Splice switching oligomers for tnf superfamily receptors and their use in treatment of disease
An oligomer, receptor technology, applied in the field of TNFR protein variants, can solve the problem of not teaching or providing the enlightenment of CD40 splicing element or region, not teaching or providing etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0472] The present invention provides a method of treating an inflammatory disease or condition comprising administering to a subject one or more splice switch oligomers (SSOs) in an amount that reduces tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) superfamily The amount of ligand activity wherein said one or more SSOs are capable of altering the splicing of pre-messenger RNA encoding said receptor, thereby increasing the production of a stably secreted ligand-bound form of said receptor.
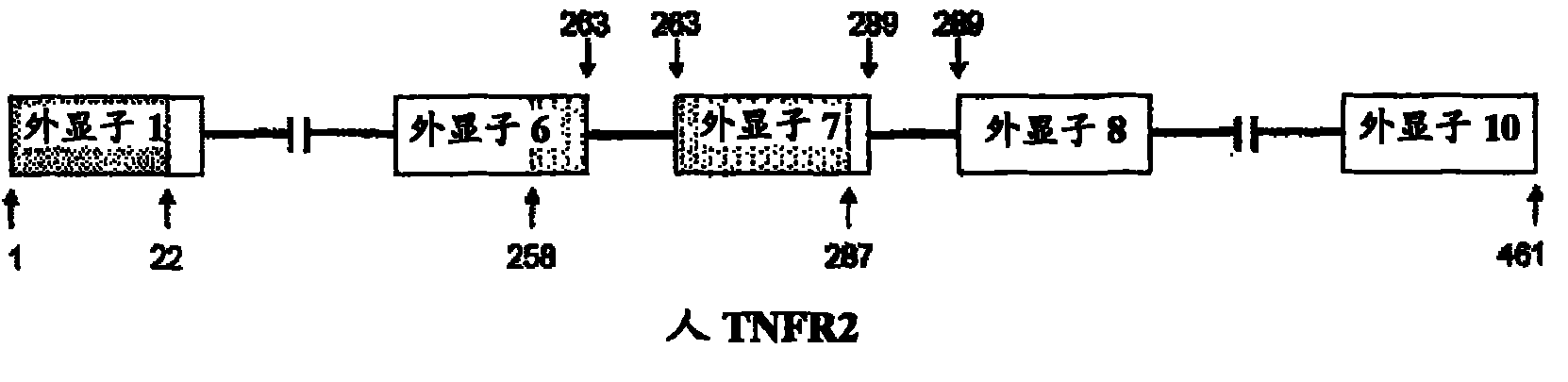
[0473] In one embodiment, the mammalian receptor is selected from the group consisting of TNFRSF1A, TNFRSF1B, TNFRSF3, TNFRSF5, TNFRSF8 and TNFRSFI1A.
[0474] In one embodiment, the receptor is human TNFRSF1A or human TNFRSF1B. In one embodiment, the receptor is human TNFRSF1B.
[0475] In one embodiment, the ligand is TNF-α., RANKL, CD40L LT-α. or LT-β.
[0476] In one embodiment, the disease or condition is selected from the group consisting of rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile rheumatoid arthrit...
Embodiment 1
[0526] Oligonucleotides. Table 6 lists the chimeric locked nucleic acids with alternating 2'deoxy- and 2'O-4'-(methylene)-bicyclic-ribonucleoside phosphorothioates and sequences as described above ( LNA) SSOs. These sequences were synthesized by Santaris Pharma in Denmark. For each SSO, the 5'-terminal nucleoside is 2'oxy-4'-methylene-ribonucleoside and the 3'-terminal nucleoside is 2'deoxyribonucleoside. Table 7 shows compounds with alternating 2'-oxo-methyl-ribonucleoside-phosphorothioate (2'-OMe) and 2'O-4'-(methylene)-bicyclic-ribonucleoside thio Sequences of chimeric LNA SSOs of phosphoesters. These sequences were synthesized by Santaris Pharma in Denmark. LNA is shown in uppercase letters, 2'-OME is shown in lowercase letters.
[0527] Cell culture and transfection. L929 cells were maintained in minimal essential medium (37°C, 5% CO2) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and antibiotics. For transfection, L929 cells were seeded into 24-well plates at 10 5 cel...
Embodiment 2
[0542] Example 2-SSO Splicing Switching Activity on TNFR mRNA
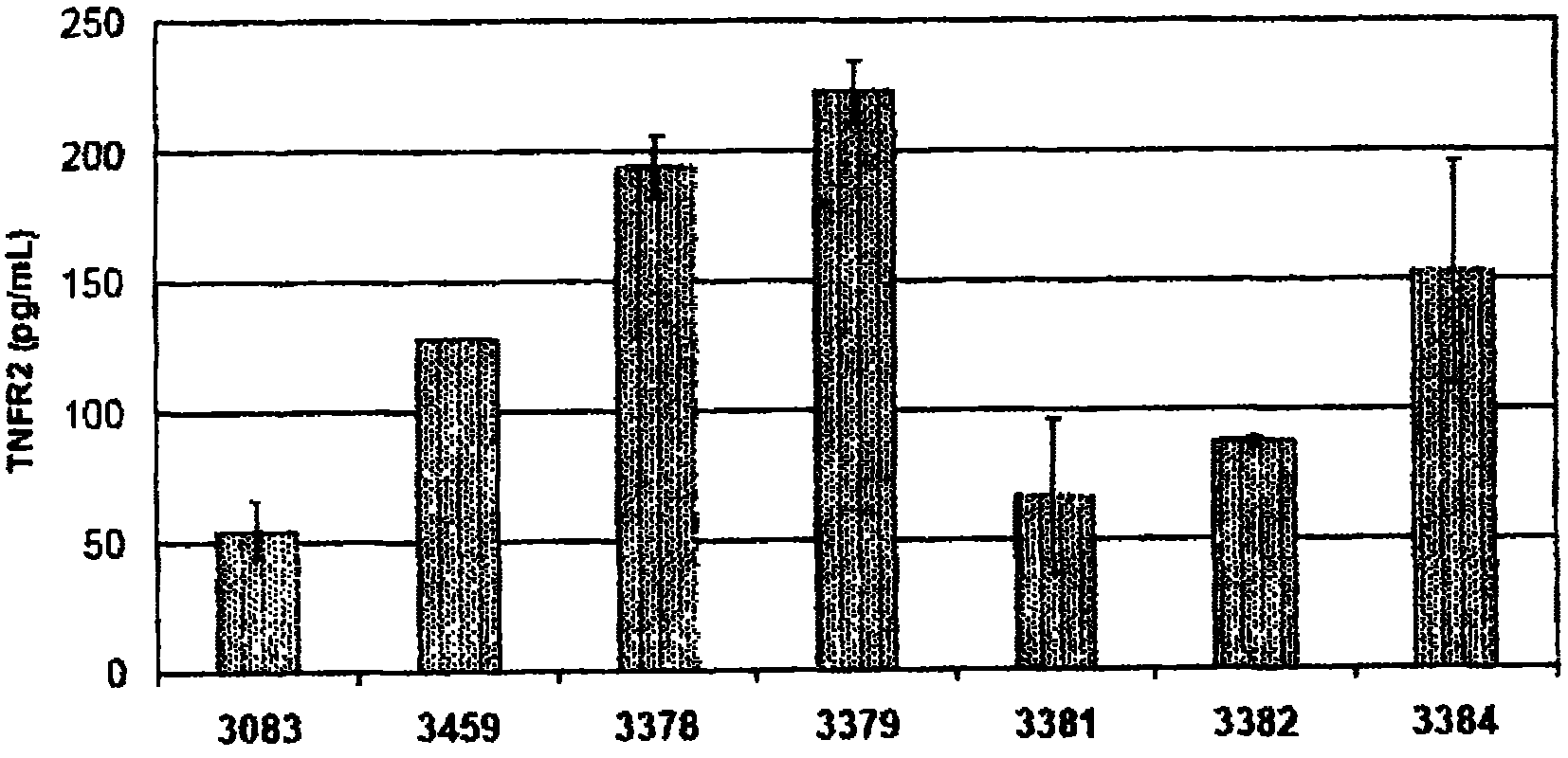
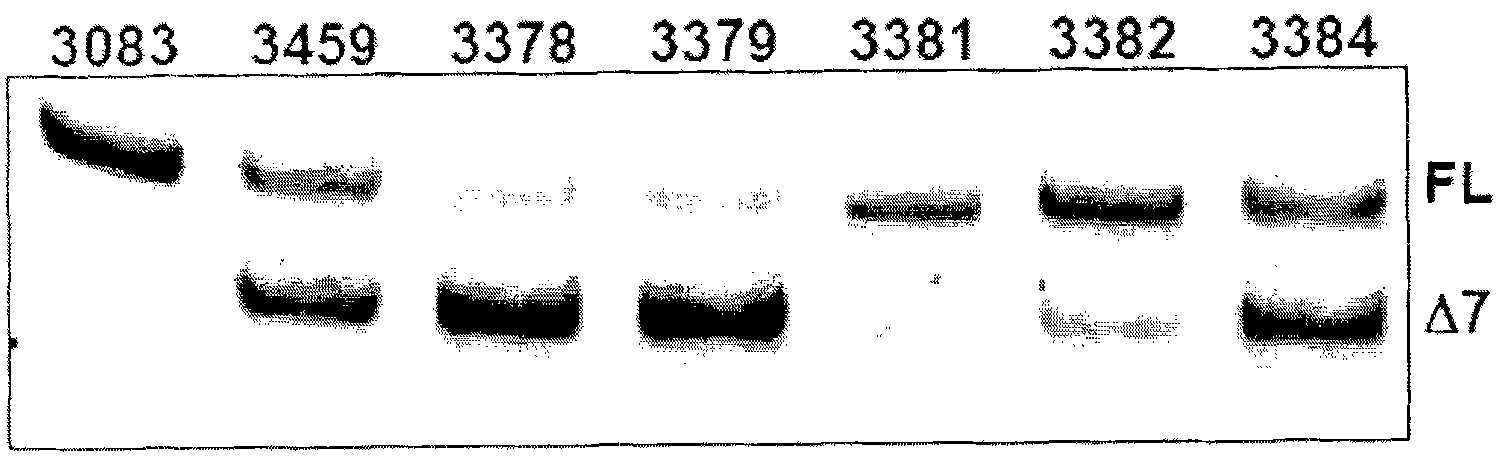
[0543] Table 6 shows the splice switch activity of SSOs having sequences as described in US Application No. 11 / 595,485 and targeting mouse and human TNFRs. At least eight of the SSOs targeting exon 7 of mouse TNFR2 produced some muTNFR2Δ7 mRNA. In particular, SSO 3312 and 3305 induced exon 7 deletions of at least 50%; SSO 3305 treatment resulted in almost complete deletions. Transfection into primary human hepatocytes and at least 7 of the SSOs targeting exon 7 of human TNFR2 produced some huTNFR2Δ7 mRNA. In particular, SSOs 3378, 3379, 3384 and 3459 induced exon 7 deletions in at least 75% ( Figure 2B ), huTNFR2Δ7 was significantly induced into the extracellular medium ( Figure 2A ).
[0544] Table 6: Splice transition activity of SSO
[0545]
[0546] Table 7 contains compounds with alternating 2'-oxy-methyl-ribonucleoside-phosphorothioate (2'-OMe) and 2'-oxo-4'-(methylene)-bicyclic-ribonucleoside thio ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com