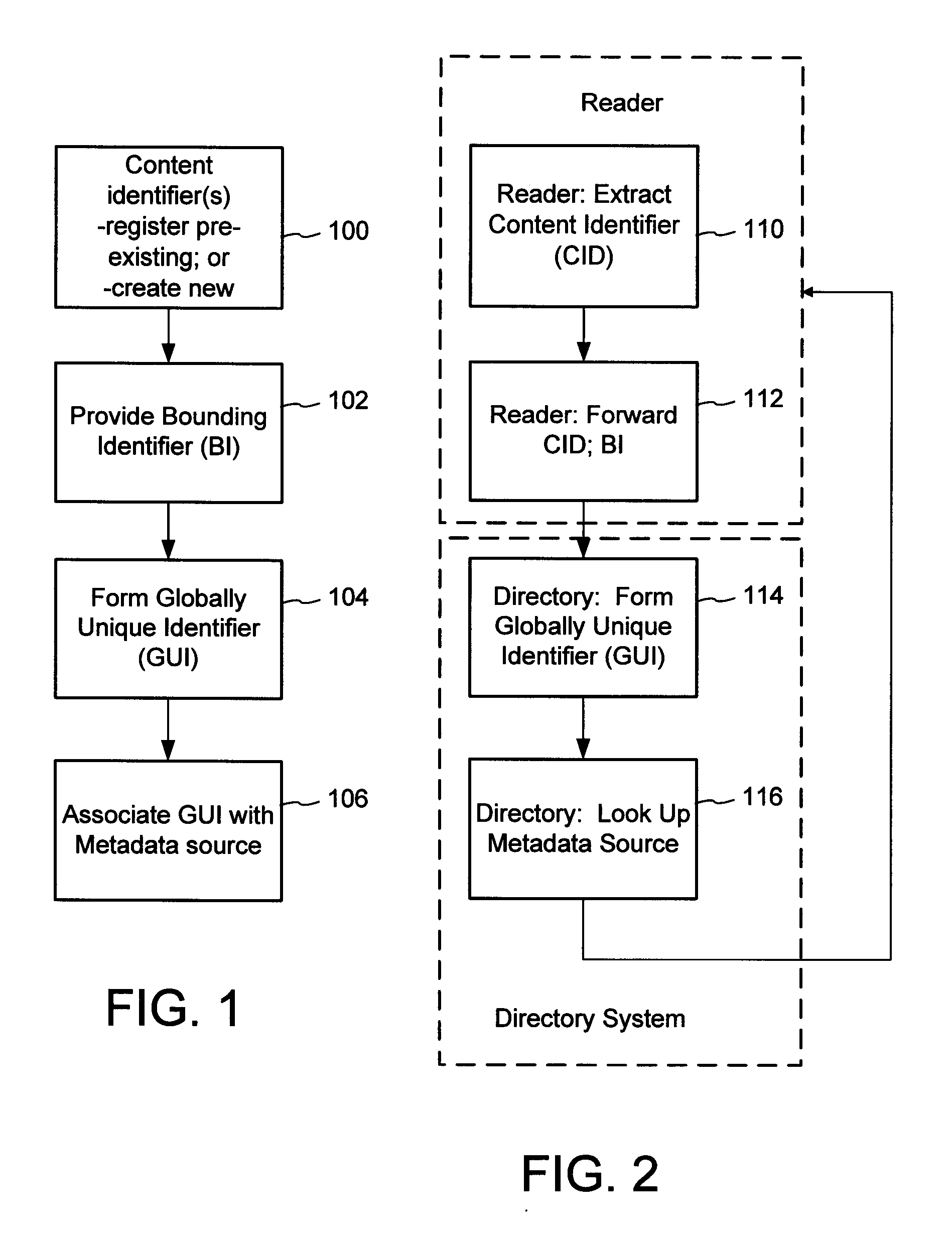
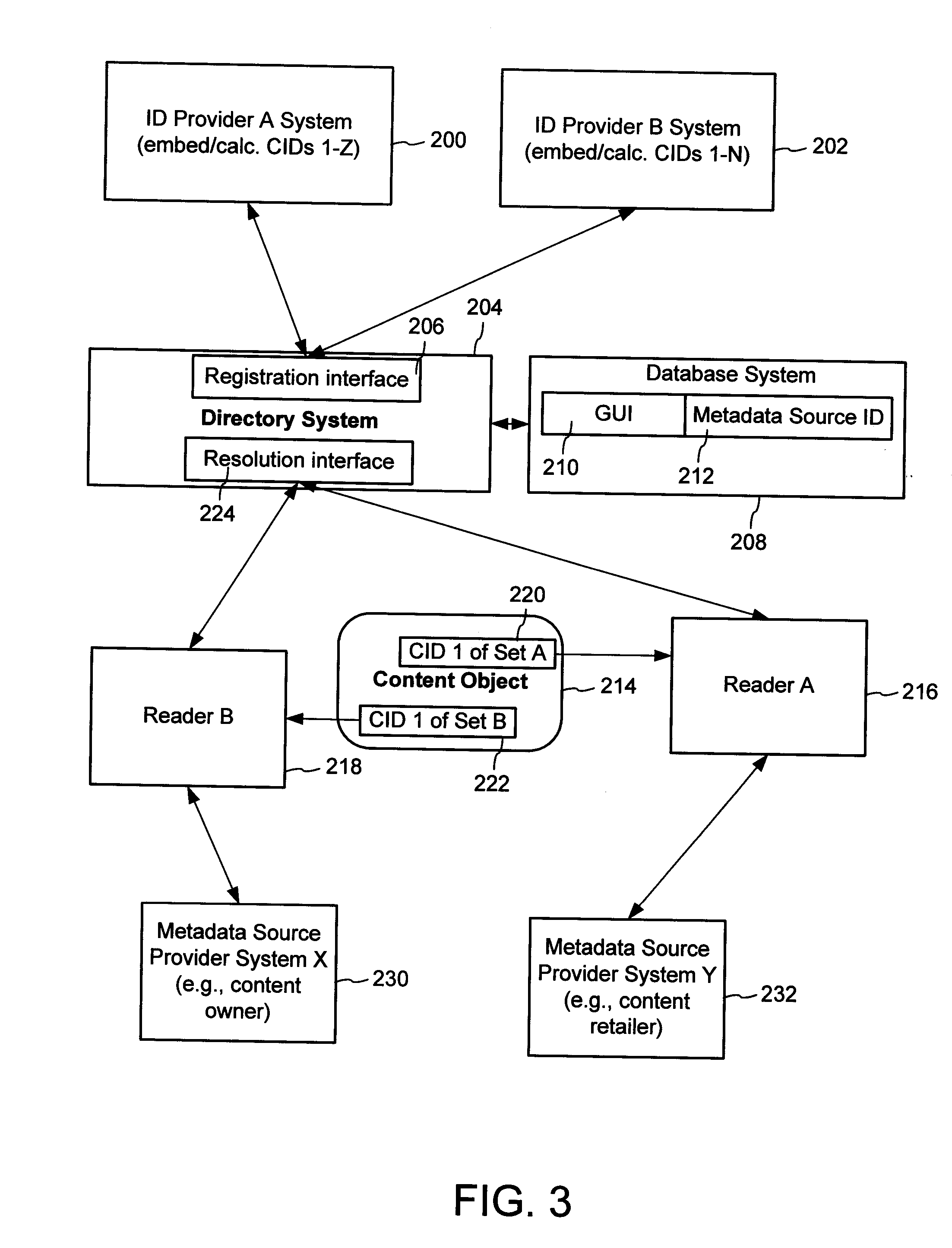
A method of associating a content object with metadata uses a combination of a content identifier and a bounding identifier to enable handling of disparate sets of content identifiers for content objects with potentially conflicting content identifiers. The method receives a content identifier for a content object from among a set of content identifiers. It provides a unique bounding identifier for the set of content identifiers. This unique bounding identifier is used in combination with the content identifier to form a globally unique identifier for the content object. This globally unique identifier is associated with a metadata source, which enables routing of a user to the metadata source. Another novel method addresses content objects with two or more content identifiers, potentially referencing different metadata sources. This method registers different globally unique identifiers for a content object. These globally unique identifiers each comprise a content identifier provided with the content object and a bounding identifier identifying a set of content identifiers of which the content identifier is a member. For each of the globally unique identifiers, information is maintained about a metadata source. The method receives a first content identifier for the content object, and uses a bounding identifier associated with the set of the first content identifier to determine the globally unique identifier for the first content identifier. The user is routed to the metadata source associated with globally unique identifier. This document describes a novel system that enables multiple identity providers (ID Providers) to register and use the system. The ID Provider registers with a metadata directory system, receives a unique bounding identifier, and uses this bounding ID (e.g., an ID provider ID) with subsequent interactions with the metadata directory system. Separately, metadata source providers register metadata sources with the metadata directory system. This enables many different participants to associate content objects with metadata sources using one or more identify providers. Examples of metadata source providers include content providers, like content owners or retailers that have the flexibility of working with different ID providers to associate content objects with metadata. Both content providers and ID providers can register and use the system. The metadata source is the system or device that provides the metadata, like a web site. The directory system uses an identifier for the metadata source, which enables it to maintain an association between a content object and its corresponding metadata source. For example, in some embodiments, a URL serves to identify the location of the source. The Content Metadata Directory Services (CMDS) is a global trusted directory service that connects consumers of identified content to content-provider authorized and managed metadata databases and other digital resources. It includes mostly links to metadata, forms globally unique IDs based upon overlapping content identifiers and unique bounding identifiers, enables multiple content identifiers within a content object, and enables multiple content identity technology providers, even when they are using different technology.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
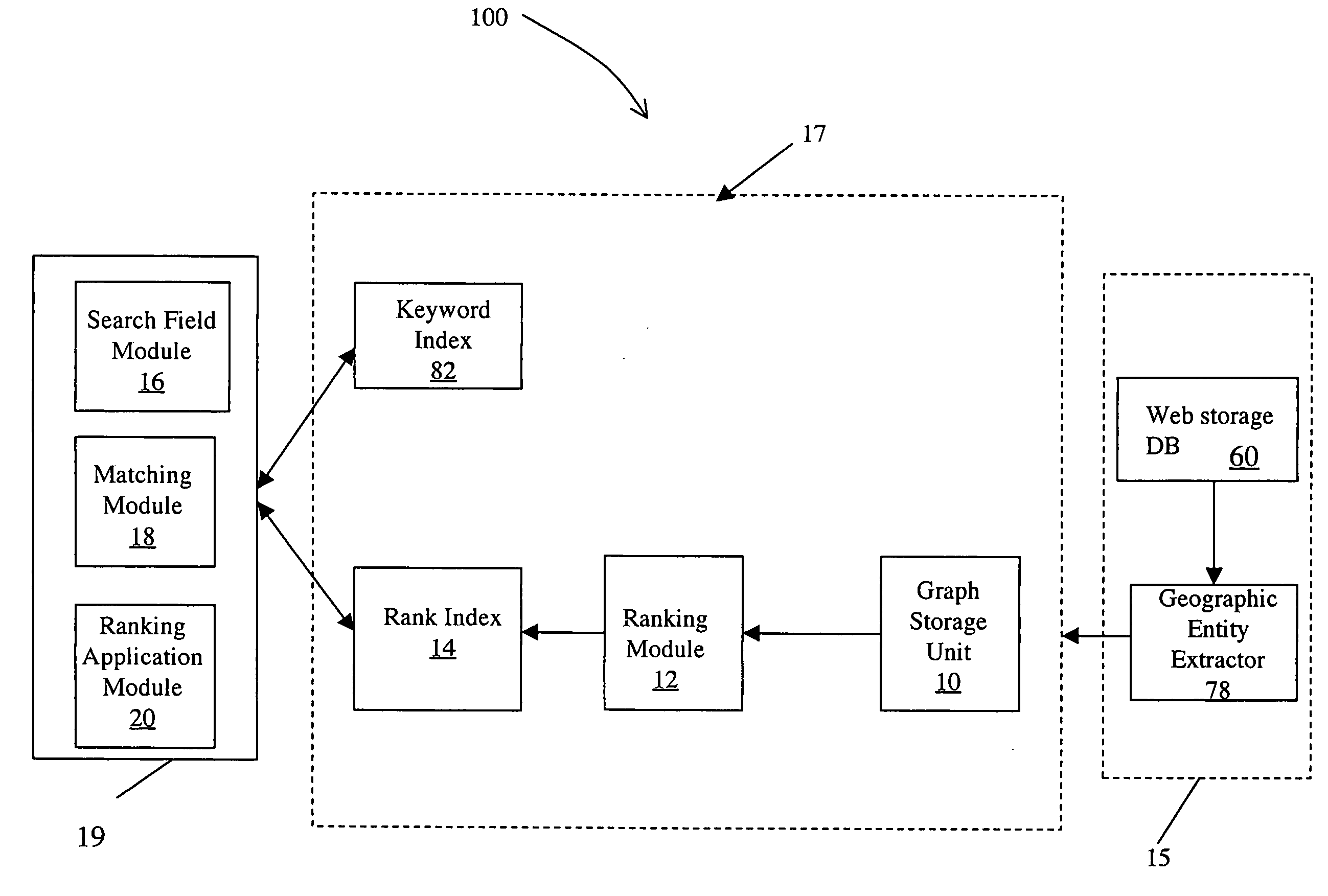
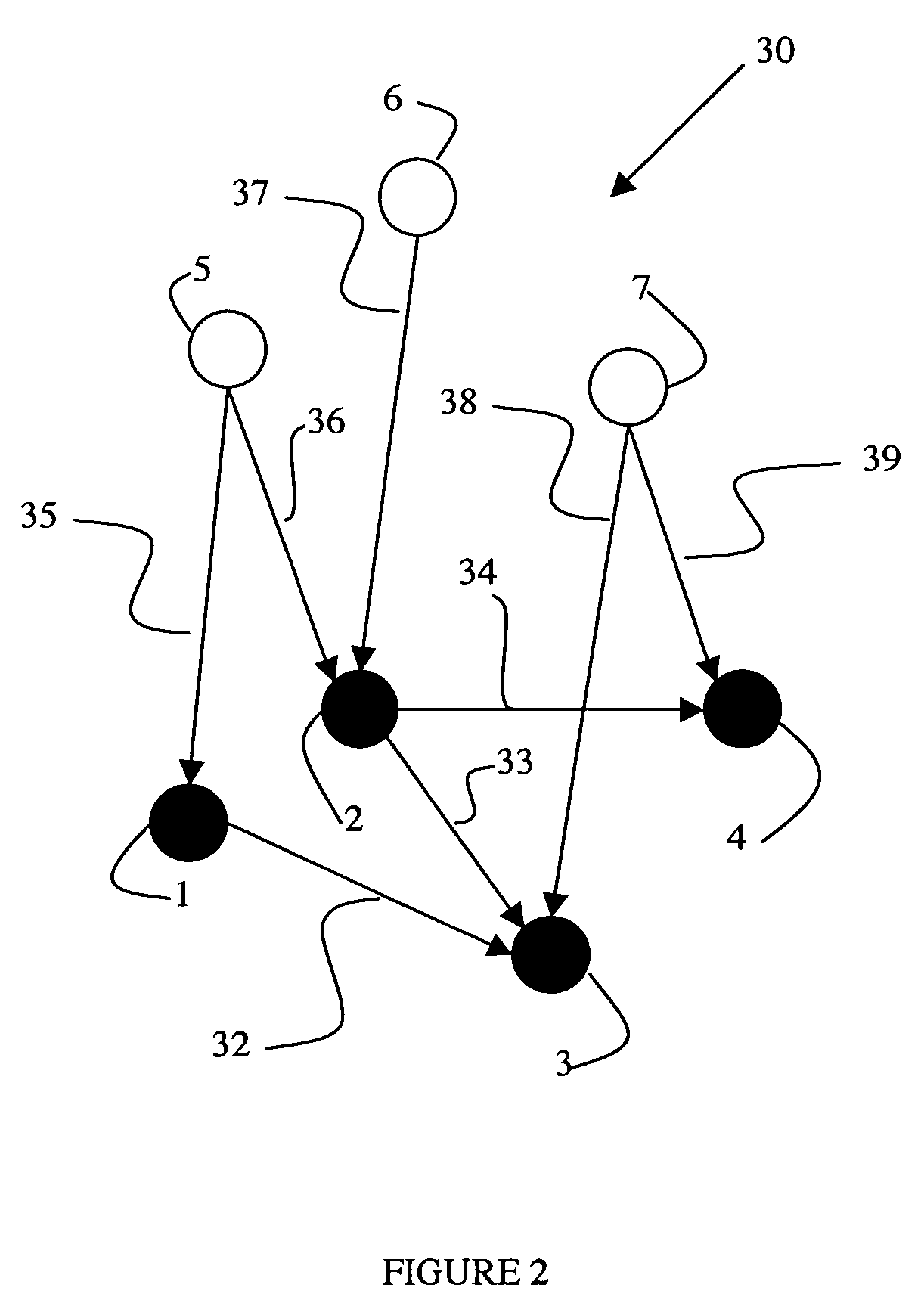
System and method for ranking web content
A system and method for ranking Web content comprising Web pages or portions of Web pages containing a geographical entity are described. The system includes a data structure that comprises a graph representing the Web content. The graph includes a plurality of page nodes, wherein each page node represents one of the Web pages, a plurality of geographic nodes, wherein each geographic node represents one of the geographic entities, a plurality of directed page edges, wherein each directed page edge represents a directed link between a pair of Web pages, and a plurality of directed geographic edges, wherein each directed geographic edge represents a directed link between one geographic entity and one Web page. The system further includes a ranking module for ranking the Web content based on at least a portion of the plurality of directed page edges and a portion of the plurality of directed geographic edges.
Owner:IT INTERACTIVE SERVICES
System for creating and editing mark up language forms and documents
ActiveUS20060031757A9Easy to useData processing applicationsNatural language data processingPaper documentDocument preparation
A system for creating and editing mark up language forms and documents in a manner that is user friendly. The system dynamically generates a user interface that is customized to the particular form or document selected by the user. The user then enters information into the plurality of fields in the user interface for the form or document. Once the form or document is completed, the user can save the form or document in a document repository. The user can also transmit the form or document as an electronic filing document. Additionally, the data entry fields of the form or document can automatically expand or contract to accommodate data of varying length. Moreover, the user can create templates that include frequently used data.
Owner:WTVIII
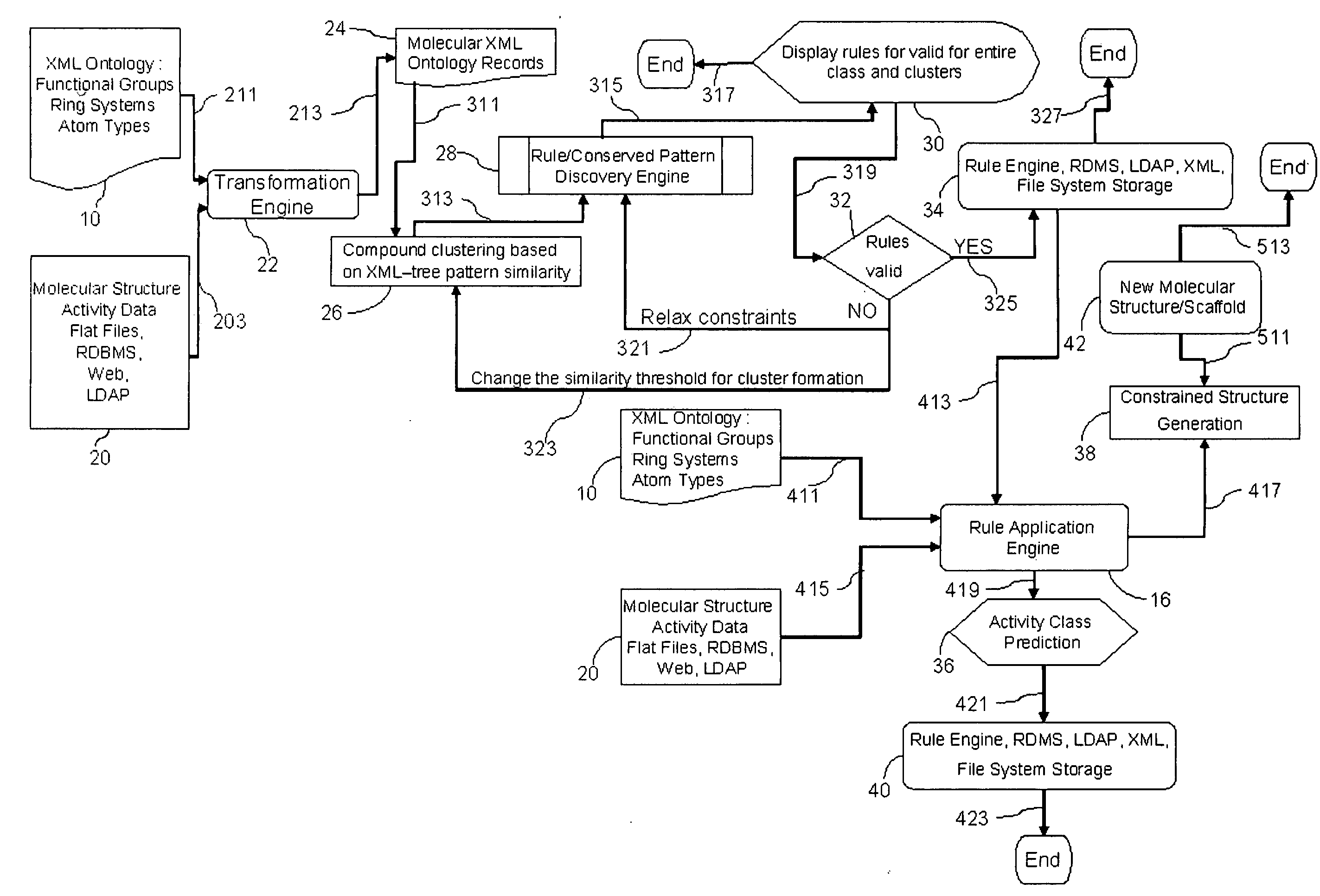
Automated molecular mining and activity prediction using XML schema, XML queries, rule inference and rule engines
InactiveUS20090228445A1Efficient and accessibleDigital data processing detailsRelational databasesXML schemaCausal inference
Method and system for analyzing relationship between molecular structure and biological activity in one or more molecules by transforming molecular structure data into a hierarchical representation of chemical concepts and descriptors and detecting common tree-like patterns in the data.
Owner:SYST BIOLOGY 1 PVT
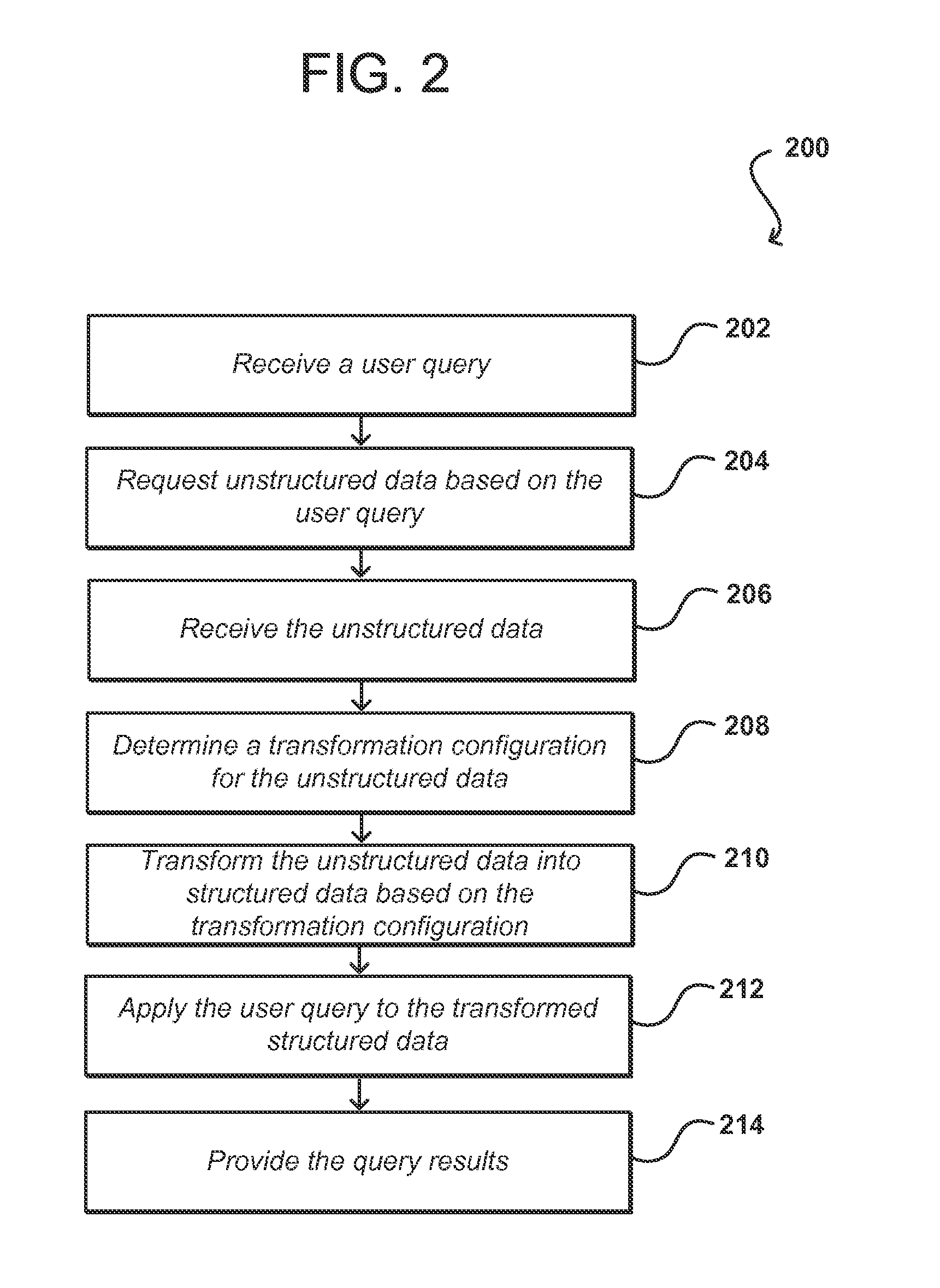
Dynamic data management
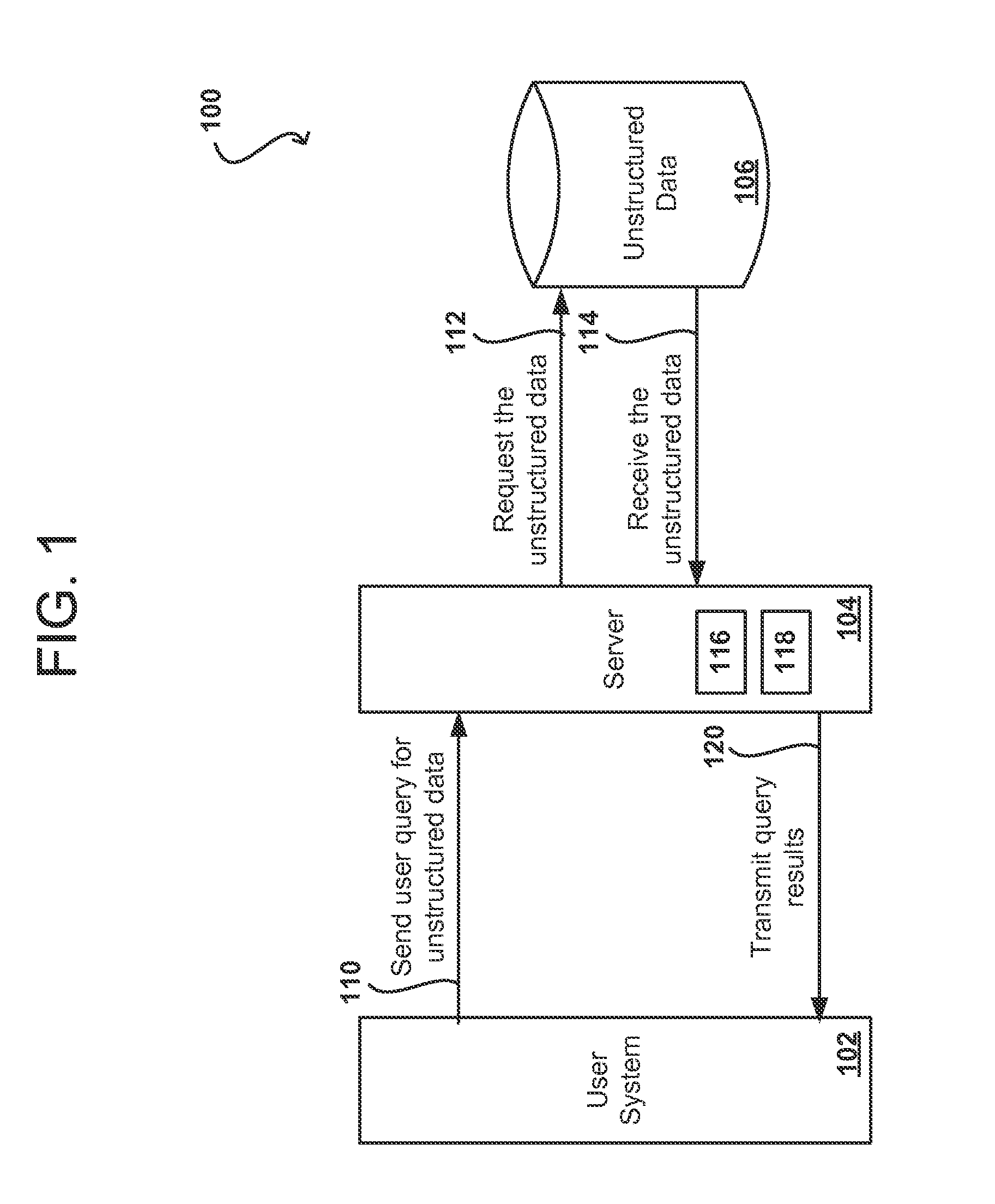
ActiveUS20130054642A1Conveniently accessConveniently manipulateDatabase management systemsDigital data processing detailsUser deviceUnstructured data
An interface for users to gain access and manipulate unstructured data is provided. In response to receiving a user query associated with a first database format, a system can request unstructured data associated with a second database format from a second database. The unstructured data can include a set of data groups where each data group has a set of values. Each value can be associated with a different tag. To generate a structured database, some embodiments can determine the number of data groups and the number of unique tags across the data groups and populate the table with data from the unstructured data. Subsequently, the system can apply the user query to the table to obtain a query result and transmit the query result to the user device.
Owner:SALESFORCE COM INC
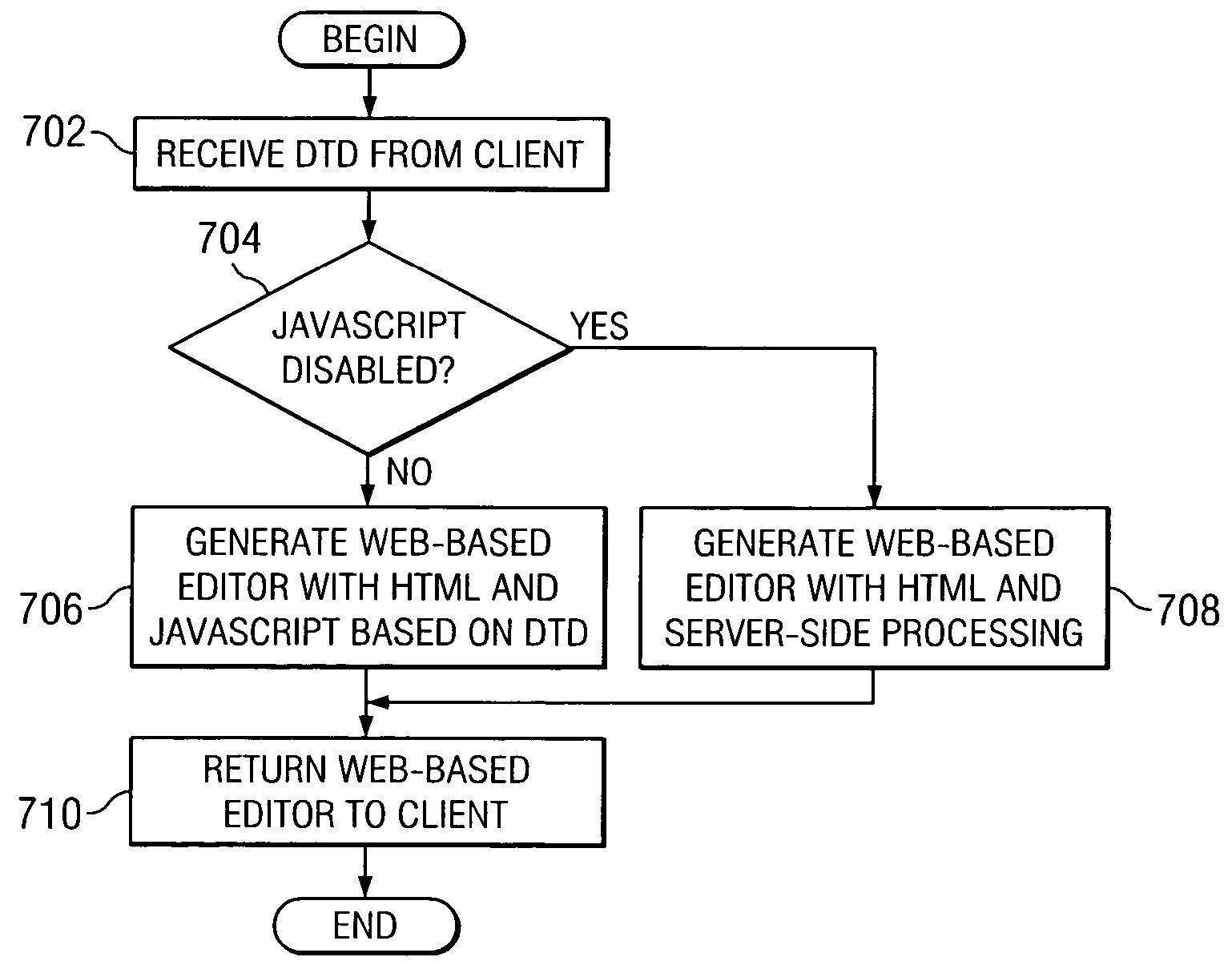
Web-enabled XML editor
InactiveUS20050102612A1Digital computer detailsNatural language data processingPaper documentDocument preparation
A Web-enabled document editor is provided that is supported by any browser application. The server receives a document type definition and creates a Web-based editor for the document type. The Web-based editor page, which may be an HTML page with JavaScript, is sent to the client for presentation on a browser. The user may add and delete elements from the document type definition using the editor interface. The user may supply content for the elements in the browser. The user may also view the XML source or the formatted document using the editor interface.
Owner:IBM CORP
Layered User Interface
InactiveUS20070288856A1Energy efficient ICTProgram control using stored programsHuman–computer interactionUser interface
A user interface for a device comprises a plurality of layers. The content for the user interface is associated with one of the plurality of layers.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Extracting structured data from weblogs
Owner:BUZZMETRICS
Methods and systems for direct execution of XML documents
InactiveUS20020111965A1Reduce program complexityDigital computer detailsSemi-structured data retrievalDocumentation procedureDocument type definition
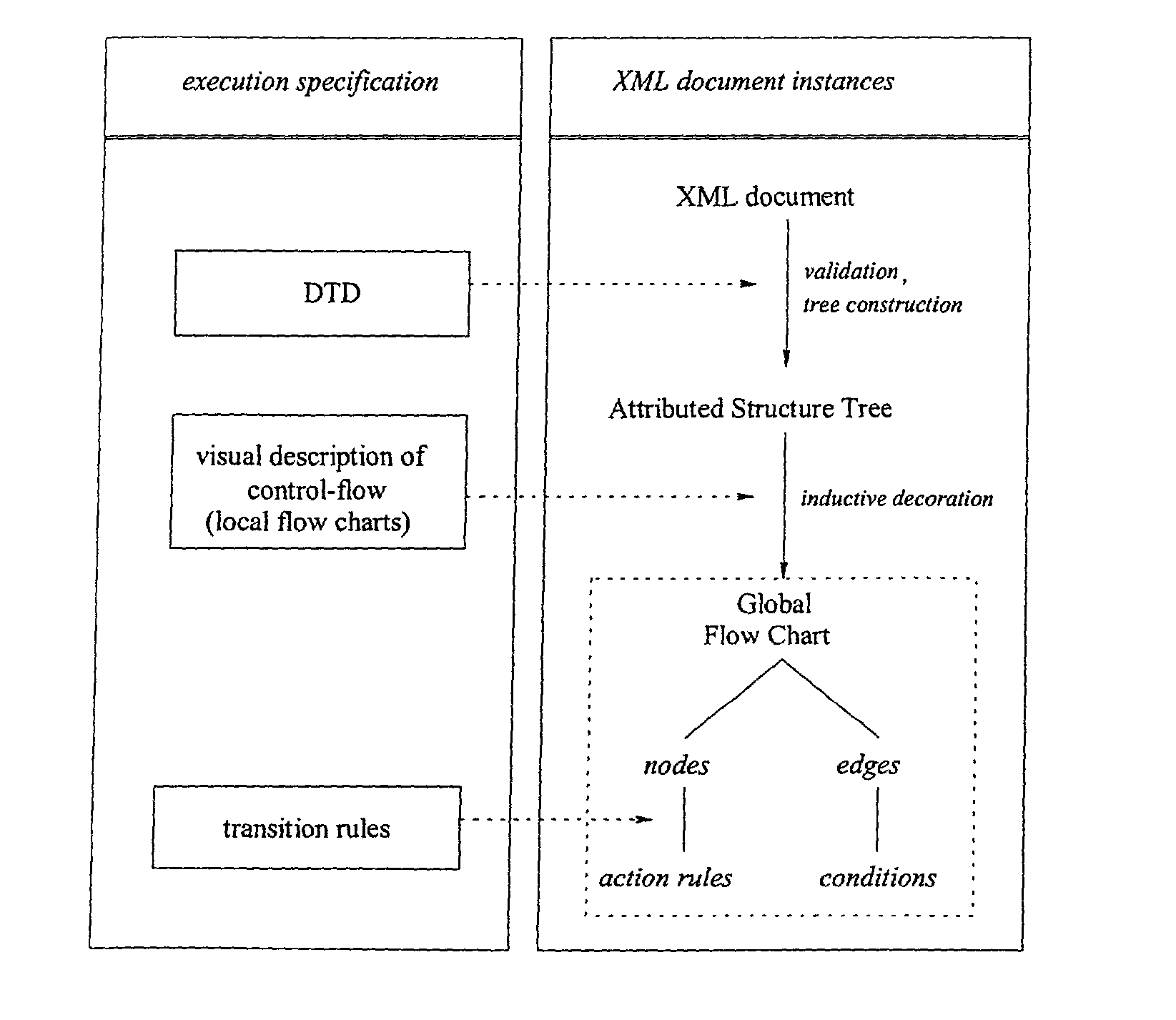
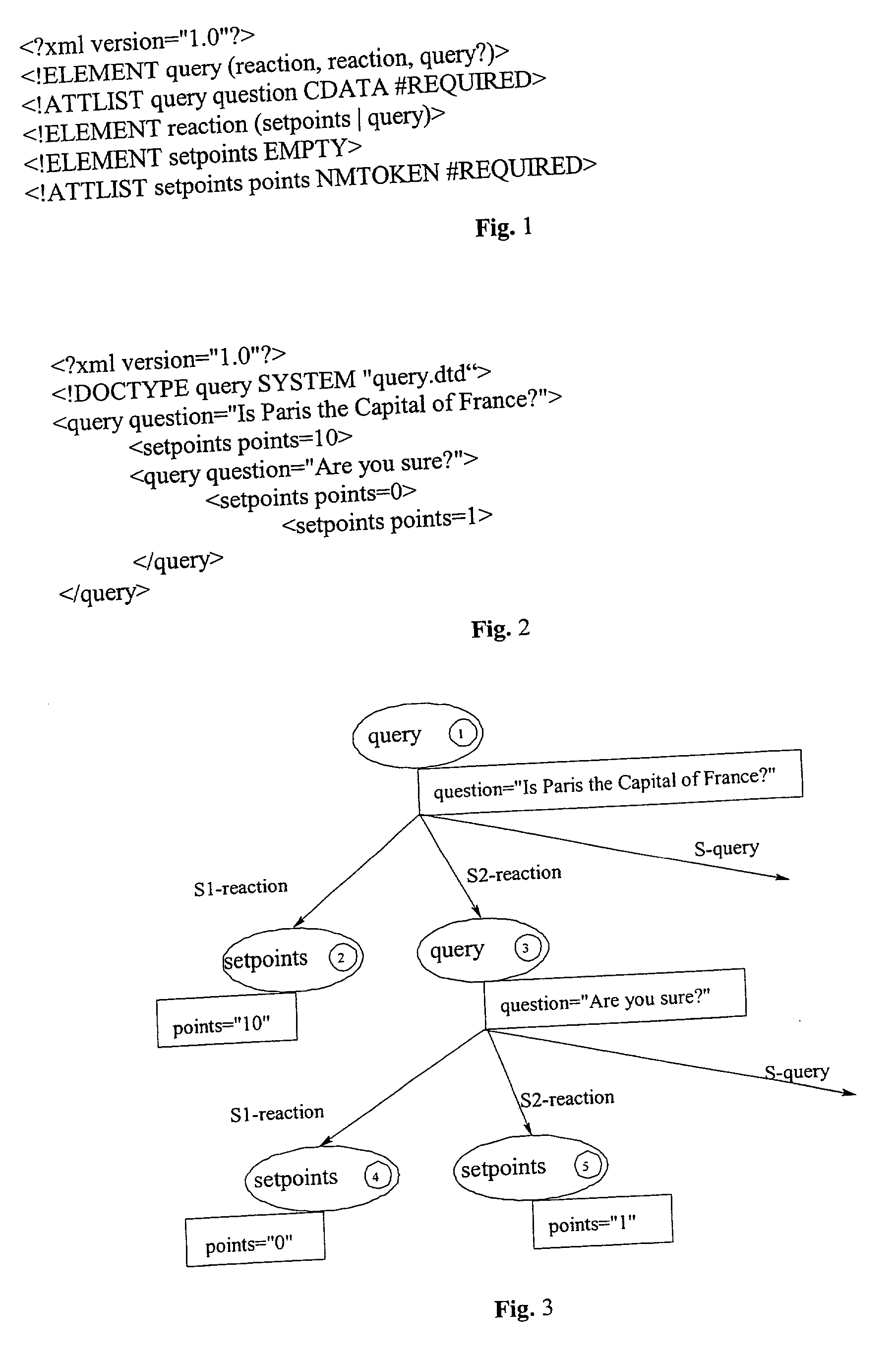
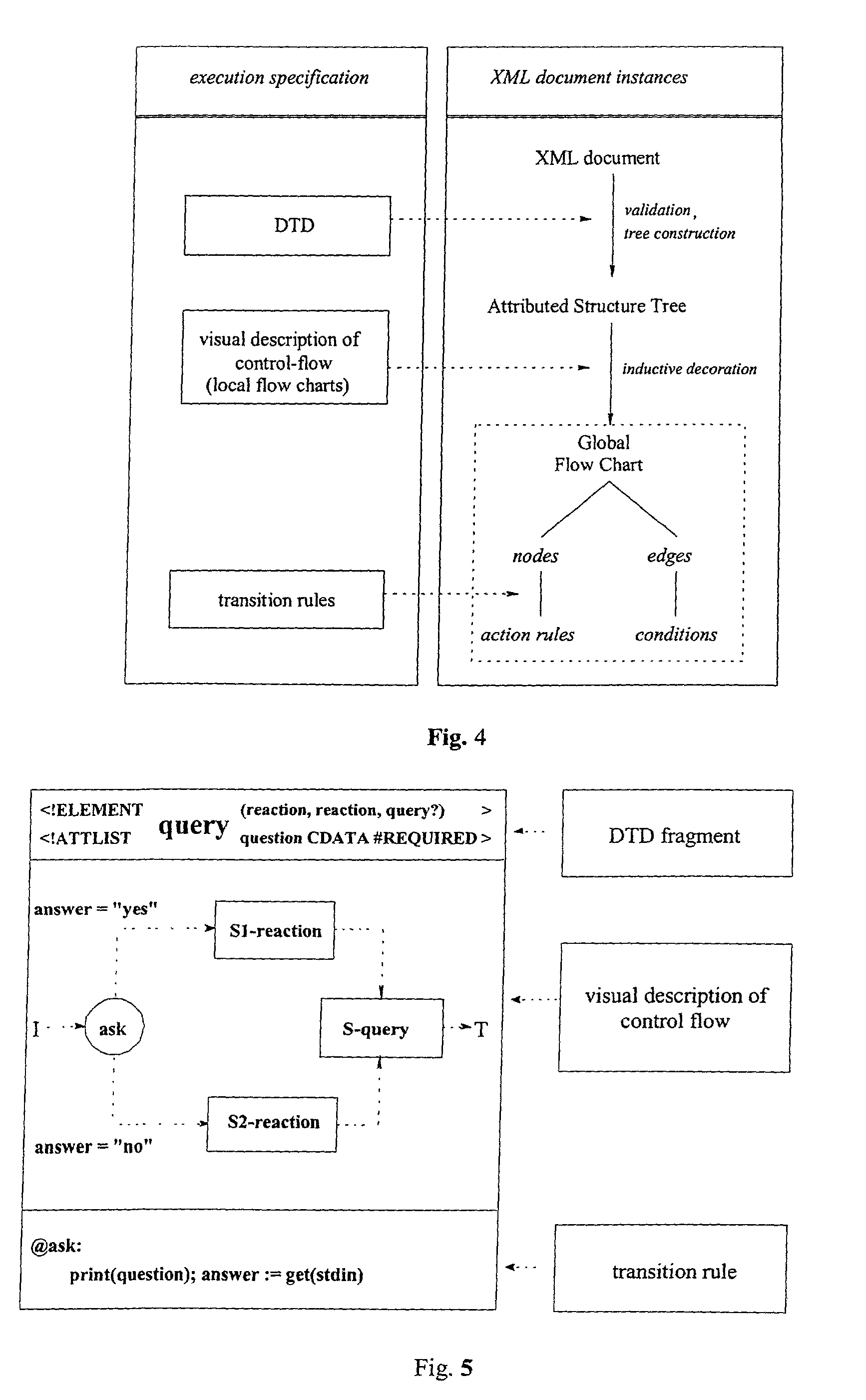
The invention relates to a method, system and apparatus for the direct execution of XML-documents by means of decoration of a XML-document, a document type definition (DTD) or their representation as structure tree, respectively, with textual or graphical flow charts. The structure of the XML-document' is reused for, and integrated with, the code processing the XML document.
Owner:KUTTER PHILIPP W
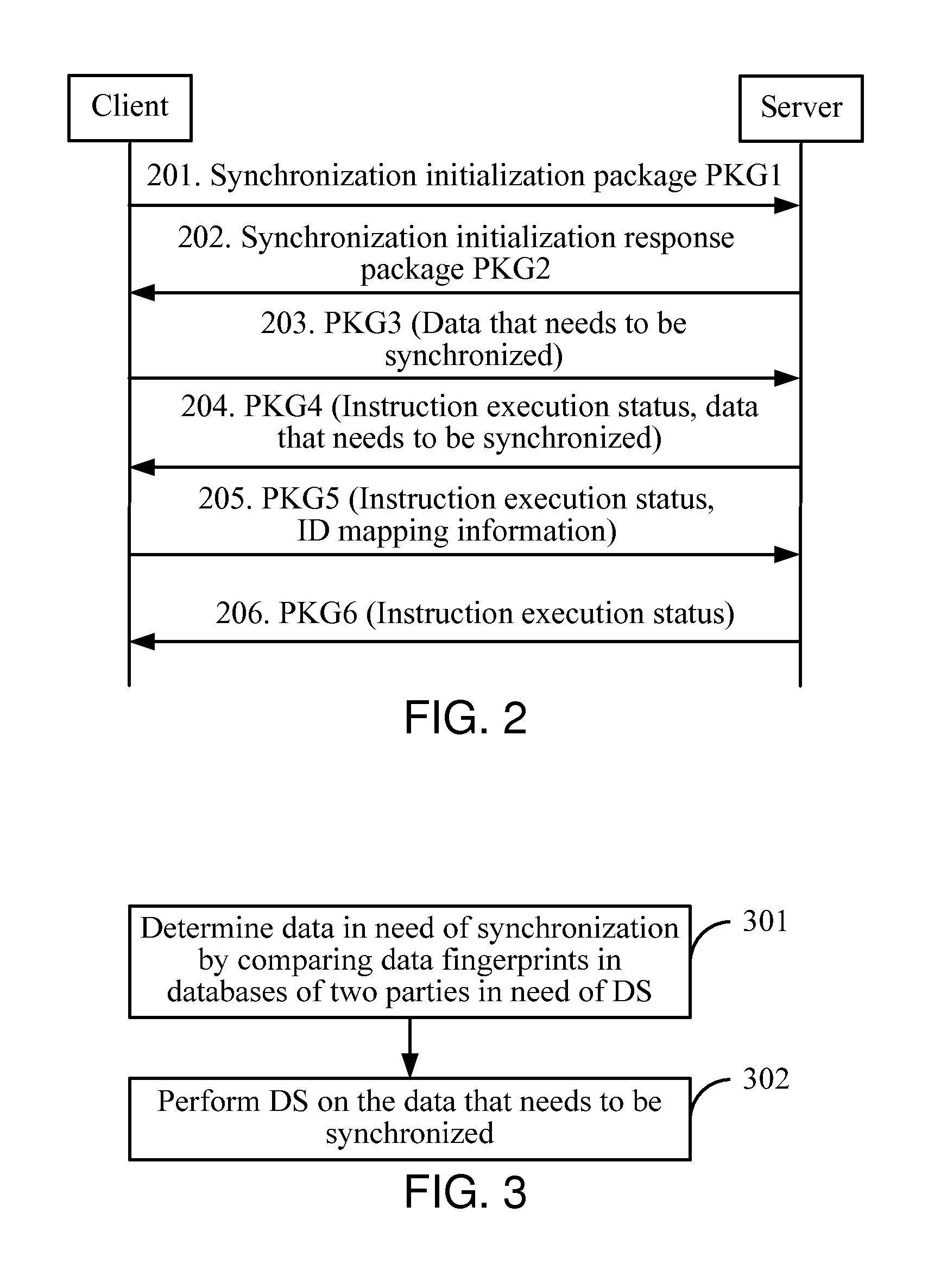
Method, system, and device for data synchronization
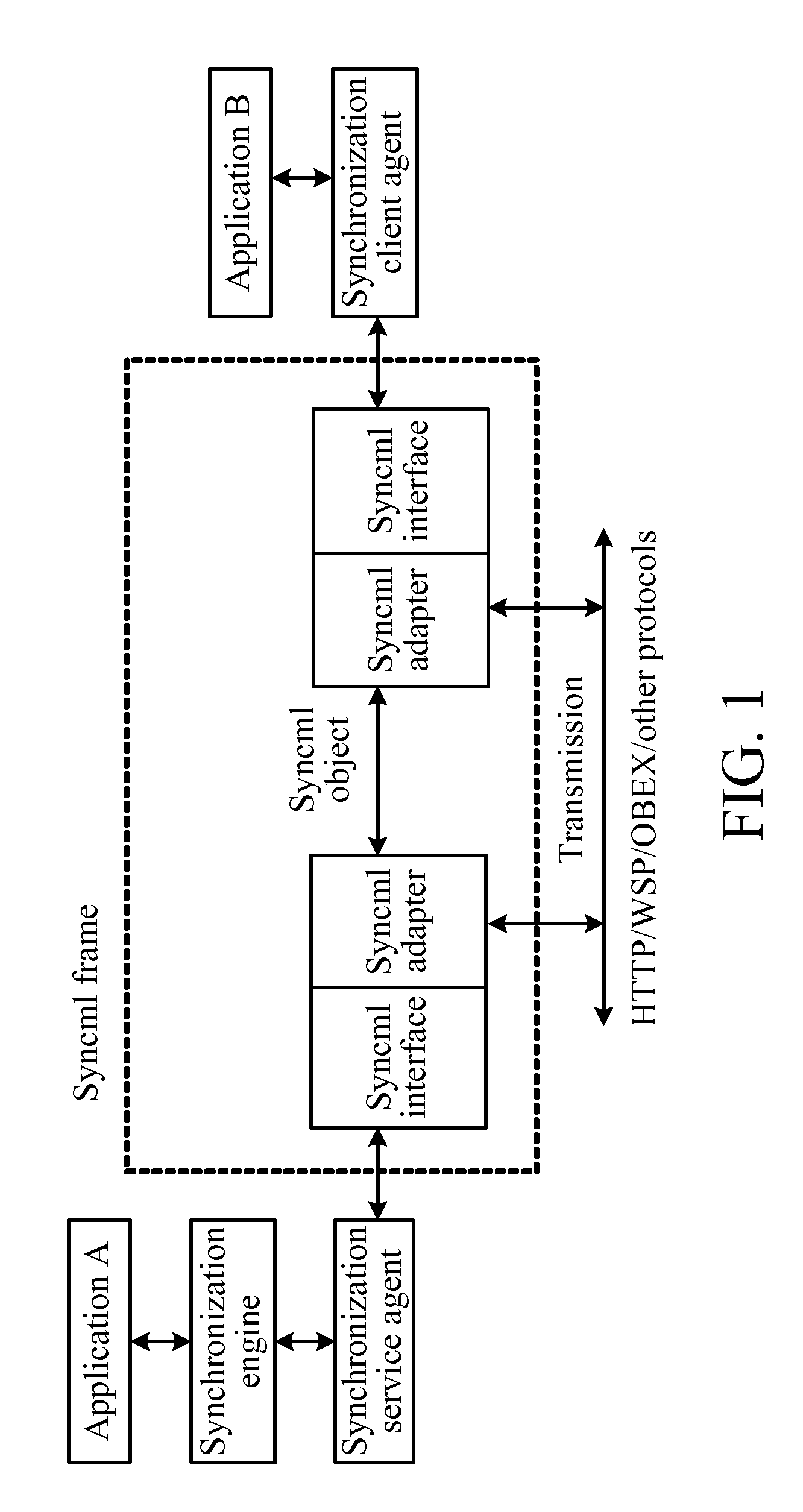
ActiveUS20100198783A1Avoid spreadingDigital data processing detailsSemi-structured data retrievalData synchronizationComputer science
A method for data synchronization (DS) is provided, which includes comparing data fingerprints in databases of two parties in need of DS, determining data that needs to be synchronized, and DS is then performed on the data that needs to be synchronized. A system and two devices for DS are further provided. Therefore, DS is implemented through data fingerprints in the technical solutions, thus avoiding transmitting a mass of data between the two parties in need of DS.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
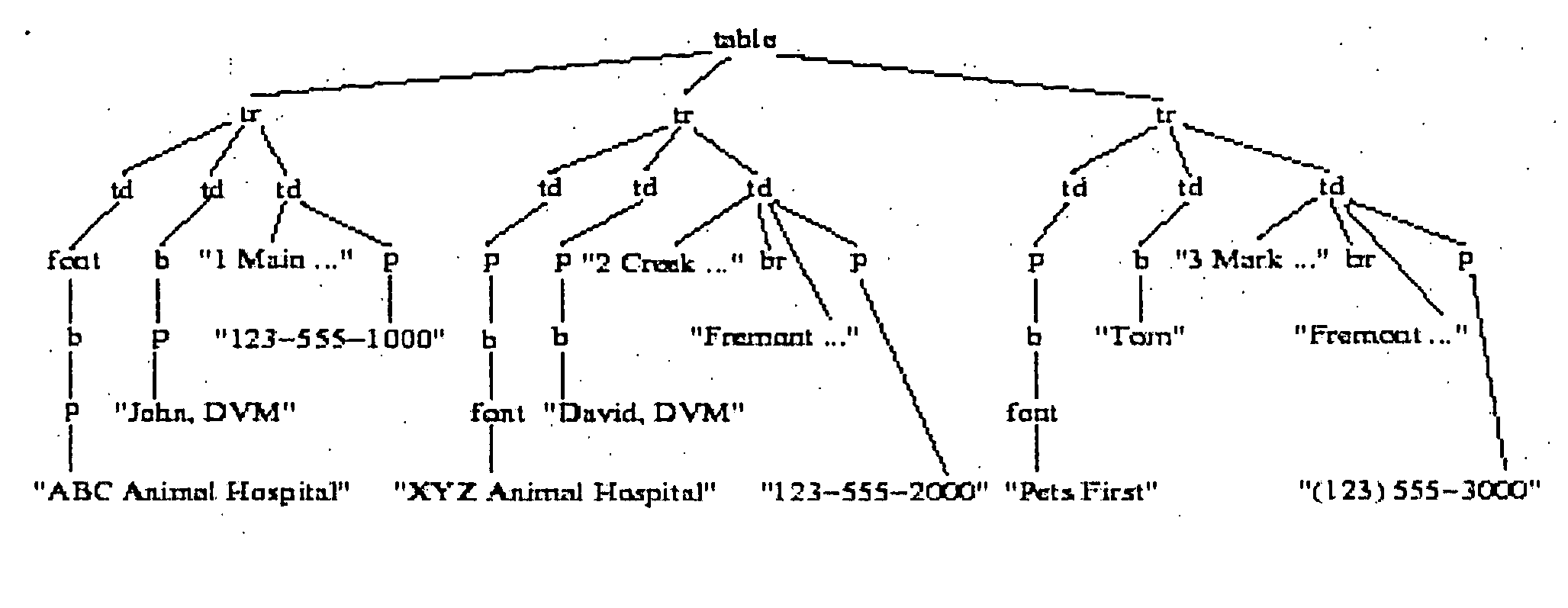
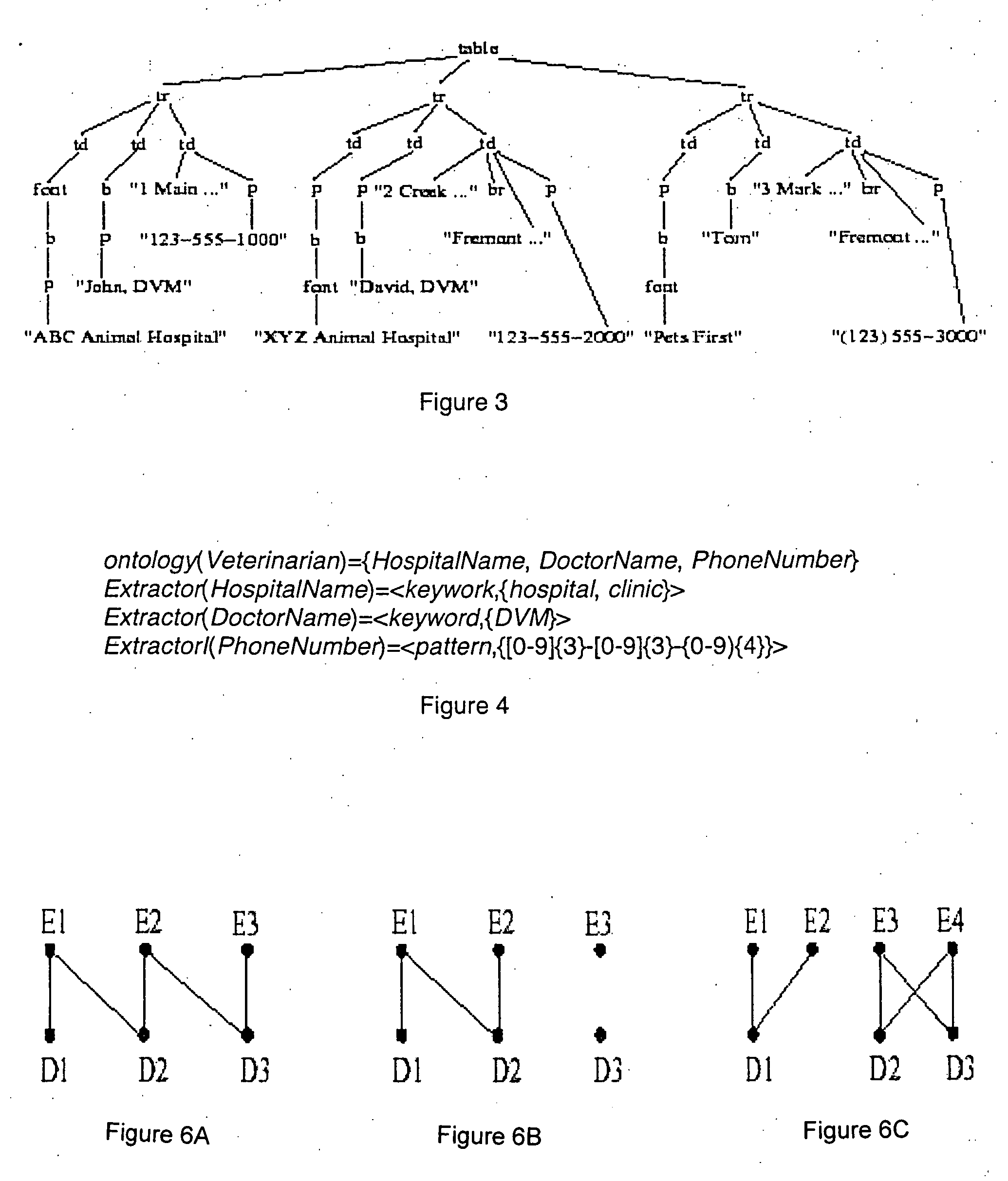
Scalable data extraction techniques for transforming electronic documents into queriable archives
InactiveUS20050055365A1Semi-structured data retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsElectronic documentData ingestion
A method for extracting an attribute occurrence from template generated semi-structured document comprising multi-attribute data records comprises identifying a first set of attribute occurrences in the template generated semi-structured document using an ontology. The method further comprises determining a boundary of each multi-attribute data record in the template generated semi-structured document, learning a pattern for an attribute corresponding to an identified attribute occurrence of the first set in the template generated semi-structured document, and applying the pattern within the boundary of each multi-attribute data record in the template generated semi-structured document to extract a second set of attribute occurrences.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
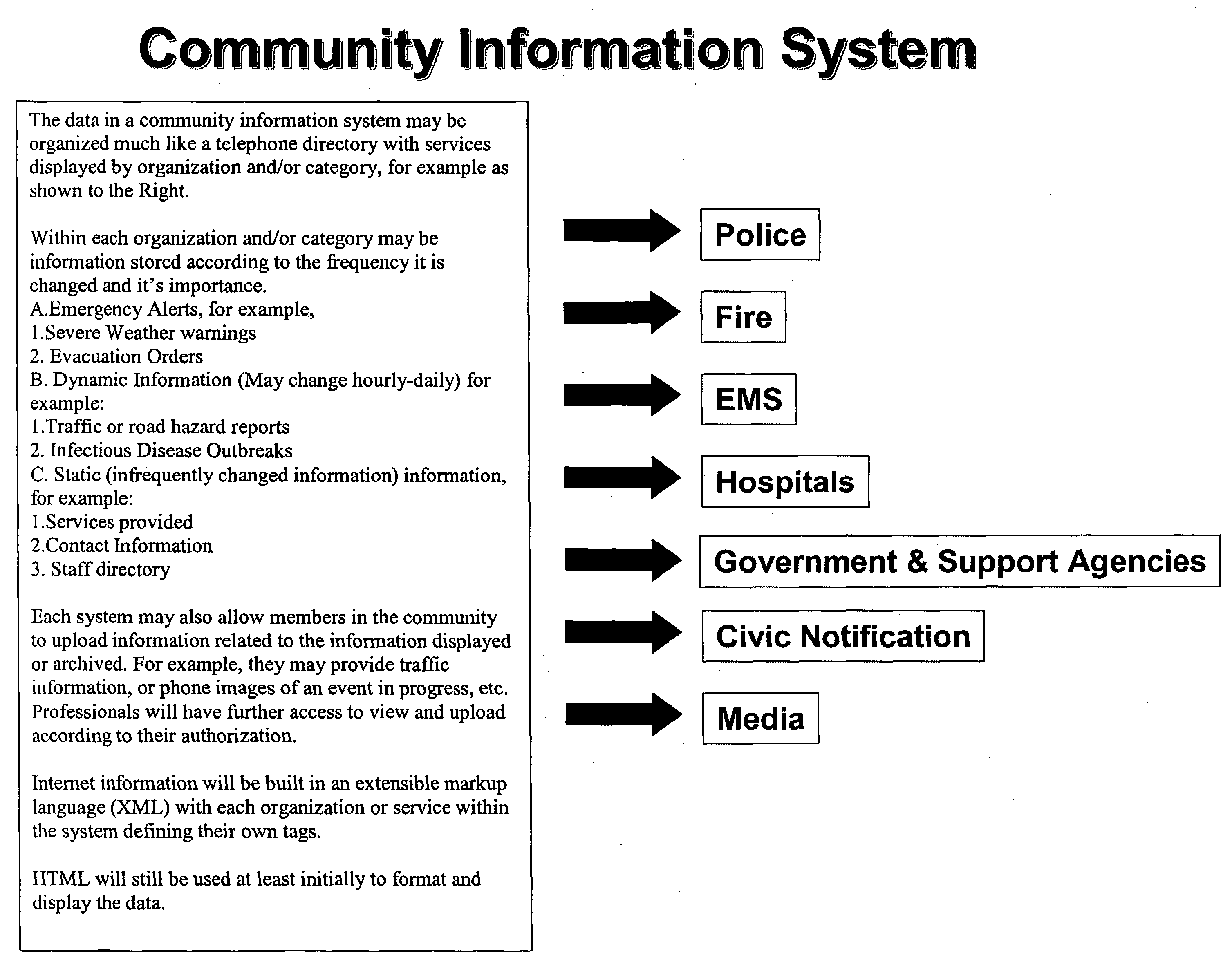
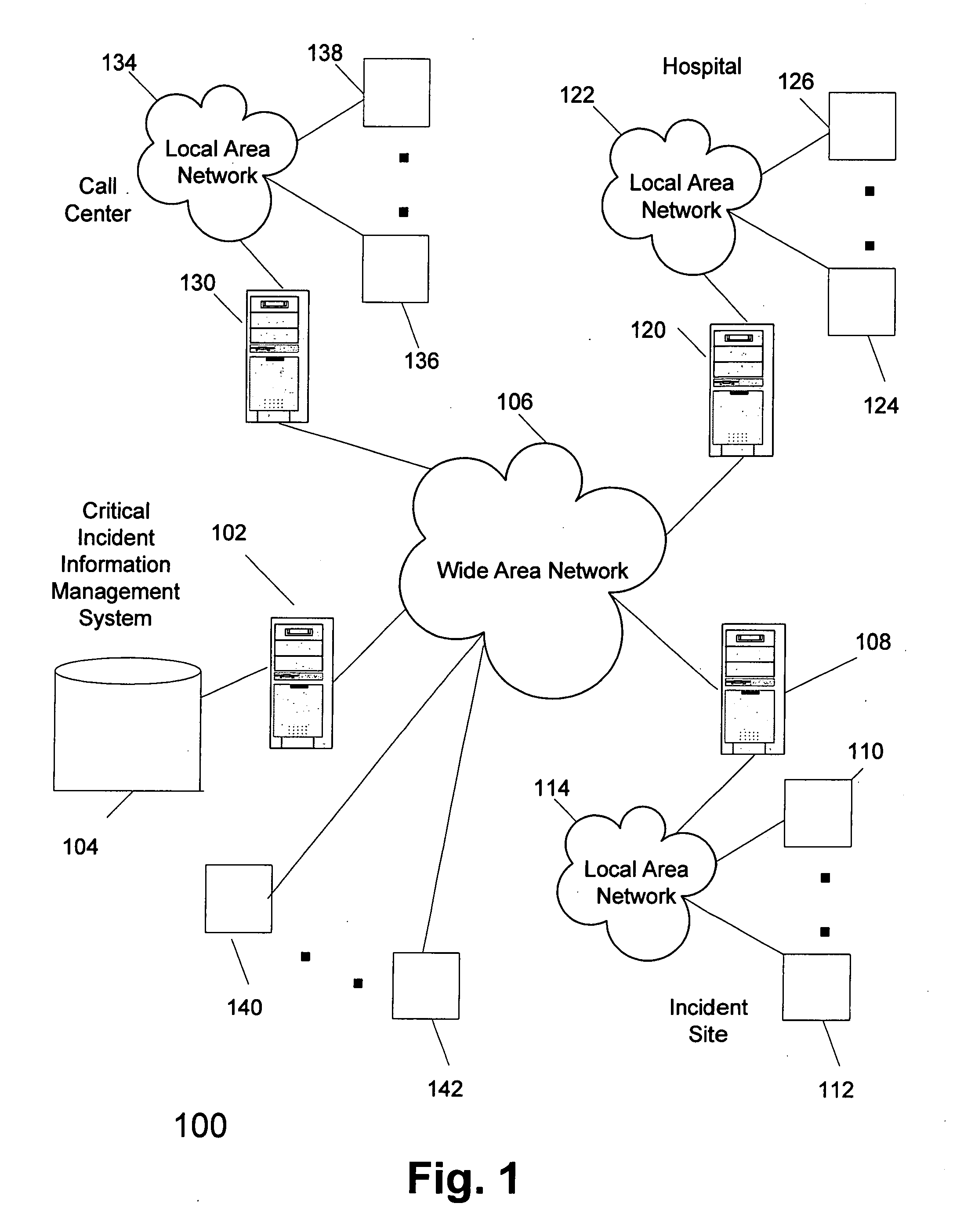
Systems and methods for emergency services, medical and community response to critical incidents
InactiveUS20080126417A1Semi-structured data retrievalOther databases retrievalCommunity responseWorld Wide Web
Systems and methods consistent with some embodiments of the present invention provide for managing a plurality of records, including storing a plurality of records, wherein each of the plurality of records includes at least one of a section and subsection; receiving a request to access one of the plurality of records, wherein the request includes identification information identifying information about a user requesting access; determining the level of access of each of the at least one section and subsection associated with the one of the plurality of records requested; selecting at least one of the section and subsection of one of the plurality of records based on the identification information of the user and the determined level of access; providing access to at least one of the selected section and subsection in a record; wherein the record may be simultaneously accessed by a plurality of users, and wherein information for updating at least one of the section and subsection in the record may be received simultaneously by a plurality of users.
Owner:MAZURIK LAUREL ANNE
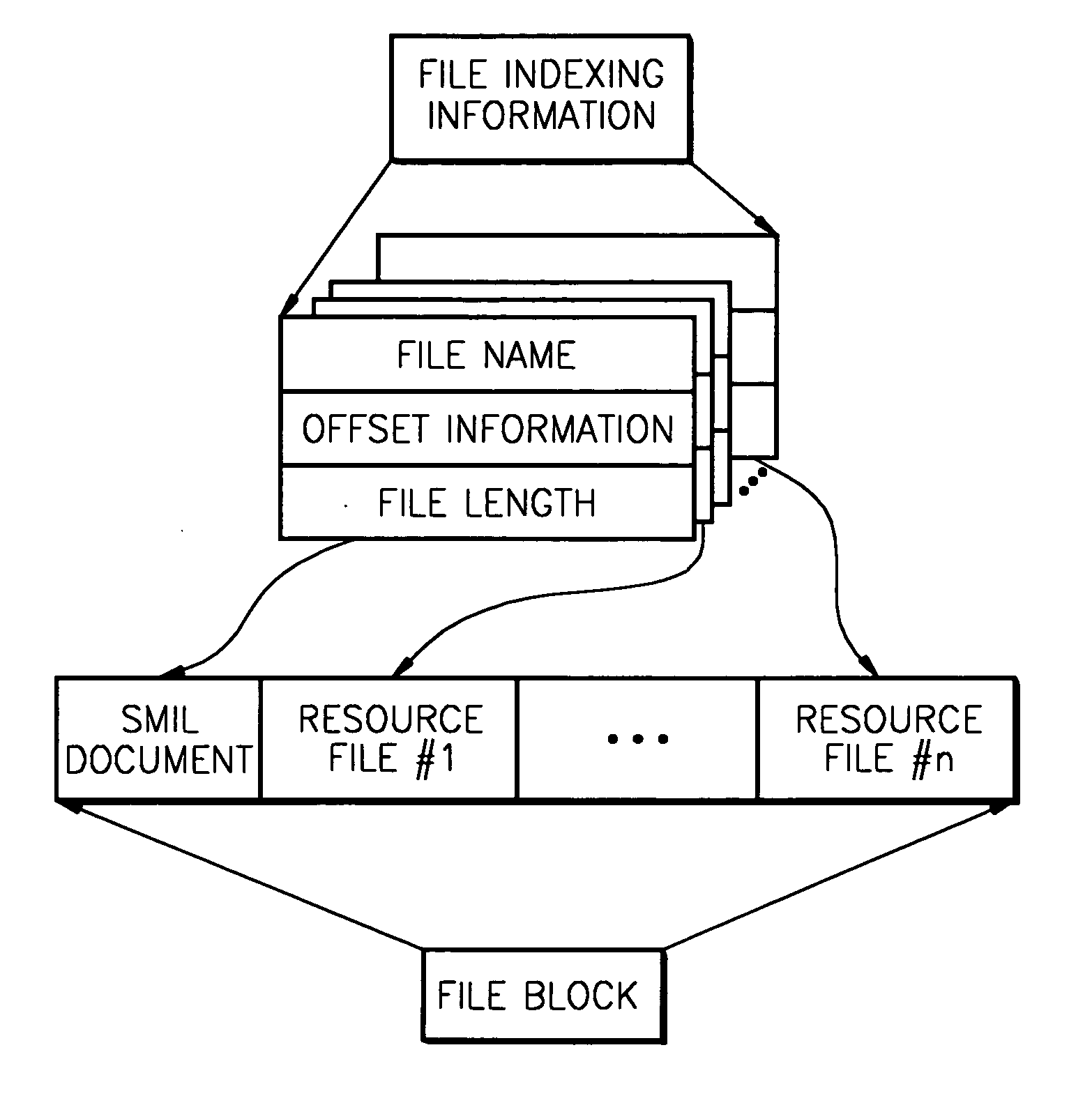
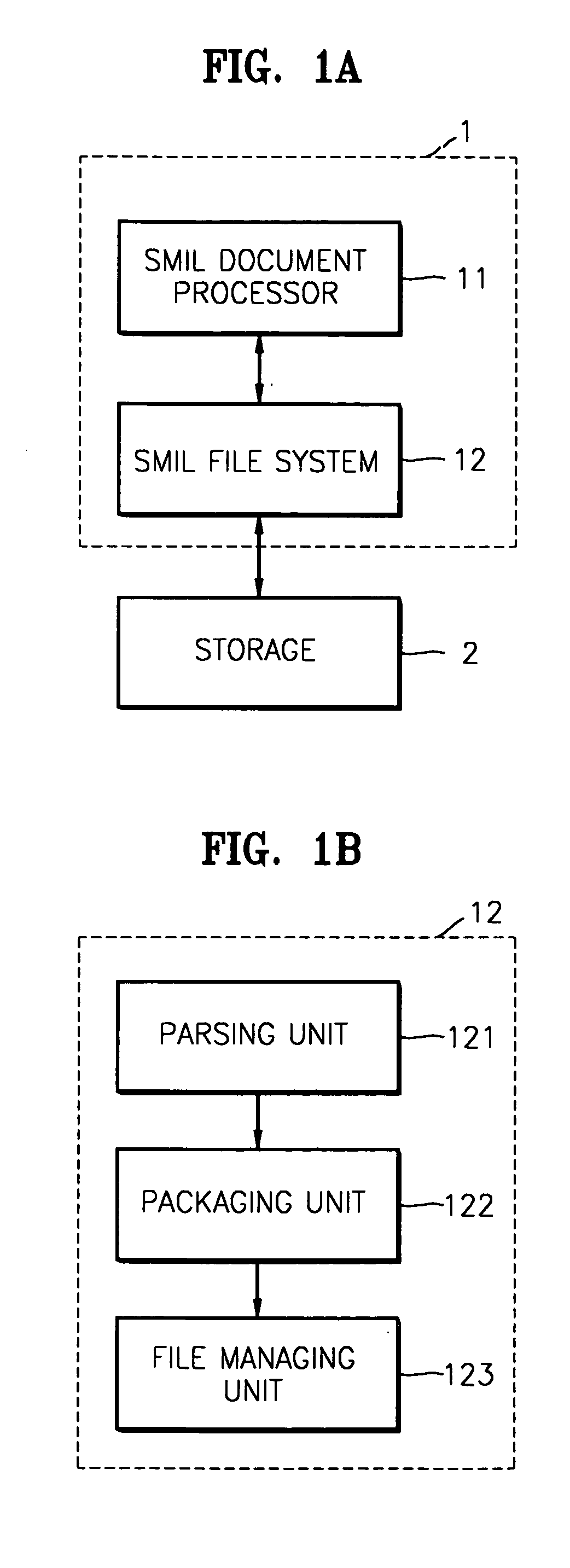
Method of managing multimedia content written in SMIL and file system thereof
InactiveUS20050038826A1Efficient storageEfficient reproductionMultimedia data indexingData processing applicationsFile systemSynchronized Multimedia Integration Language
A method of managing multimedia content created using synchronous multimedia integration language (SMIL) and a file system thereof are provided. The method involves (a) extracting information on at least one resource file by parsing an SMIL document; and (b) packaging the SMIL document and the at least one resource file into a single file using the extracted information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
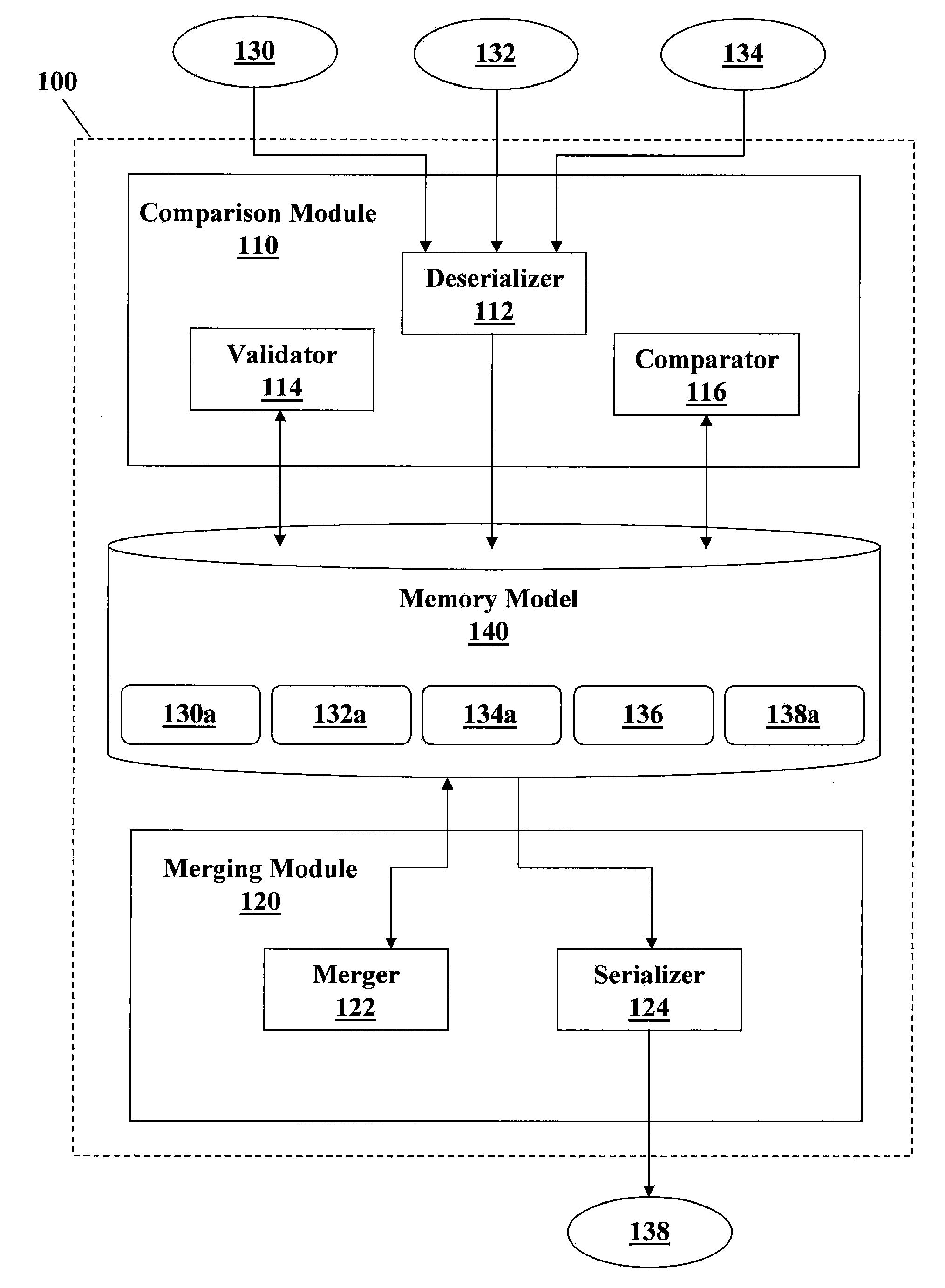
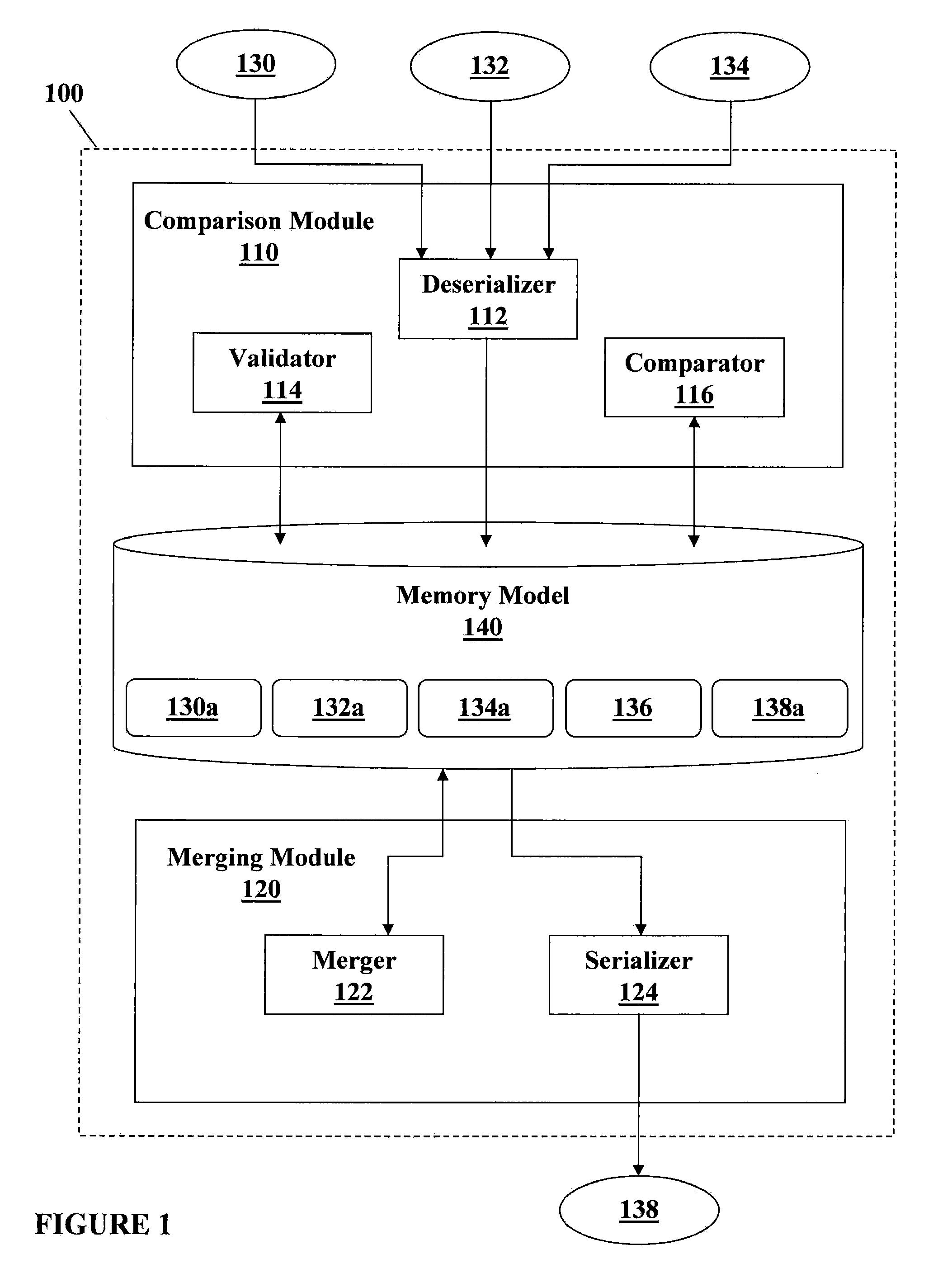
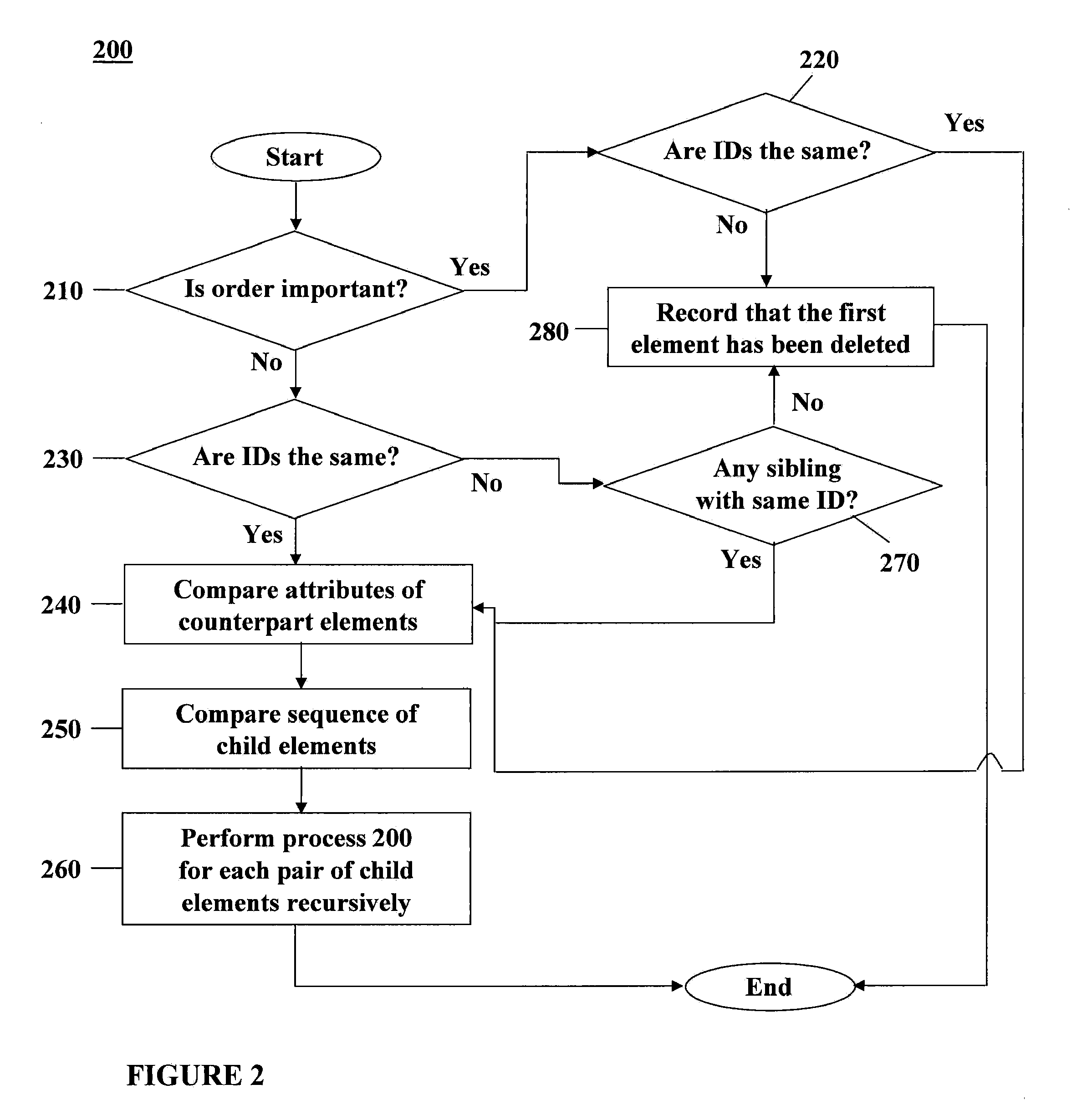
Comparing and merging structured documents syntactically and semantically
InactiveUS20100088676A1Natural language data processingSemi-structured data retrievalTree structured dataStructured document
A method of performing a three-way merge includes receiving first, second, and third versions of a structured document containing first, second, and third pluralities of elements respectively; deserializing the first, second, and third versions to generate first, second, and third tree-structured data models respectively representing the first, second, and third versions; generating an identifier for each node of each data model that is unique within the data model by applying identifier determination rules to a context describing the element corresponding to the node; comparing each identifier in the first data model with each identifier in the second data model to identify each node in the first data model not having matching identifiers with any node in the second data model and to link each pair of nodes having matching identifiers; and applying comparison rules to the contexts of each linked pair of nodes to identify differences therebetween.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods and systems for creating a semantic object
Among other disclosure, a knowledge network and semcards enabling intelligent matching of offers and requests, involving all types of information and knowledge, including information such as classified ads, data about products and services, or knowledge, expertise, ideas, suggestions, opinions, and other forms of tacit knowledge is described.
Owner:FIVER LLC
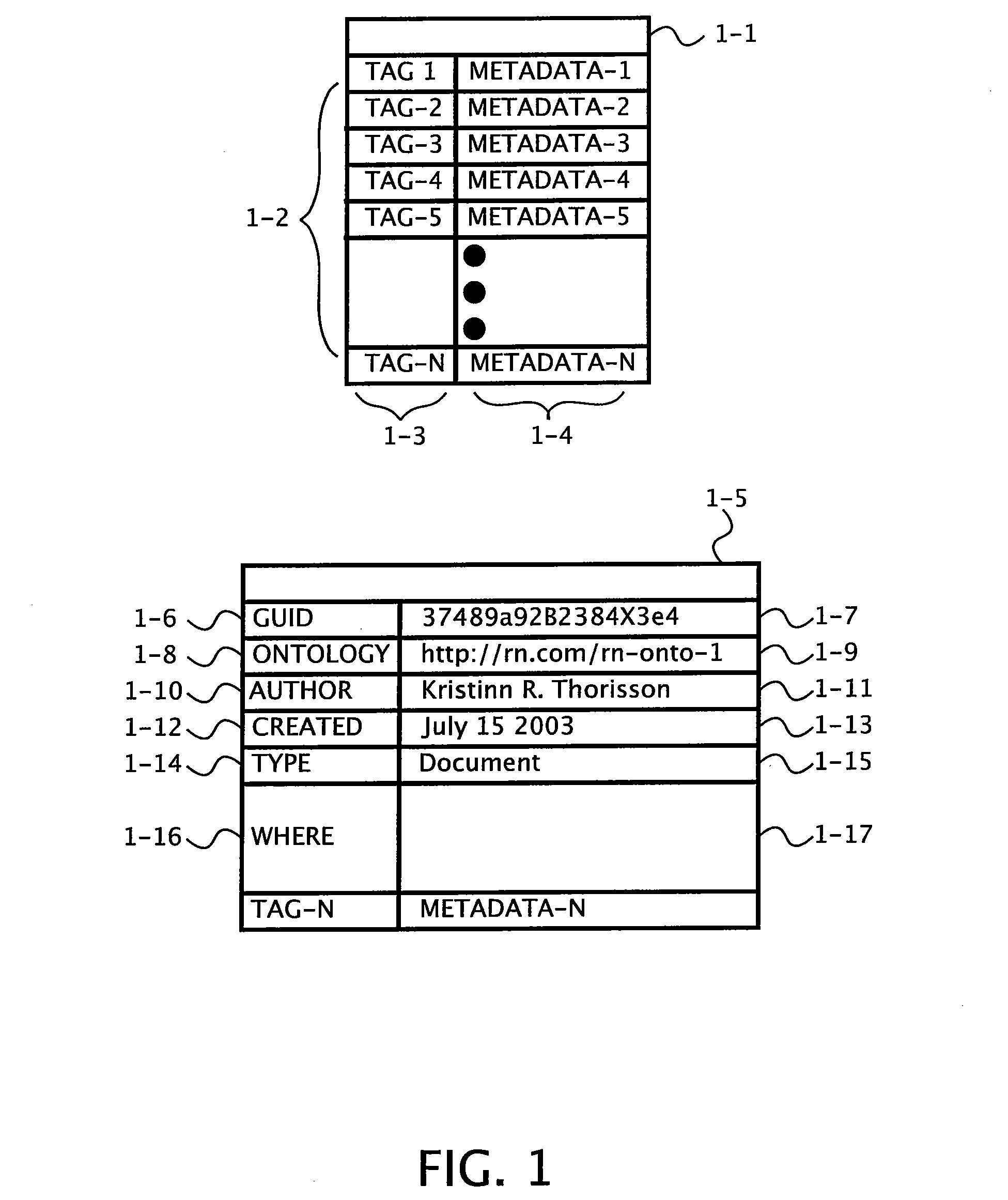
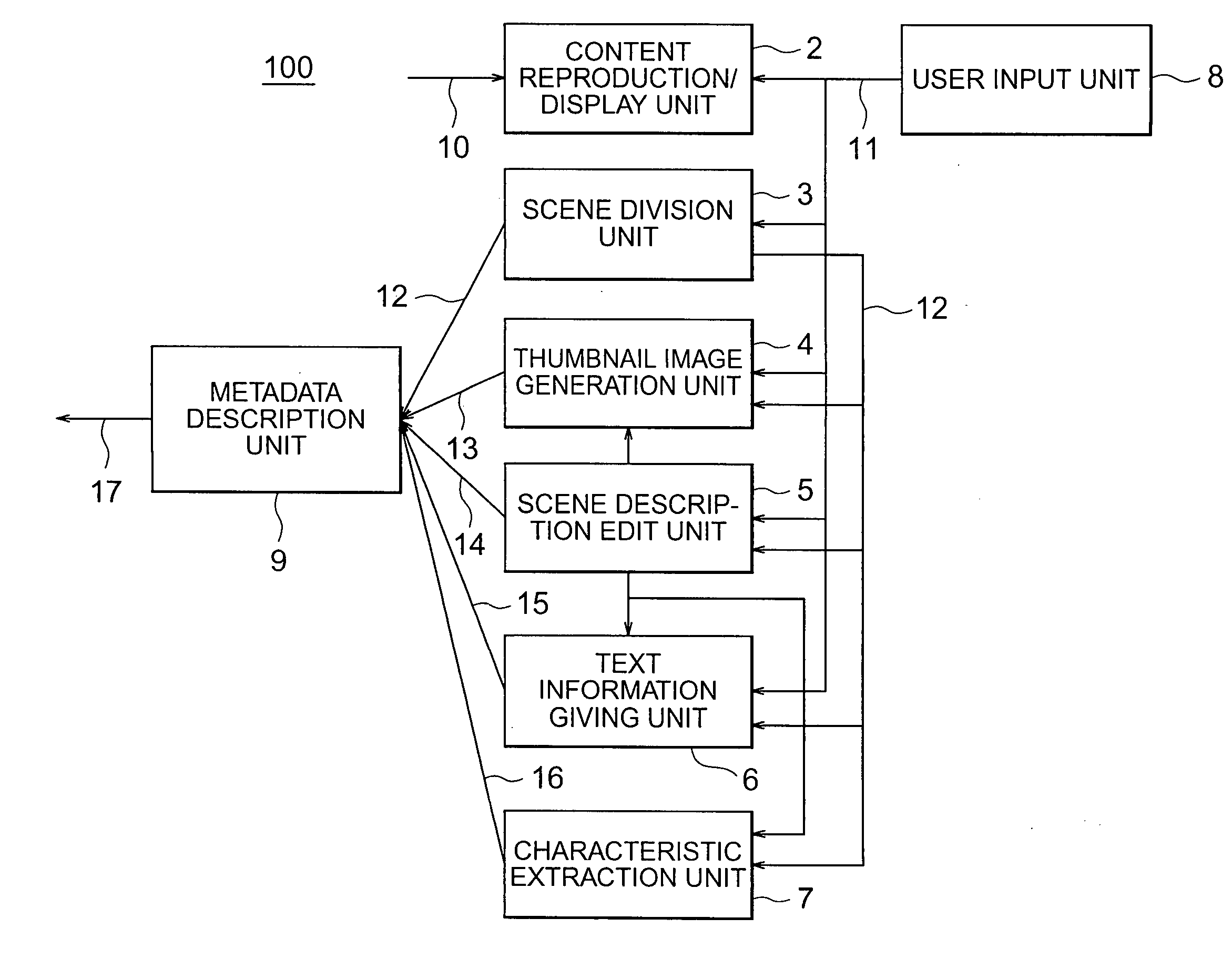
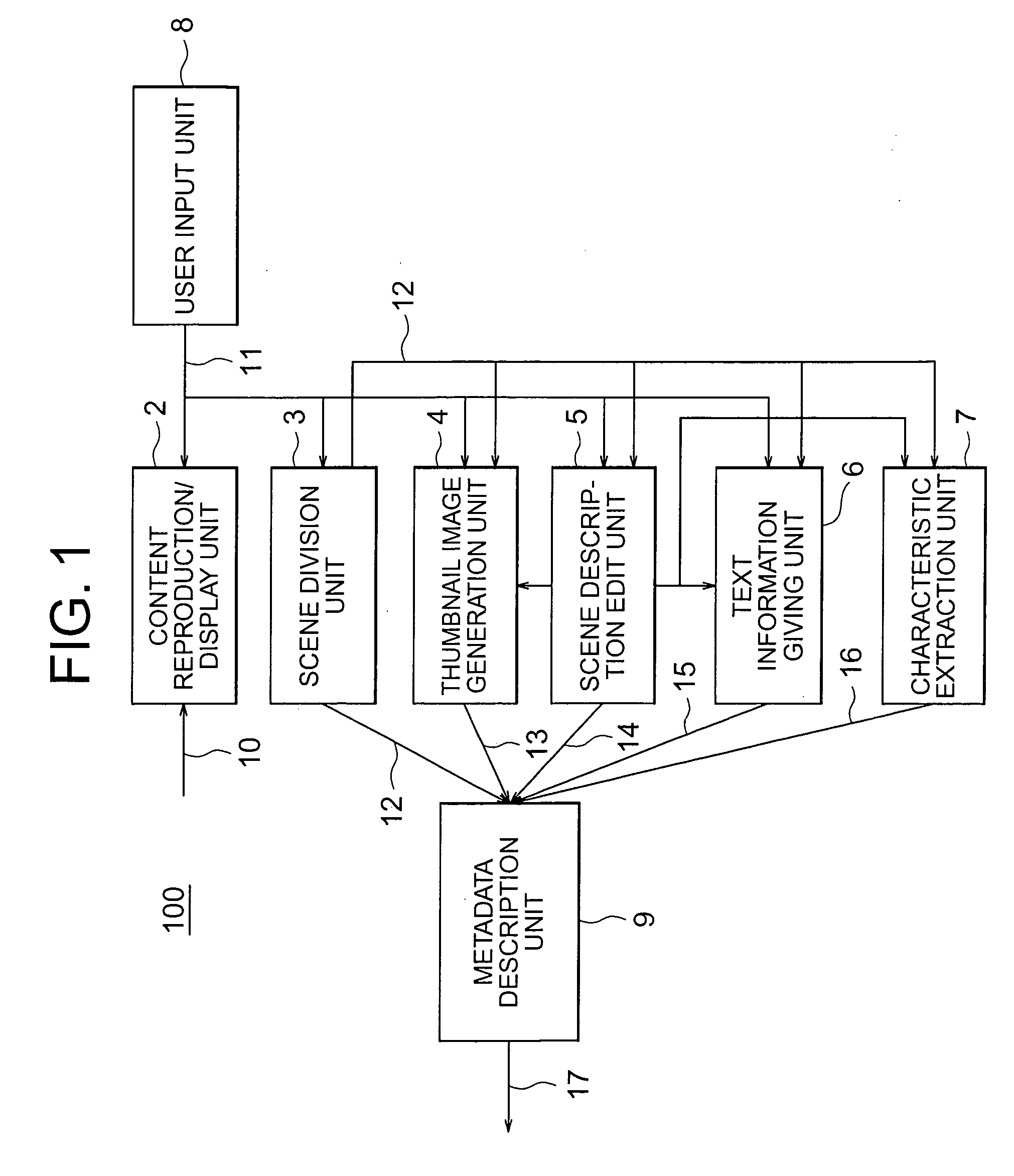
Meta data edition device, meta data reproduction device, meta data distribution device, meta data search device, meta data reproduction condition setting device, and meta data distribution method
InactiveUS20050149557A1Television system detailsDigital data processing detailsDistribution methodReproduction
Multimedia content containing moving pictures and audio is divided into multiple scenes and metadata is generated for each of the scenes obtained as a result of the division. It is possible to generate metadata containing scene structure information metadata that describes the hierarchical structure of the content in addition to scene section information and titles. Also, a name or an identifier of each descriptor contained in the metadata is described as hint information for manipulation of metadata composed of at least one descriptor describing semantic content, a structure, and characteristics of content.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
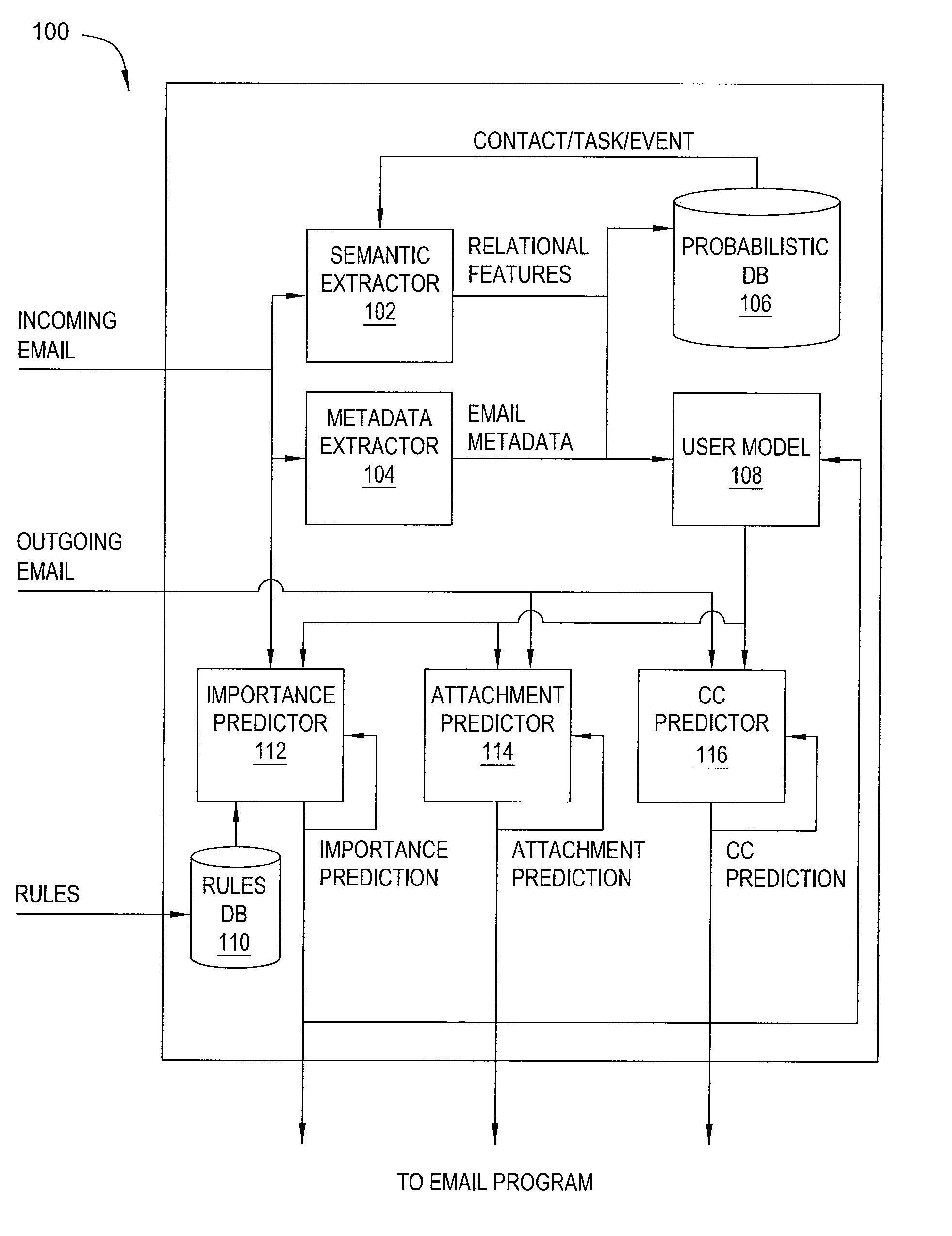
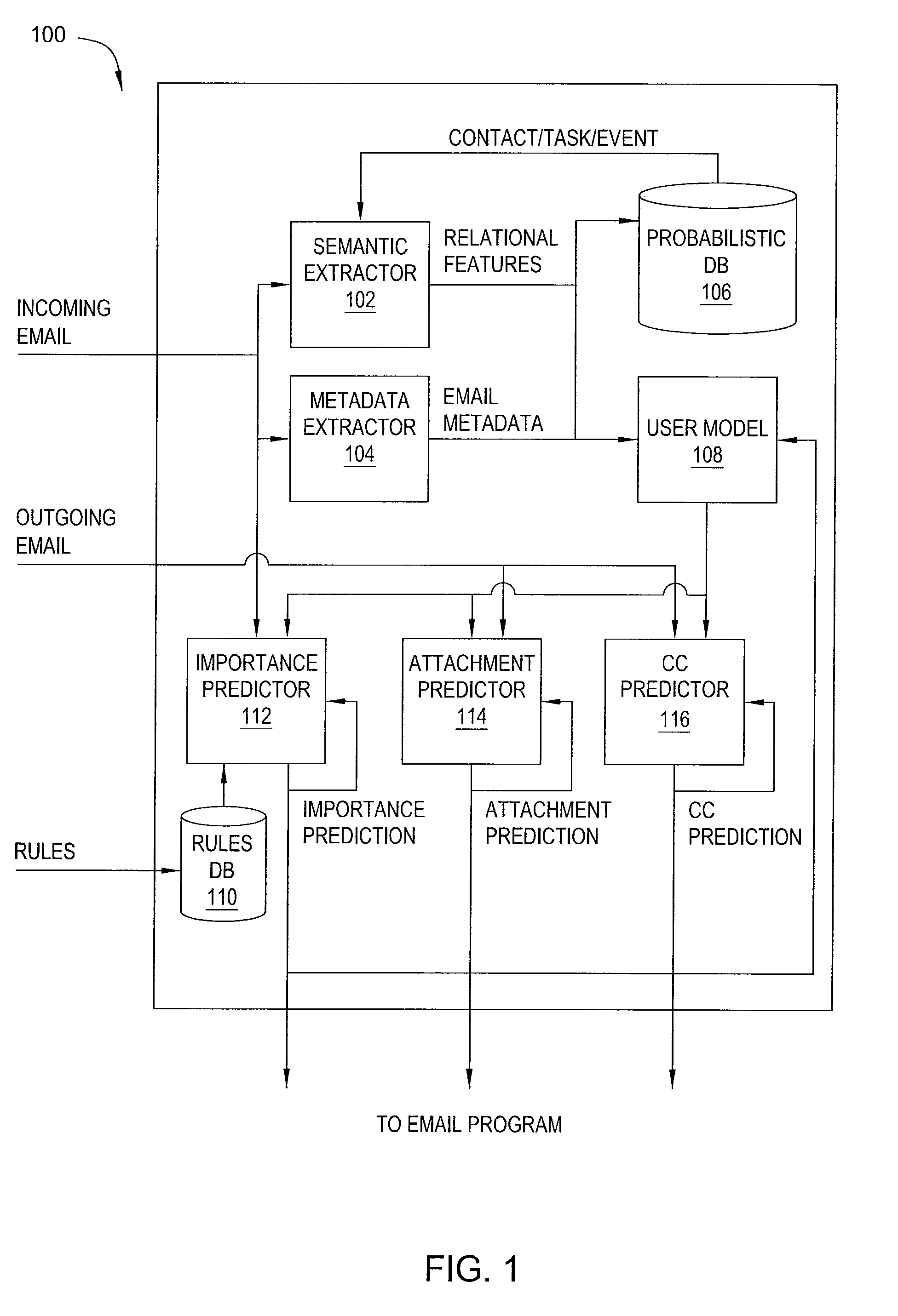
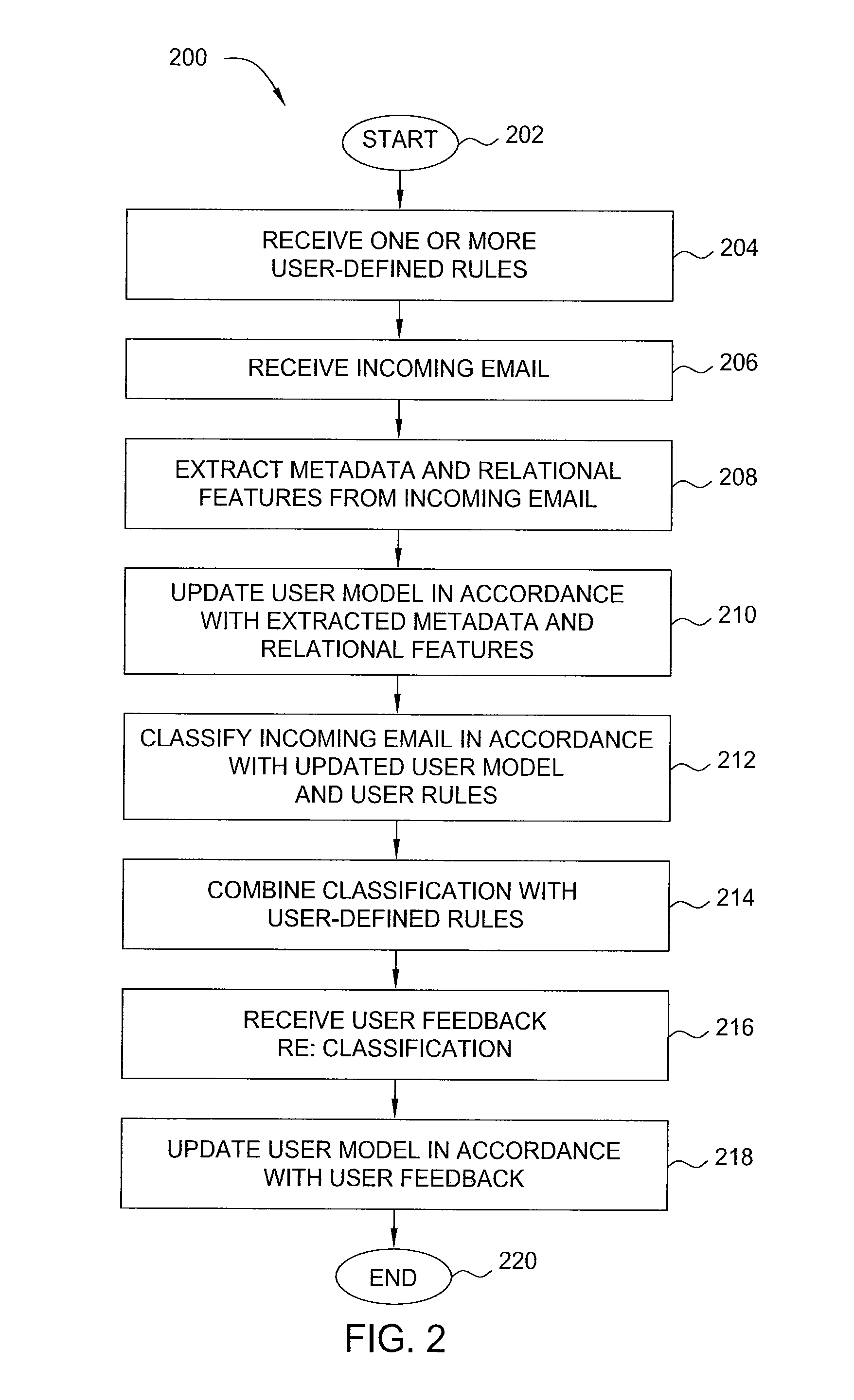
Electronic assistant
ActiveUS20100179961A1Digital data processing detailsNatural language data processingHigh level modelWorld Wide Web
The present invention relates to an electronic assistant. In one embodiment, a system for processing data on a computing device includes at least one extractor for extracting data from an email to produce extracted data, a user model for generating a high-level model of an email environment on the computing device, based on the extracted data, and at least one predictor for generating a prediction related to the email, based on the extracted data and on the high-level model. In another embodiment, a system for scheduling an event includes an extractor for extracting constraints from a request for the event, a user model for receiving and storing scheduling preferences from a user, and a predictor coupled to the extractor and to the user model, for generating a candidate schedule for the event in accordance with the constraints and the scheduling preferences.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
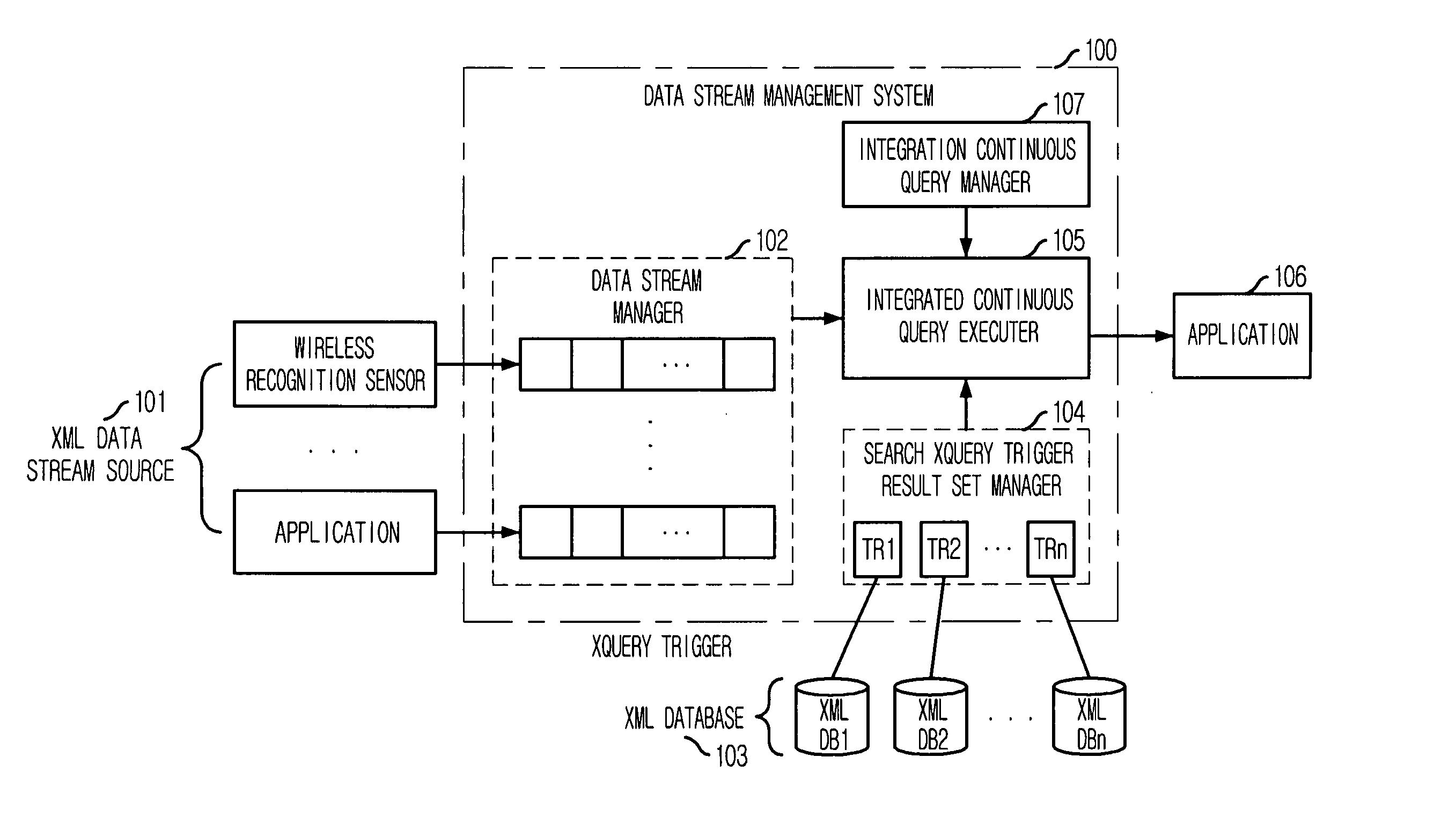
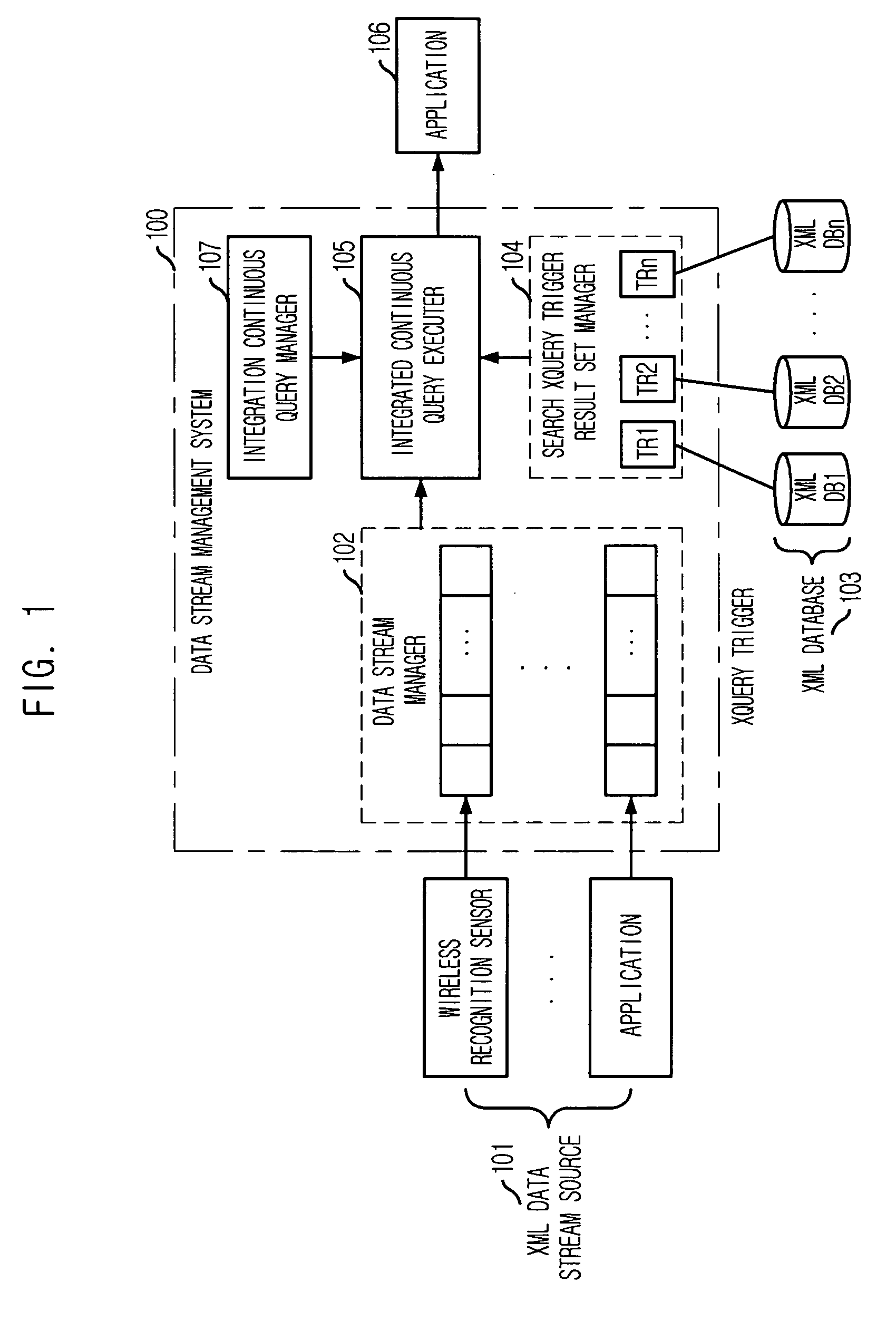
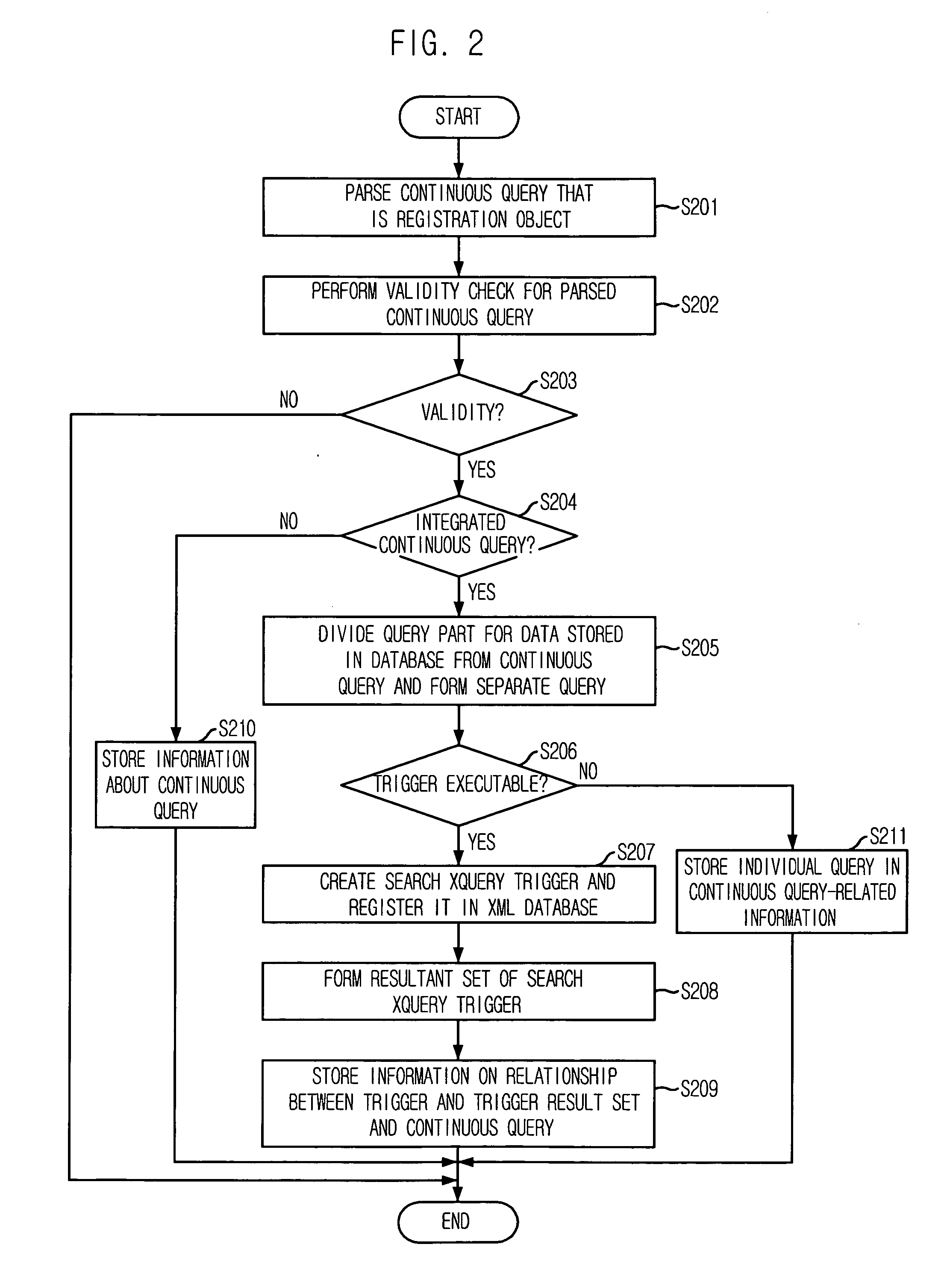
System and method for processing integrated queries against input data stream and data stored in database using trigger
InactiveUS20070136254A1Improve query performanceShorten the timeDigital data processing detailsSemi-structured data retrievalData streamActuator
Provided are a system and a method for processing integrated queries against an input data stream and data stored in a database using trigger. The system for processing an integrated query against an input data stream and data stored in a database using a trigger, including: a data stream manager for managing a continuously inputted data stream; a trigger result manager for registering a trigger in a database which interworks with the trigger result manager and forming a set of results that are obtained by executing the registered trigger to thereby provide the set of results in real time; and an executer for processing an integrated query against the data stream from the data stream manager and data stored in the database, wherein the integrated query is processed by referring to the set of results from the trigger result manager for the data stored in the database.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Array-based extensible document storage format
InactiveUS6938204B1Meet growth requirementsExtension of timeData processing applicationsSemi-structured data retrievalArray data structureData mining
Systems and computer program products are provided having a plurality of arrays used to represent structured documents. The arrays include an element name array including an element name entry for each element in the structure document, an element value array including an element value entry for each element in the structured document, an attribute array including an attribute entry for each element in the structured document, a parent array including a parent entry for each element in the structured document and a child array including a child entry for each element in the structured document, The value of each parent entry identifies a parent of the element and the value of each child entry identifies zero or more children of the element.
Owner:IBM CORP
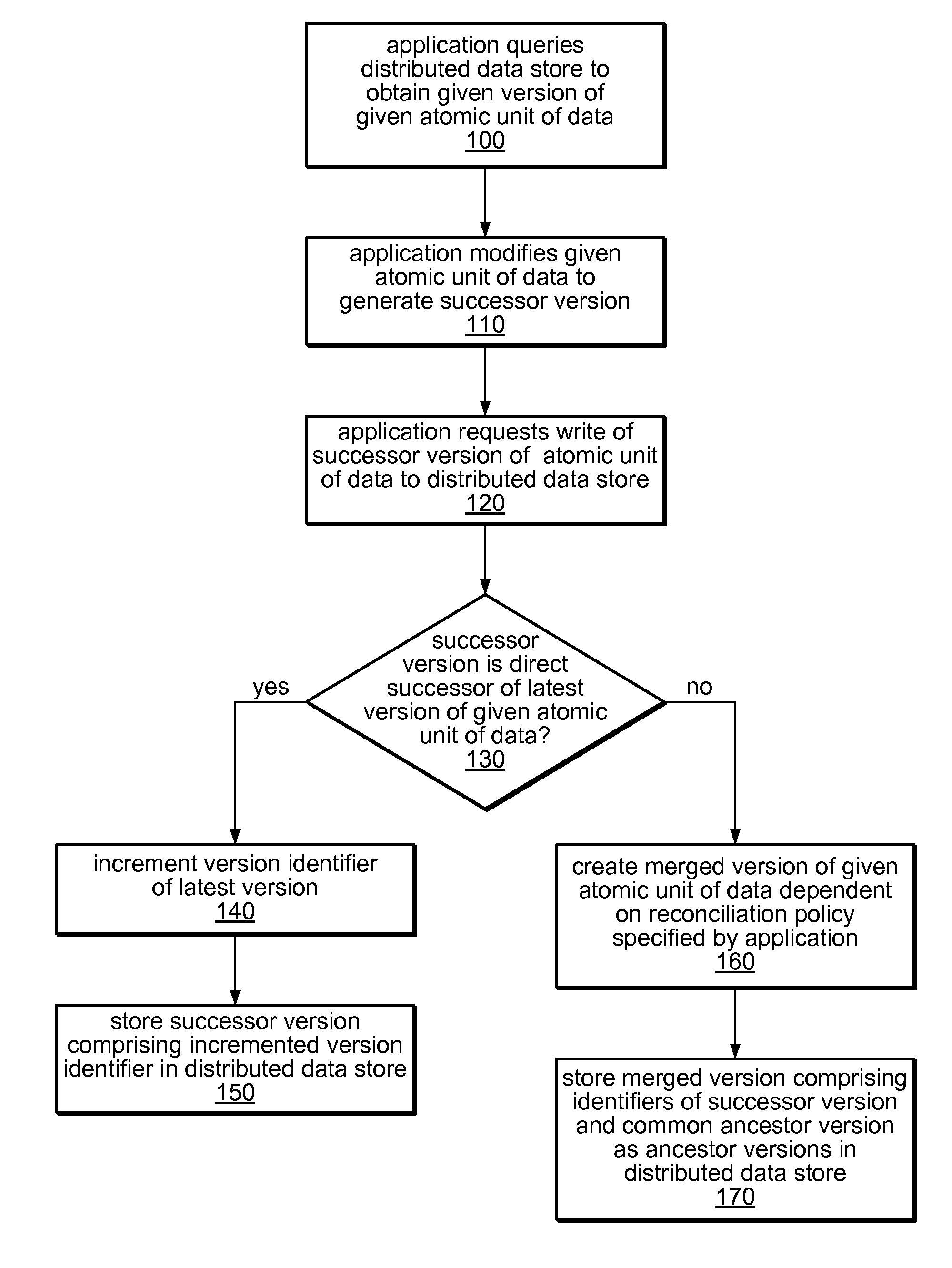
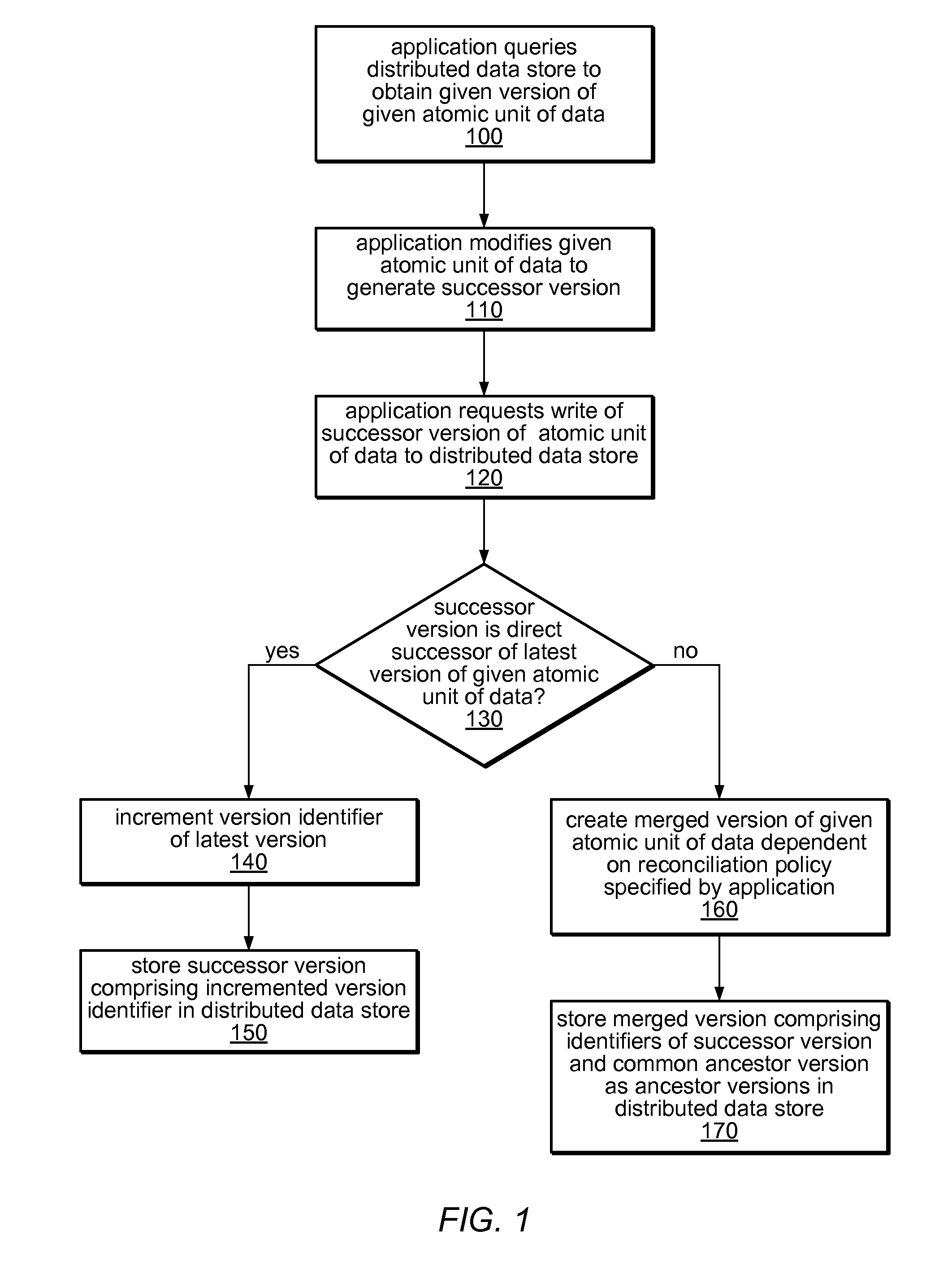
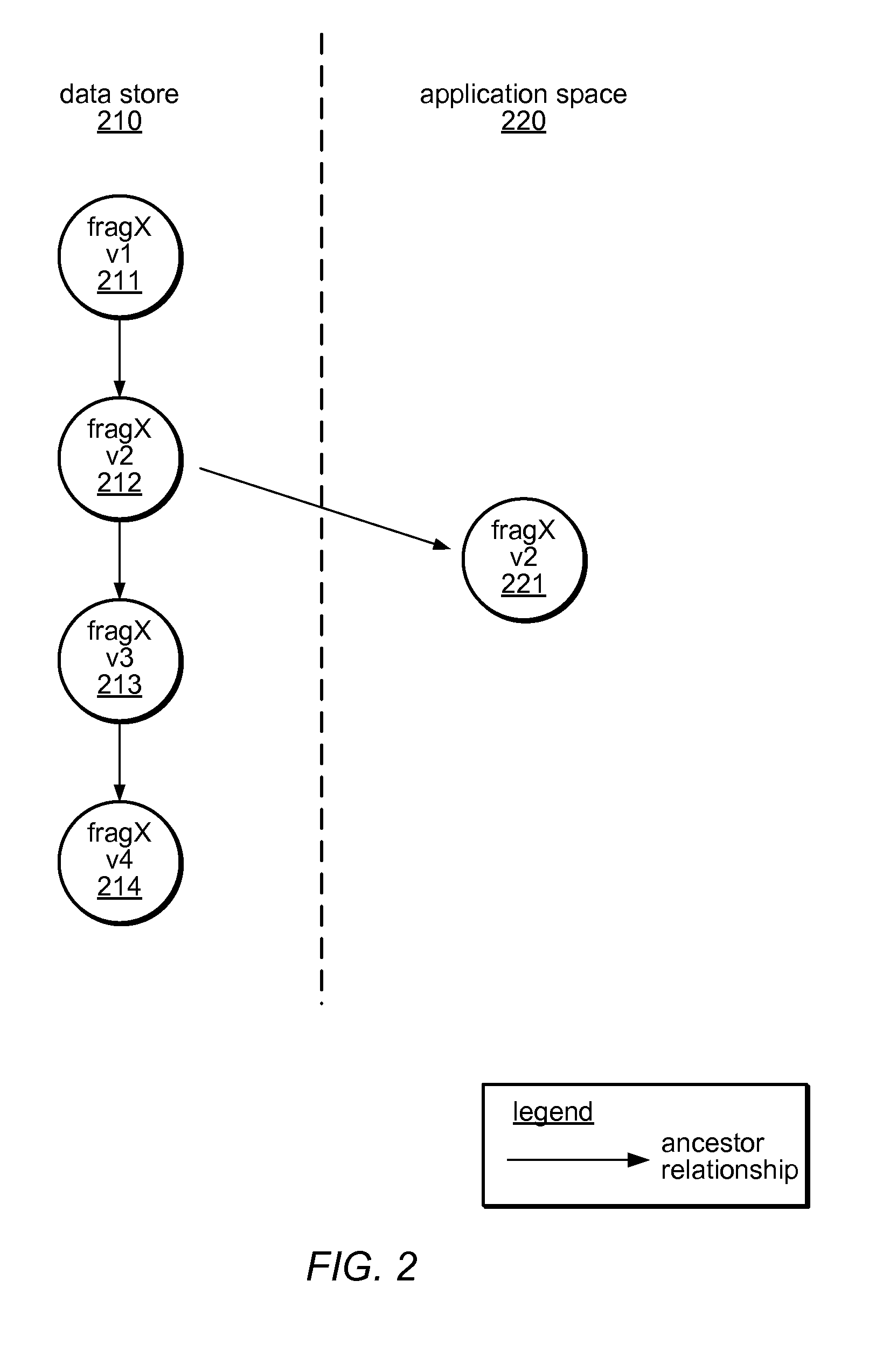
System and method for versioning data in a distributed data store
InactiveUS8266122B1Digital data processing detailsDatabase distribution/replicationApplication programming interfaceDistributed data store
A system and method for versioning of atomic units of data (such as XML fragments) in a distributed data store are disclosed. The distributed data store may maintain a linear version history for each fragment, such that each has no more than one successor and one predecessor, with no implicit branching. An application programming interface may provide an explicit branching request (indicating an intent to merge modified data in a child branch into its parent branch), along with read, create, create-merge, and / or integrate requests. A reconciliation policy may be specified on a per-application basis, and may include automatic reconciliation using a callback function or interactive reconciliation, with inputs returned to the application. Writes to a minority side of a network partition may be refused unless an explicit branch is requested. Transactions may not be supported in client applications or may be supported through explicit branching. Transactions may be used internally.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
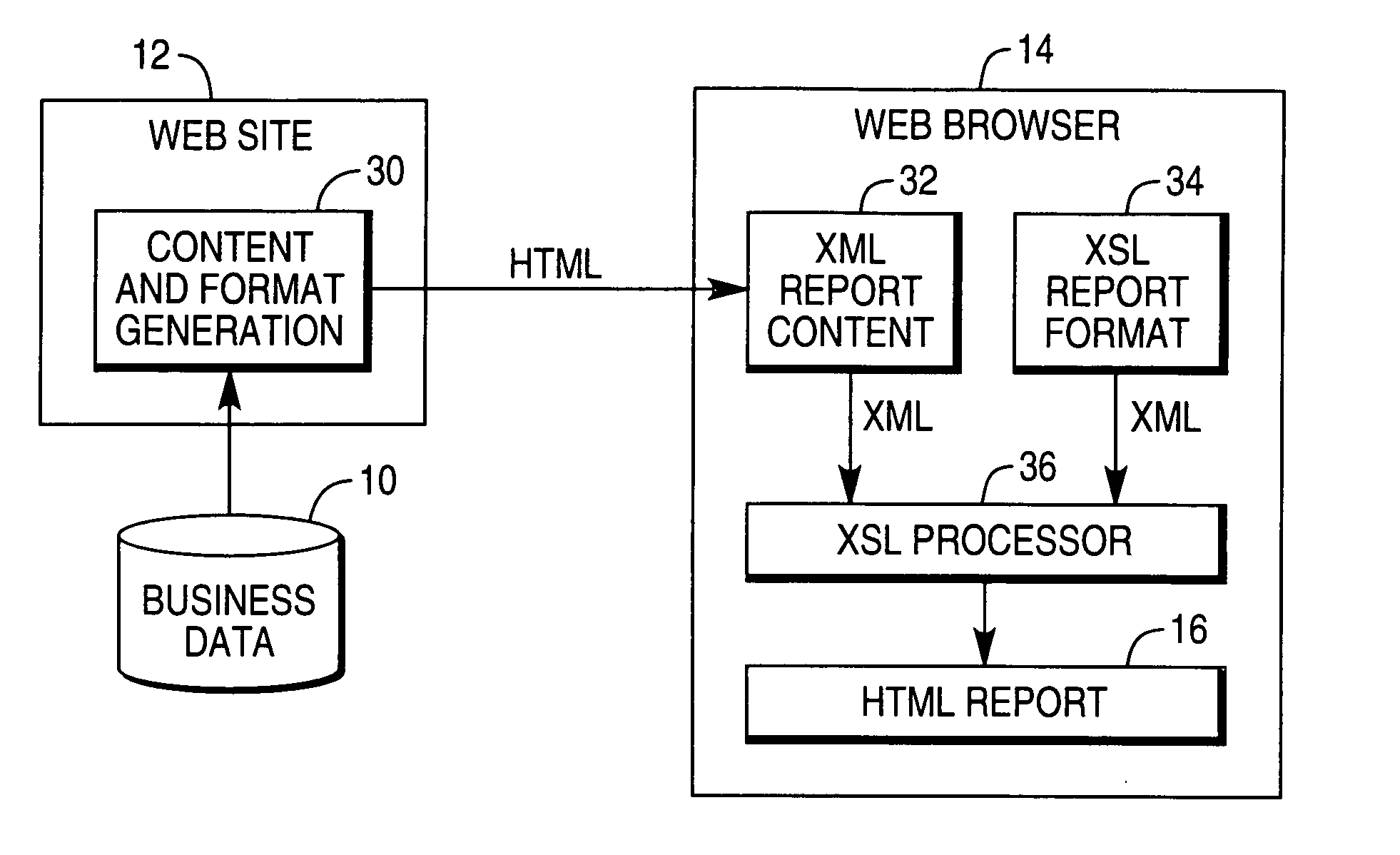
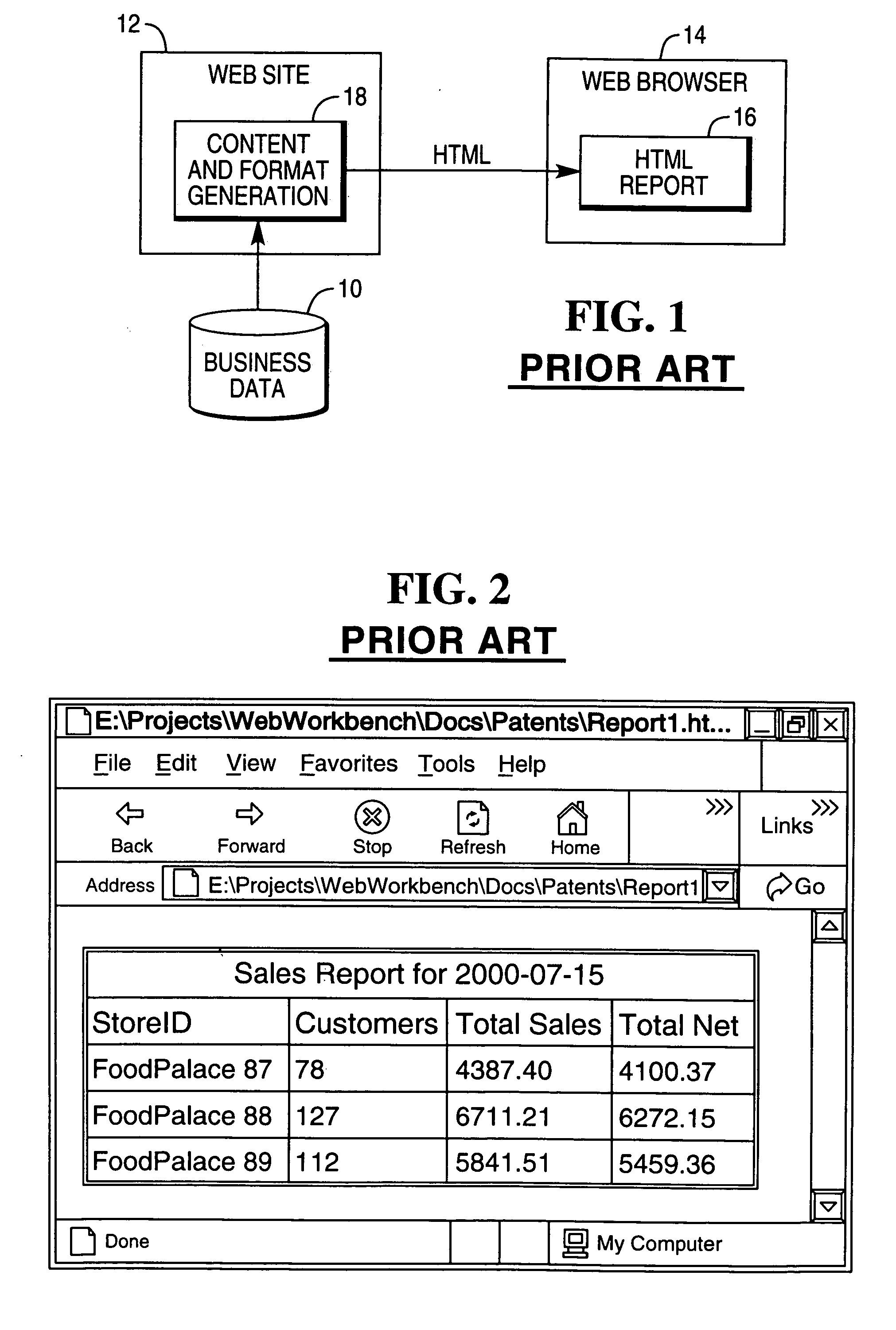
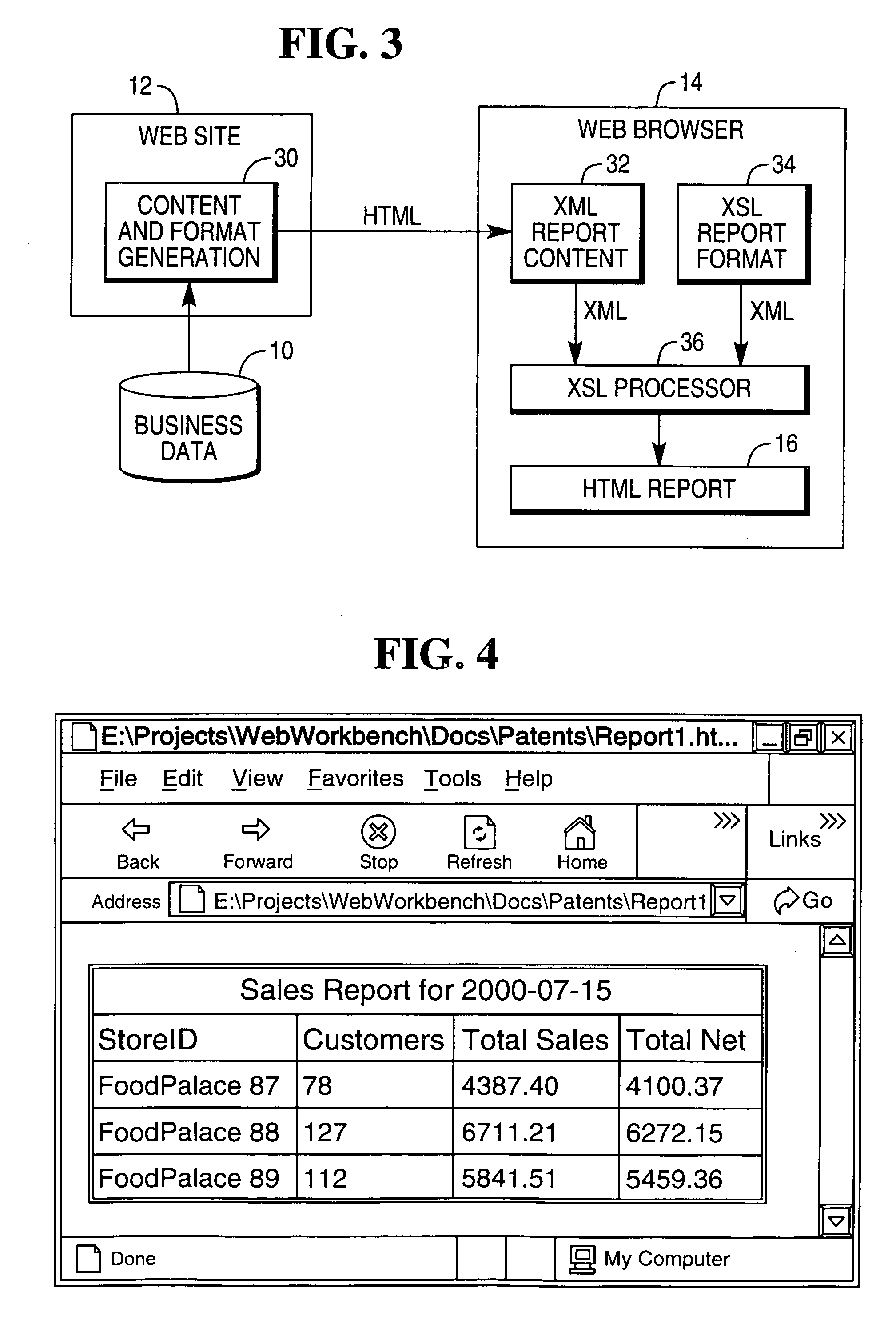
Custom report generation using XML and XSL
InactiveUS20040205617A1Semi-structured data retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsWeb siteXML Base
A method of generating a report using XML and XSL is described. A user browses to a web site and obtains XML-based report content to be formatted. The XML-based report content is received and processed. An HTML-based format report is generated by applying an XSL-based format to the XML-based report content.
Owner:NCR CORP
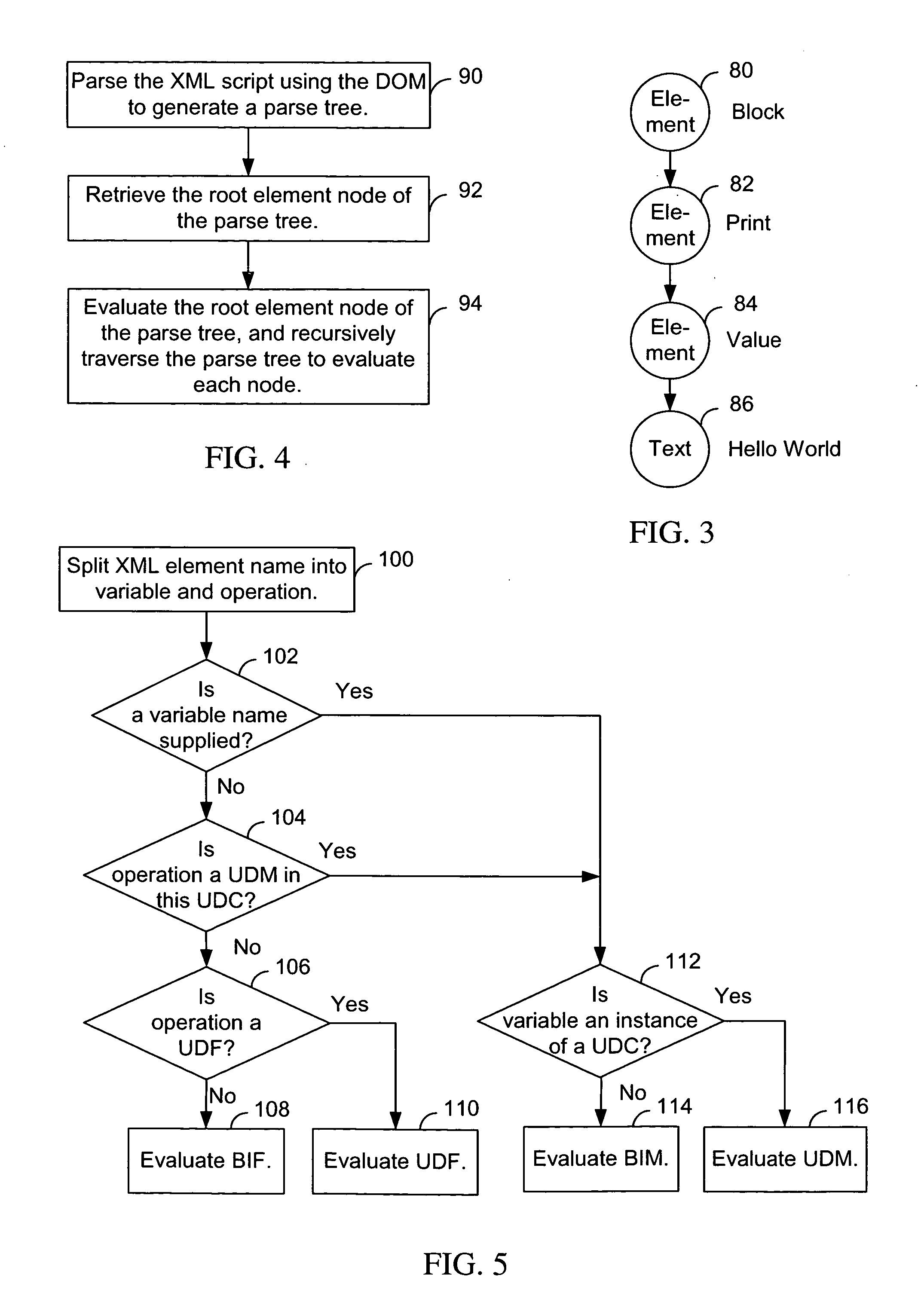
XML based scripting language
InactiveUS20060004827A1Data processing applicationsSemi-structured data retrievalScripting languageExtensible markup
Various embodiments of a method, apparatus, and article of manufacture for processing an extensible markup language (XML) script using an XML based scripting language are provided. The XML script is parsed. The XML script comprises element nodes. Each element node comprises a component name. A first element node comprises a first component name referencing a first user-defined component. An argument is passed to the first user-defined component. The argument is evaluated when an element node associated with the first user-defined component comprises an evaluate-component name that explicitly specifies that the argument be evaluated.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for integrating relational and hierarchical data
InactiveUS20080082514A1Semi-structured data retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsProgramming languageData processing system
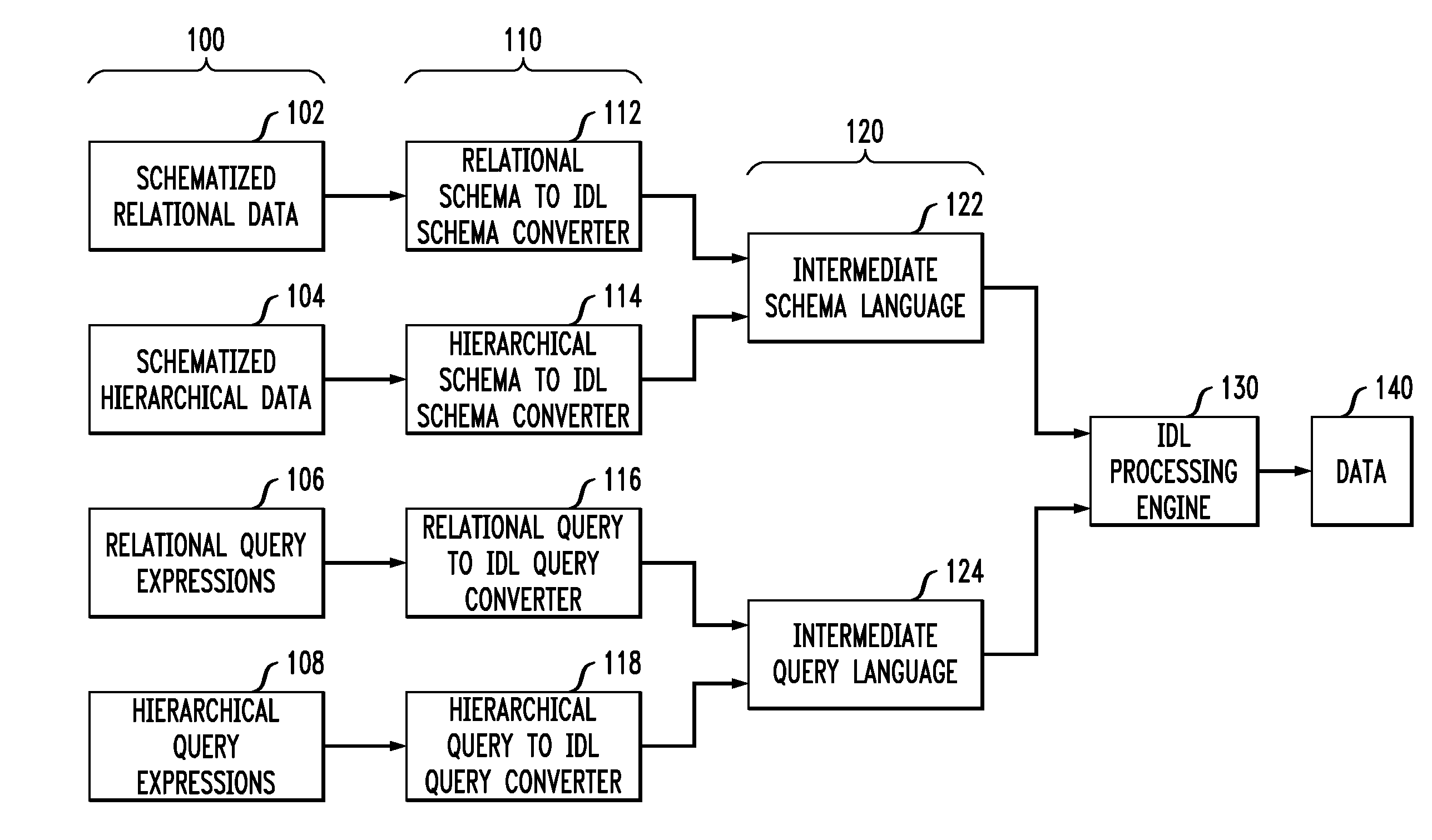
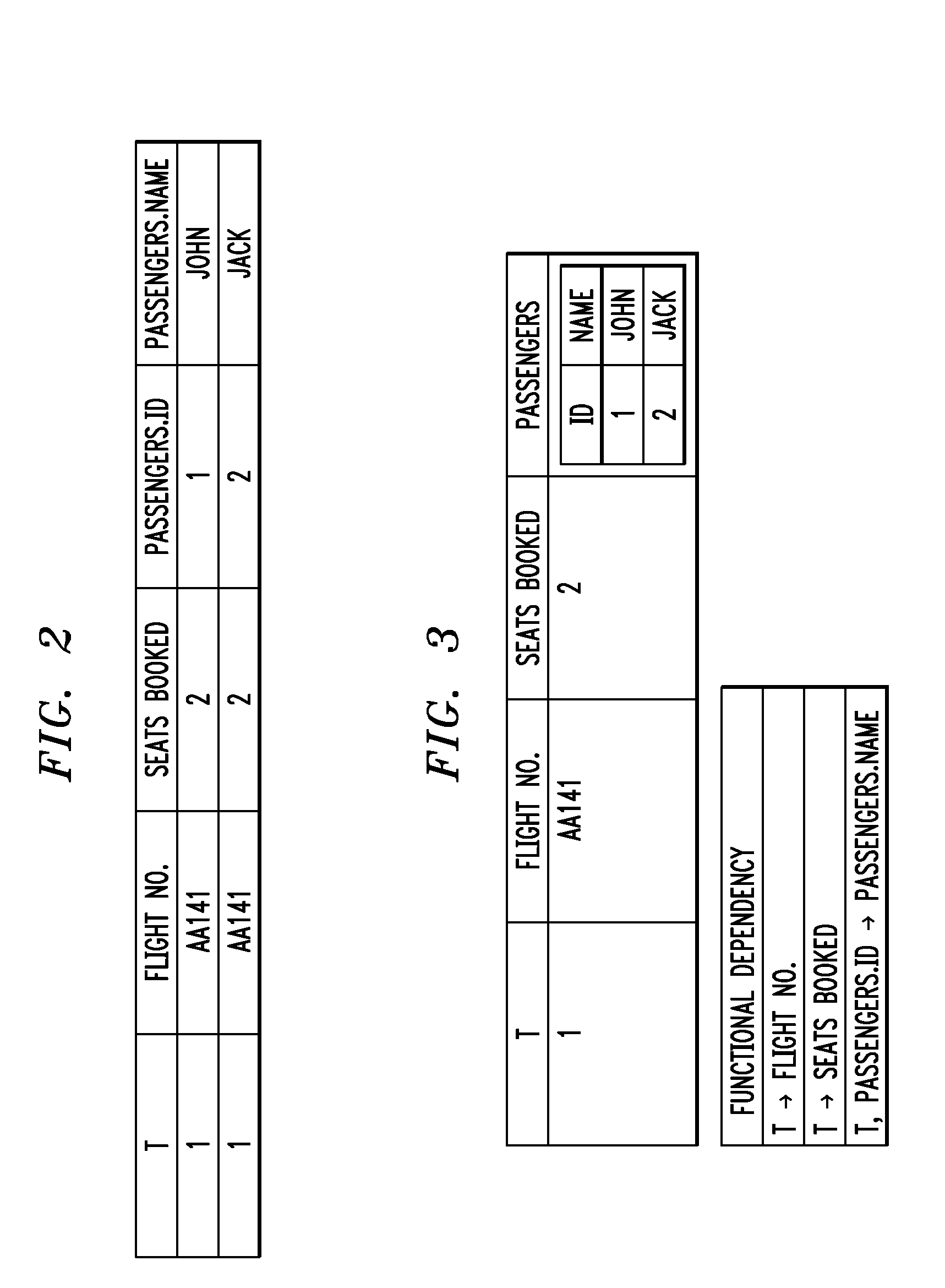
Methods and apparatus for integrating relational and hierarchical data, schema definitions, and queries in a data processing system are provided. It is determined if one or more schema definitions or one or more query expressions are provided as input to the data processing system. The one or more schema definitions are converted into an intermediate schema language component of an intermediate data language when one or more schema definitions are provided. The one or more query expressions are converted into an intermediate query language component of the intermediate data language when one or more query expressions are provided. The intermediate schema language component or the intermediate query language component is compiled in an intermediate data language processing engine into a run-time representation in accordance with a relational-hierarchical analysis.
Owner:IBM CORP
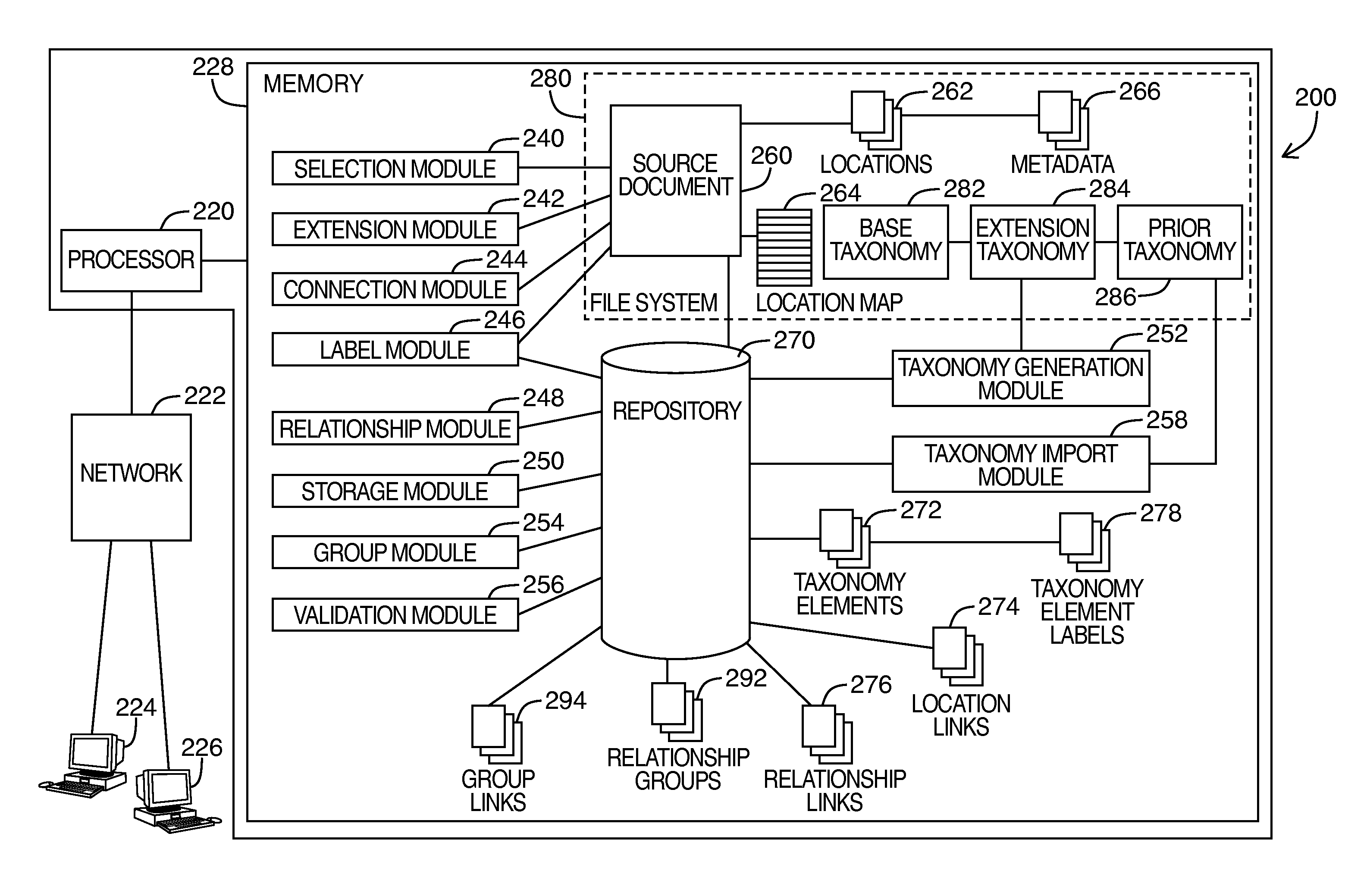
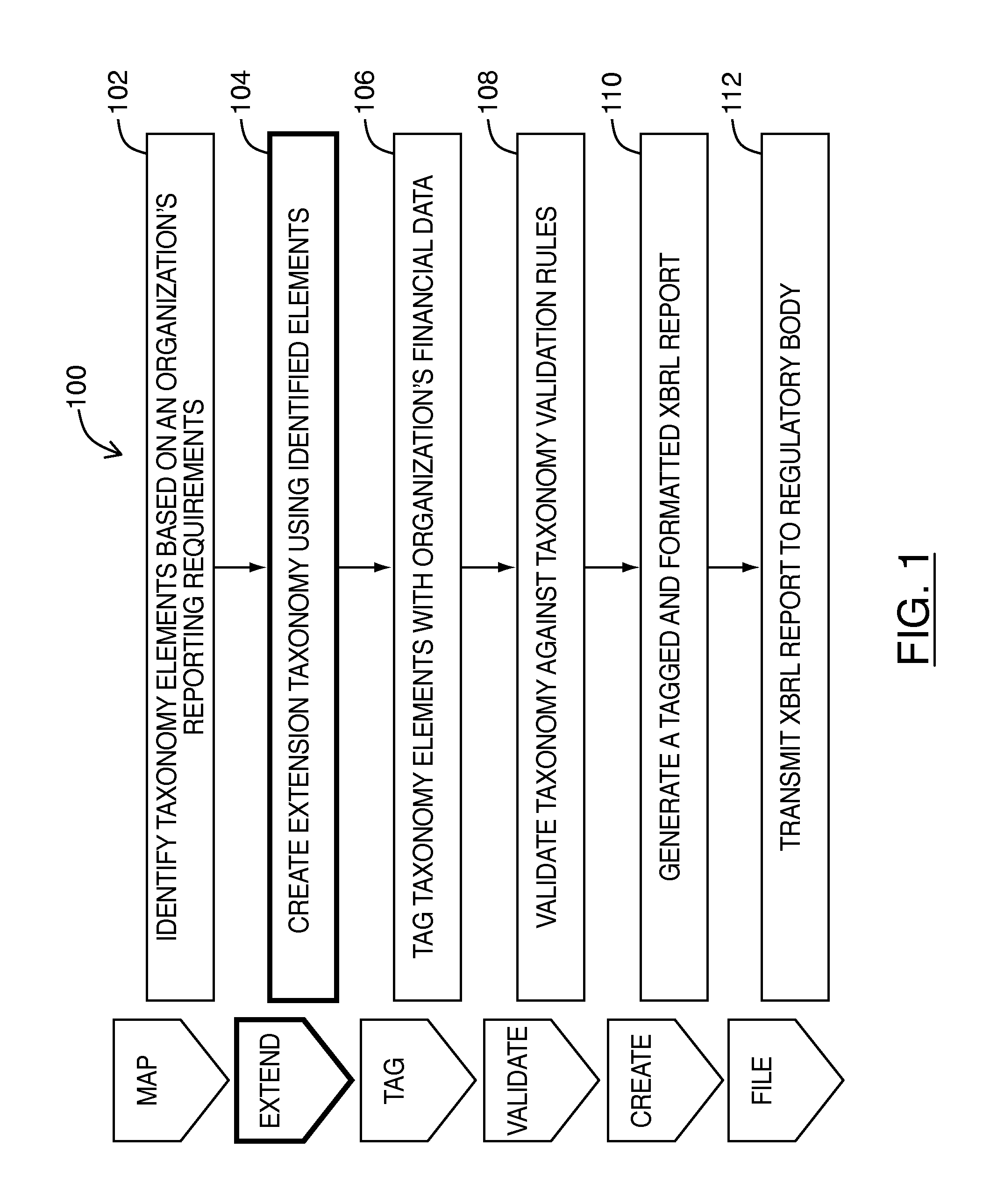
Method and system for defining an extension taxonomy
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a computer system, method implemented on a computer, and computer readable medium storing instructions for defining an extension taxonomy. The computer system comprises a processor and a memory storing instructions, the instructions being executable to configure the processor to provide a selection module operable to designate a selected portion of a source document, wherein the source document comprises a set of locations and a location map for identifying each location in the set of locations; wherein each location is configured to receive text-based content and wherein the selected portion comprises at least one location in the set of locations. The processor is also configured to provide: an extension module operable to associate a taxonomy element with a location in the selected portion; a connection module operable to define a location link between the identified taxonomy element and the location in the selected portion; and, a storage module operable to store the taxonomy element and the location link in a repository.
Owner:IBM CORP
Dynamic object type for information management and real time graphic collaboration
The creation and management of a new dynamic object format referred to as an Information Graphic Object (IGO). The IGO enables intuitive capturing, managing and sharing of dynamic content. These objects may be created manually using a conventional mouse, or automatically using an "Automatic Scan Manager (ASM) Engine". The ASM includes an Article Recognition Engine" (ARE(TM)) for capturing actual articles, with multiple formats, from a plurality of content sources simultaneously. These articles are converted into IGO and can be subsequently manipulated, managed and shared with other users. The IGO are dynamic objects that can be sent to other users using the Player 2 Player (PL2PL) capabilities of the system. These capabilities furthermore enable graphic chatting in real time. The IGO can also be stored with their live properties, whereupon extraction of an IGO from an IGO gallery activates the live properties.
Owner:INFODRAW
Describing documents and expressing document structure
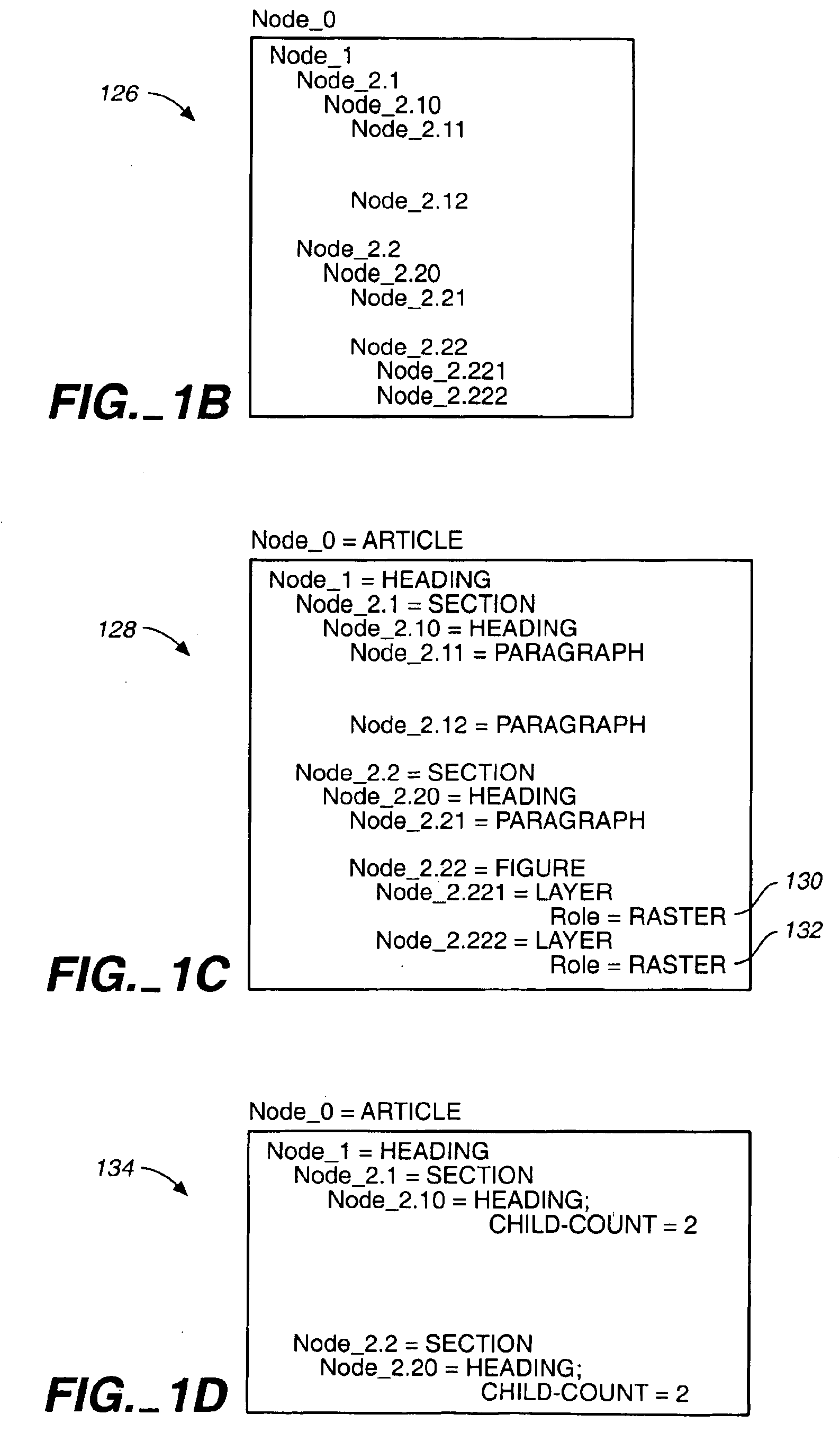
InactiveUS6993527B1Certain in operationSmall sizeData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsSemantic representationCharacteristic type
Apparatus and methods of revealing the hierarchical structure of a document having content of a characteristic type of content are described (100). The hierarchical structure may be expressed, independently of document content type, as a tree structure of one or more nodes (126) A semantic representation for interpreting the tree structure may also be provided, document description files are used to encapsulate structural and meta information associated with a document stored on a computer-readable medium (156). Document description files are external to native application files and have a set of required fields. Document description files point to the referenced document data using uniform resource locators (URLS) and serve as virtual documents. In addition to the required fields, applications can choose to encode additional structural information in the document description files.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com