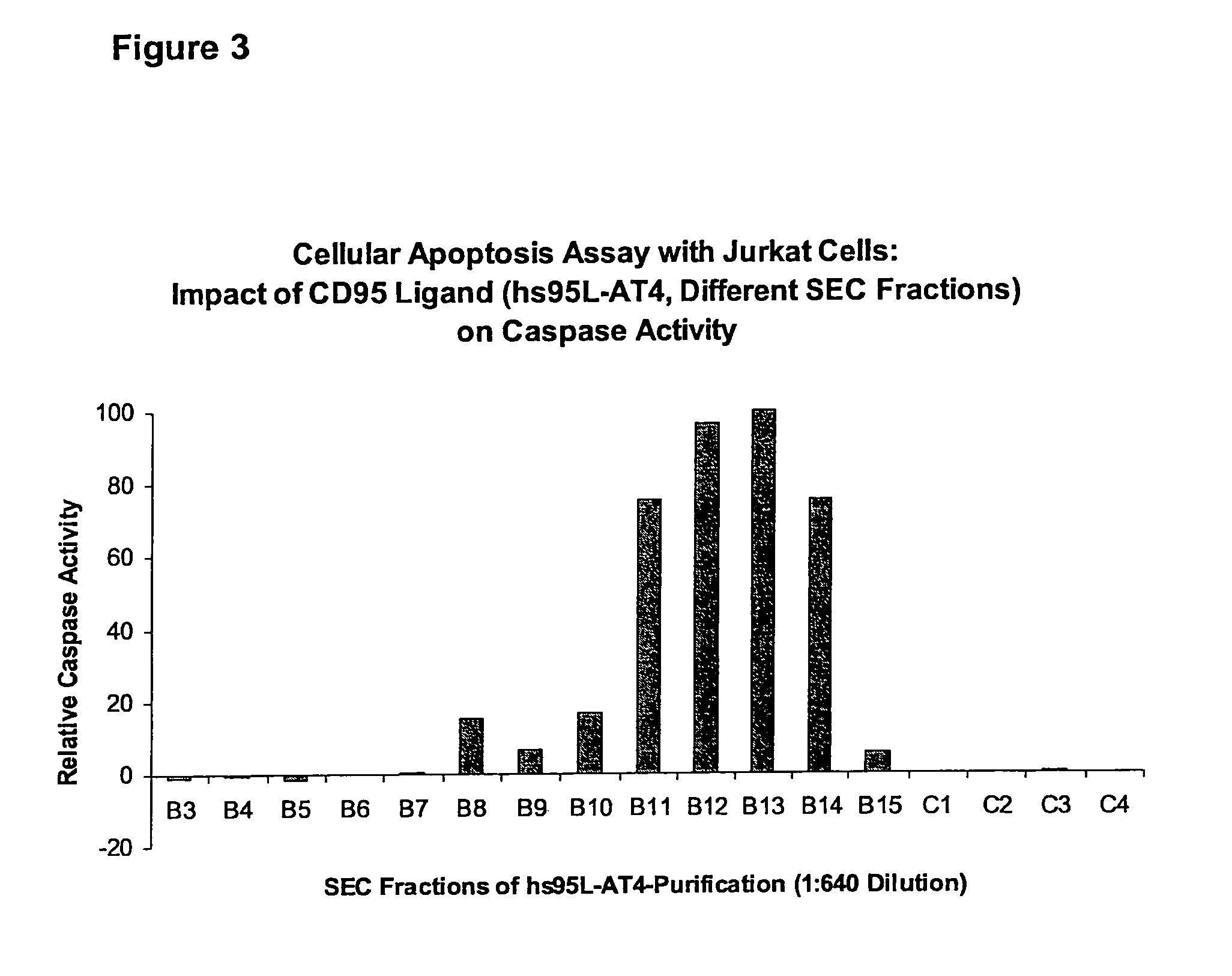
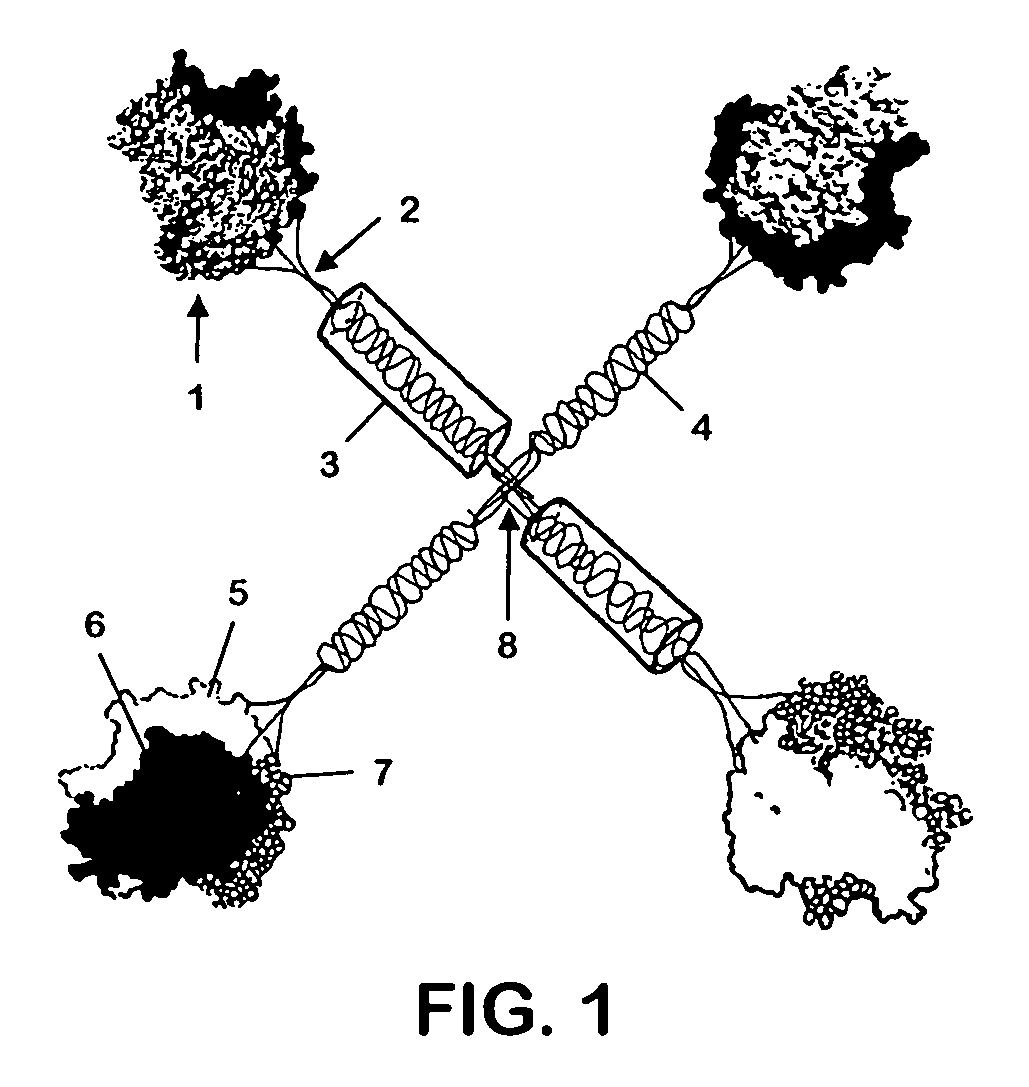
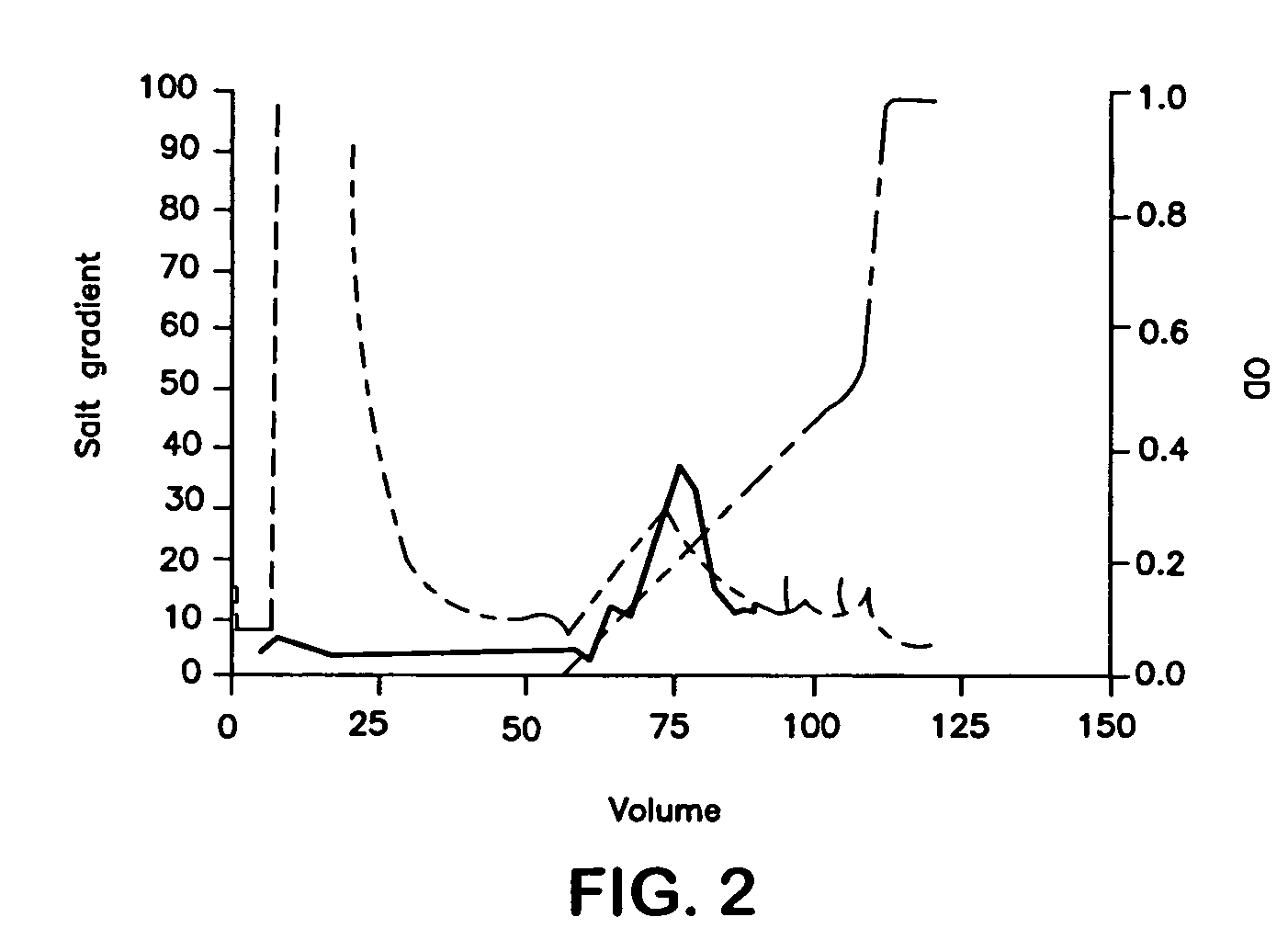
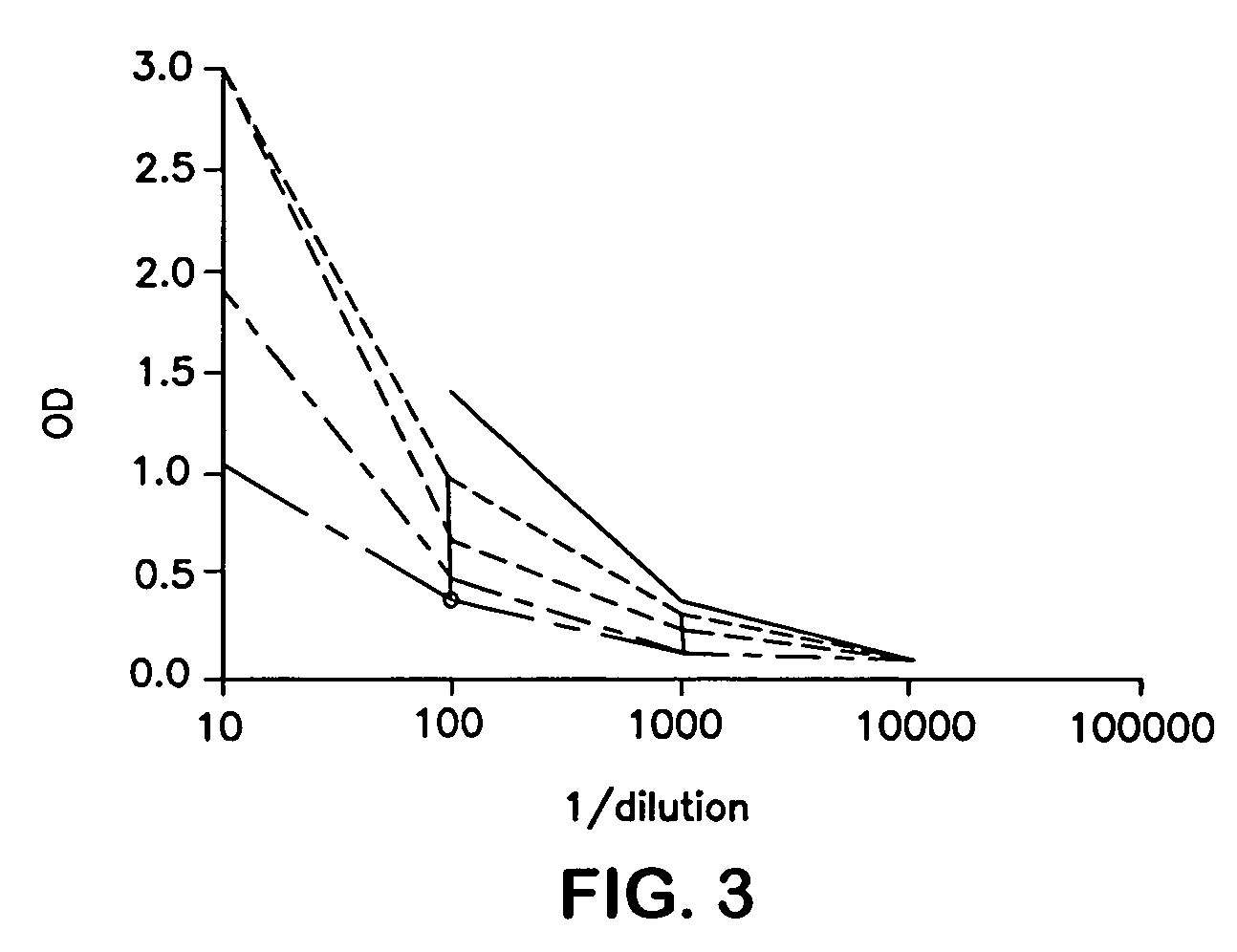
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Tnf superfamily" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The tumor necrosis factor ( TNF) superfamily is a protein superfamily of type II transmembrane proteins containing TNF homology domain and forming trimers. Members of this superfamily can be released from the cell membrane by extracellular proteolytic cleavage and function as a cytokine.
Single-chain TNFSF fusion polypeptides
Owner:APOGENIX AG
Splice switch oligomers for TNF superfamily receptors and their use in treatment of disease
InactiveUS20070105807A1High expressionReduce expressionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSplice switchingPrecursor mRNA
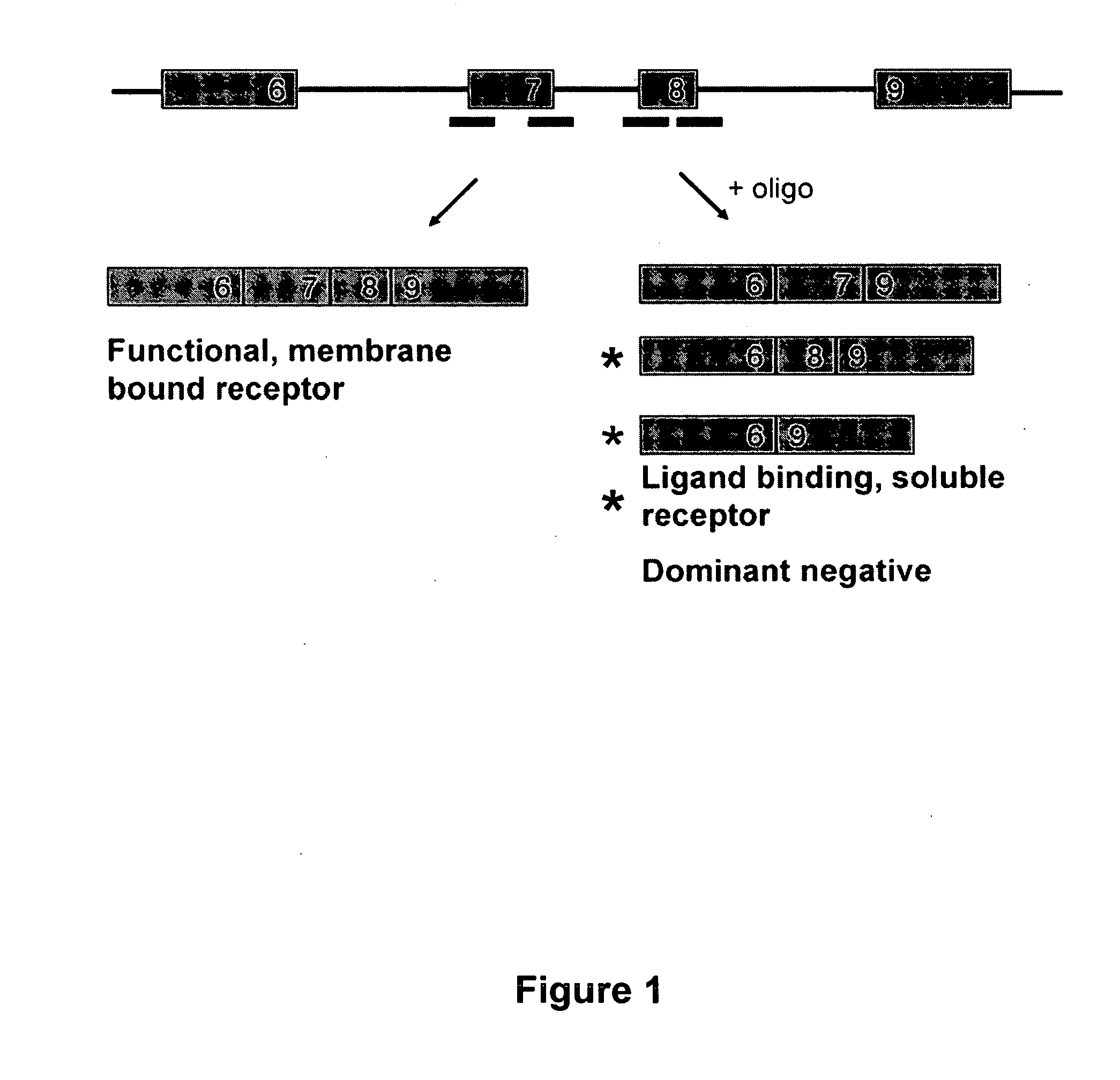
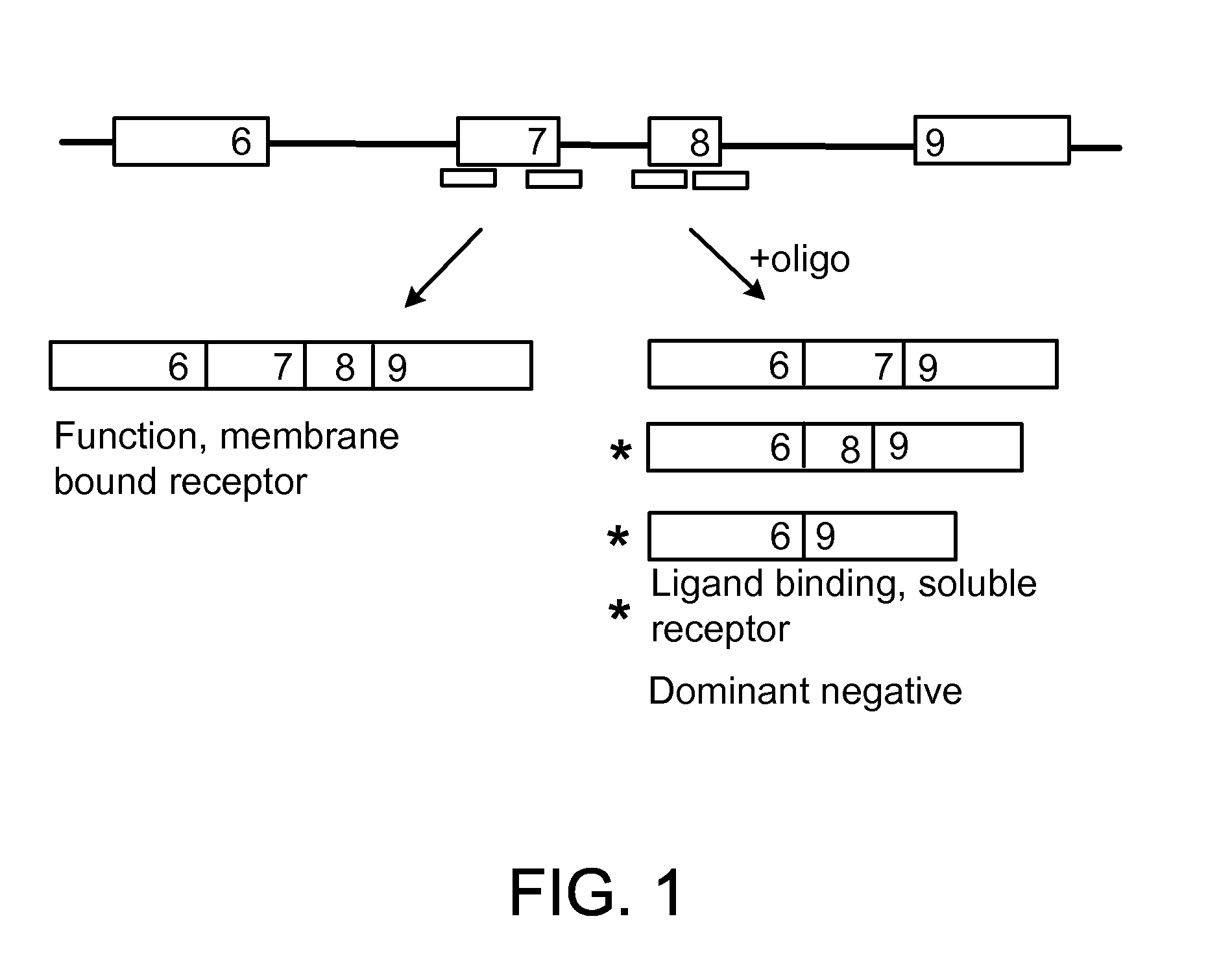
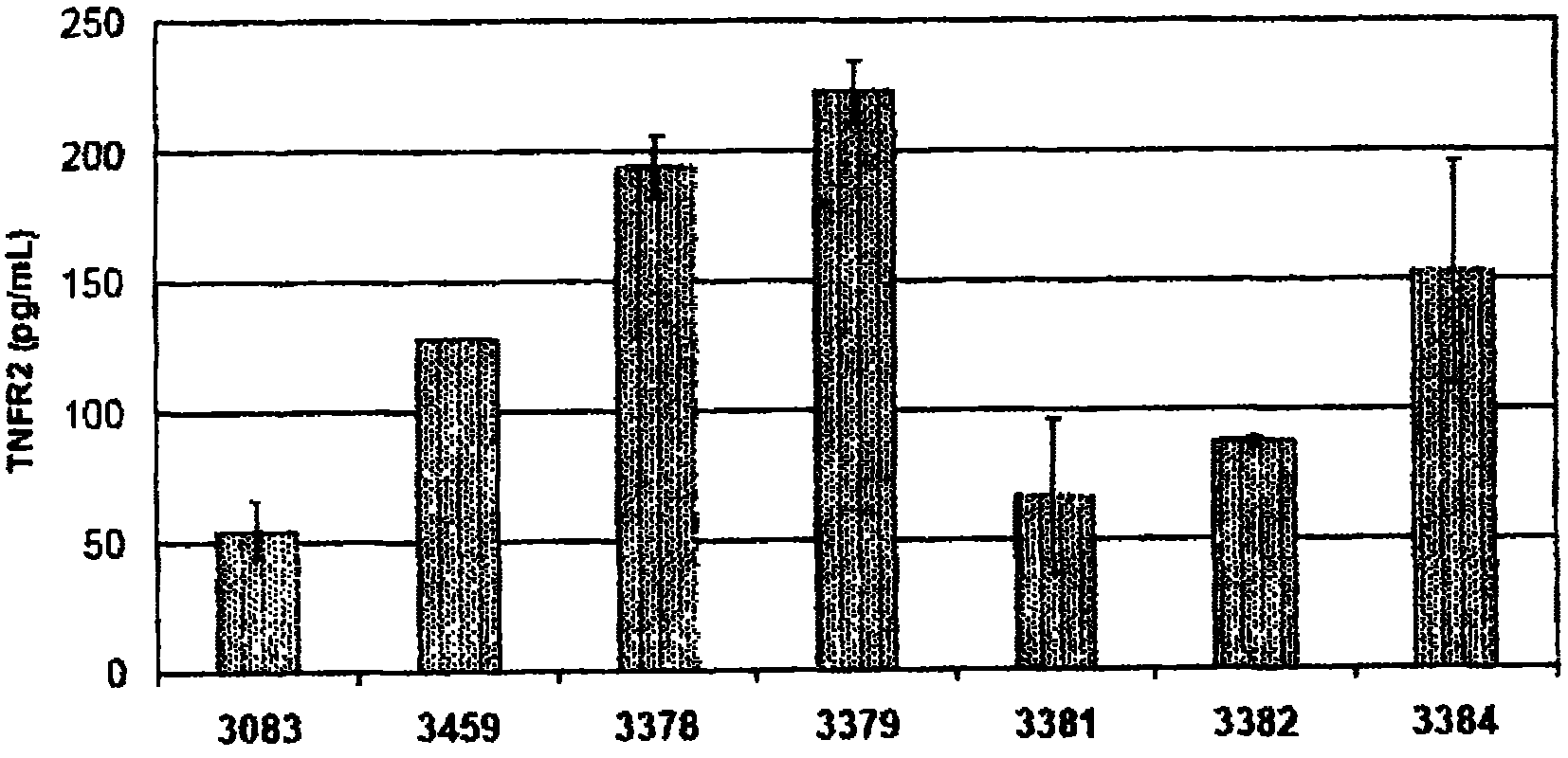
Methods and compositions are disclosed for controlling expression of TNF receptors (TNFR1 and TNFR2) and of other receptors in the TNFR superfamily using compounds that modulate splicing of pre-mRNA encoding these receptors. More specifically these compounds cause the removal of the transmembrane domains of these receptors and produce soluble forms of the receptor which act as an antagonist to reduce TNF-α activity or activity of the relevant ligand. Reducing TNF-α activity provides a method of treating or ameliorating inflammatory diseases or conditions associated with TNF-α activity. Similarly, diseases associated with other ligands can be treated in like manner. In particular, the compounds of the invention are splice-splice switching oligomers (SSOs) which are small molecules that are stable in vivo, hybridize to the RNA in a sequence specific manner and, in conjunction with their target, are not degraded by RNAse H.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS +3
TNF superfamily fusion proteins
The present invention refers to fusion proteins comprising a TNF superfamily (TNFSF) cytokine or a receptor binding domain thereof fused to a trimerization domain and a nucleic acid molecule encoding the fusion protein. The fusion protein is present as a trimeric complex or as an oligomer thereof and is suitable for therapeutic, diagnostic and / or research applications.
Owner:APOGENIX AG
Splice Switching Oligomers for TNF Superfamily Receptors and their Use in Treatment of Disease
InactiveUS20090264353A1Reduce the amount requiredVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseSplice switching
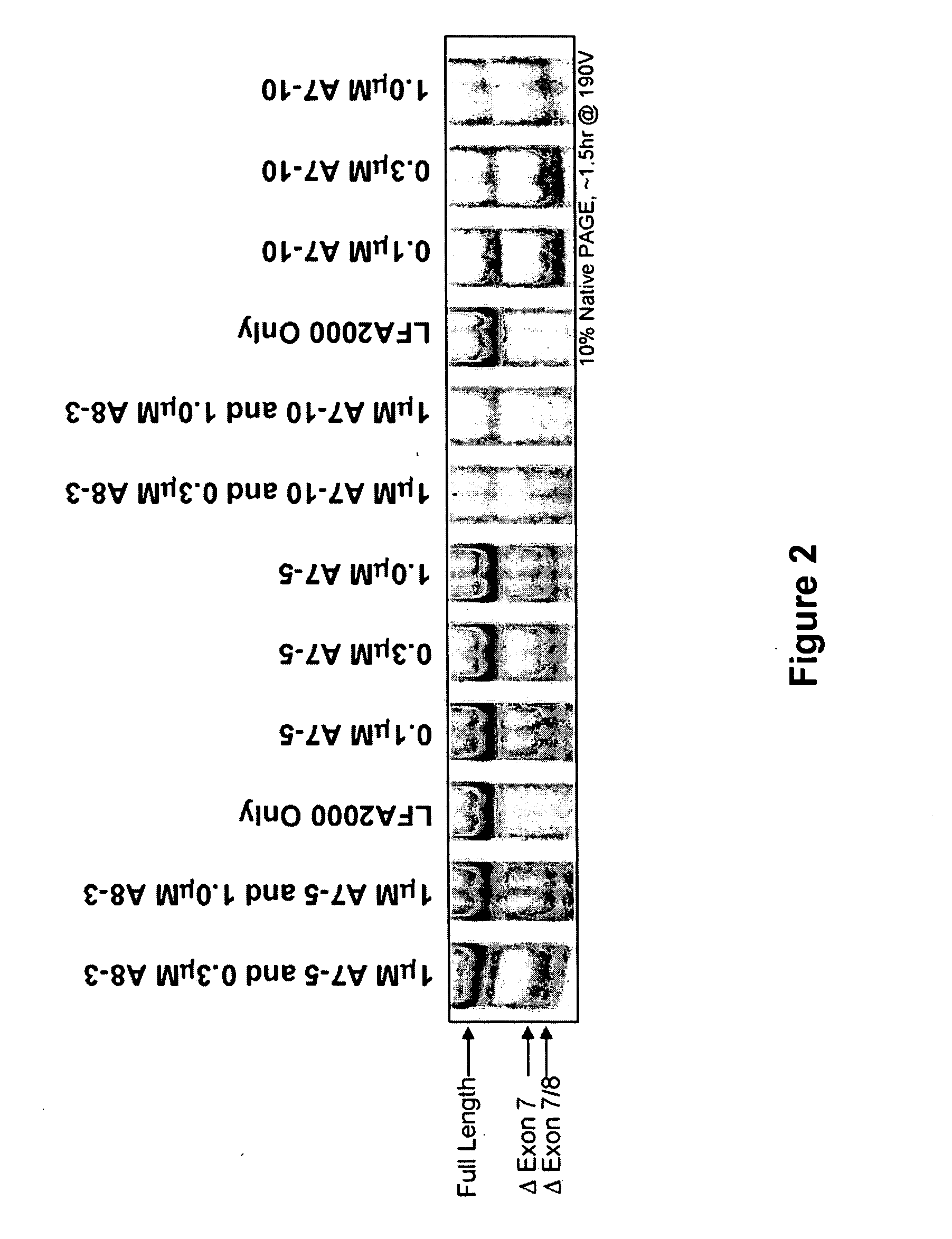
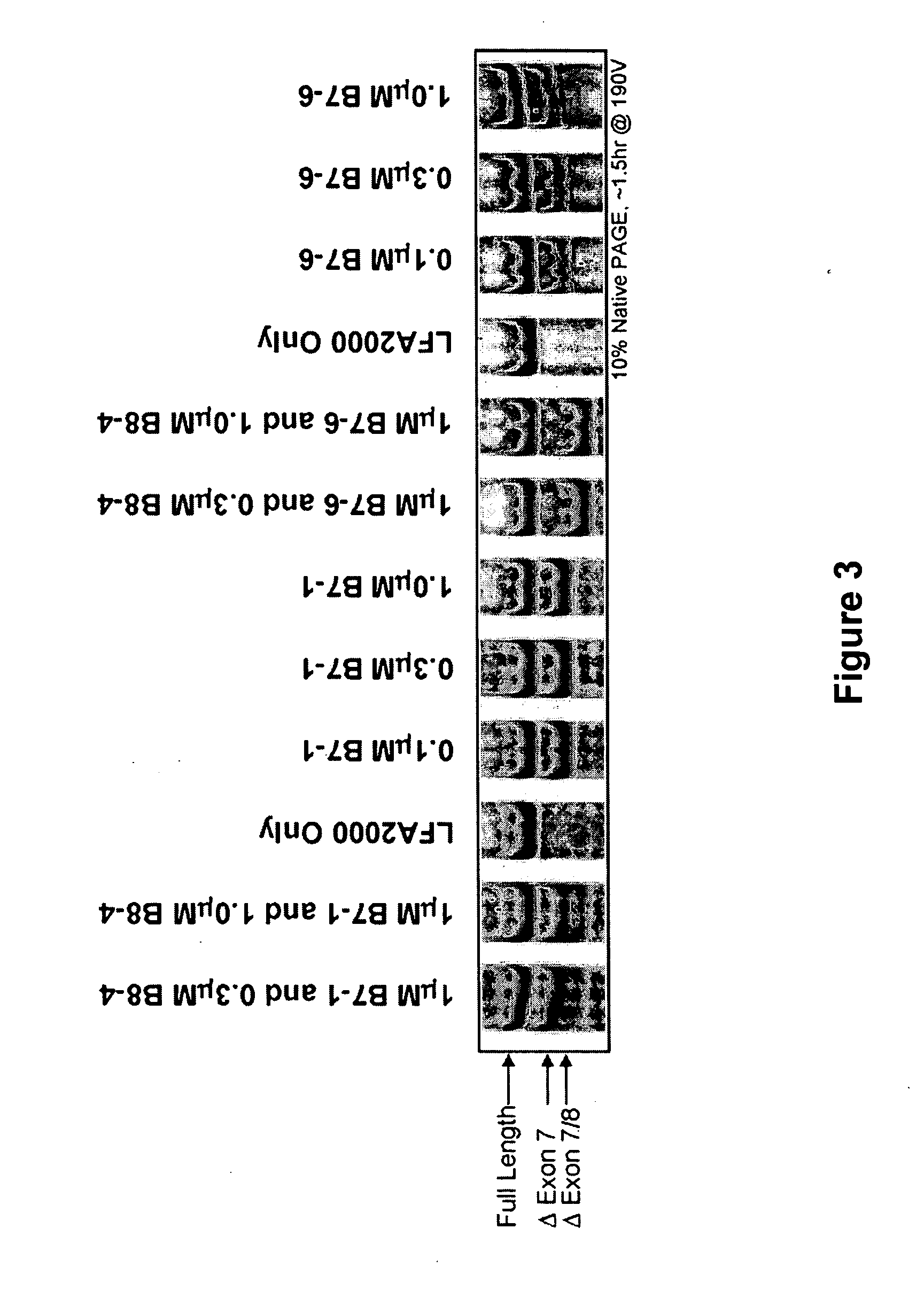
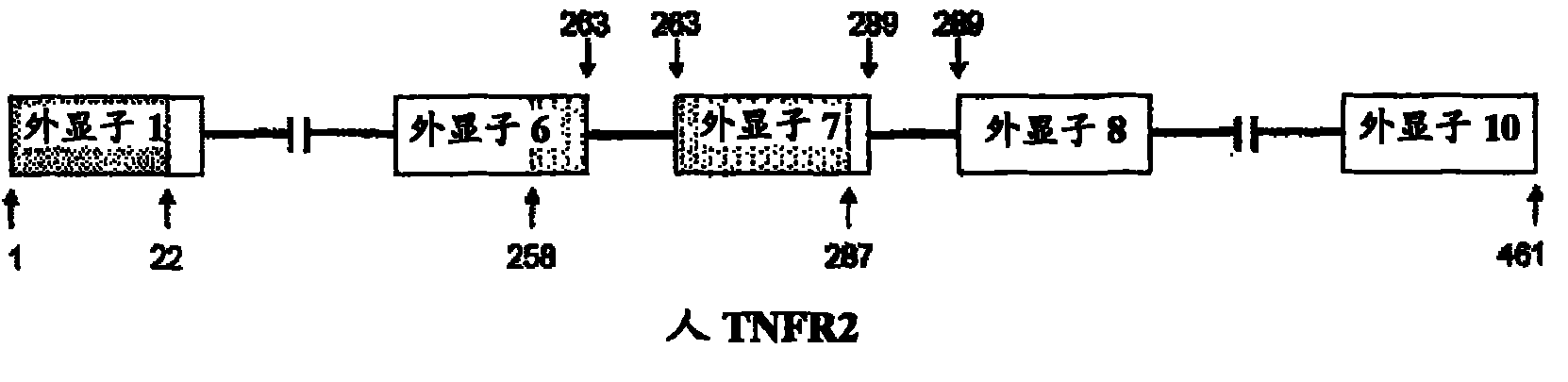
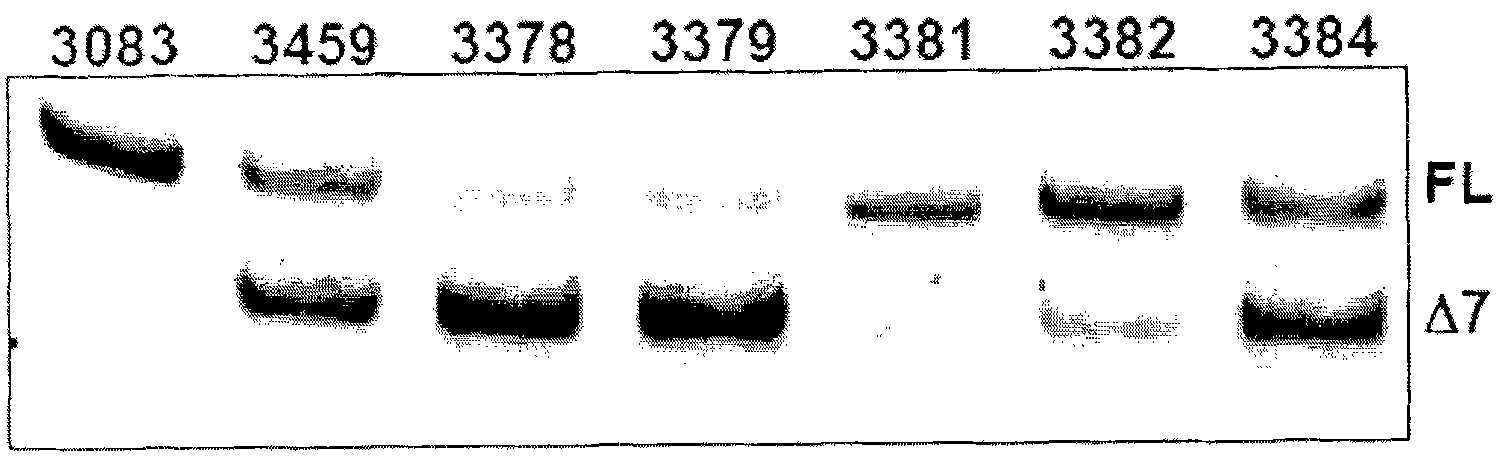
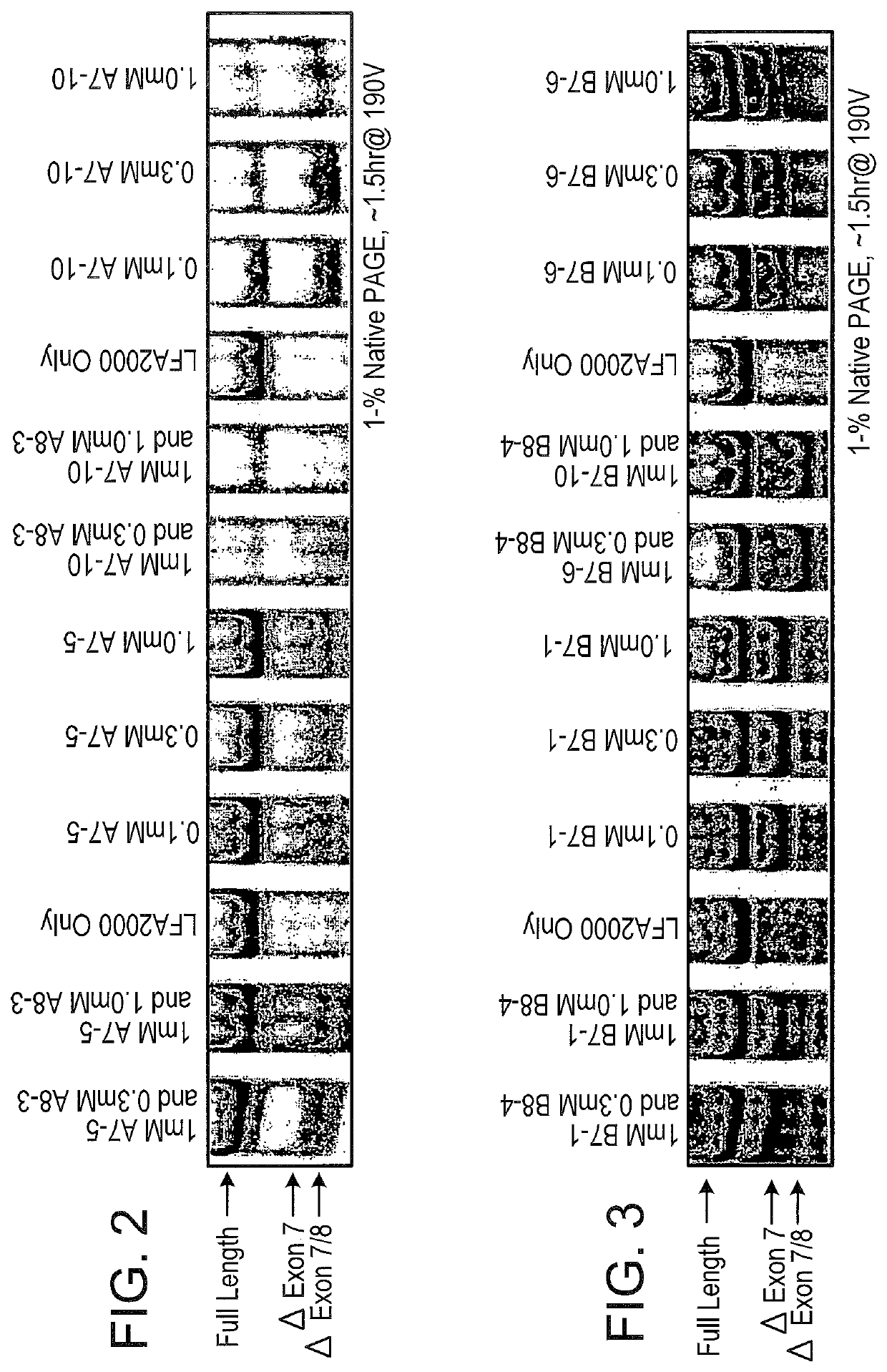
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for preparing splice variants of TNFalpha receptor (TNFR) in vivo or in vitro, and the resulting TNFR protein variants. Such variants may be prepared by controlling the splicing of pre-mRNA molecules and regulating protein expression with splice switching oligonucleotides or splice switching oligomers (SSOs). The preferred SSOs according to the invention target exon 7 or 8 of TNFR1 (TNFRSF1A) or TNFR2 (TNFRSF1A) pre-mRNA, typically resulting in the production of TNFR variants which comprise a deletion in part or the entire exon 7 or 8 respectfully. SSOs targeting exon 7 are found to result in a soluble form of the TNFR, which has therapeutic benefit for treatment of inflammatory diseases. The SSO's are characterized in that they are substantially incapable or incapable of recruiting RNaseH.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS +1
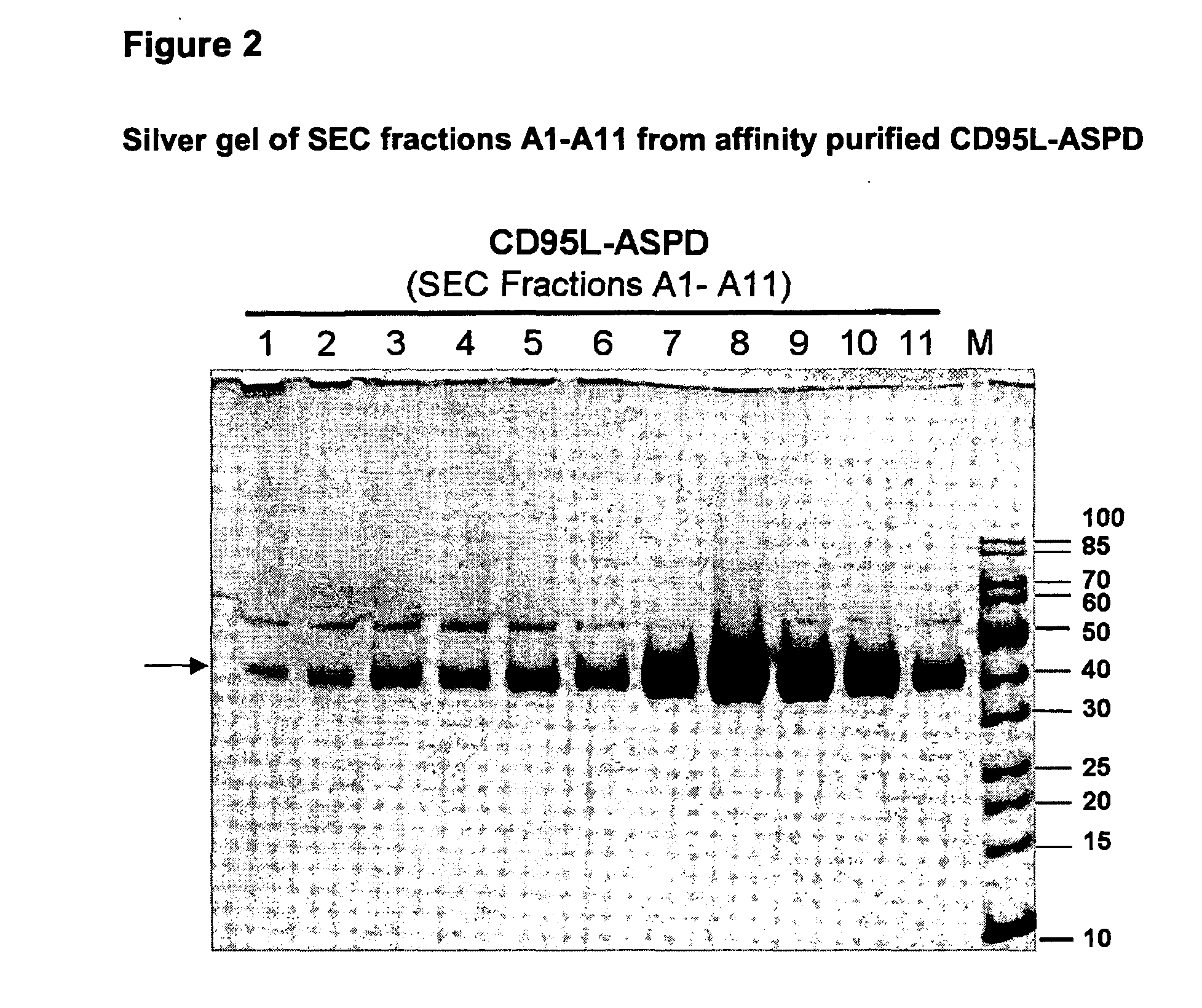
CD95L or trail fusion proteins
The present invention refers to fusion proteins comprising a TNF superfamily (TNFSF) cytokine or a receptor binding domain thereof fused to a trimerization domain and a nucleic acid molecule encoding the fusion protein. The fusion protein is present as a trimeric complex or as an oligomer thereof and is suitable for therapeutic, diagnostic and / or research applications.
Owner:APOGENIX AG
Multimeric fusion proteins of the TNF superfamily ligands
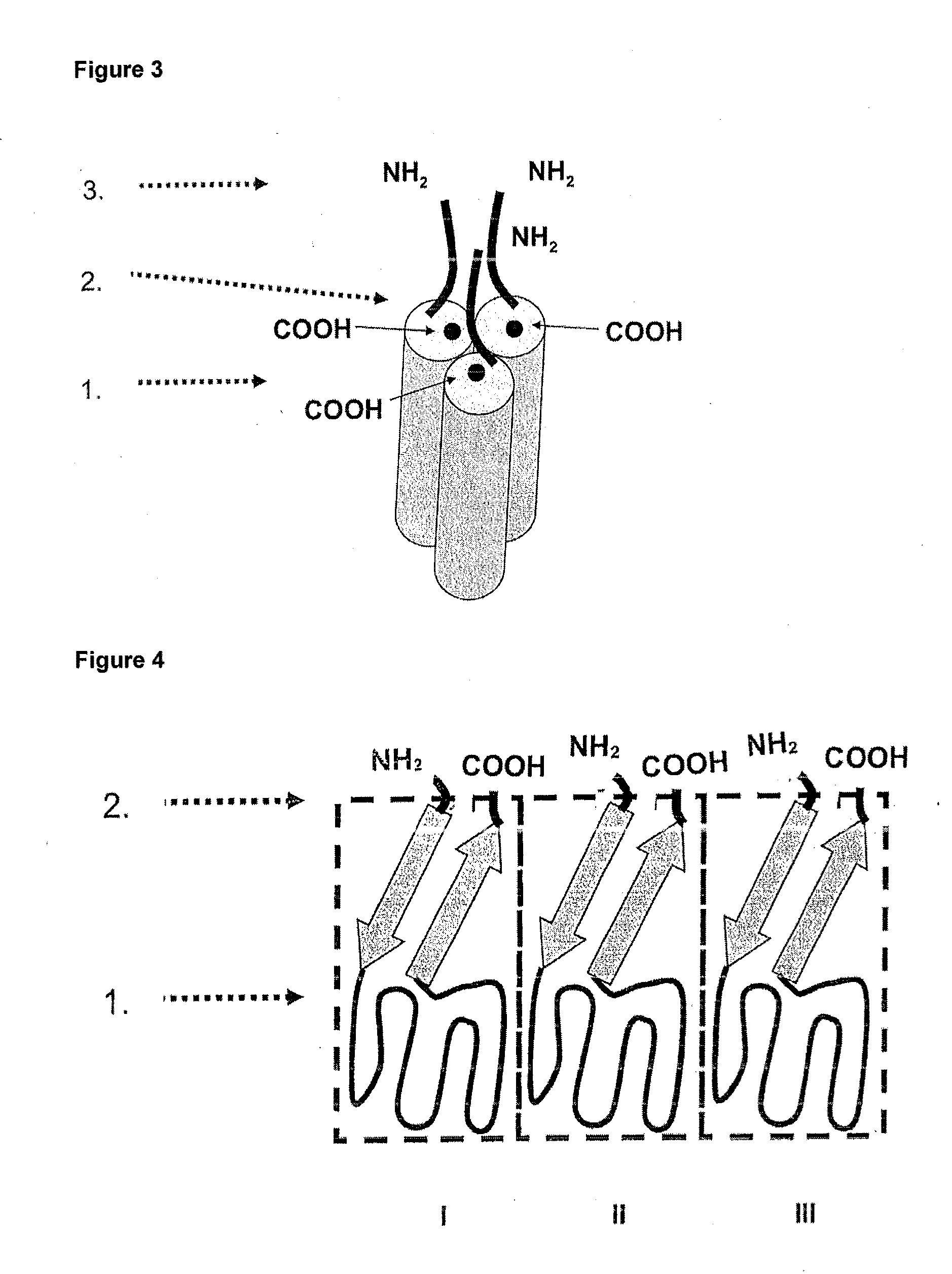
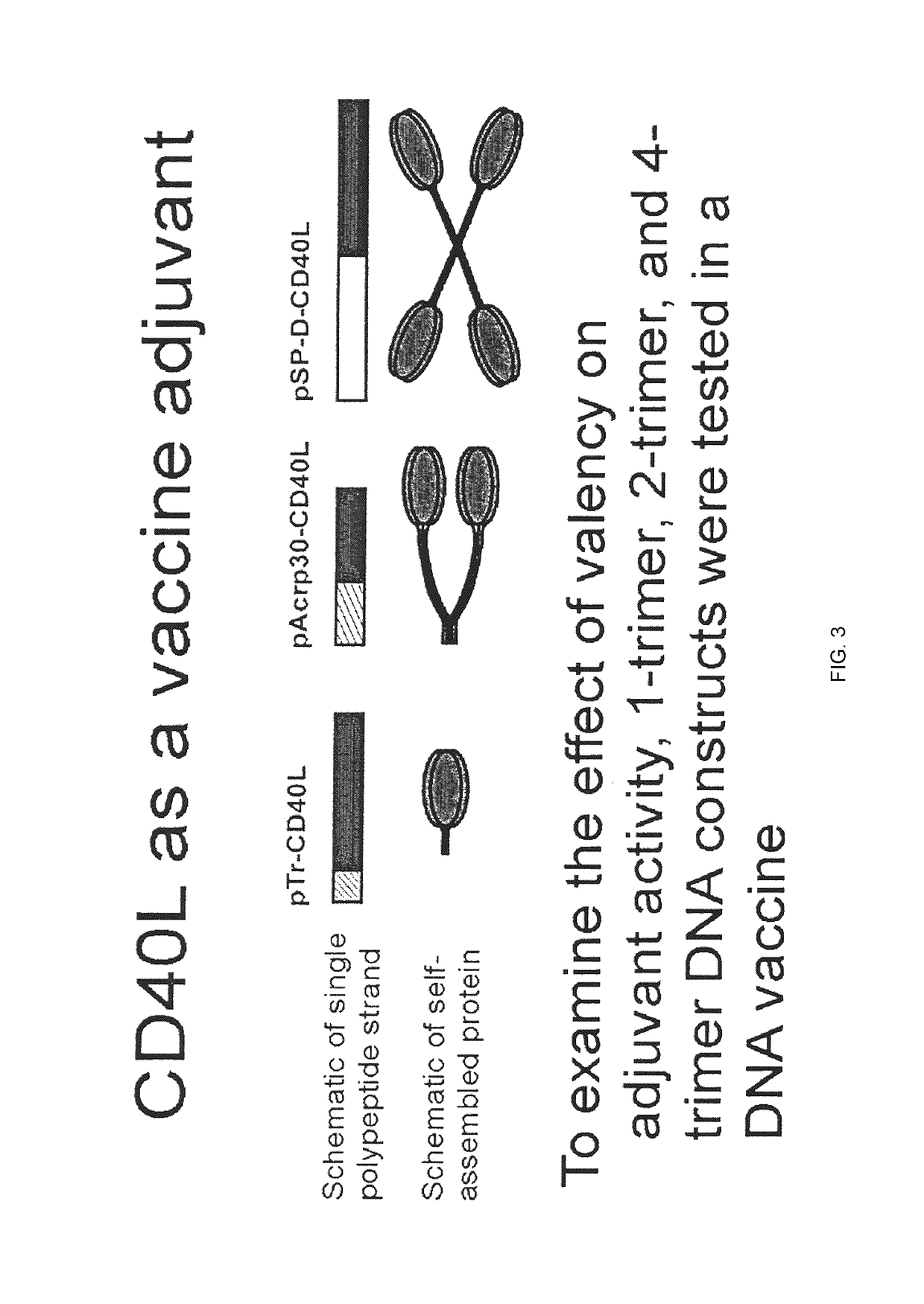
A method for constructing stable bioactive fusion proteins of the difficult to express tumor necrosis factor superfamily (TNFSF), and particularly members CD40L (CD154) and RANKL / TRANCE, with collecting, particularly pulmonary surfactant protein D (SPD) is described. Single trimers of these proteins lack the full stimulatory efficacy of the natural membrane forms of these proteins in many cases. The multimeric nature of these soluble fusion proteins enables them to engage multiple receptors on the responding cells, thereby, mimicking the effects of the membrane forms of these ligands. For CD40L-SPD, the resulting protein stimulates B cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells, indicating its potential usefulness as a vaccine adjuvant. The large size of these fusion proteins makes them less likely to diffuse into the circulation, thereby limiting their potential systemic toxicity. This property may be especially useful when these proteins are injected locally as a vaccine adjuvant or tumor immunotherapy agent to prevent them from diffusing away. In addition, these and other TNFSF-collectin fusion proteins present new possibilities for the expression of highly active, multimeric, soluble TNFSF members.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
TNF superfamily trimerization inhibitors
InactiveUS20140165223A1Inhibits osteoclast formationDecreasing bone lossOrganic active ingredientsBacteriaRANKL ProteinDisease
Described are methods and compositions for inhibiting the trimerization of ligands belonging to the TNF superfamily, in particular, inhibiting RANKL trimerization. Accordingly, the methods and compositions provided herein can be used to treat disorders associated with increased RANK signaling, in particular those related to bone loss. Compounds that inhibit trimerization of ligands belonging to the TNF superfamily are also described.
Owner:B S R C ALEXANDER FLEMING
TNFSF Single Chain Molecules
The present invention refers to single-chain fusion proteins comprising three soluble TNF superfamily (TNFSF) cytokine domains and nucleic acid molecules encoding these fusion proteins. The fusion proteins are substantially non-aggregating and suitable for therapeutic, diagnostic and / or research applications.
Owner:APOGENIX AG
TNF superfamily collectin fusion proteins
The present invention refers to a fusion protein comprising a TNF-superfamily (TNFSF) cytokine or a receptor binding domain thereof fused to a collectin trimerization domain, to a nucleic acid molecule encoding the fusion protein, and to a cell comprising the nucleic acid molecule. The fusion protein is present as a trimeric complex or as an oligomer thereof. The fusion protein, the nucleic acid, and the cell is suitable as pharmaceutical composition or for therapeutic, diagnostic and / or research applications.
Owner:APOGENIX AG
Humanized antibodies against TL1A
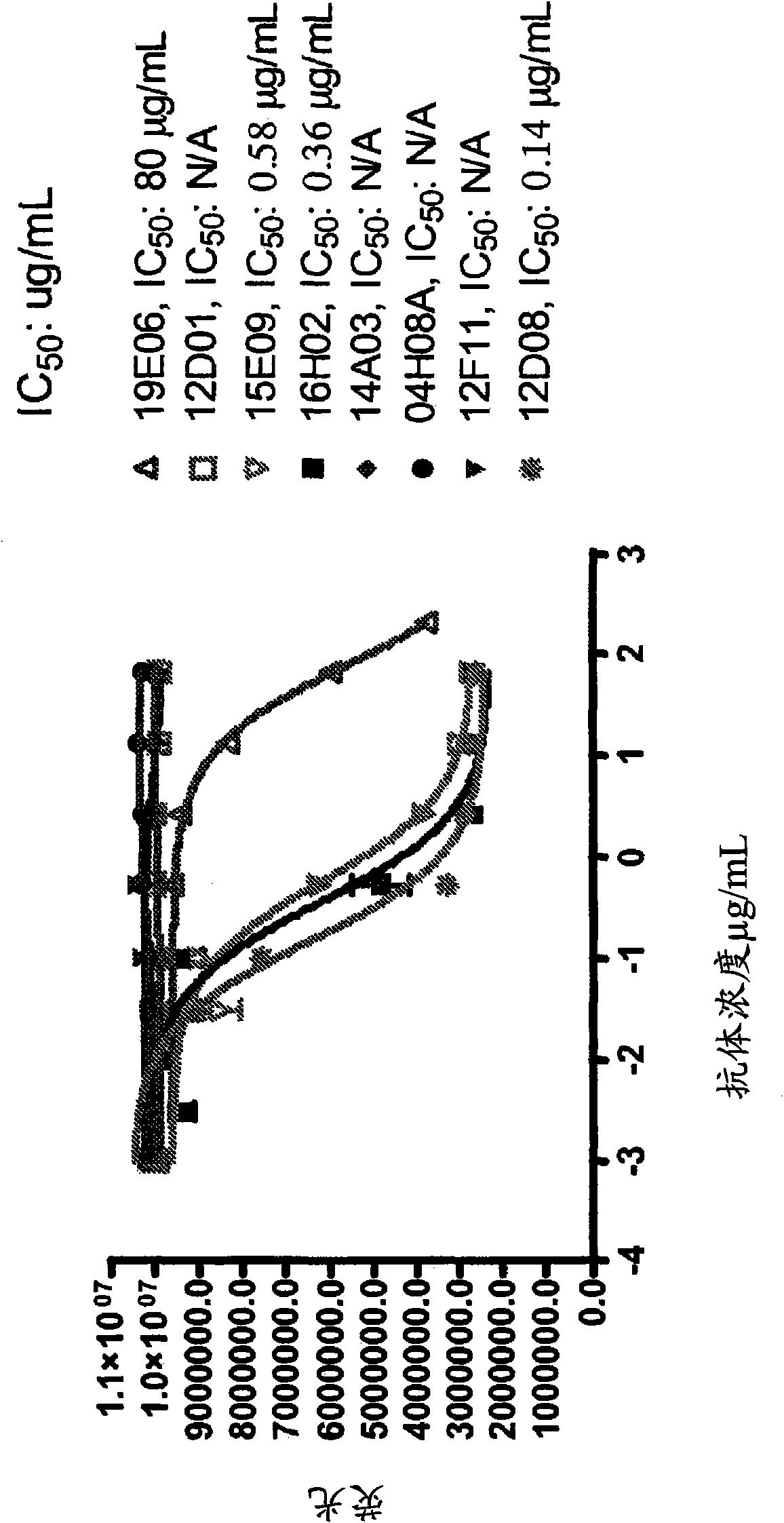
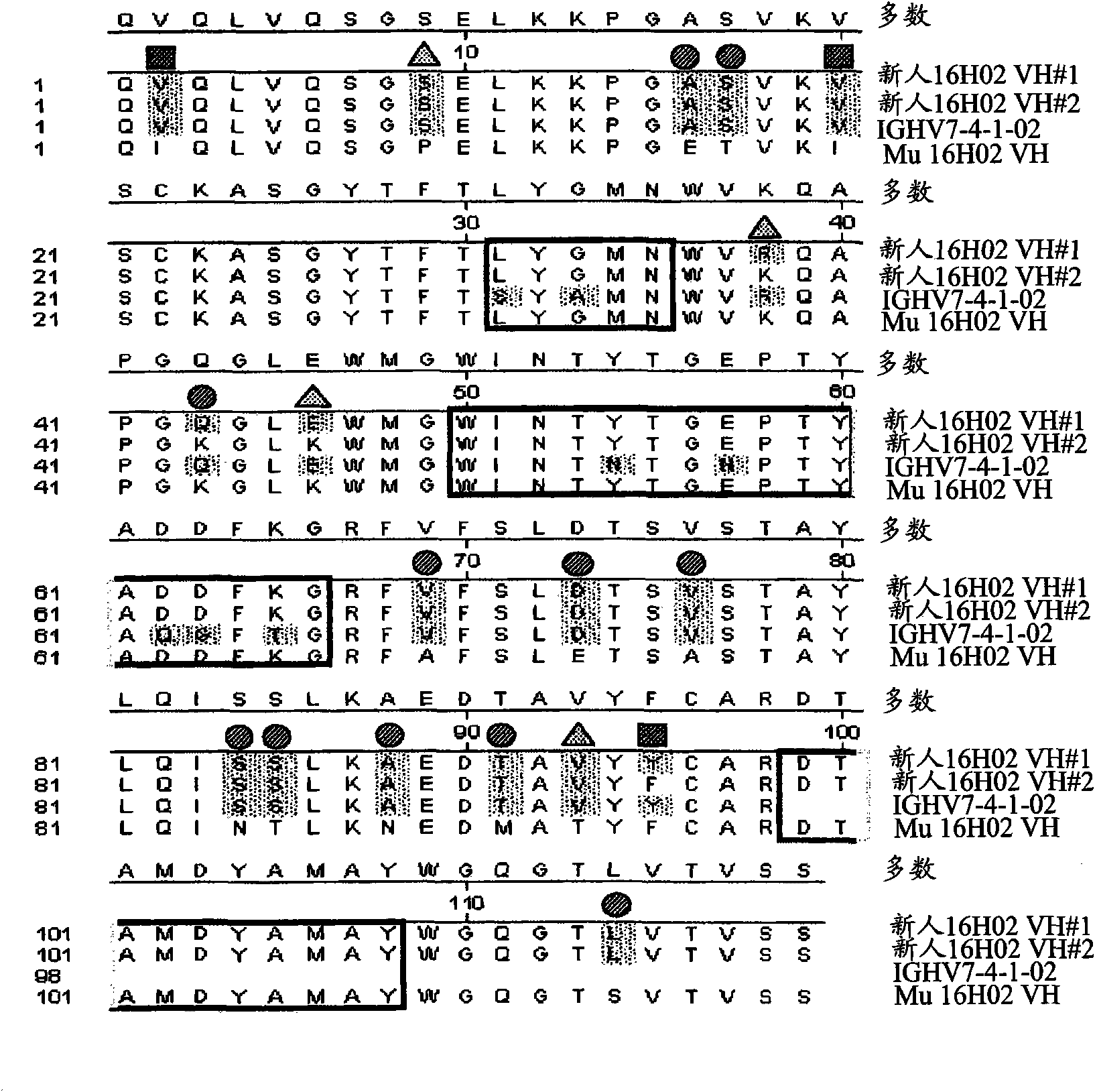
Disclosed are humanized antibodies that bind specifically to TNF superfamily member 15 (TNFSF 15), also known as TLlA. Methods of making and using the anti-TLl A antibodies are also described. The humanized antibodies may be antagonists and may used to treat or diagnose conditions associated with TLlA function.
Owner:TEVA BIOPHARM USA
Medical Uses of Carrier Conjugates of Non-Human Tnf -Peptides
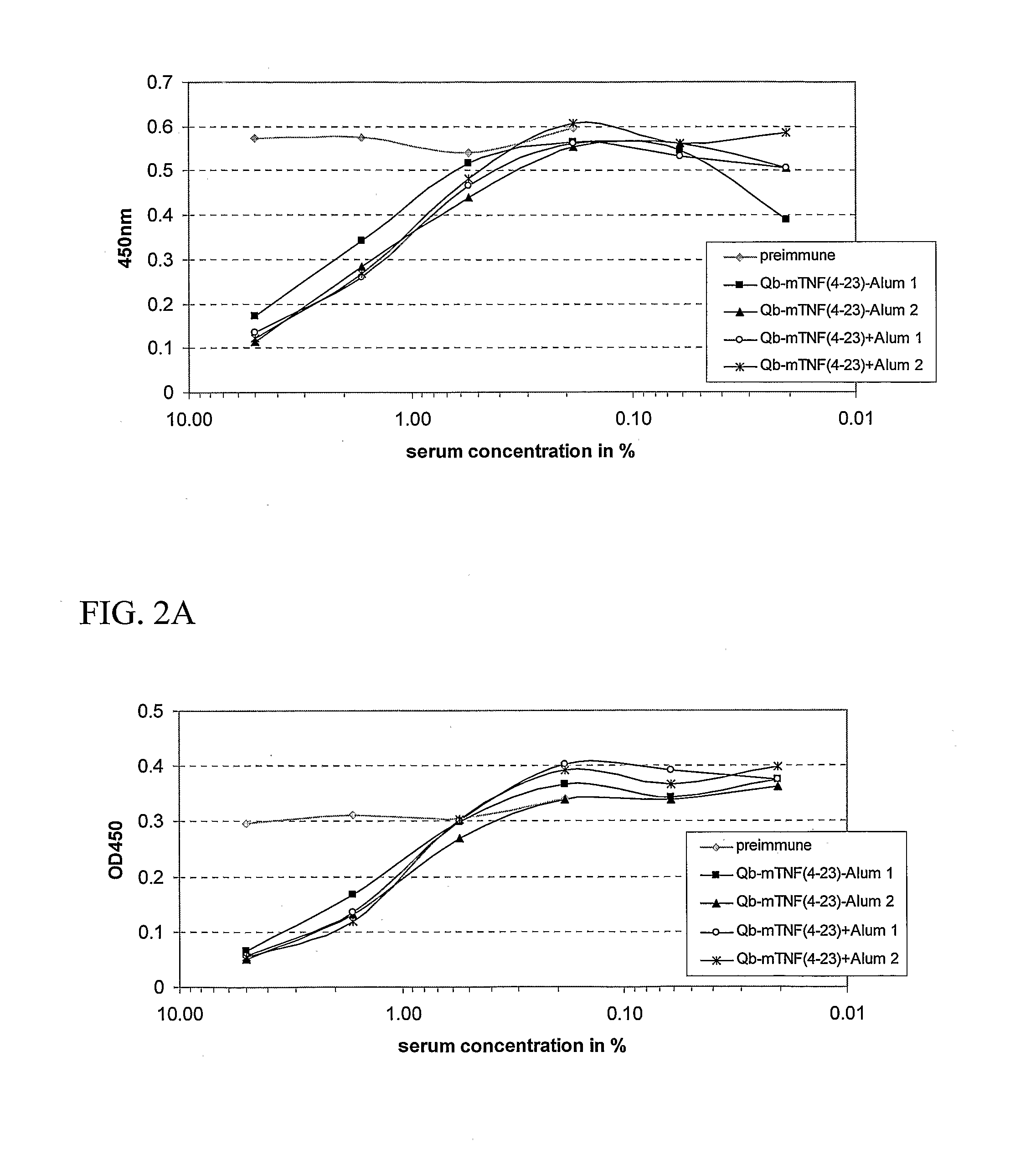
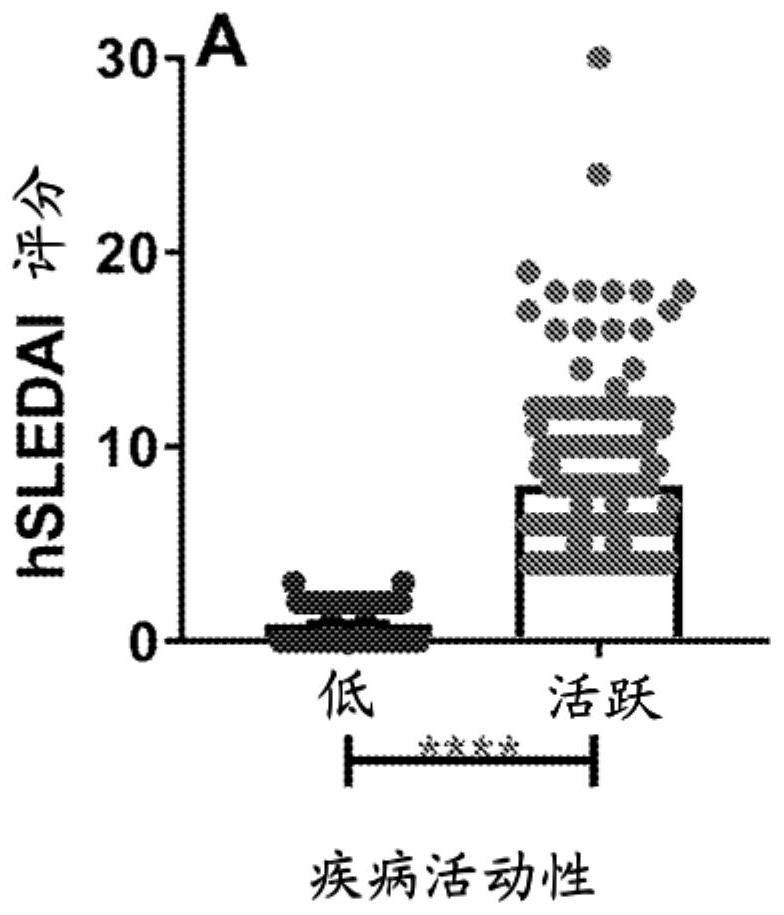
InactiveUS20070248617A1Good skin permeabilityEnhance antigen absorptionNervous disorderAntipyreticAutoimmune conditionVirus-like particle
The present invention is related to the fields of molecular biology, virology, immunology and medicine. The invention provides a modified virus-like particle (VLP) comprising—a VLP and a particular peptide derived from a polypeptide from the TNF-superfamily linked thereto for use in the production of vaccines for the treatment of autoimmune diseases and bone-related diseases and to efficiently induce immune responses, in particular antibody responses. Furthermore, the compositions of the invention are particularly useful to efficiently induce self-specific immune responses within the indicated context.
Owner:CYTOS BIOTECHNOLOGY AG
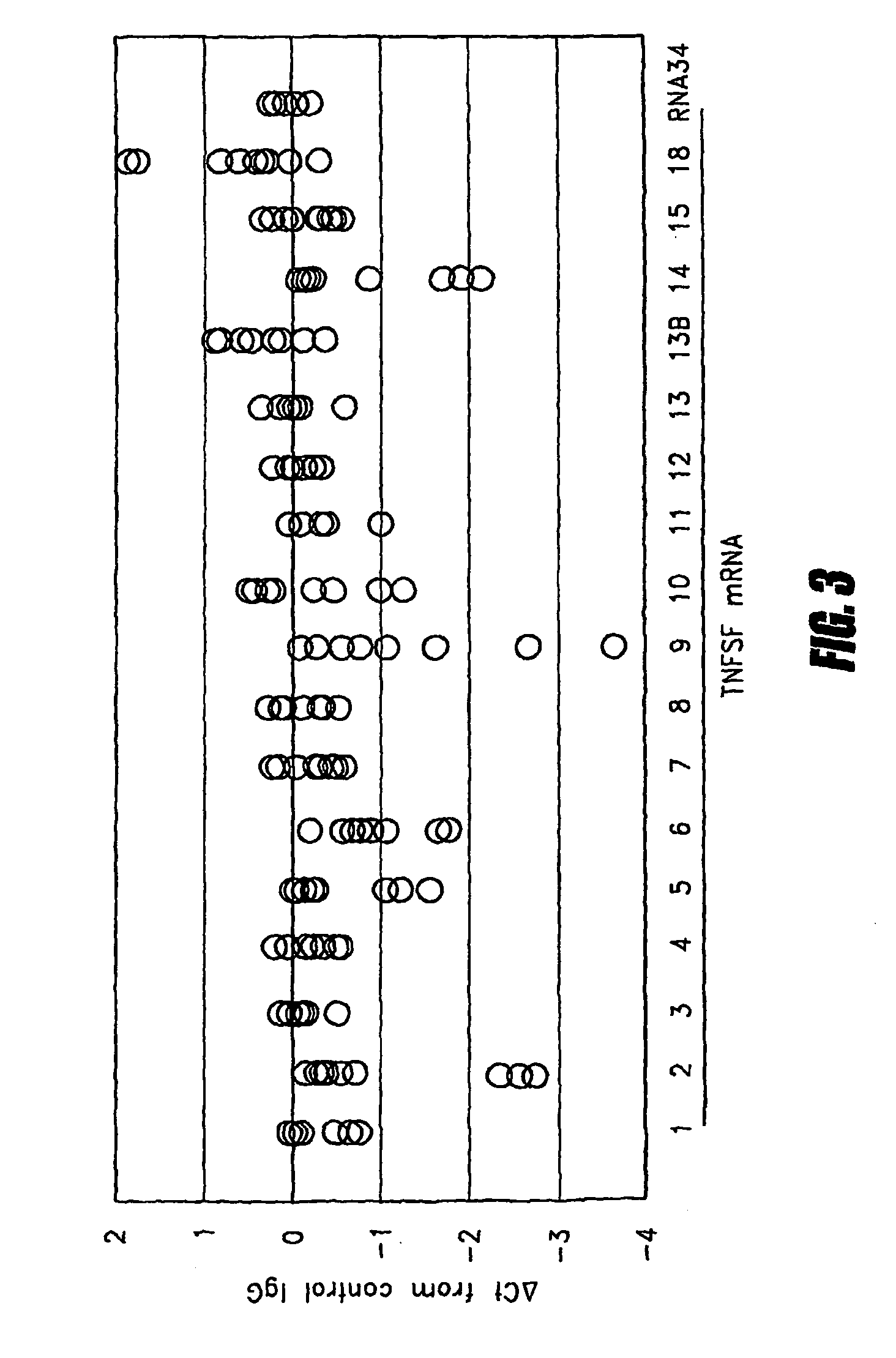
Method for predicting immune response to neoplastic disease based on mRNA expression profile in neoplastic cells and stimulated leukocytes
InactiveUS7741023B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingAbnormal tissue growthDisease
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is capable of inducing apoptosis by interacting with specific TNF receptors on the surface of cancer cells. Because multiple members of TNF ligand and receptor are present within each superfamily, over 300 different ligand-receptor combinations exist. Activated blood leukocytes produce TNF as part of the immune response to cancer, as well as producing chemokines to attract other leukocytes to the site. A method is disclosed of detecting significant induction of a variety of TNF superfamily subtype and chemokine mRNAs in blood leukocytes when whole blood is exposed to heat-aggregated IgG or anti-T cell receptor antibodies as a model of immune system interactions. Substantial individual-to-individual variation is observed in TNF subtypes and chemokines induced. Since peripheral blood leukocytes are the supply of anti-cancer immune cells, the quantitation of ex vivo inducibility of appropriate TNF ligands and chemokines in blood will be useful in individualized cancer immunotherapy. If the tumor mass is small, such as with early invisible metastatic lesions, appropriate TNF assaults may be sufficient to prevent relapse.
Owner:RESONAC CORPORATION +1
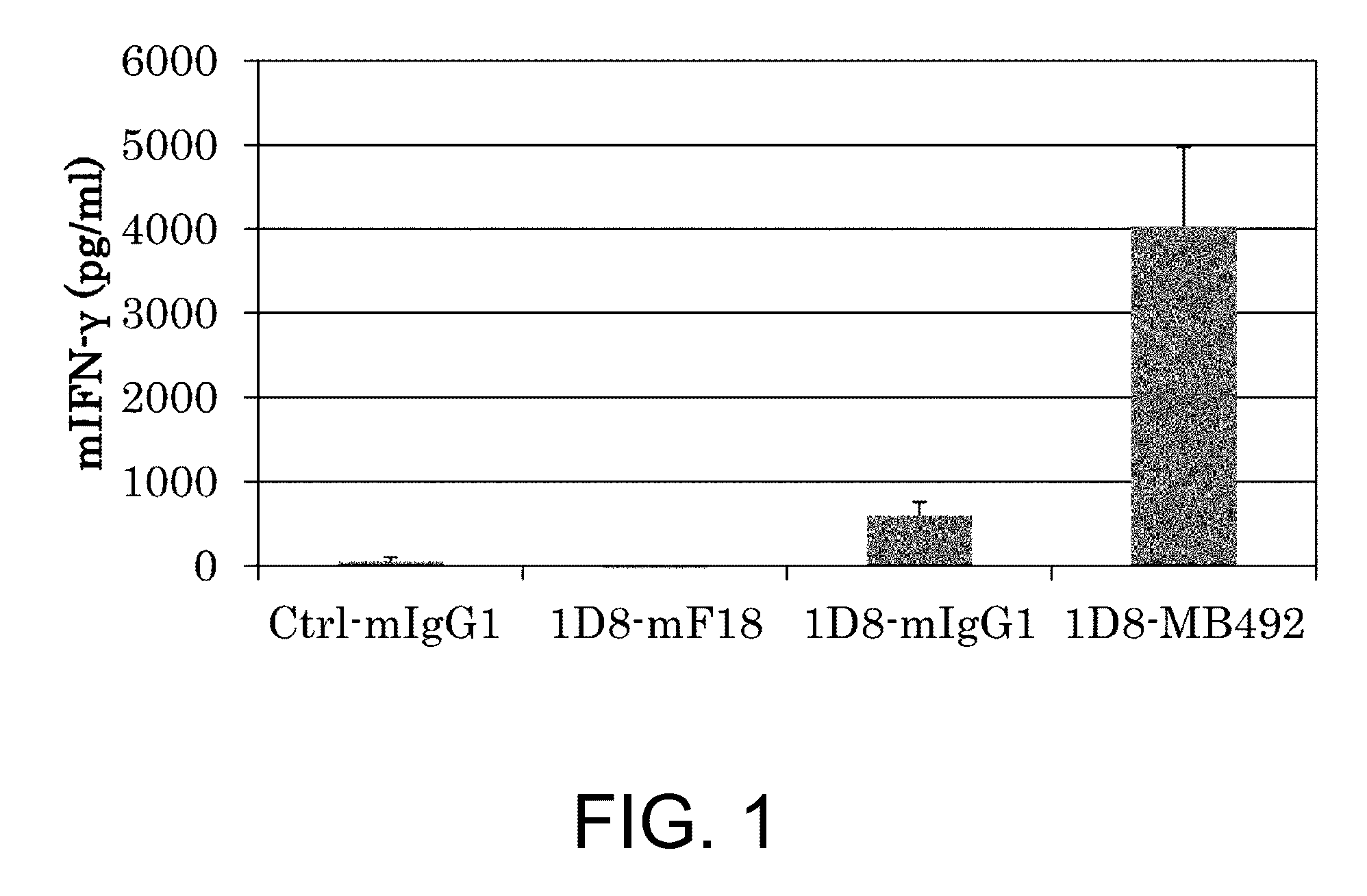
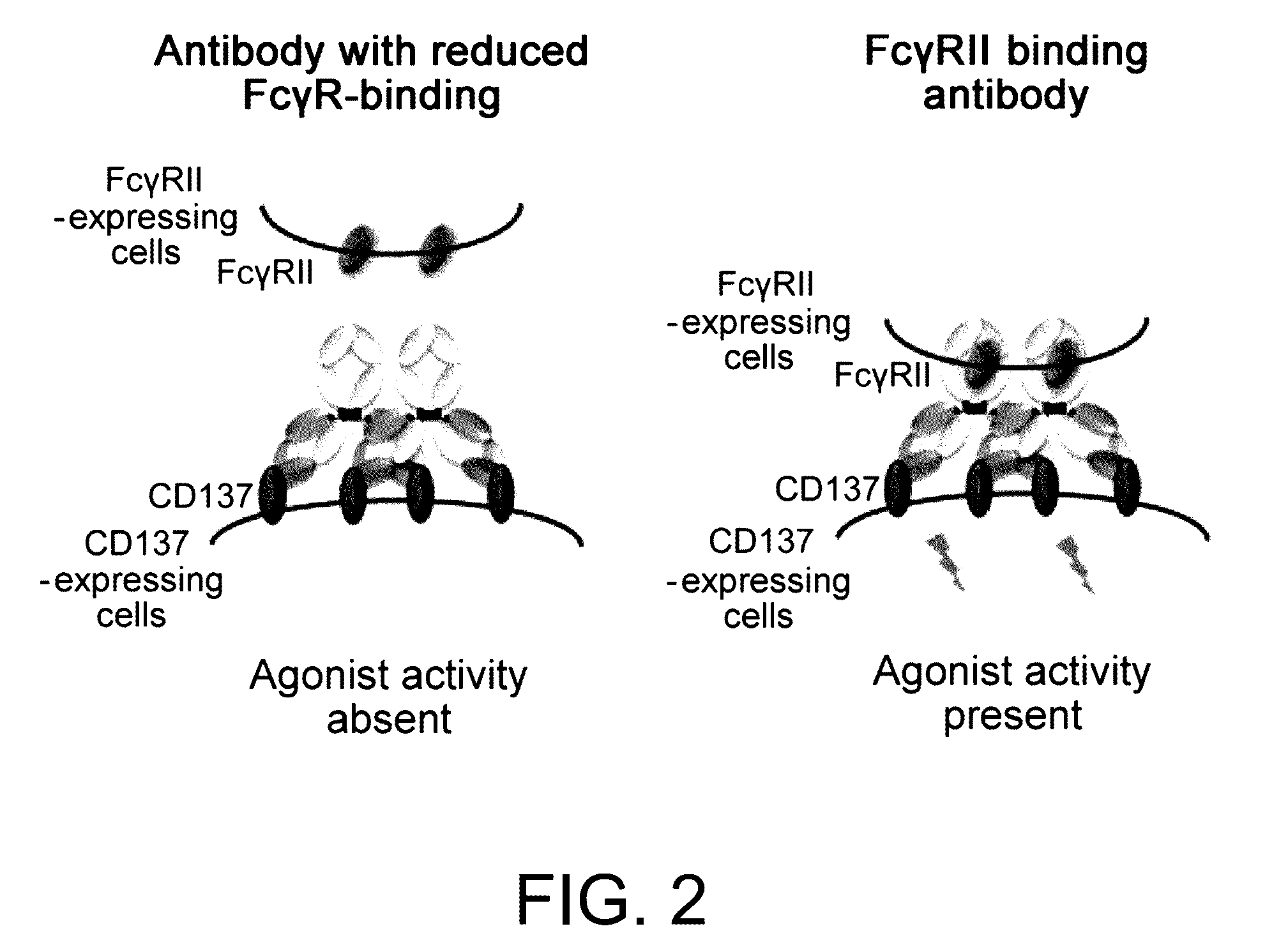
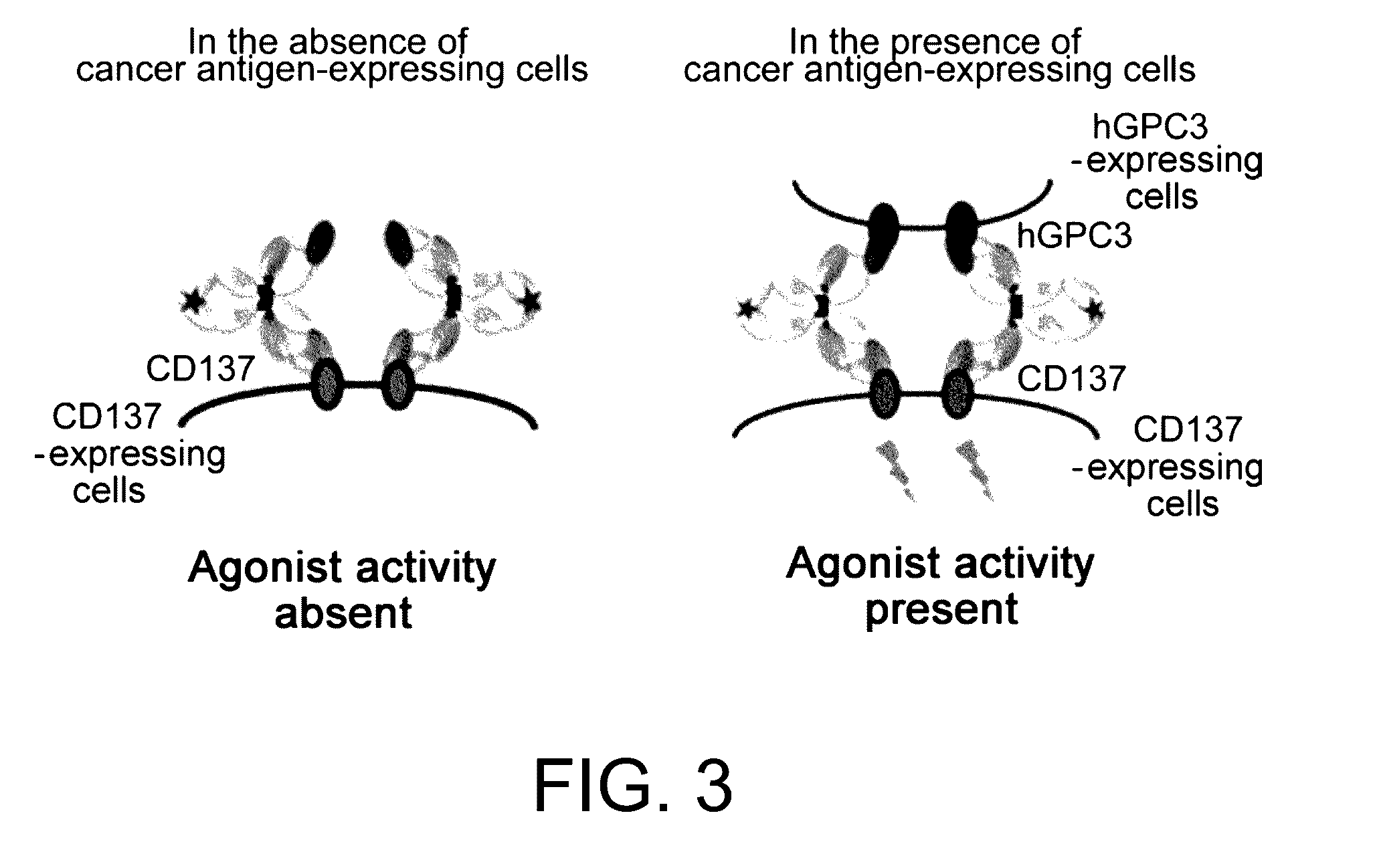
Immunoactivating Antigen-Binding Molecule
ActiveUS20170022287A1Improve anti-tumor effectAvoid toxicityHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsSide effectAntigen binding
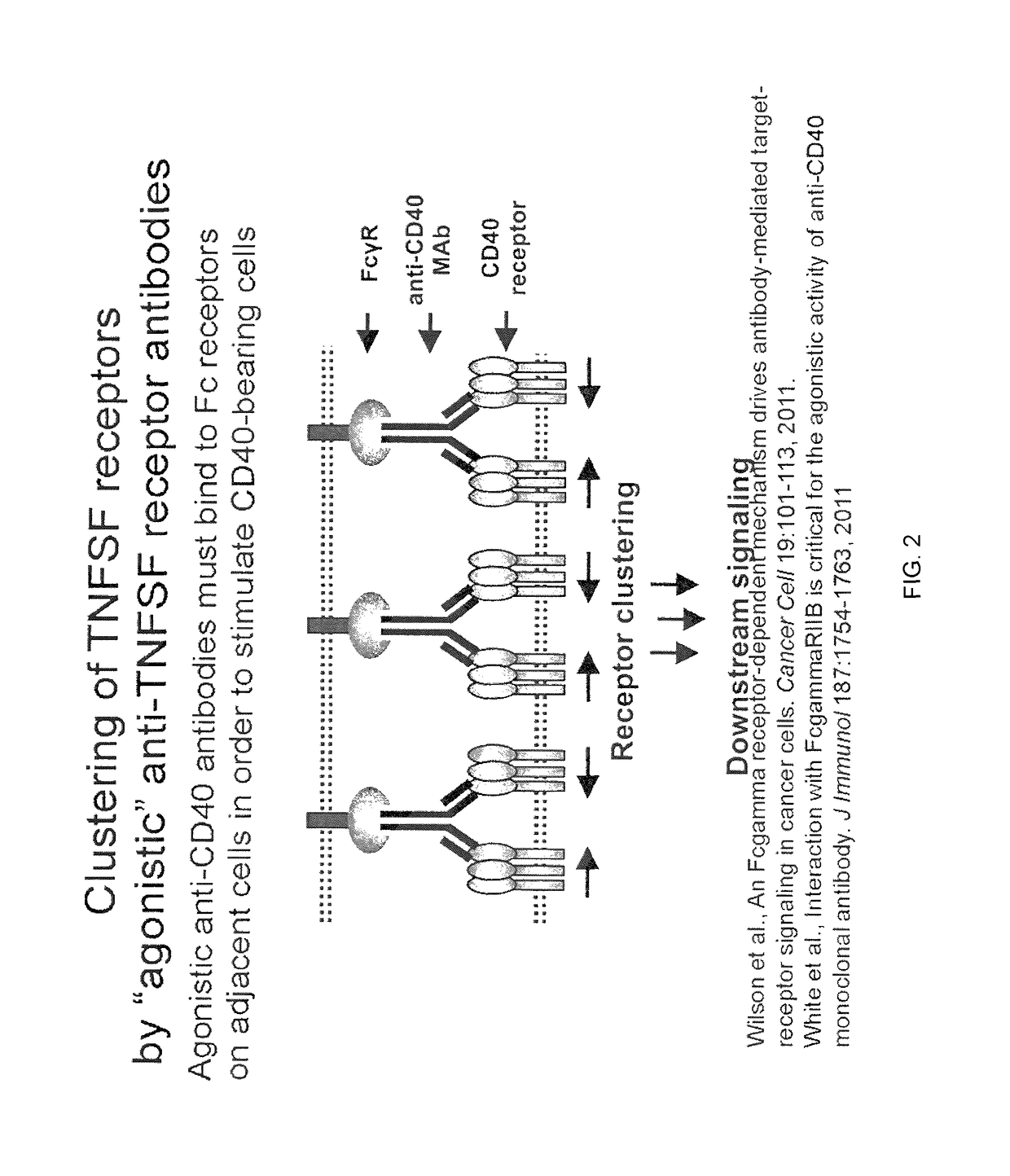
It was discovered that the use of an antigen-binding molecule having a cancer-specific antigen-binding domain, and a TNF superfamily-binding domain or a TNF receptor superfamily-binding domain enables agonist activity against a factor belonging to the TNF superfamily or the TNF receptor superfamily to be exhibited only in the presence of cancer-specific antigen-expressing cells, thus leading to activation of immune cells and thereby maintain anti-tumor activity while avoiding side effects such as hepatotoxicity. It was also discovered that concomitant use of the antigen-binding molecule with an antigen-binding molecule having a cancer-specific antigen-binding domain and a T cell receptor complex-binding domain can avoid side effects while increasing the anti-tumor activity.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
METHOD FOR PREDICTING IMMUNE RESPONSE TO NEOPLASTIC DISEASE BASED ON mRNA EXPRESSION PROFILE IN NEOPLASTIC CELLS AND STIMULATED LEUKOCYTES
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is capable of inducing apoptosis by interacting with specific TNF receptors on the surface of cancer cells. Because multiple members of TNF ligand and receptor are present within each superfamily, over 300 different ligand-receptor combinations exist. Activated blood leukocytes produce TNF as part of the immune response to cancer, as well as producing chemokines to attract other leukocytes to the site. A method is disclosed of detecting significant induction of a variety of TNF superfamily subtype and chemokine mRNAs in blood leukocytes when whole blood is exposed to heat-aggregated IgG or anti-T cell receptor antibodies as a model of immune system interactions. Substantial individual-to-individual variation is observed in TNF subtypes and chemokines induced. Since peripheral blood leukocytes are the supply of anti-cancer immune cells, the quantitation of ex vivo inducibility of appropriate TNF ligands and chemokines in blood will be useful in individualized cancer immunotherapy. If the tumor mass is small, such as with early invisible metastatic lesions, appropriate TNF assaults may be sufficient to prevent relapse.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD +1
Splice Switching Oligomers for TNF Superfamily Receptors and Their Use in Treatment of Disease
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for preparing splice variants of TNFalpha receptor (TNFR) in vivo or in vitro, and the resulting TNFR protein variants. Such variants may be prepared by controlling the splicing of pre-mRNA molecules and regulating protein expression with splice switching oligonucleotides or splice switching oligomers (SSOs). The preferred SSOs according to the invention target exon 7 or 8 of TNFR1 (TNFRSF1A) or TNFR2 (TNFRSF1A) pre-mRNA, typically resulting in the production of TNFR variants which comprise a deletion in part or the entire exon 7 or 8 respectfully. SSOs targeting exon 7 are found to result in a soluble form of the TNFR, which has therapeutic benefit for treatment of inflammatory diseases. The SSO's are characterized in that they are substantially incapable or incapable of recruiting RNaseH.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
Collectin fusion proteins comprising TNF or trail
Owner:APOGENIX AG
TNF superfamily trimerization inhibitors
The invention relates to methods and compositions for inhibiting the trimerization of ligands belonging to the TNF superfamily. In particular, the invention relates to inhibiting RANKL trimerization. Accordingly, the methods and compositions provided herein can be used to treat disorders associated with increased RANK signalling, in particular those related to bone loss. Novel compounds that inhibit trimerization of ligands belonging to the TNF superfamily are also provided.
Owner:B S R C ALEXANDER FLEMING
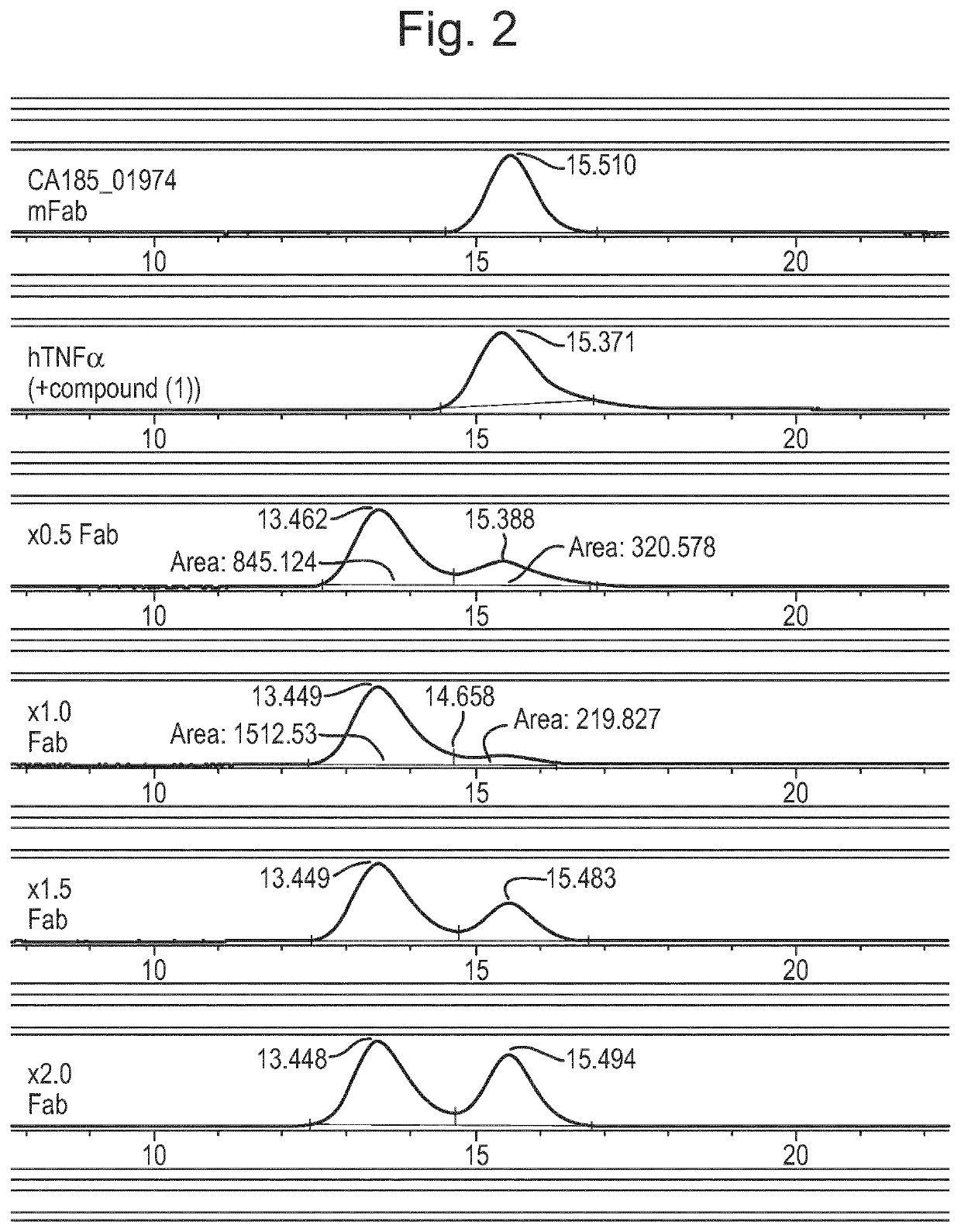
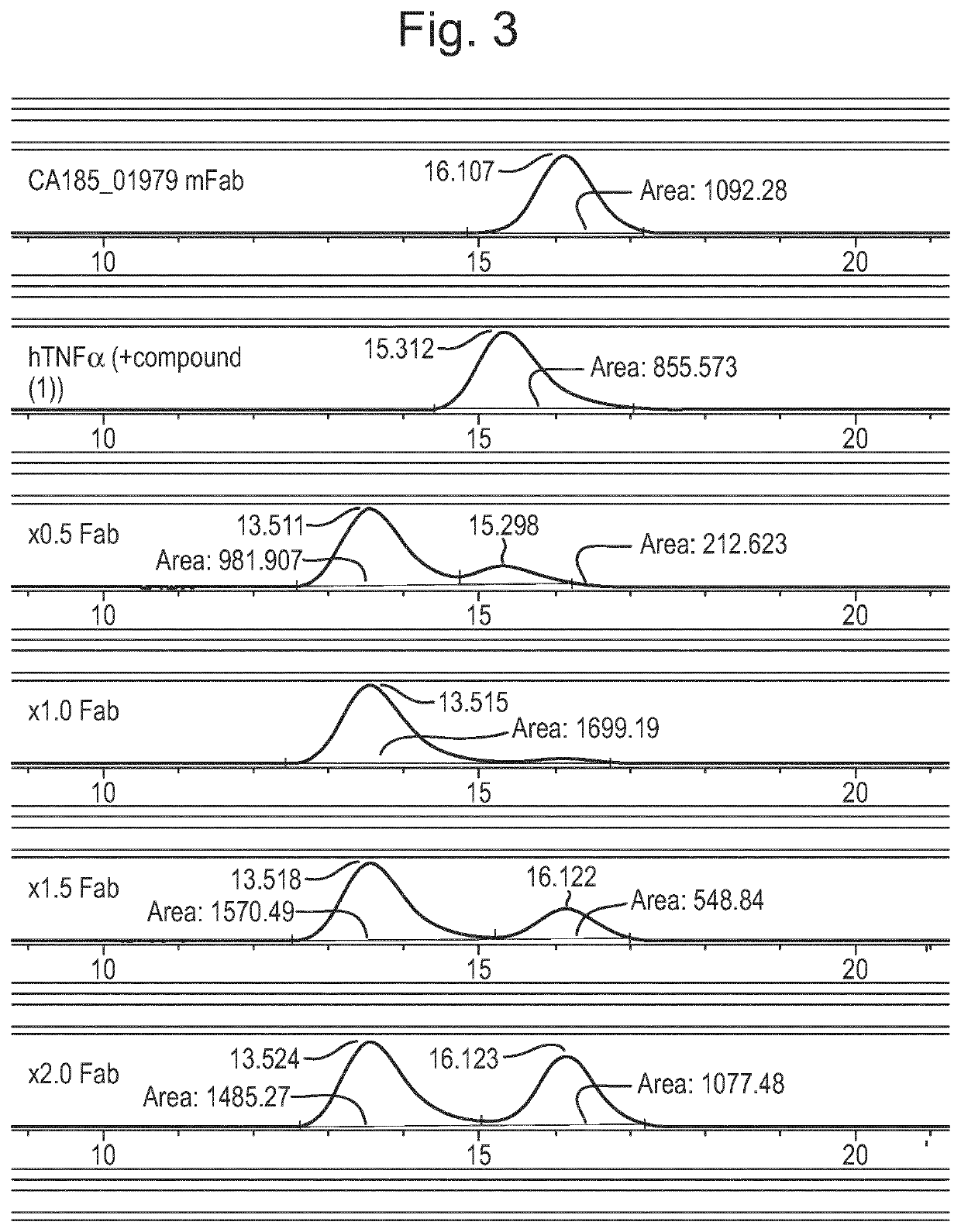
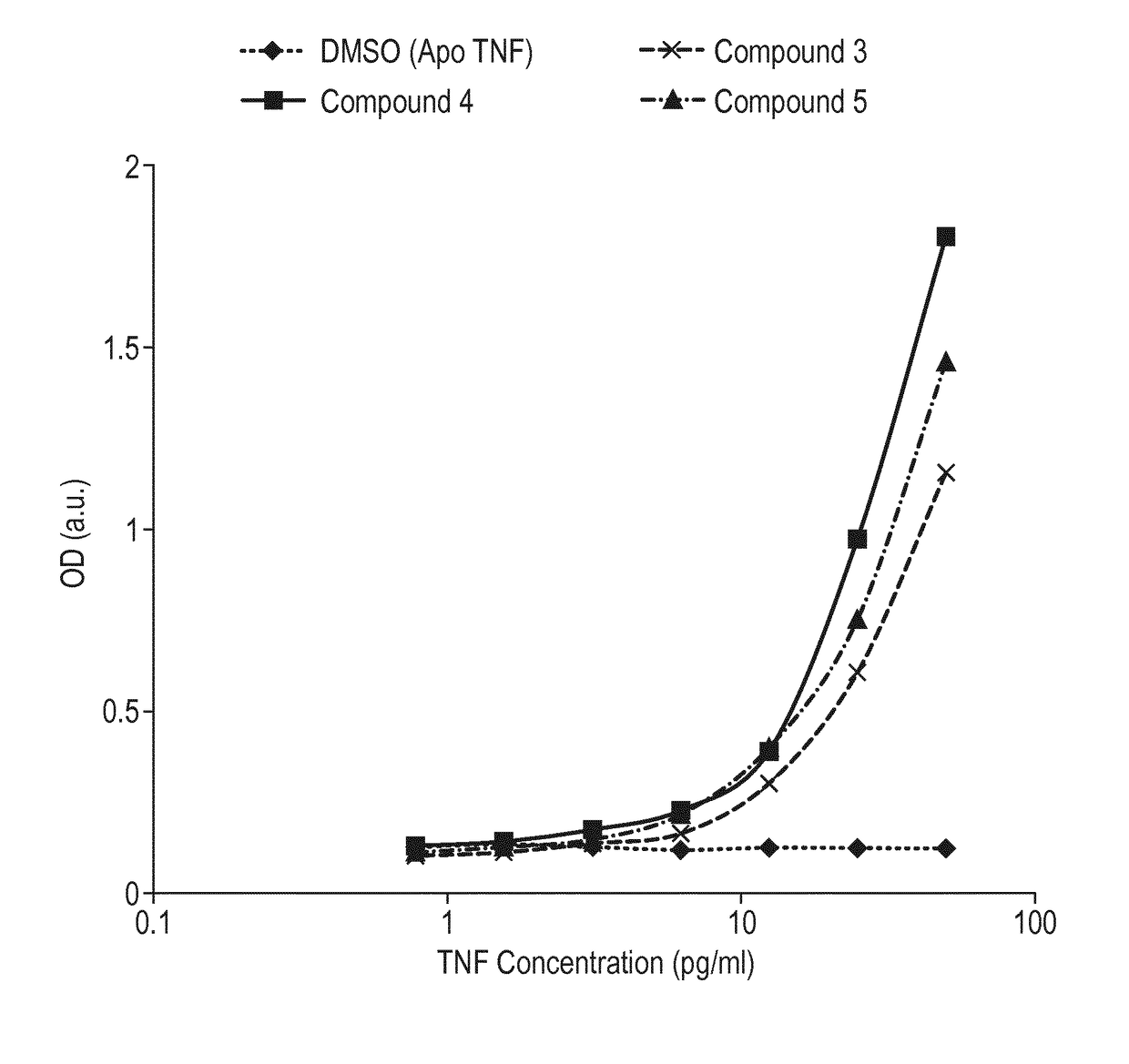
Antibody against trimeric TNFα complex
It has been demonstrated that certain compounds bind to TNF and stabilise a conformation of trimeric TNF that binds to the TNF receptor. Antibodies which selectively bind to complexes of such compounds with TNF superfamily members are disclosed. These antibodies may be used to detect further compounds with the same activity, and as target engagement biomarker.
Owner:SANOFI SA
Antibody epitope
It has been demonstrated that certain compounds bind to TNF and stabilise a conformation of trimeric TNF that binds to the TNF receptor. Antibodies which selectively bind to complexes of such compounds with TNF superfamily members are disclosed. These antibodies may be used to detect further compounds with the same activity, and as target engagement biomarker.
Owner:SANOFI SA
Carrier Conjugates Of Tnf-Peptides
InactiveUS20080019991A1Good skin permeabilityEnhance antigen absorptionBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAutoimmune conditionVirus-like particle
The present invention is related to the fields of molecular biology, virology, immunology and medicine. The invention provides a modified virus-like particle (VLP) comprising a VLP and a particular peptide derived from a polypeptide from the TNF-superfamily linked thereto. The invention also provides a process for producing the modified VLP. The modified VLPs of the invention are useful in the production of vaccines for the treatment of autoimmune diseases and bone-related diseases and to efficiently induce immune responses, in particular antibody responses. Furthermore, the compositions of the invention are particularly useful to efficiently induce self-specific immune responses within the indicated context.
Owner:CYTOS BIOTECHNOLOGY AG
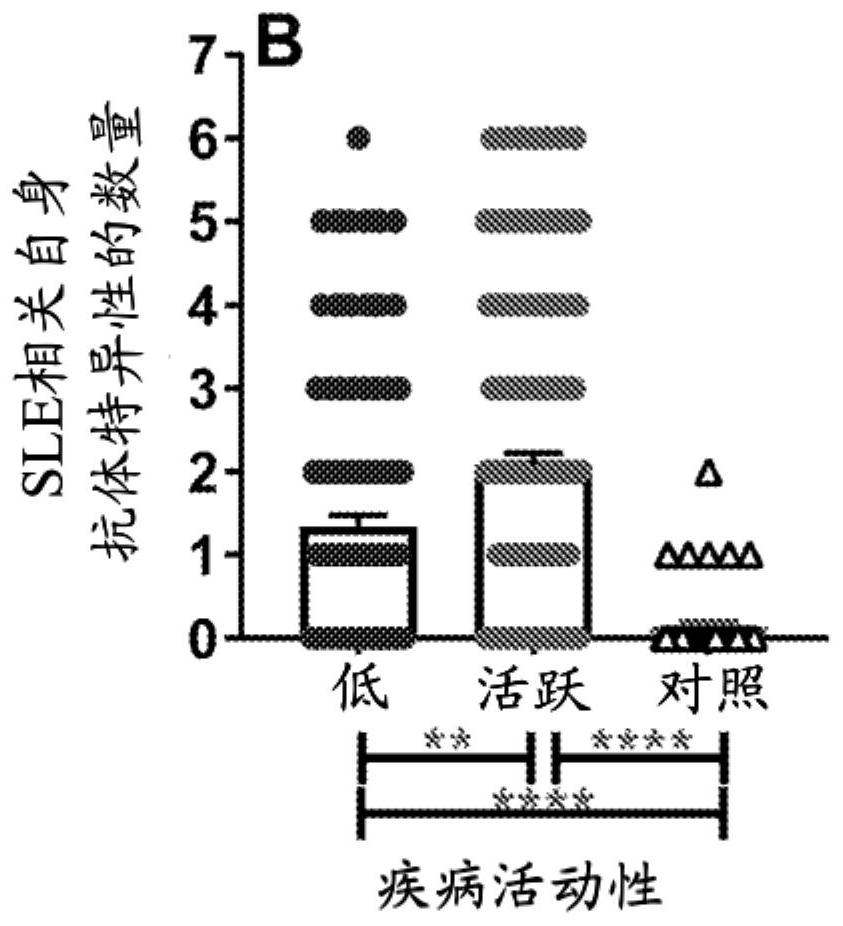
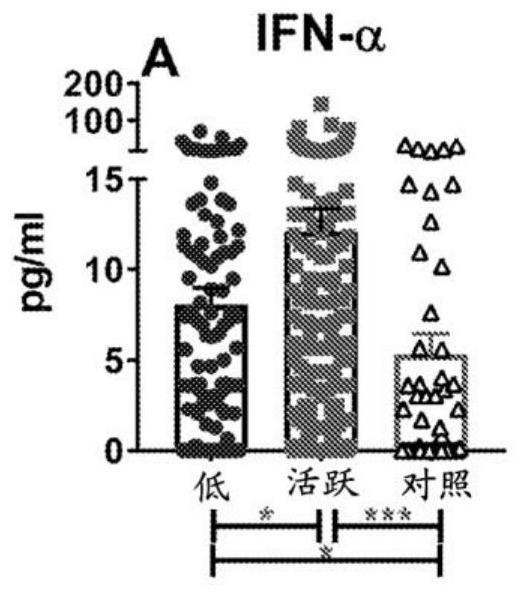
Biomarkers for a systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) disease activity immune index that characterizes disease activity
PendingCN113196059APromote progressIncrease mobilityHealth-index calculationMedical automated diagnosisAutoantibodySystemic lupus erythematosus
The present invention includes a method of characterizing disease activity in a systemic lupus erythematosus patient (SEE), comprising: obtaining a dataset associated with a blood, serum, plasma or urine sample from the patient, wherein the dataset comprises data representing the level of one or more biomarkers in the blood, serum, plasma or urine sample from each of (b) to (g); at least one innate serum or plasma mediator biomarker; at least one adaptive serum or plasma mediator; at least one chemokine / adhesion molecule biomarker; at least one soluble TNF superfamily biomarker; the inflammatory mediator biomarker SCF; at least one SLE-associated autoantibody specificity biomarker; and calculating a Lupus Disease Activity Immune Index (LDAII) score.
Owner:OKLAHOMA MEDICAL RES FOUND
Splice switching oligomers for TNF superfamily receptors and their use in treatment of disease
Methods and compositions are disclosed for controlling expression of TNF receptors (TNFR1 and TNFR2) and of other receptors in the TNFR superfamily using compounds that modulate splicing of pre-mRNA encoding these receptors. More specifically these compounds cause the removal of the transmembrane domains of these receptors and produce soluble forms of the receptor which act as an antagonist to reduce TNF-α activity or activity of the relevant ligand. Reducing TNF-α activity provides a method of treating or ameliorating inflammatory diseases or conditions associated with TNF-α activity. Similarly, diseases associated with other ligands can be treated in like manner. In particular, the compounds of the invention are splice-splice switching oligomers (SSOs) which are small molecules that are stable in vivo, hybridize to the RNA in a sequence specific manner and, in conjunction with their target, are not degraded by RNAse H.
Owner:SAZANI PETER L +2
Splice Switching Oligomers for TNF Superfamily Receptors and Their Use in Treatment of Disease
InactiveUS20150252371A1High expressionReduce expressionSplicing alterationFermentationDiseaseTnfr superfamily
Methods and compositions are disclosed for controlling expression of TNF receptors (TNFR1 and TNFR2) and of other receptors in the TNFR superfamily using compounds that modulate splicing of pre-mRNA encoding these receptors. More specifically these compounds cause the removal of the transmembrane domains of these receptors and produce soluble forms of the receptor which act as an antagonist to reduce TNF-α activity or activity of the relevant ligand. Reducing TNF-α activity provides a method of treating or ameliorating inflammatory diseases or conditions associated with TNF-α activity. Similarly, diseases associated with other ligands can be treated in like manner. In particular, the compounds of the invention are splice-splice switching oligomers (SSOs) which are small molecules that are stable in vivo, hybridize to the RNA in a sequence specific manner and, in conjunction with their target, are not degraded by RNAse H.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL +2
Composition comprised of antigen linked to a TNF superfamily ligand
The invention provides fusion proteins comprising antigens of infectious disease agents and cancer cells linked to multiple-trimer forms of TNF SuperFamily (TNFSF) ligands. The TNFSFs serve as vaccine adjuvants for increasing the immune response to the antigens. In particular, a fusion polypeptide strand that self-assembles inside cells into a multiple-trimer form of CD40 ligand (CD40L, TNFSF5) is provided. Other similar fusion proteins are also disclosed. The fusion proteins can be delivered to a host as isolated proteins, as nucleic acids used directly in DNA vaccination or carried and expressed by a viral vector such as adenovirus. In addition to use as a vaccine to prevent or ameliorate disease caused by an infectious agent, compositions of the invention may be used for the treatment of ongoing infection or for cancer immunotherapy.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
Antibody epitope
It has been demonstrated that certain compounds bind to TNF and stabilise a conformation of trimeric TNF that binds to the TNF receptor. Antibodies which selectively bind to complexes of such compounds with TNF superfamily members are disclosed. These antibodies may be used to detect further compounds with the same activity, and as target engagement biomarker.
Owner:SANOFI SA
Splice switching oligomers for tnf superfamily receptors and their use in treatment of disease
The present invention relates to splice switching oligonucleotides or splice switching oligomers (SSOs). The preferred SSOs according to the invention target exon 7 of TNFRl (TNFRSFlA) or TNFR2 (TNFRSFlA) pre-mRNA, typically resulting in the production of TNFR variants which comprise a deletion in part or the entire exon 7 respectfully. SSOs targeting exon 7 are found to result in a soluble form of the TNFR, which has thereputic benefit for treatment of inflammatory diseases. The SSO's are characterized in that they are substantially incapable or incapable of recruiting RNaseH.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS +1
Antibody epitope
It has been demonstrated that certain compounds bind to TNF and stabilise a conformation of trimeric TNF that binds to the TNF receptor. Antibodies which selectively bind to complexes of such compounds with TNF superfamily members are disclosed. These antibodies may be used to detect further compounds with the same activity, and as target engagement biomarker.
Owner:SANOFI SA
Humanized antibodies against TL1A
The present invention discloses a humanized antibody specifically binding to TNF superfamily member 15 (TNFSF 15) (also known as TL1A). The invention also describes methods of making and using anti-TL1A antibodies. The humanized antibodies can be antagonists and can be used to treat or diagnose disorders related to TL1A function.
Owner:TEVA BIOPHARM USA
Methods for exp anding adipose-derived stem cells
PendingUS20210137990A1Cell dissociation methodsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsMesenchymal stem cellCell type
The invention concerns methods for propagating mesenchymal stem cells (MSC), and in particular adipose derived stem cells, comprising incubating cells isolated from a body tissue with at least one TNF superfamily ligand, and at least one apoptosis inhibitory agent. The cells can be used for transplantation into subjects in need thereof or be induced to differentiate into various cell types that can be used in transplantation.
Owner:CELLECT BIOTHERAPEUTICS LTD
Splice switching oligomers for TNF superfamily receptors and their use in treatment of disease
InactiveUS20190359986A1Reduce the amount requiredSplicing alterationDNA/RNA fragmentationSplice switchingADAMTS Proteins
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for preparing splice variants of TNFalpha receptor (TNFR) in vivo or in vitro, and the resulting TNFR protein variants. Such variants may be prepared by controlling the splicing of pre-mRNA molecules and regulating protein expression with splice switching oligonucleotides or splice switching oligomers (SSOs) The preferred SSOs according to the invention target exon 7 or 8 of TNFR1 (TNFRSF1A) or TNFR2 (TNFRSF1A) pre-MRNA, typically resulting in the production of TNFR variants which comprise a deletion in part or the entire exon 7 or 8 respectfully. SSOs targeting exon 7 are found to result in a soluble form of the TNFR, which has therapeutic benefit for treatment of inflammatory diseases. The SSO's are characterised in that they are substantially incapable or incapable of recruiting RNaseH.
Owner:ROCHE INNOVATION CENT COPENHAGEN +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com