Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
115 results about "Screening call" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
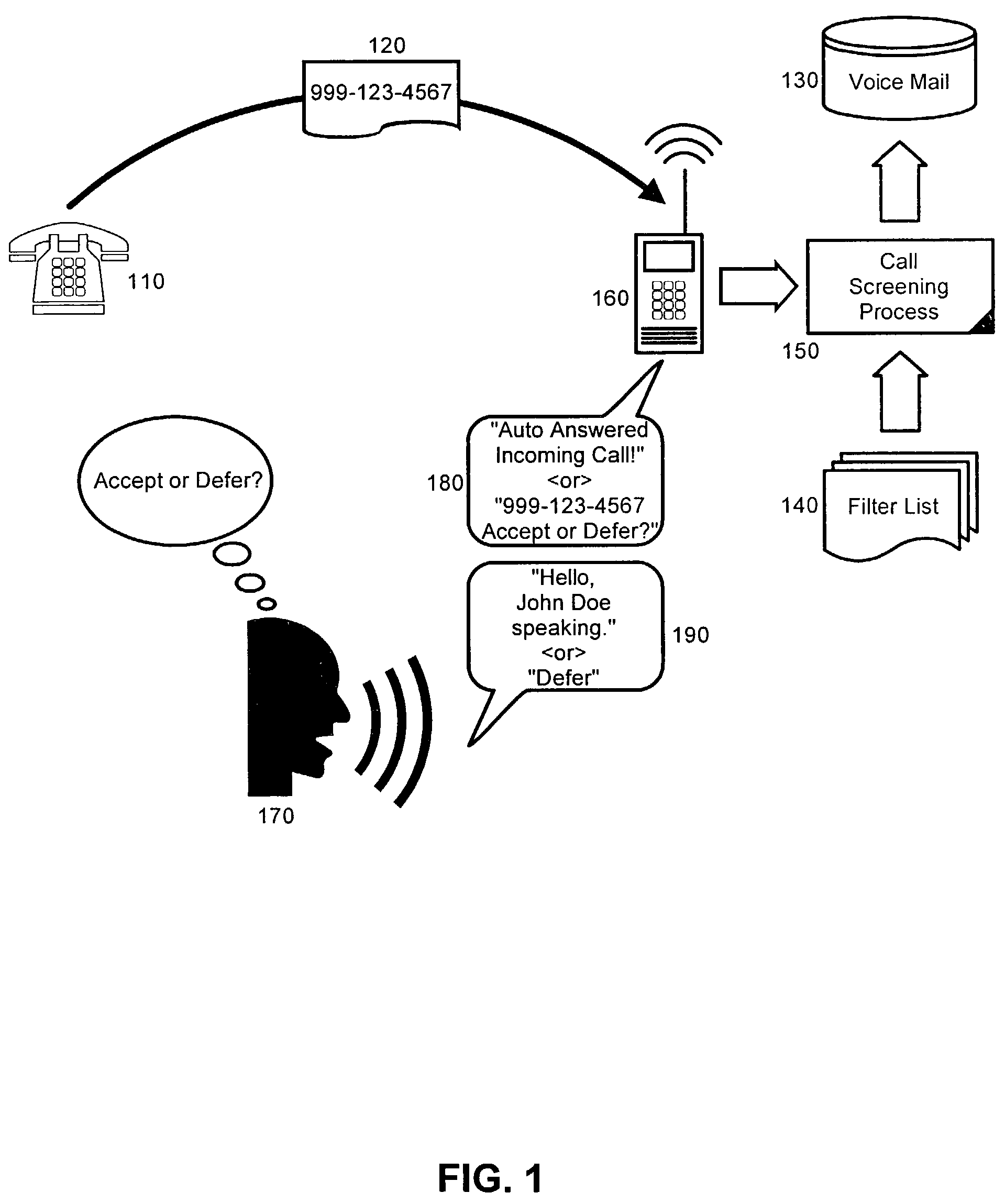
Call screening is the process of evaluating the characteristics of a telephone call before deciding how or whether to answer it. Some methods may include: listening to the message being recorded on an answering machine or voice mail. checking a caller ID display to see who or where the call is from.
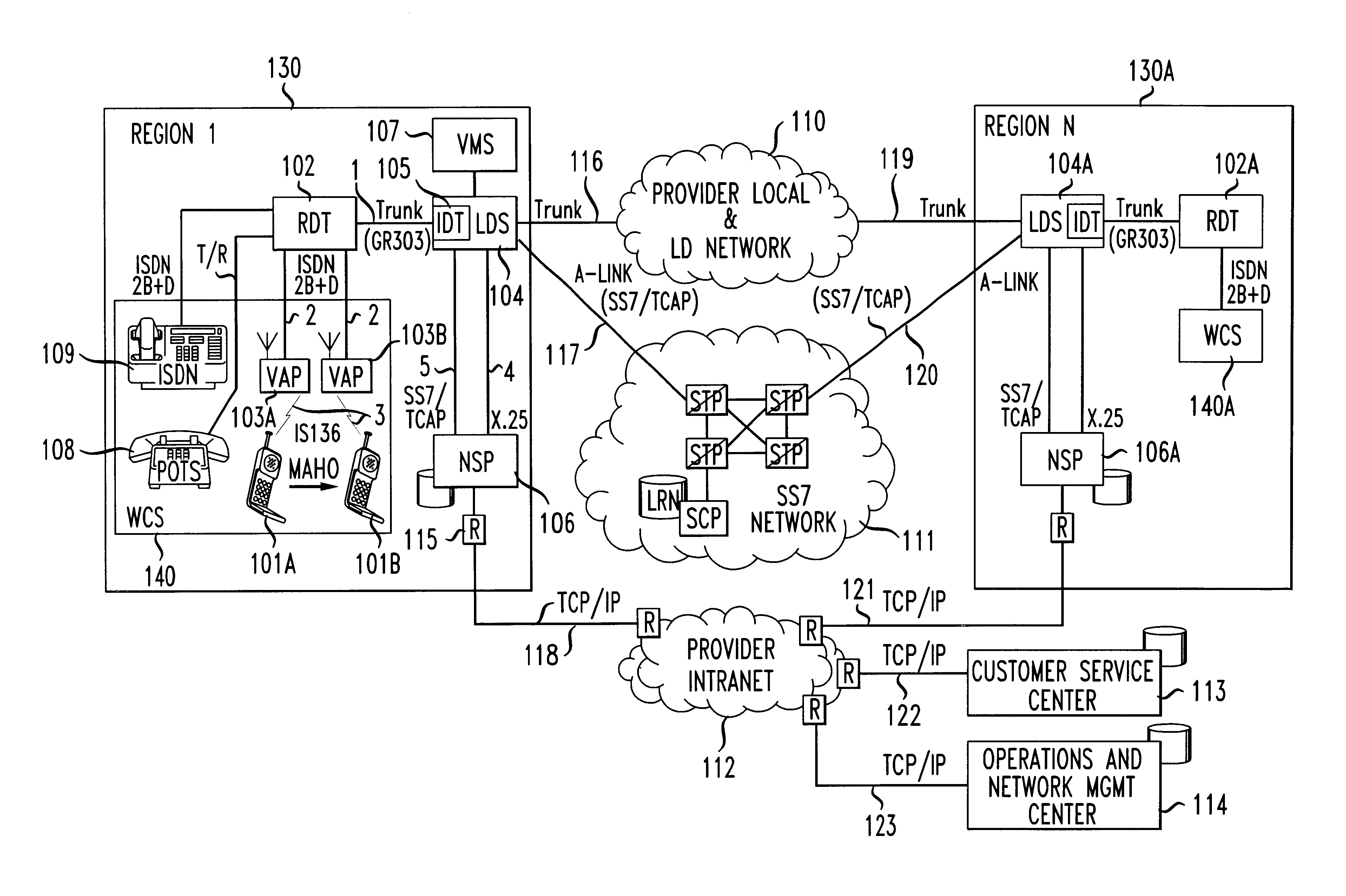
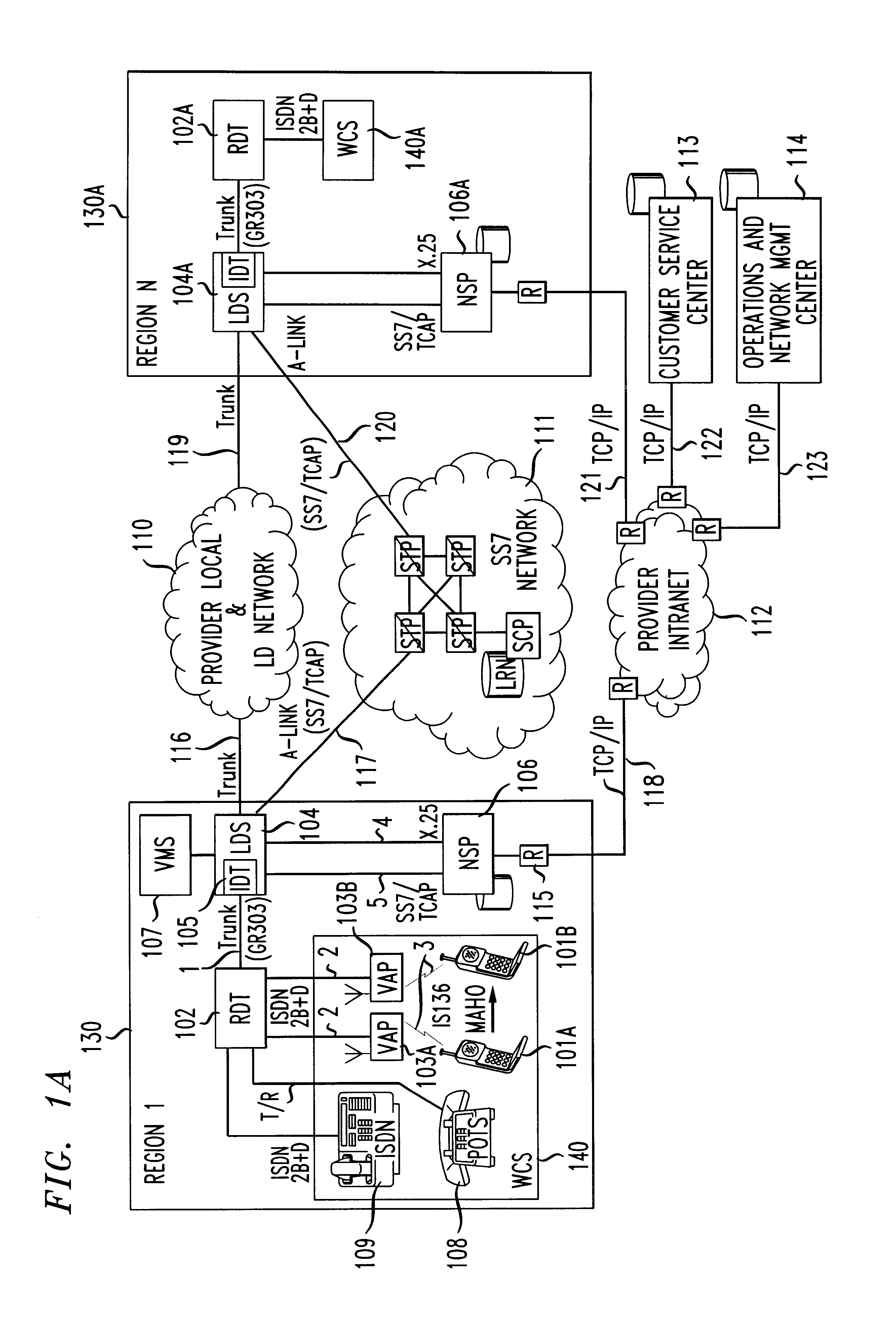
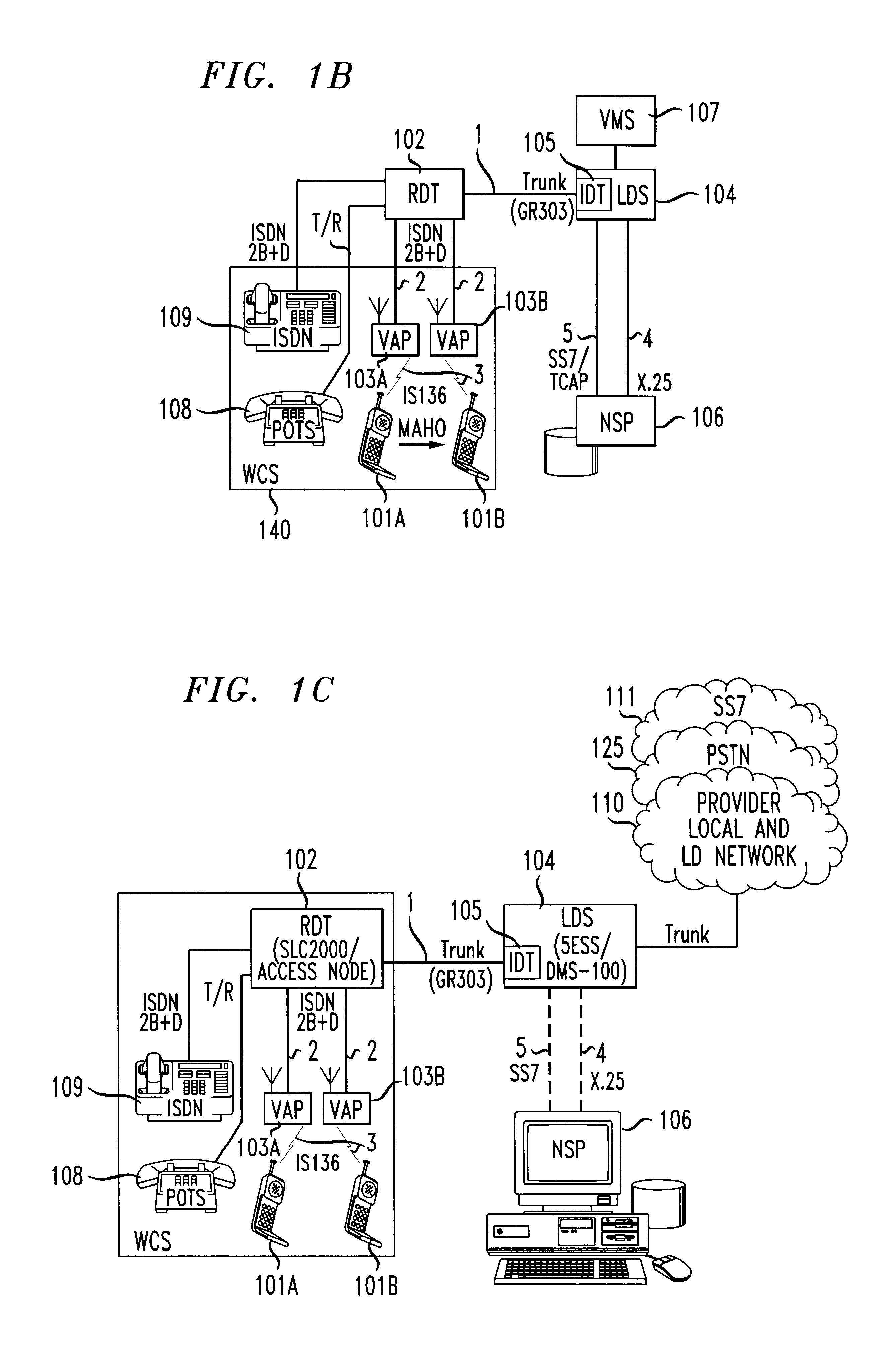
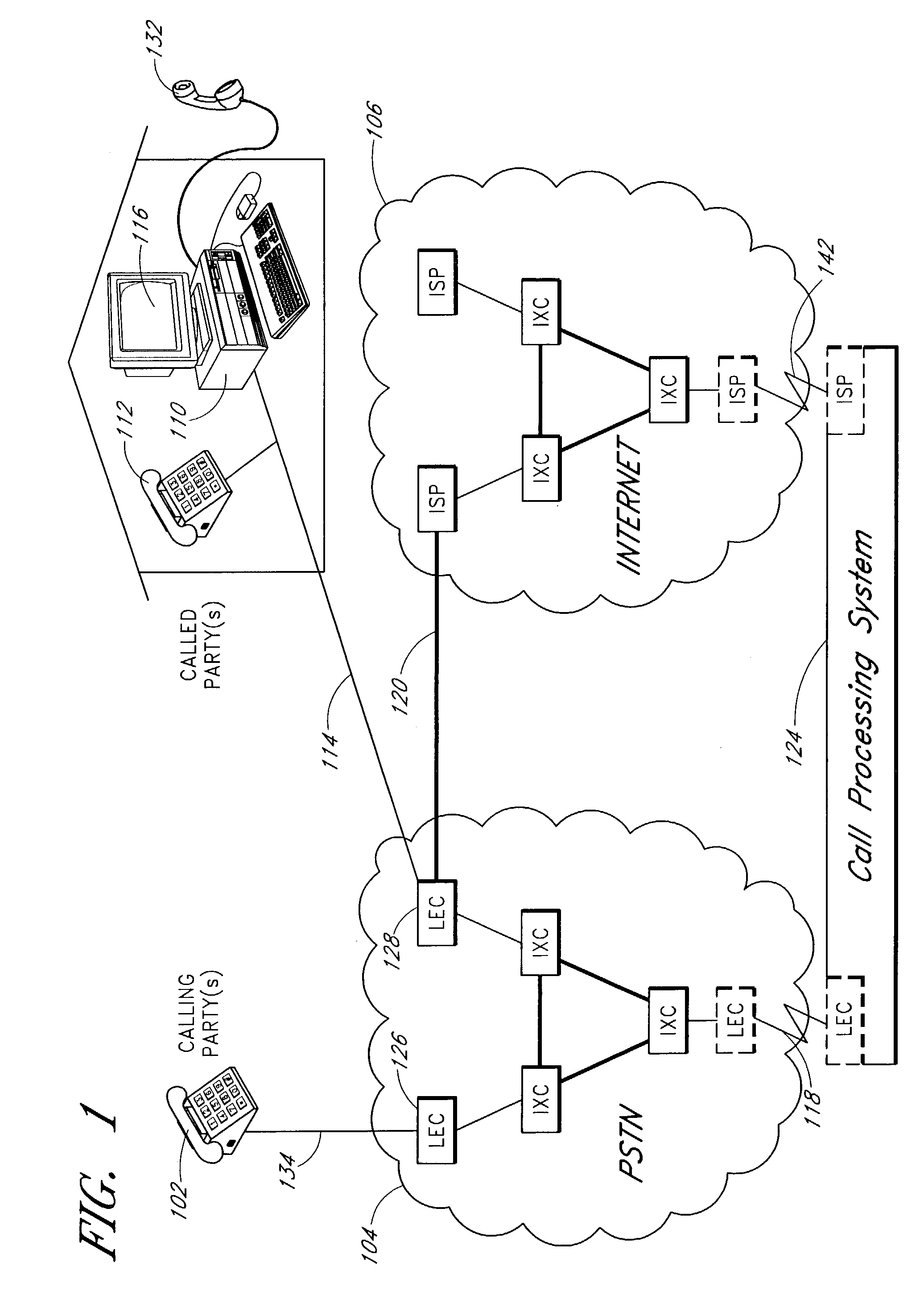
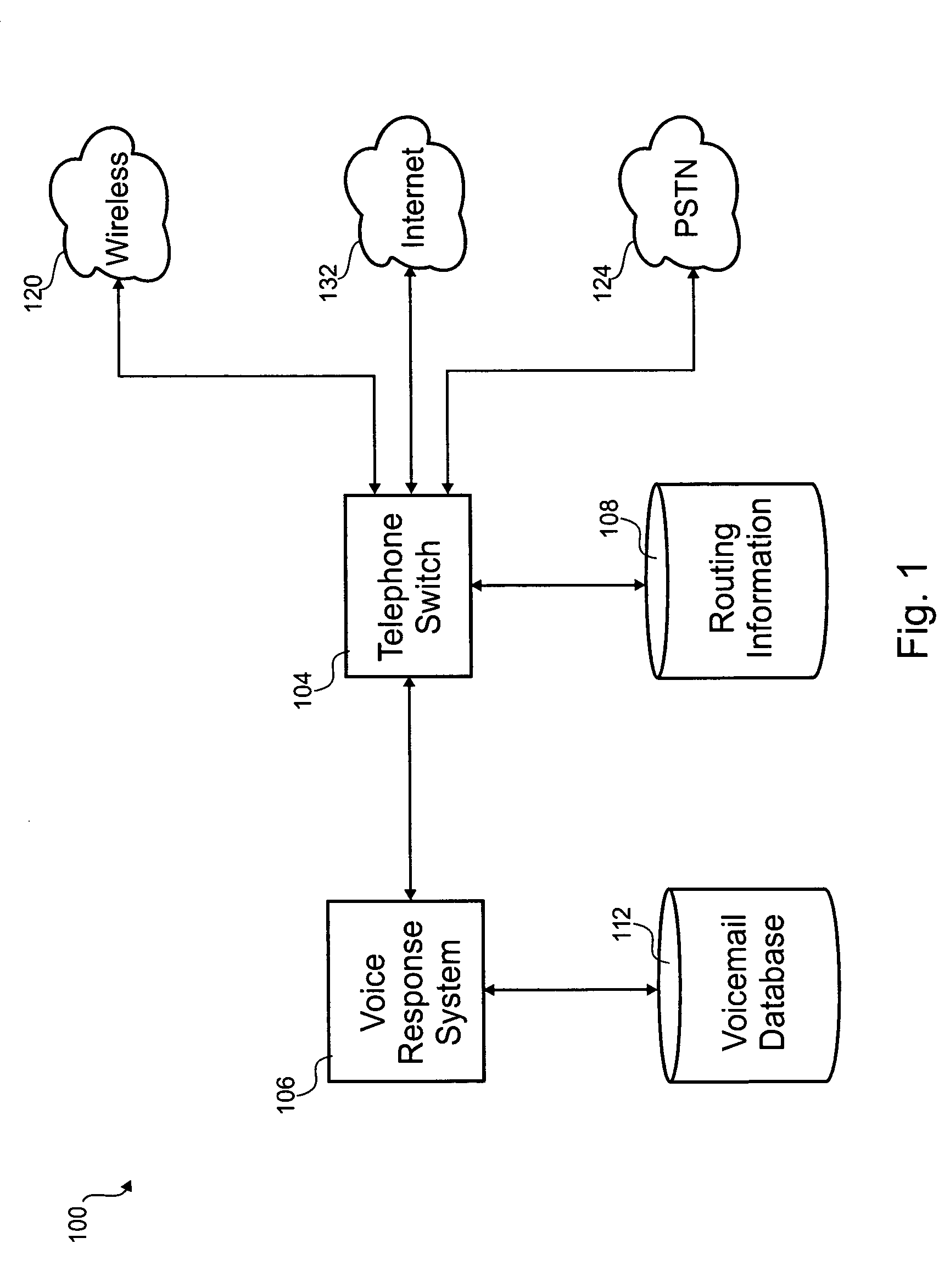
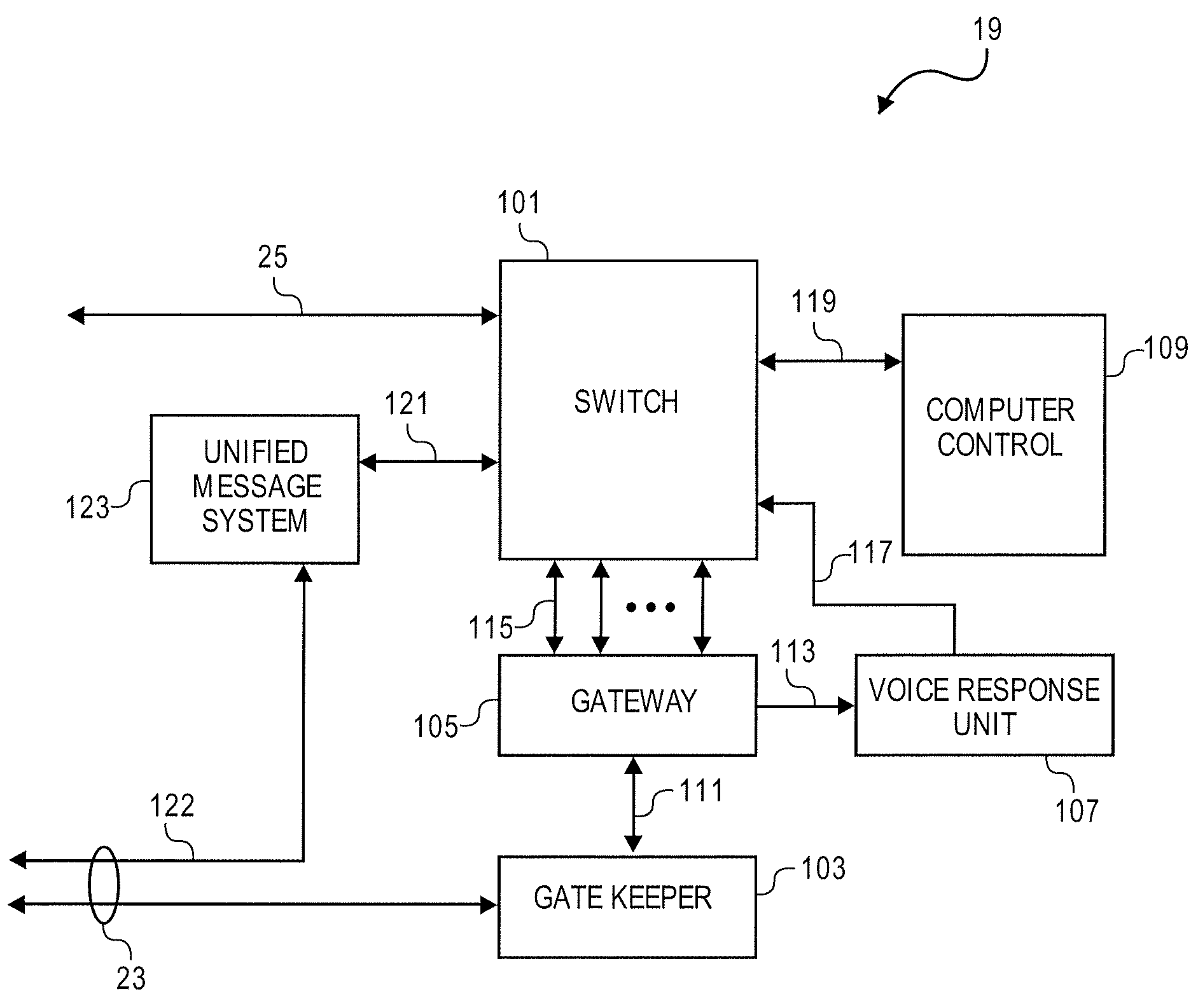
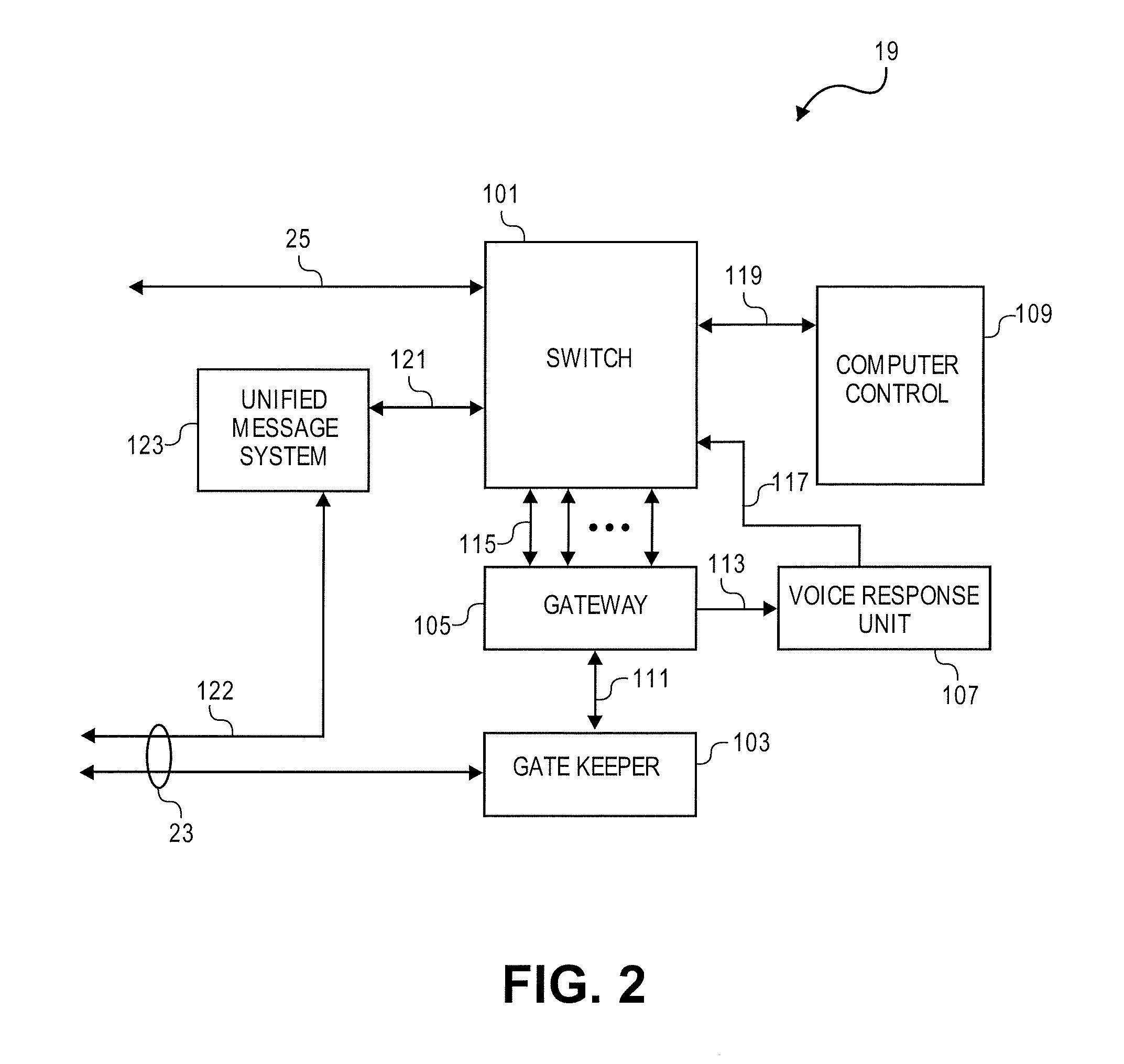
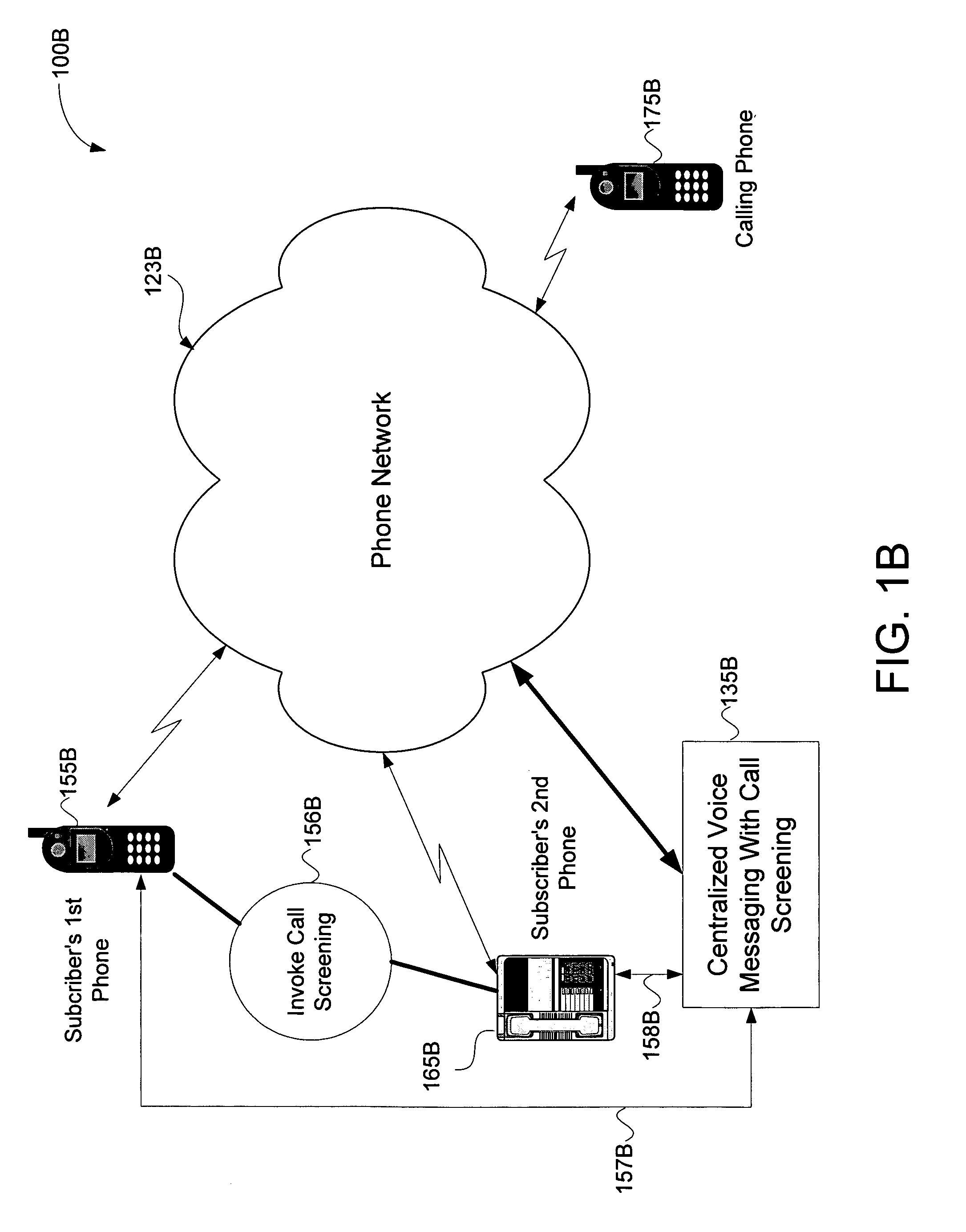
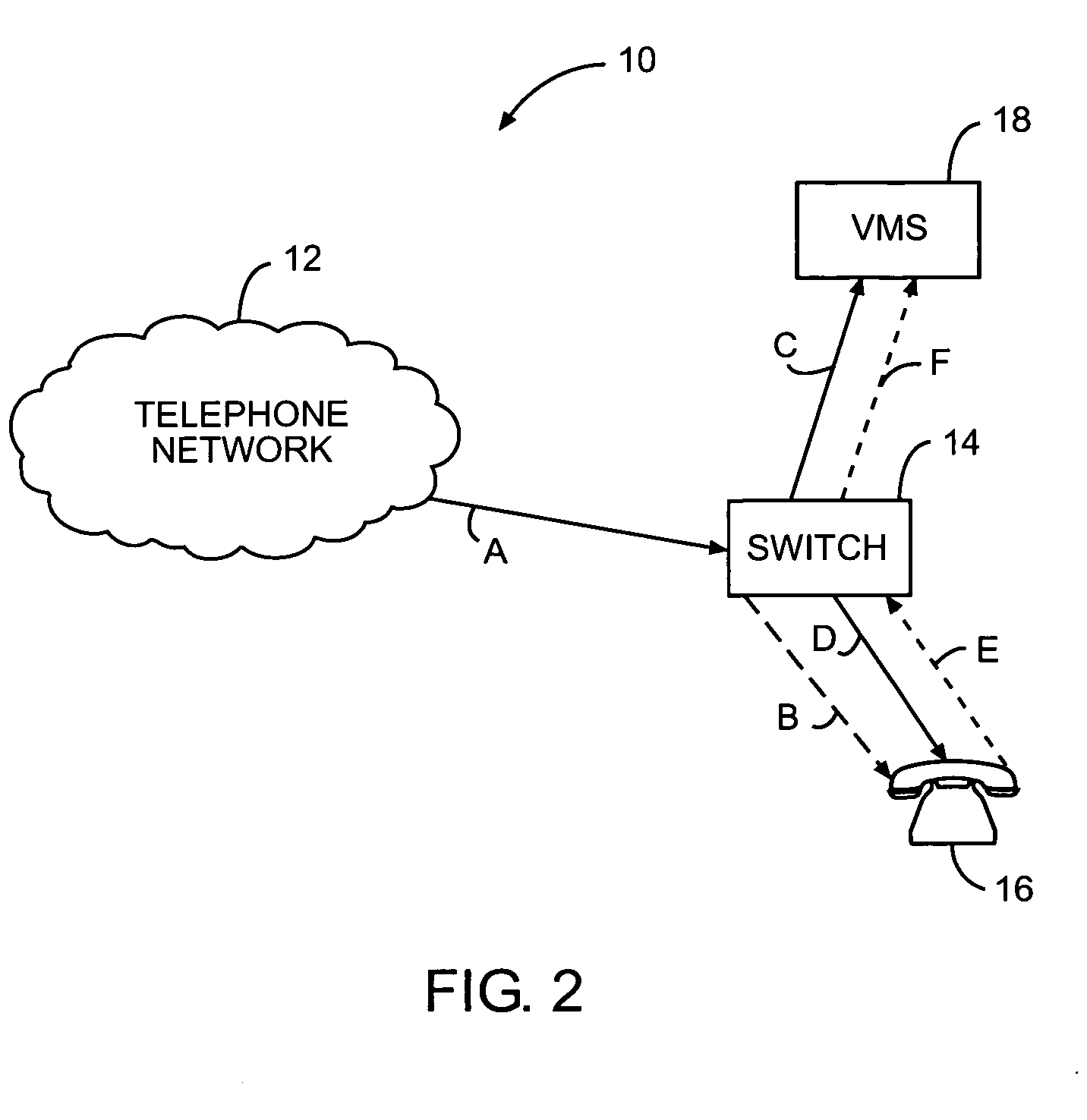
Distributed network voice messaging for wireless centrex telephony
A method and system for distributing voice prompts and messaging closer to the calling or called party via the Voice Access Port (VAP) of a wireless centrex system comprises the steps of transmitting a message request to the VAP from a network server platform, retrieving a selected message and forwarding the message, for example, to the calling party, for example, when the called party is not available or during conference call set-up, call hold or call screening. In accordance with a further embodiment, the voice prompt or message may be personalized with the calling / called party's name, address or other personalized information as appropriate.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Systems and methods for call screening
InactiveUS7103167B2Special service for subscribersSubstation equipmentTelecommunicationsScreening call
The present invention provides flexible, user-definable call screening processes. The user can optionally define to which telecommunication terminals a screened call is to be broadcast to and under what conditions. An incoming call is forwarded to a call management system that asks the caller to leave a voice message. The call management system selectively couples the call to a POTS line or a VoIP-capable device so that the user can listen to the incoming message and thereby screen the incoming call. Based on the screening, the user can instruct the call management system to connect the caller to the user.
Owner:CALLWAVE COMM
Arrangement for managing voice over IP (VoIP) telephone calls, especially unsolicited or unwanted calls
InactiveUS20060182029A1Reduce probabilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemScreening call
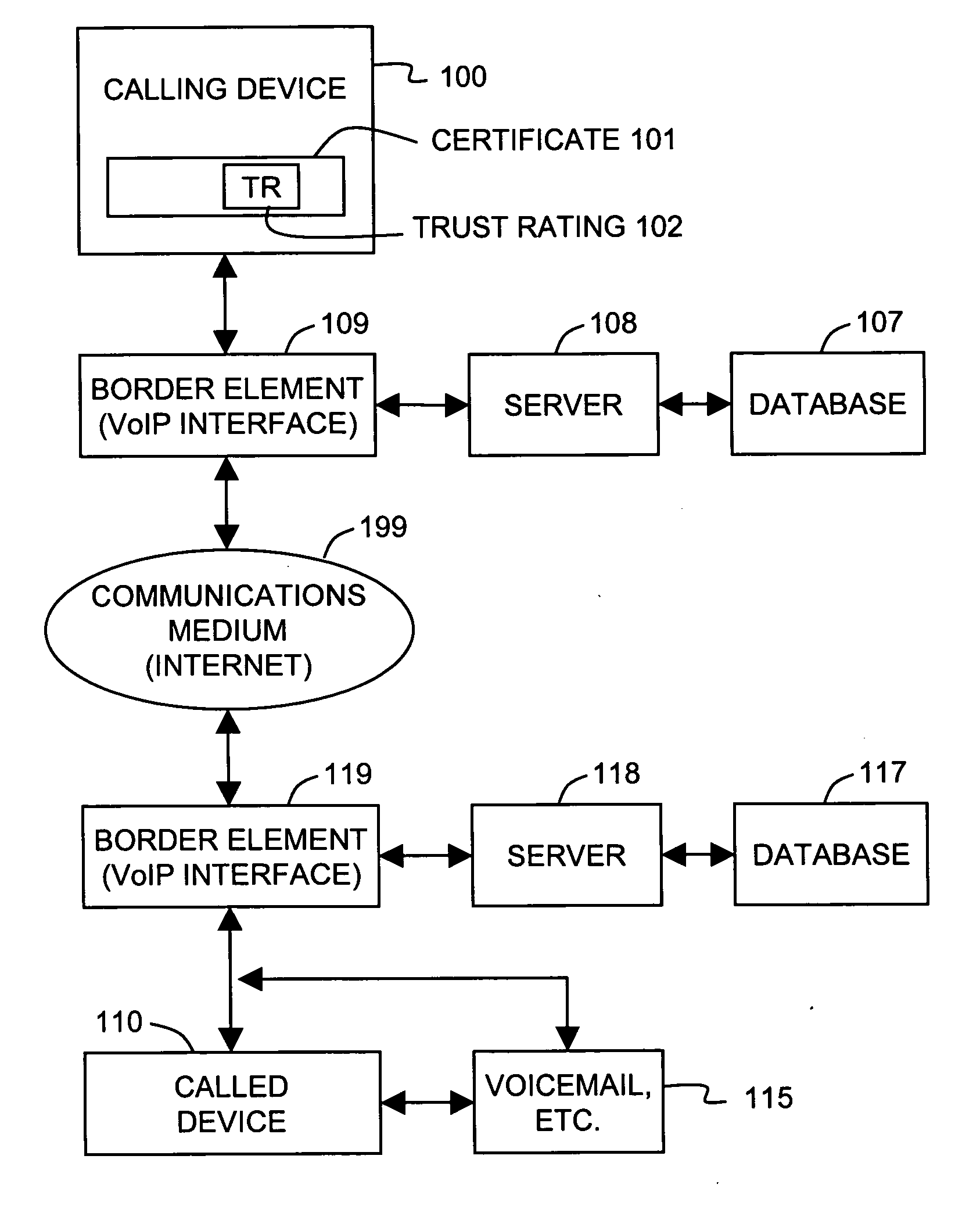
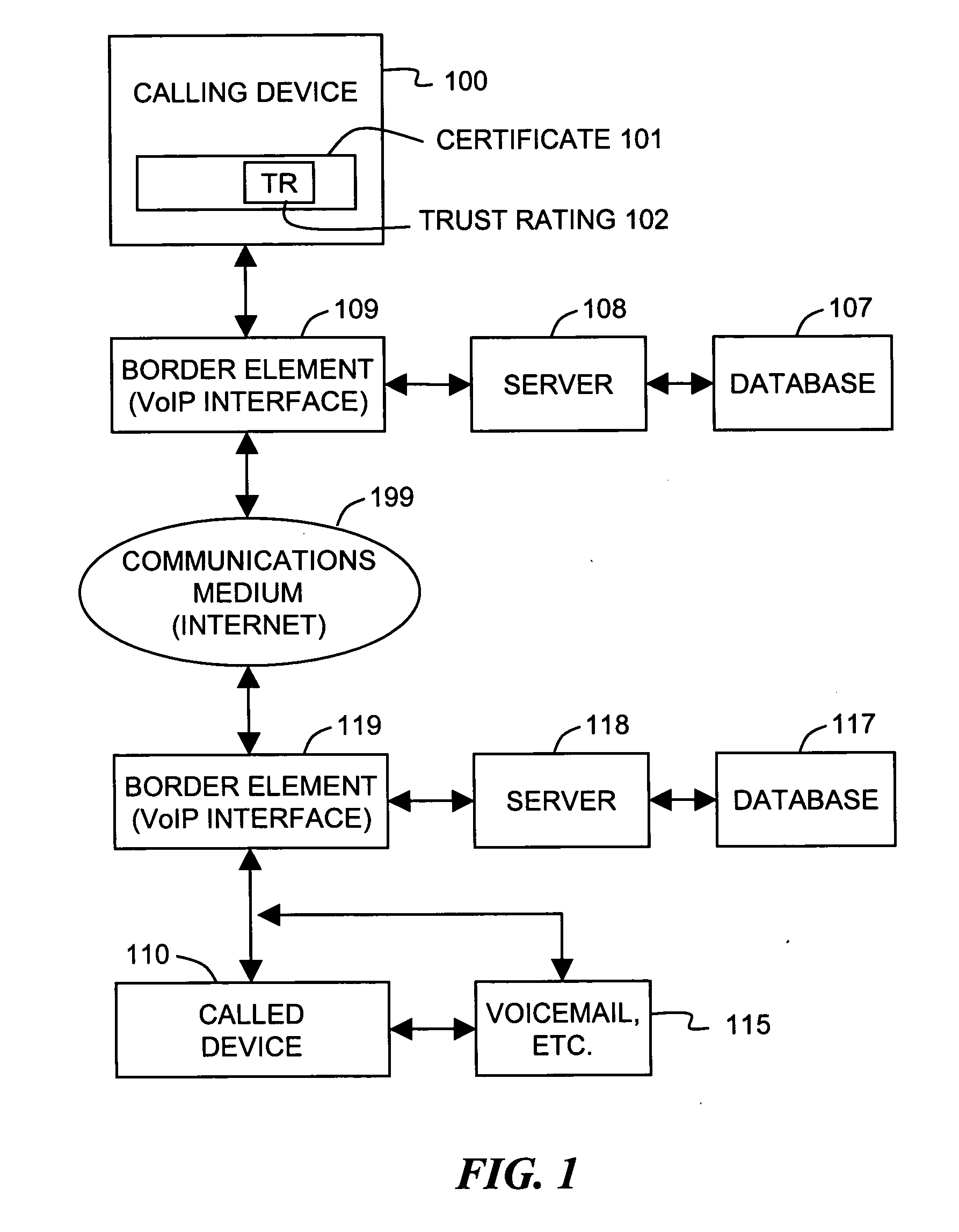
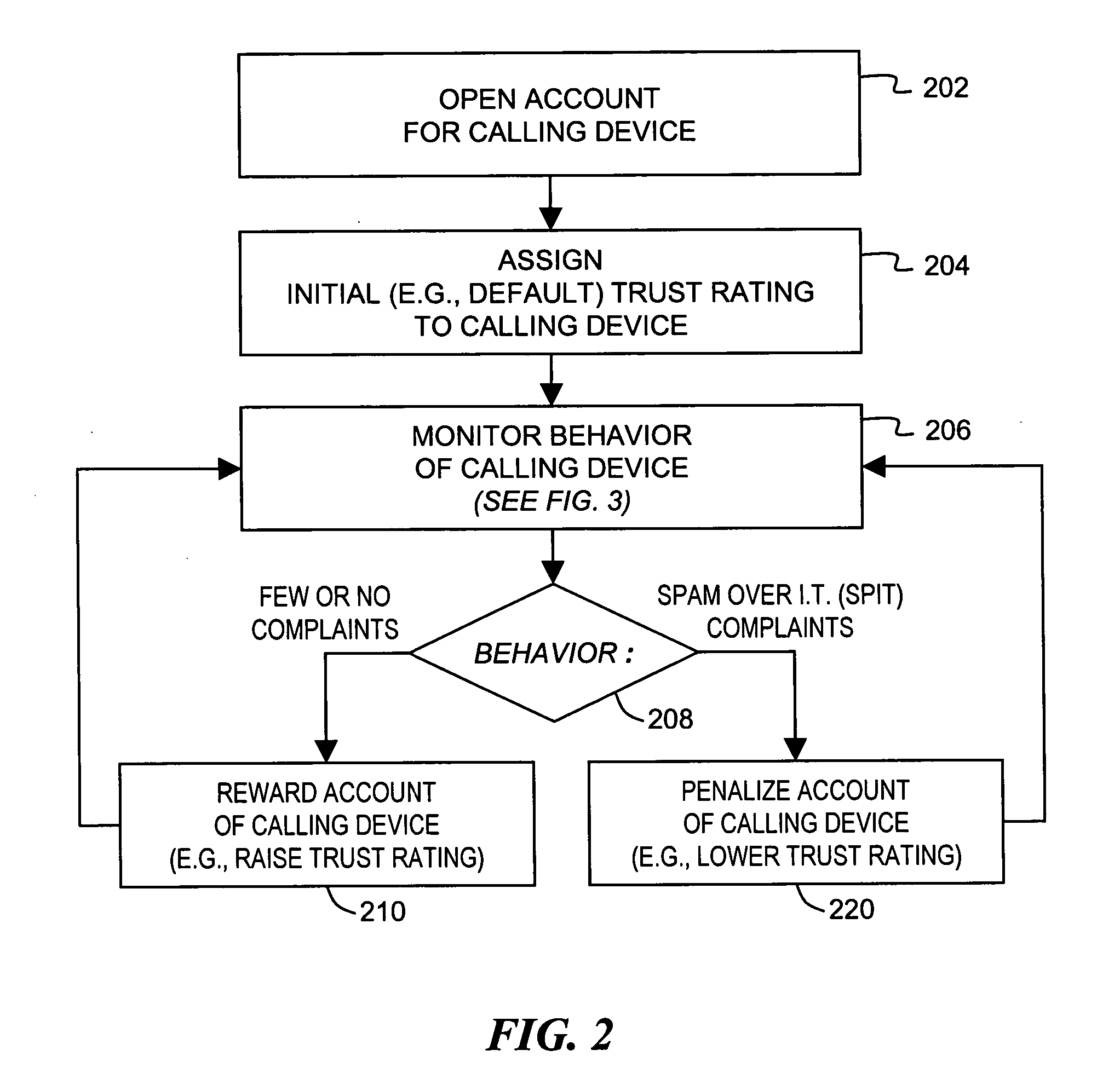
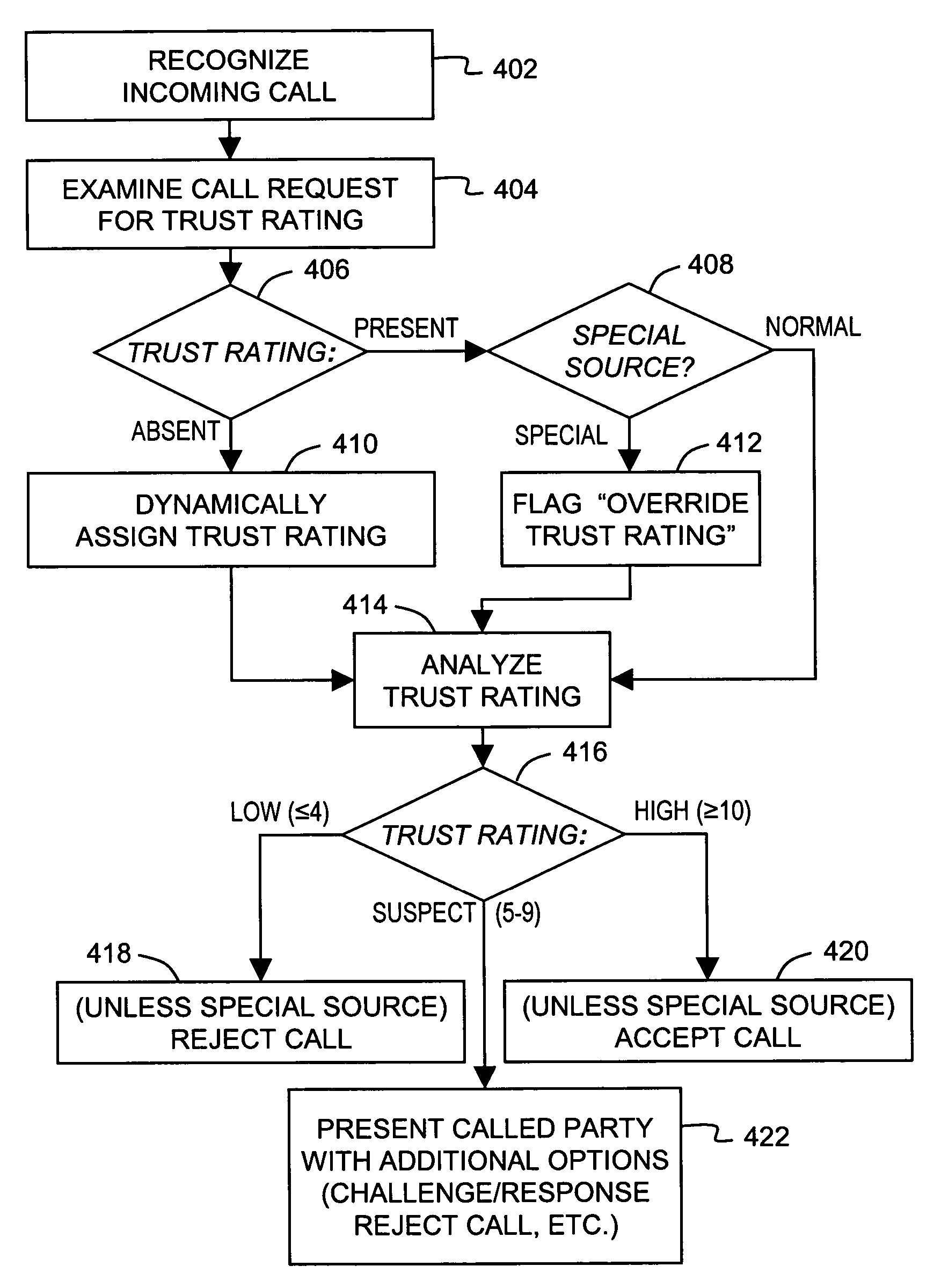
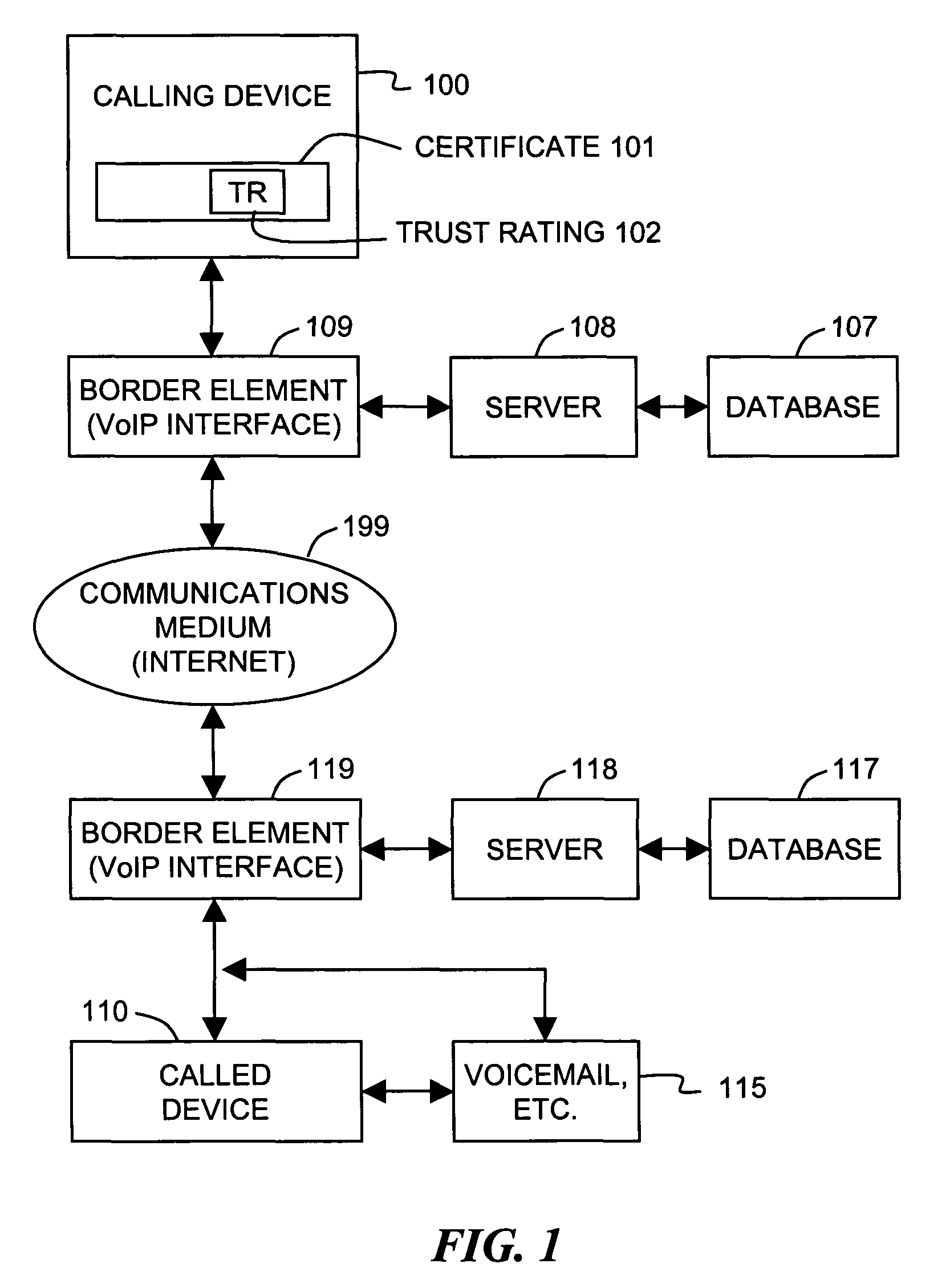
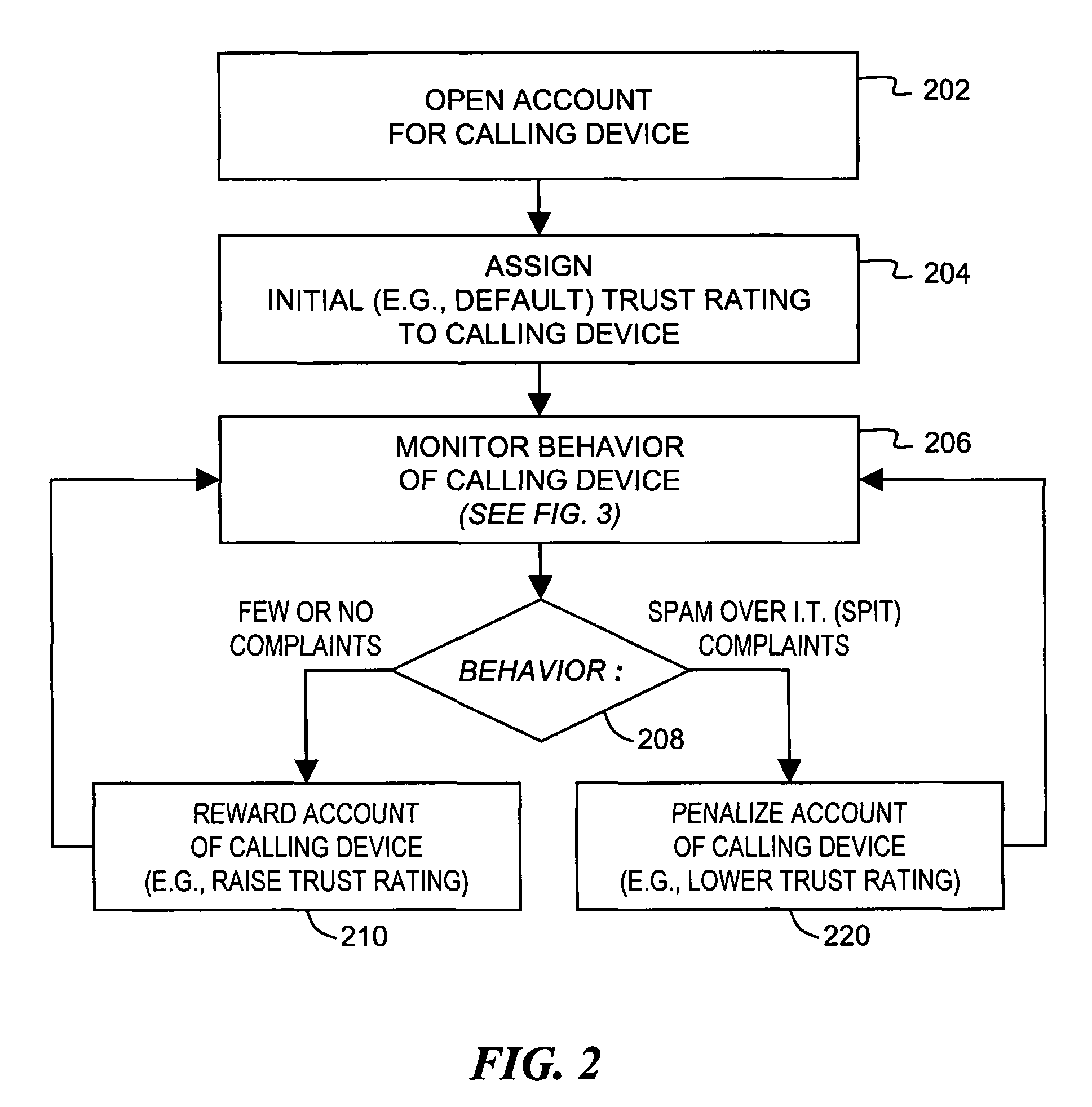
Trust ratings are embedded in certificates of calling devices in a Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) communications system. A method of managing trust ratings involves automatically accumulating complaints concerning VoIP calls initiated from calling devices, and comparing respective quantities of accumulated complaints associated with each calling device. When a quantity of accumulated complaints associated with a given calling device exceeds a given threshold, a trust rating of the given calling device is reduced. In subsequent VoIP calls the given calling device attempts to place, the reduced trust rating is included in the call request so that the subsequent calls are subject to more austere call screening operations than calls having the unreduced trust rating. Call recipients thus affect the calling device's trust rating simply by entering complaints associated with received calls. The method effectively combats spam over Internet telephony (SPIT) through participation of called parties.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
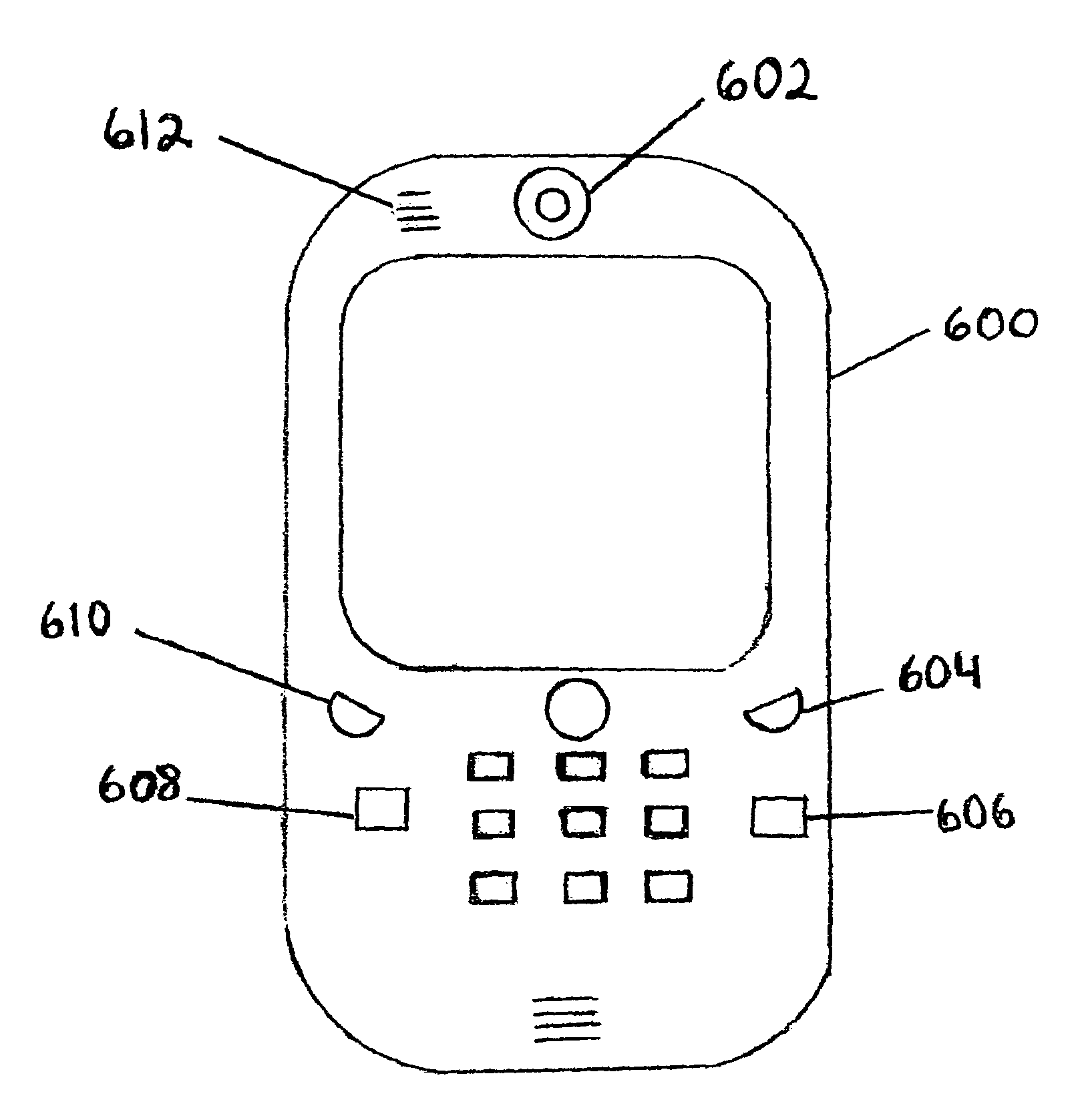
Incoming call screening, control and prioritisation in a telephone device
ActiveUS20060182248A1Special service for subscribersAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingScreening callOperation mode
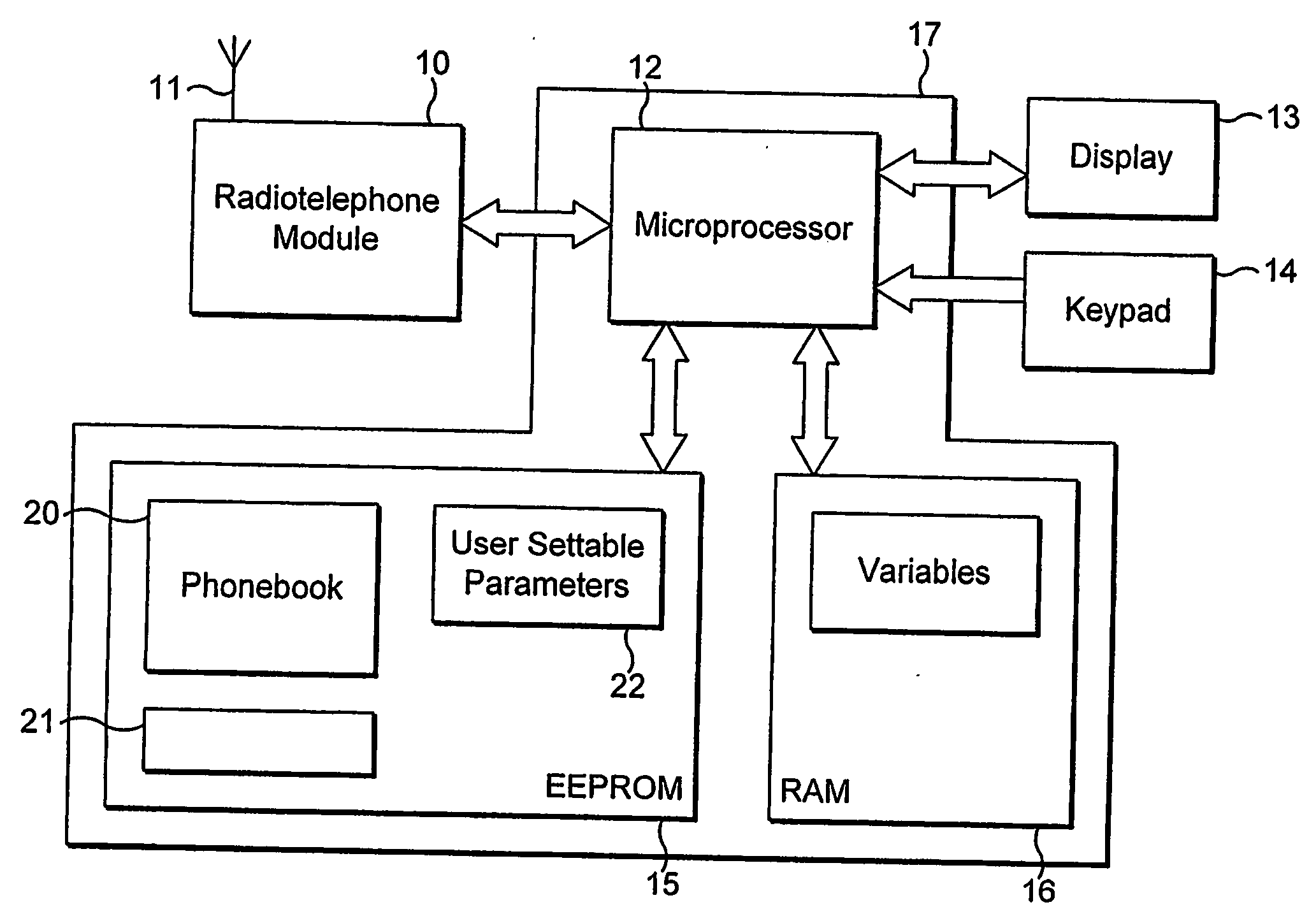
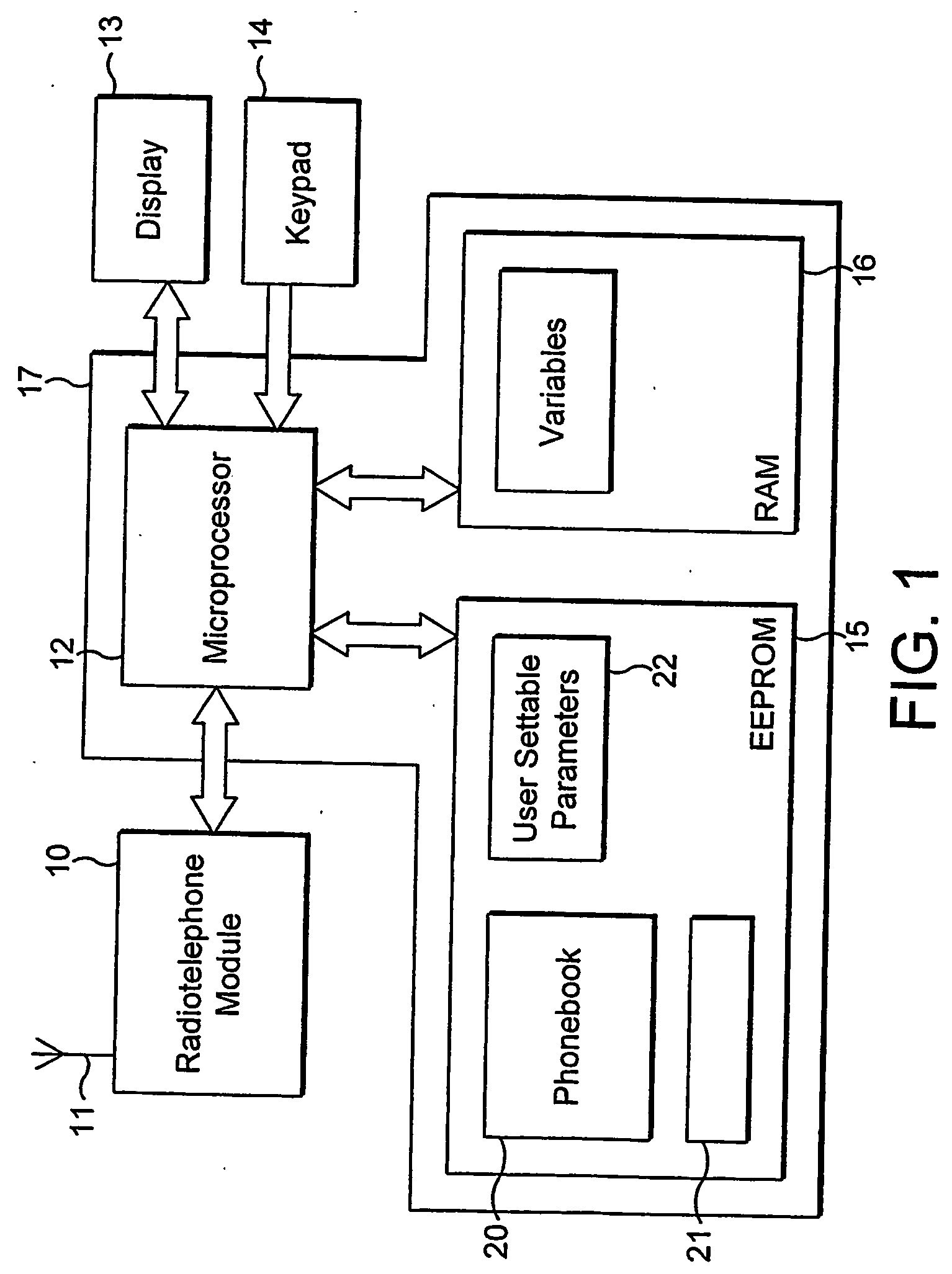
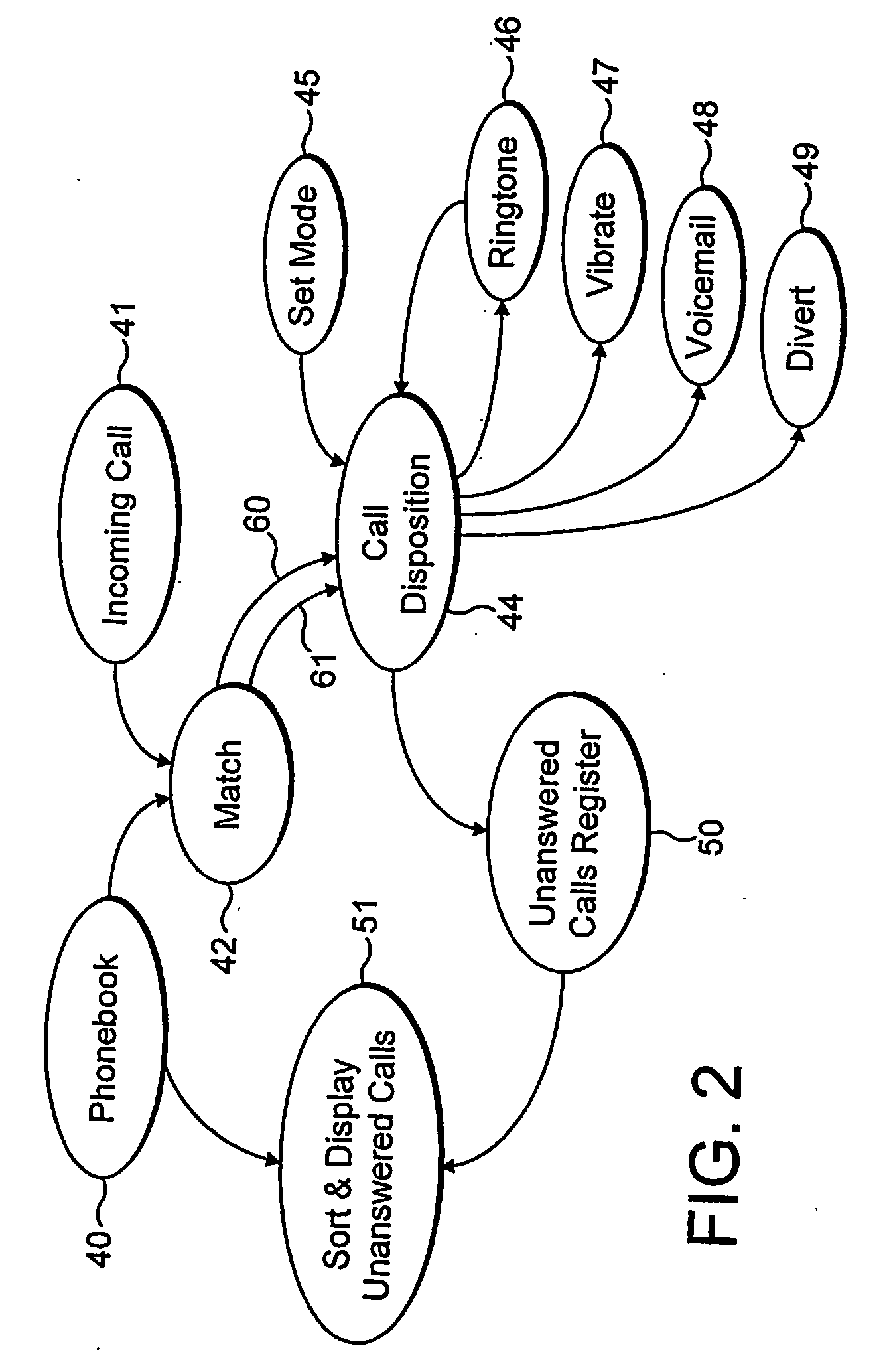
A circuit for a telephone such as a mobile radiotelephone. The circuit has a memory for storing phonebook items and for storing group attributes associated with phonebook items, a connection to a radiotelephone receiver for receiving telephone calls and calling party identifications, and a controller for selecting the disposition of received calls. An operating mode is selected (45) from a plurality of operating modes, e.g. “Personal”, “emergency”, “personal-plus-emergency”, “all calls”, “no calls”, etc. A received calling party identification is compared (42) with a phonebook item, and a disposition for a received call (46, 47, 48, 49) is selected dependent on a group attribute for that phonebook item and a present opersting mode.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
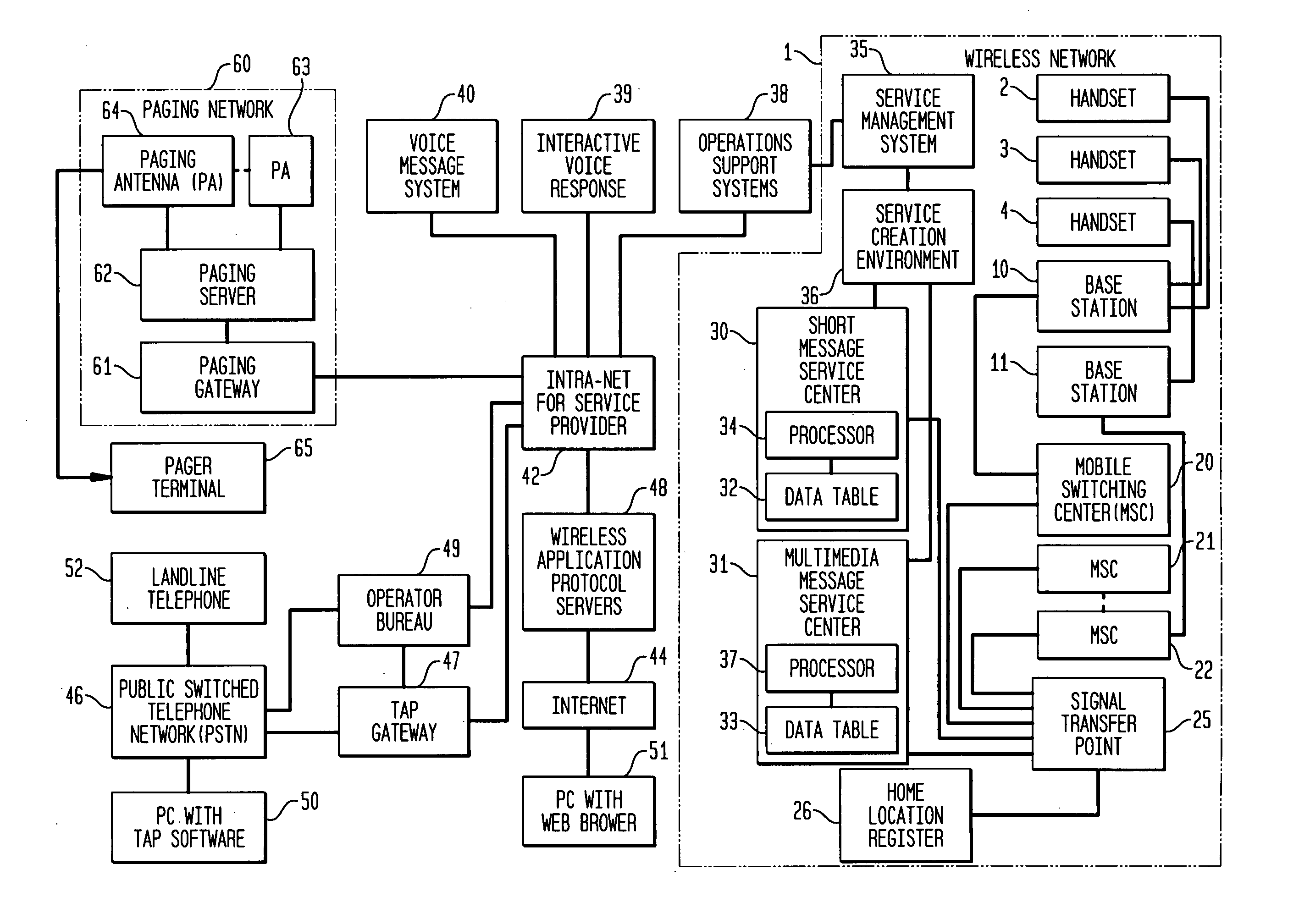
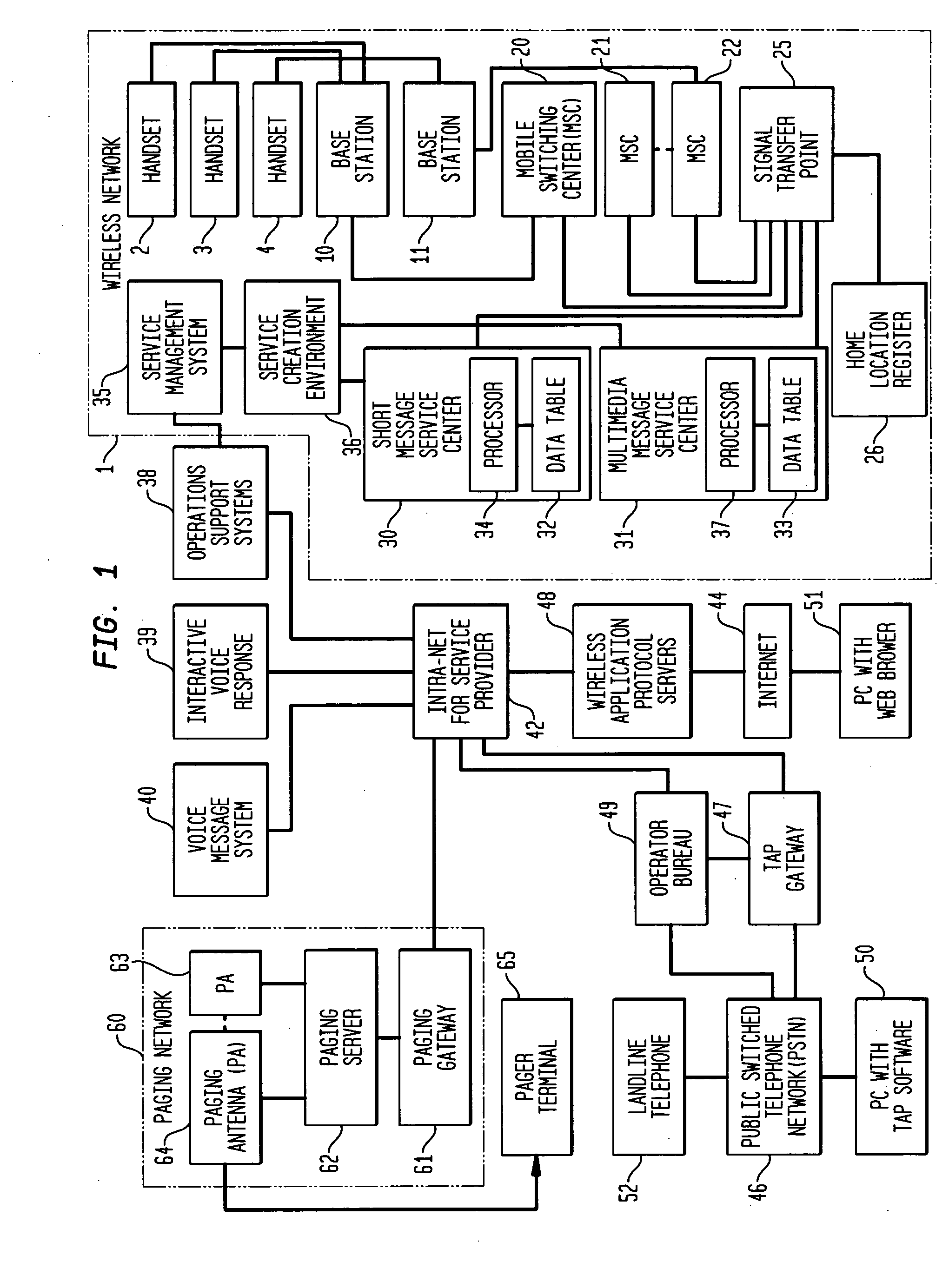
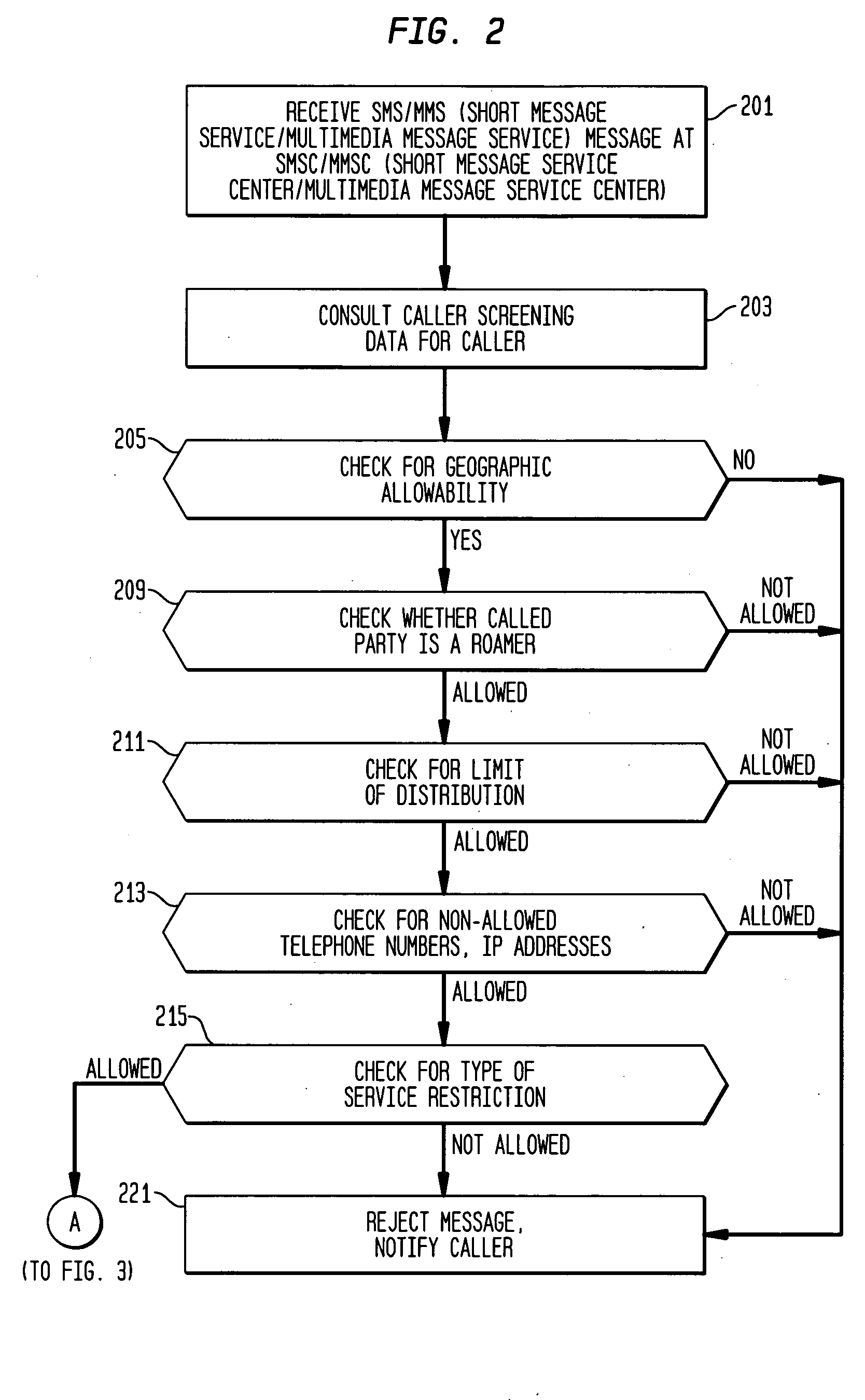
Short message service (SMS), multimedia message service (MMS), call screening and filtering
InactiveUS20050186974A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsAutomatic exchangesTelecommunications networkScreening call
A method and apparatus for screening short message service (SMS) and / or multimedia message service (MMS) calls. An originator of an SMS / MMS call is checked for authorization to send the type of message (e.g., to roamers, to non-local destinations, broadcast messages). If the caller is found to be authorized then the called party or parties are checked to determine whether they are screening calls of the type and from the source of the caller. In either case, if the telecommunications network determines that the call should be blocked the caller is notified and the call is not completed. Advantageously, this arrangement sharply reduces the amount of SPAM delivered by SMS / MMS service.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
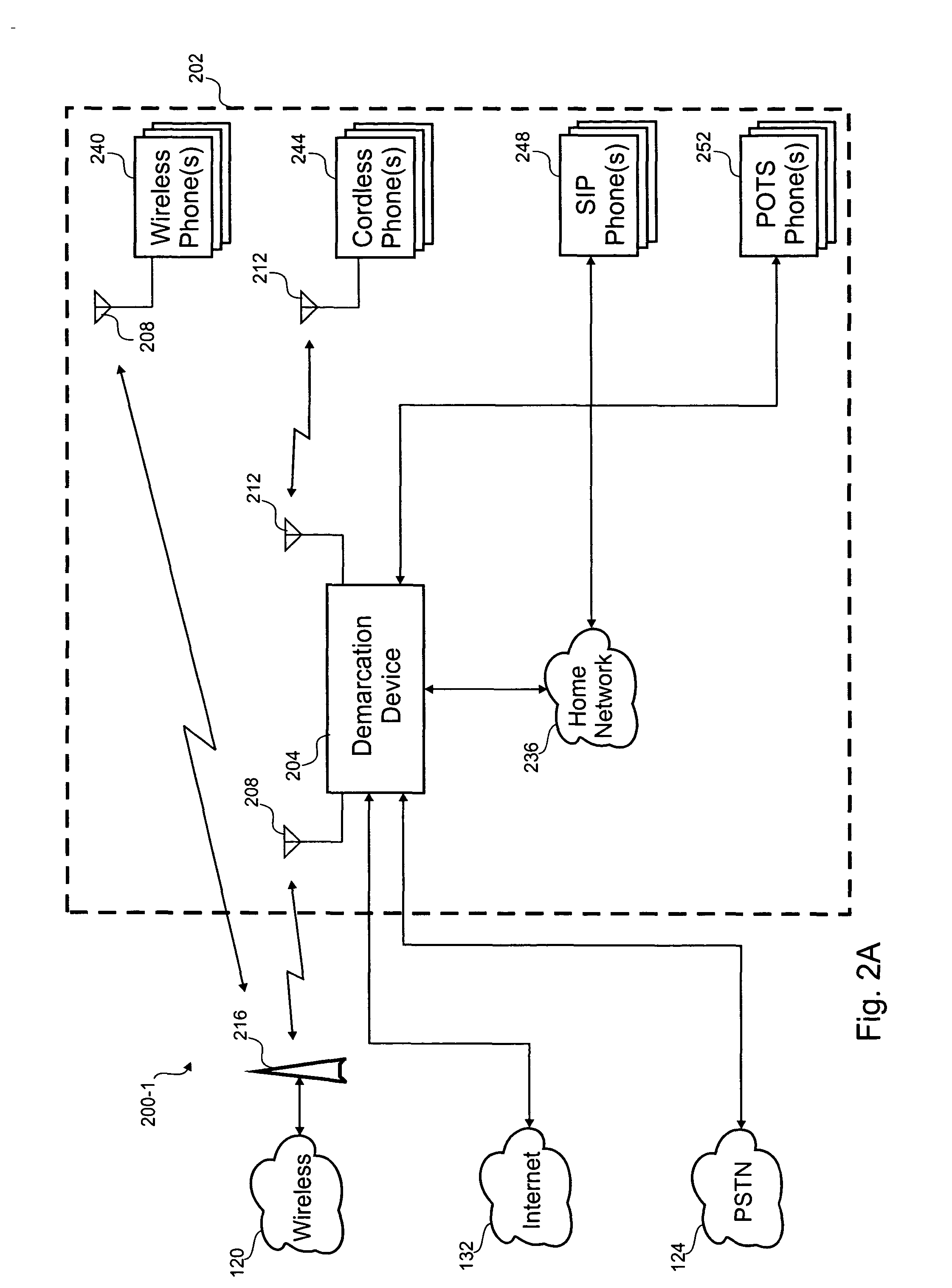
Advanced call screening appliance
ActiveUS20050041787A1Hybrid switching systemsSpecial service for subscribersCommunication interfaceScreening call
According to the invention, a network interface device for processing a telephone call is disclosed. The network interface device includes a first and second communication interfaces, a telephone switch and a controller. The first communication interface is coupled to at least one of a wireless phone network, a public switched telephone network (PSTN), and a voice over Internet protocol (VOIP) network. The first communication interface receives the telephone call from any of a number of callers that are remote to the network interface device. The second communication interface coupled to one or more phones at a user location where the one or more phones are associated with a telephone number that any of the callers can use to call the one or more phones. The telephone switch is coupled to both of the first communication interface and second communication interface and optionally routes an incoming phone call to the second communication interface if one or more access control rules permit routing the incoming phone call to the second communication interface. The controller analyzes the one or more access control rules and either routes the incoming phone call from the first communication interface to the second communication interface or prevents the incoming phone call from reaching the second communication interface. The one or more phones ring when the incoming call is routed to the second communication interface.
Owner:QWEST
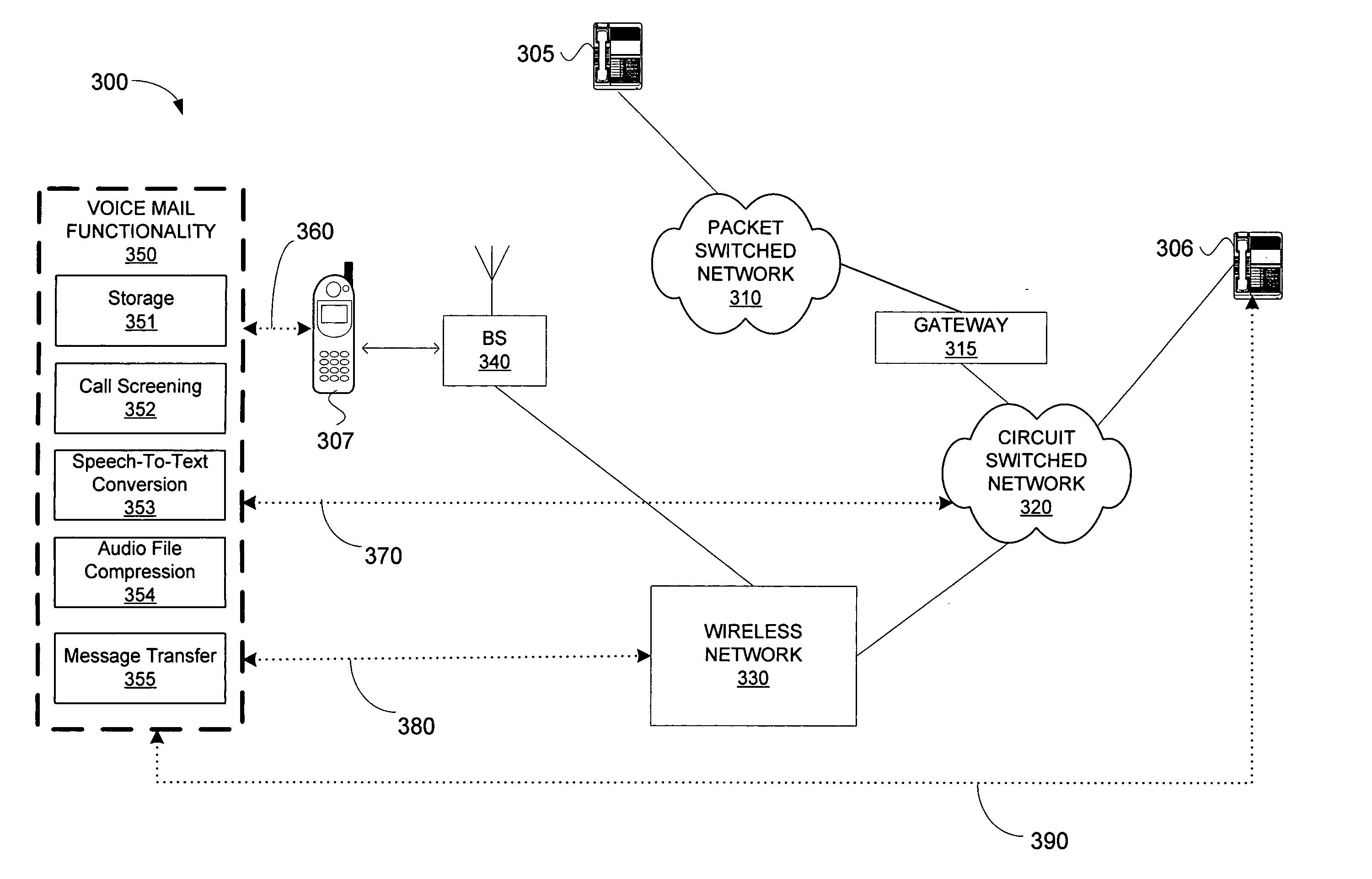
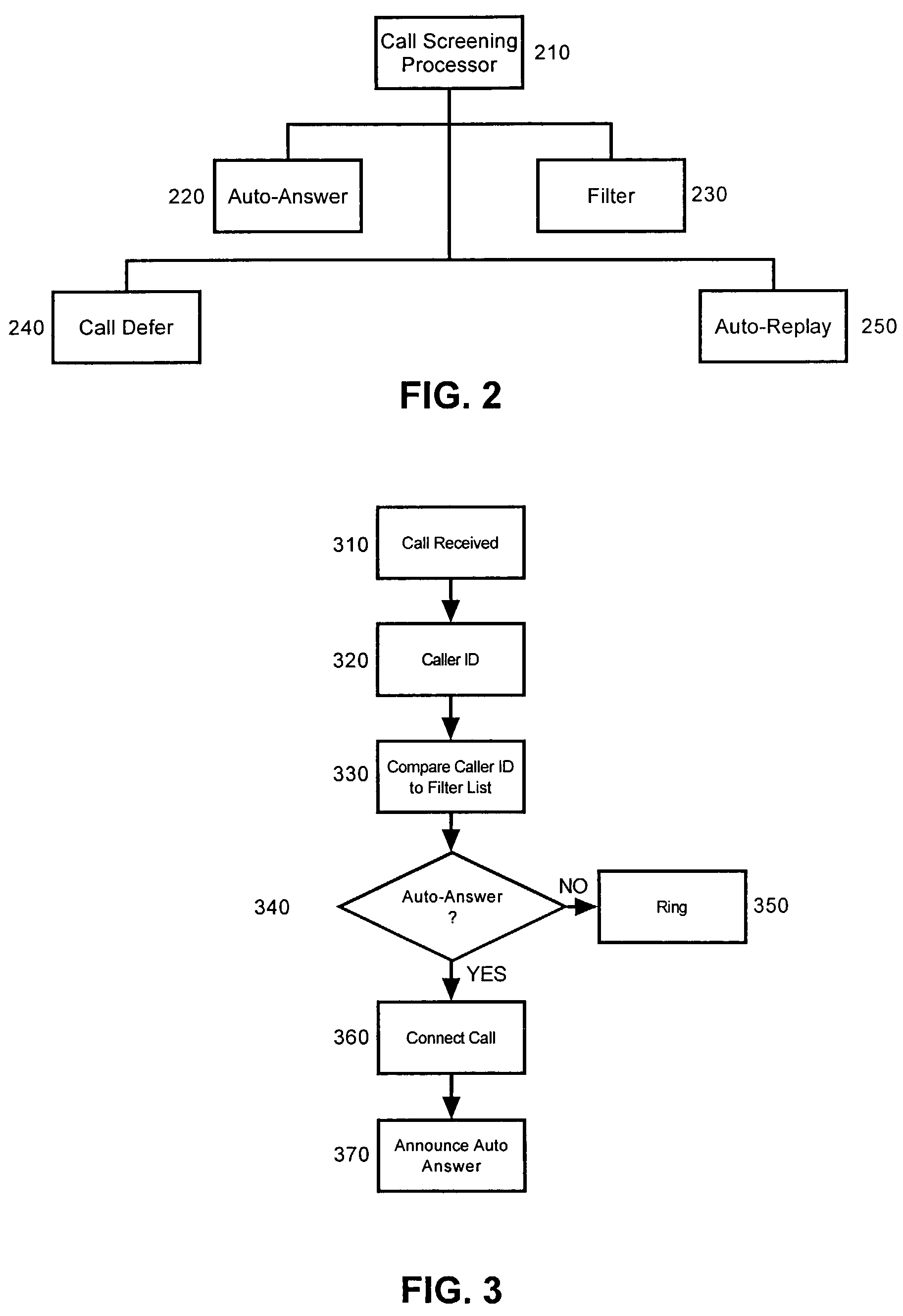
Method and system for screening calls during voicemail messaging
InactiveUS7035385B2Automatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingAutomatic exchangesScreening callSpeech sound
The present invention relates to systems and methods for monitoring and intercepting messages to a voicemail system connected to an AIN or WIN network for screening calls incoming to a landline or wireless telephone. After a call is forwarded to voicemail system, the called party is provided an opportunity to monitor a message as it is spoken into a voicemail system. The called party may intercept the message at any time during delivery of the message to answer the telephone call.
Owner:IBM CORP
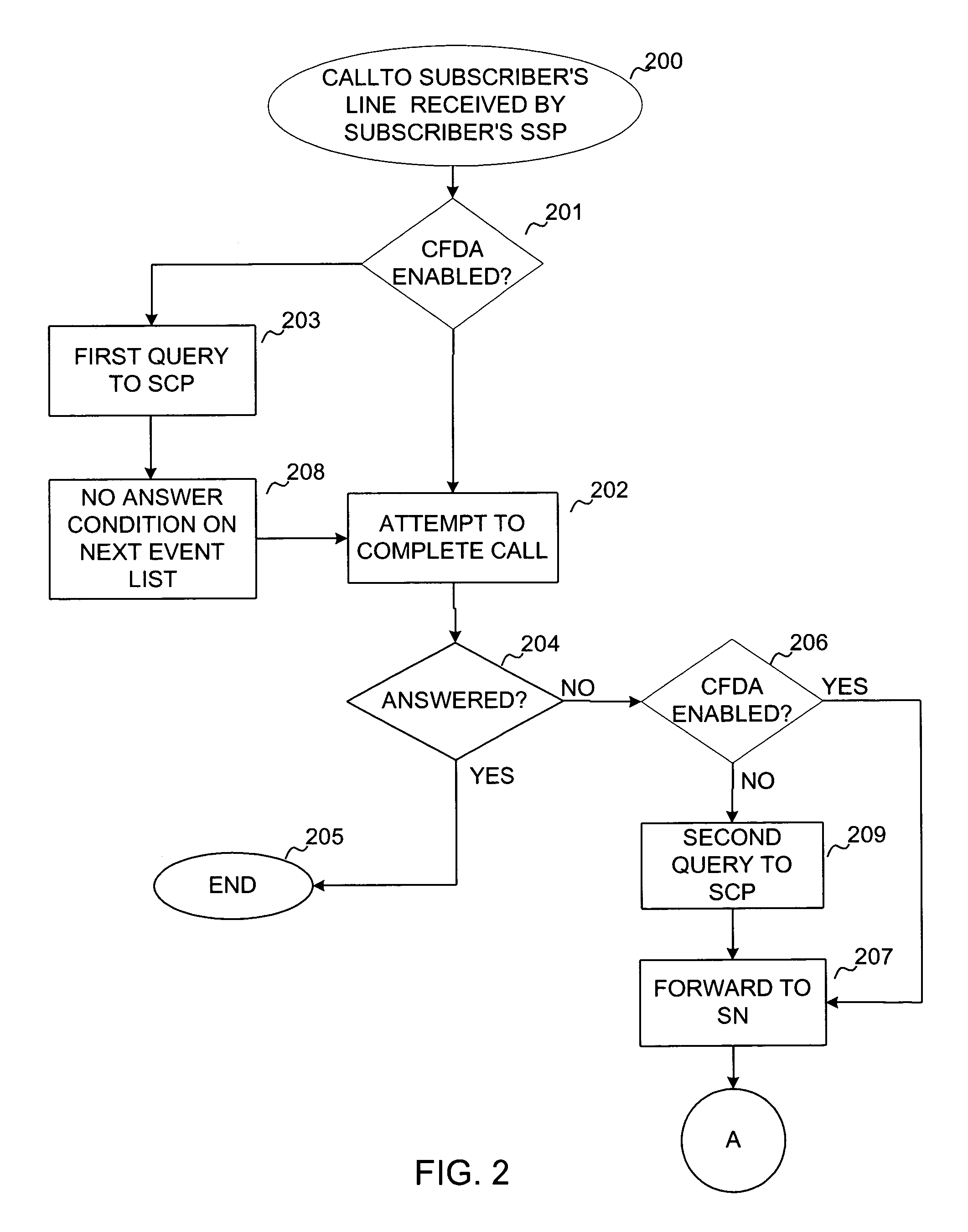
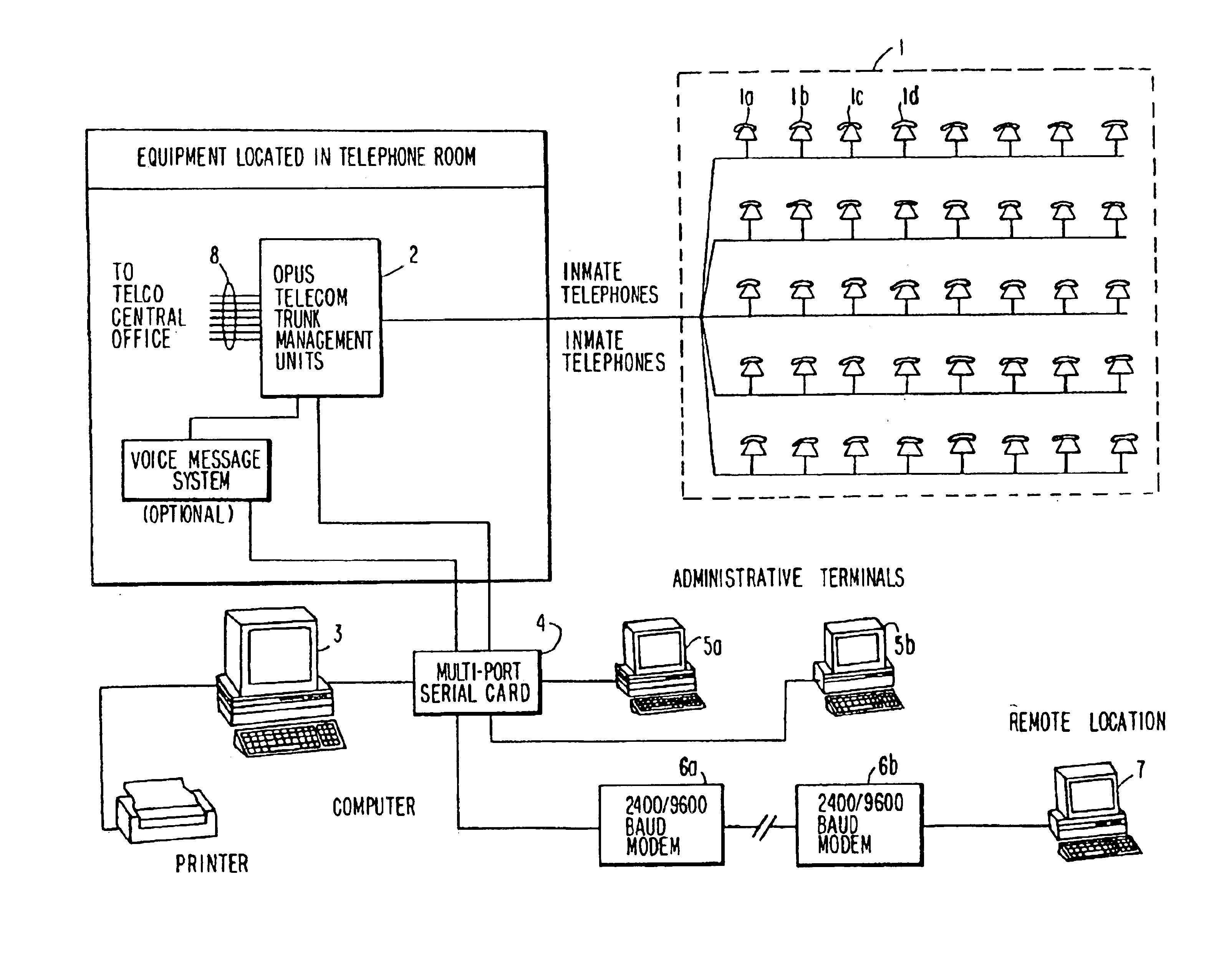
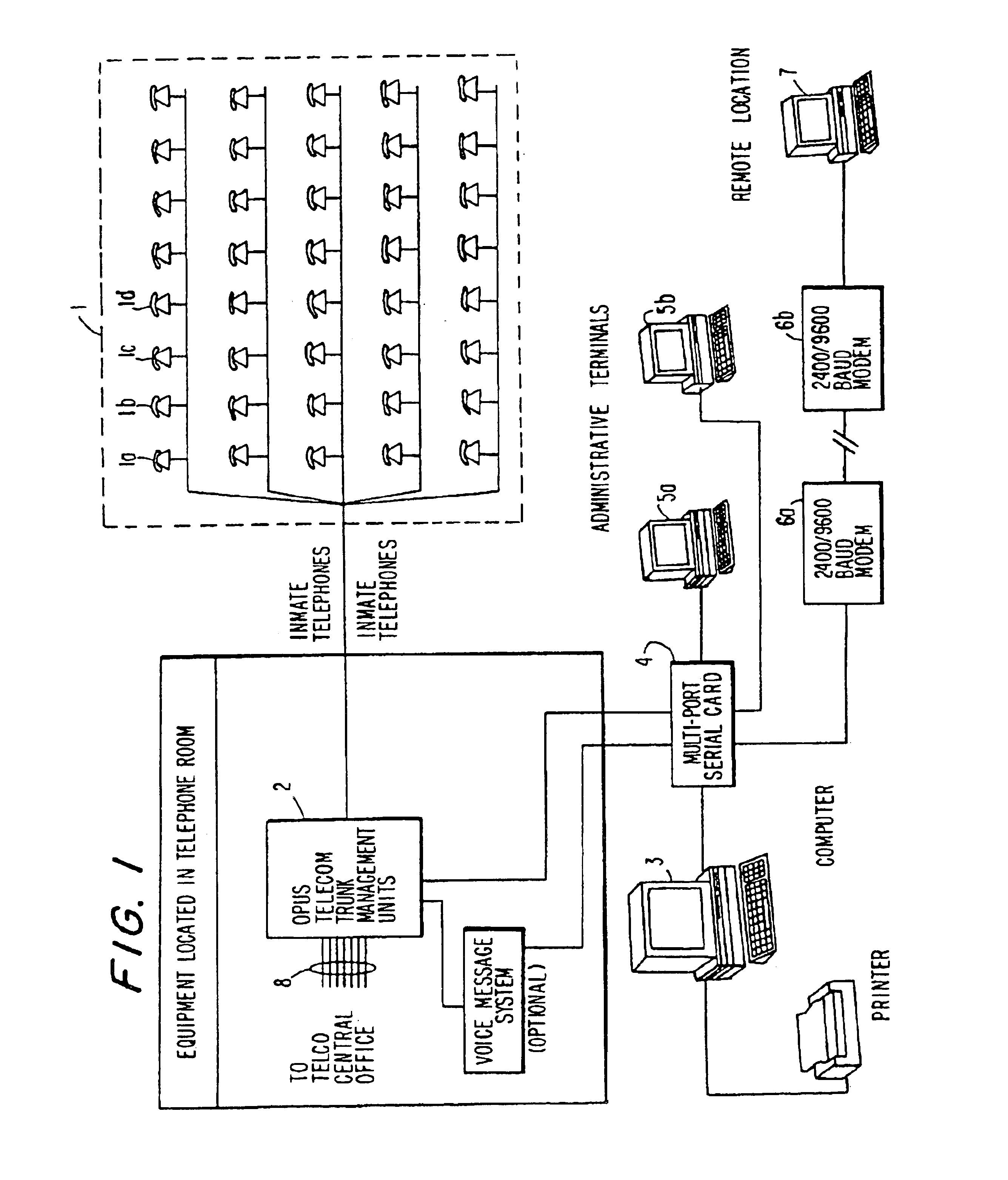
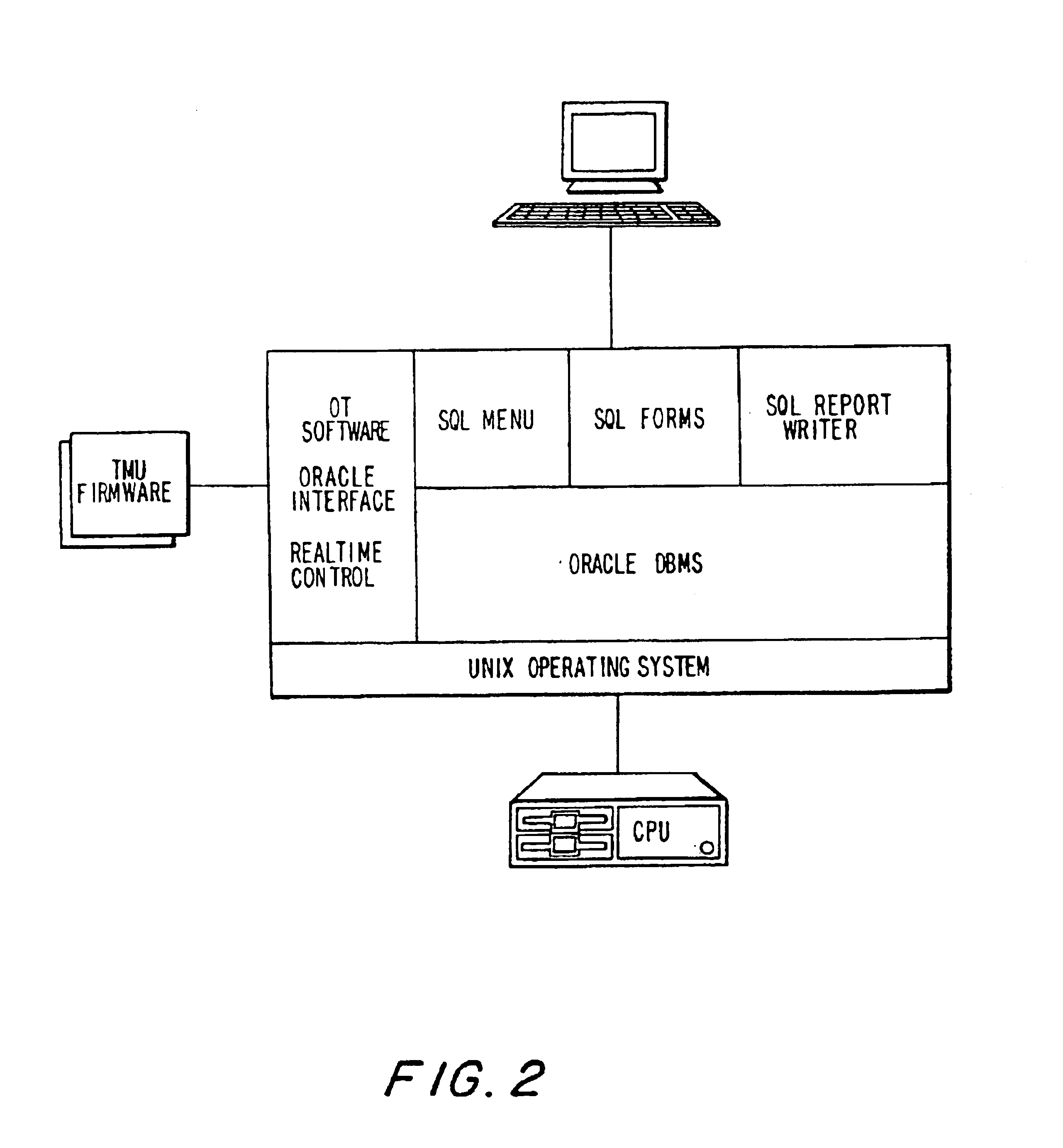
Computer-based method and apparatus for controlling, monitoring, recording and reporting telephone access
InactiveUS6920209B1Prevent PIN abuseImprove securityUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionSpecial service for subscribersManagement unitScreening call
A method and apparatus for managing institutional telephone activity utilizes a computer control unit to control a trunk management unit, which connects institutional telephones to outside telephone lines. The computer control unit contains a database for storing the calling privileges and restrictions of institutional users and for recording calling transactions made by the users. The computer control unit implements a prospective call screening feature whereby outside recipients of undesired calls from the institution may enter a code that directs the computer control unit to prohibit similar calls in the future.
Owner:SECURUS TECH +1
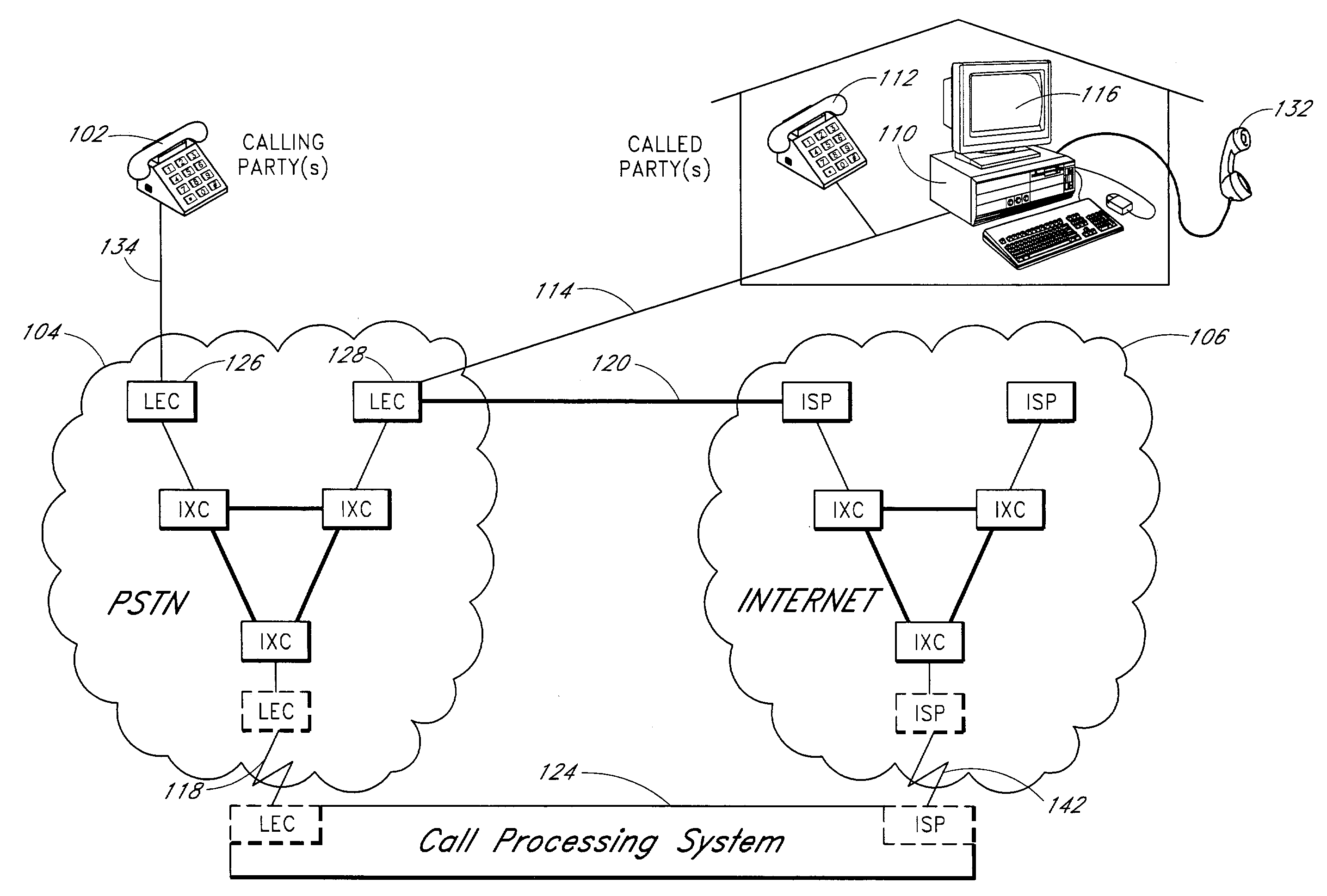
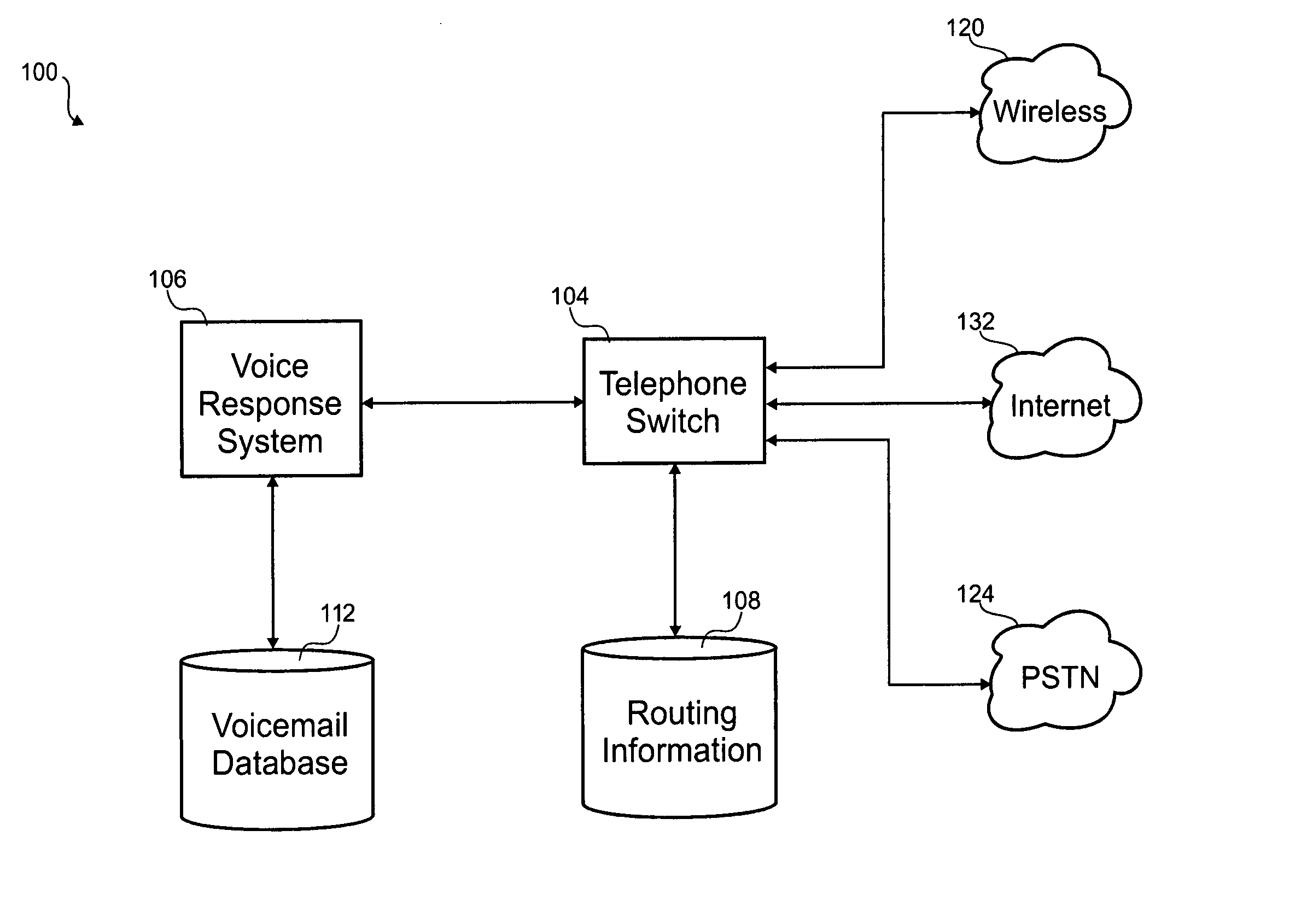
Method and apparatus for interfacing a public switched telephone network and an internet protocol network for multi-media communication
A real-time interface between the public switched telephone network (PSTN) and an Internet Protocol (IP) network provides voice to data and data to voice conversion between the PSTN and the IP network in a seamless process. The interface, a central communication network, performs Class 5 switching between the PSTN and the IP network, besides providing enhanced services. Receiving a call, the central communication network simultaneously routes the call to a plurality of pre-programmed numbers on the PSTN and on the IP network. The central communication network provides call screening, takes voice messages and converts them to e-mail messages, takes e-mail or facsimile messages and converts them to voice messages. Communication between a PSTN phone on a local PSTN, a computer hooked up to the IP network, a phone hooked up to the IP network by a gateway, a private branch exchange (PBX) on a local PSTN, a wireless communication system with pagers and / or cell phones hooked up to a local PSTN, and facsimile machines on a local PSTN, for example, is provided by the central communication network. Through the central communication network, a computer hooked up to the IP network can exchange voice messages and facsimile messages with a PSTN connected device and conduct conference calling with a plurality of PSTN devices.
Owner:CENT ONE
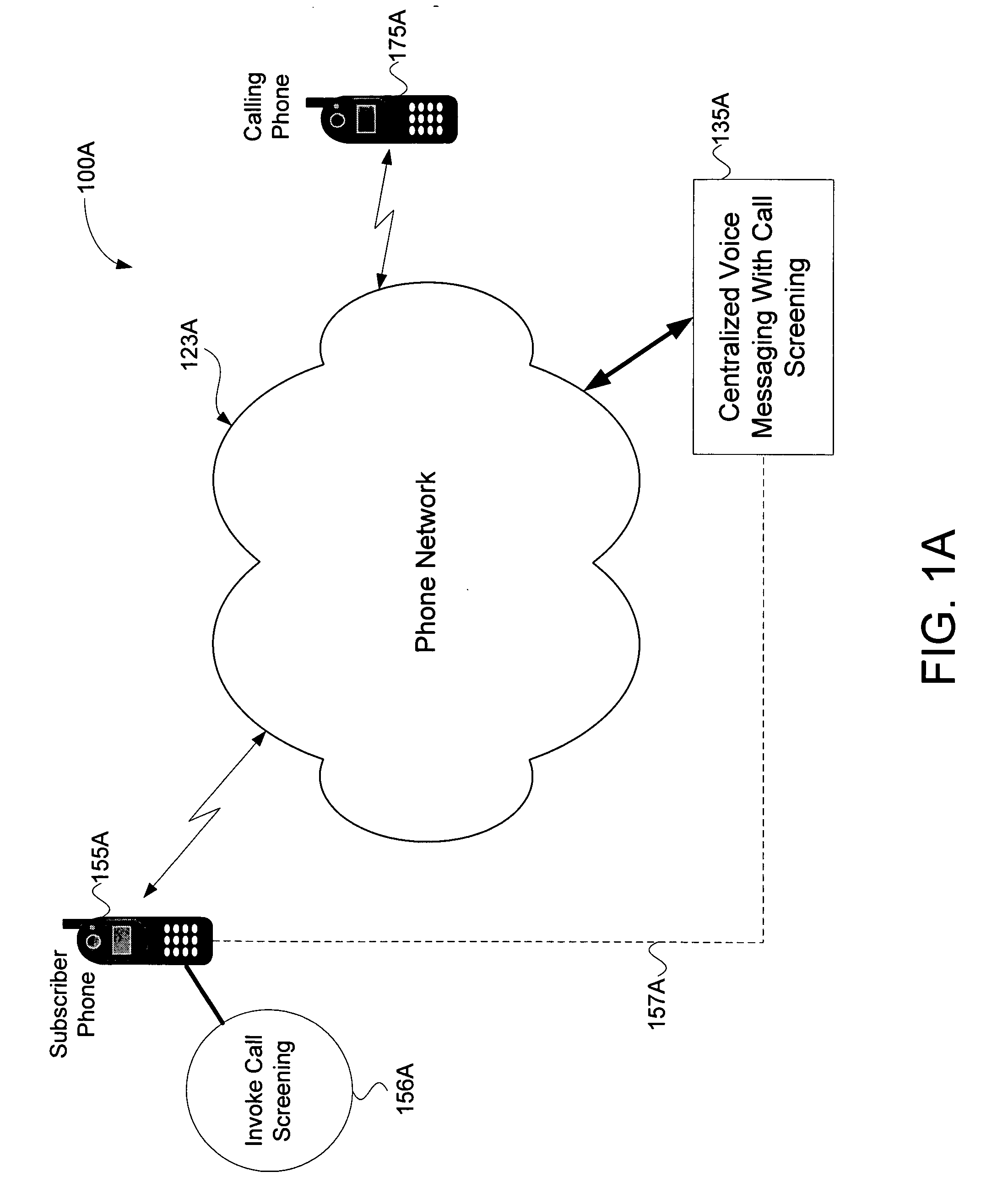
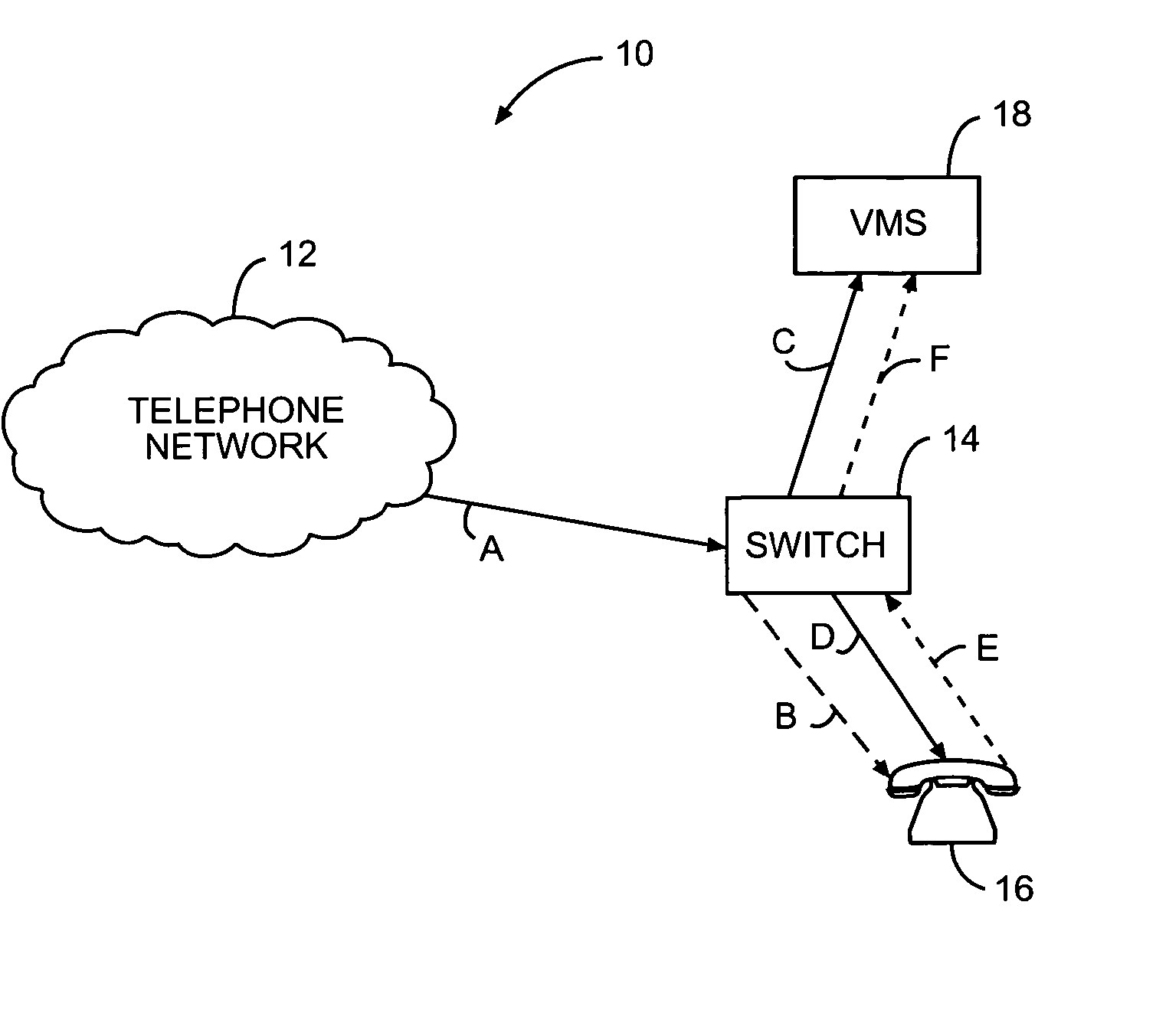
Method for call screening in a voice mail system
InactiveUS20050201534A1Automatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingAutomatic exchangesScreening callSpeech sound
Methods of call screening in a voice mail system are provided. In one embodiment, the method may comprise, for example, one or more of the following: receiving an indication of an incoming call for a voice mail system subscriber, the incoming call originating from a caller's telephone to a subscriber's telephone; indicating by the subscriber that call screening of the incoming call is desired; routing the incoming call to be recorded in a subscriber's voice mail box as a caller's voice message; and initiating call screening of the caller's voice message by establishing a three-way connection between the caller's telephone, the subscriber's telephone, and the centralized voice mail system, the subscriber's telephone being in a “mute” mode.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Session initiation protocol enabled set-top device
InactiveUS7024461B1Substations coupling interface circuitsMultiple digital computer combinationsSession Initiation ProtocolRemote control
A method and apparatus for handling subscriber services from different sources without requiring interaction with different devices. The present invention also provides a method and apparatus for receiving multimedia services using session initiation protocol (SIP) messages received from a source, such as a server on a network. In one embodiment, a set-top device is provided in which a SIP control is provided to register a subscriber with a server using SIP messages. A connection to a network, such as the Internet, is provided to communicate with the server. The set-top device is placed in line with the audio and video source to control audio and video streams presented to the subscriber. The set-top device is also configured to receive voice calls from a public switched telephone network (PSTN). Further, the set-top device includes a remote control mechanism, such as an infrared (IR) transmitter and receiver to receive input from the subscriber and to control other devices using IR signals. Also, subscriber services customized for a particular subscriber may be directed to the subscriber at a location when the subscriber registers with the server through a set-top device at that location using SIP. Services, such as, for example, call screening, channel guides, video on demand, and Web browsing are provided through the set-top device and messaging with a server using SIP messages.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Methods and systems for preemptive rejection of calls
ActiveUS20050053206A1Automatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingAutomatic exchangesTelecommunicationsScreening call
Methods and systems for screening a call are disclosed. Methods and systems consistent with the present invention screen calls. A first server receives information pertaining to a call to a user from a calling party. The first server then determines whether a real-time call management function is enabled for the user and determines whether a calling party number associated with the calling party is valid when the real-time call management function is not enabled. A call screening function is performed when the calling party number is invalid. The first server provides a notification of the call to a device associated with the user when the real-time call management function is enabled. A second server initiates the call screening function when the user selects a call screening option included in the notification.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
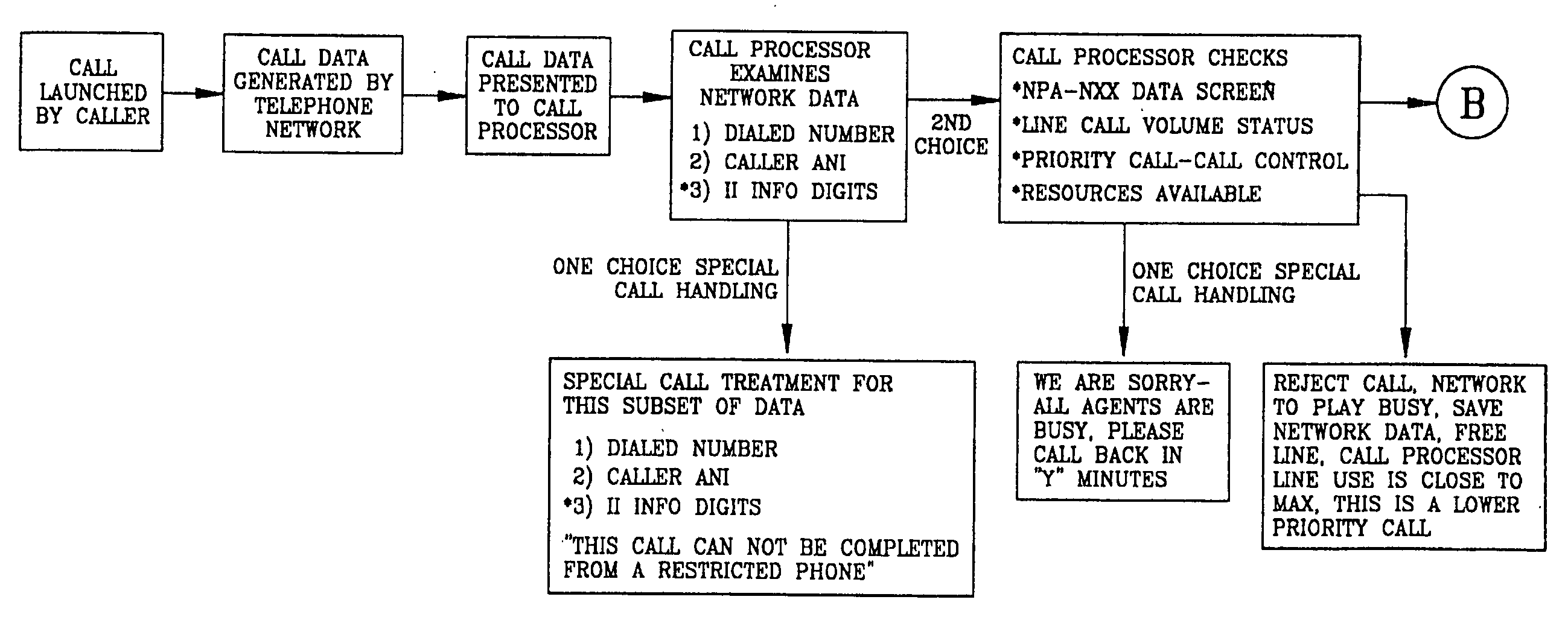
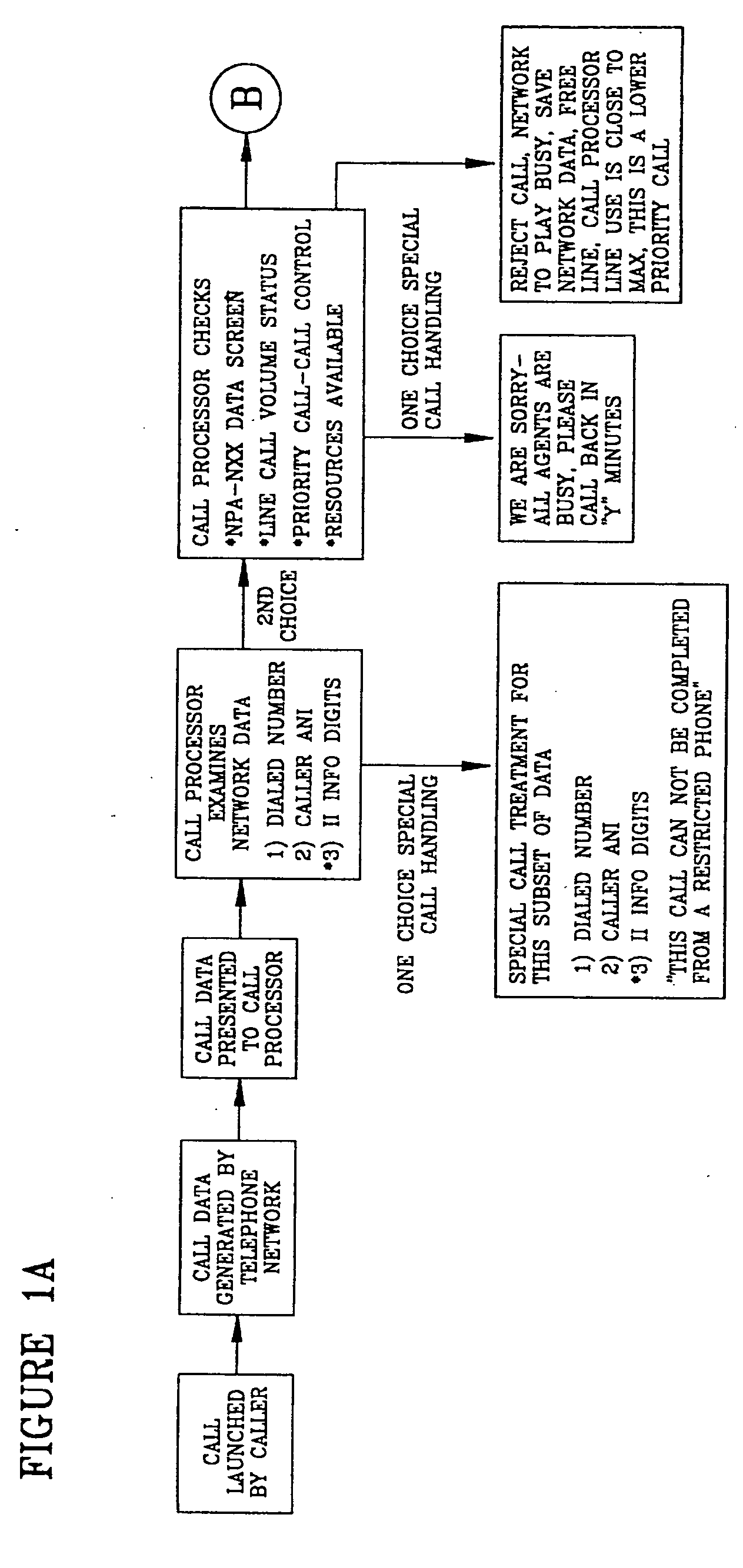
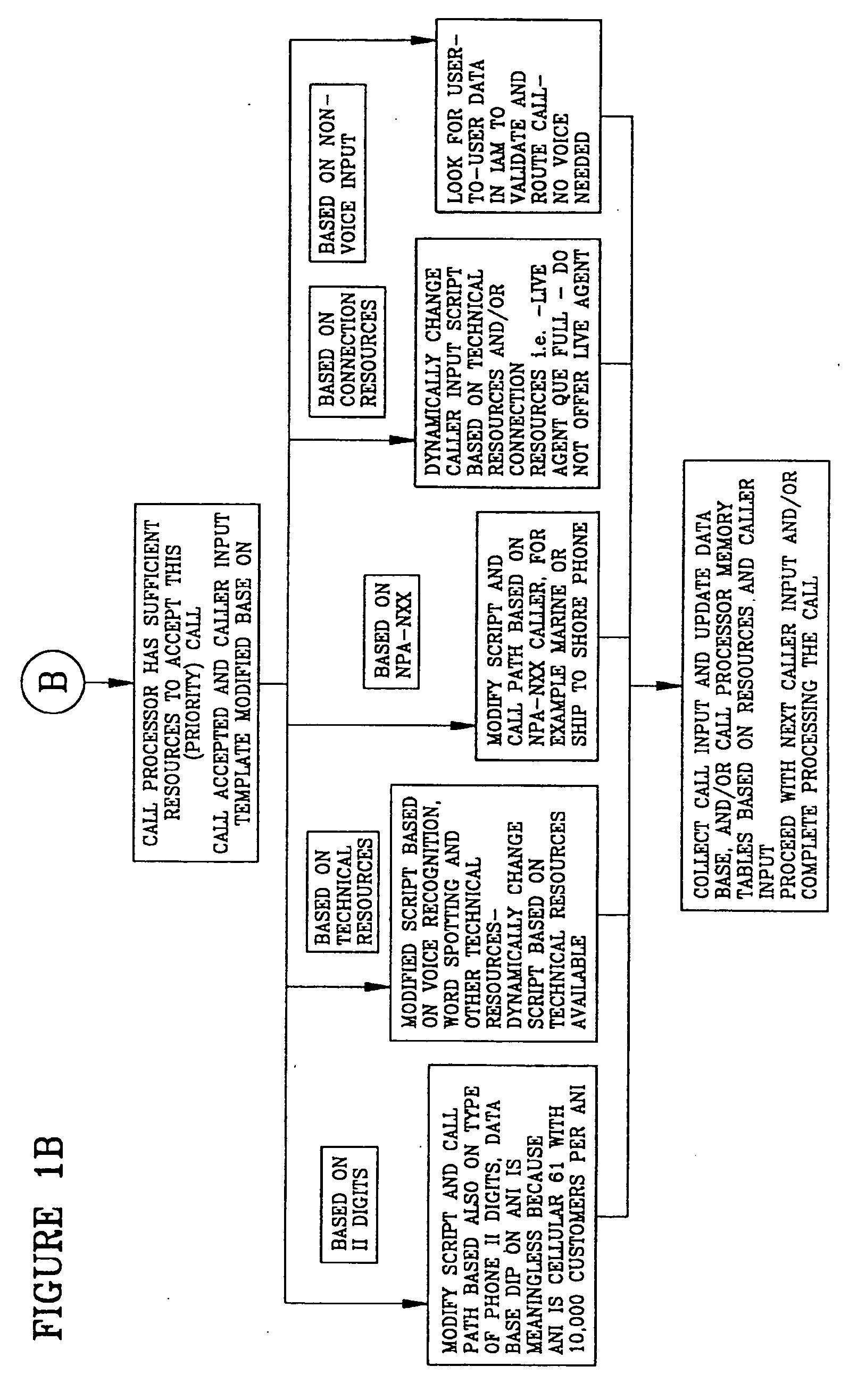
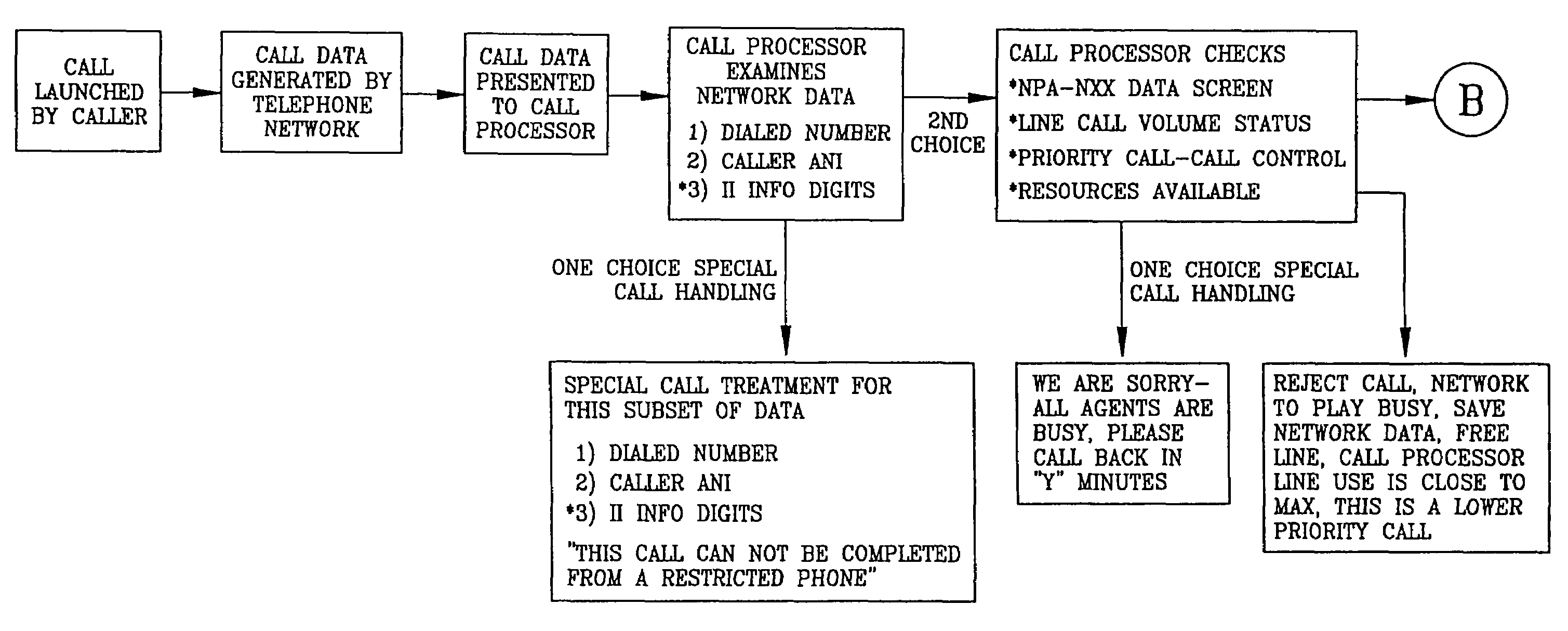
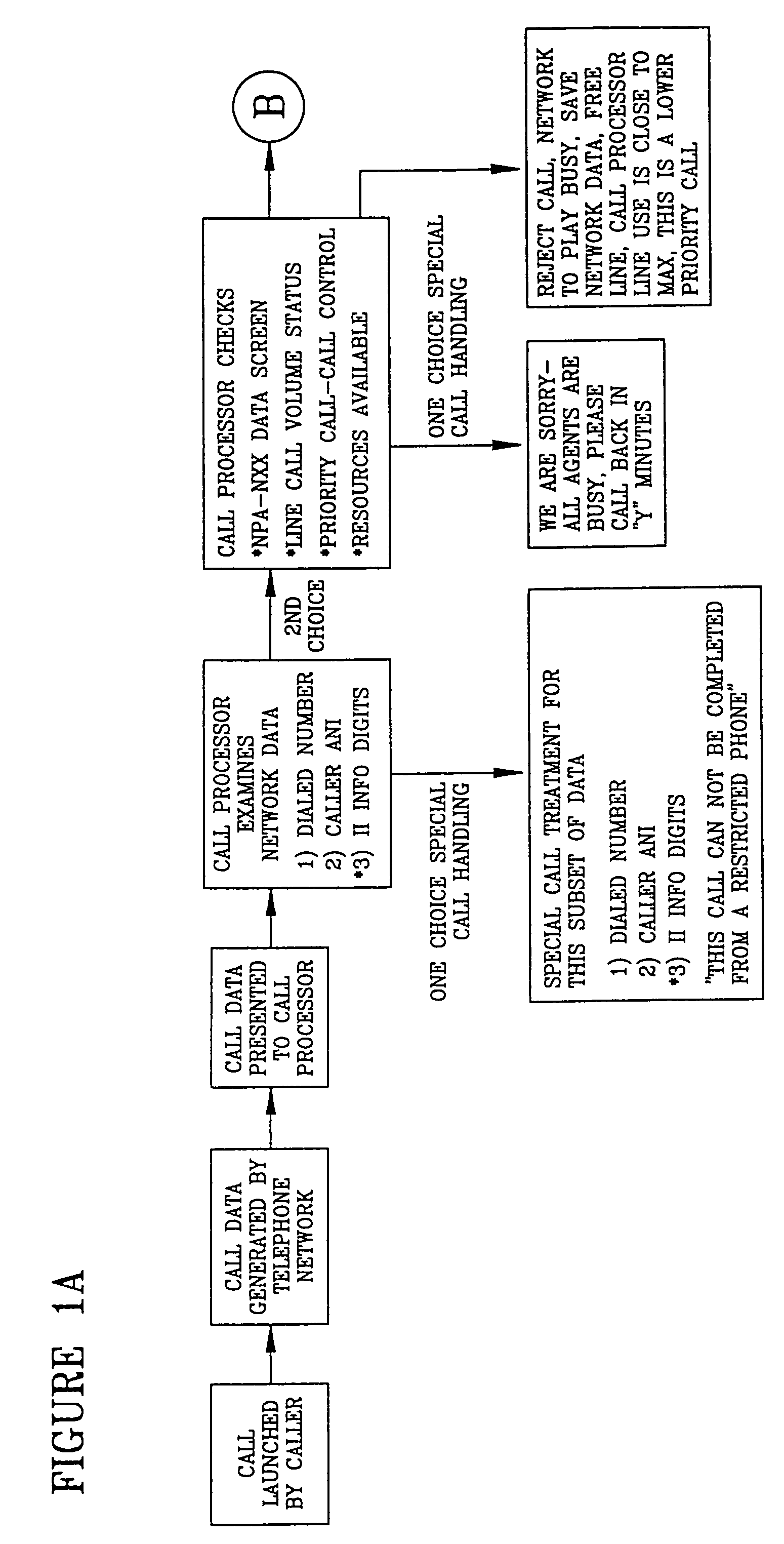
Call processing system with call screening
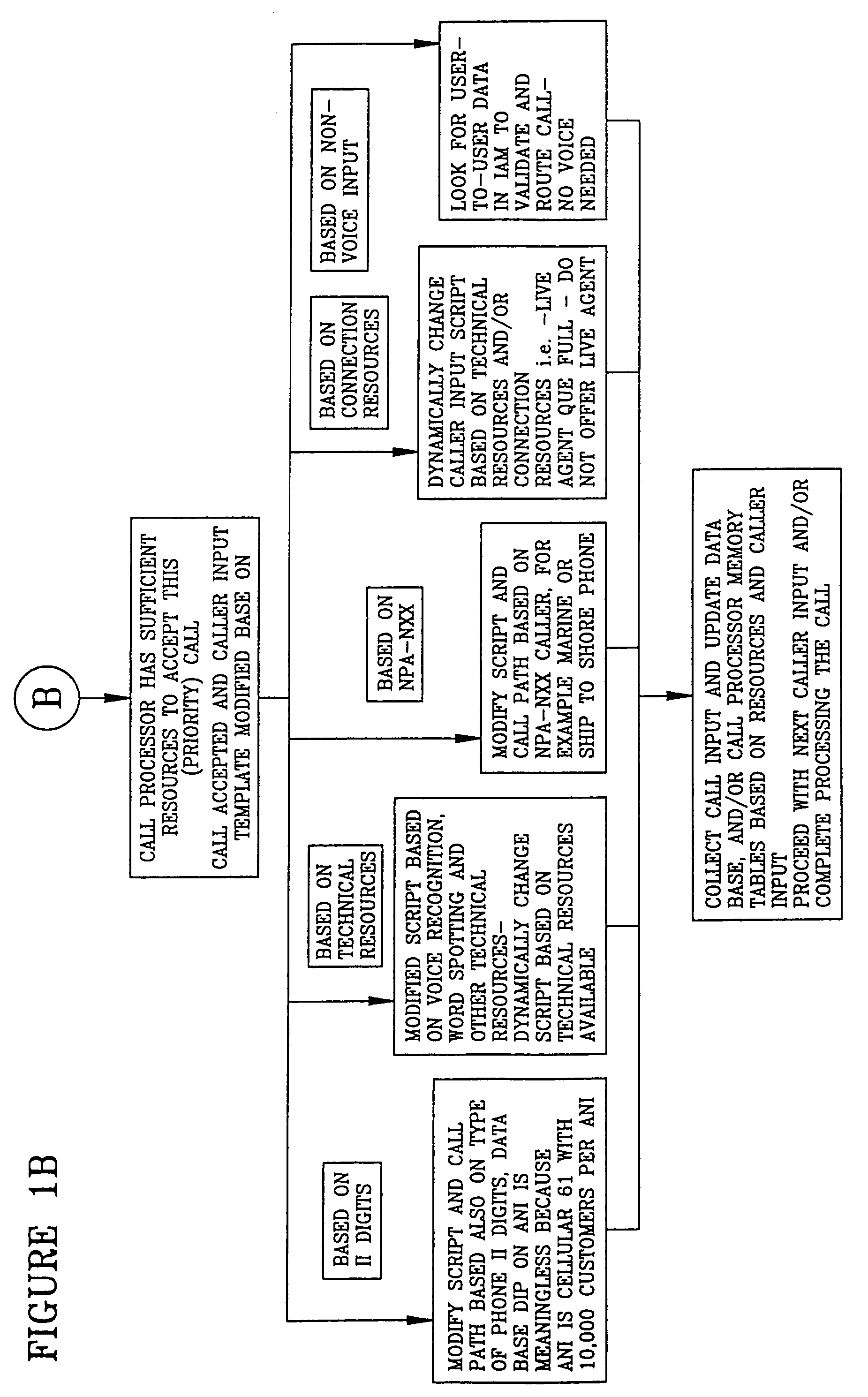
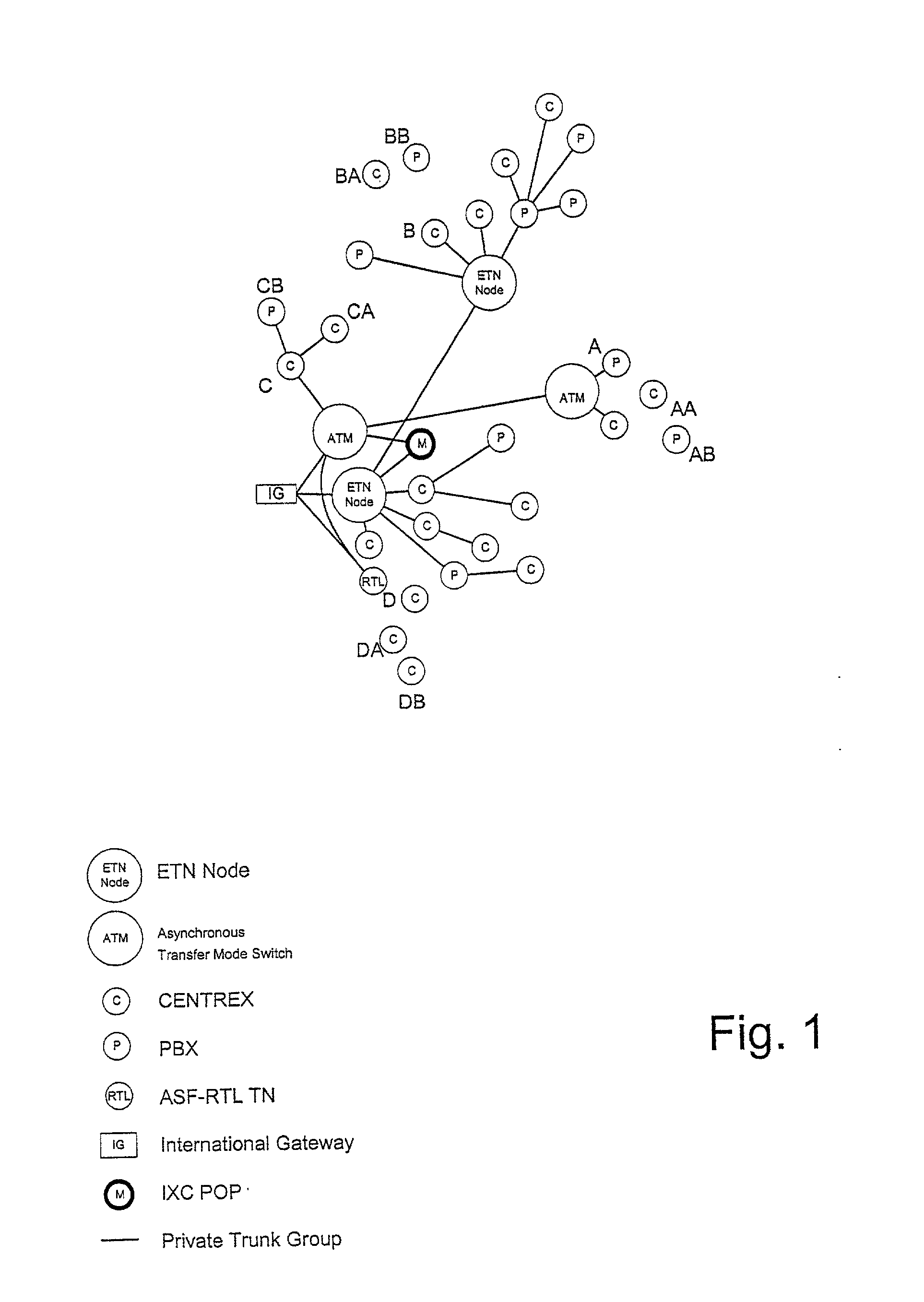
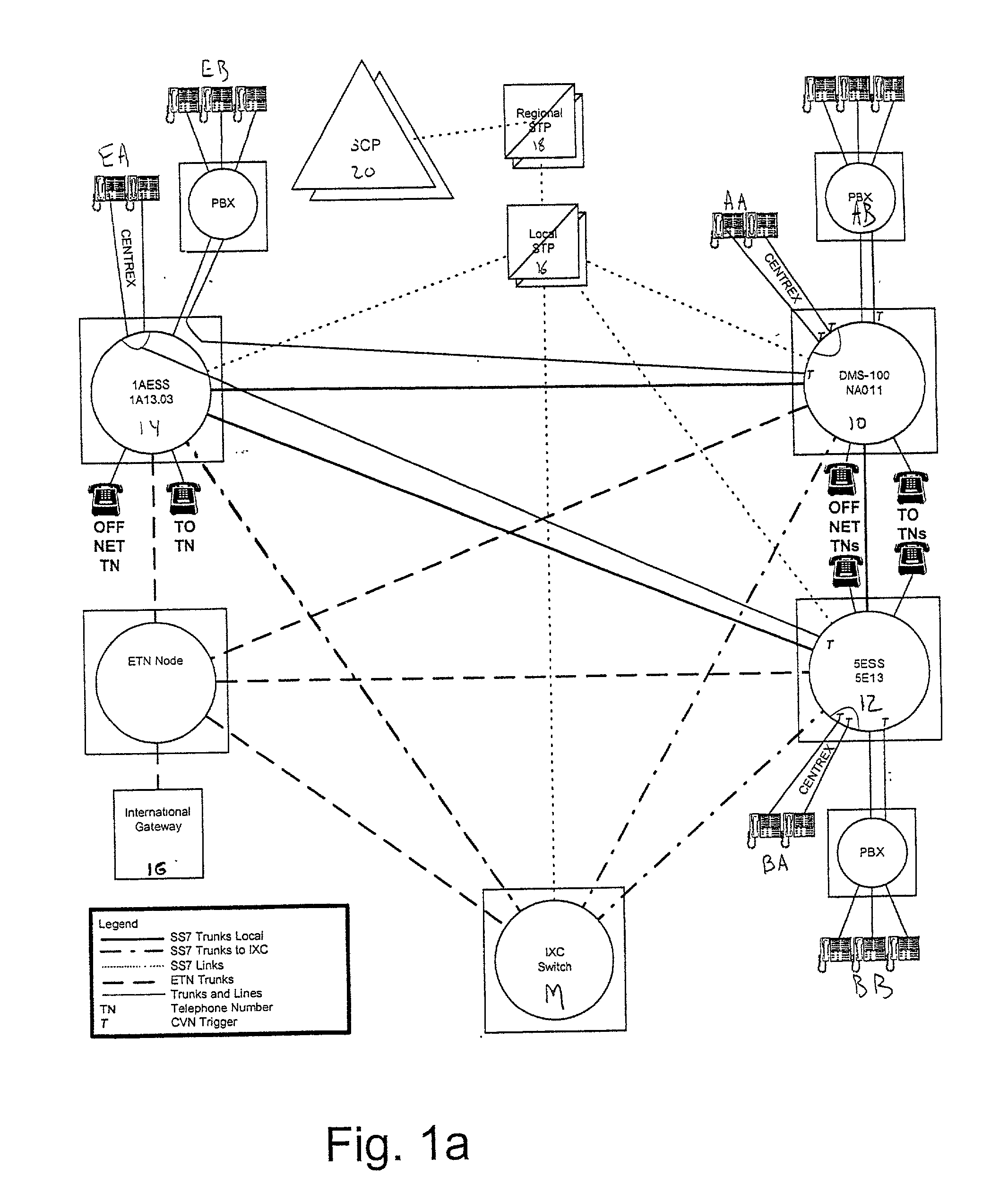
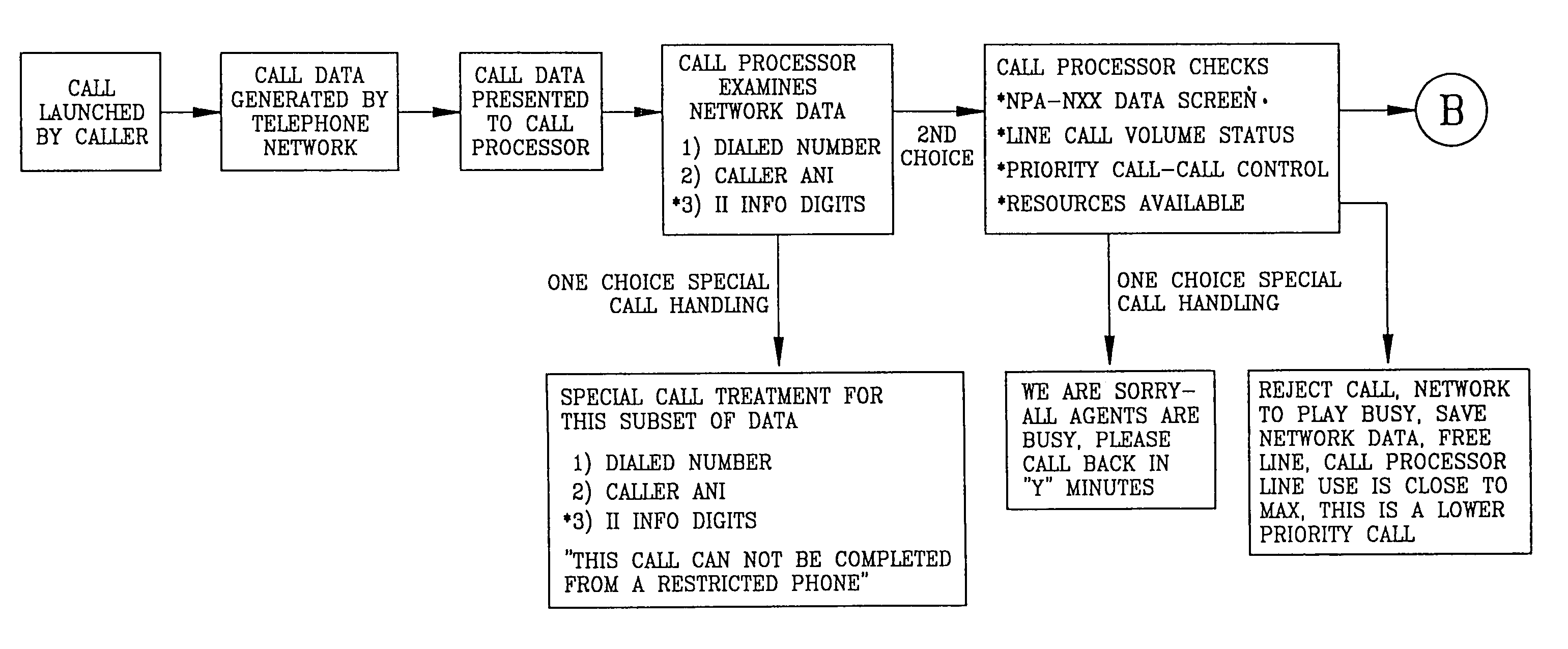
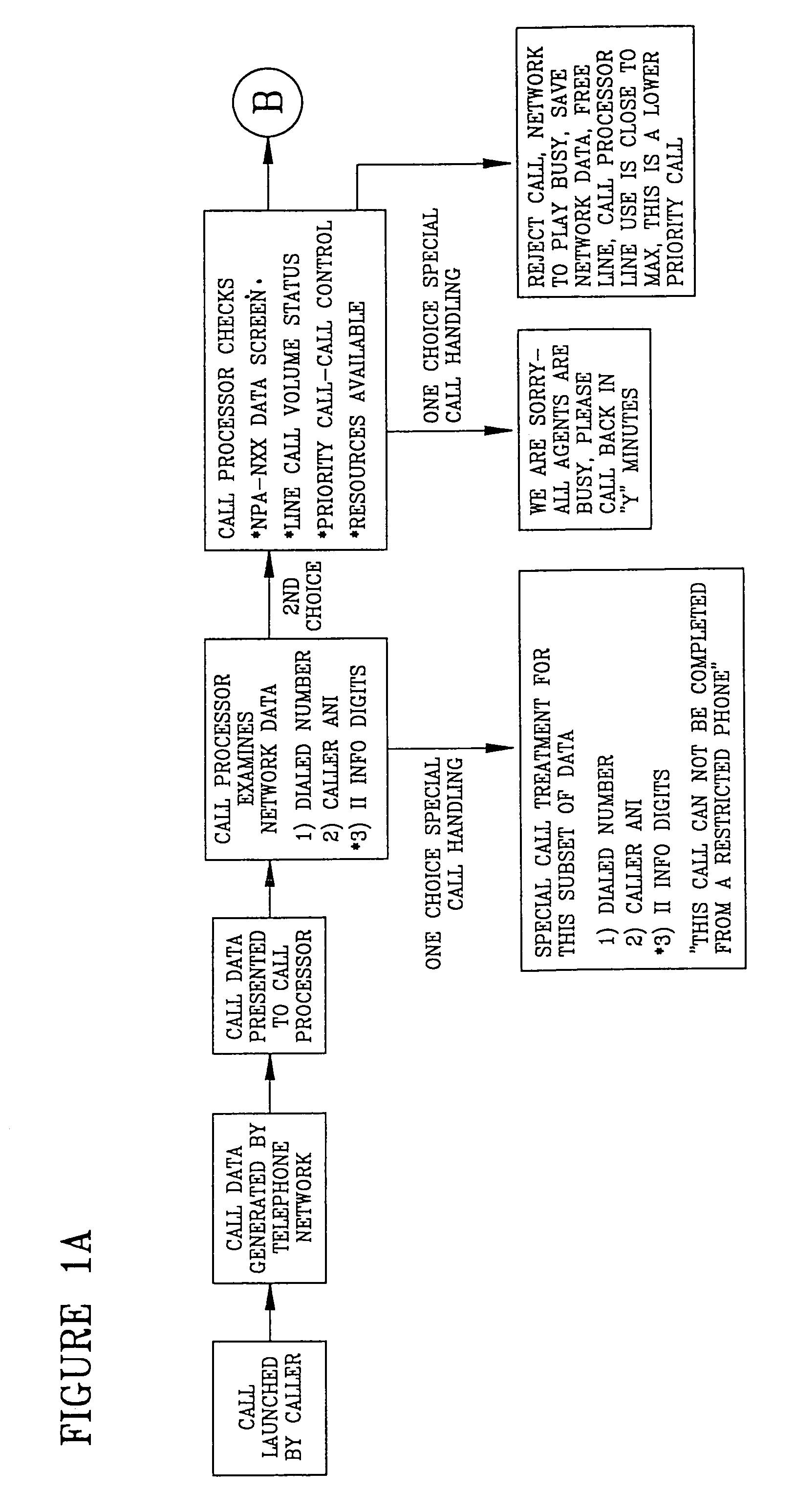
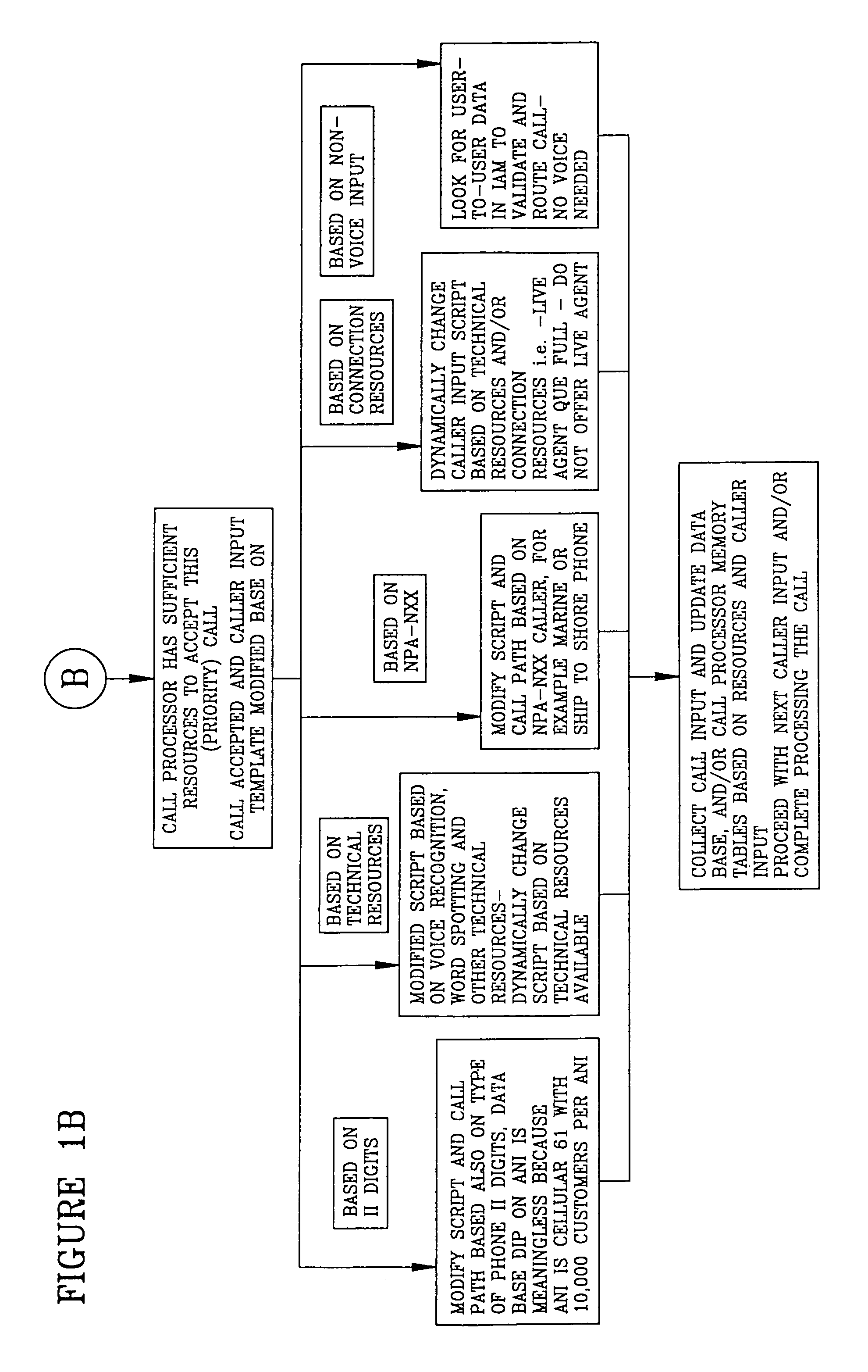
InactiveUS6975708B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsTelecommunicationsScreening call
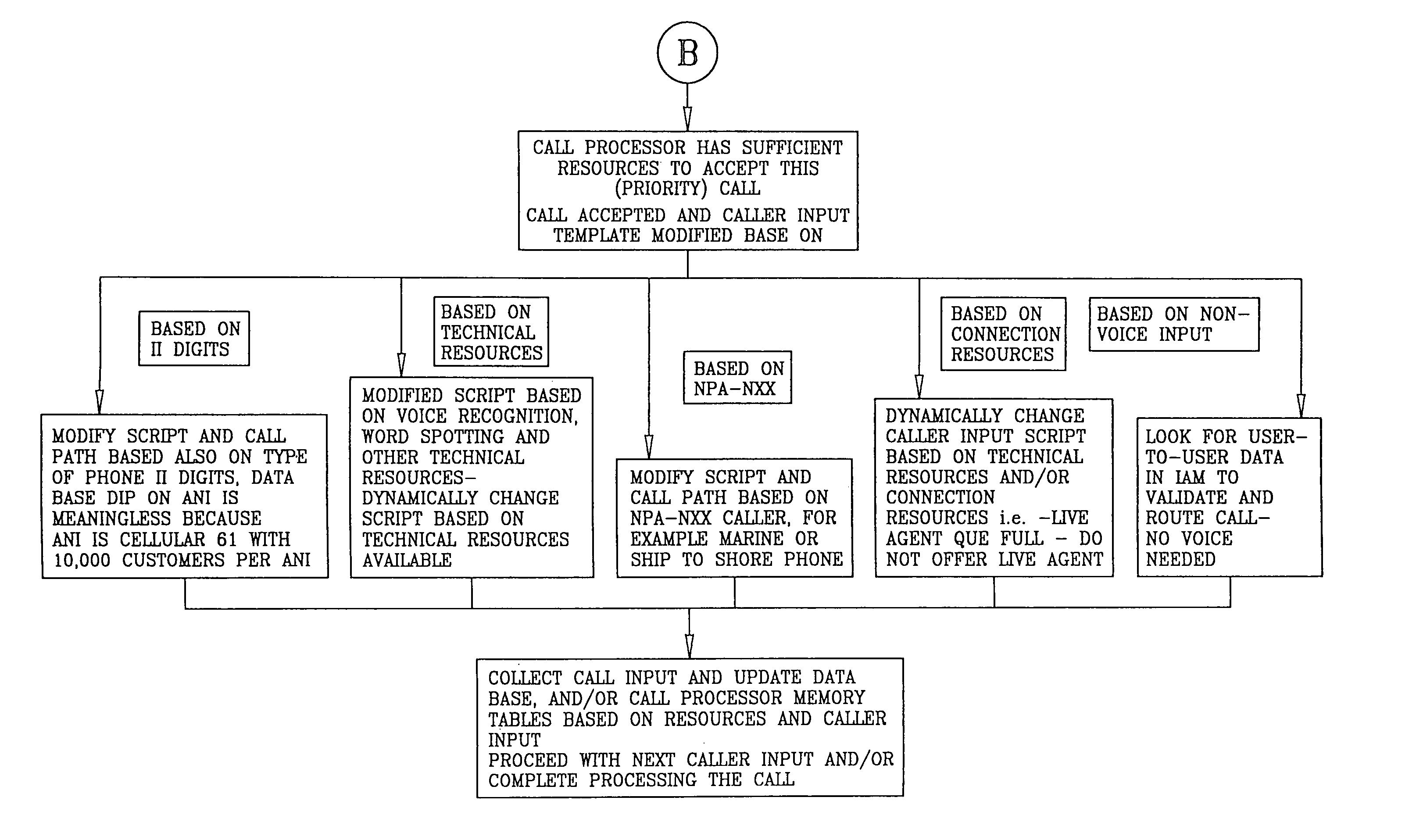
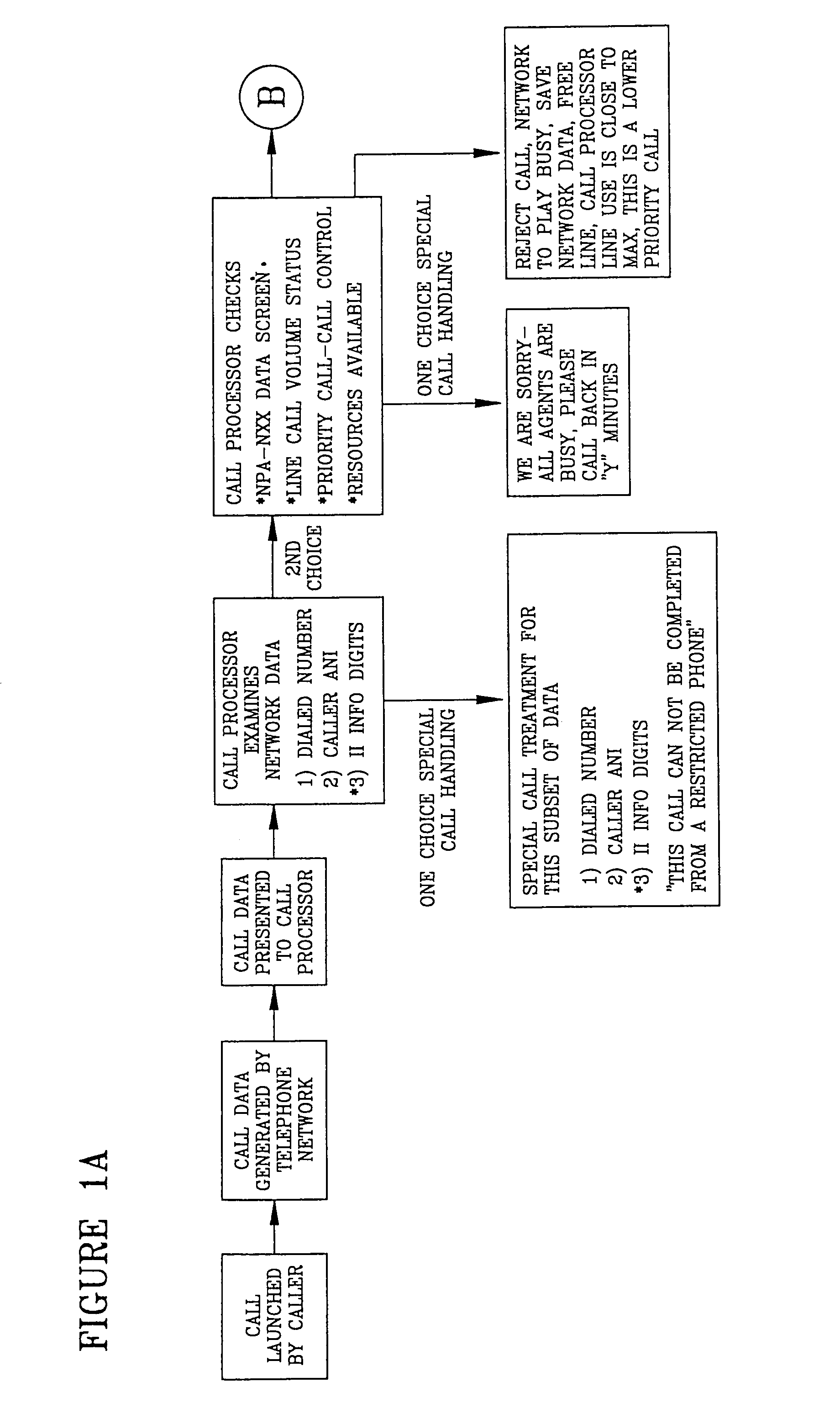
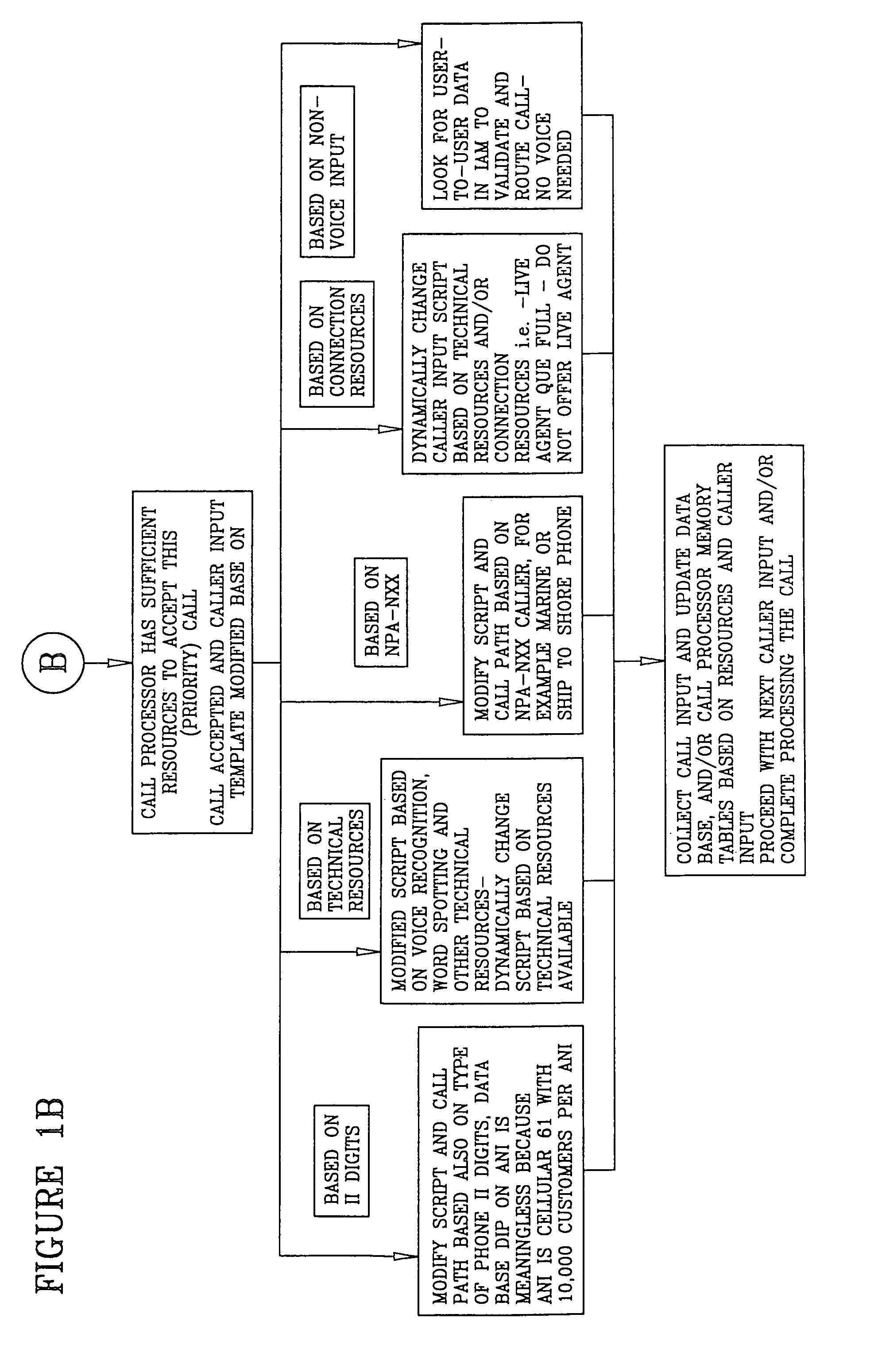
A system is described in which call processing considers unique information about the call to better serve the caller and / or to enable the called party to more efficiently handle the call. In one embodiment, the unique information considered by the call processor is information indicator digits, which may indicate to the called party whether to accept the call before the voice portion of the call is initiated.
Owner:CONVERGYS CUSTOMER MANAGEMENT DELAWARE
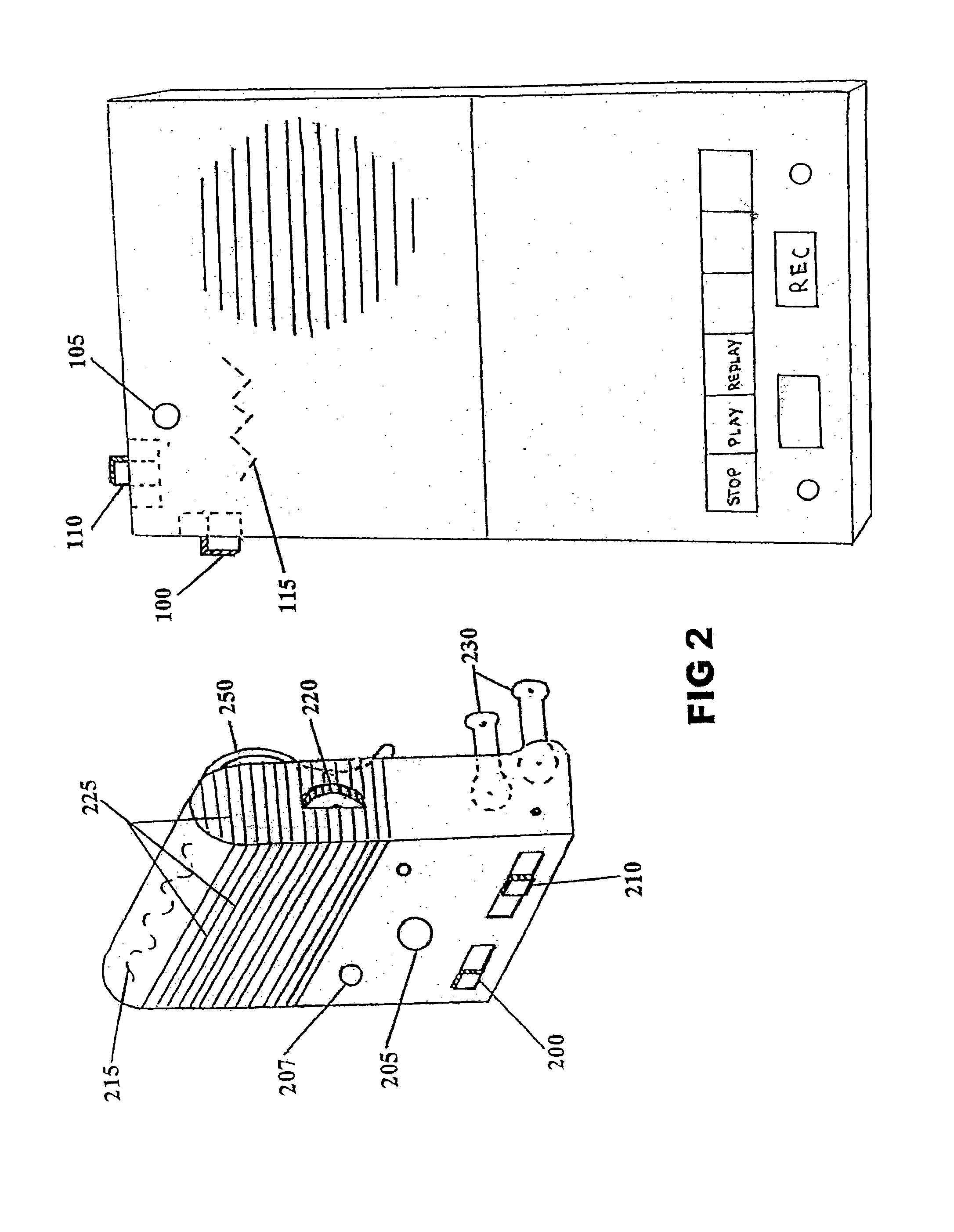
Remote operational screener
InactiveUS7224962B1Not limitedAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingSpecial service for subscribersRemote function callScreening call
This invention provides an audible remote screening function or device for use with an answering device or machine and may also combine this screening function with an ability for remote operational control of an answering device or machine. Preferred forms of the invention provide for remote call screening of an answering device or machine, or remote call screening of an answering device or machine together with remote operational control of an answering device or machine, with the capability to remotely operate and / or remotely screen calls (incoming or pre-recorded) of that of an answering device or machine from a remote area or room via the remote function or device. In preferred forms: the audible remote screening from the device can be heard across a room or from another room; the remote device can be made to stay in an active ON mode eliminating any need for the user to search, locate, or activate the remote device or any command signal per call being screened; the remote operational control and / or screening device can be directly plugged in allowing for simultaneous power and recharge abilities for continuous power and uninterrupted operation ability; a remote-override switch located on an answering device or machine for privacy control over unauthorized access to the answering device or machine from the remote device; and small size for portability. The functions and capabilities of the remote device can be implemented, combined and used in conjunction with / into any other unit or housing. This invention also provides visual screening functions.
Owner:KITE KAREN JEANNE
Call processing system with call screening
InactiveUS20050286688A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsTelecommunicationsScreening call
A system is described in which call processing considers unique information about the call to better serve the caller and / or to enable the called party to more efficiently handle the call. In one embodiment, the unique information considered by the call processor is information indicator digits, which may indicate to the called party whether to accept the call before the voice portion of the call is initiated.
Owner:CONVERGYS CMG UTAH
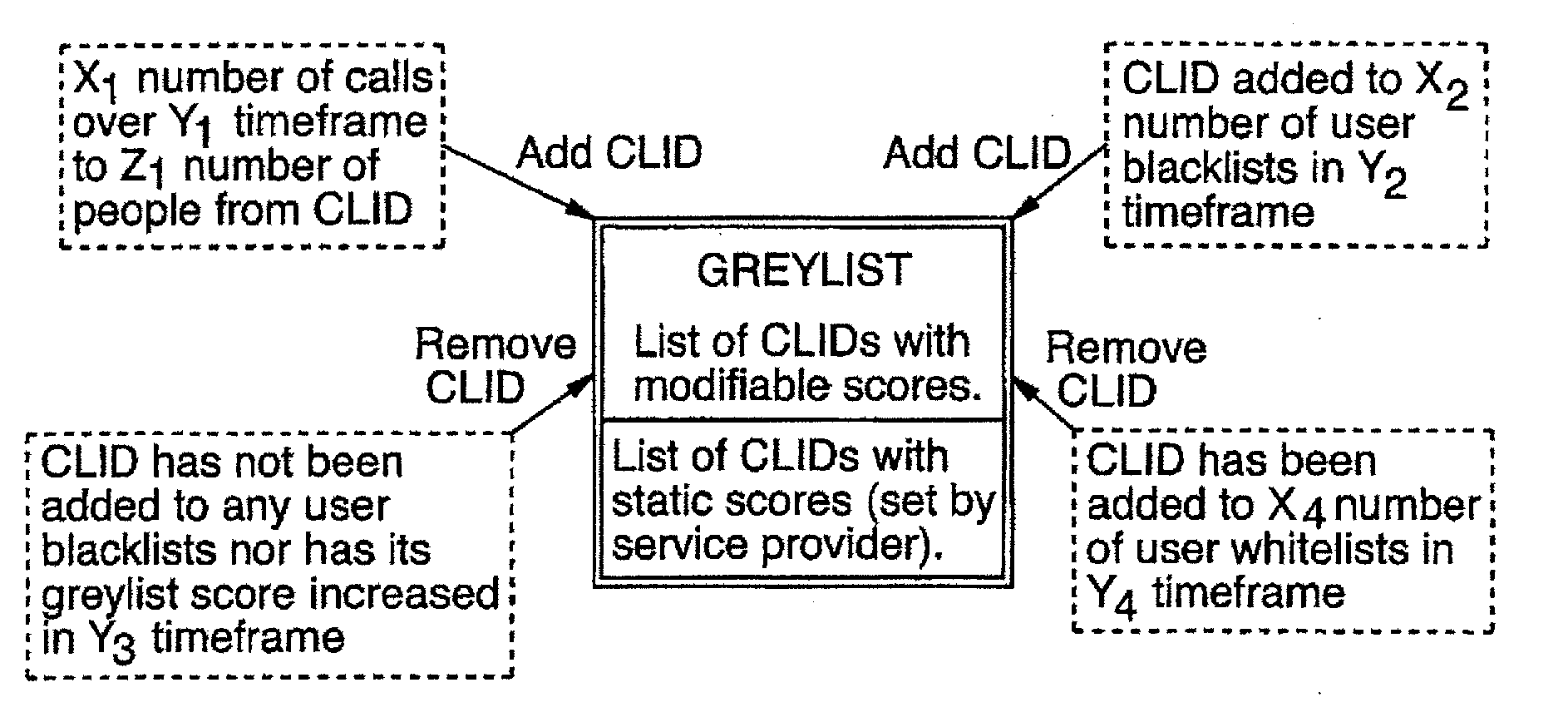
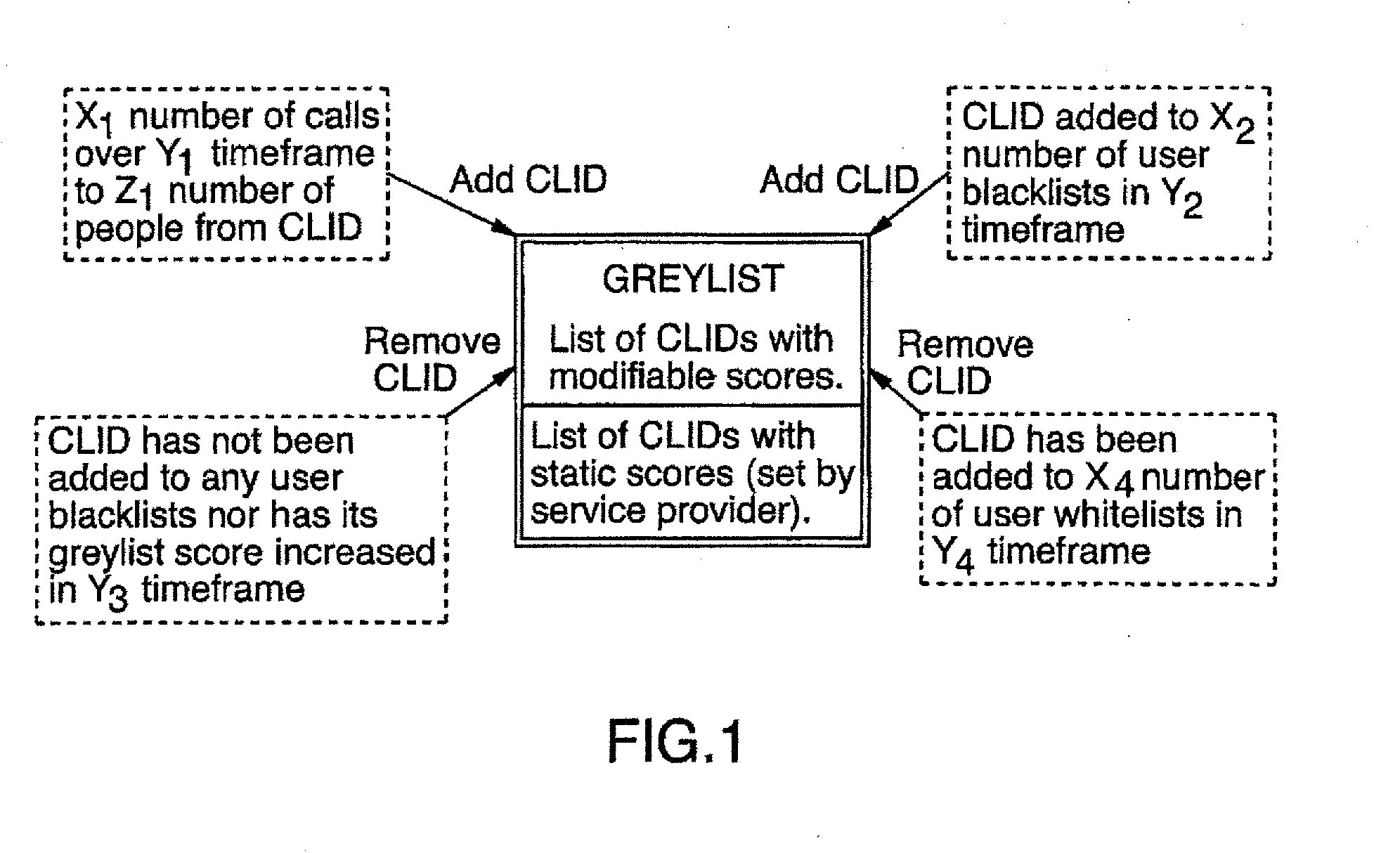
Call Screening System and Method
A system and method for screening telephone calls to a subscriber telephone number comprises a screening list of telephone numbers assigned to suspect callers and rules defining when a telephone number will be added to or removed from the screening list or ‘greylist,’ and / or modifying a screening value to be assigned to a telephone number in the greylist. Data relating to calls is received from subscribers and processed, and the telephone number is screened in accordance with the rules, based on the screening value assigned to the telephone number and optionally a selected subscriber tolerance level. Subscribers may add any telephone number to a personal list of telephone numbers to be blocked (blacklist) or telephone numbers to be accepted (whitelist).
Owner:PRIMUS MANAGEMENT ULC
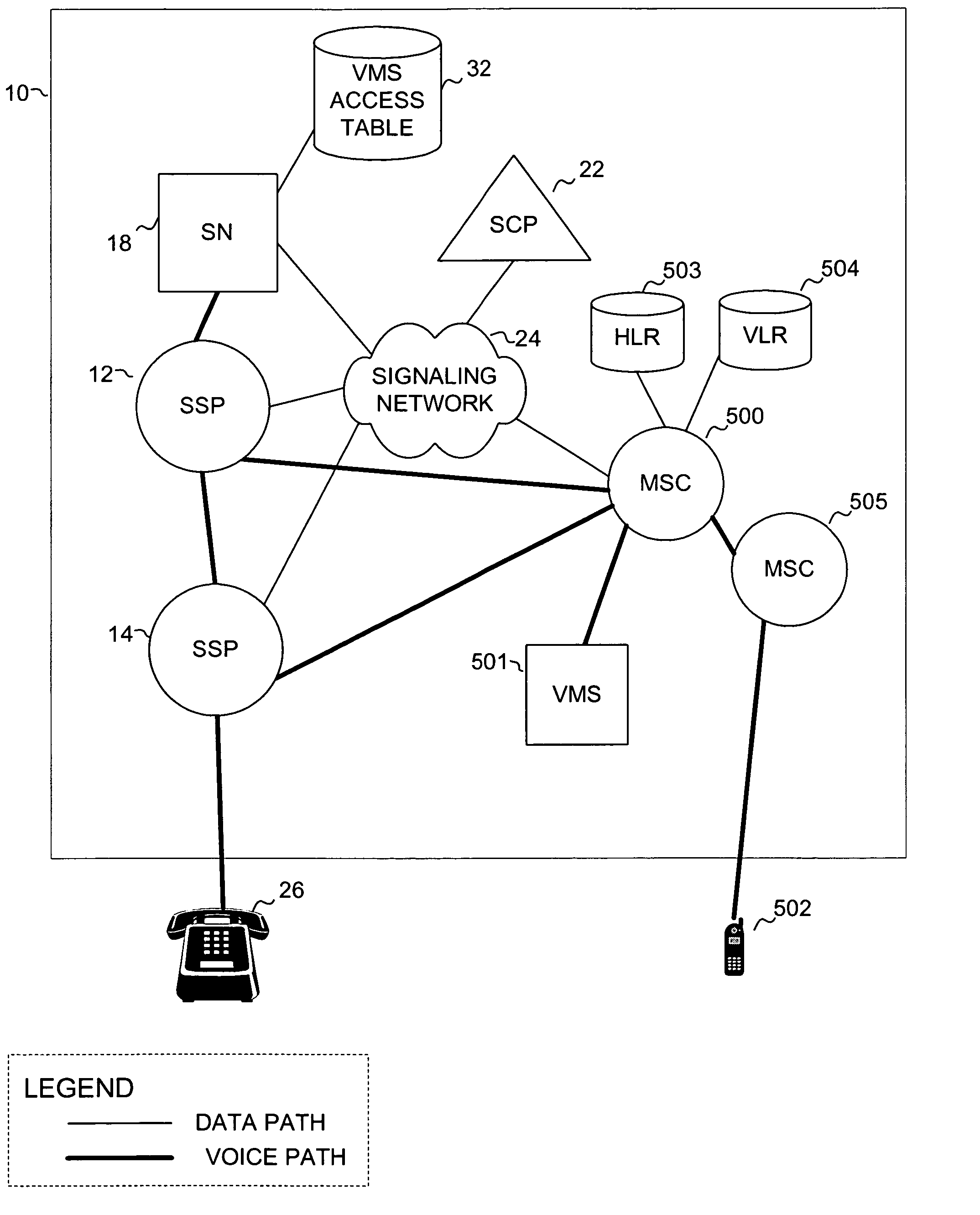
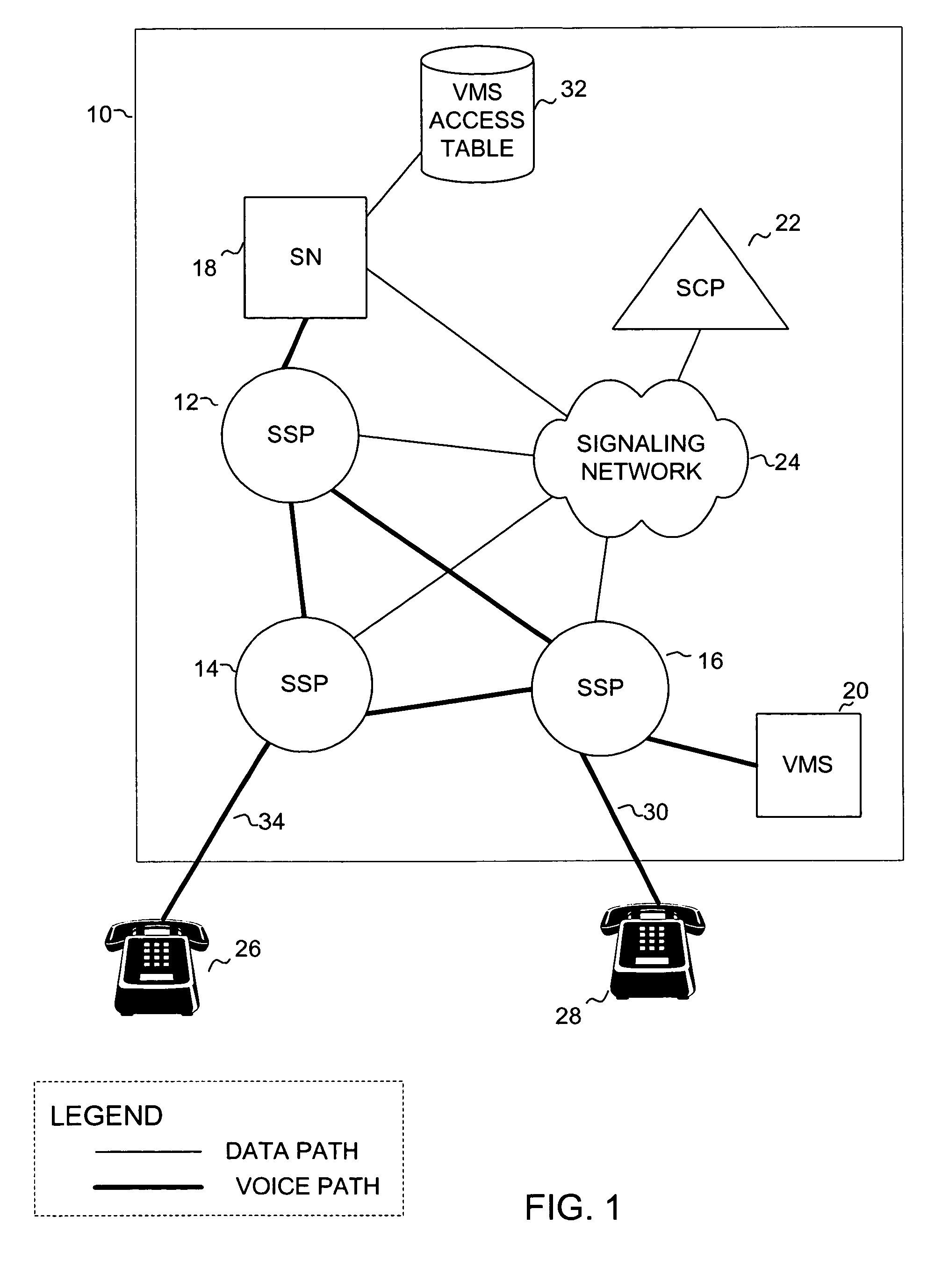
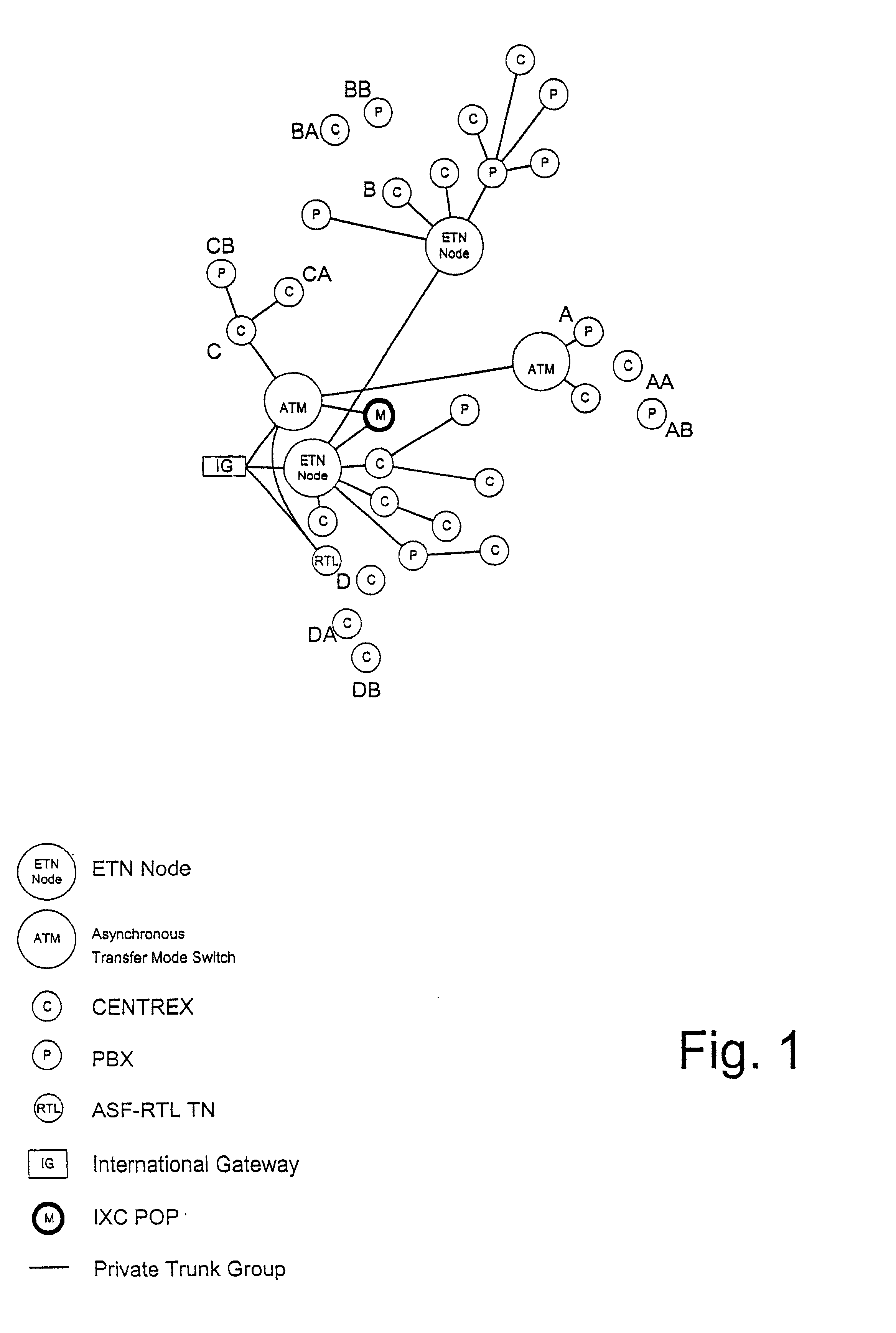
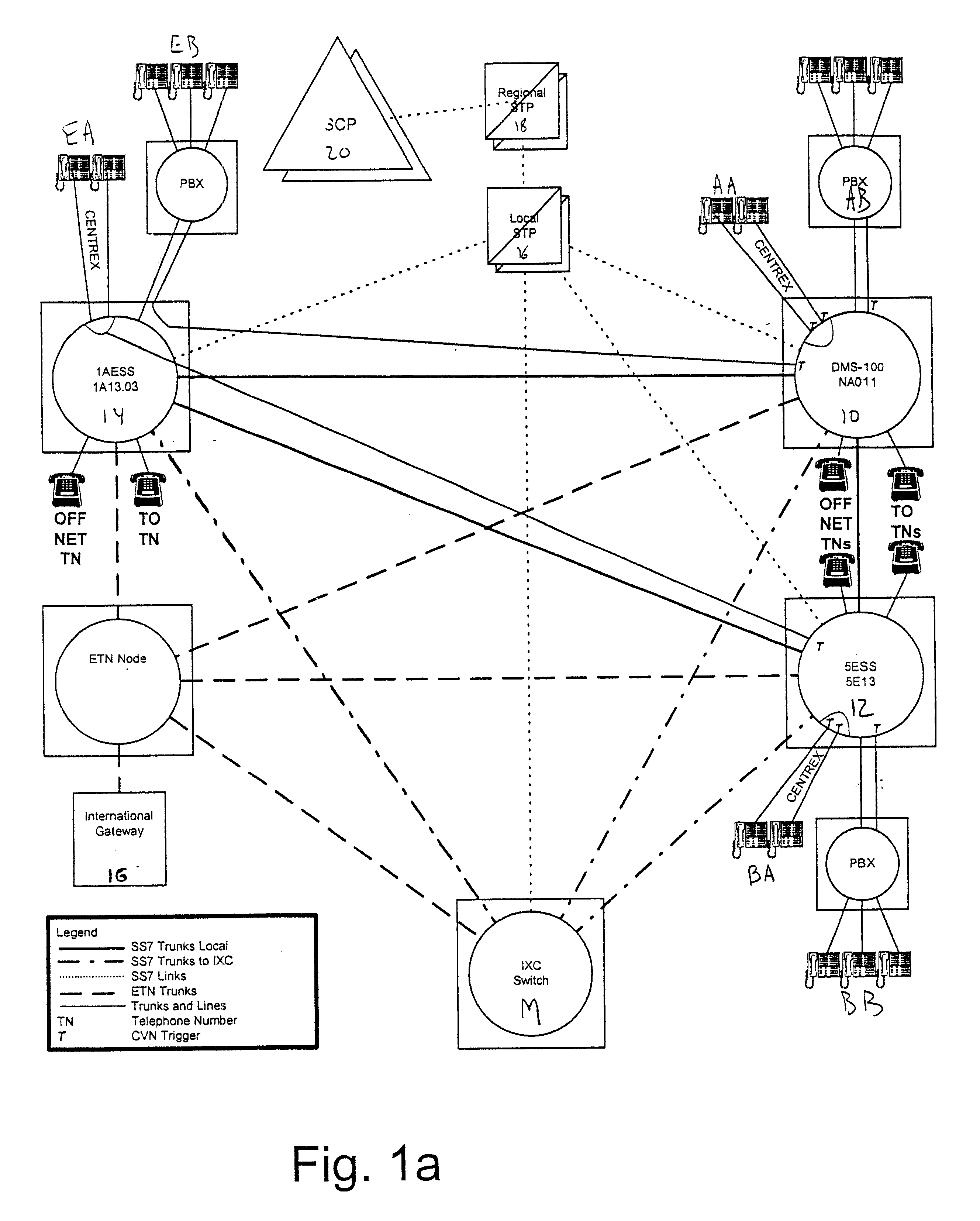
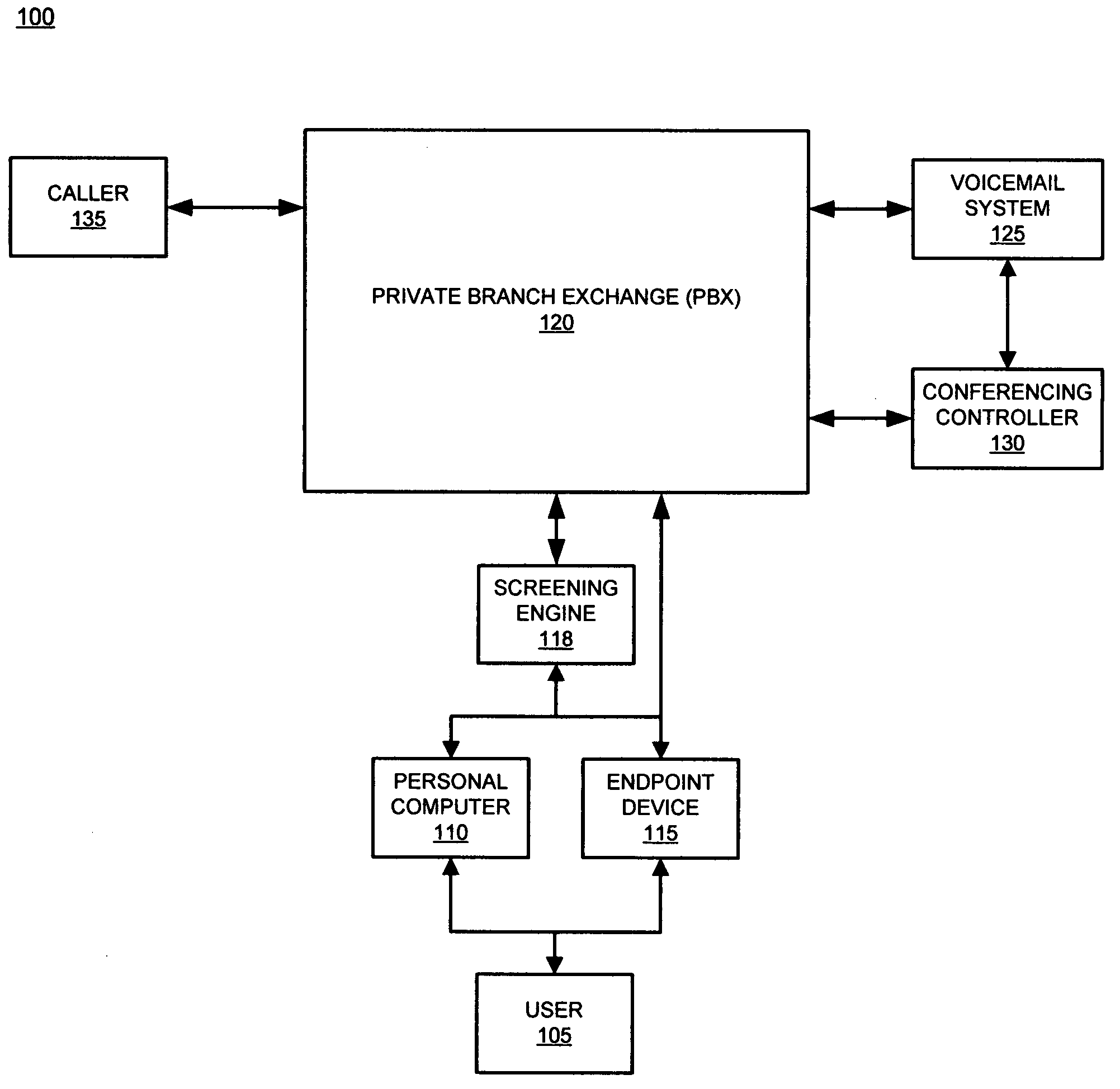
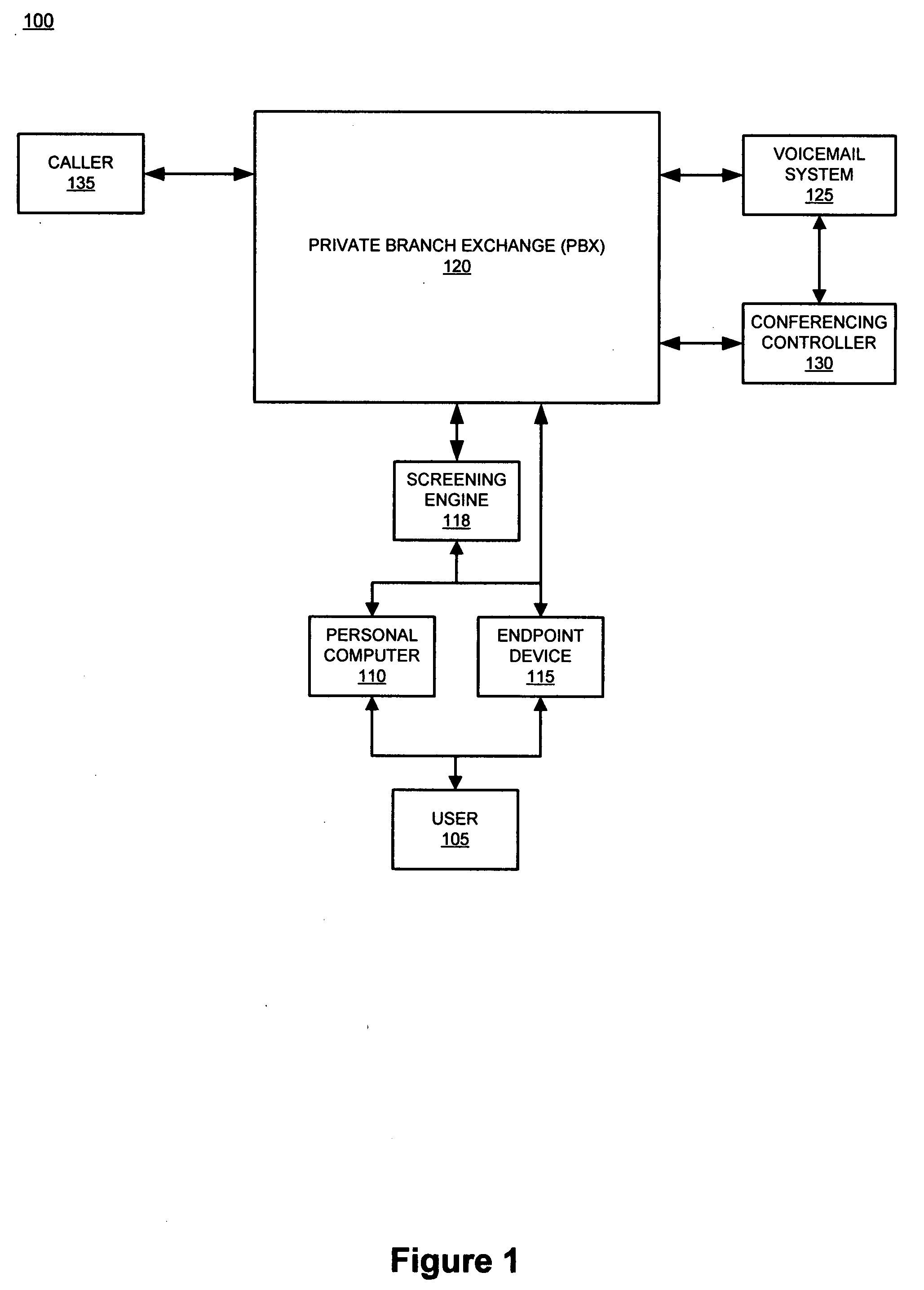
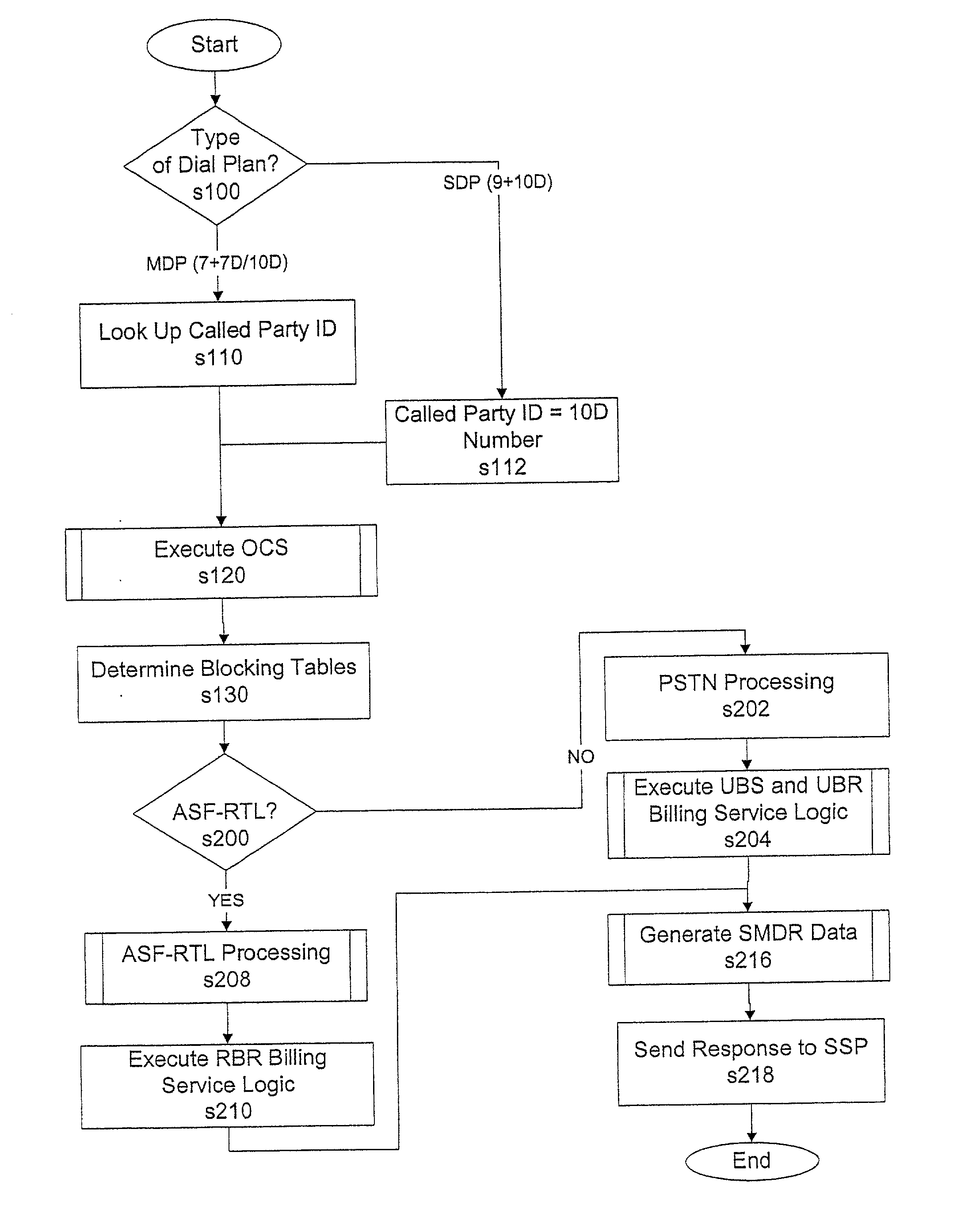
Dialing plan service including outgoing call screening, remote tie-line routing, call data reporting and billing
A method and system include screening and routing telephone calls, generating calling data reports and discounting billing for a customer's wide area centrex / PBX network, which includes an abbreviated dialing plan. A service control point (SCP) determines whether to block an outgoing call based on stored blocking tables and a privilege class of the calling station. The SCP determines whether to route the call through a private trunk group from a host switch to a private facility, and through an alternative trunk group when the private trunk group is unavailable. The SCP determines whether the call is eligible for discounted billing and generates a billing record, which is modified by a service switching point to indicate the discount. The SCP also samples calling data from service switching points and transmits the sampled data to a front end processor for formatting into station message detail recording (SMDR) data.
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
Call processing system with call screening
InactiveUS7215744B2Interconnection arrangementsAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingComputer networkTelecommunications
Owner:CONVERGYS CUSTOMER MANAGEMENT DELAWARE
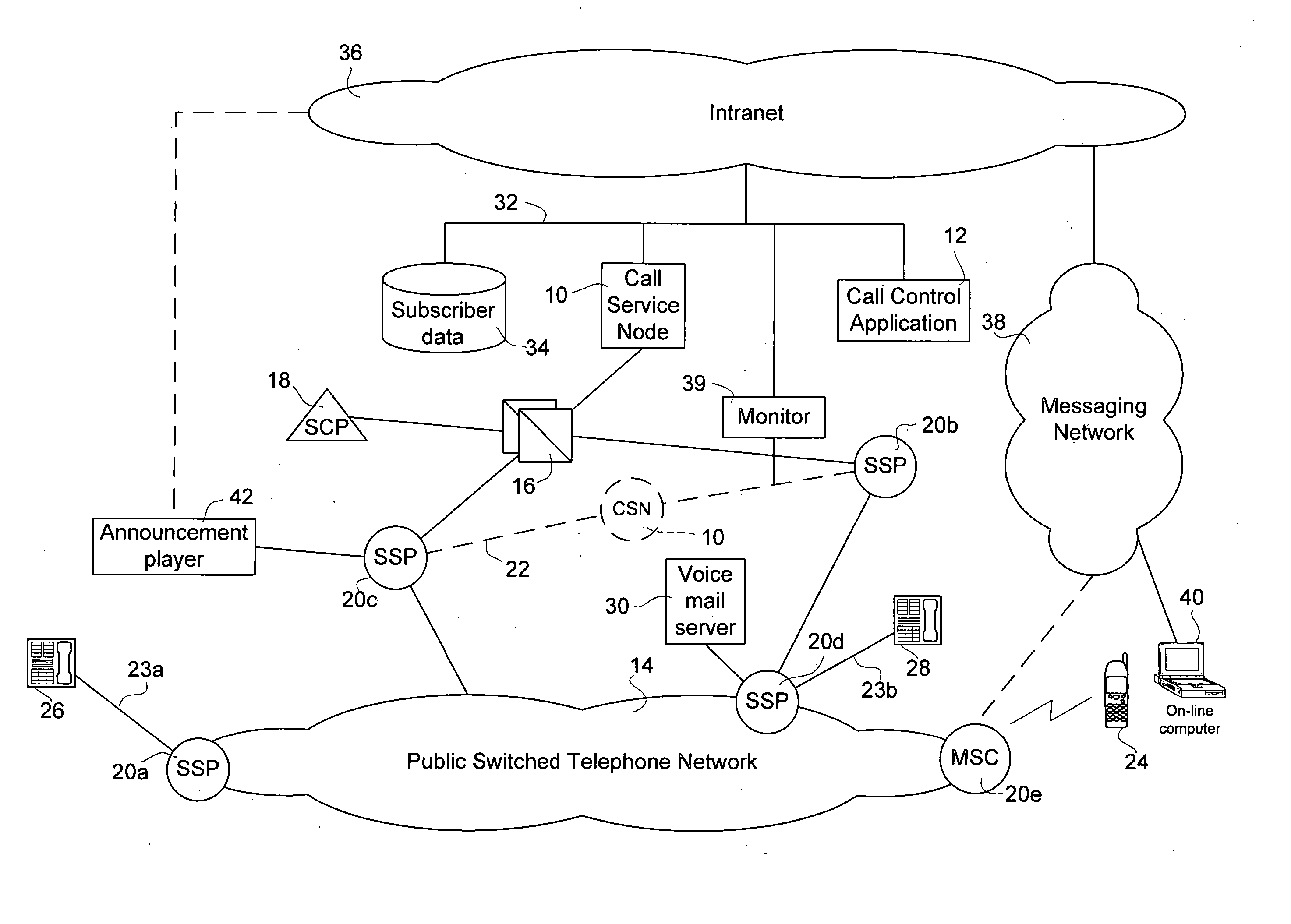
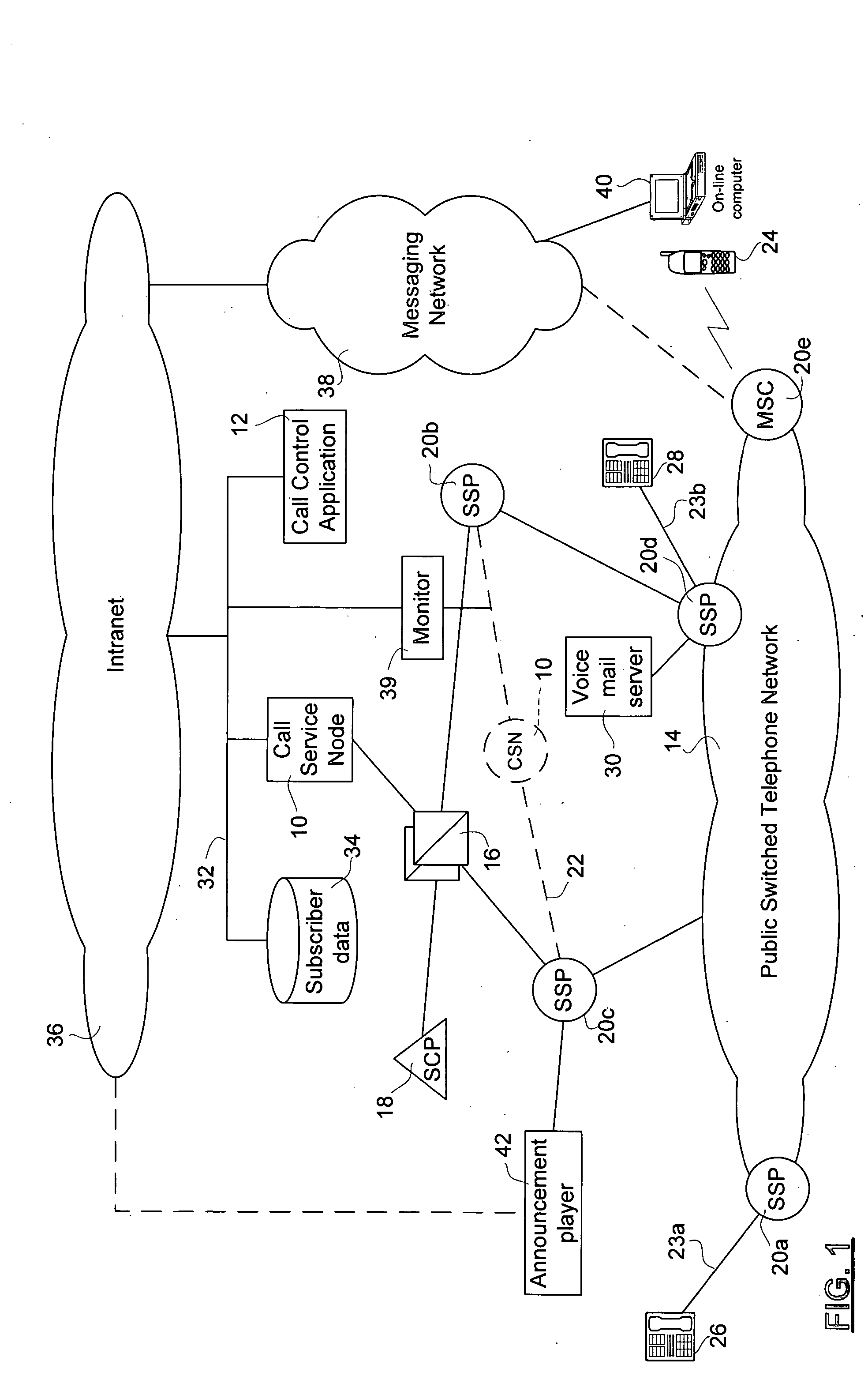
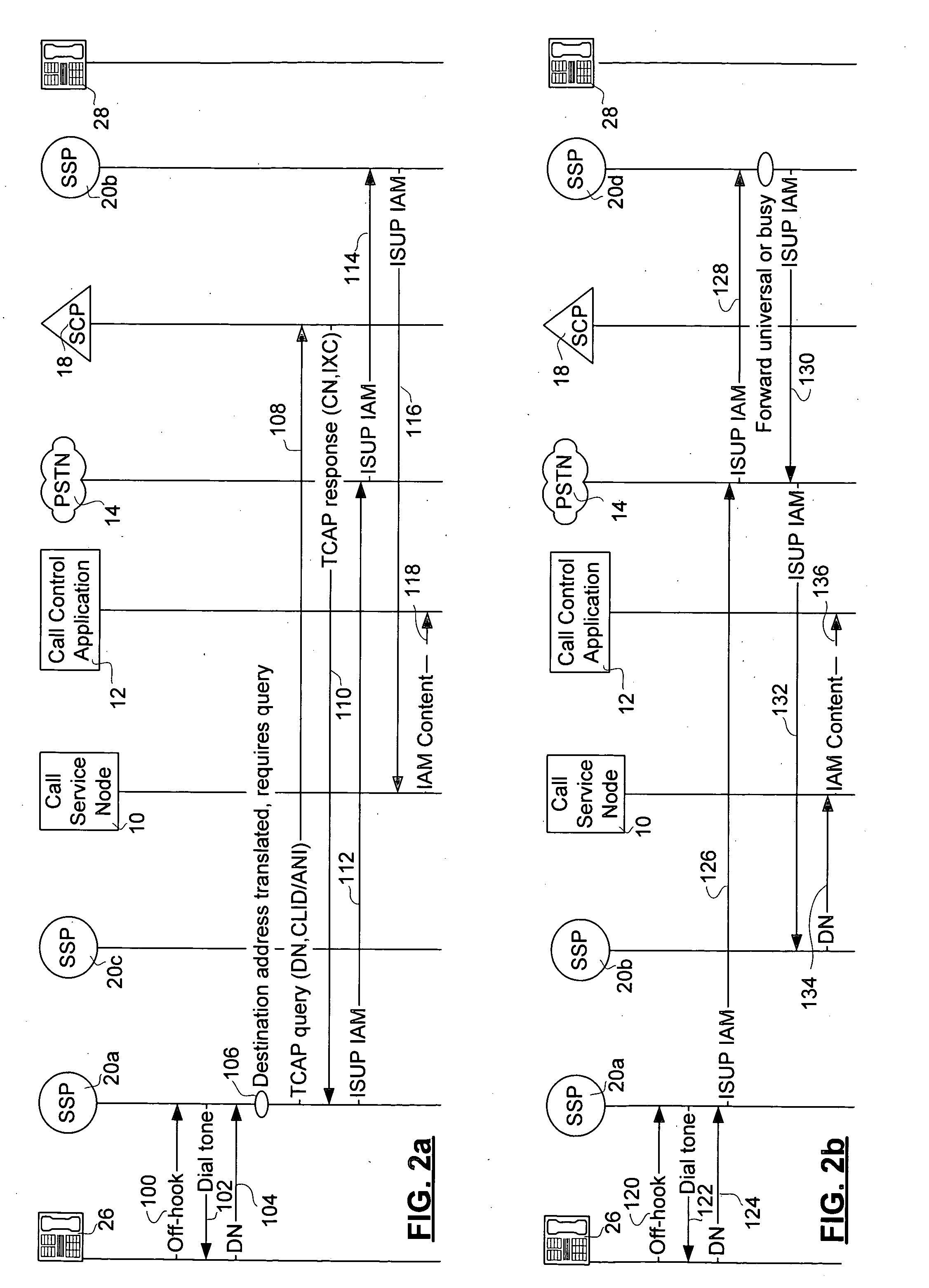
Method and apparatus for subscriber control of an inbound call
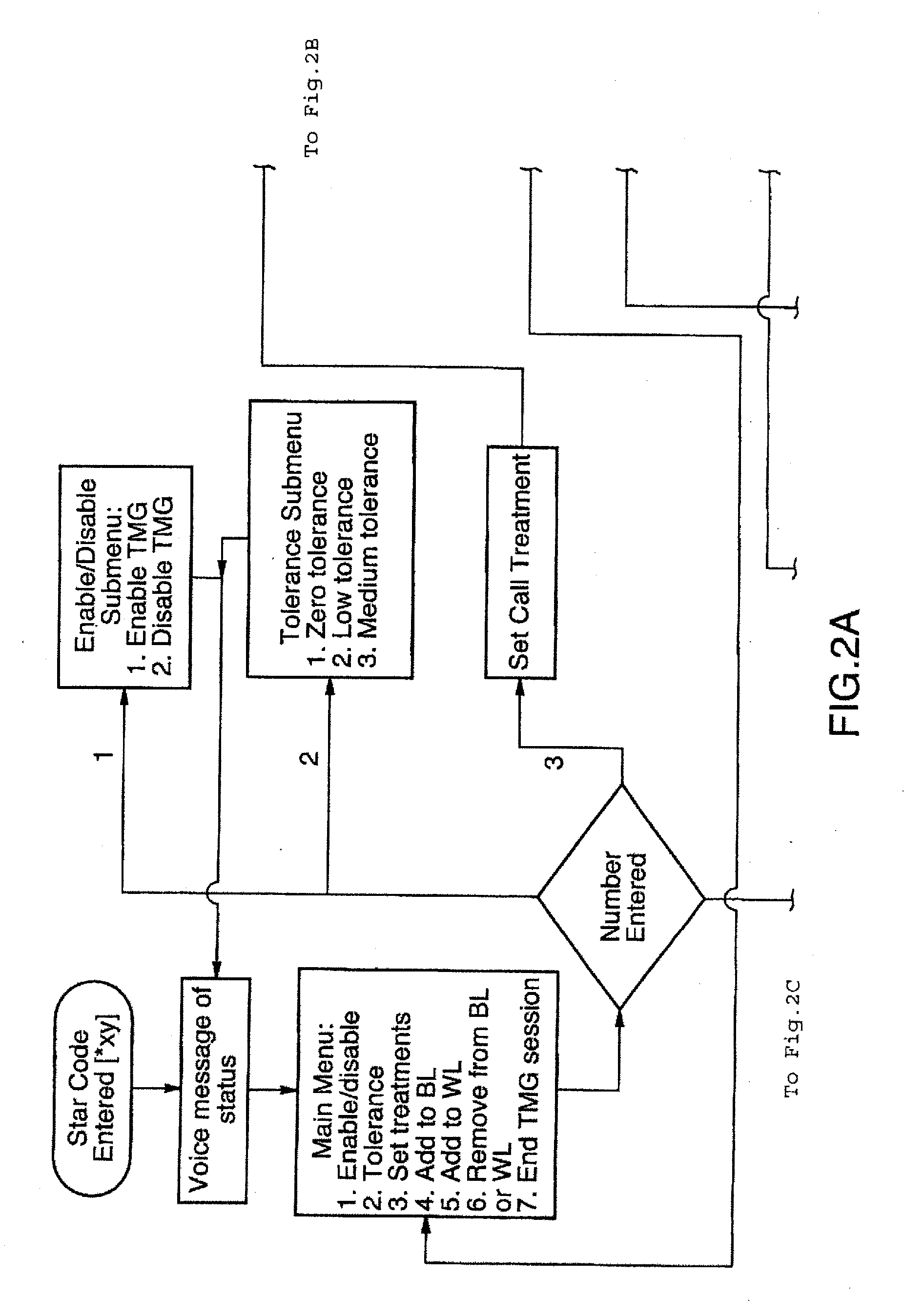
ActiveUS20050213740A1Enhance inbound call controlEasy to controlTelephone data network interconnectionsSpecial service for subscribersScreening callTreatment options
Service subscriber inbound call control is effected from within a public switched telephone network (PSTN) using a Call Service Node (CSN). On receipt of a call directed to the service subscriber, at least one messaging network message is sent to the service subscriber to request a call treatment option. Pending receipt of a reply from the subscriber, the call is routed by the CSN to a call parking facility in the PSTN. The call parking facility may be a voice mail box of the subscriber or an announcement facility. After a call treatment option is received, the call is released from the call parking facility the call treatment is effected. The service enables single number service for multiple service subscriber directory numbers, unified voice mail for multiple service subscriber telephone numbers, or segregated voice mail boxes for a single service subscriber number, as well as real-time, interactive inbound call screening.
Owner:WINDSTREAM INTPROP SERVICES LLC
Remote operational screener
InactiveUS7039393B1Not limitedSubstation equipmentRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRemote function callScreening call
This invention provides an audible remote screening function or device for use with an answering device or machine and may also combine this screening function with an ability for remote operational control of an answering device or machine. Preferred forms of the invention provide for remote call screening of an answering device or machine, or remote call screening of an answering device or machine together with remote operational control of an answering device or machine with the capability to remotely operate and / or remotely screen calls (incoming or pre- recorded) of that of an answering device or machine from a remote area or room via the remote function or device. In preferred forms: the audible remote screening from the device can be heard across a room or from another room; the remote device can be made to stay in an active ON mode eliminating any need for the user to search, locate, or activate the remote device or any command signal per call being screened; the remote operational control and / or screening device can be directly plugged in allowing for simultaneous power and recharge abilities for continuous power and uninterrupted operation ability; a remote-override switch located on an answering device or machine for privacy control over unauthorized access to the answering device or machine from the remote device; and a small size for portability. The functions and capabilities of the remote device can be implemented, combined and used in conjunction with / into any other unit or housing. This invention also provides visual screening functions.
Owner:KITE KAREN JEANNE
System and method for voice message call screening
InactiveUS20080107244A1Simple methodSpecial service for subscribersAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingScreening callTextual notation
A mail delivery service that allows users of a networked call processing system to listen to messages that are being left to their mailbox in real time. Improvements applied to this invention allow full control of both the message and the call that is leaving the message to more effectively screen the call and enhance follow up communication with the calling party. The system further enables users to forward messages in real-time to other users within the telephone network, conference in other users, and discuss the message as the call is being recorded by a voicemail system. Other monitoring options are provided whereby the caller may, for example, add a textual notation to a call, terminate the call, and apply a custom configured hot rule to manage the call in accordance with the user's wishes.
Owner:INTER TEL INC
Dialing plan service including outgoing call screening, remote tie-line routing, call data reporting and billing
InactiveUS20020136374A1Reduce network expenseAddress rising pricesAutomatic exchangesScreening callService control
A method and system include screening and routing telephone calls, generating calling data reports and discounting billing for a customer's wide area centrex / PBX network, which includes an abbreviated dialing plan. A service control point (SCP) determines whether to block an outgoing call based on stored blocking tables and a privilege class of the calling station. The SCP determines whether to route the call through a private trunk group from a host switch to a private facility, and through an alternative trunk group when the private trunk group is unavailable. The SCP determines whether the call is eligible for discounted billing and generates a billing record, which is modified by a service switching point to indicate the discount. The SCP also samples calling data from service switching points and transmits the sampled data to a front end processor for formatting into station message detail recording (SMDR) data.
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
Call processing system with call screening
InactiveUS7035384B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsTelecommunicationsScreening call
A system is described in which call processing considers unique information about the call to better serve the caller and / or to enable the called party to more efficiently handle the call. In one embodiment, the unique information considered by the call processor is information indicator digits, which may indicate to the called party whether to accept the call before the voice portion of the call is initiated.
Owner:CONVERGYS CUSTOMER MANAGEMENT DELAWARE
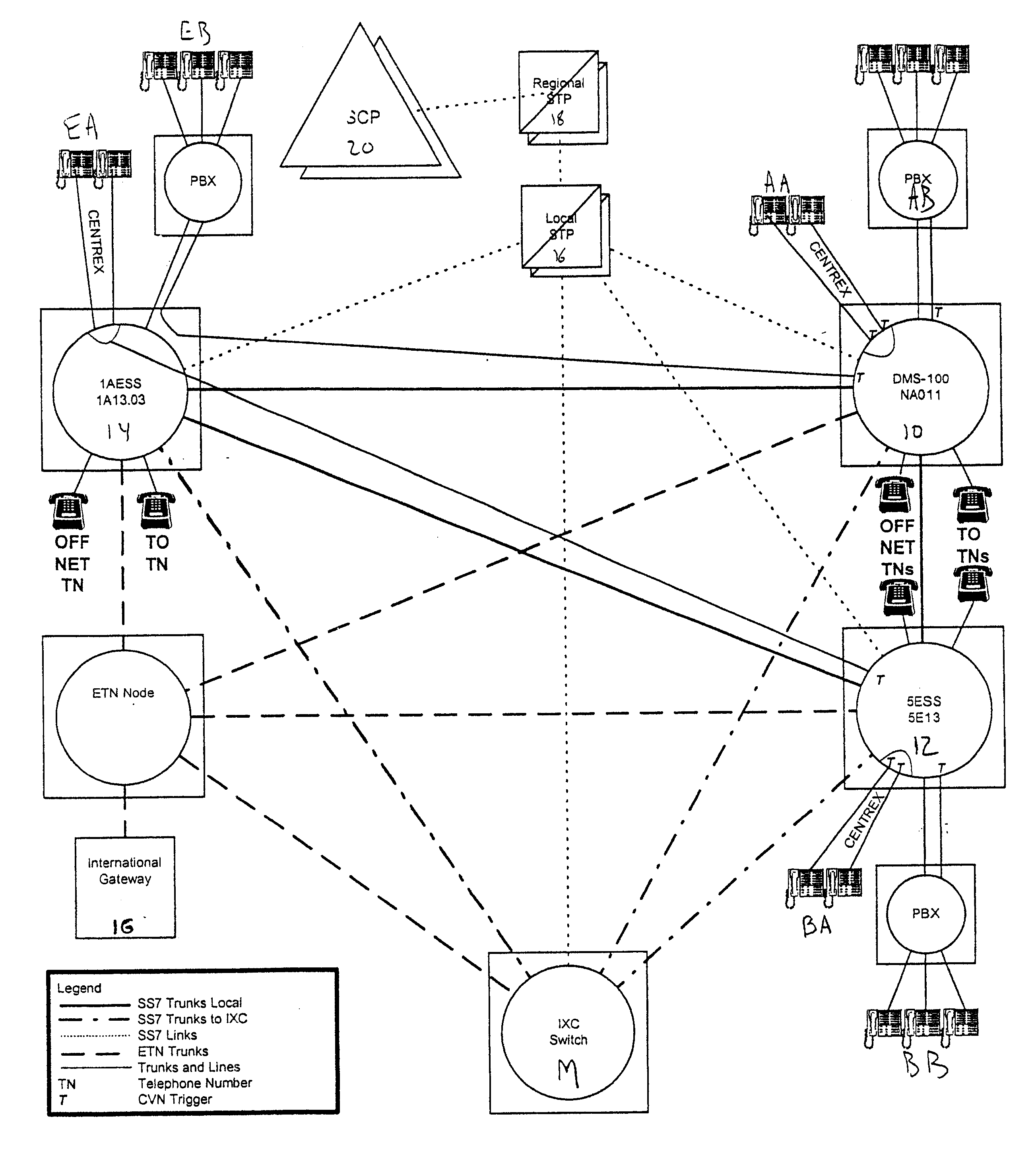
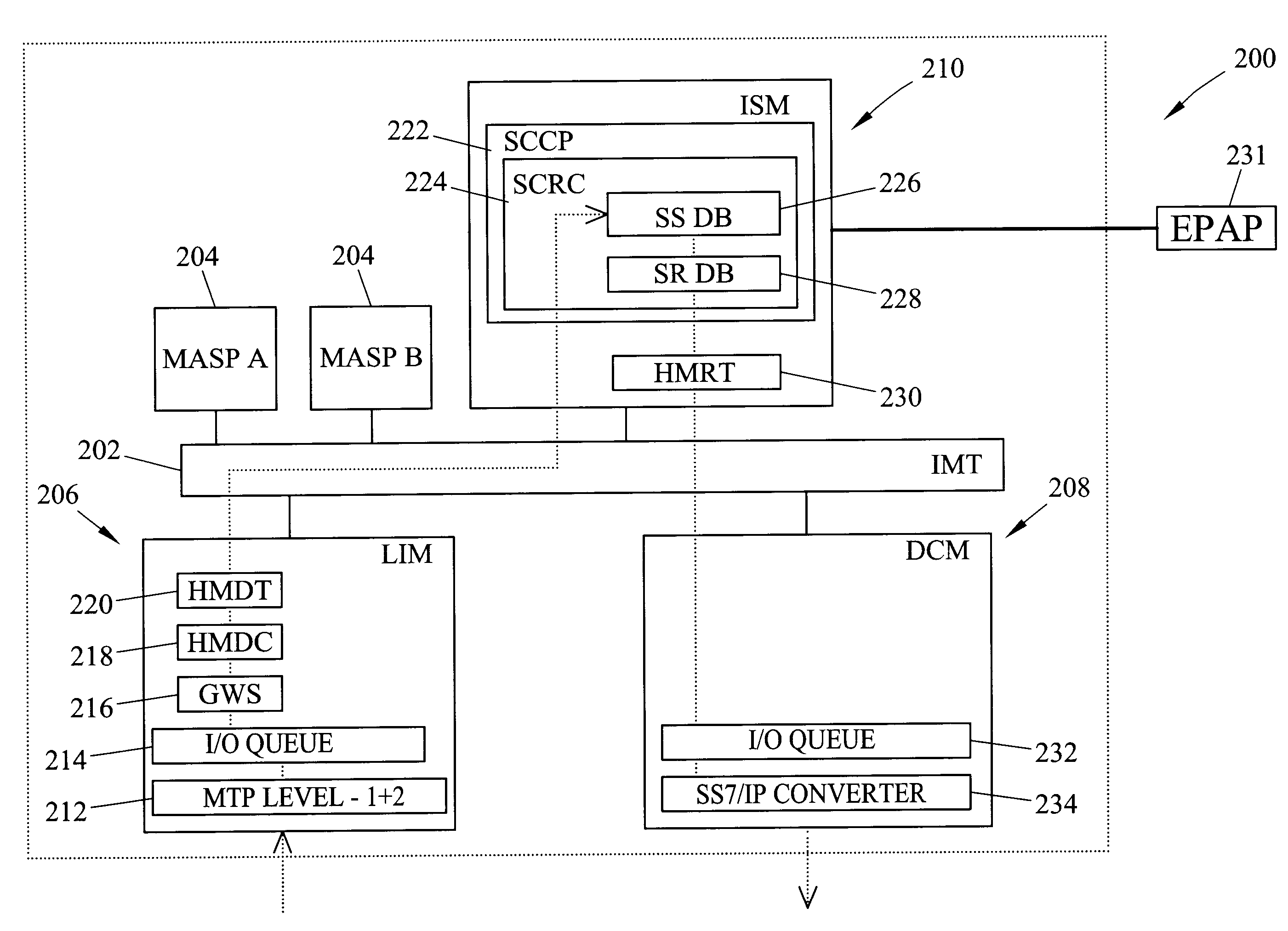
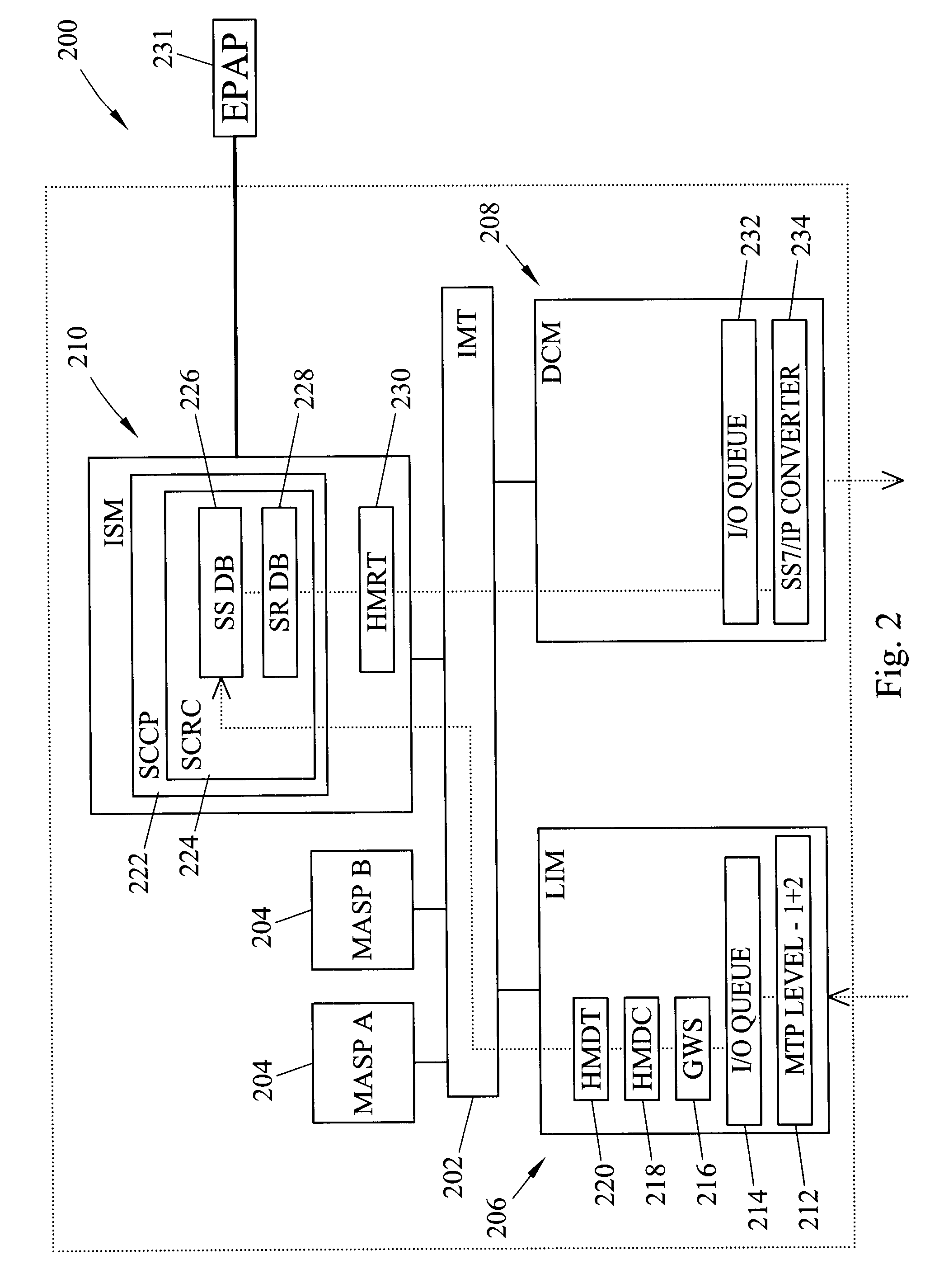
Methods and systems for providing triggerless intelligent network (IN) screening services based on call setup messages
ActiveUS6959076B2Interconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersIntelligent NetworkScreening call
Method and systems for providing triggerless screening services include a triggerless screening service routing node and a message processing platform. The triggerless screening service routing node identifies call setup messages that require one or more call screening services and diverts the messages to a message processing platform. The message processing platform performs at least one screening action on the call setup messages and modifies the messages to include the type and result of the screening action.
Owner:TEKELEC GLOBAL INC
Internet call waiting with voicemail system that provides monitoring during recording
ActiveUS7245612B2Automatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingSpecial service for subscribersScreening callVoice over IP
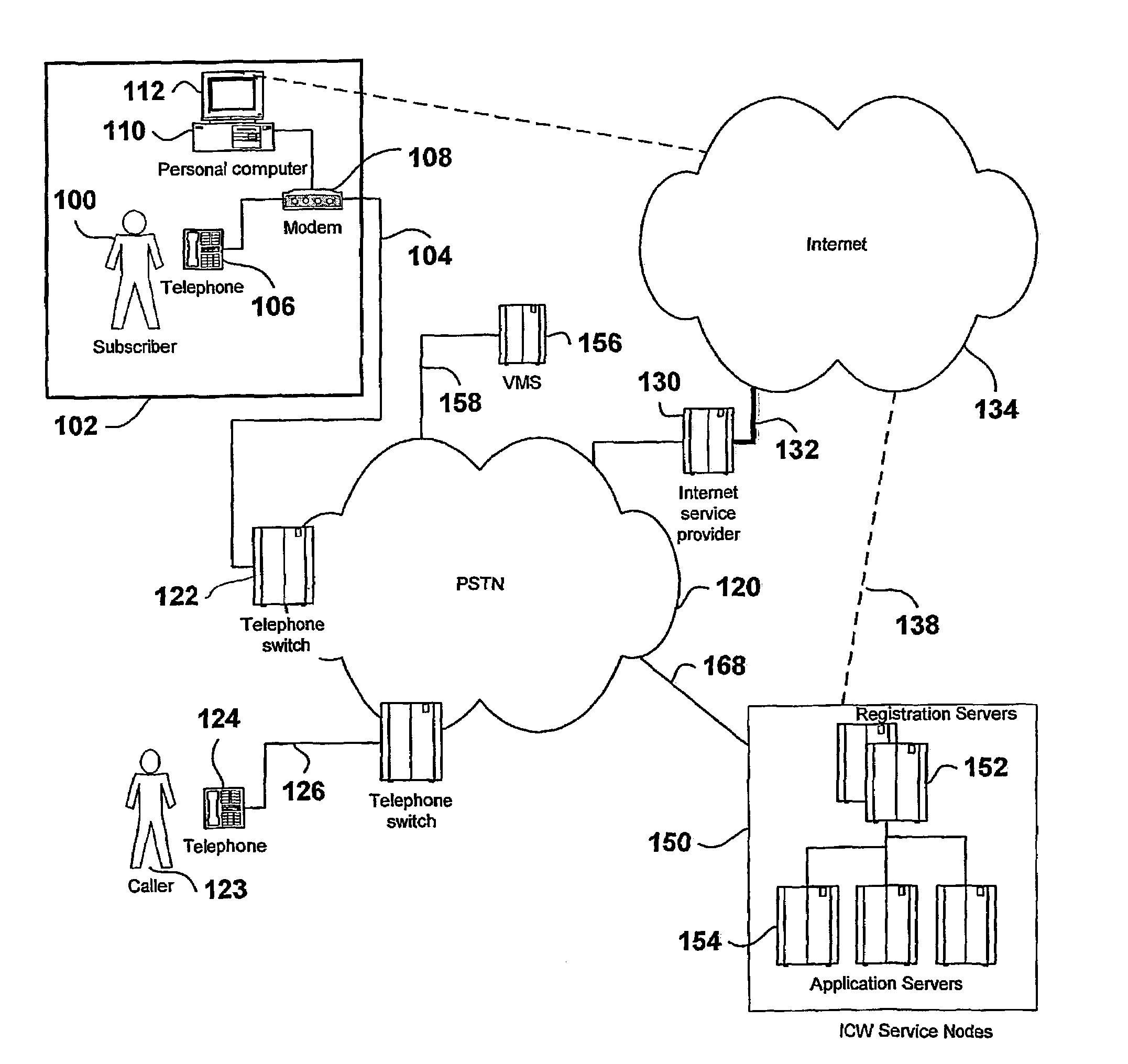
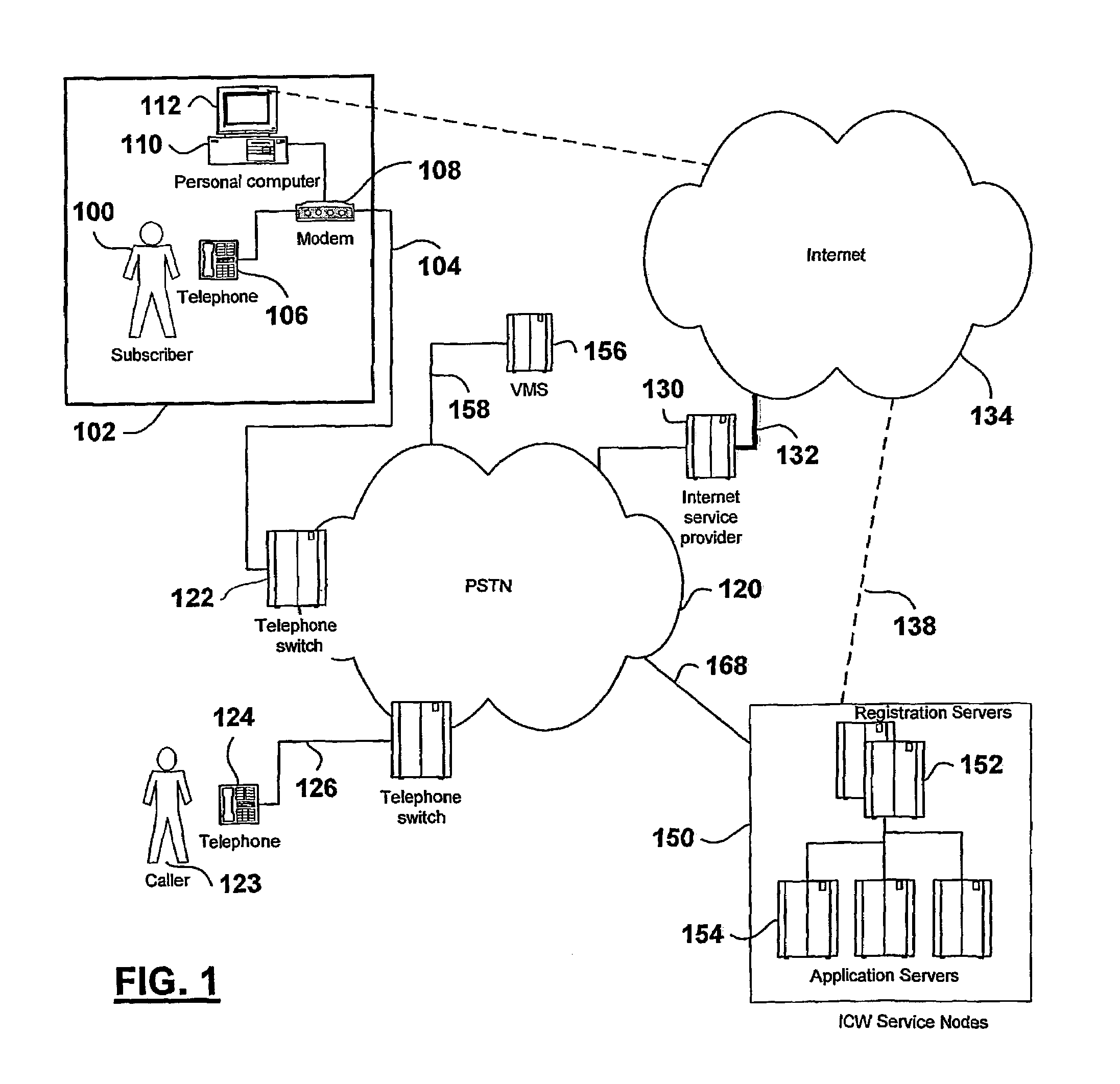
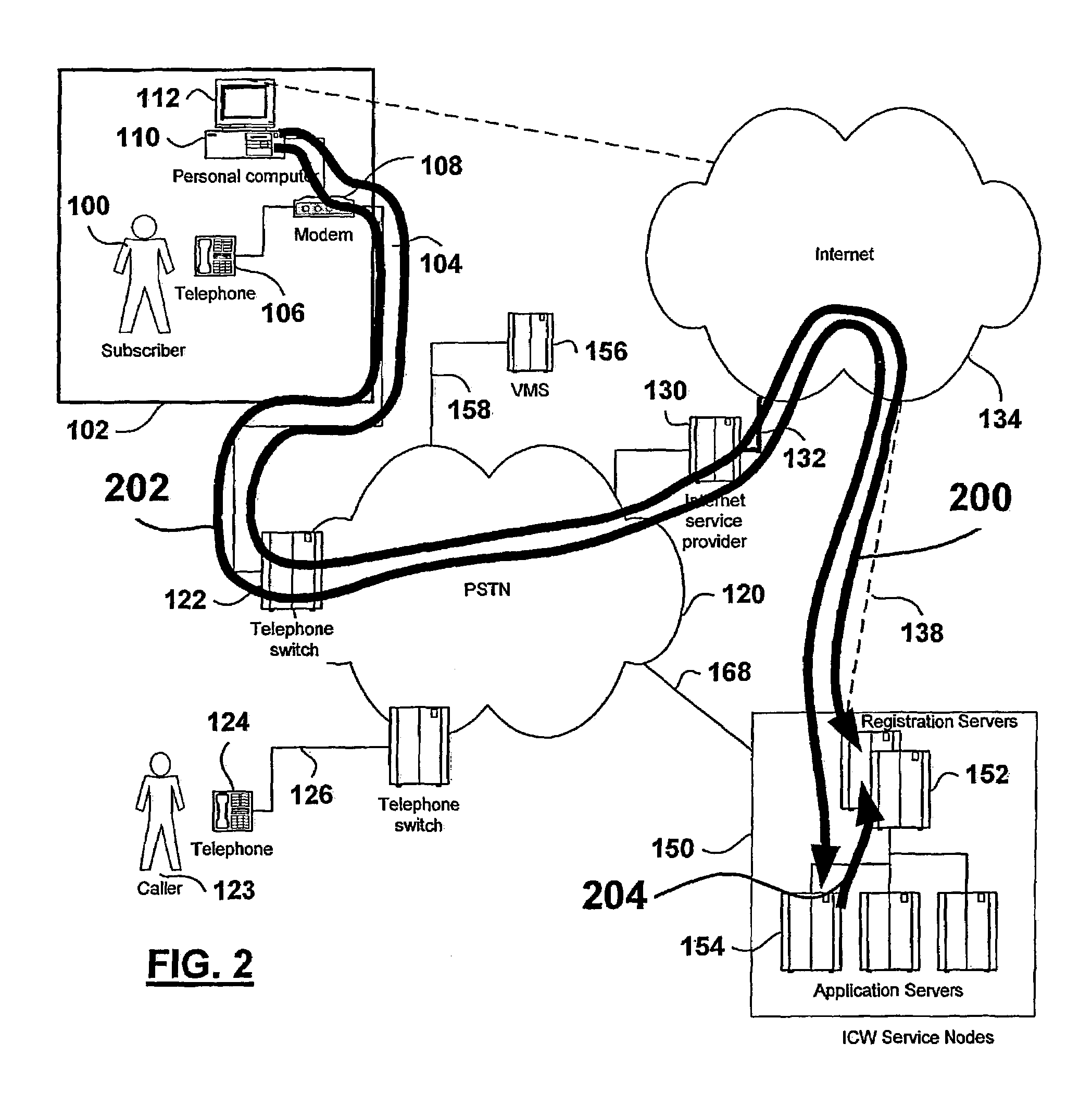
An Internet Call Waiting (ICW) service provides single-line subscribers (100) connected to the Internet with incoming call information, call screening and voice messaging capabilities. An incoming call is terminated at an ICW server (154). The caller is prompted to leave a voice message and the voice message is relayed in real-time over the Internet connection (138) to permit the subscriber to monitor the message. The subscriber can choose to answer the call at any time before the caller disconnects. Subscriber profile options specify how calls are treated. Calls may be forwarded to a second directory number, directed to a Voice-over-IP (VoIP) connection, or the Internet connection may be dropped and the call completed to the subscriber's directory number. The subscriber benefits from being able to screen voice messages in real-time, which assists the subscriber in determining how the call should be terminated.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Call screening system and method
ActiveUS7236577B2Easy to operateMake up for deficienciesSubstation speech amplifiersSpecial service for subscribersScreening callSpeech sound
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Audio call screening for hosted voicemail systems
ActiveUS20050025295A1Easy to monitorEasy to takeAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingAutomatic exchangesScreening callTelephone terminal
The present invention allows a user to screen messages being left at a hosted voicemail system from a telephone terminal. Incoming calls intended for the telephone terminal are routed to the voicemail system immediately or after attempting to connect incoming call to the telephone terminal. As the caller is leaving a message at the voicemail system, a connection between the incoming call, voicemail system, and telephone terminal is established to allow the user to listen to the message and decide whether to take the call. The user may decide to take the call or let the caller finish leaving the message. In one embodiment, the telephone terminal is equipped to open only the speaker channel for monitoring the message and will provide a fully bi-directional connection if the user takes the call. The supporting switch and telephone terminal communicate with each other to facilitate the monitoring and taking of calls.
Owner:APPLE INC
Arrangement for managing voice over IP (VoIP) telephone calls, especially unsolicited or unwanted calls
Trust ratings are embedded in certificates of calling devices in a Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) communications system. A method of managing trust ratings involves automatically accumulating complaints concerning VoIP calls initiated from calling devices, and comparing respective quantities of accumulated complaints associated with each calling device. When a quantity of accumulated complaints associated with a given calling device exceeds a given threshold, a trust rating of the given calling device is reduced. In subsequent VoIP calls the given calling device attempts to place, the reduced trust rating is included in the call request so that the subsequent calls are subject to more austere call screening operations than calls having the unreduced trust rating. Call recipients thus affect the calling device's trust rating simply by entering complaints associated with received calls. The method effectively combats spam over Internet telephony (SPIT) through participation of called parties.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
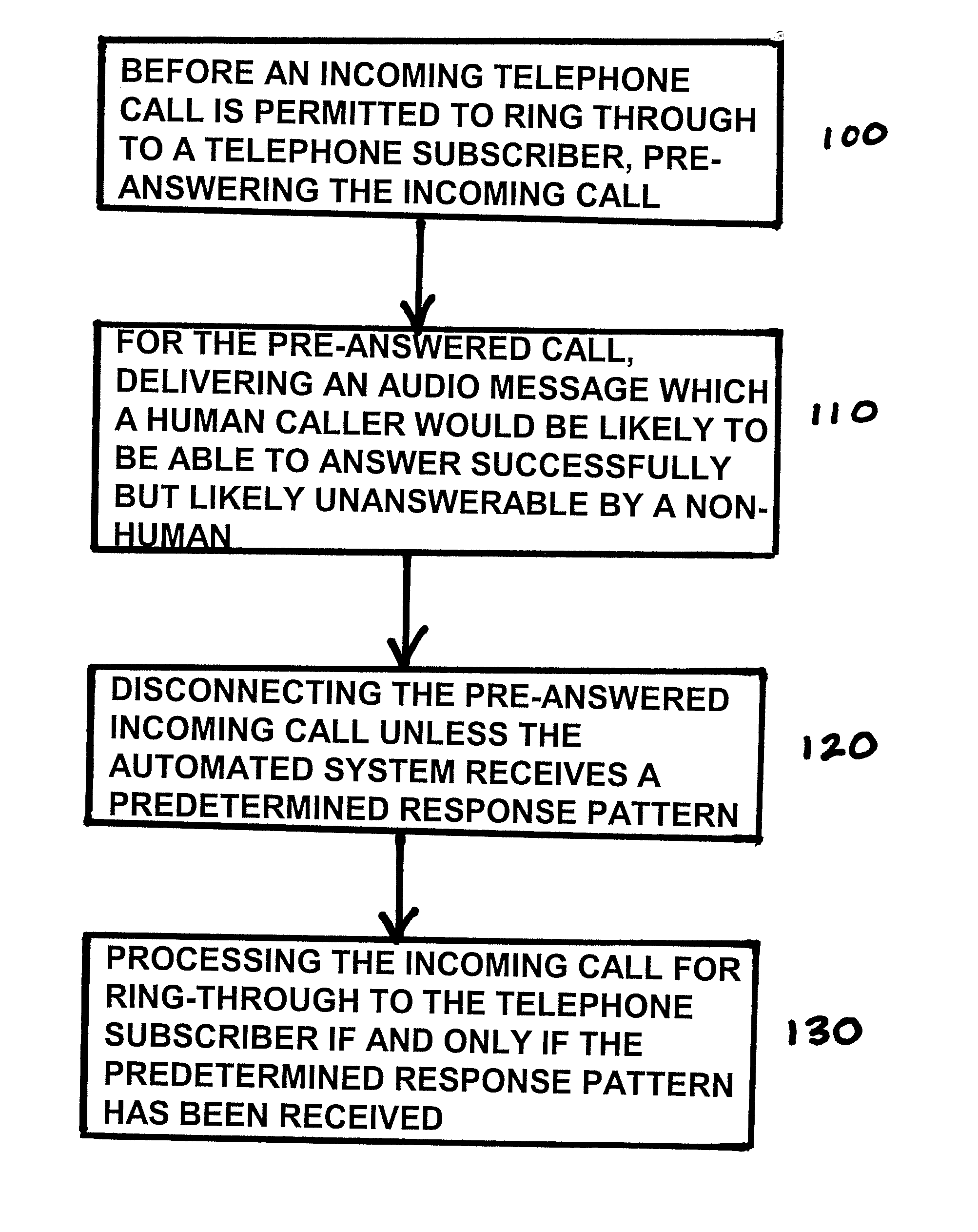
Stopping robocalls
A robocall is prevented from reaching a telephone subscriber, by an automated calling screening system that tests for presence of a human caller on the line, and disconnects calls absent a predetermined response. Audio messages to stymy a robocaller but answerable by a human are used.
Owner:GOULET MARY ELIZABETH +1
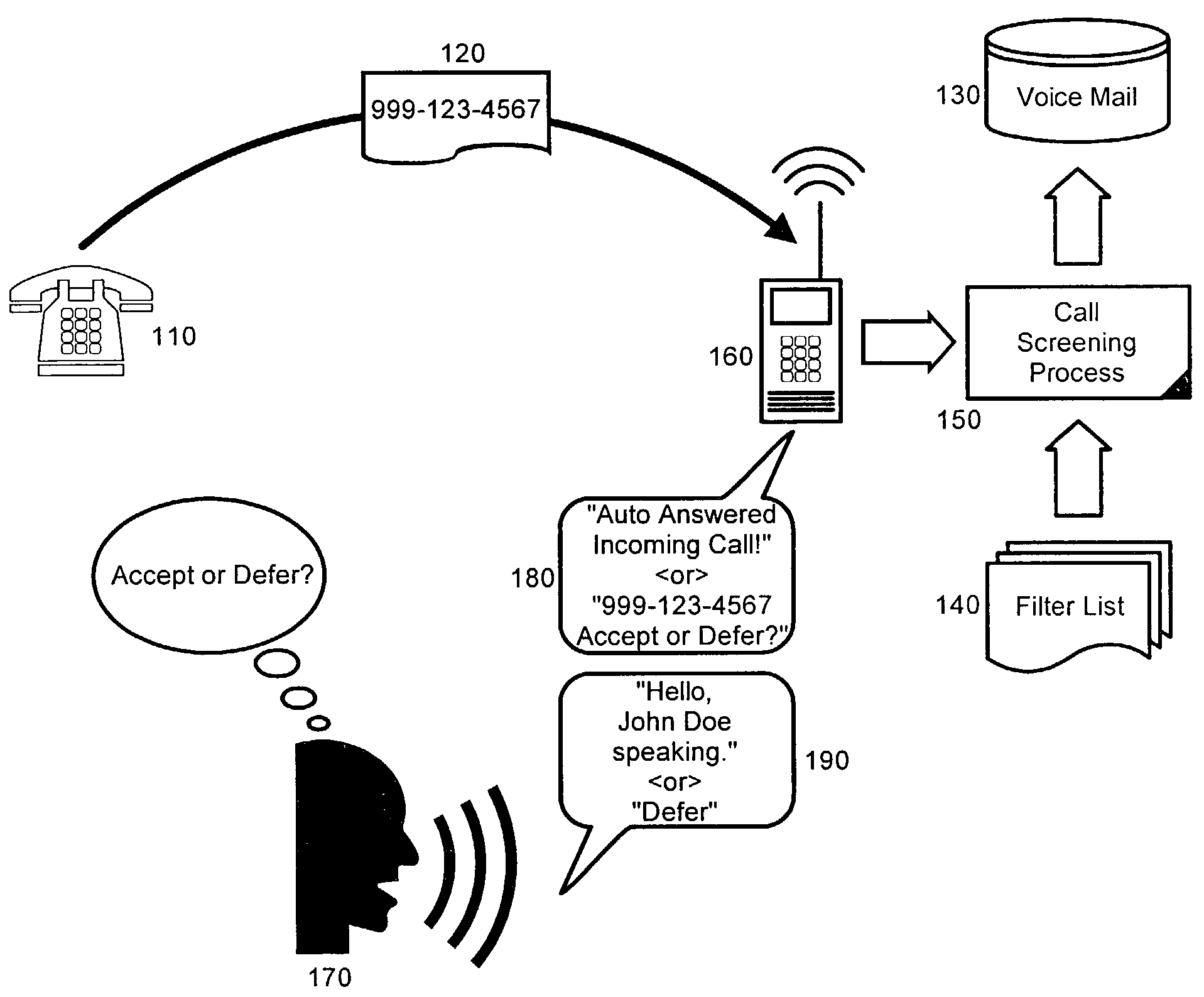
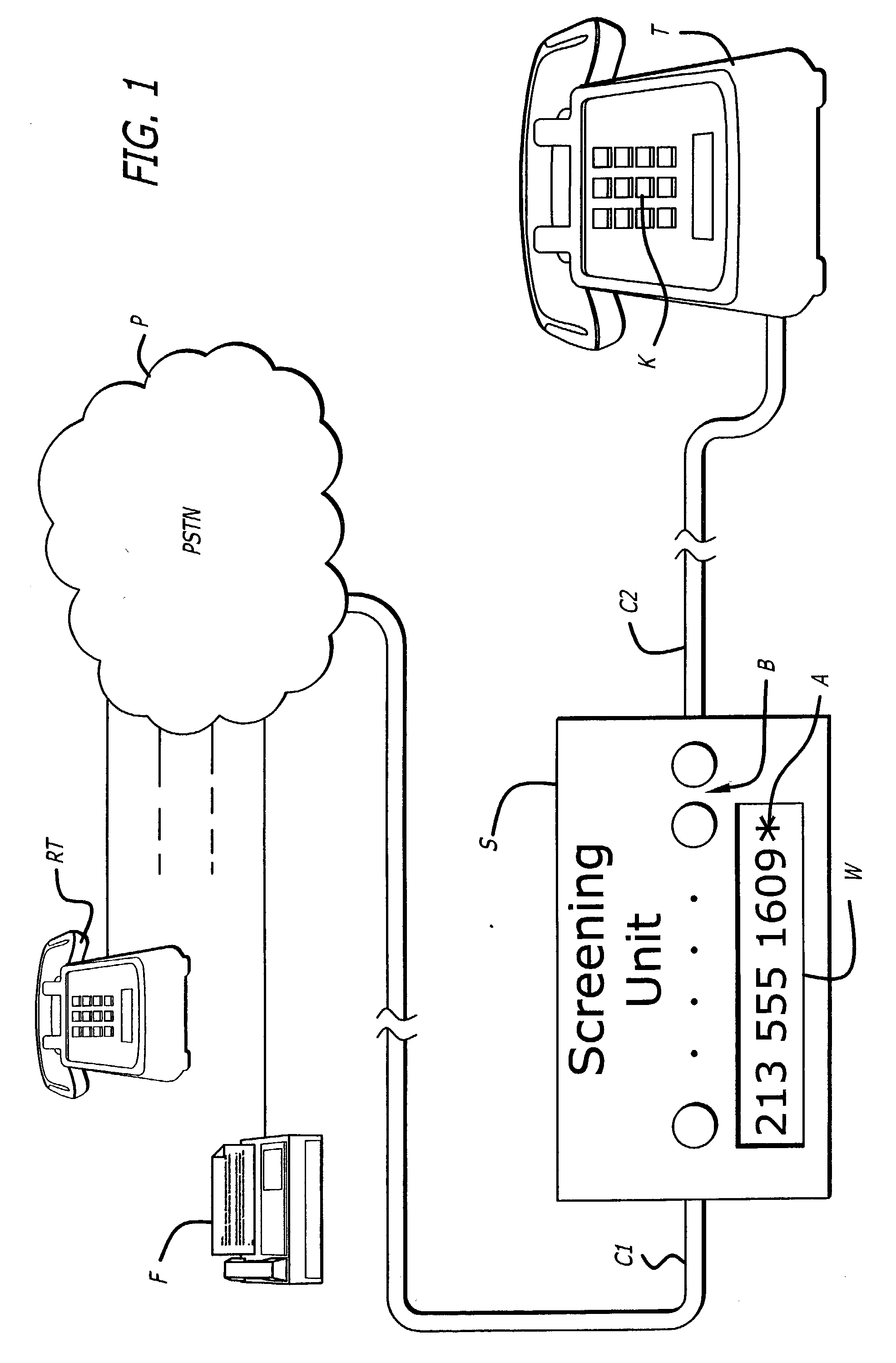
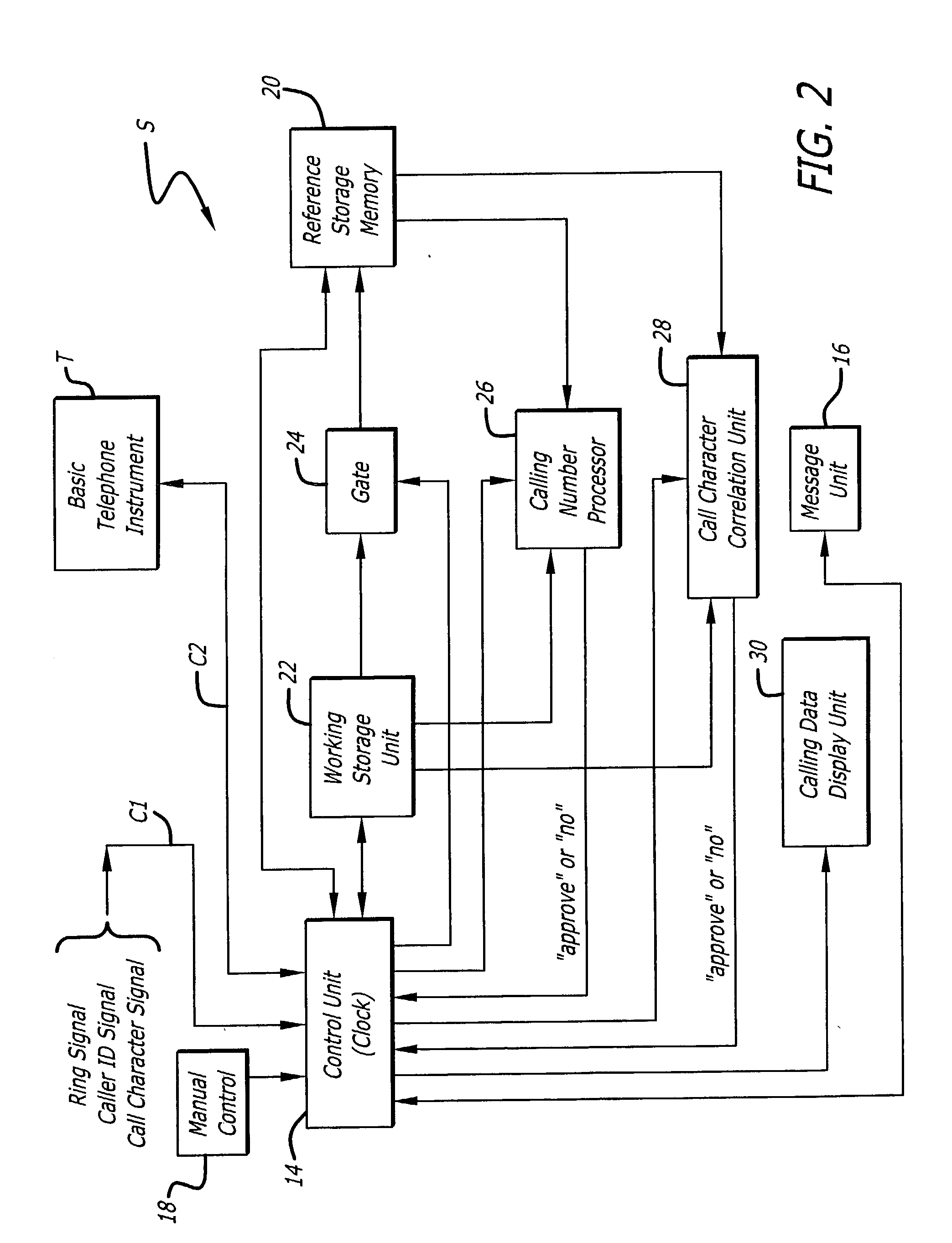
Comprehensive telephone call screening system
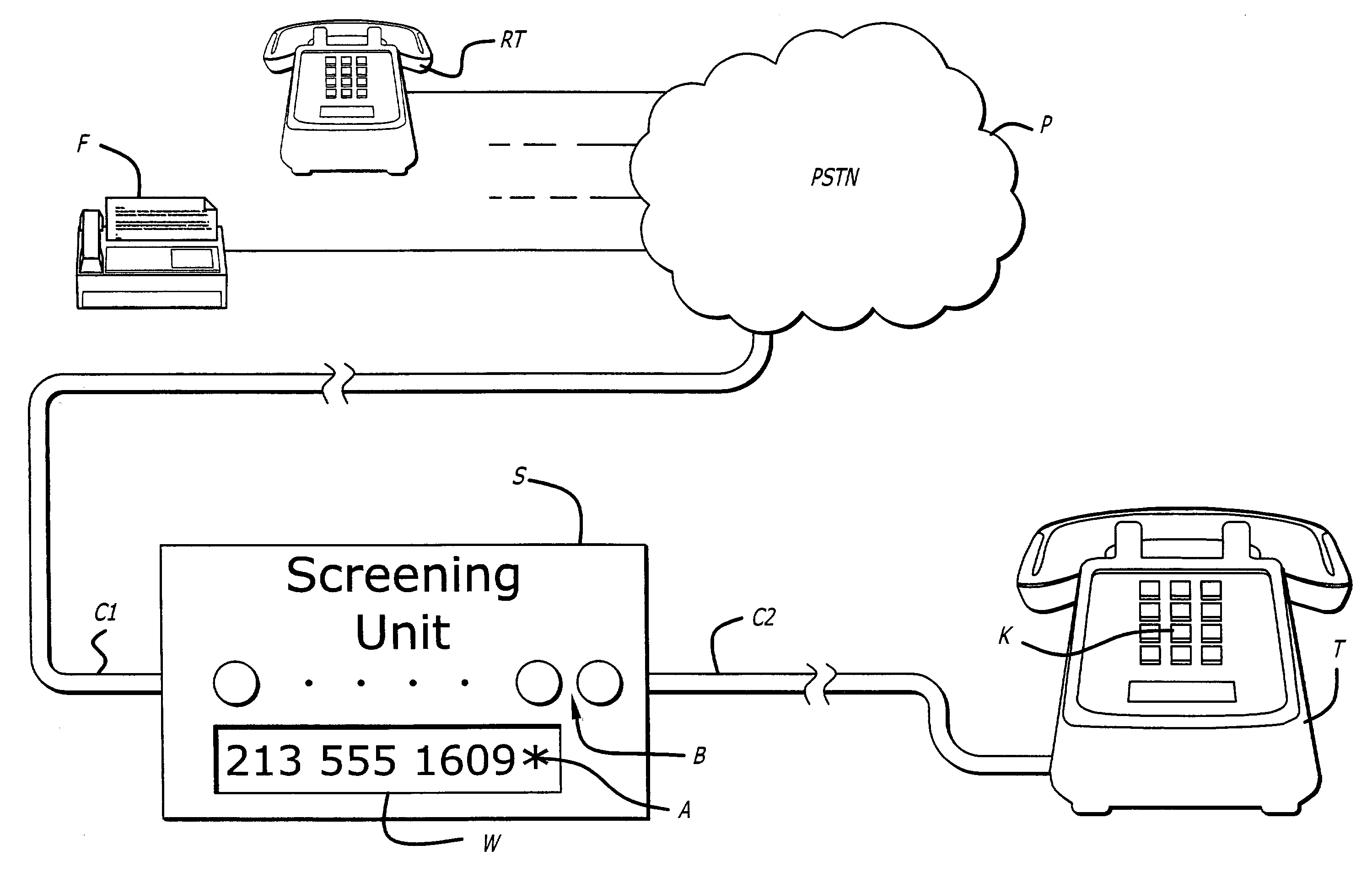
InactiveUS20040086101A1Special service for subscribersCalling susbscriber number recording/indicationScreening callTelephony
A dynamic telephone-call screening system detects indications of the character for incoming calls as a basis to determine acceptance. Calls that are identified and indicated to be undesirable, as from a facsimile machine, may be categorically screened on the basis of character. Calls identified to be from an undesired terminal also are recognized and screened. Indications of undesired character calls and undesired calling terminal are stored for reference testing. Upon receiving an undesired call, its character and source may be stored for future reference.
Owner:TELEBUYER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com