Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44 results about "Paravalvular leak" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
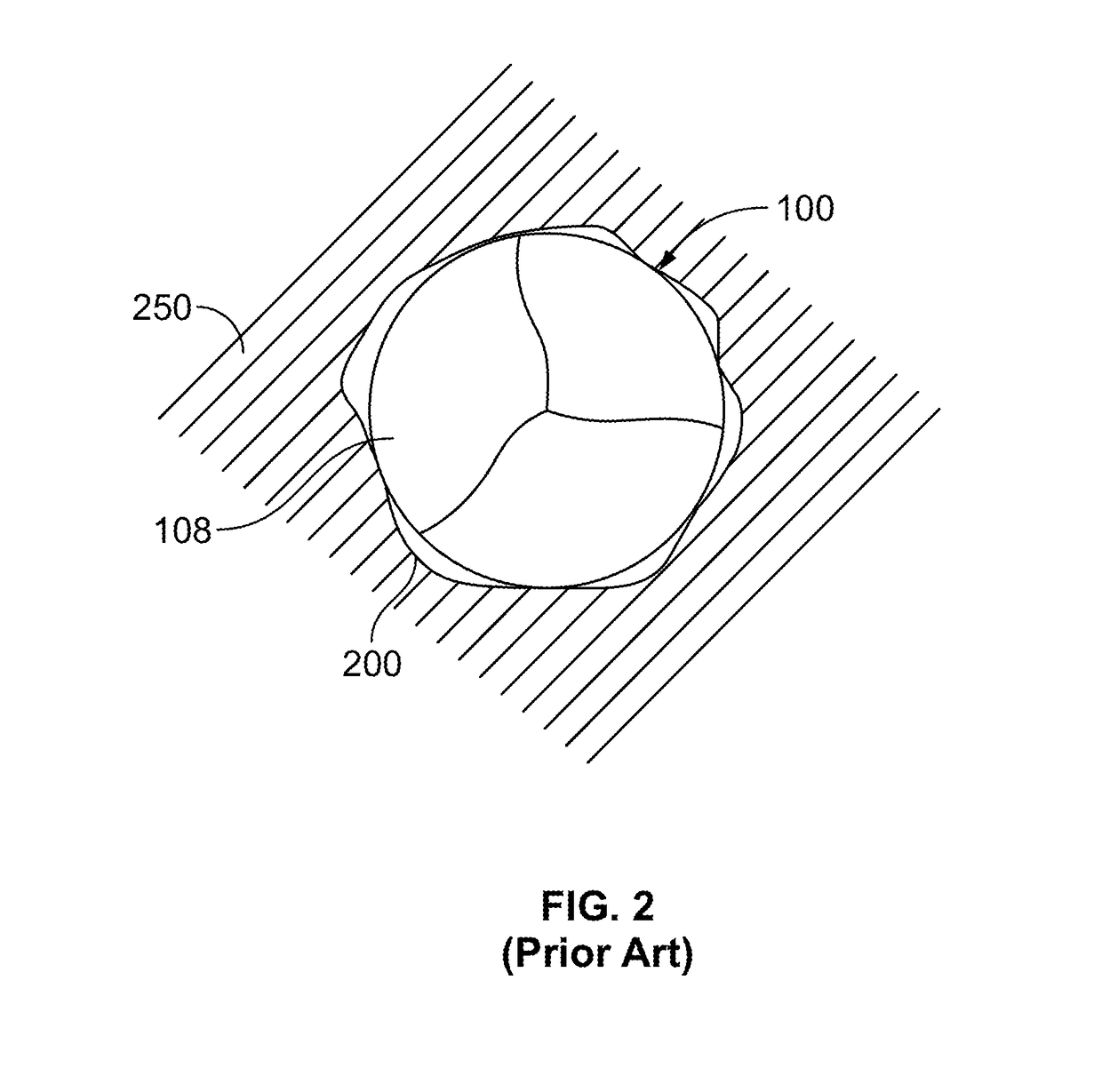
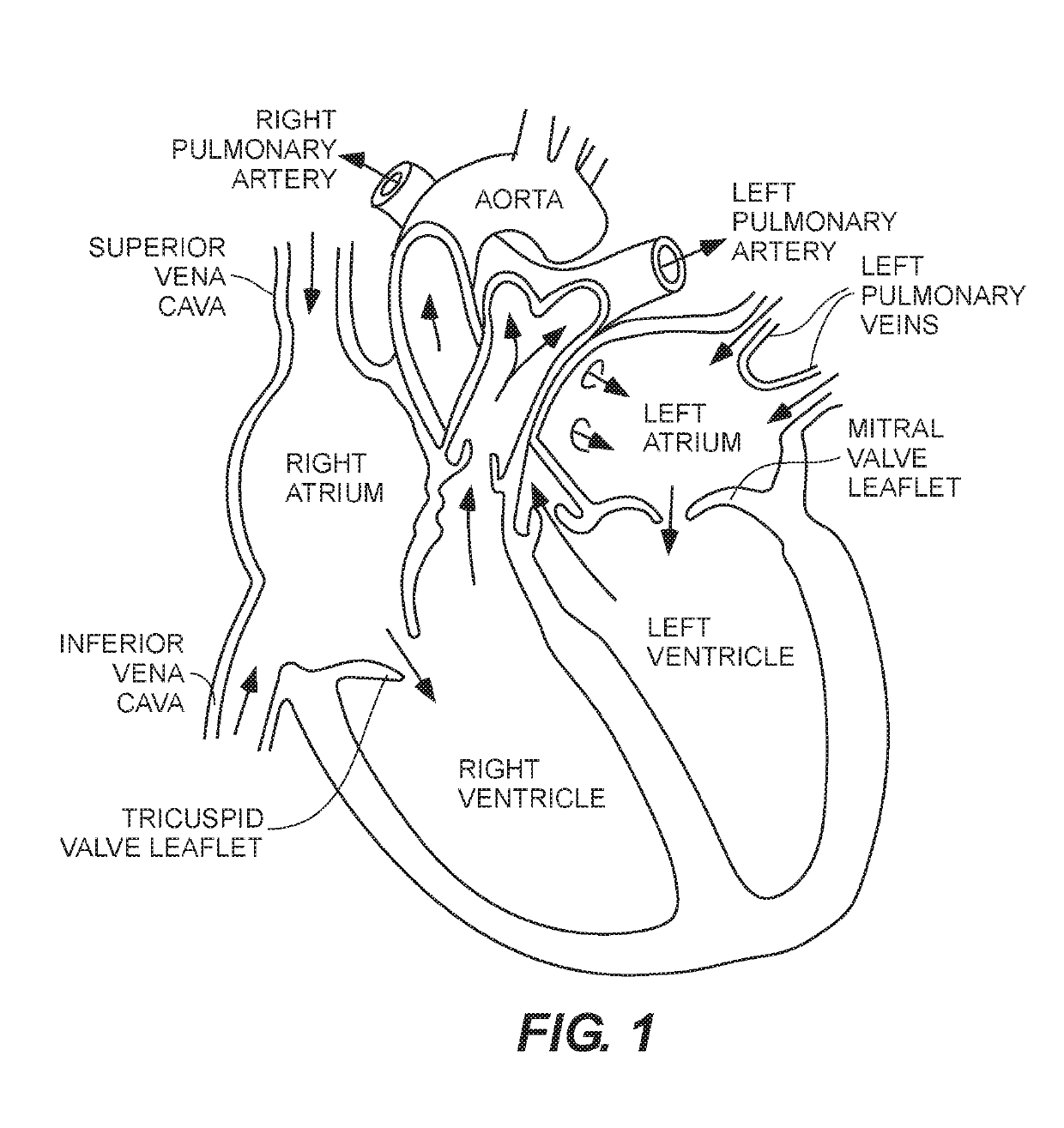
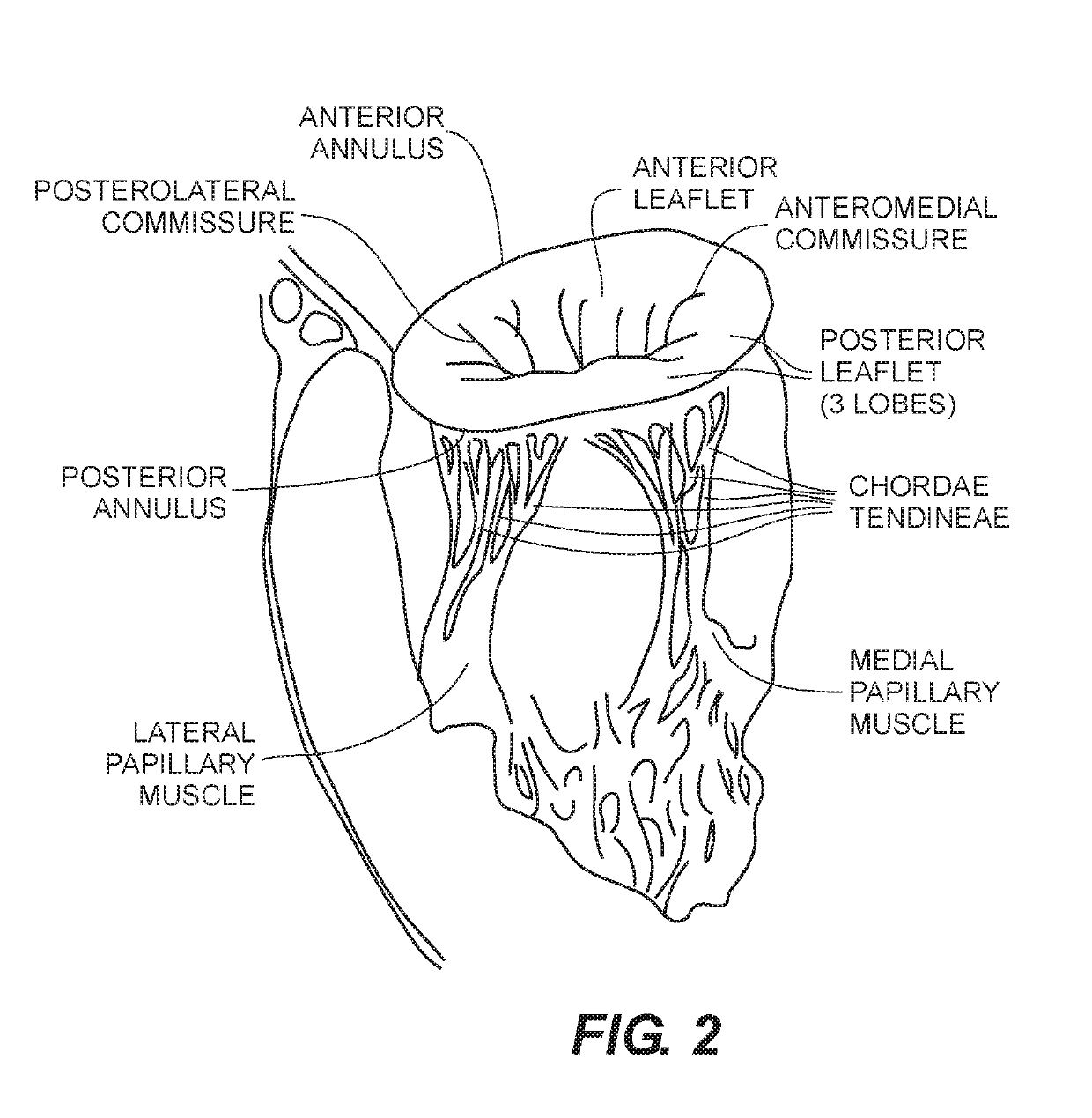
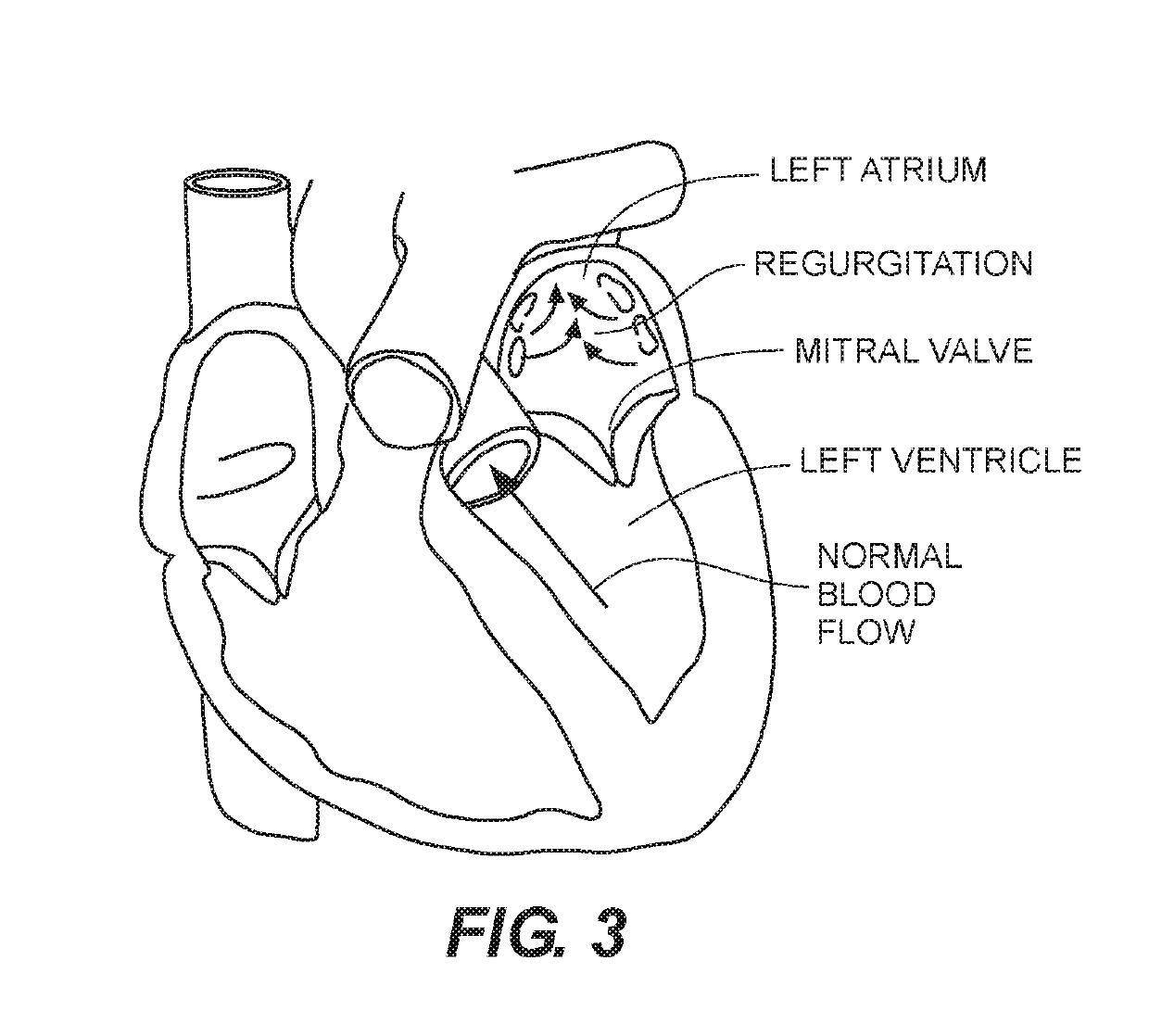
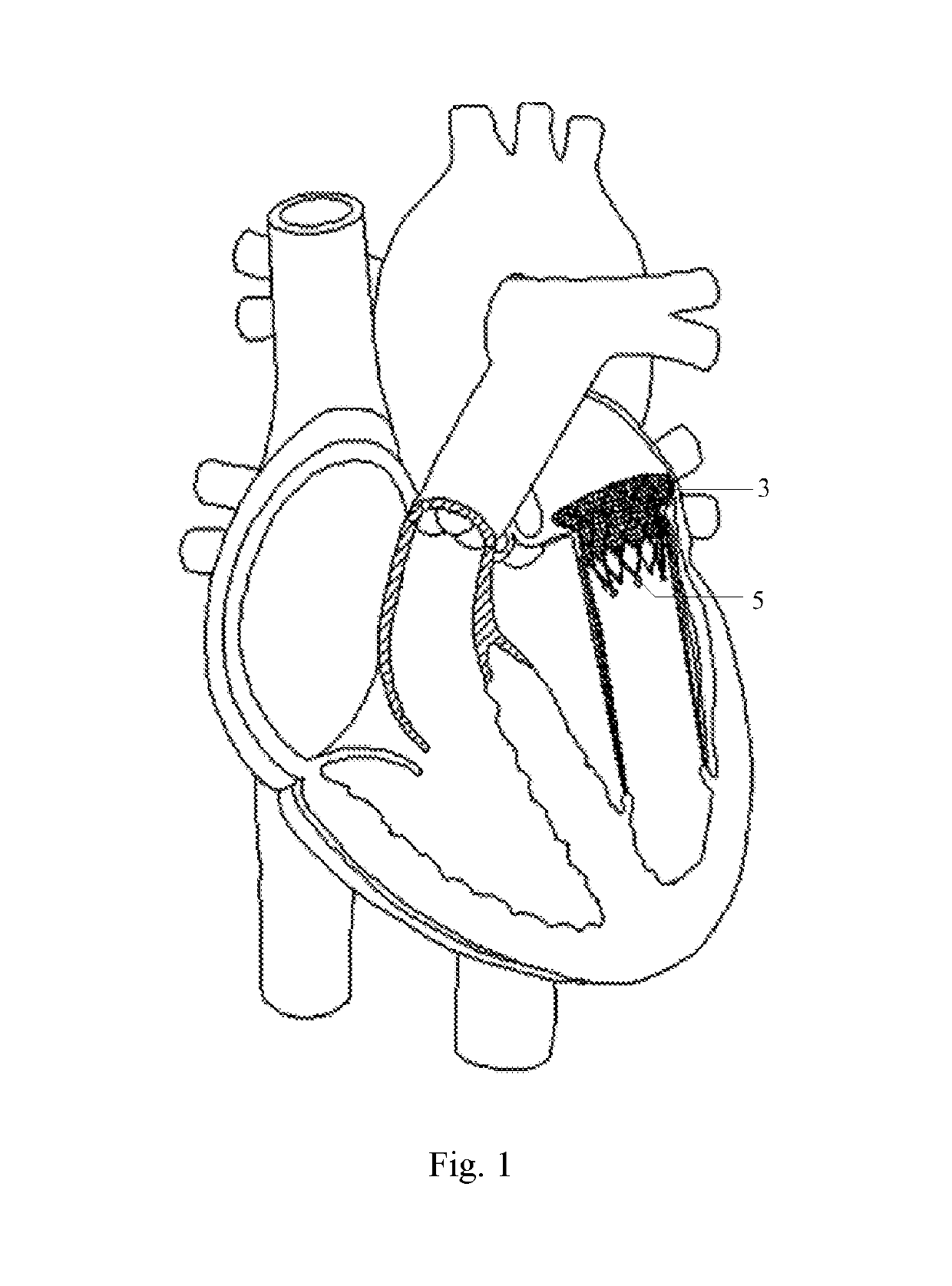
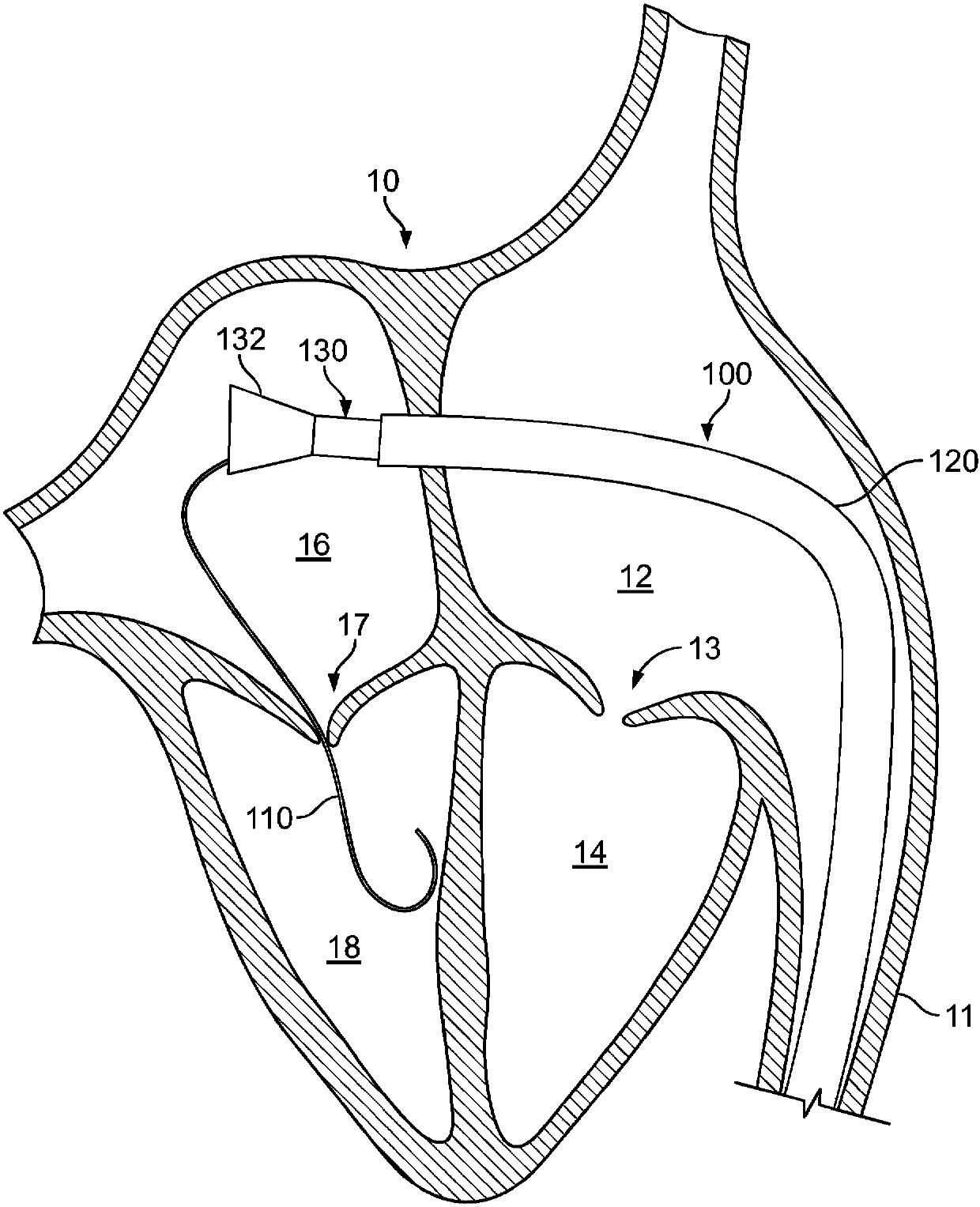
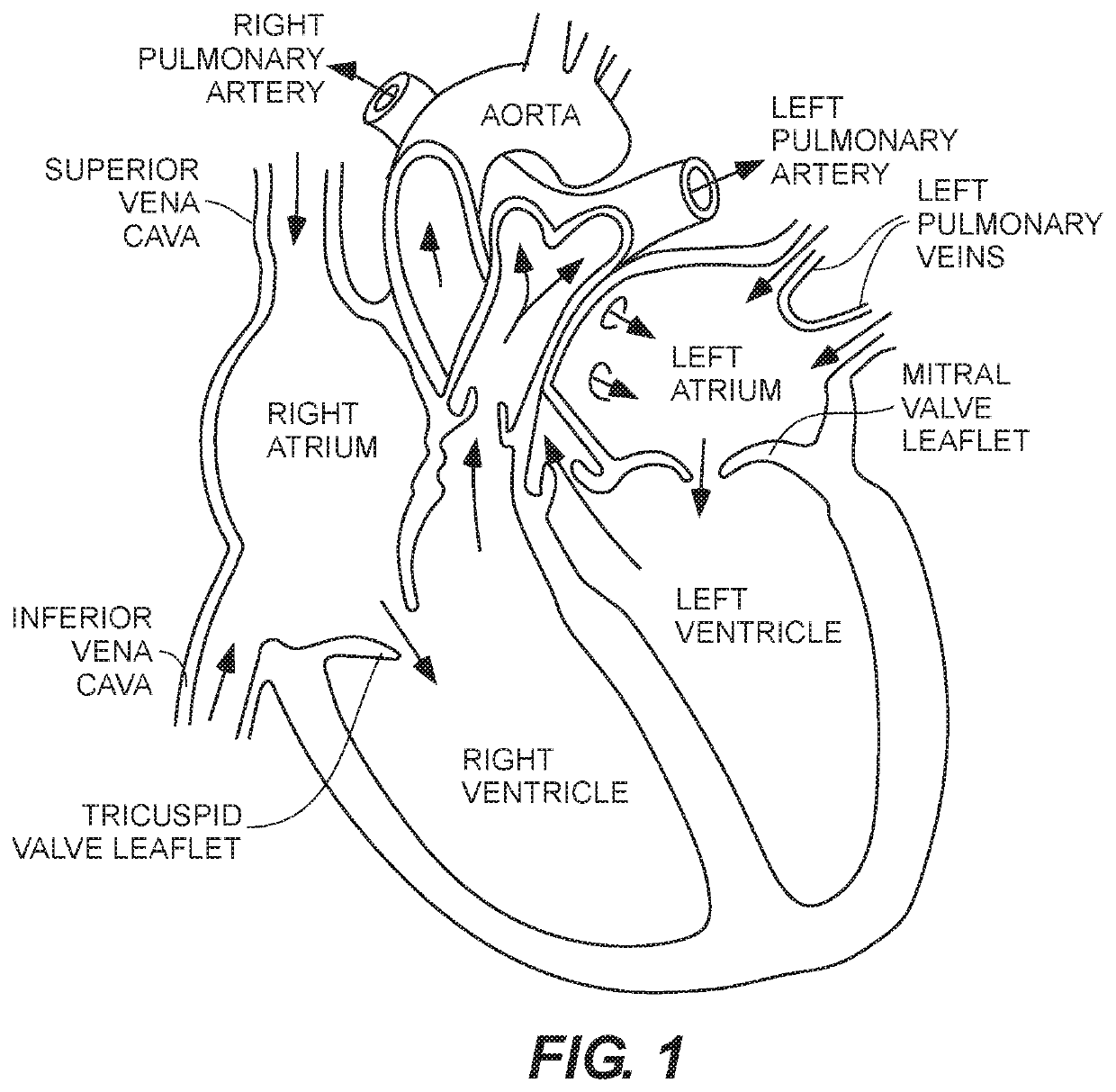
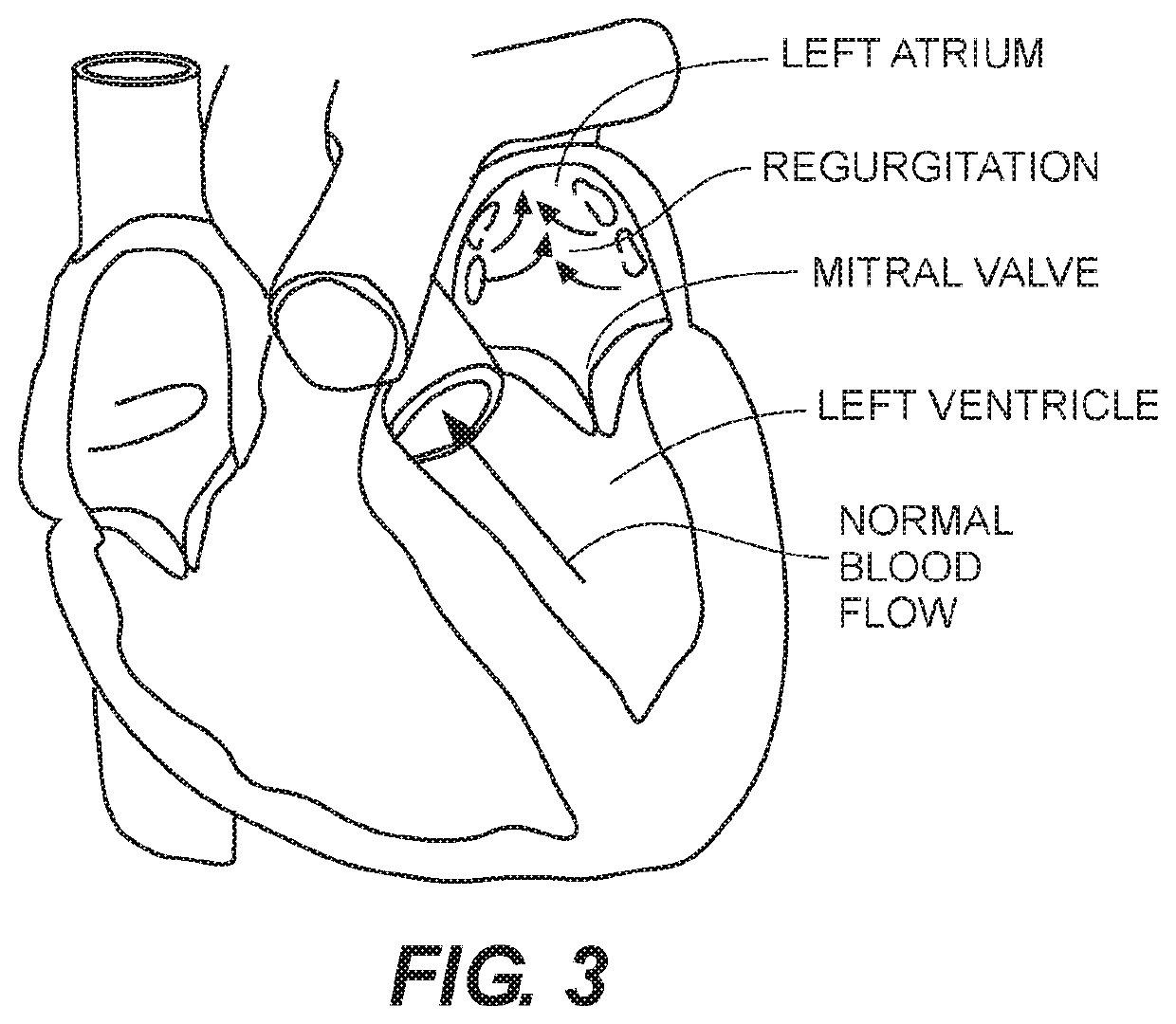
Paravalvular leak is a leak around a valve replacement. A form of leaky heart valve. When someone has valve replacement surgery they have a new valve put in place.
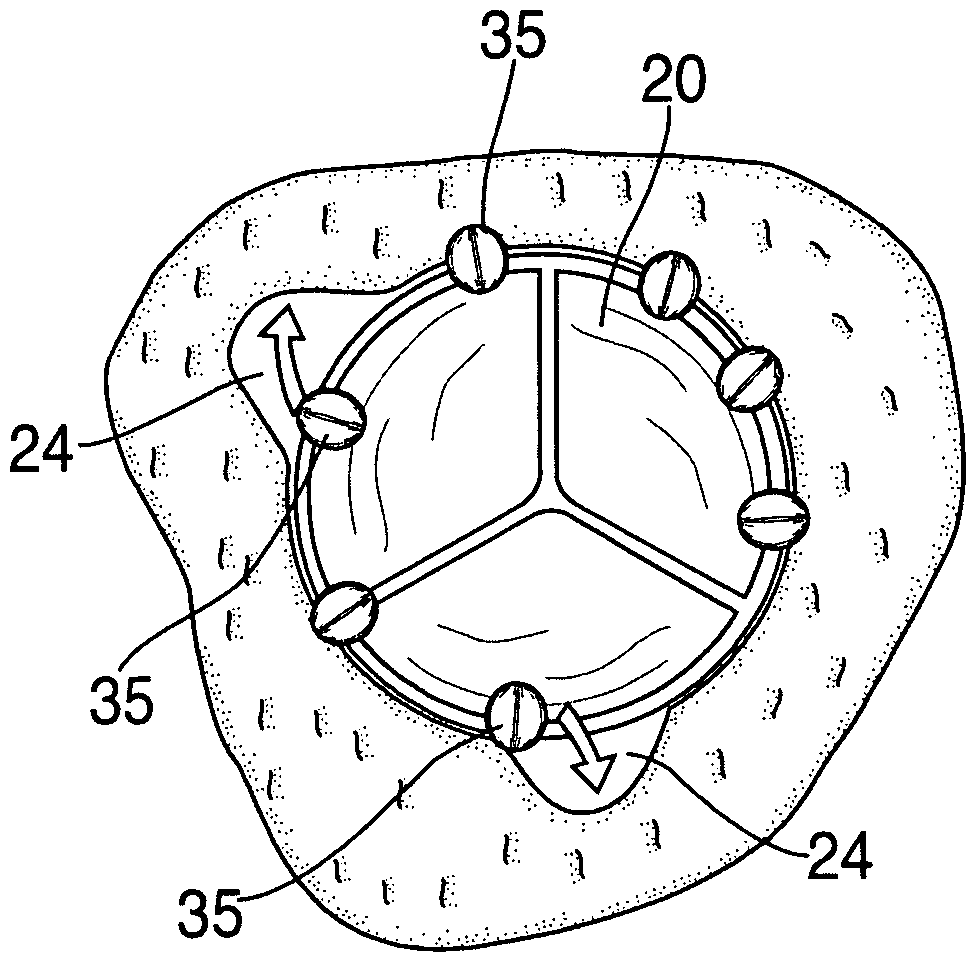
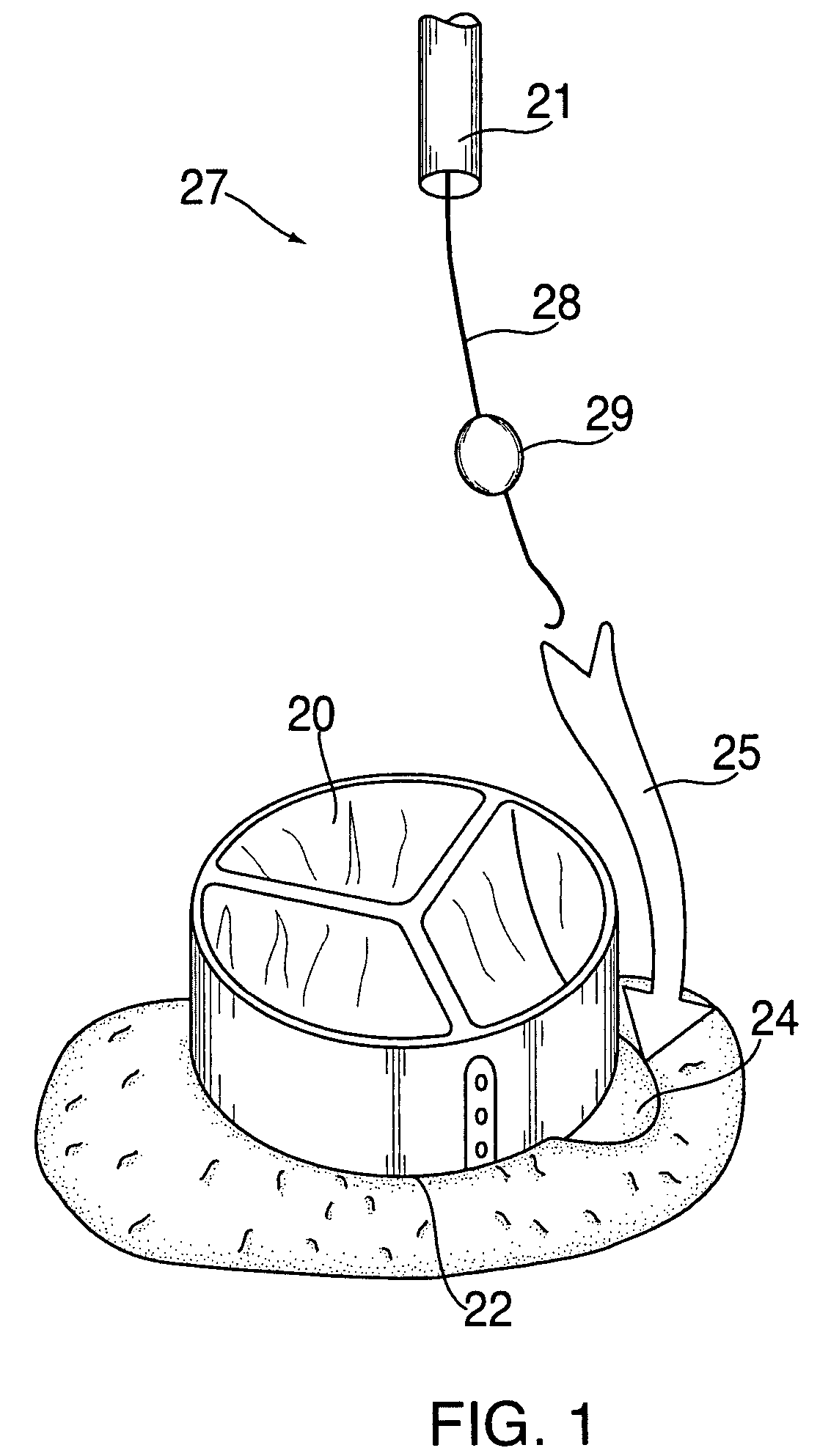
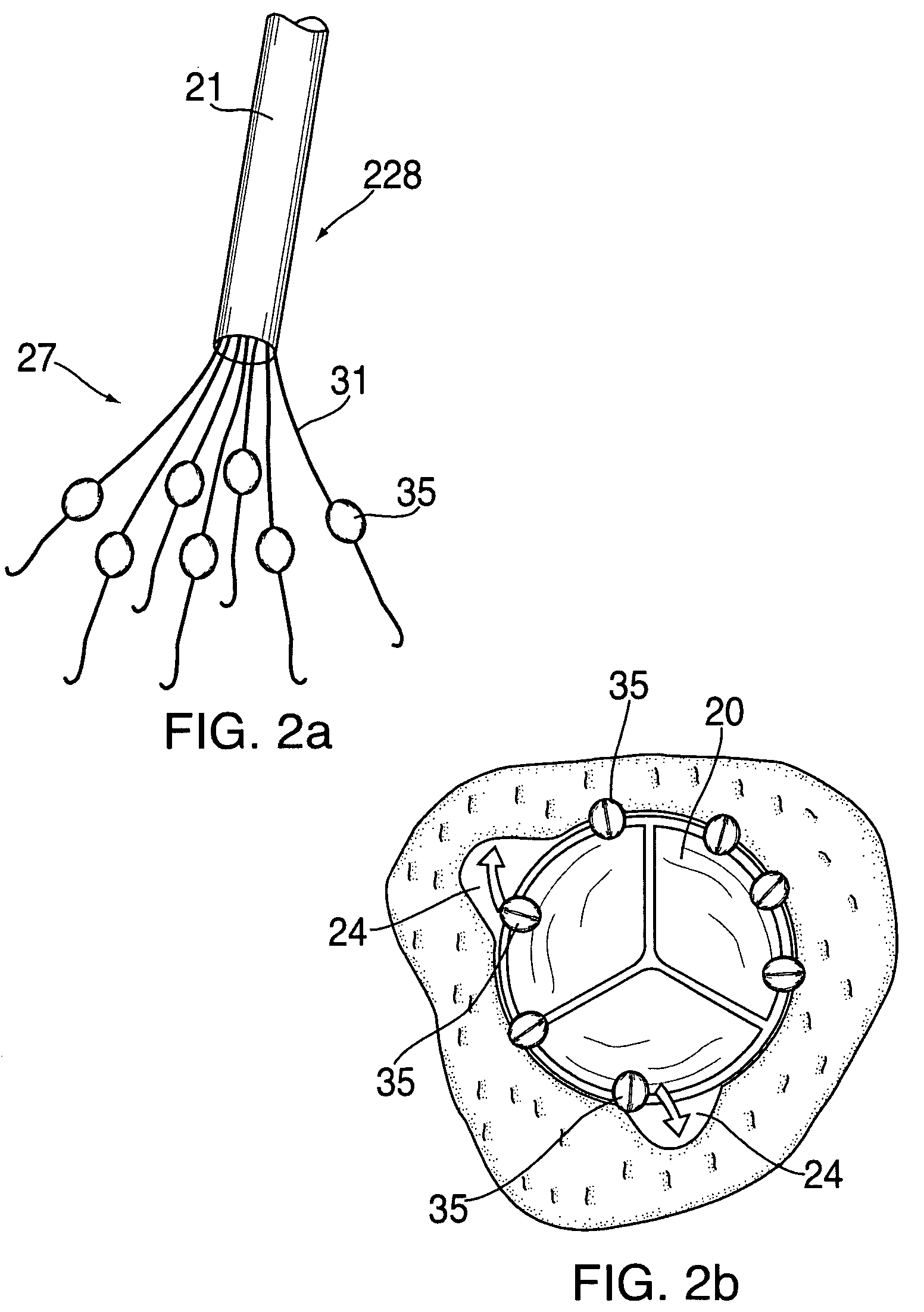
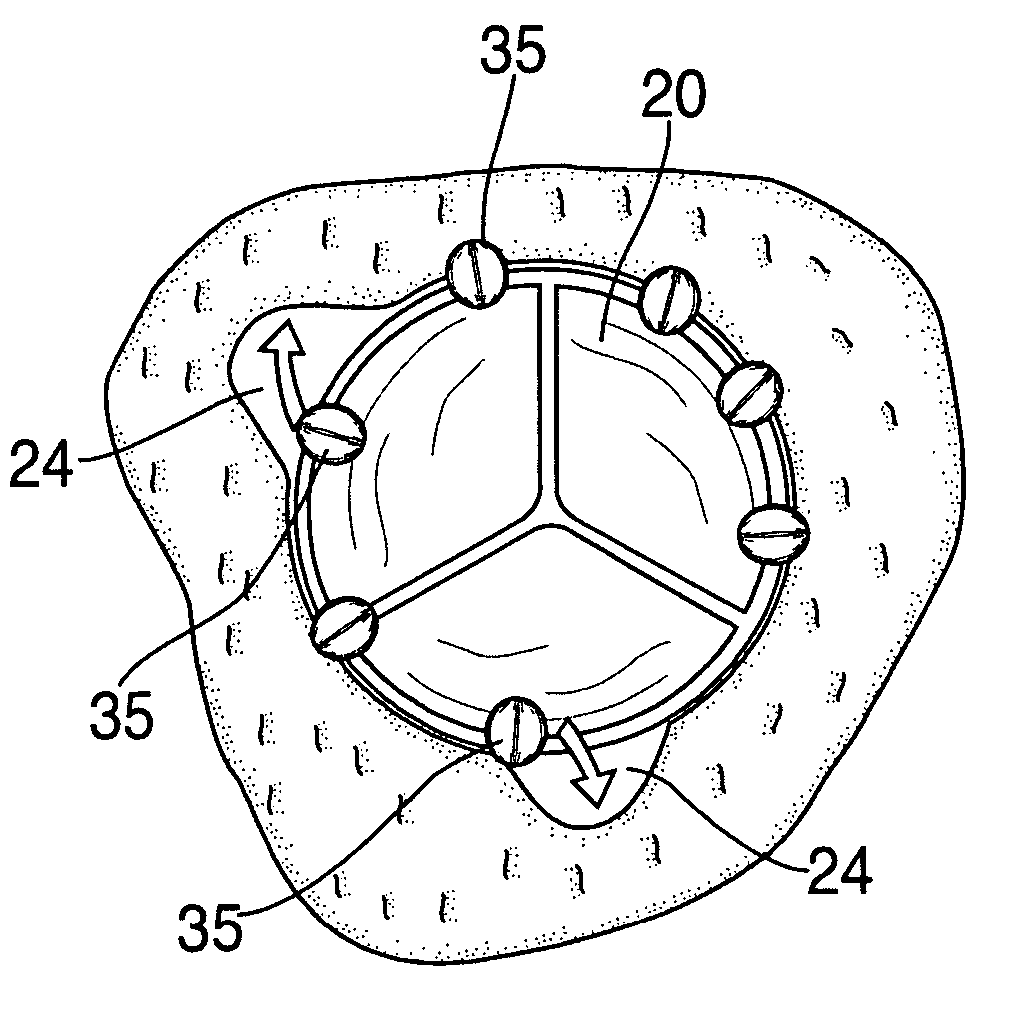
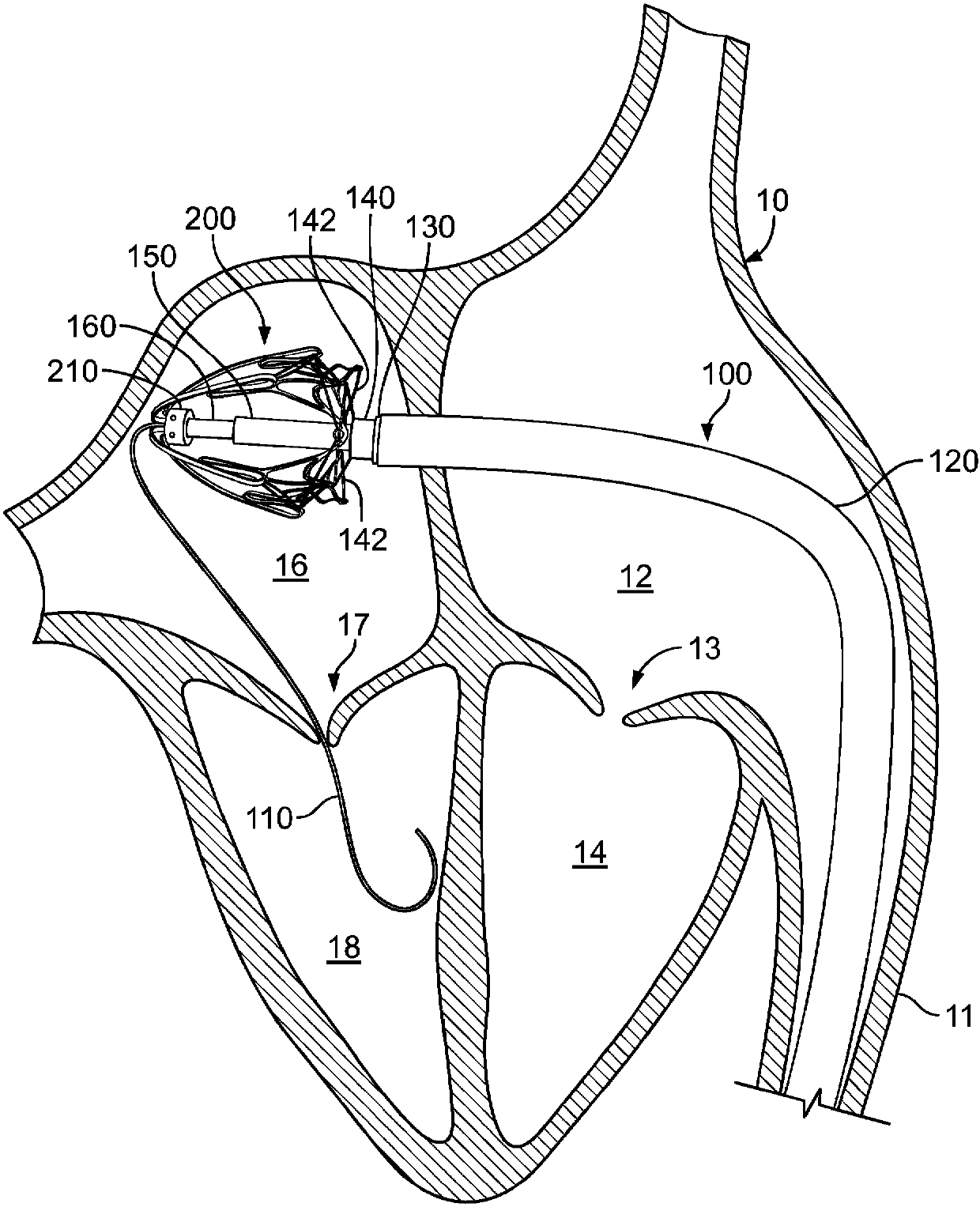
Paravalvular leak detection, sealing, and prevention
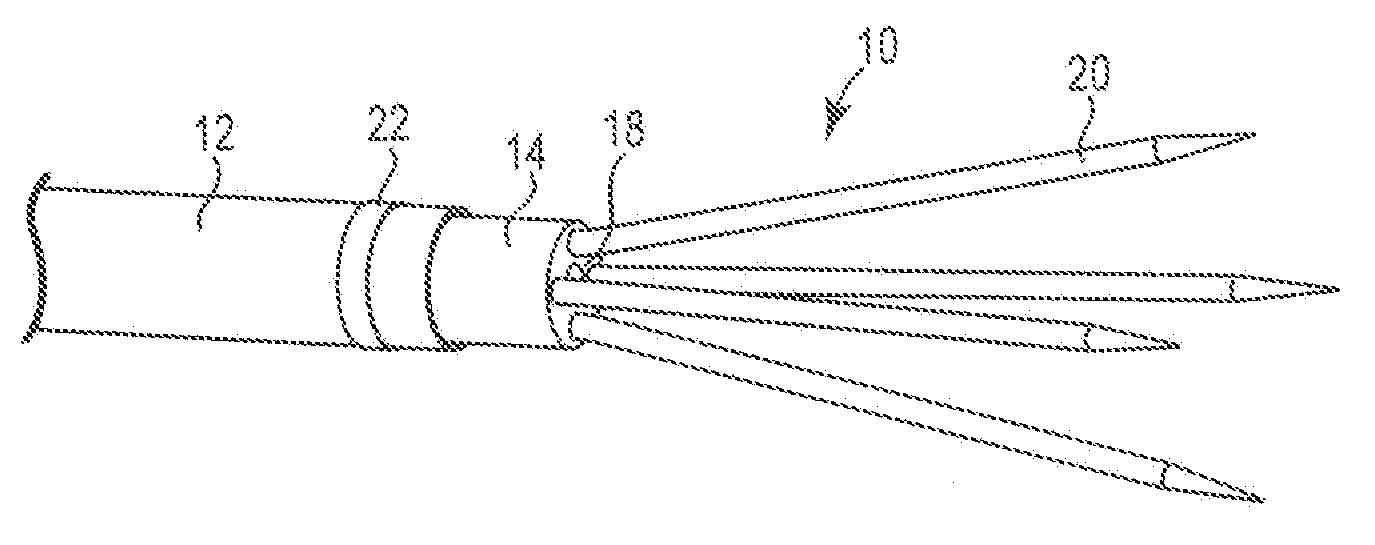
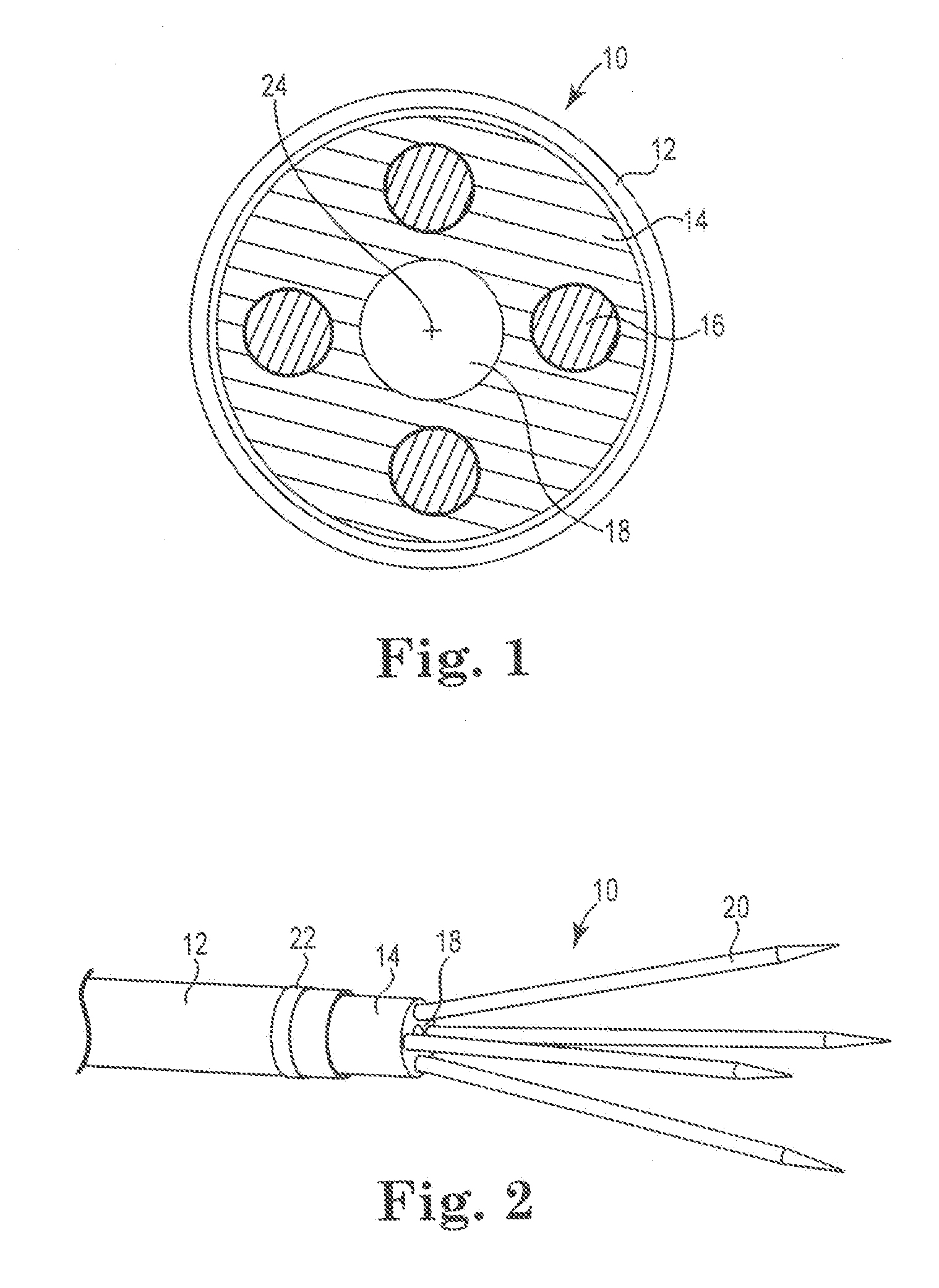
The present invention provides a series of new percutaneous concepts of paravalvular repairs including identifying the leak location, several repair techniques and finally built-in means for leak prevention, built on percutaneous valves. A catheter-delivered device locates cavities occurring between a prosthetic valve and the wall of the body vessel where the valve is implanted, the cavities producing paravalvular leaks during diastole, the device comprising at least one of a plurality of flexible wires, the wire having attached to it a balloon, wherein the balloon is pulled by the leak through the cavity and wherein the wire then serves to mark the cavity location.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI PVT
Paravalvular leak detection, sealing, and prevention
The present invention provides a series of new percutaneous concepts of paravalvular repairs including identifying the leak location, several repair techniques and finally built-in means for leak prevention, built on percutaneous valves. A catheter-delivered device locates cavities occurring between a prosthetic valve and the wall of the body vessel where the valve is implanted, the cavities producing paravalvular leaks during diastole, the device comprising at least one of a plurality of flexible wires, the wire having attached to it a balloon, wherein the balloon is pulled by the leak through the cavity and wherein the wire then serves to mark the cavity location.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI PVT
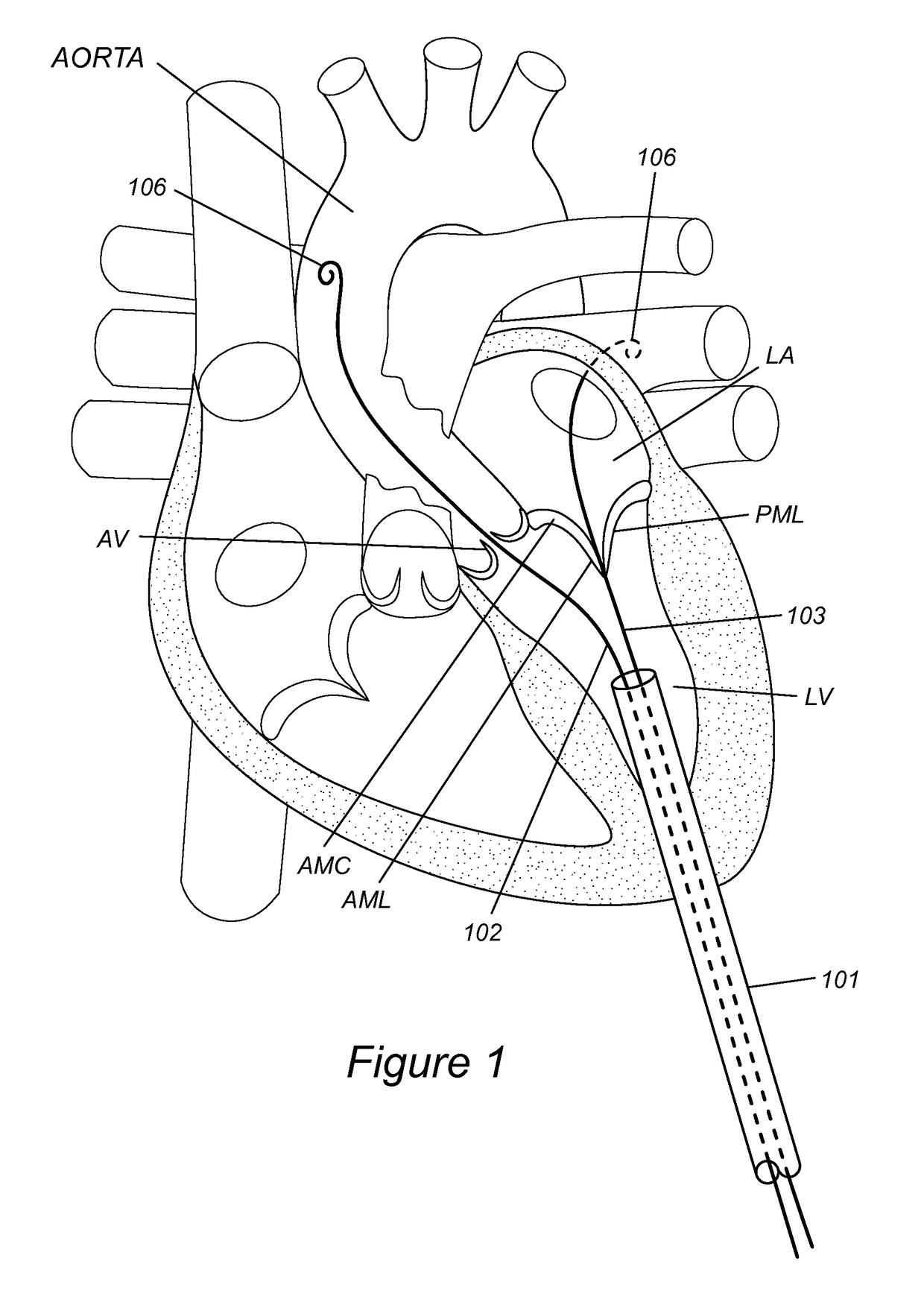
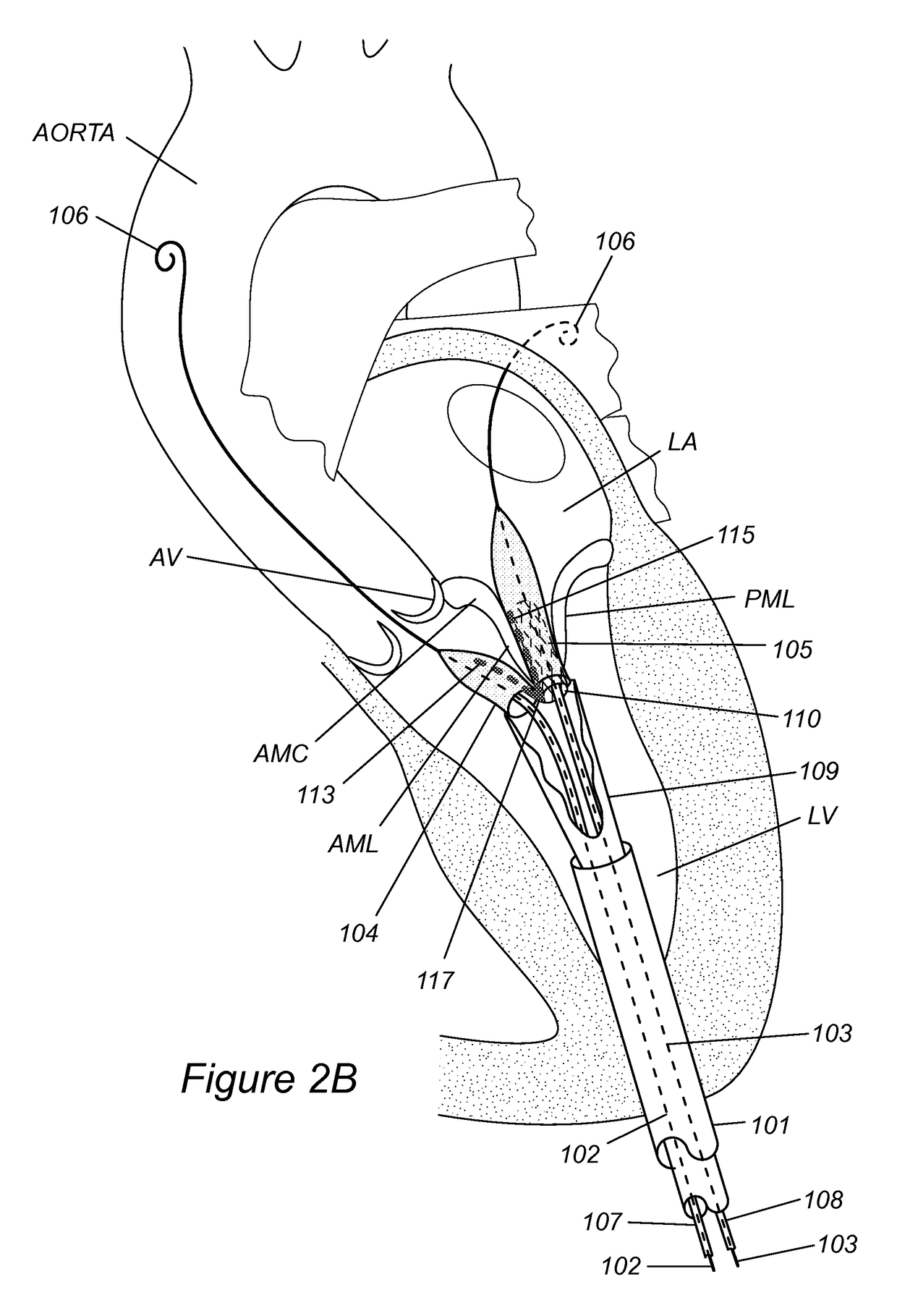
Prosthetic mitral valve
A prosthetic mitral valve with a frame comprises at least one arm shaped to deploy among a region of chordae tendineae of the native mitral valve to deflect these chords in order to pull the native valve leaflets around the frame to avoid paravalvular leaks. The frame may be made from two parts that are connected by sutures. The prosthetic valve may be deployed by a catherer comprising a deployment clamp attached to the valve frame where the deployment clamp is actuable to induce rotation of the frame.
Owner:TEL HASHOMER MEDICAL RES INFRASTRUCTURE & SERVICES
Artificial Heart Valve Stent and Weaving Method Thereof
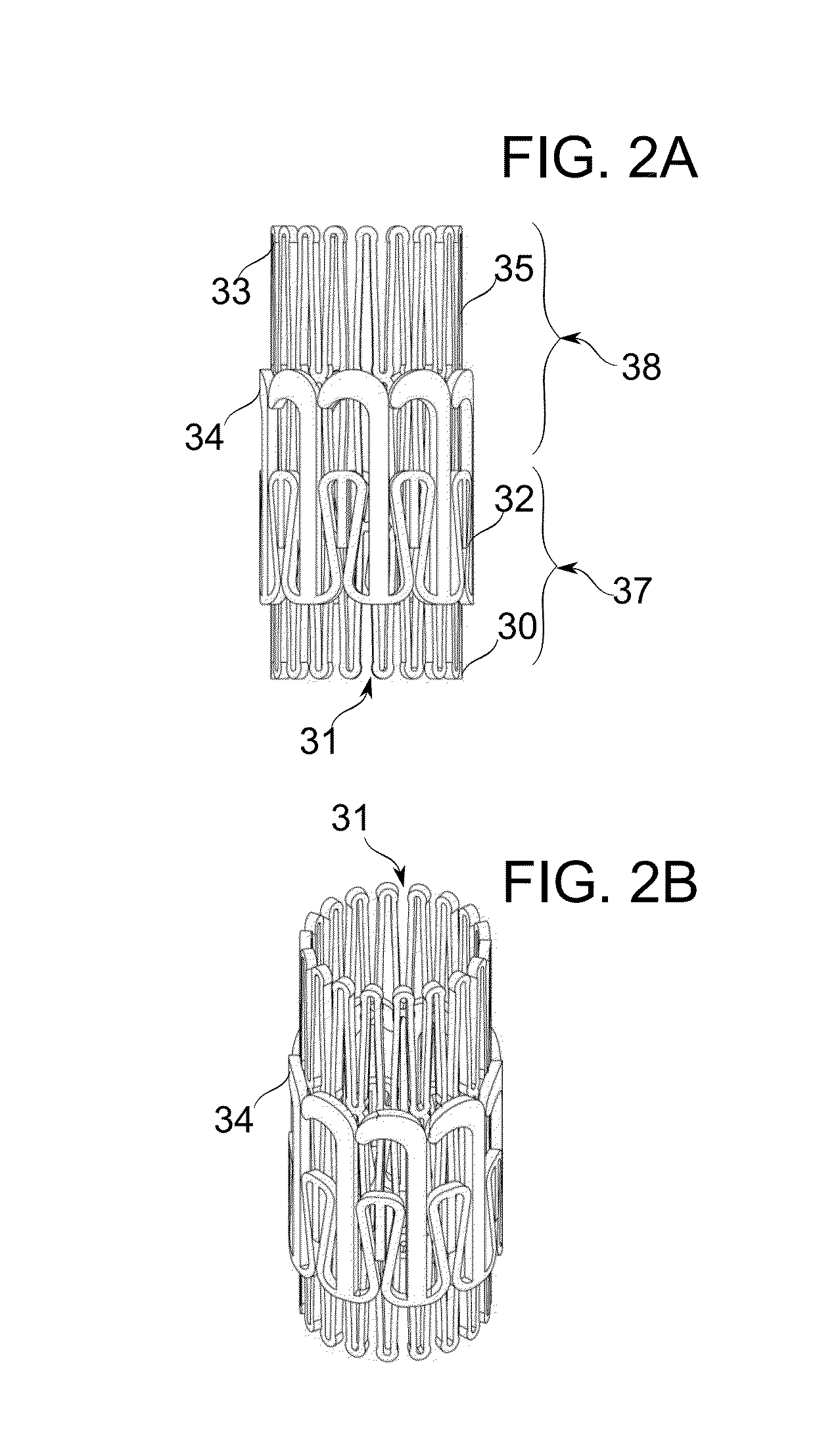
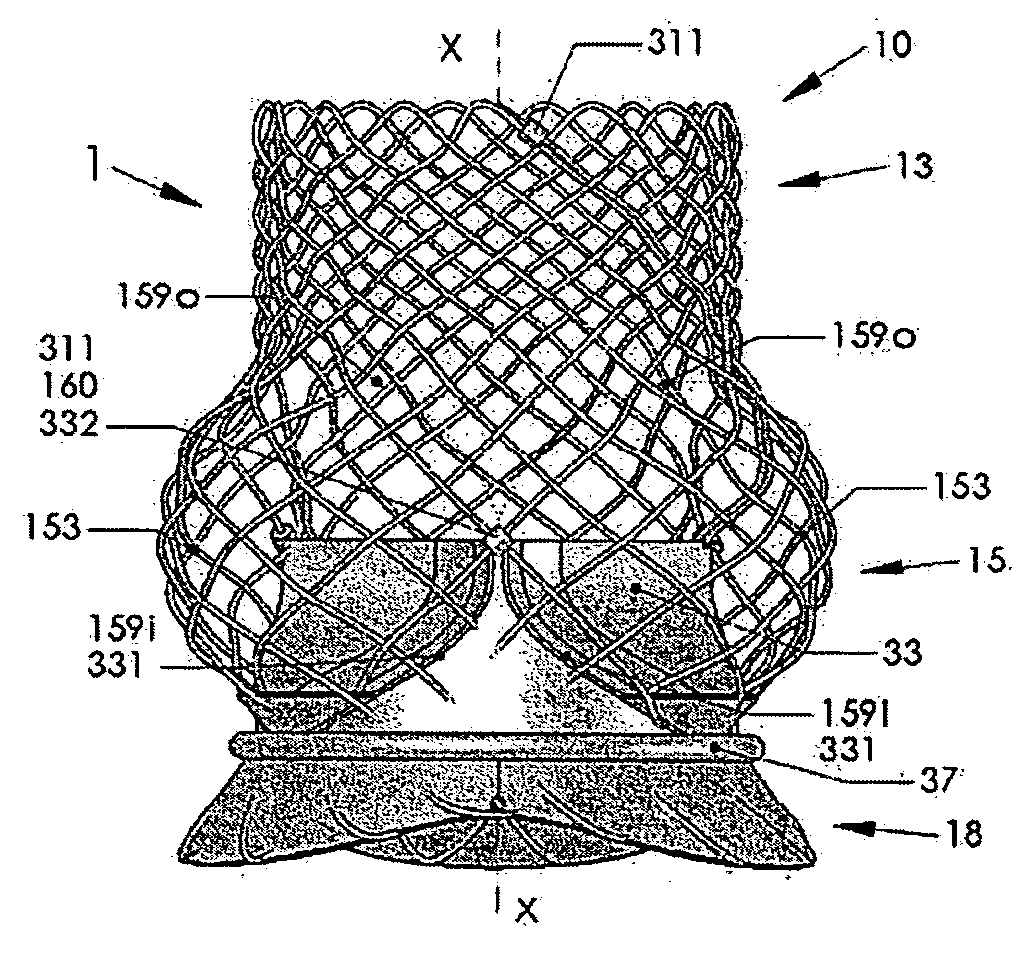
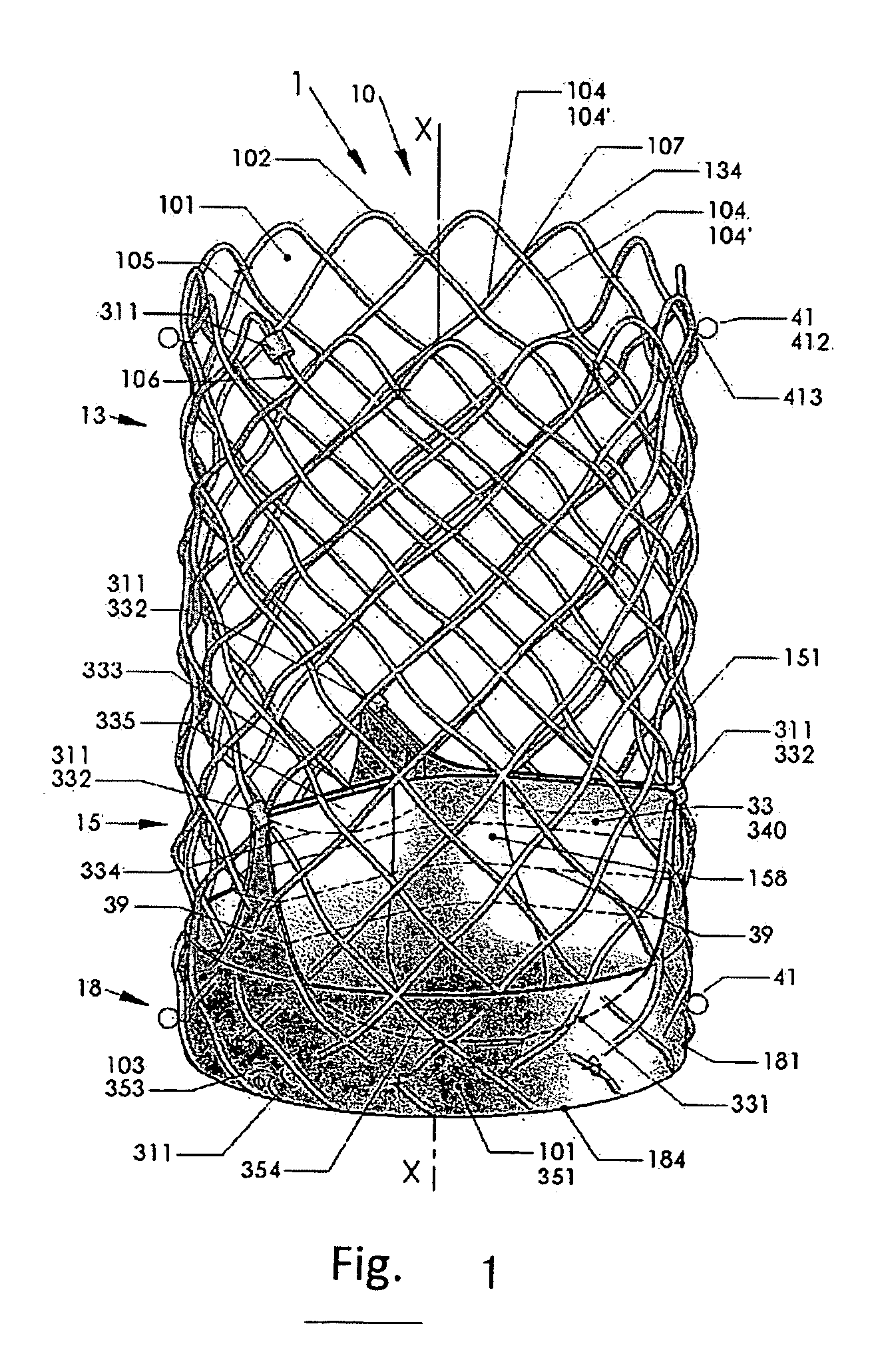
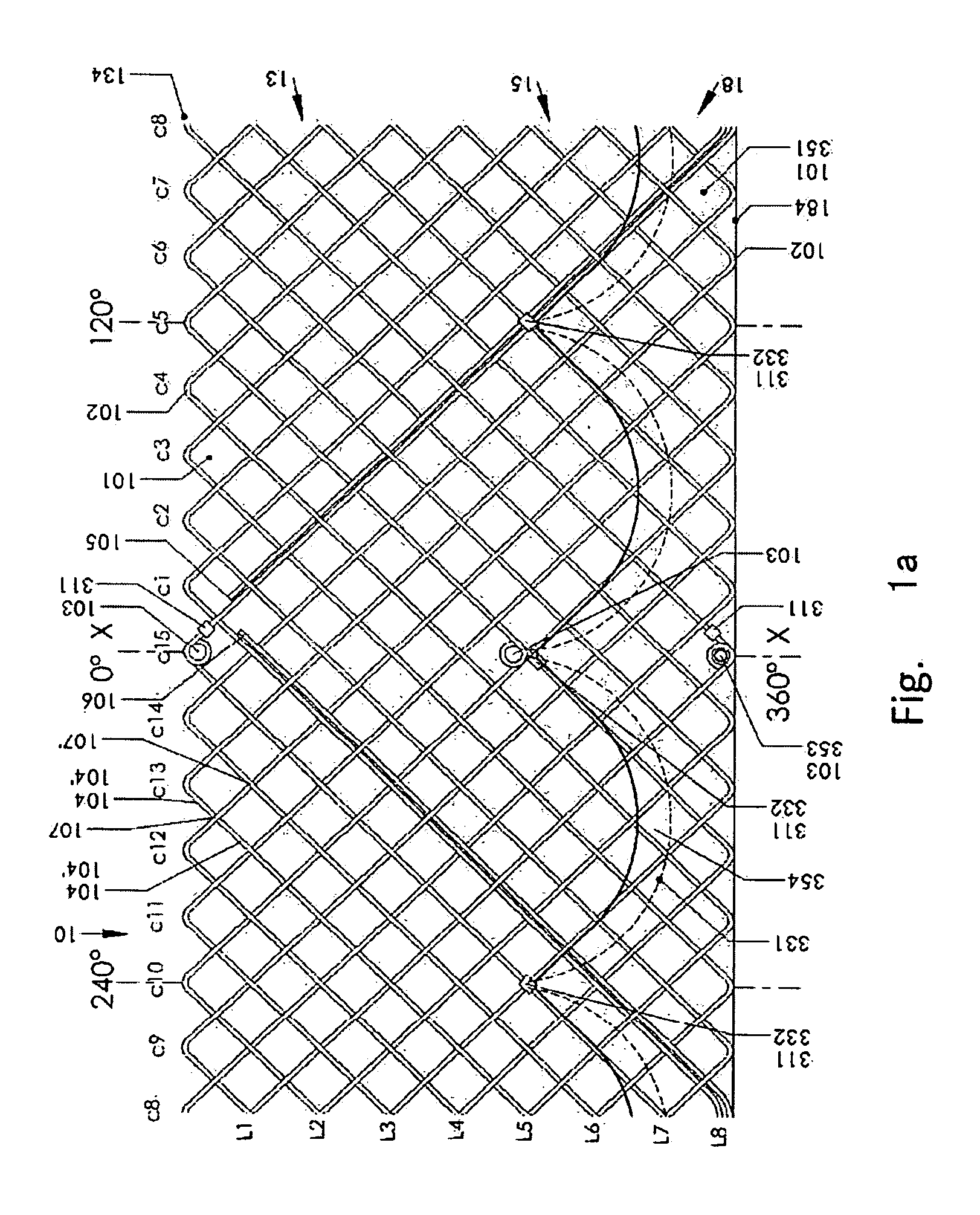
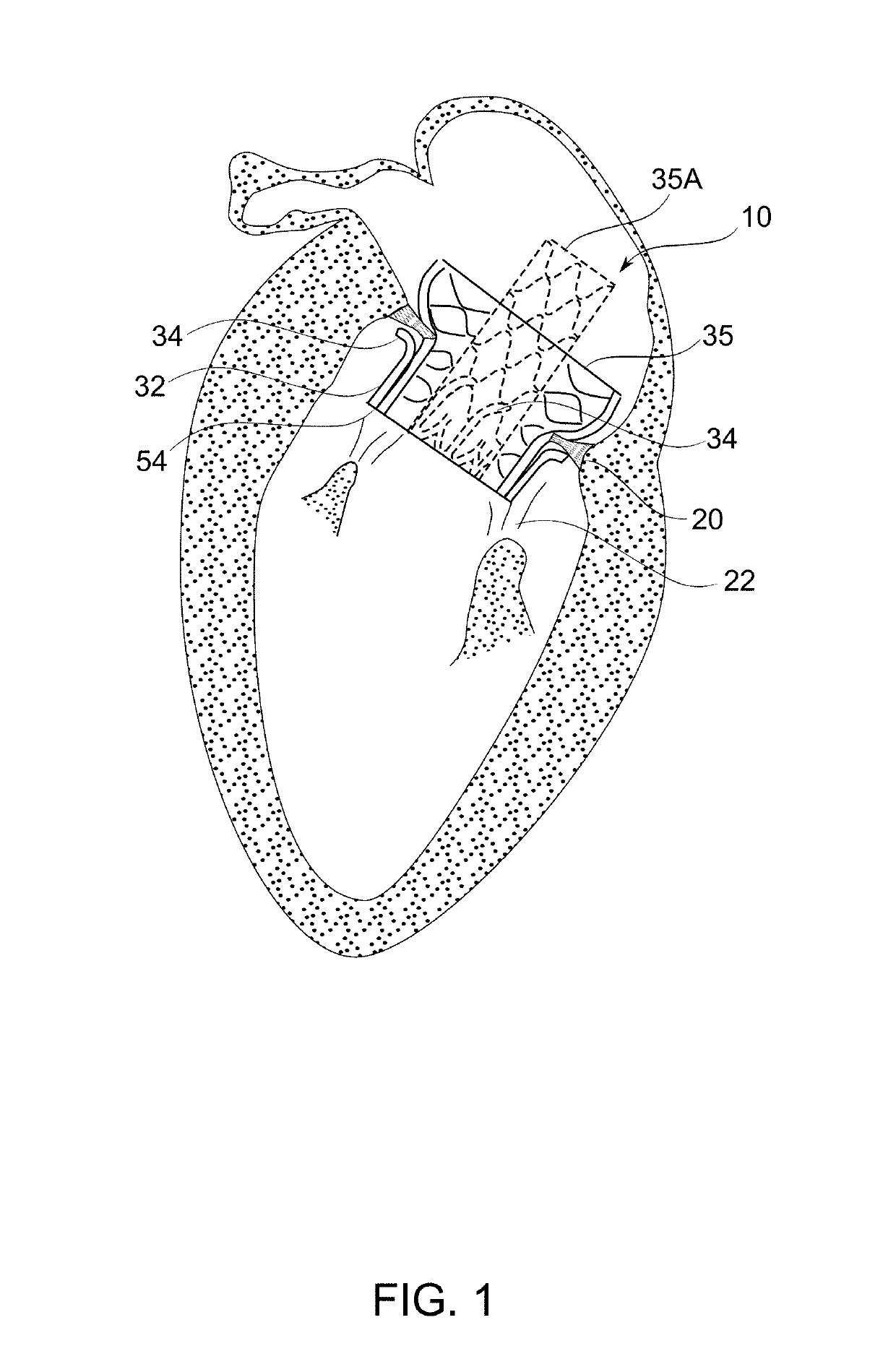
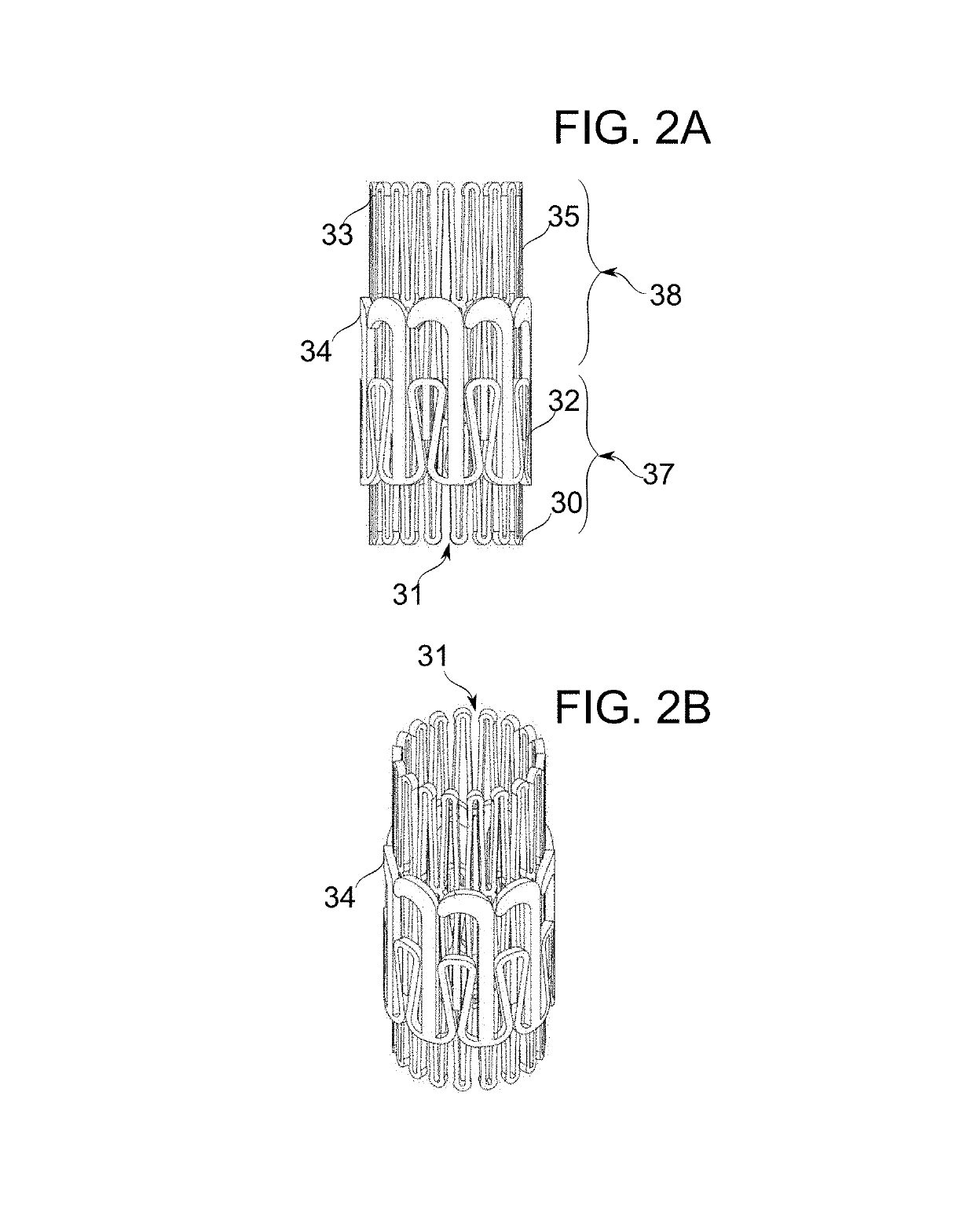
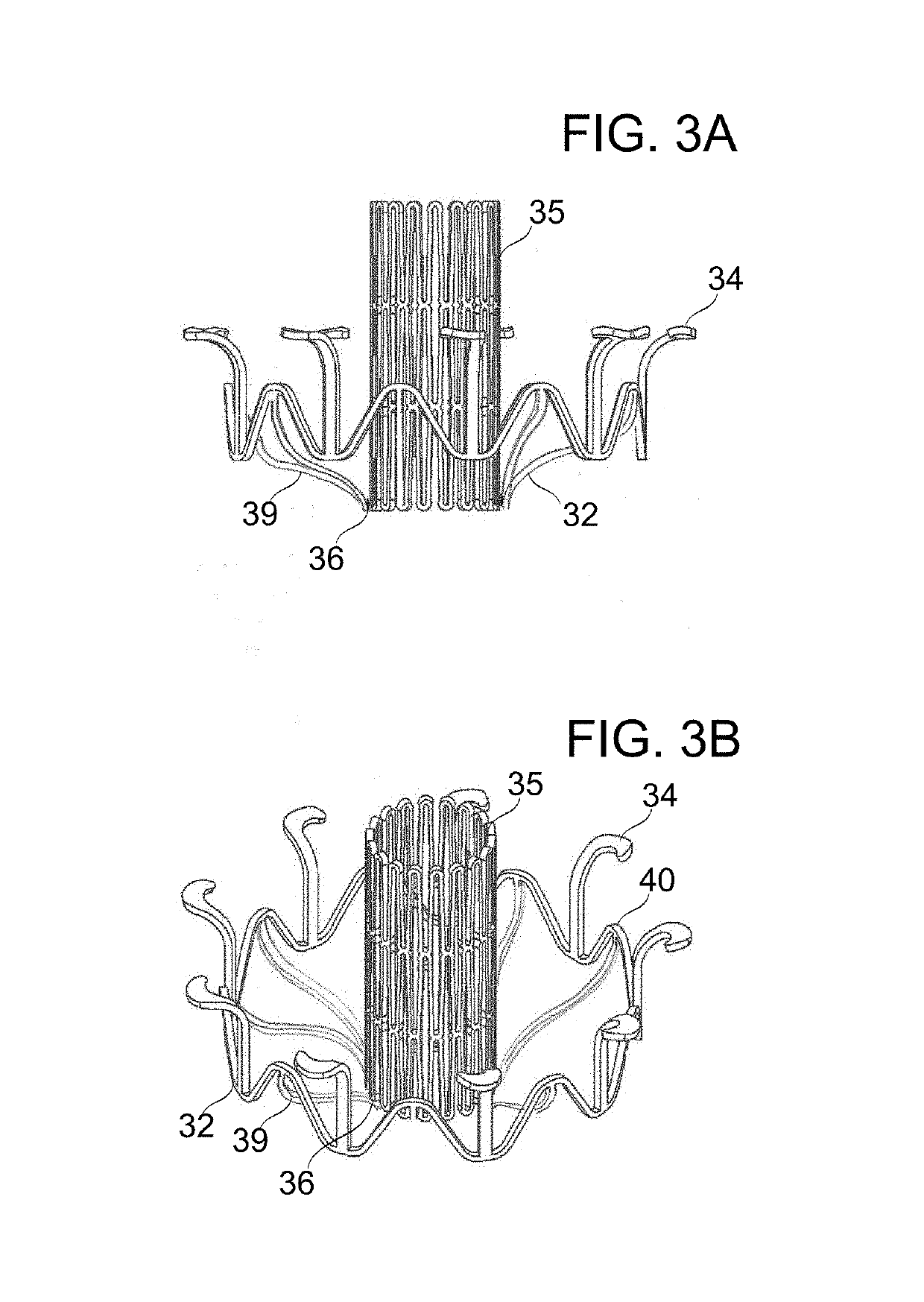
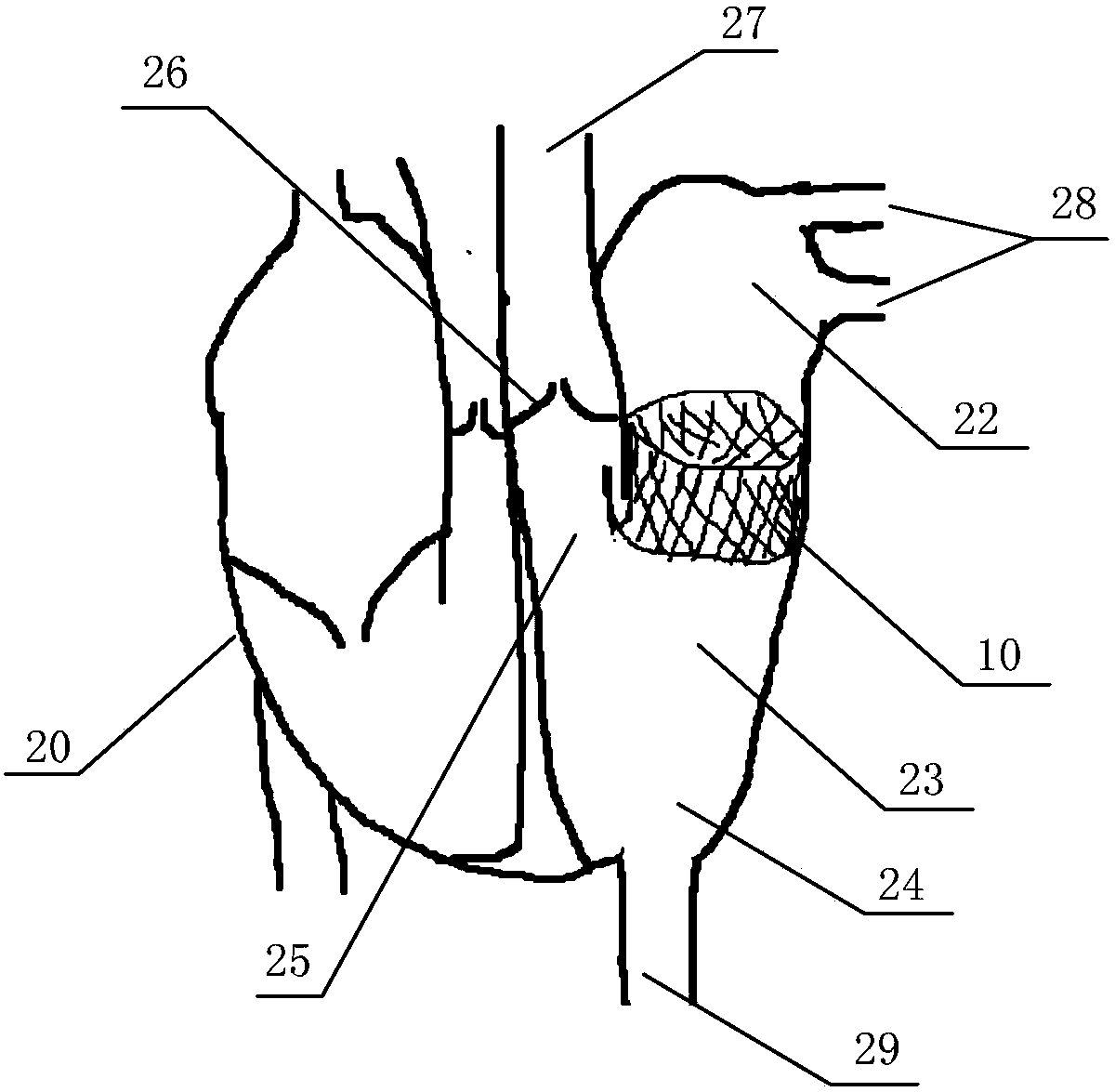
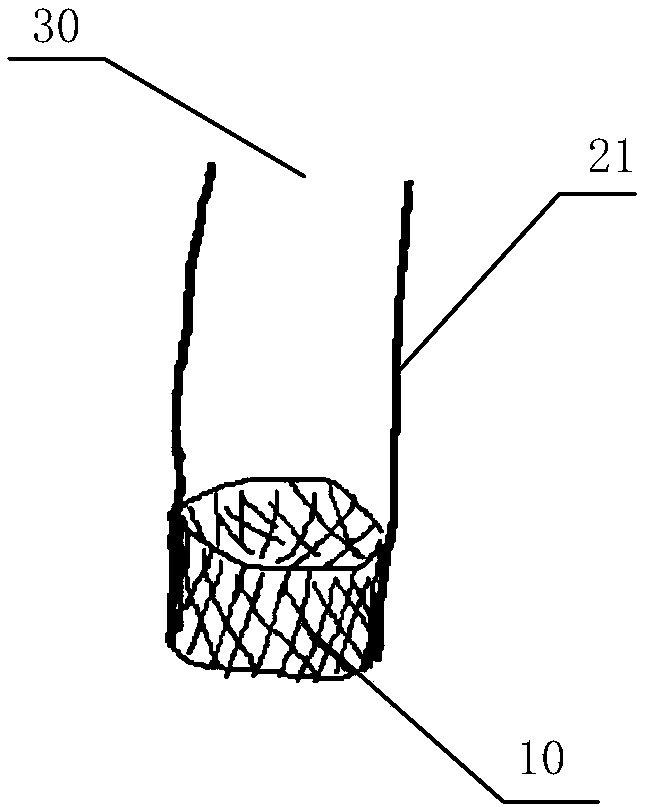
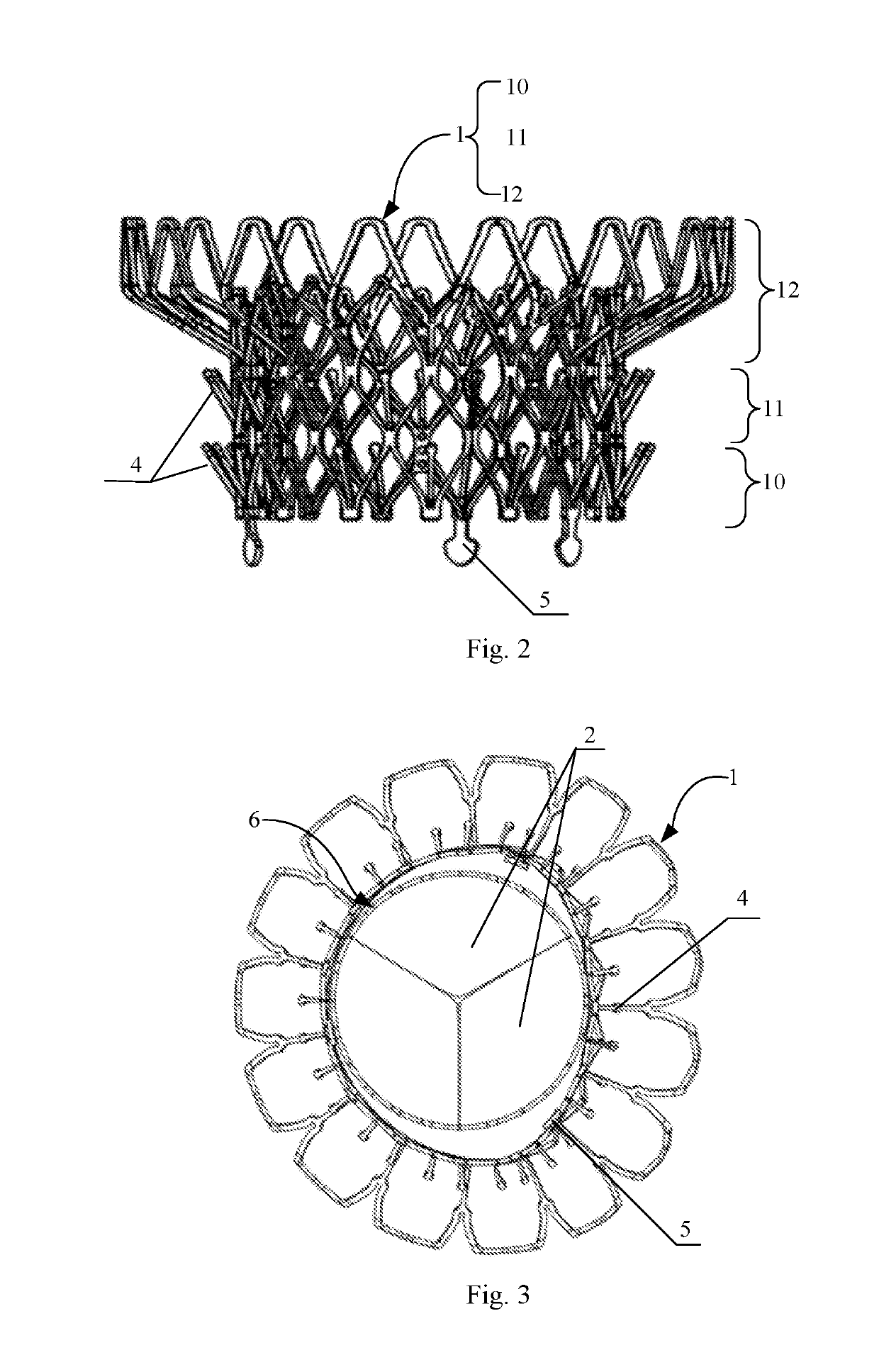
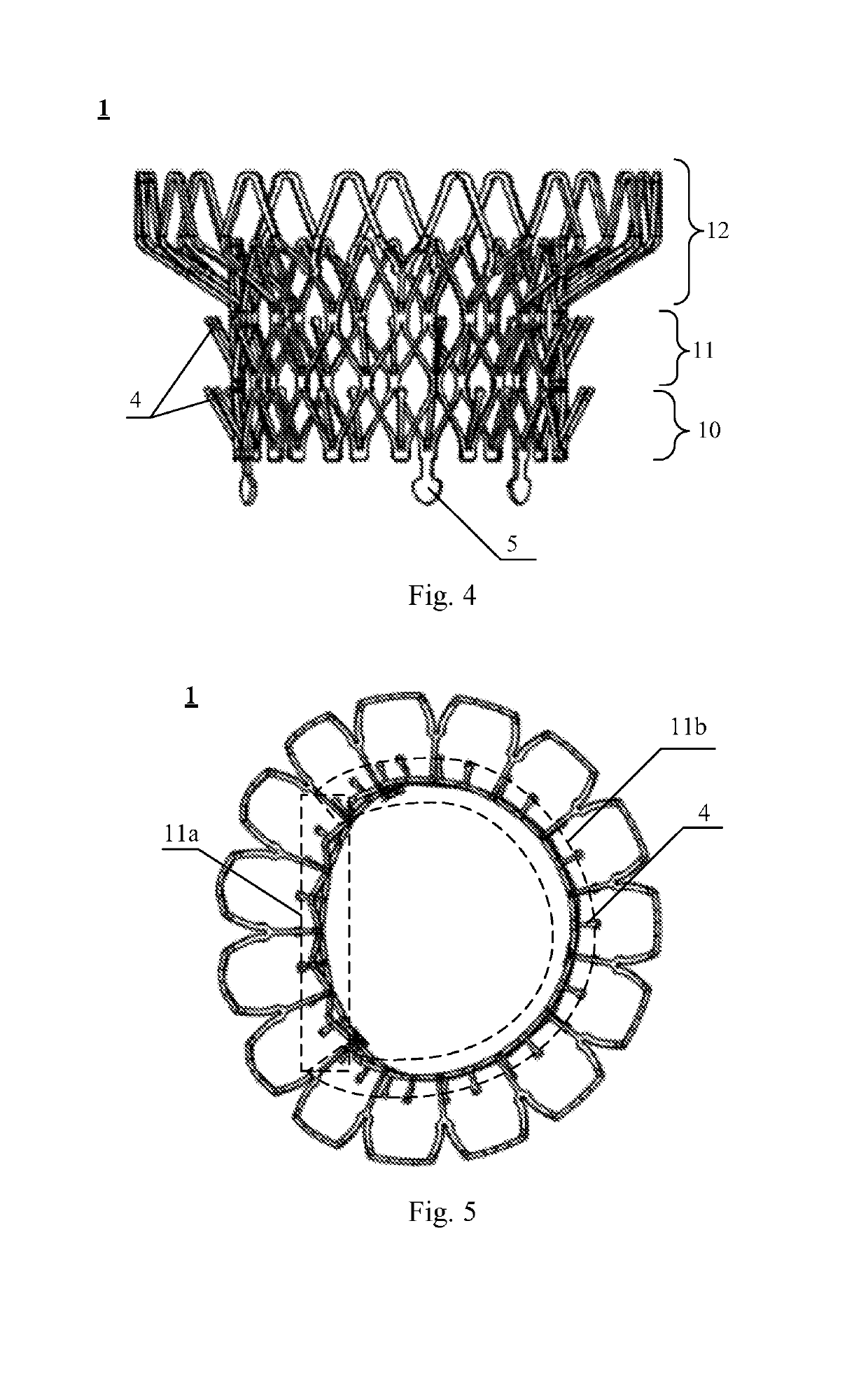
An artificial heart valve and weaving method thereof are disclosed. The valve stent includes a tubular stent (10), valve leaflets (33), sealing membranes (351, 354), x-ray opaque markers (311, 312) and flexible connecting loops (41). The middle segment (15) of the net stent (10) is tubular or drum-shaped, or provided with radial protrusion structures (153), or provided with outer annular structures (155), or provided with outer free tongues (156), or provided with radial protrusion structures (153) and outer free tongues (156). The stent can be made by up and down interweaving the same one elastic metal wire, and also can be made by up and down interweaving different elastic metal wires. Moreover, the structure, shape and function of the valve stent are optimized; in radical compression, the valve can be transported to the right place with the help of interventional device; after expansion, fitted with figure of the vascular wall in the radical and axial direction, the artificial heart valve stent will not produce paravalvular leak; even more after implanting, the valve has a normal effect on prevent the slippage of artificial valve, which is caused by the blood reflux through the closed valve.
Owner:WEN NING +1
Paravalvular Leak Closure Devices and Methods
ActiveUS20110054466A1Reduce space sizeSmall sizeStentsSurgical needlesRadio frequency energyCatheter
An ablation catheter including an inner tube having a length, a distal end and a longitudinal axis, a plurality of needles extending from the distal end of the inner tube and biased away from the longitudinal axis, an outer sheath slideably moveable relative to the inner tube to surround at least a portion of the length of the inner tube and its extending needles, and a radio frequency energy source electrically connected to the plurality of needles.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
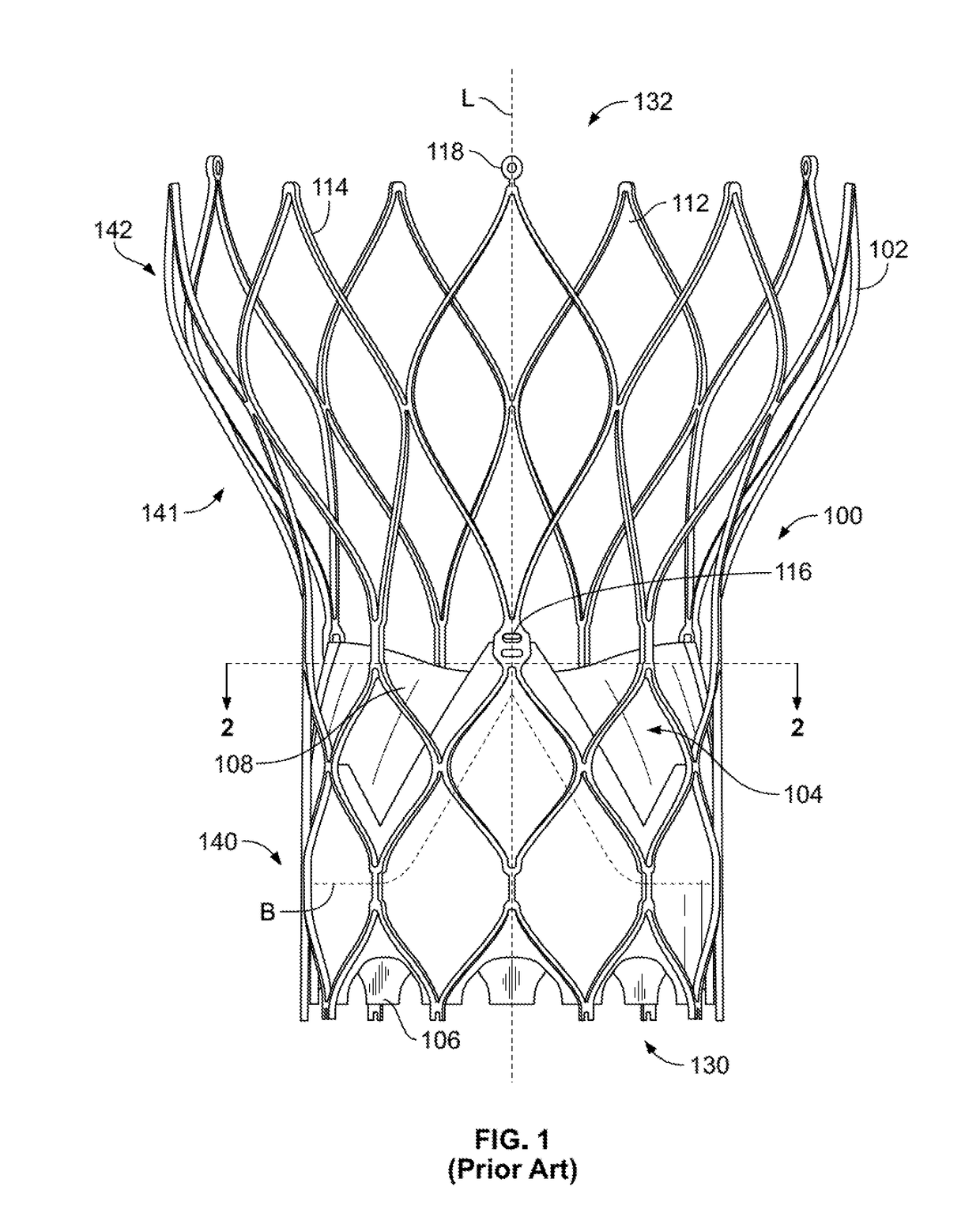
Collapsible valve having paravalvular leak protection
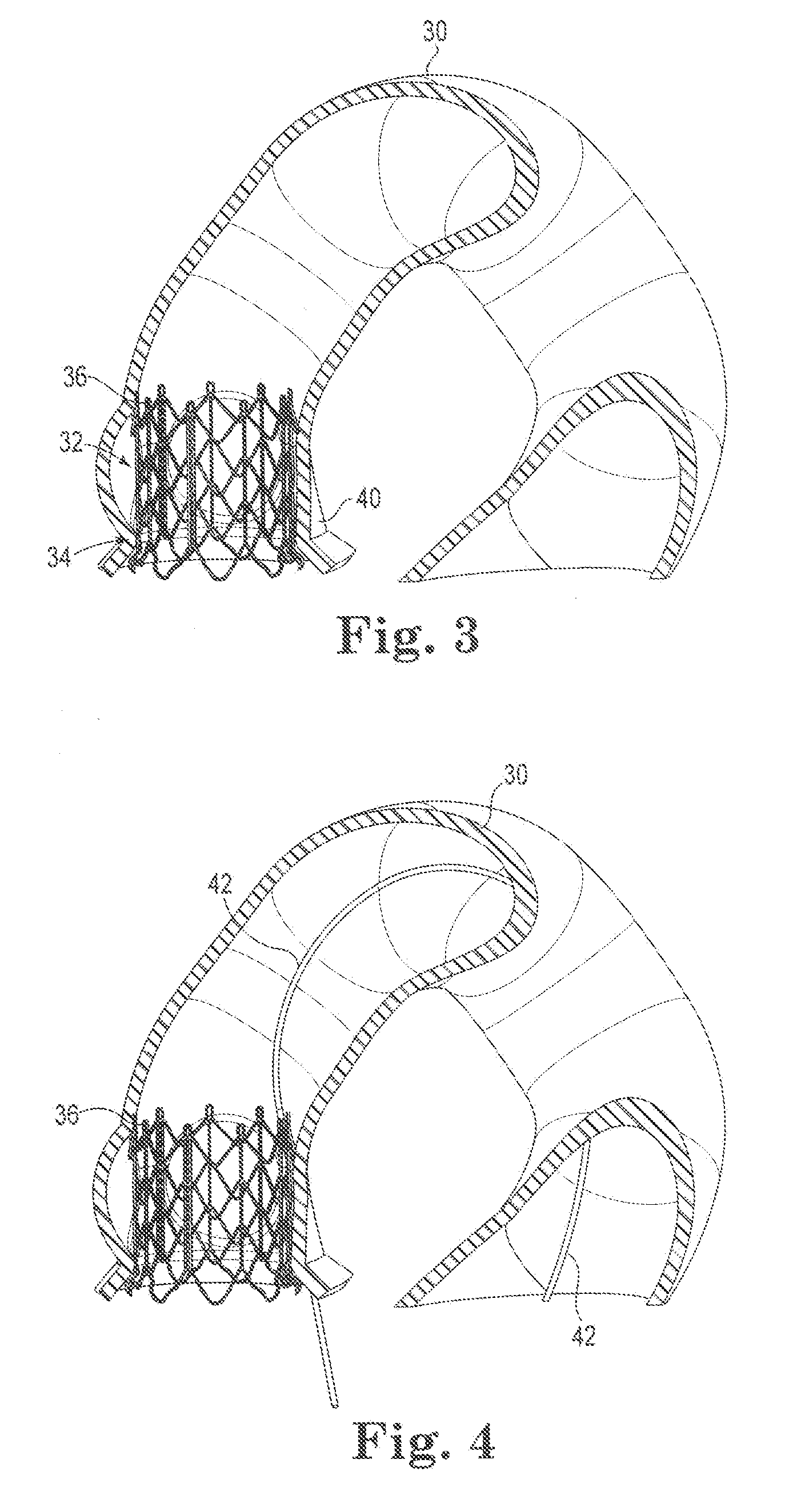
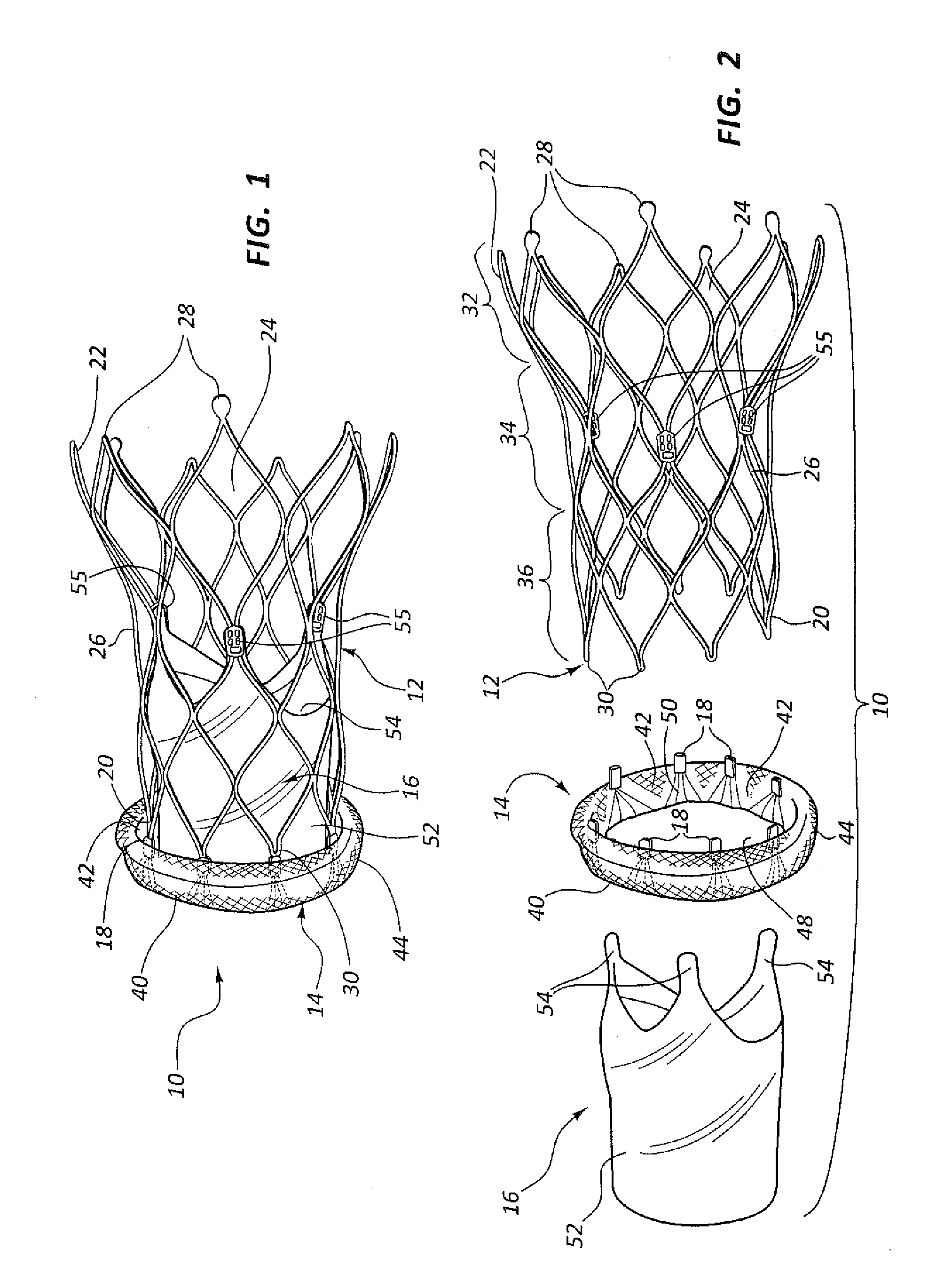
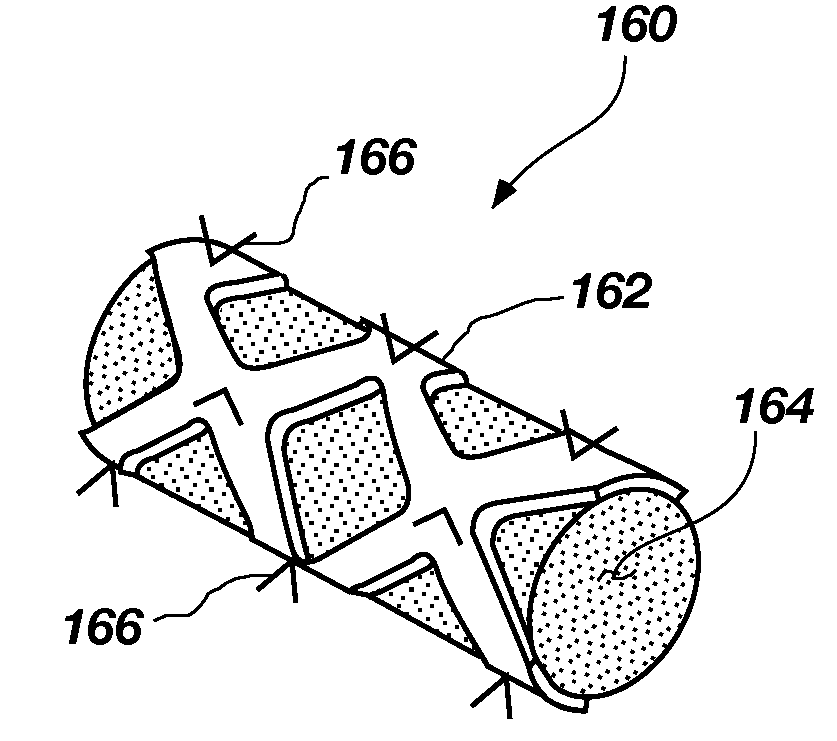
A heart valve assembly (100) includes a heart valve (116), a self-expandable and collapsible stent (112), and a sealing member (114). The stent (112) includes an inflow end (120) and an outflow end (122), and surrounds and supports the heart valve (116). The sealing member (114) is connected to the inflow end (120) of the stent (112) and extends around a periphery of the stent (112). The sealing member (114) is connected to the inflow end (120) of the stent (112), overlaps a portion of the heart valve (116), and extends around an outer periphery of the stent (112).
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Paravalvular leak detection, sealing and prevention
The present invention provides a series of new percutaneous concepts of paravalvular repairs including identifying the leak location, several repair techniques and finally built-in means for leak prevention, built on percutaneous valves. A catheter-delivered device locates cavities occurring between a prosthetic valve and the wall of the body vessel where the valve is implanted, the cavities producing paravalvular leaks during diastole, the device comprising at least one of a plurality of flexible wires, the wire having attached to it a balloon, wherein the balloon is pulled by the leak through the cavity and wherein the wire then serves to mark the cavity location.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI PVT
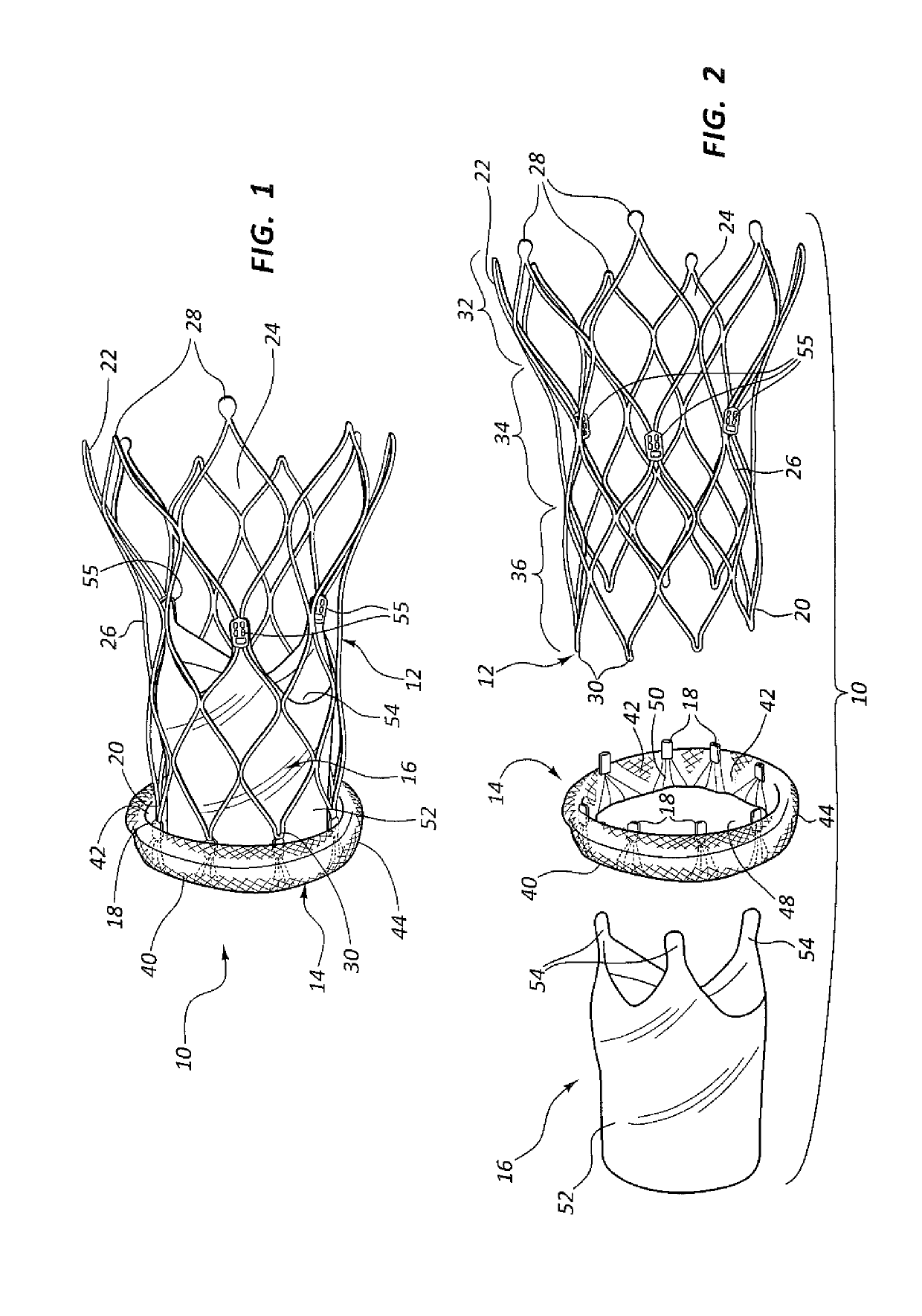
Transcatheter valve with paravalvular leak sealing ring
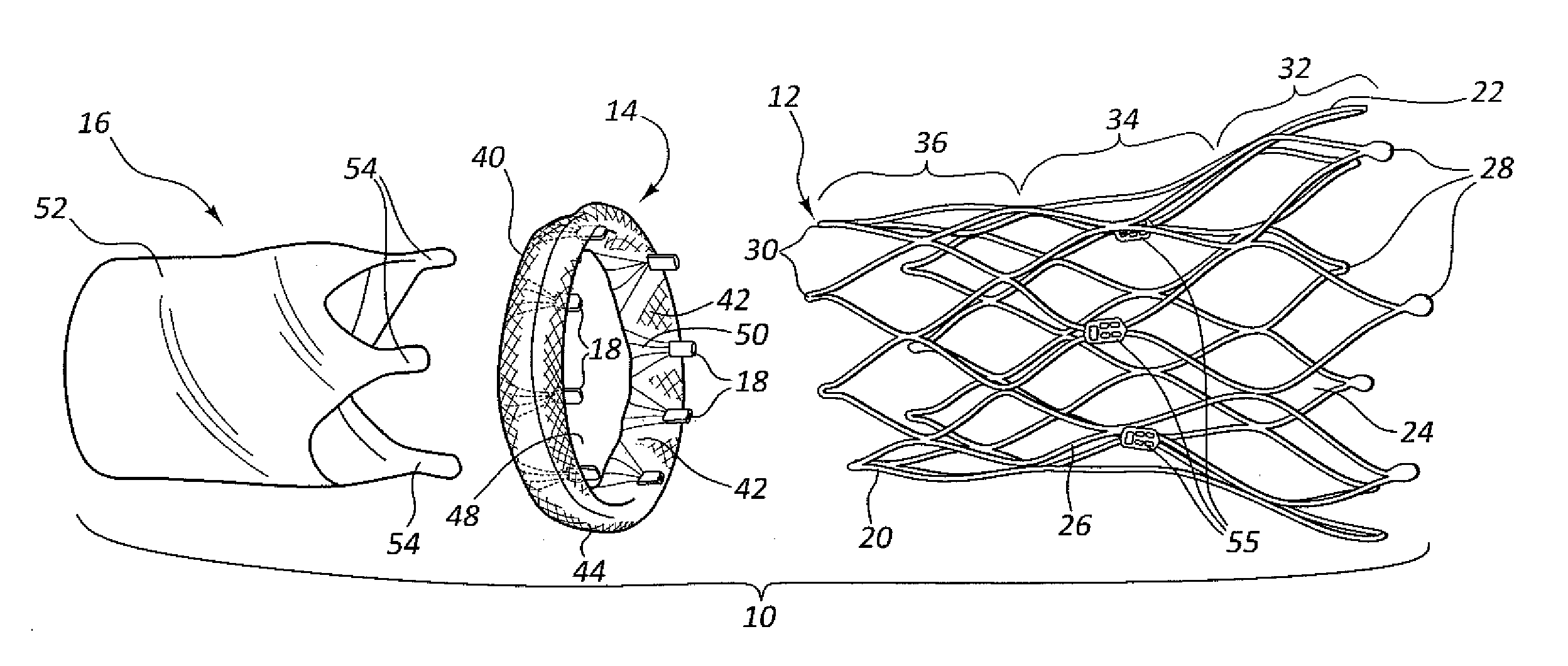
A prosthetic heart valve includes a collapsible and expandable stent extending from an inflow end to an outflow end and a plurality of prosthetic valve leaflets coupled to the stent. The prosthetic heart valve may also include a sealing ring coupled to the inflow end of the stent, the sealing ring comprising a tube extending circumferentially around the inflow end of the stent. The tube may be formed from a wire coiled into a repeating shape, such as a rectangle or a diamond, so that the tube is collapsible. A covering may at least partially surround the tube. The sealing ring may include a first filler positioned within the tube and / or a second filler positioned between the tube and the covering.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Anatomically-orientated and self-positioning transcatheter mitral valve
ActiveUS20160206424A1Easy to conformEasily orientBalloon catheterHeart valvesMitral valve stenosisParavalvular leak
Described herein is a mitral valve and systems and methods for implanting the same. The mitral valve device is designed to easily orient to and conform to the mitral orifice natural morphology. This mitral valve system may be implanted using a system of 2 guide wires that facilitate orientation of the flat portion of the stent properly with the flat portion of the mitral valve that is adjacent to the aortic valve. Additionally, the disclosed valve may have multiple mounds distributed across the outer surface of the valve / stent complex so as to prevent or reduce paravalvular leak after implantation.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Medical device for percutaneous paravalvular leak and related systems and methods
The present invention provides devices, systems and methods for closing a paravalvular leak. In accordance with one embodiment, a medical device includes at least one multicellular frame member configured to be implanted at a paravalvular leak. The medical device further includes at least one tissue in-growth member associated with the frame member, the tissue in-growth member being configured to promote tissue growth and permanently maintain the frame member at the leak. The frame member may be self expanding device formed, for example, of a shape-memory alloy. The tissue in-growth member may be formed from a polymer material. In one particular embodiment, the frame member may be a substantially tubular structure and the tissue in-growth member may be disposed within an interior space defined by the tubular structure. In another embodiment, the frame ember may be a substantially flat or planar structure.
Owner:COHEREX MEDICAL
Self-expandable filler for mitigating paravalvular leak
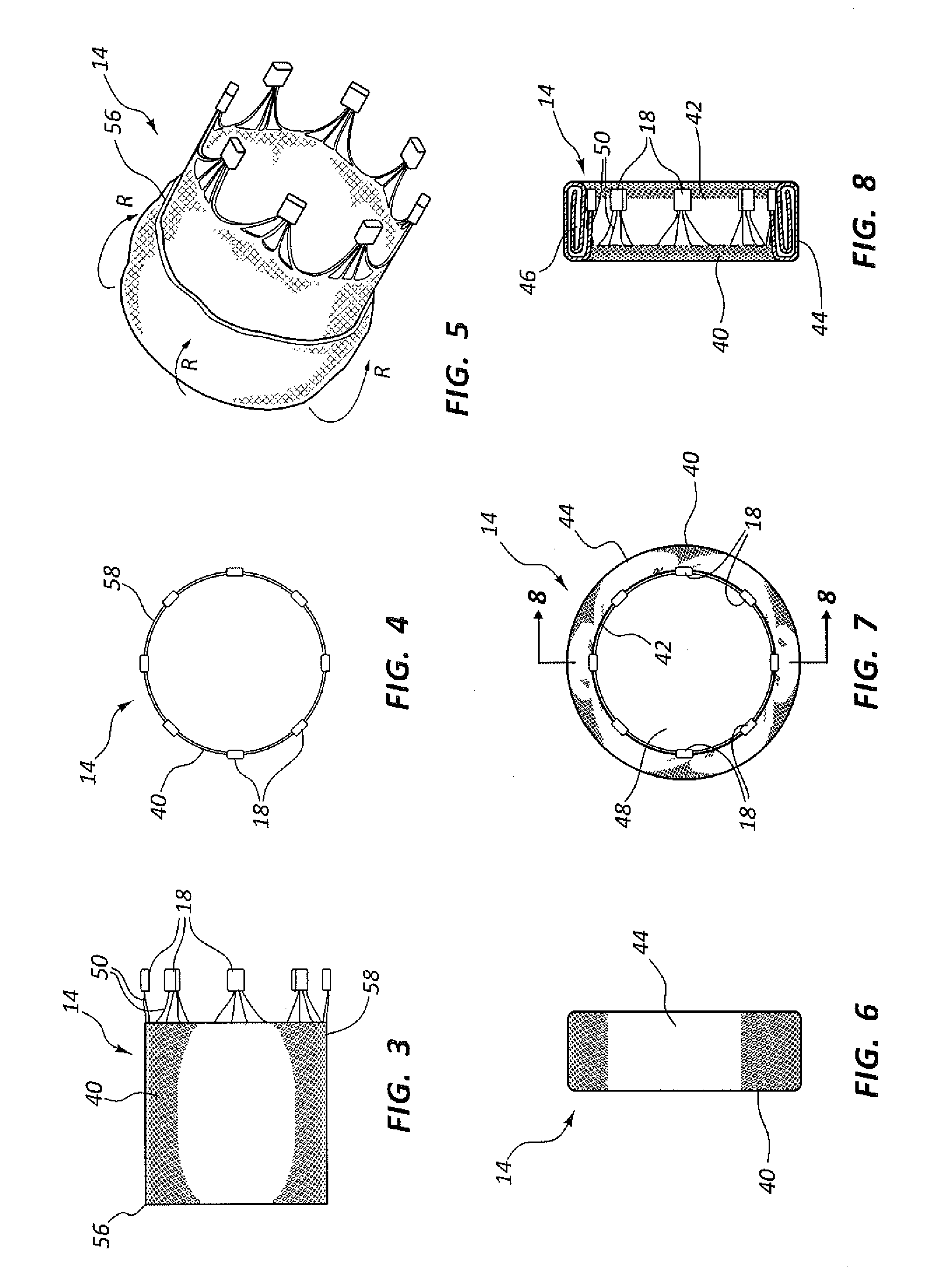
A prosthetic heart valve includes a collapsible stent and a valve assembly disposed within the stent. A first cuff is disposed adjacent the stent. A filler is annularly disposed about the stent radially outward of the first cuff and radially outward of the stent. The filler has a first circumferential layer with a first inner wall, a first outer wall, and a plurality of first ribs connecting the first inner wall to the first outer wall. The filler has an expanded condition in which the first inner wall is spaced a first distance from the first outer wall in a radial direction transverse to the longitudinal direction of the stent, and a collapsed condition in which the first inner wall is spaced a second distance from the first outer wall in the radial direction, the first distance being greater than the second distance.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Prosthetic mitral valve
A prosthetic mitral valve with a frame comprises at least one arm shaped to deploy among a region of chordae tendineae of the native mitral valve to deflect these chords in order to pull the native valve leaflets around the frame to avoid paravalvular leaks. The frame may be made from two parts that are connected by sutures. The prosthetic valve may be deployed by a catherer comprising a deployment clamp attached to the valve frame where the deployment clamp is actuable to induce rotation of the frame.
Owner:TEL HASHOMER MEDICAL RES INFRASTRUCTURE & SERVICES
Prosthetic heart valve with paravalvular leak mitigation features
A prosthetic heart valve includes a collapsible stent and a valve assembly disposed within the stent. A first cuff is disposed adjacent the stent. A second cuff having a distal edge facing the outflow end of the stent is disposed about the stent radially outward of the first cuff and the stent. The stent may include a plurality of fingers each having a first end coupled to a corresponding cell of the stent and a free end adapted to extend radially outward of the corresponding cell. The distal edge of the second cuff may be coupled to the fingers at spaced locations around the circumference of the stent to position the distal edge radially outward from the corresponding cells at the spaced locations. Various stent struts may be tapered to reduce the stent circumference in the collapsed condition, and to improve the fatigue resistance and / or bendability of the stent.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Paravalvular leak closure devices and methods
ActiveUS8801706B2Minimized in shapeMinimized in sizeStentsSurgical needlesRadio frequency energyCatheter
An ablation catheter including an inner tube having a length, a distal end and a longitudinal axis, a plurality of needles extending from the distal end of the inner tube and biased away from the longitudinal axis, an outer sheath slideably moveable relative to the inner tube to surround at least a portion of the length of the inner tube and its extending needles, and a radio frequency energy source electrically connected to the plurality of needles.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
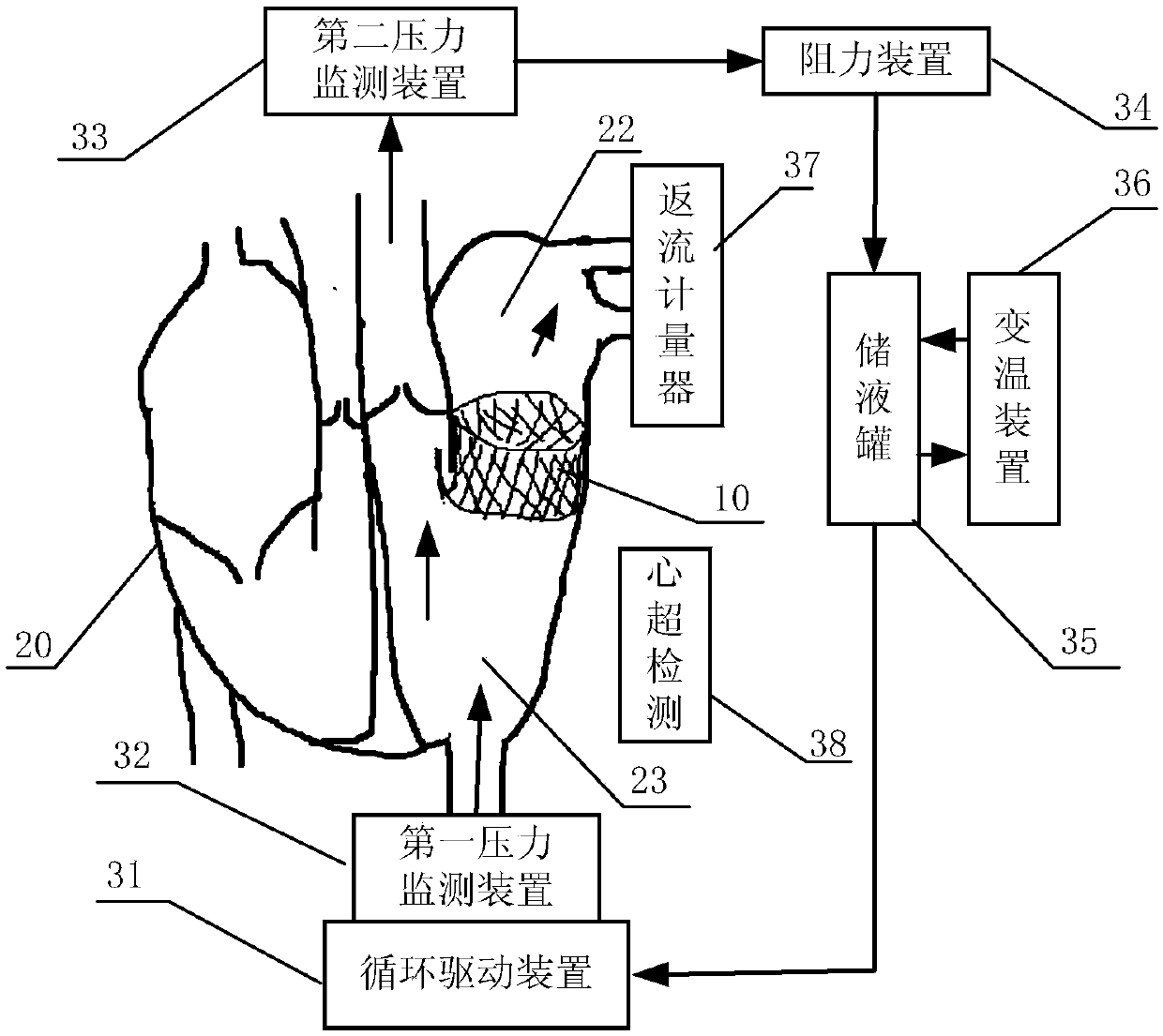
In-vitro performance testing system and testing method of transcatheter bicuspid valve valved stent
PendingCN107773328AAchieve hydrodynamic performanceEnables in vitro performance testingHeart valvesStationary stateIn vivo
The invention discloses an in-vitro performance testing system and testing method of a transcatheter bicuspid valve valved stent, and relates to prostheses capable of being implanted in vivo, in particular to a testing device and testing method applied to heart valve performance testing. The in-vitro performance testing system comprises a valve testing part which is internally provided with the bicuspid valve valved stent, a liquid circulation device and a monitoring device; a first testing part is a heart specimen of which the left ventricular apex is provided with a circulation inlet, and asecond testing part is a section of artificial blood vessel or a section of blood vessel specimen for sewing the tested bicuspid valve valved stent; the liquid testing device is connected with the first testing part to constitute a first testing circulating path for steady flow circulation and a second testing circulating path for simulating the ventricular beat of the human body; the liquid circulation device is connected with the second testing part to constitute a third testing circulating path which is connected with circulation lateral branches, in vitro tests of fluid mechanic performance, support fixing states, valve backflow, perivalvular leakage, and influences on surrounding important organization structures of the bicuspid valve valved stent can be achieved, and a durability experiment of the bicuspid valve valved stent is completed.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGJI HOSPITAL
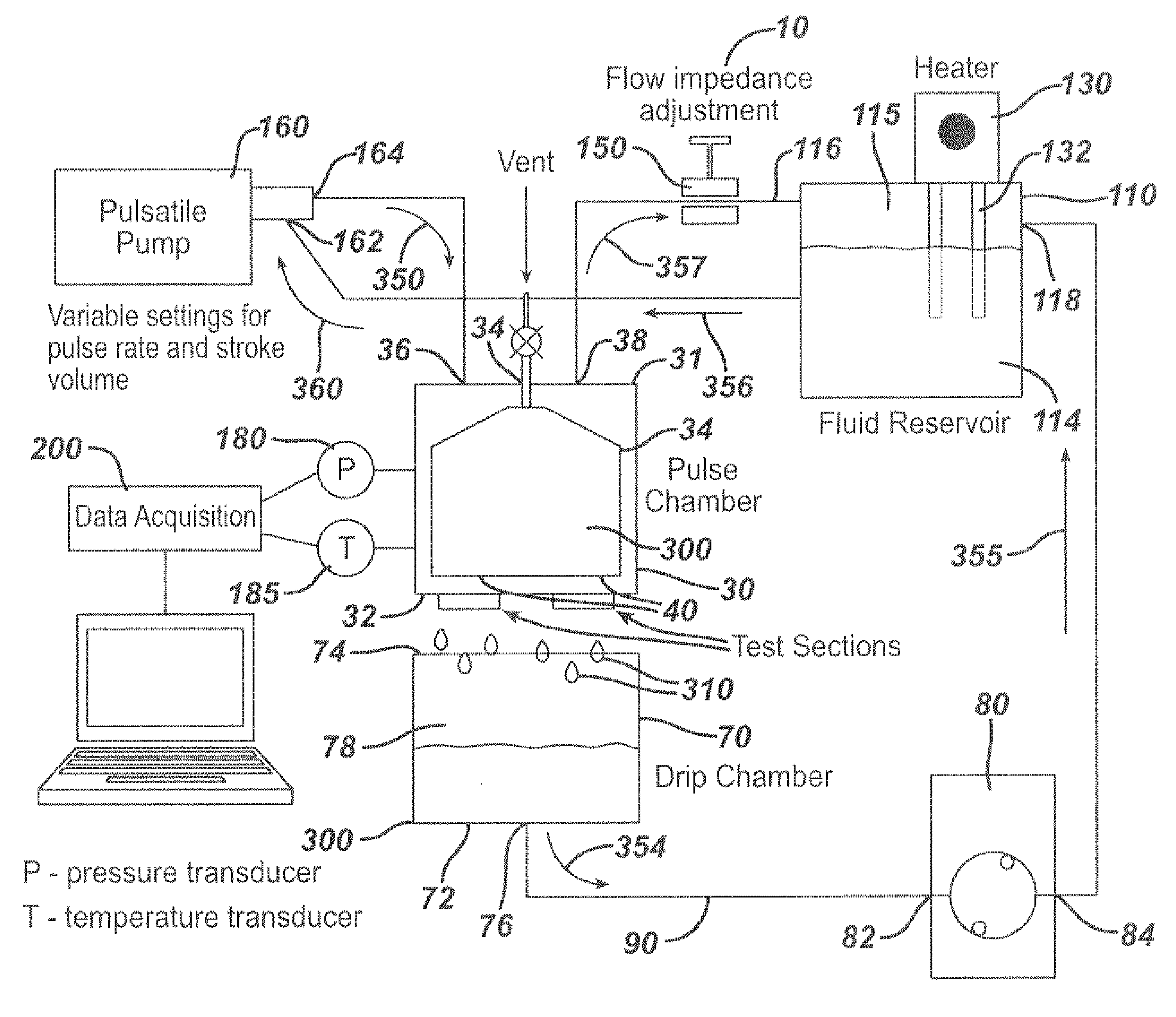
Paravalvular Leak Test Apparatus and Method
An apparatus and method for measuring paravalvular leakage from a prosthetic heart valve in vitro. The apparatus has a pulse chamber pressure vessel and a pulsatile pump. The sewing ring of a prosthetic heart valve is mounted to a mounting member which is affixed to the pressure chamber, and paravalvular leakage from the heart valve is collected and measured.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Transcatheter valve with paravalvular leak sealing ring
A prosthetic heart valve includes a collapsible and expandable stent extending from an inflow end to an outflow end and a plurality of prosthetic valve leaflets coupled to the stent. The prosthetic heart valve may also include a sealing ring coupled to the inflow end of the stent, the sealing ring comprising a tube extending circumferentially around the inflow end of the stent. The tube may be formed from a wire coiled into a repeating shape, such as a rectangle or a diamond, so that the tube is collapsible. A covering may at least partially surround the tube. The sealing ring may include a first filler positioned within the tube and / or a second filler positioned between the tube and the covering.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Method for reducing paravalvular leaks with decellularized tissue
ActiveUS20170119928A1Improves the swelling behaviour of the tissueImprove mechanical propertiesHeart valvesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismProsthesisPericardium
A method for preparing tissue, in particular pericardial tissue, in particular for use as a sealing means for a heart valve prosthesis for paravalvular leaks, characterised in that the tissue, in particular pericardial tissue, is decellularized (4), subjected to a cross-linking (6) with a glutaraldehyde-containing solution, and subjected to a shape- and a structure-stabilising step (7, 8, 9). The invention also relates to a heart valve prosthesis.
Owner:BIOTRONIK AG
Collapsible valve having paravalvular leak protection
A heart valve assembly (100) includes a heart valve (116), a self-expandable and collapsible stent (112), and a sealing member (114). The stent (112) includes an inflow end (120) and an outflow end (122), and surrounds and supports the heart valve (116). The sealing member (114) is connected to the inflow end (120) of the stent (112) and extends around a periphery of the stent (112). The sealing member (114) is connected to the inflow end (120) of the stent (112), overlaps a portion of the heart valve (116), and extends around an outer periphery of the stent (112).
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Expandable frames and paravalvular leak mitigation systems for implantable prosthetic heart valve devices
A collapsible and expandable prosthetic heart valve stent is provided and comprising an outer section, a valve support defining a flow channel therethrough, a transition section configured to smoothly transition the outer section to the valve support. The valve support is disposed within an interior defined by the outer section, with the inflow end of the valve support disposed inside the outer section's interior. In some cases, the outflow end of the valve support is at least partially defined by the transition section. The prosthetic leaflets are disposed on the inner surface of the valve support's flow channel and are located at or above the annulus of the heart chamber. A paravalvular leakage mitigation system is attached to the stent to mitigate retrograde blood flow and / or regurgitation.
Owner:C MEDICAL TECH INC
Anatomically-orientated and self-positioning transcatheter mitral valve
ActiveUS10226333B2Easy to conformEasily orientBalloon catheterHeart valvesMitral valve stenosisMitral valve leaflet
Described herein is a mitral valve and systems and methods for implanting the same. The mitral valve device is designed to easily orient to and conform to the mitral orifice natural morphology. This mitral valve system may be implanted using a system of 2 guide wires that facilitate orientation of the flat portion of the stent properly with the flat portion of the mitral valve that is adjacent to the aortic valve. Additionally, the disclosed valve may have multiple mounds distributed across the outer surface of the valve / stent complex so as to prevent or reduce paravalvular leak after implantation.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Paravalvular leak sealing mechanism
A collapsible and expandable stent body includes a generally tubular annulus section, one or more prosthetic valve elements mounted to the stent body, and a cuff attached to the stent body. The prosthetic valve is operative to allow flow in an antegrade direction but to substantially block flow in a retrograde direction. The prosthetic heart valve may include paravalvular leak mitigation features in the form of first and second sealing members. The sealing members are attached to the cuff and extend circumferentially around an abluminal surface of the stent body. The sealing members each have an open side facing in a first axial direction and a closed side facing in an opposite second axial direction. Flow of blood in the second axial direction will tend to force blood into the sealing members and cause the sealing members to billow outwardly relative to the stent body, helping to mitigate paravalvular leak.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Paravalvular leak sealing mechanism
ActiveUS20160250022A1Facilitate sealing against paravalvular leakImprove sealingHeart valvesProsthetic valveProsthesis
A collapsible and expandable stent body includes a generally tubular annulus section, one or more prosthetic valve elements mounted to the stent body, and a cuff attached to the stent body. The prosthetic valve is operative to allow flow in an antegrade direction but to substantially block flow in a retrograde direction. The prosthetic heart valve may include paravalvular leak mitigation features in the form of first and second sealing members. The sealing members are attached to the cuff and extend circumferentially around an abluminal surface of the stent body. The sealing members each have an open side facing in a first axial direction and a closed side facing in an opposite second axial direction. Flow of blood in the second axial direction will tend to force blood into the sealing members and cause the sealing members to billow outwardly relative to the stent body, helping to mitigate paravalvular leak.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Paravalvular leak sealing mechanism
A prosthetic heart valve includes a stent body with a generally tubular annulus section, which may include one or more circumferential rows of cells. One or more prosthetic valve elements mounted to the stent body operate to allow blood flow in an antegrade direction but to substantially block flow in a retrograde direction. A cuff is attached to the stent body and positioned on a luminal surface of the stent body. At least one sealing member is attached to the cuff. The sealing member may be patch with an open side facing in a first axial direction and a closed side facing in a second axial direction opposite to the first axial direction. Flow of blood in the second axial direction will tend to force blood into the sealing member and cause the sealing member to billow outwardly relative to the stent body.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Perivalvular leakage-proof transcatheter valve system and implanting method
InactiveCN107411849AReduce incidenceReduce weekly leakageBalloon catheterHeart valvesEngineeringCatheter
The invention provides a transcatheter valve system. The transcatheter valve system includes a valve portion and a perivalvular leakage-proof portion independent of the valve portion. The valve portion includes a valve frame, valve leaflets, sealing skirts and sutures for suturing the valve leaflets, the valve frame and the sealing skirts together. The perivalvular leakage-proof portion is independent of the valve portion and includes a fixing portion and a sealing portion; the fixing portion is used for anchoring the perivalvular leakage-proof portion on a corresponding position of lesion in the valve; and the sealing portion is used for filling a gap due to the fact that the valve cannot be attached on a wall well after being implanted. In operation, the perivalvular leakage-proof portion is implanted in a human body, and then the valve portion is implanted in the human body; on a good-adherent part, the implanted valve can compact the sealing portion of the perivalvular leakage-proof portion; on a poor-adherent part, the sealing portion is not fully compressed, and can fill the corresponding gap. The transcatheter valve system can effectively reduce the conveying diameter, can effectively select different perivalvular leakage-proof portion designs according to the lesion characteristics of different implanting points, and can greatly lower the occurrence rate of perivalvular leakage after the transcatheter valve is implanted.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Artificial cardiac valve
ActiveUS20190192293A1Extended service lifeShorten the lengthHeart valvesInsertion stentMaximum diameter
An artificial cardiac valve is disclosed, which includes an outer stent; an inner stent nested within and connected to the outer stent; leaflets disposed inside the inner stent; and membranes attached to walls of the outer and inner stents. The inner stent is a cylindrical mesh tube, and the outer stent includes a first stent segment, a second stent segment and a third stent segment which are connected sequentially. The first stent segment is a mesh tube. The second stent is a mesh tube having a substantially D-shaped cross-section, and the third stent segment is a flared mesh tube. The first stent segment has a maximum diameter that is equal to a diameter of the second stent segment and to a minimum diameter of the third stent segment. In this stent design, the inner stent can withstand traction forces from the leaflets, and the outer stent is adapted to match the anatomy of the native valve. As a result, after release, the artificial cardiac valve will seldom experience displacement and be rarely associated with paravalvular leaks. Moreover, it has a prolonged service life.
Owner:SHANGHAI NEWMED MEDICAL CO LTD
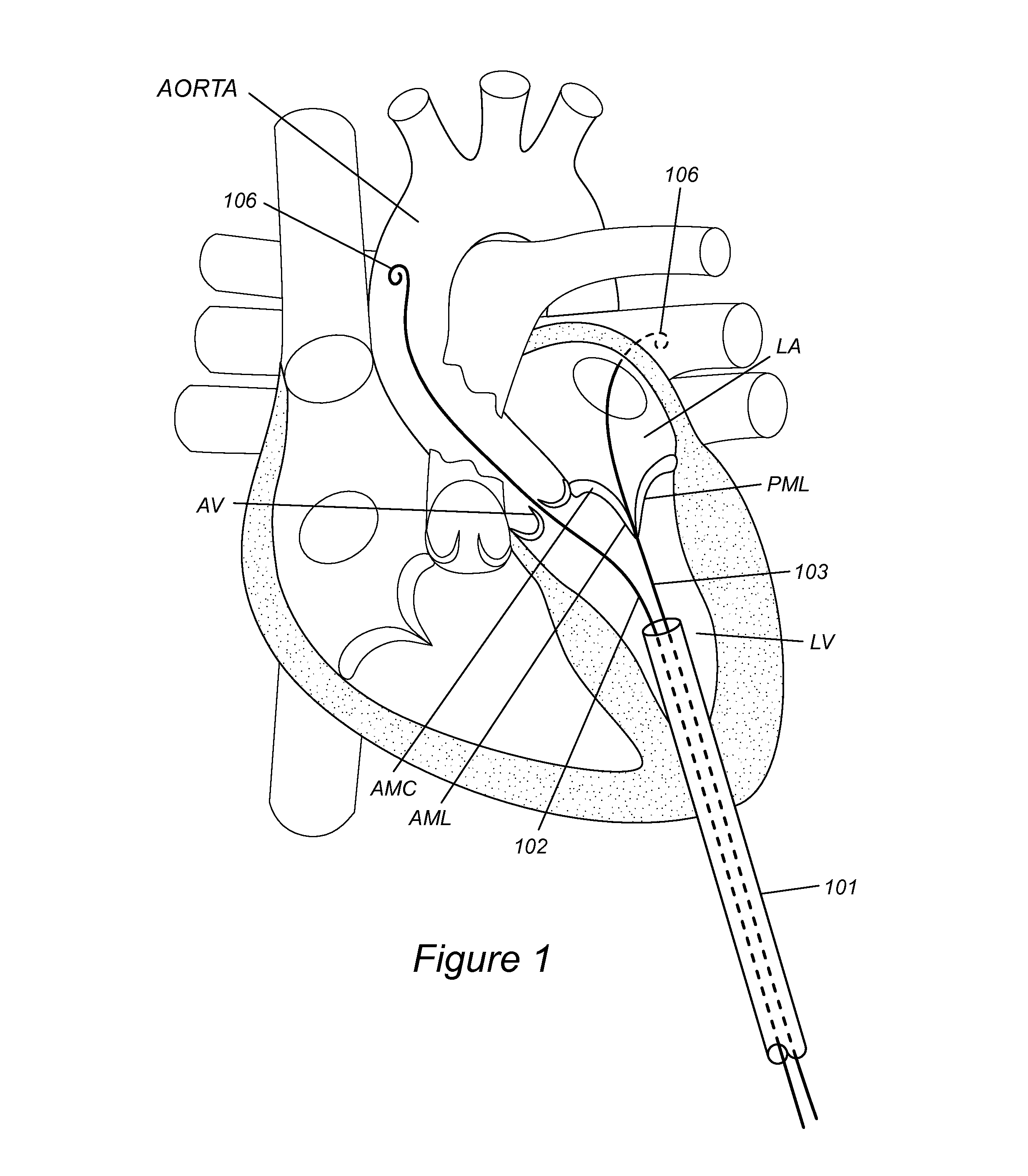
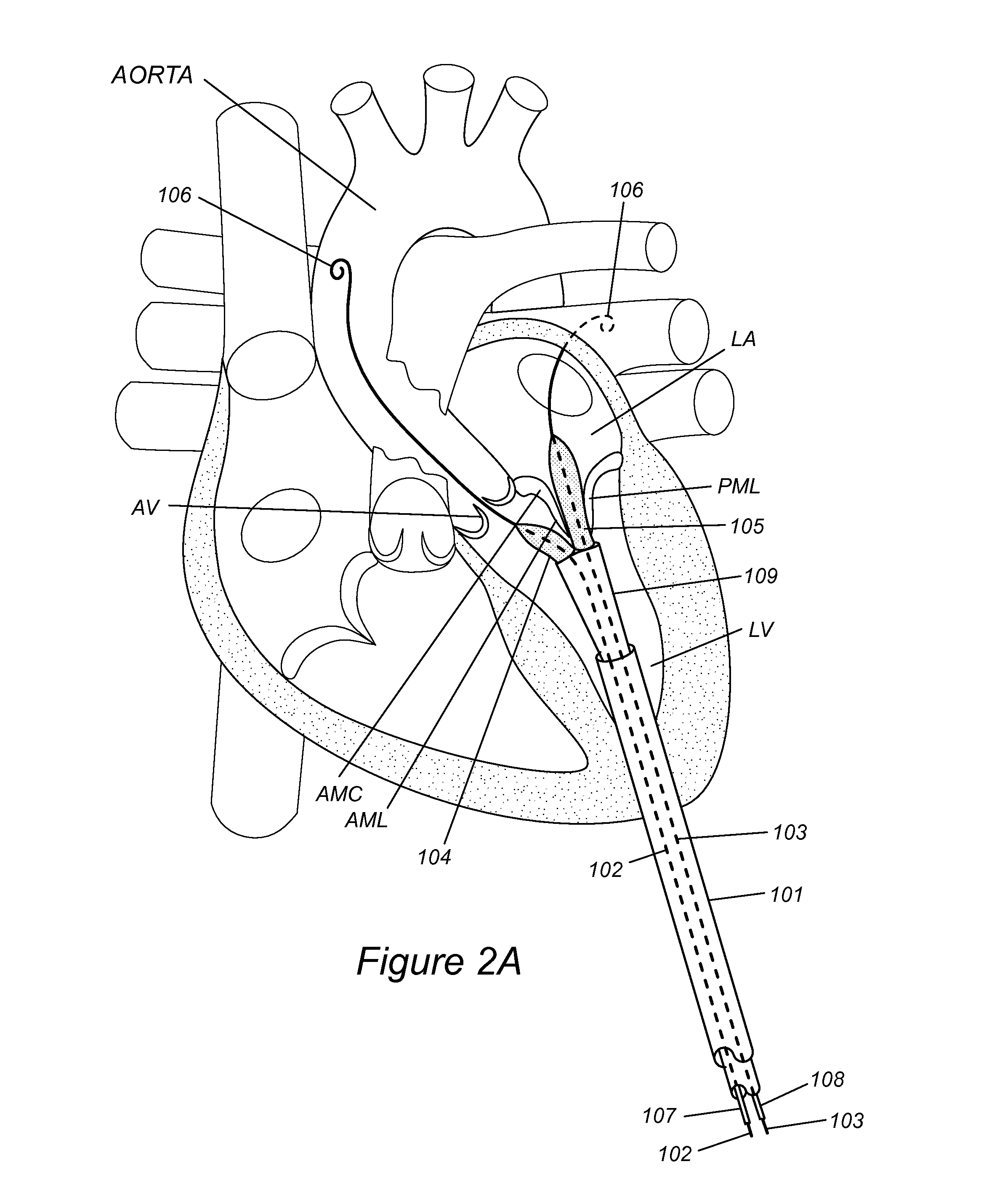
Ultrasound-guided delivery system for accurate positioning/repositioning of transcatheter heart valves
ActiveUS20190015203A1Avoiding and minimizingHeart valvesOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic sensorTransducer
Some embodiments relate to Some embodiments relate to an integrated ultrasound guided delivery system for positioning or repositioning of a transcatheter heart valve including: a delivery catheter coupled to the transcatheter heart valve, and an intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) catheter operably coupled to the delivery catheter, wherein the IVUS catheter includes an ultrasound transducer tip that is aligned with a base of leaflets of the transcatheter heart valve. Also disclosed is a method for positioning or repositioning a transcatheter heart valve at a target site in a subject including: providing an integrated ultrasound guided delivery system as disclosed herein; advancing the transcatheter heart valve in the vicinity of a native valve, viewing the native valve and the target site in real-time with the IVUS catheter, and deploying the transcatheter heart valve at the target site aiming to maintain a conformal placement within the native valve annulus, thereby avoiding or minimizing paravalvular leak.
Systems and methods for heart valve therapy
ActiveCN107920862AFull retentionLess intrusiveAnnuloplasty ringsSurgical robotsAnatomical structuresLeft ventricular size
Prosthetic mitral valves described herein can be deployed using a transcatheter mitral valve delivery system and technique to interface and anchor in cooperation with the anatomical structures of a native mitral valve. This document describes prosthetic heart valve designs that interface with native mitral valve structures to create a fluid seal, thereby minimizing mitral regurgitation and paravalvular leaks. This document also describes prosthetic heart valve designs and techniques to manage blood flow through the left ventricular outflow tract. In addition, this document describes prostheticheart valve designs and techniques that reduce the risk of interference between the prosthetic valves and chordae tendineae.
Owner:CAISSON INT LLC
Prosthetic heart valve with paravalvular leak mitigation features
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Expandable frames and paravalvular leak mitigation systems for implantable prosthetic heart valve devices
A collapsible and expandable prosthetic heart valve stent is provided and comprising an outer section, a valve support defining a flow channel therethrough, a transition section configured to smoothly transition the outer section to the valve support. The valve support is disposed within an interior defined by the outer section, with the inflow end of the valve support disposed inside the outer section's interior. In some cases, the outflow end of the valve support is at least partially defined by the transition section. The prosthetic leaflets are disposed on the inner surface of the valve support's flow channel and are located at or above the annulus of the heart chamber. A paravalvular leakage mitigation system is attached to the stent to mitigate retrograde blood flow and / or regurgitation.
Owner:C MEDICAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com