Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
68 results about "Paravalvular leakage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
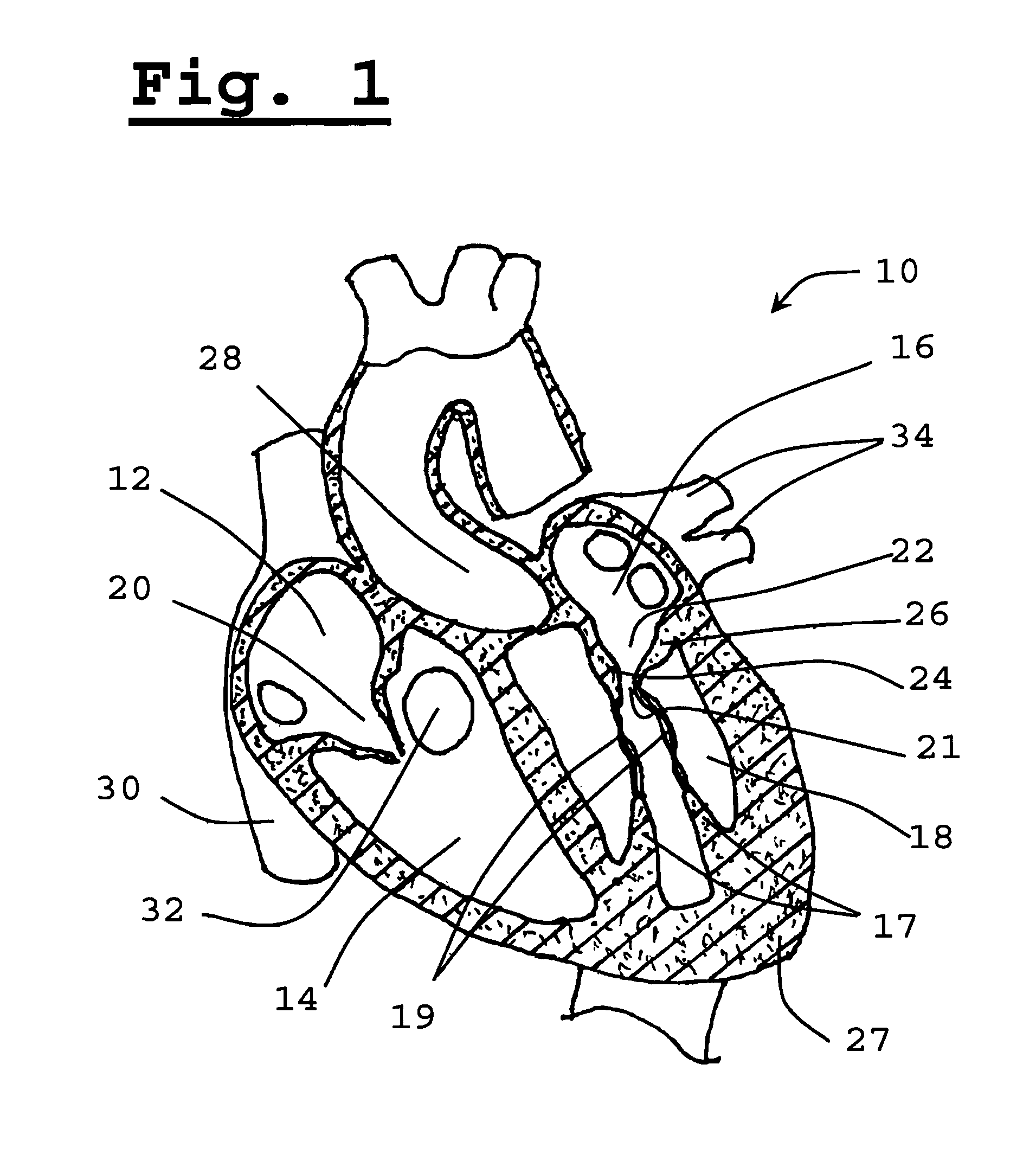
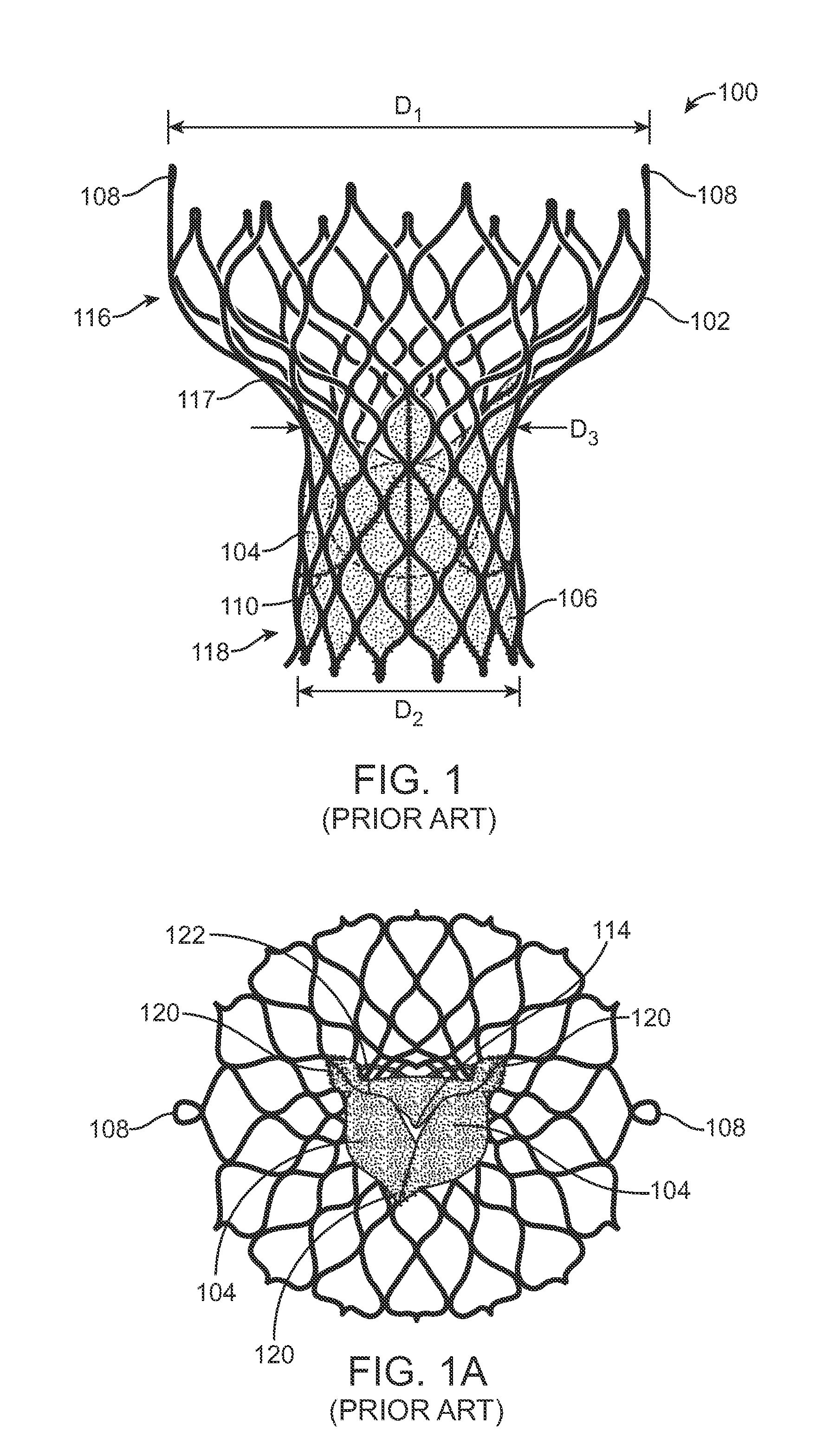
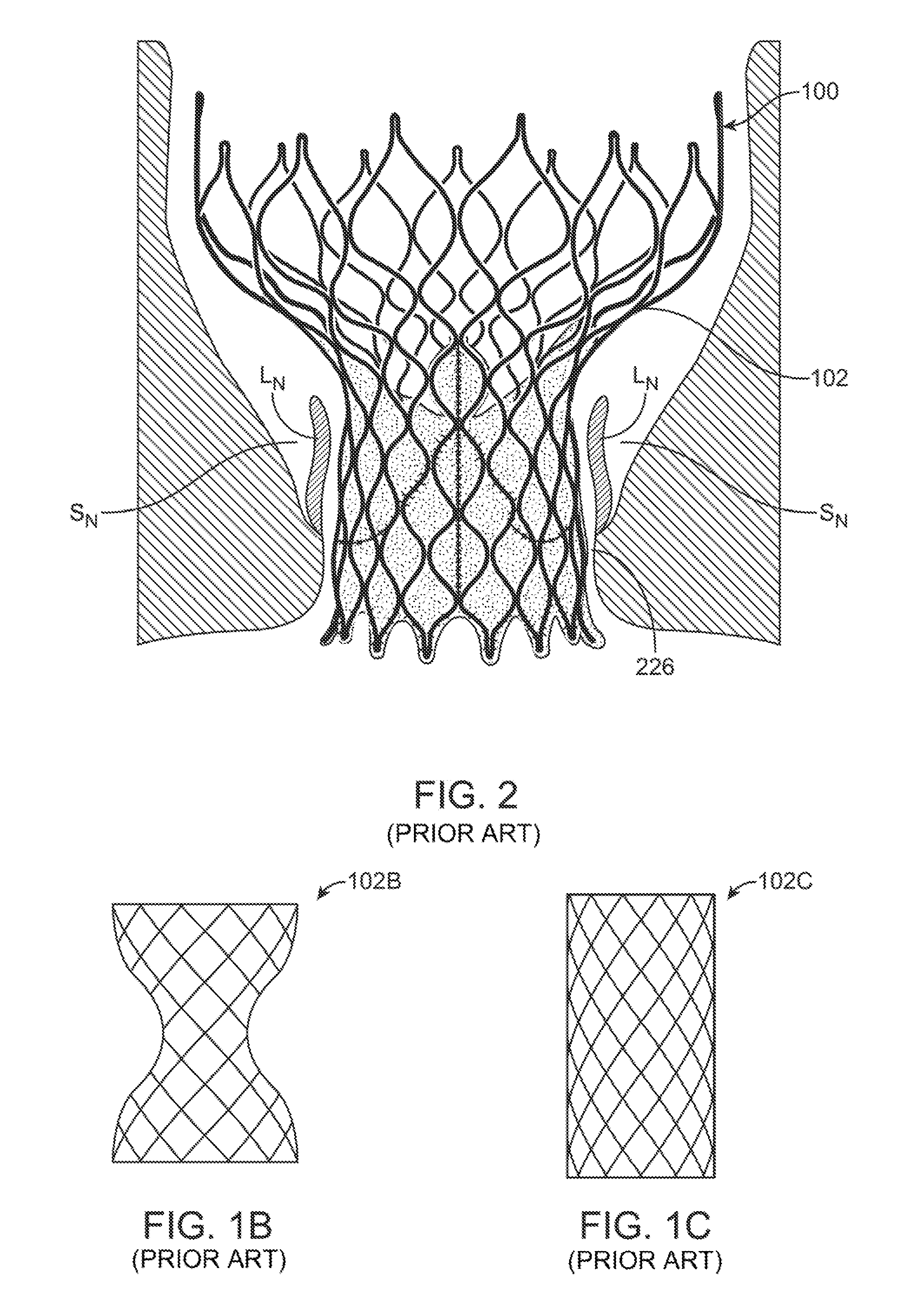
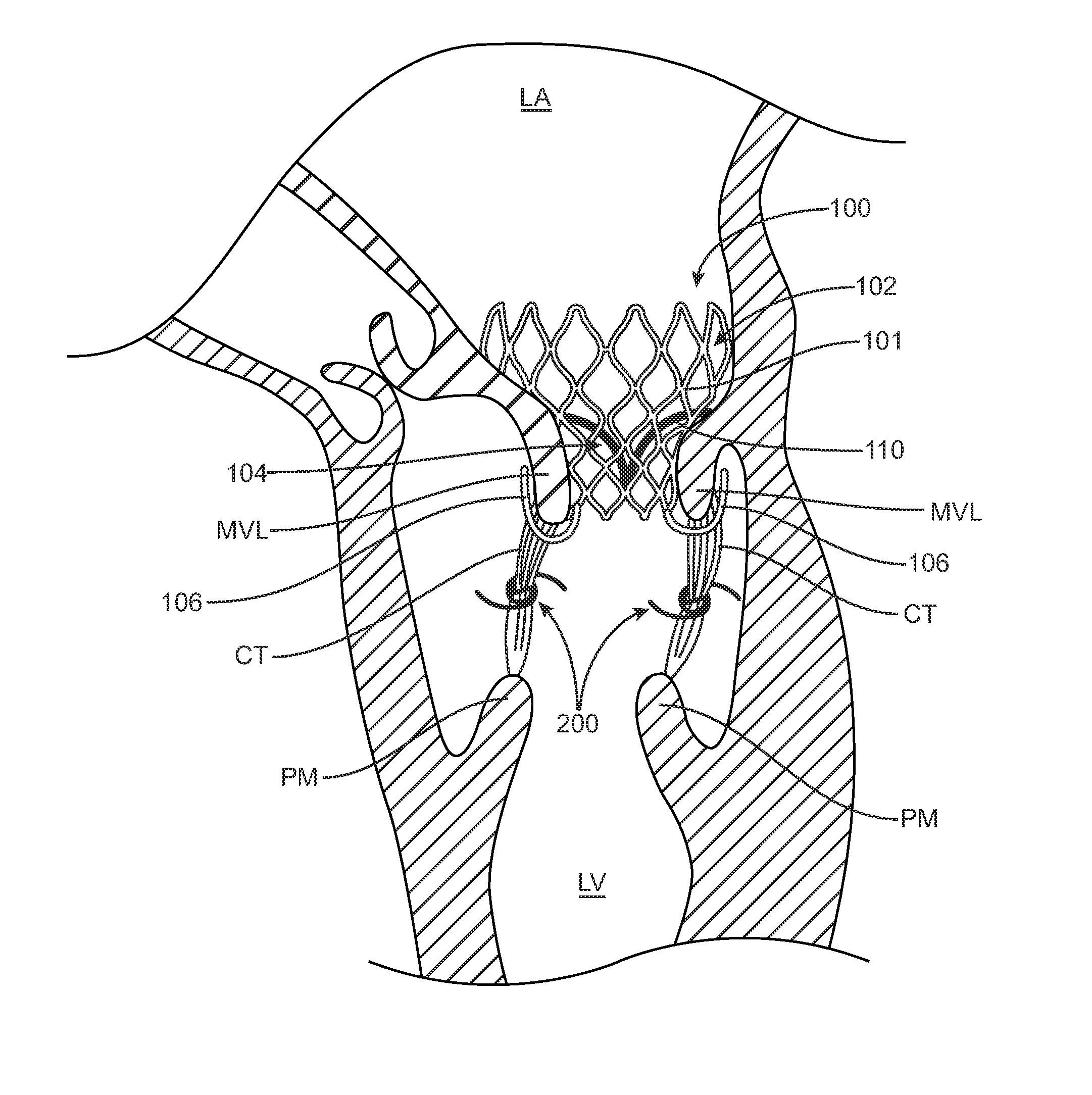
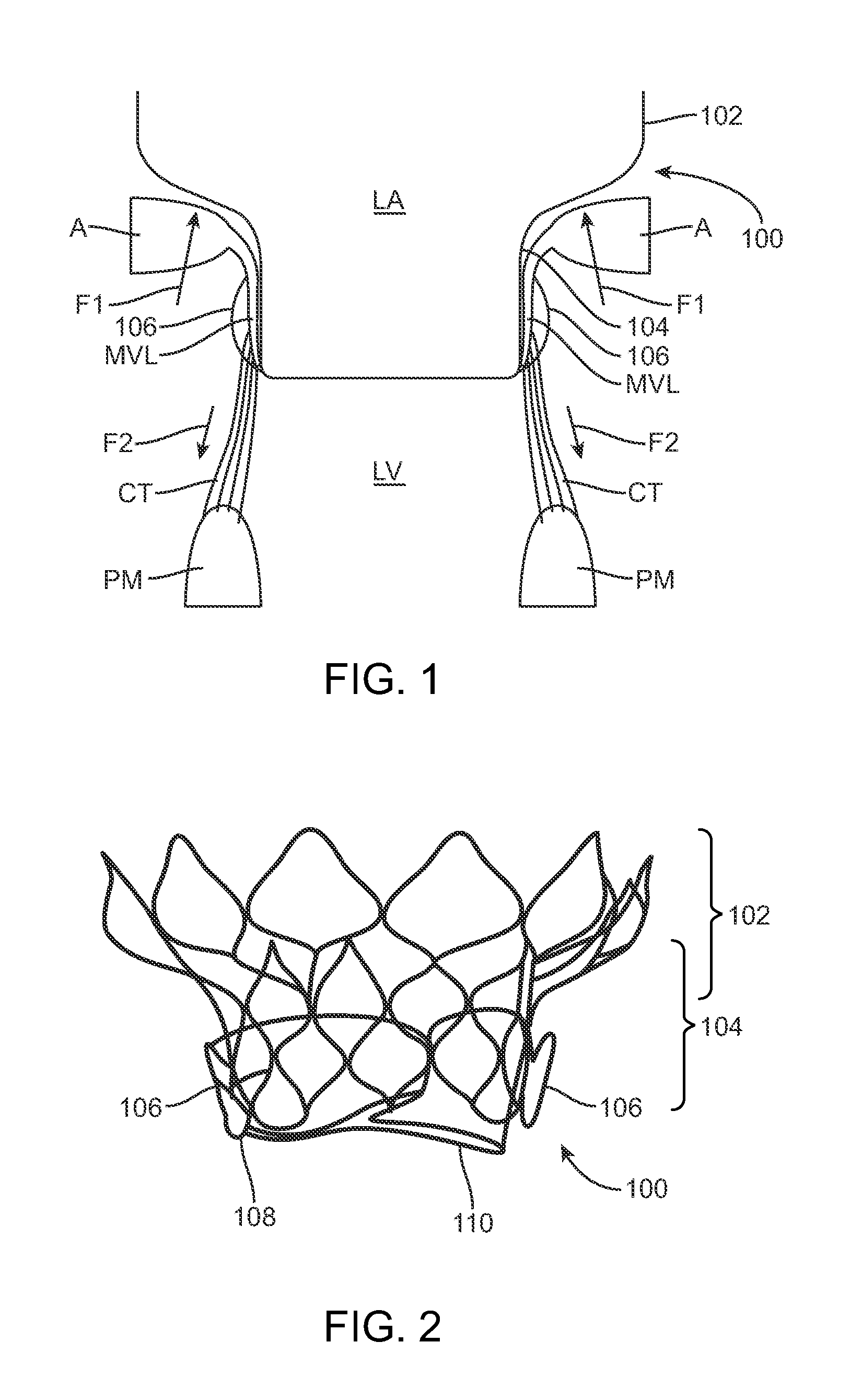
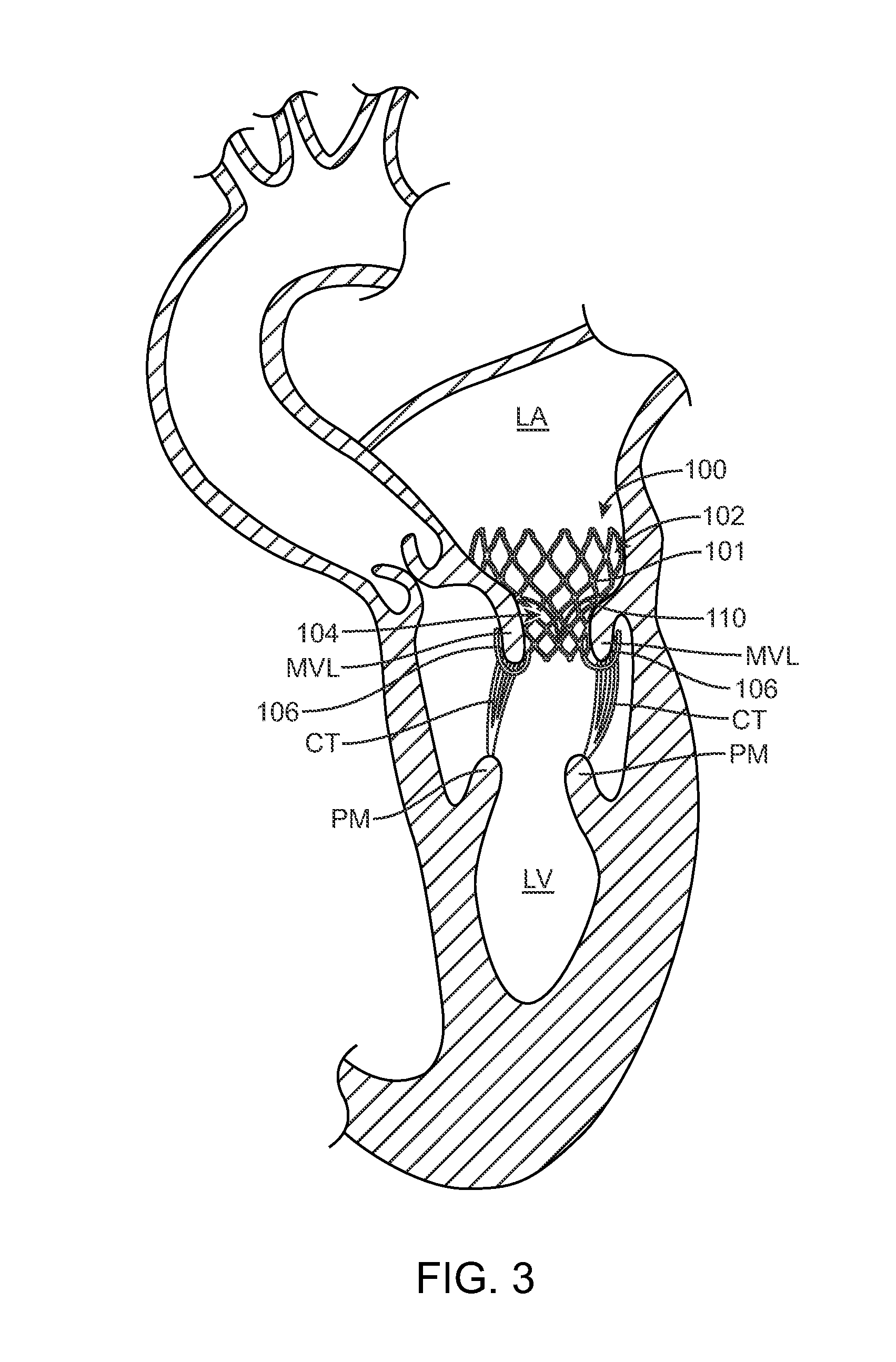
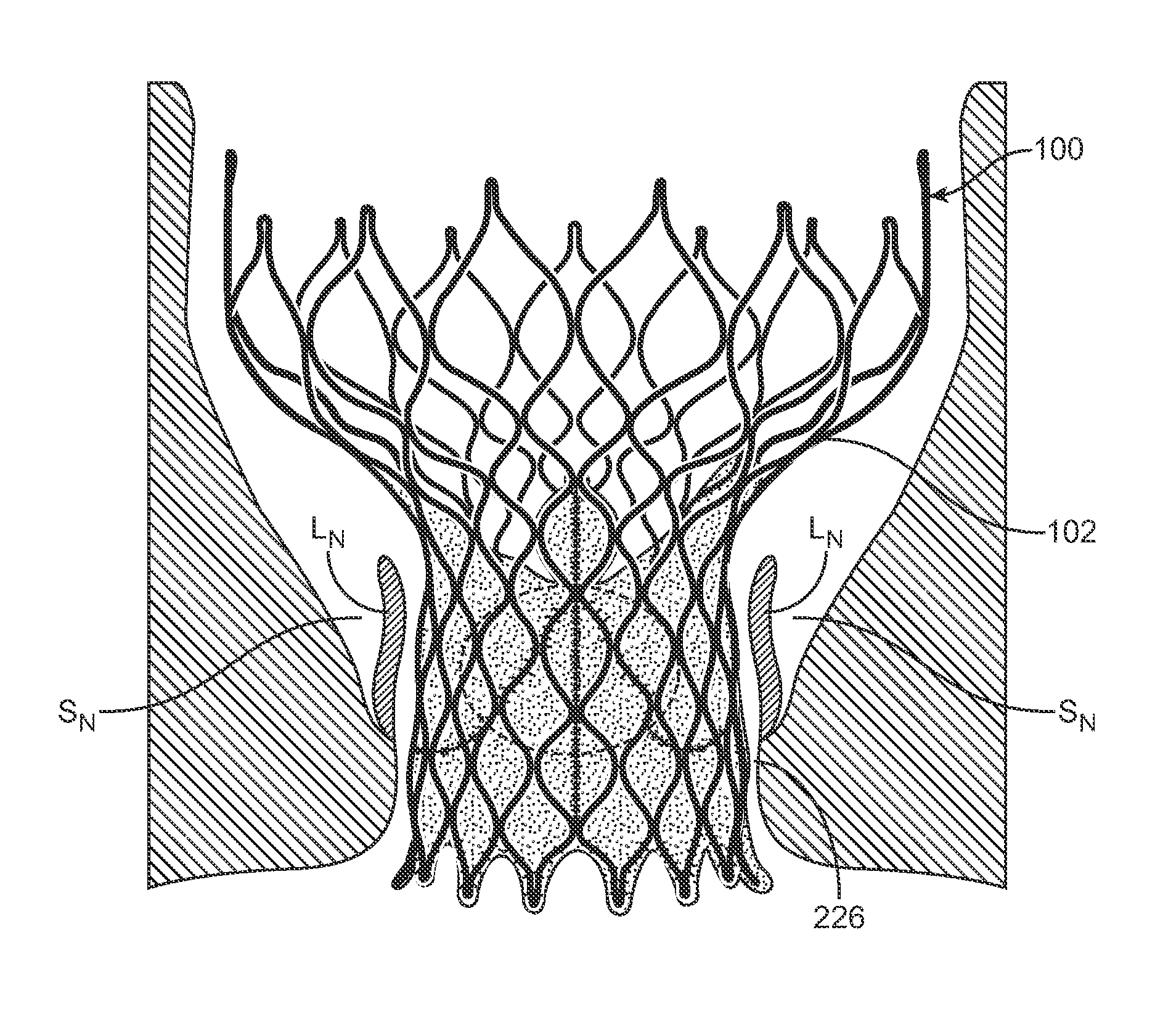
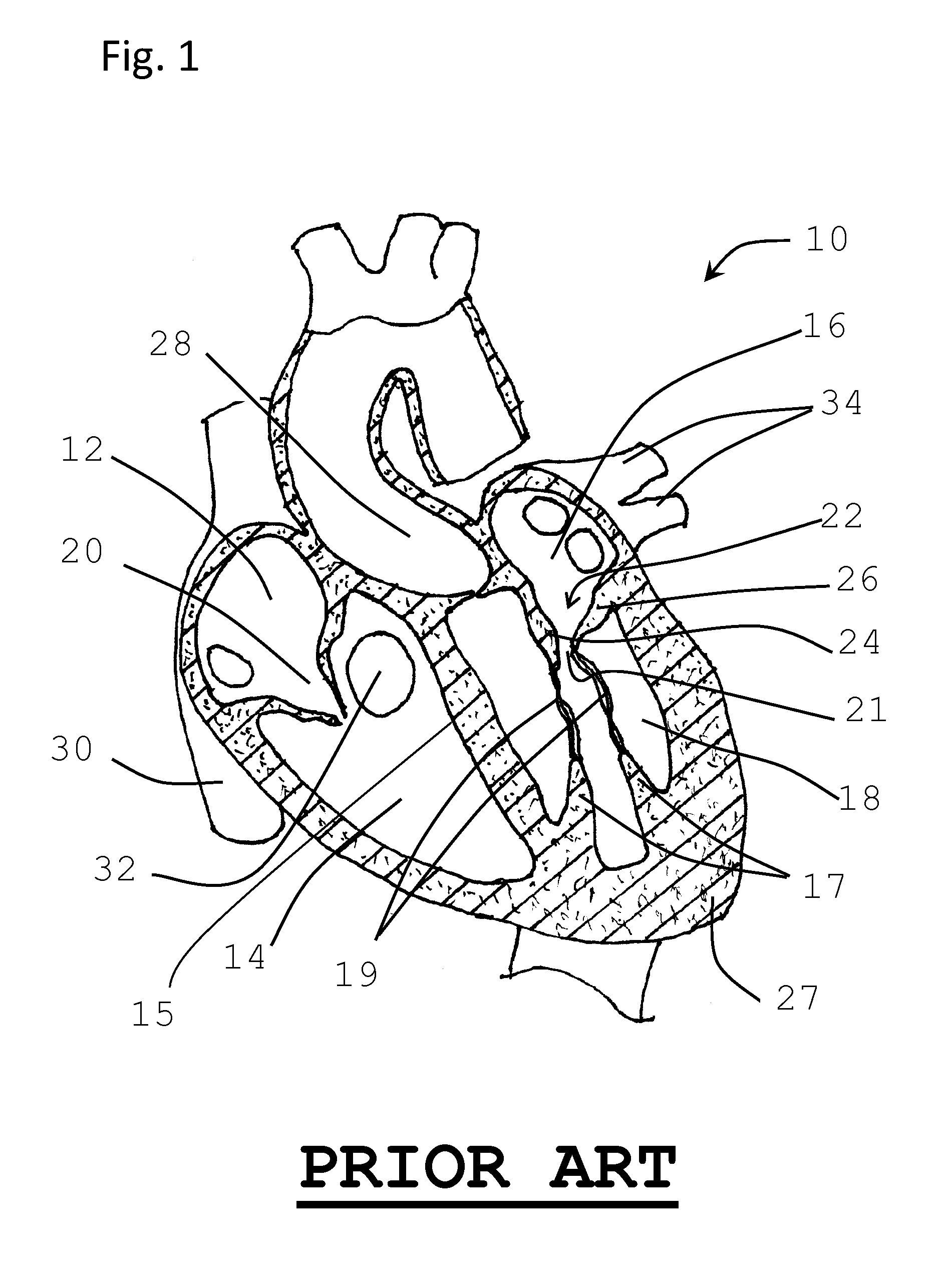
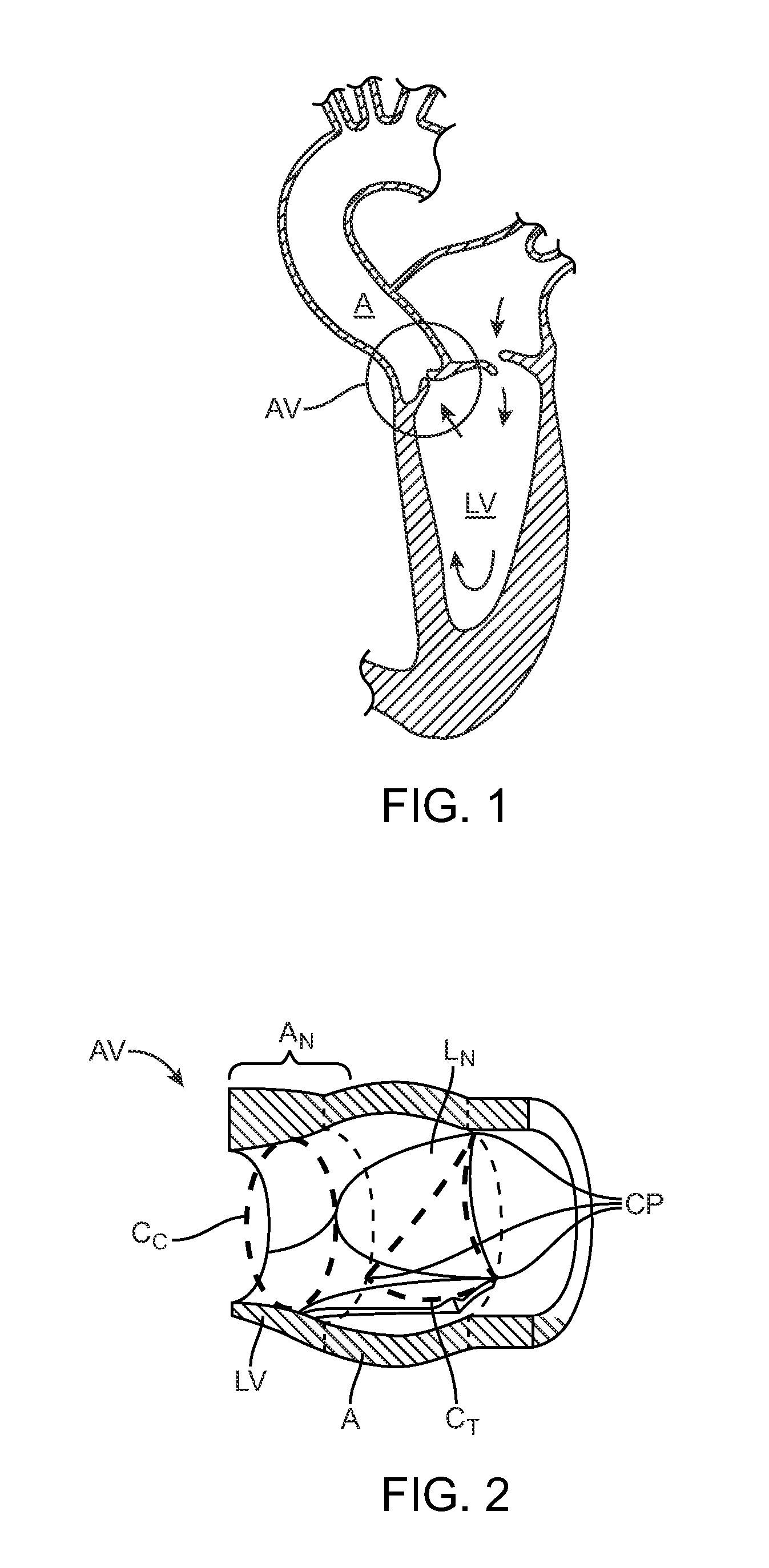
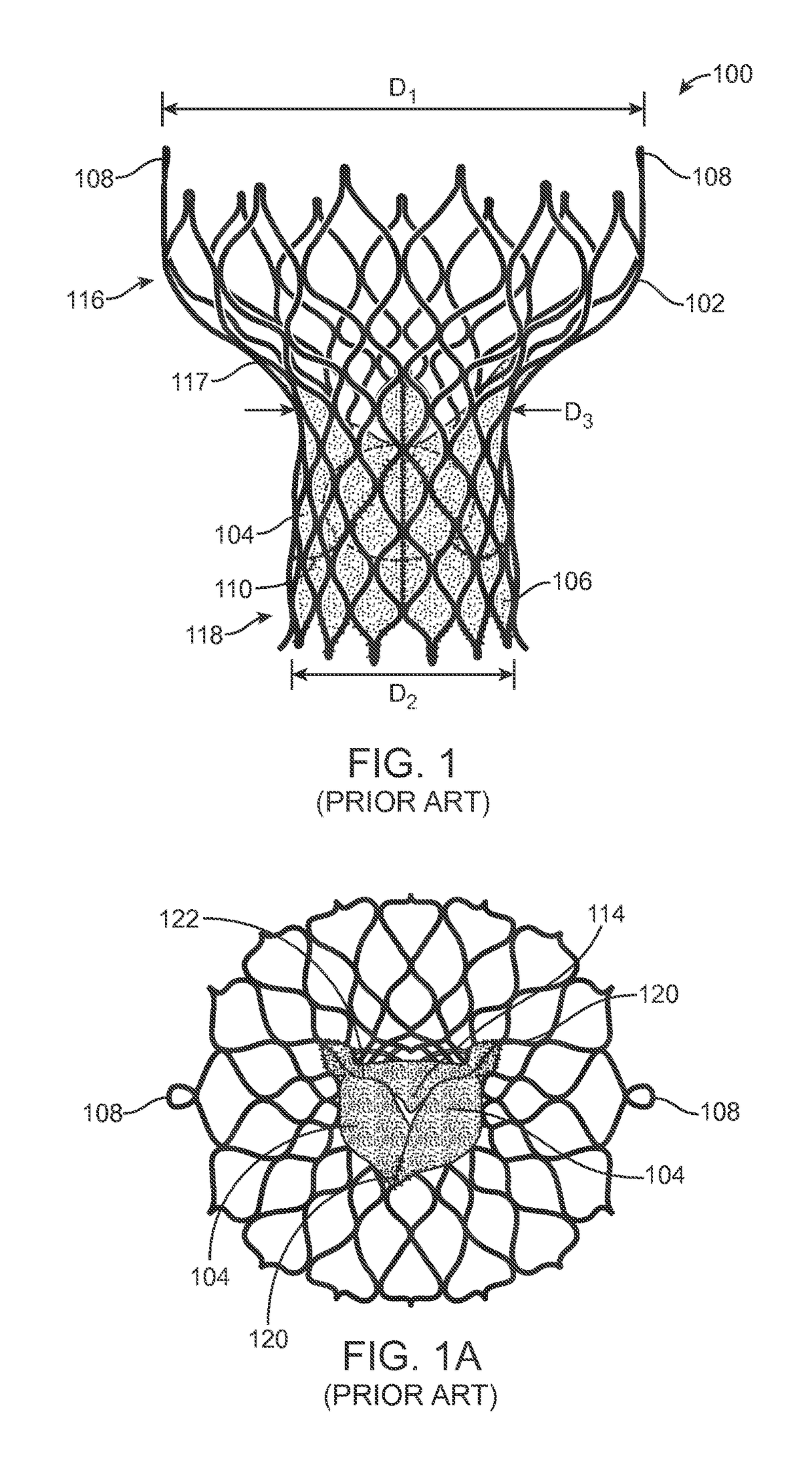
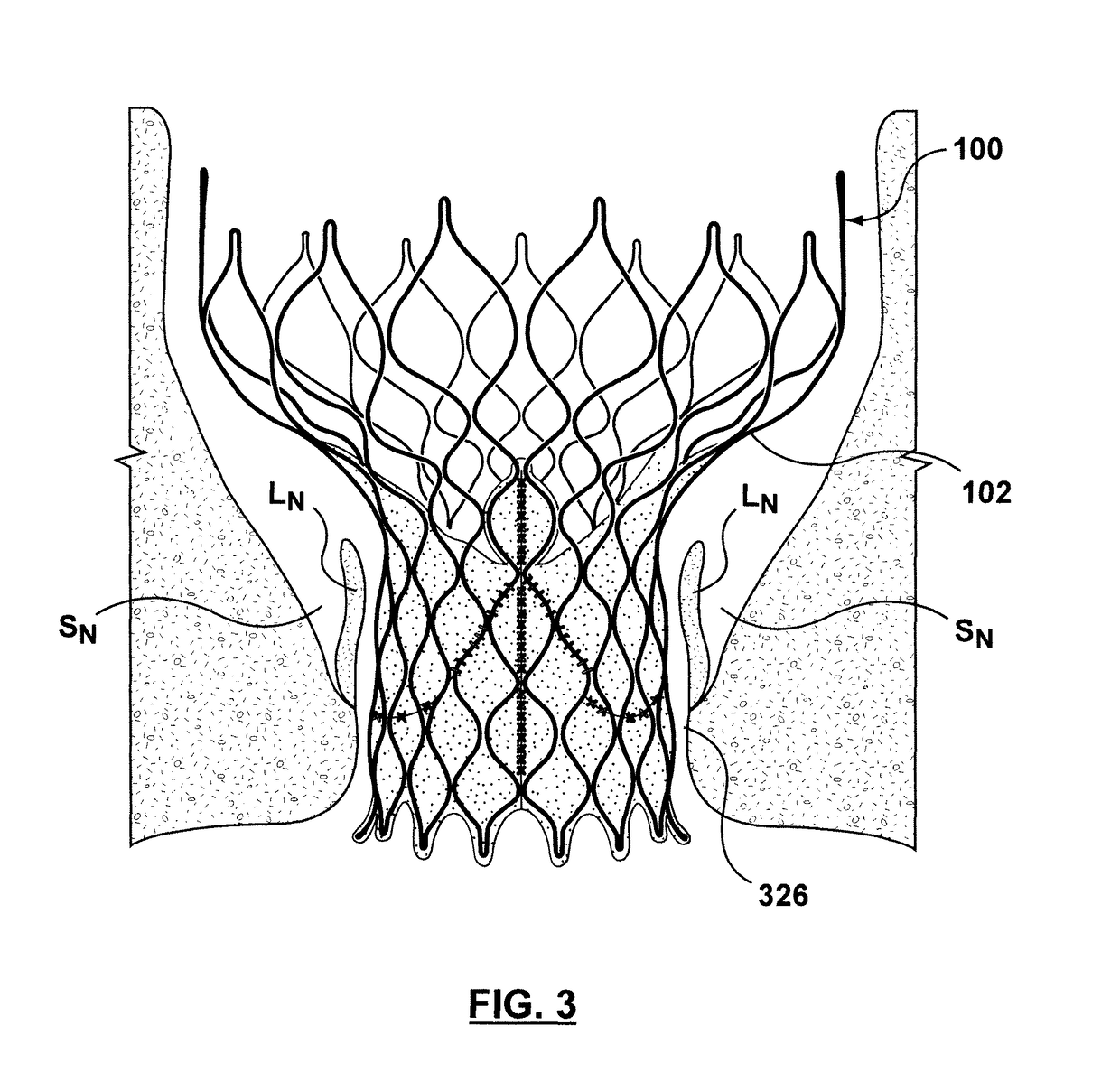
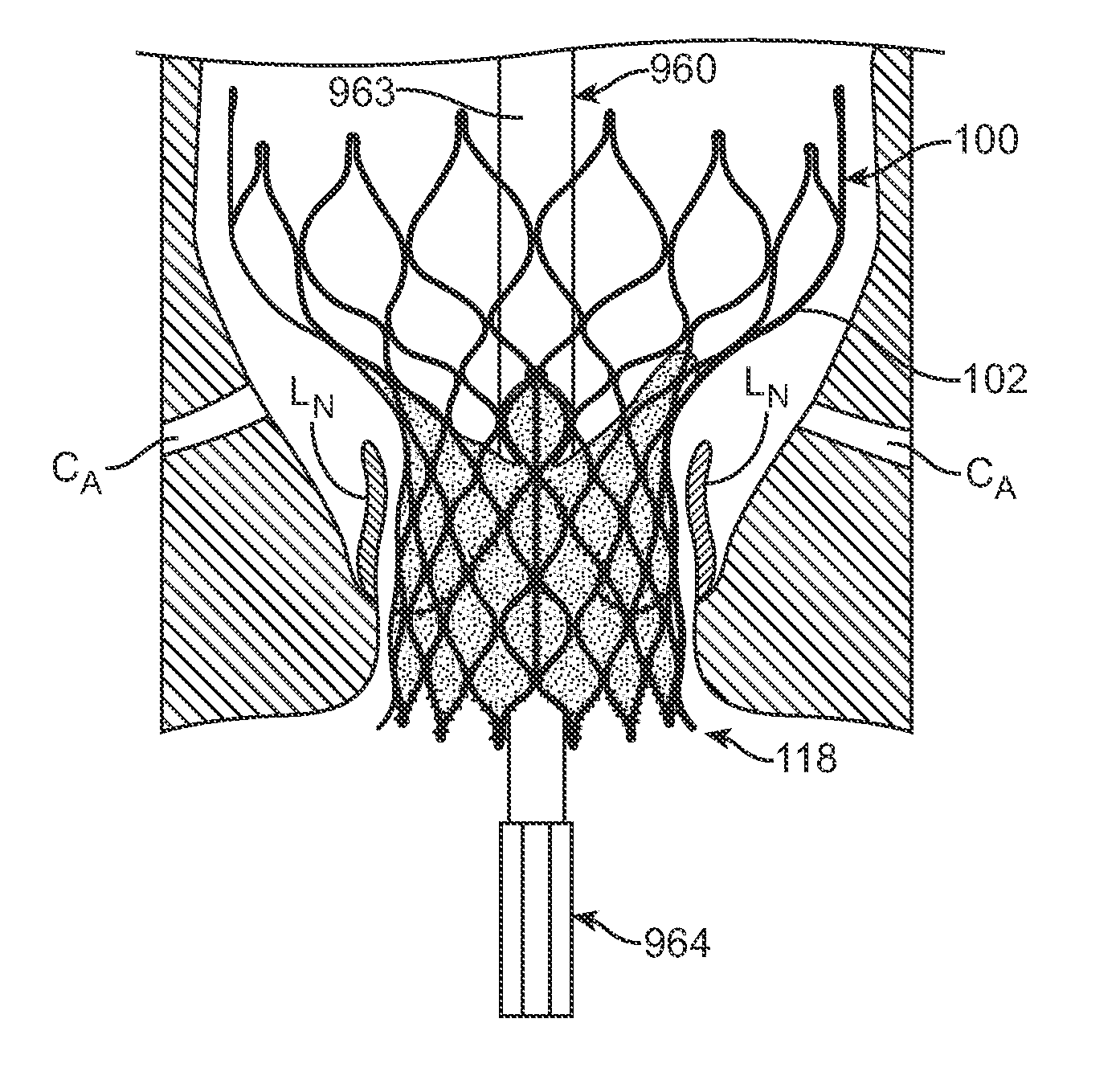
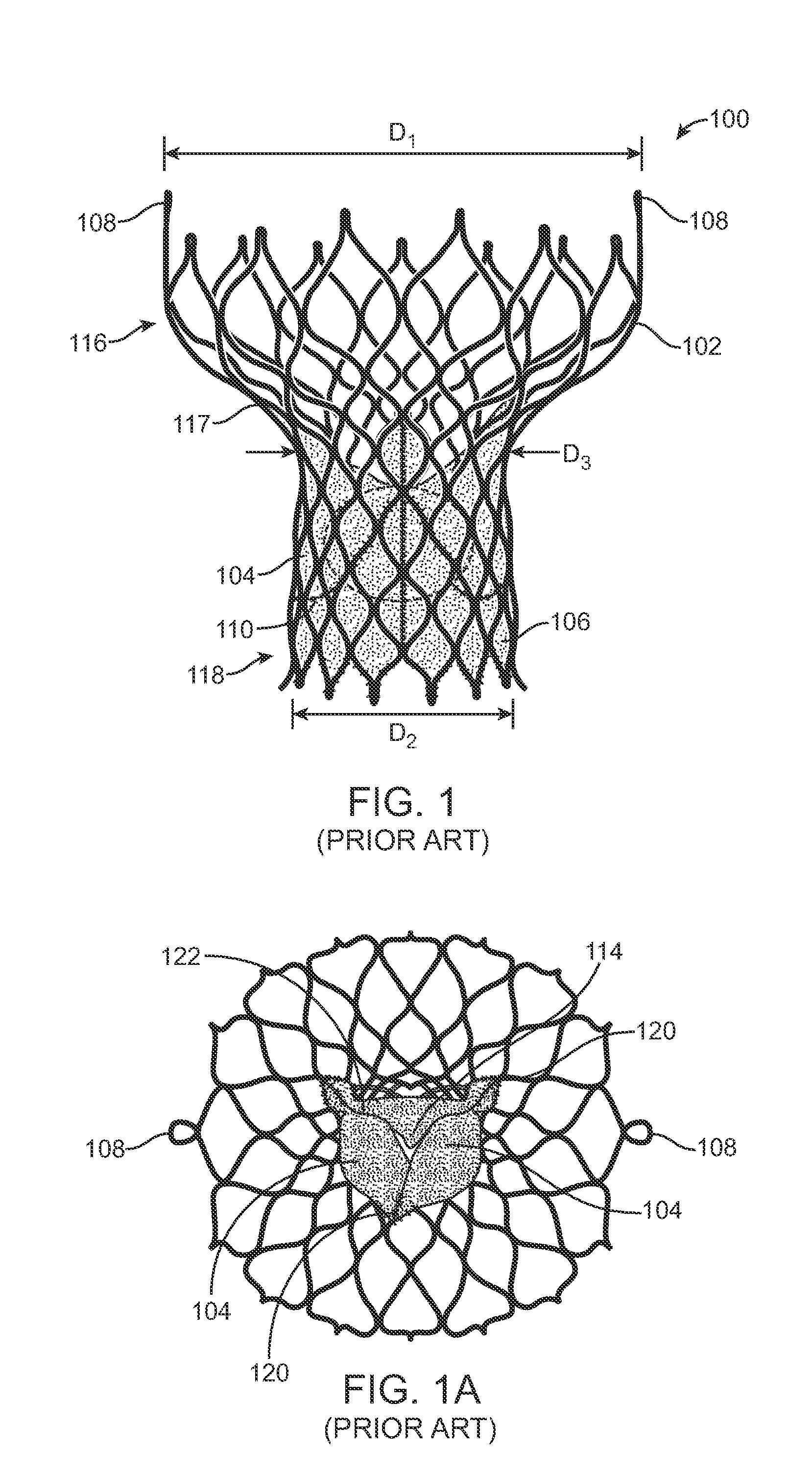
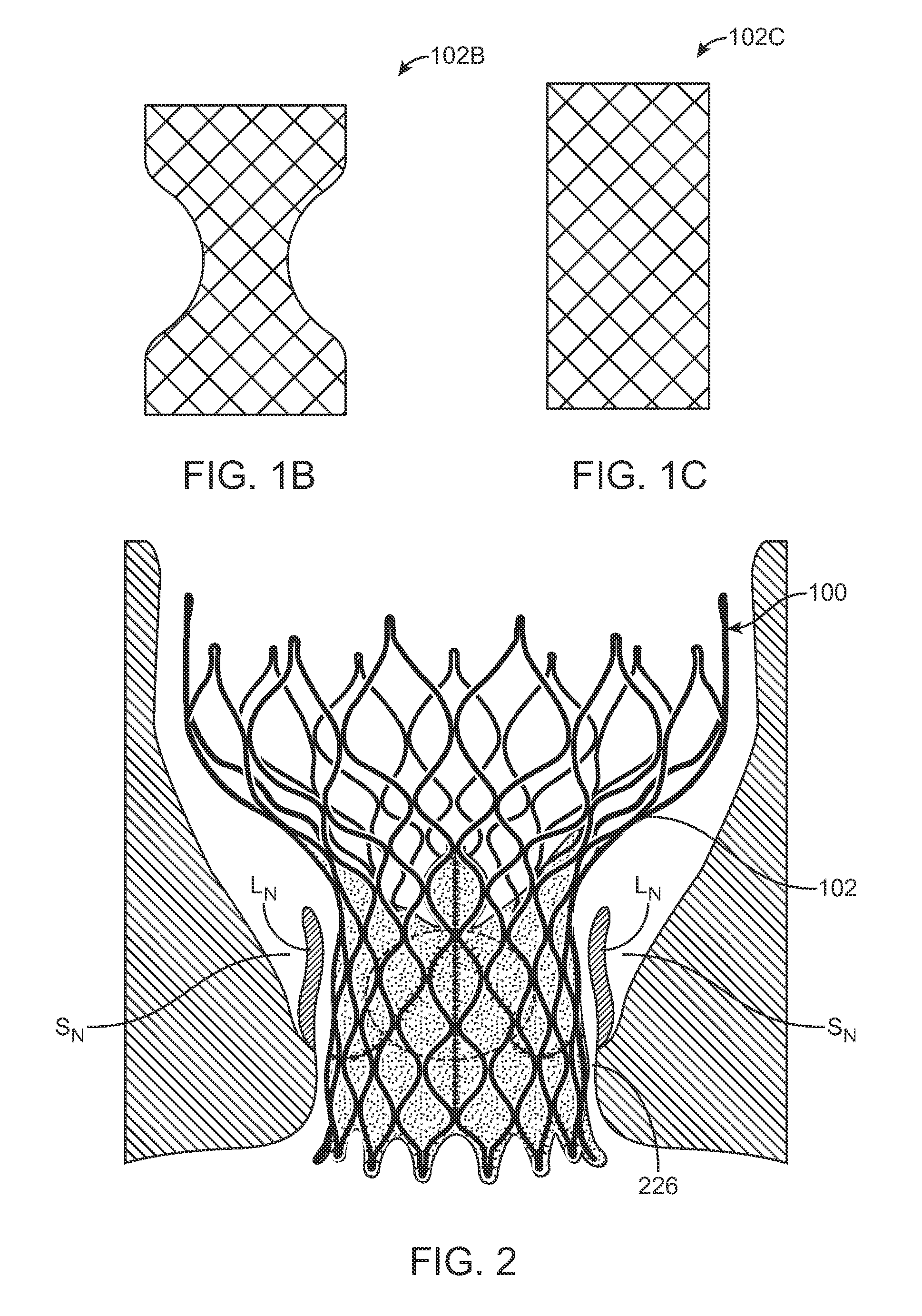
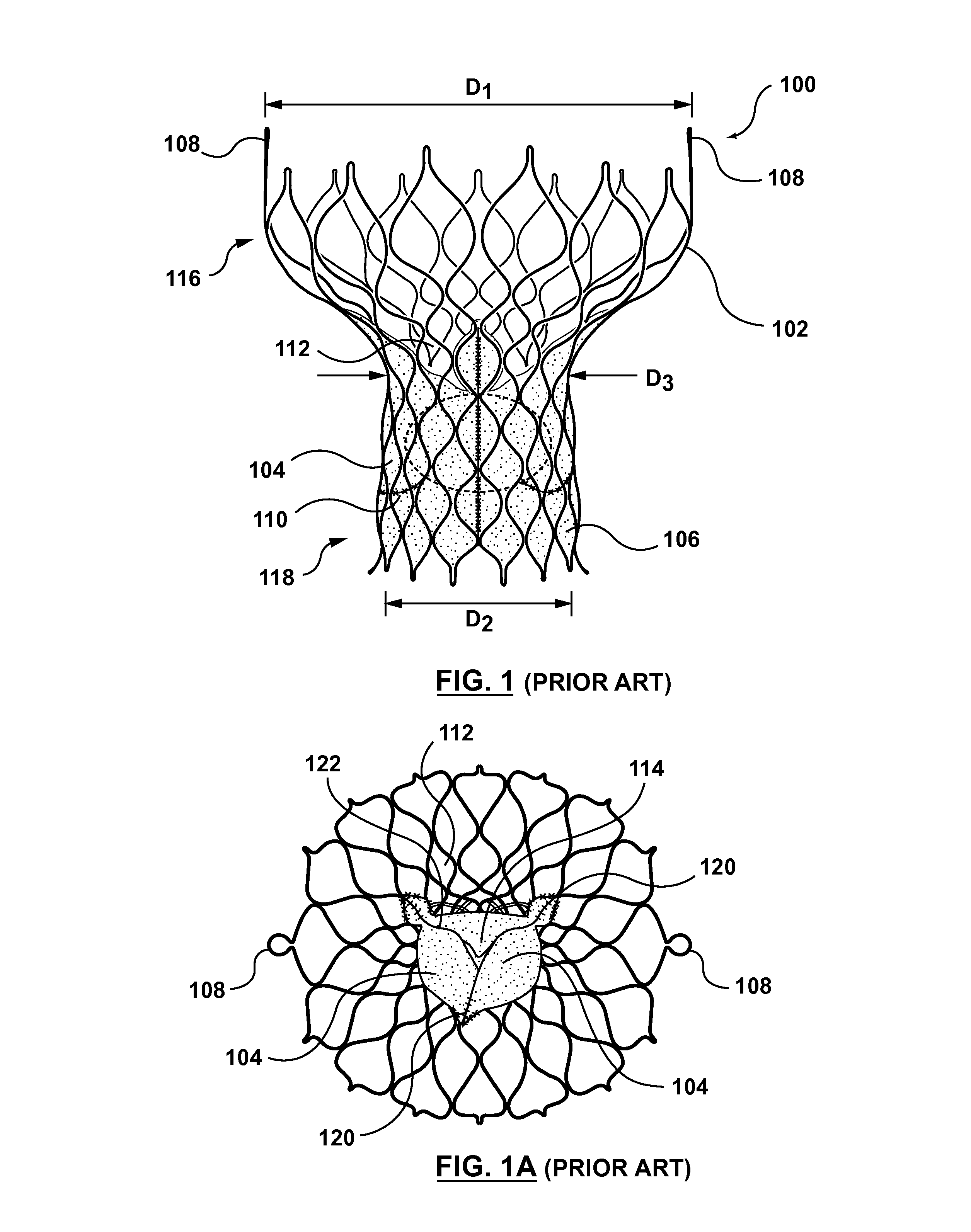
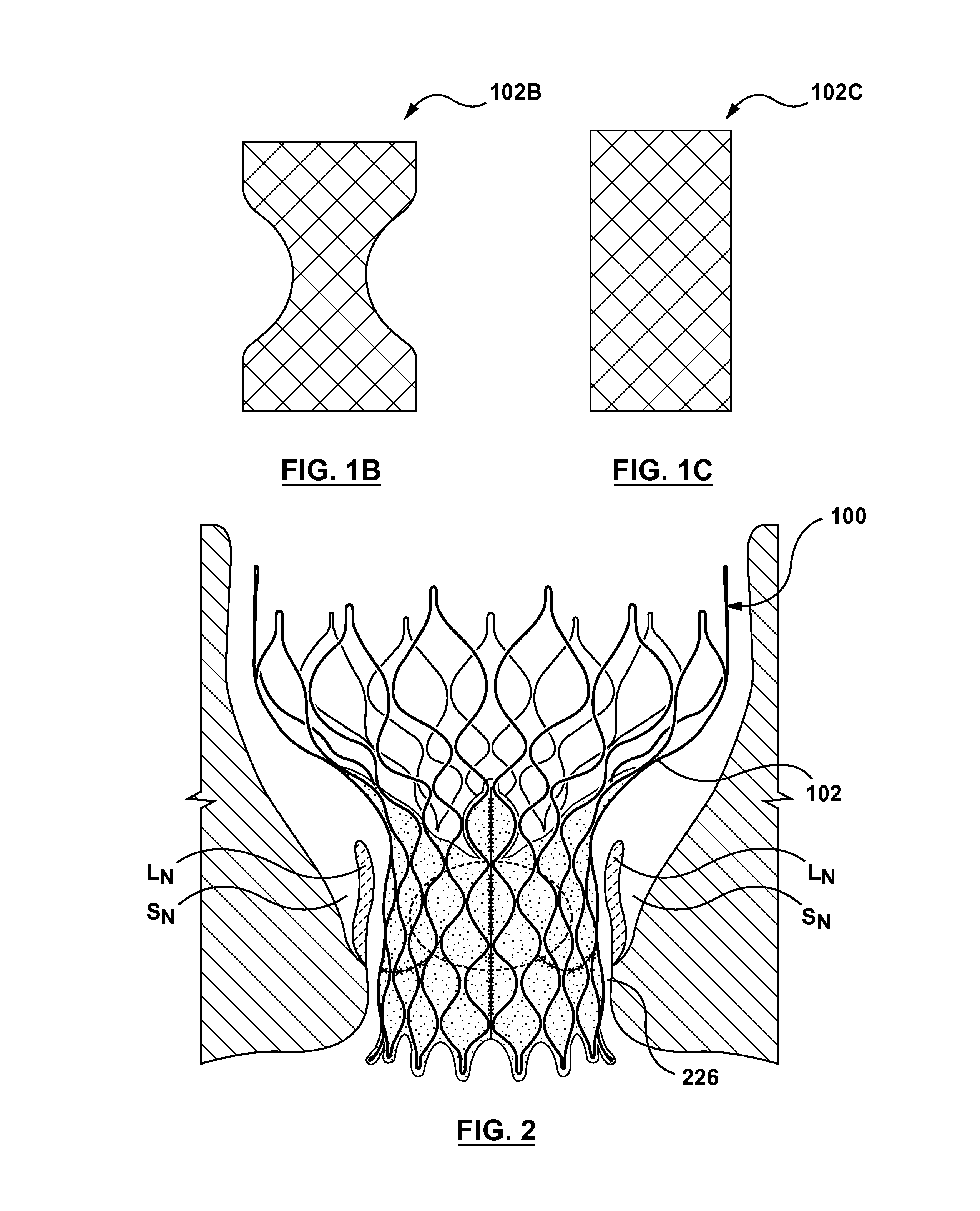
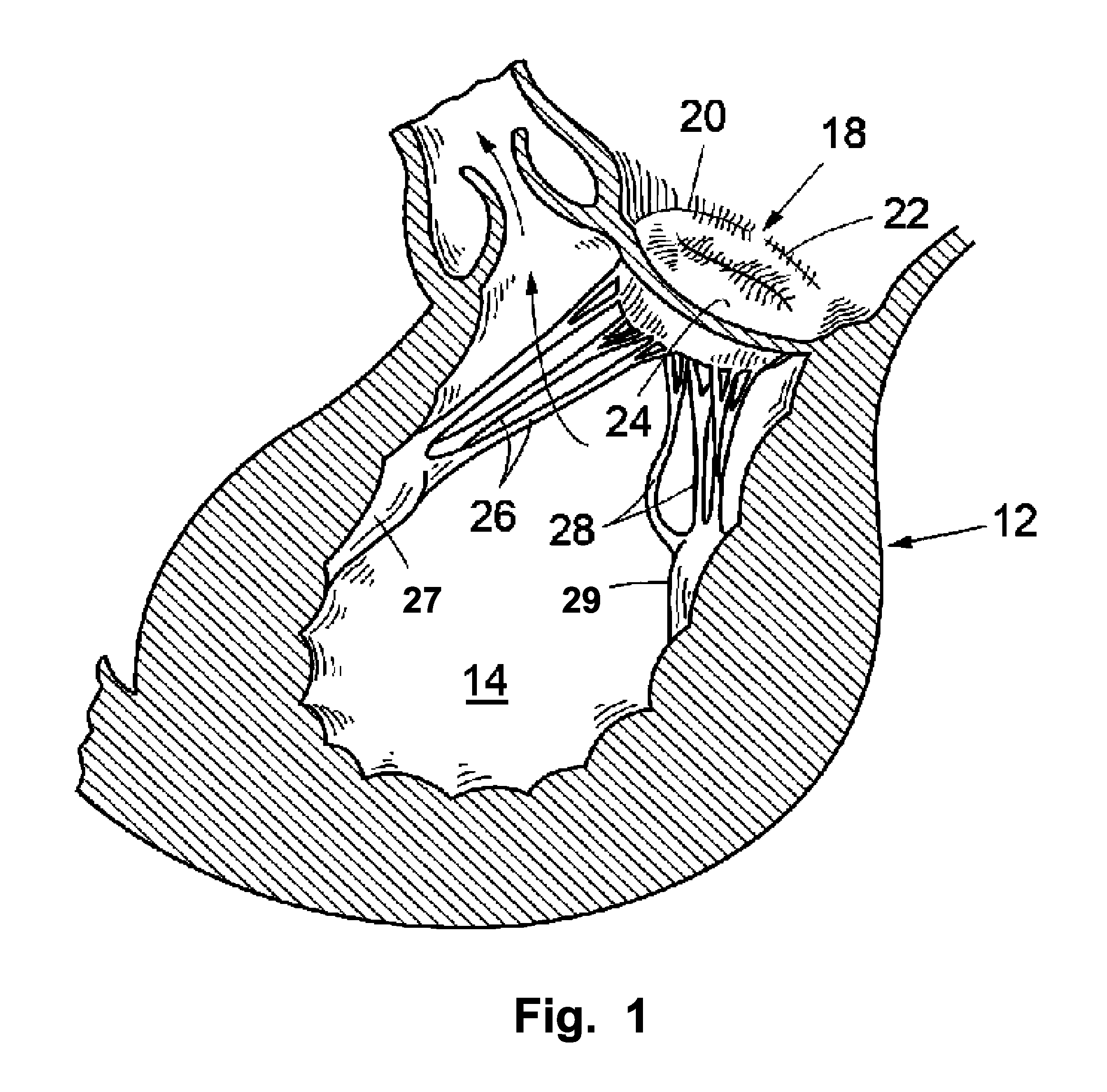
A paravalvular leak is an opening that forms on the outer edge of a prosthetic (artificial) valve where it is secured to the heart tissue. Paravalvular leaks may occur at the site of a loose or broken suture, which can result from endocarditis (inflammation of the lining inside the heart) or poor valve placement.
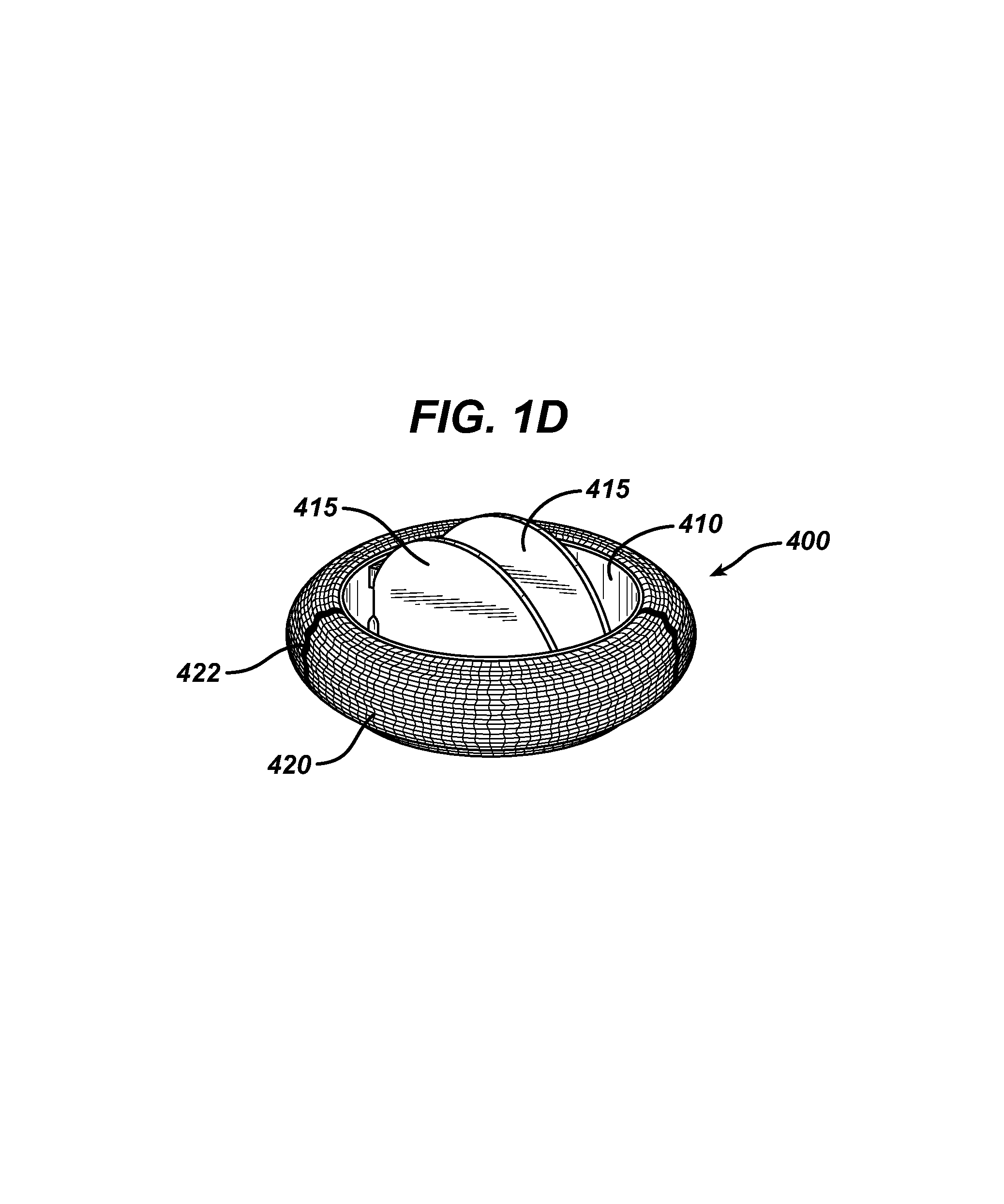
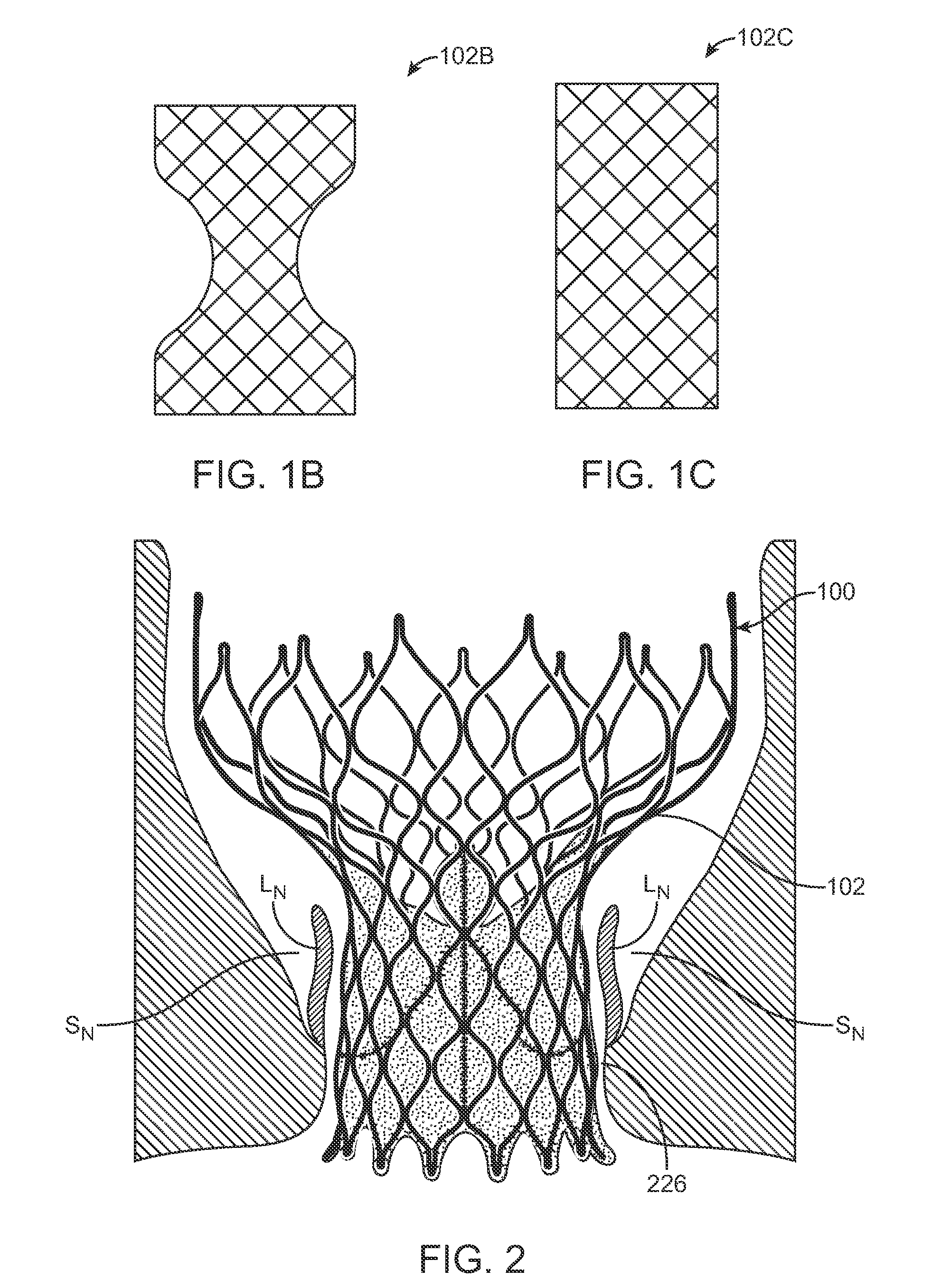
Anti-Paravalvular Leakage Components for a Transcatheter Valve Prosthesis
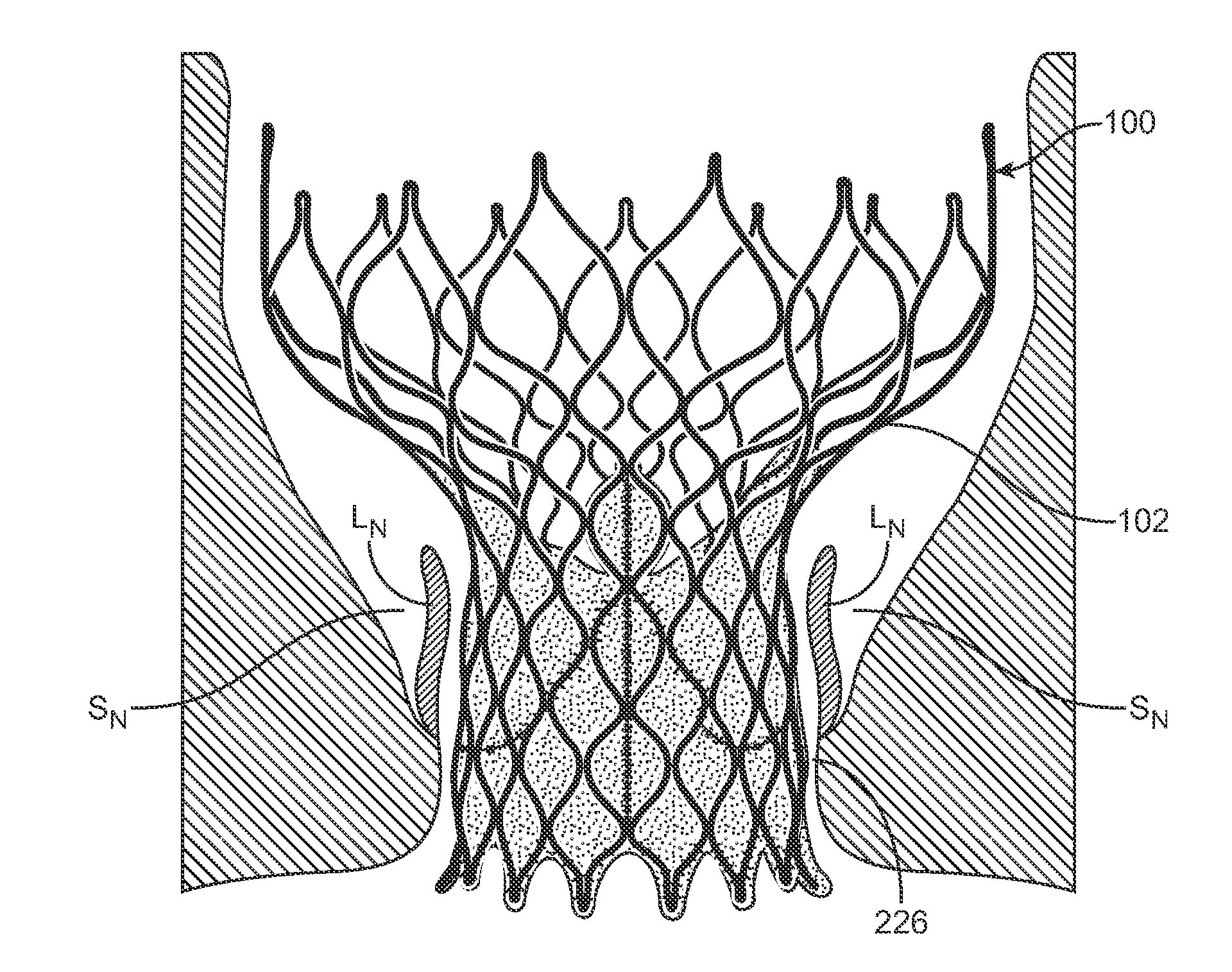
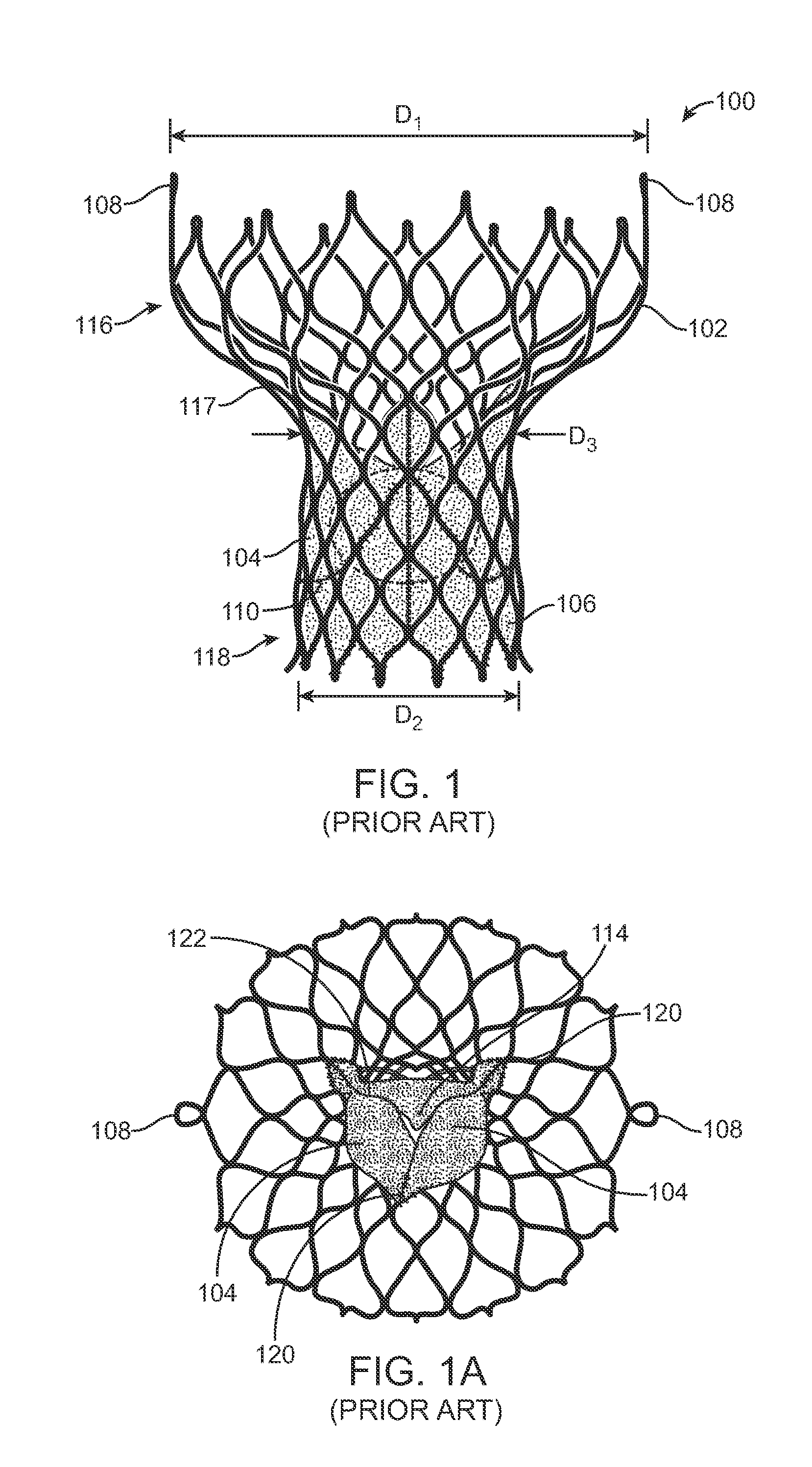
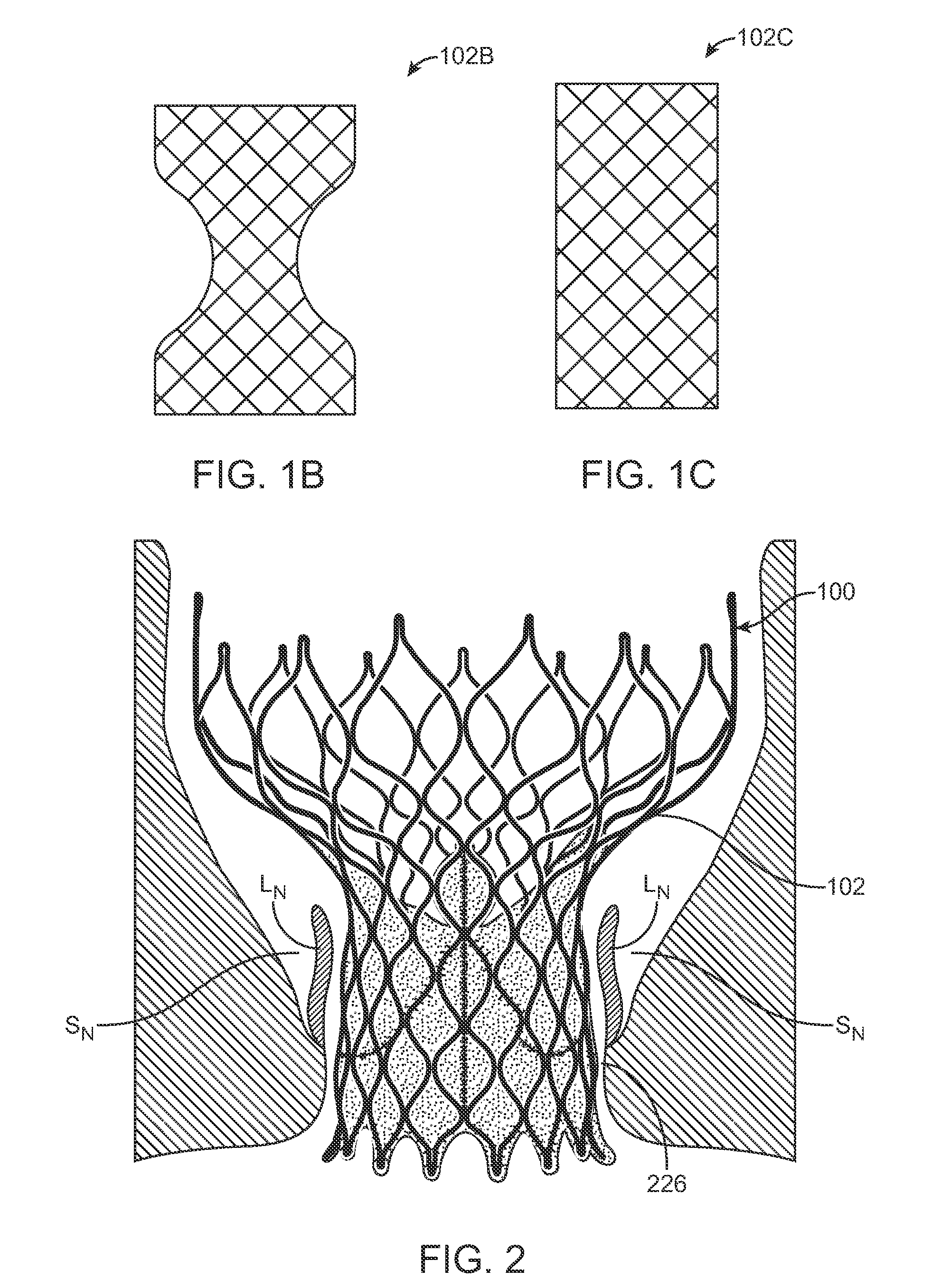
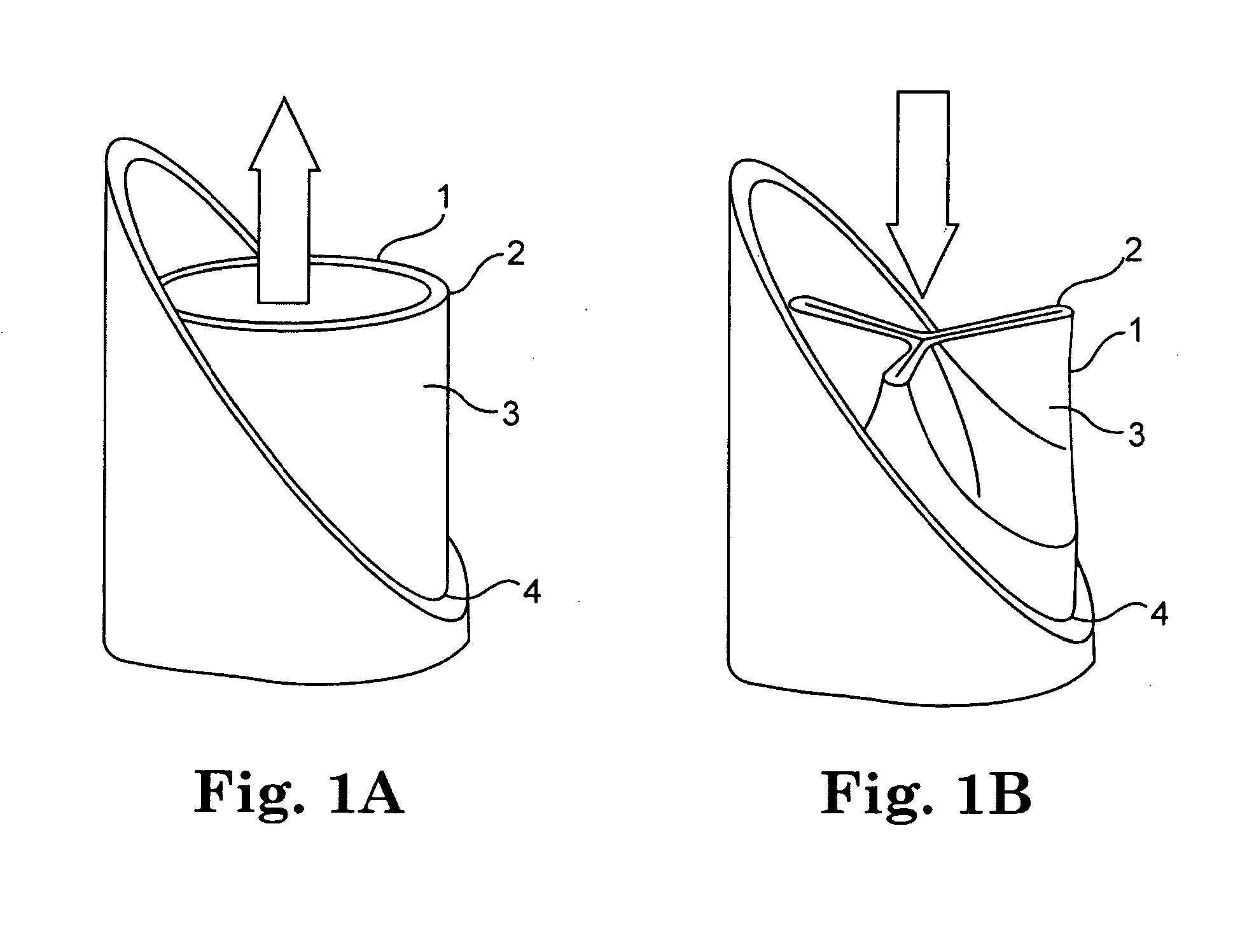
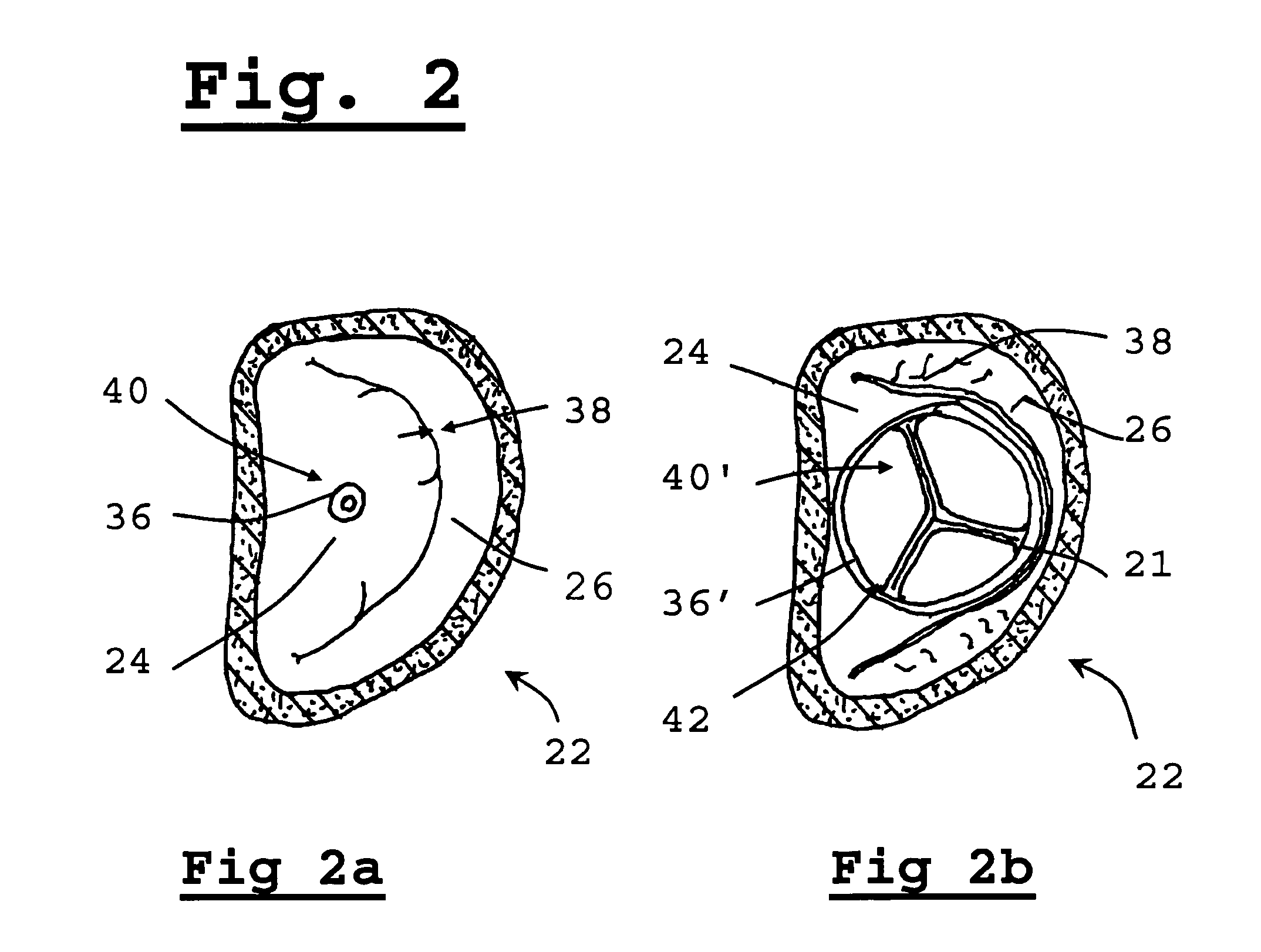
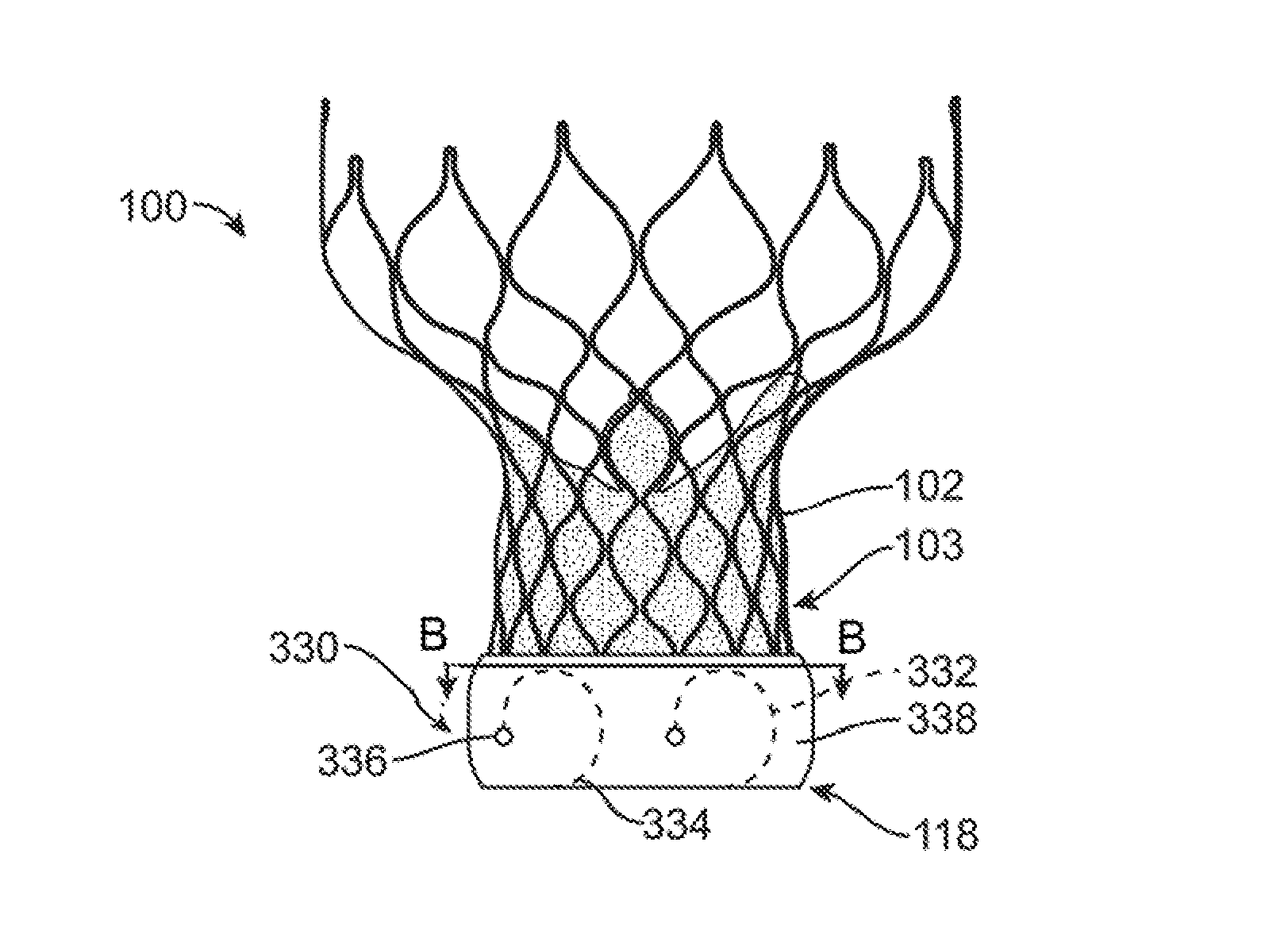
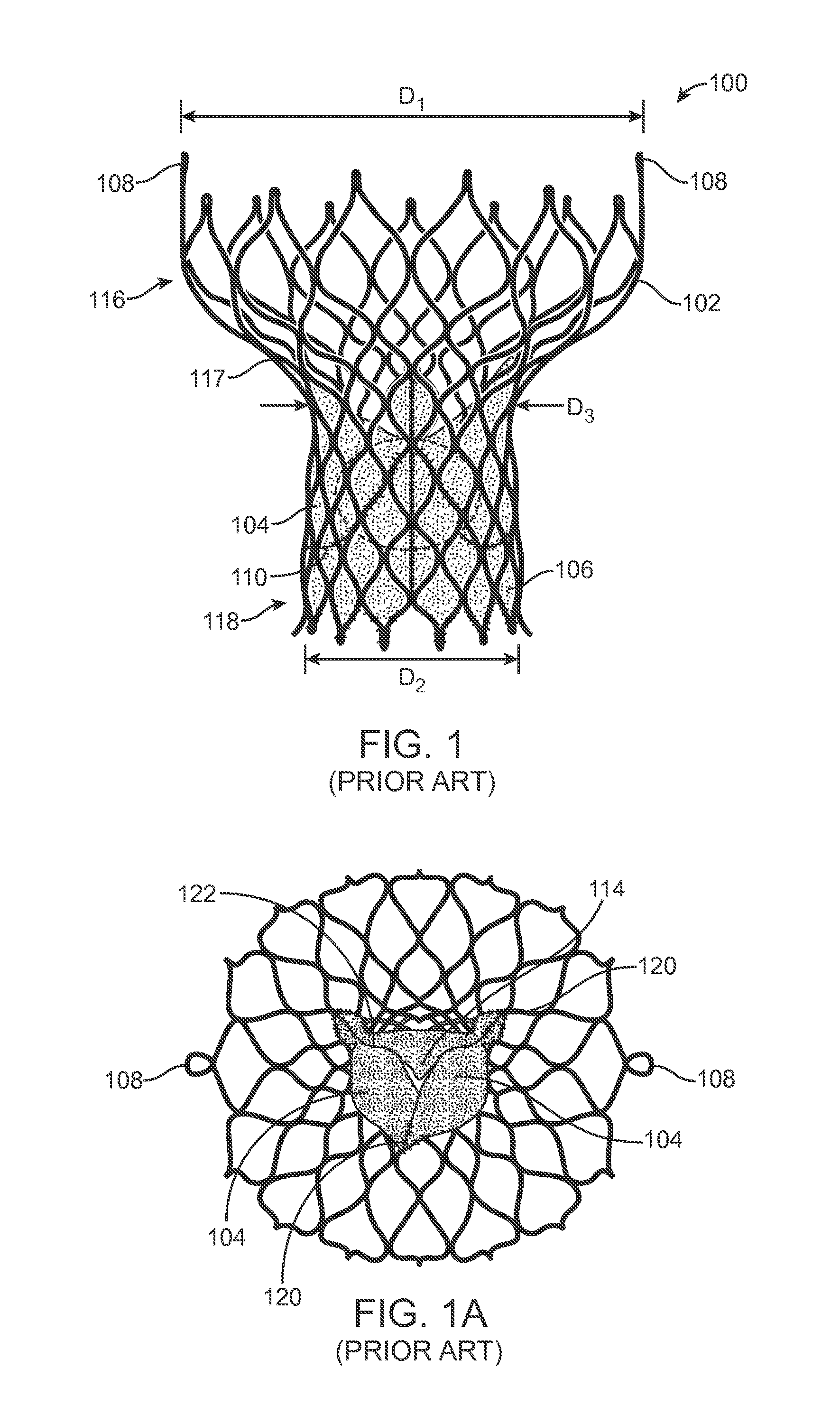
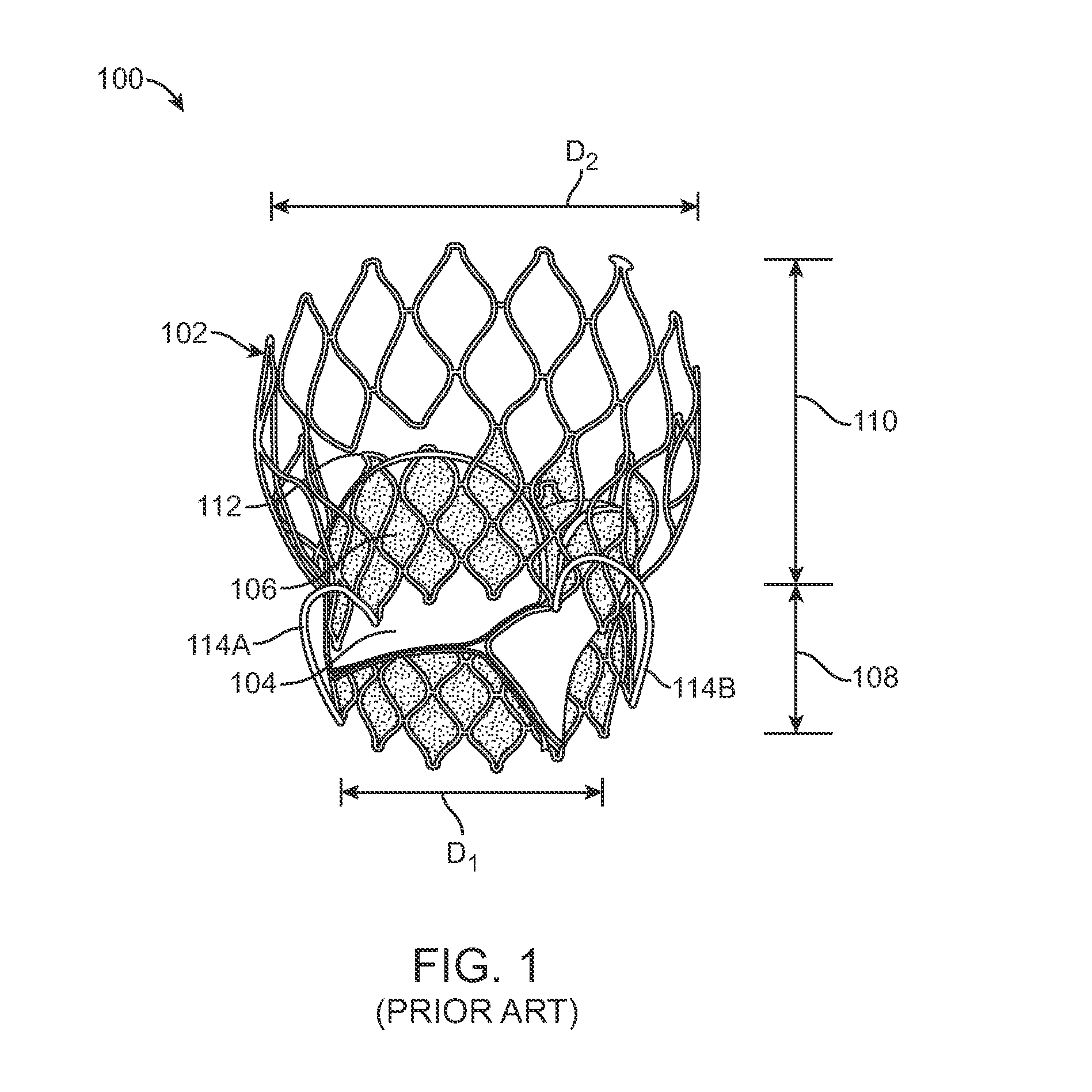
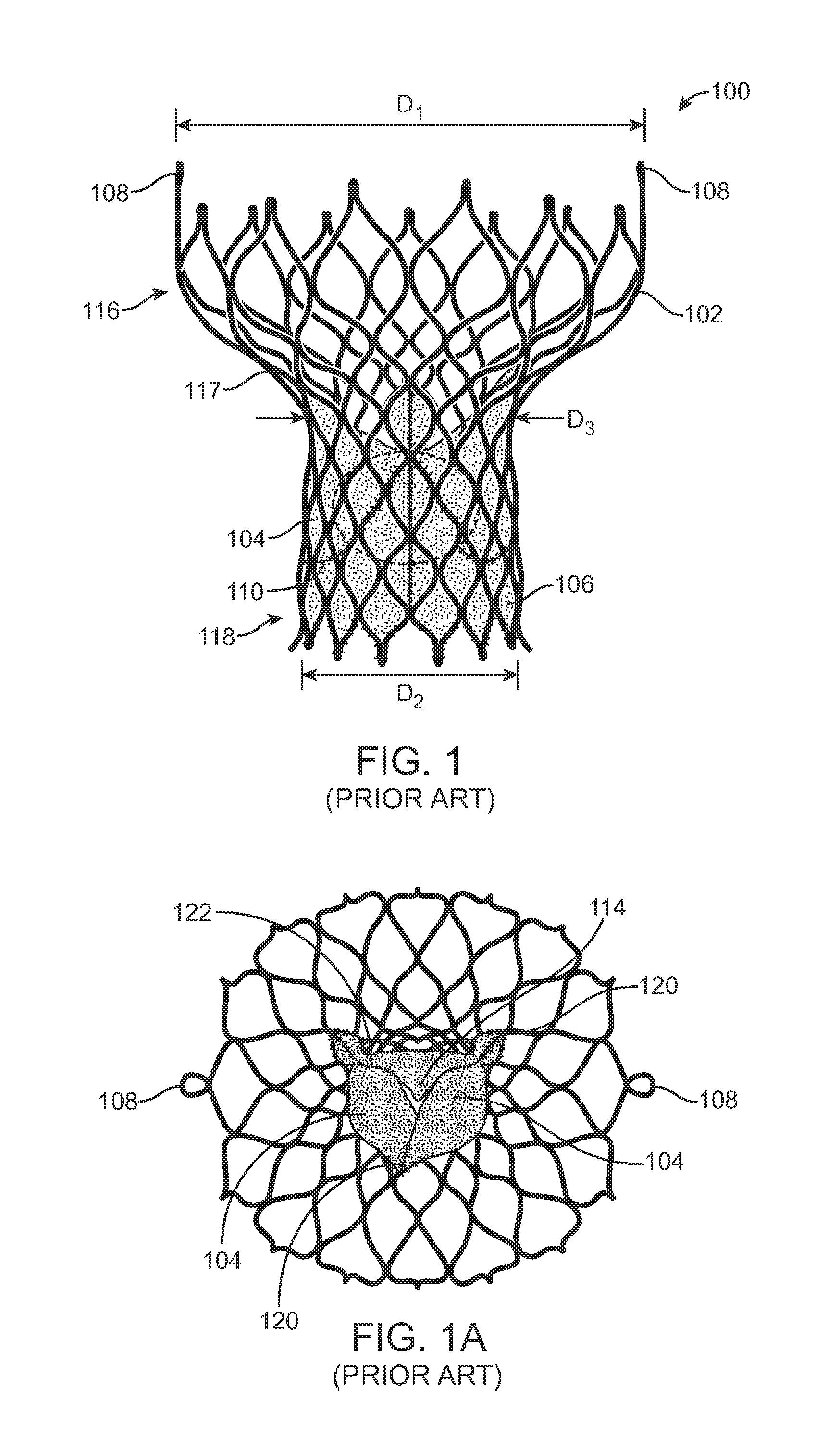
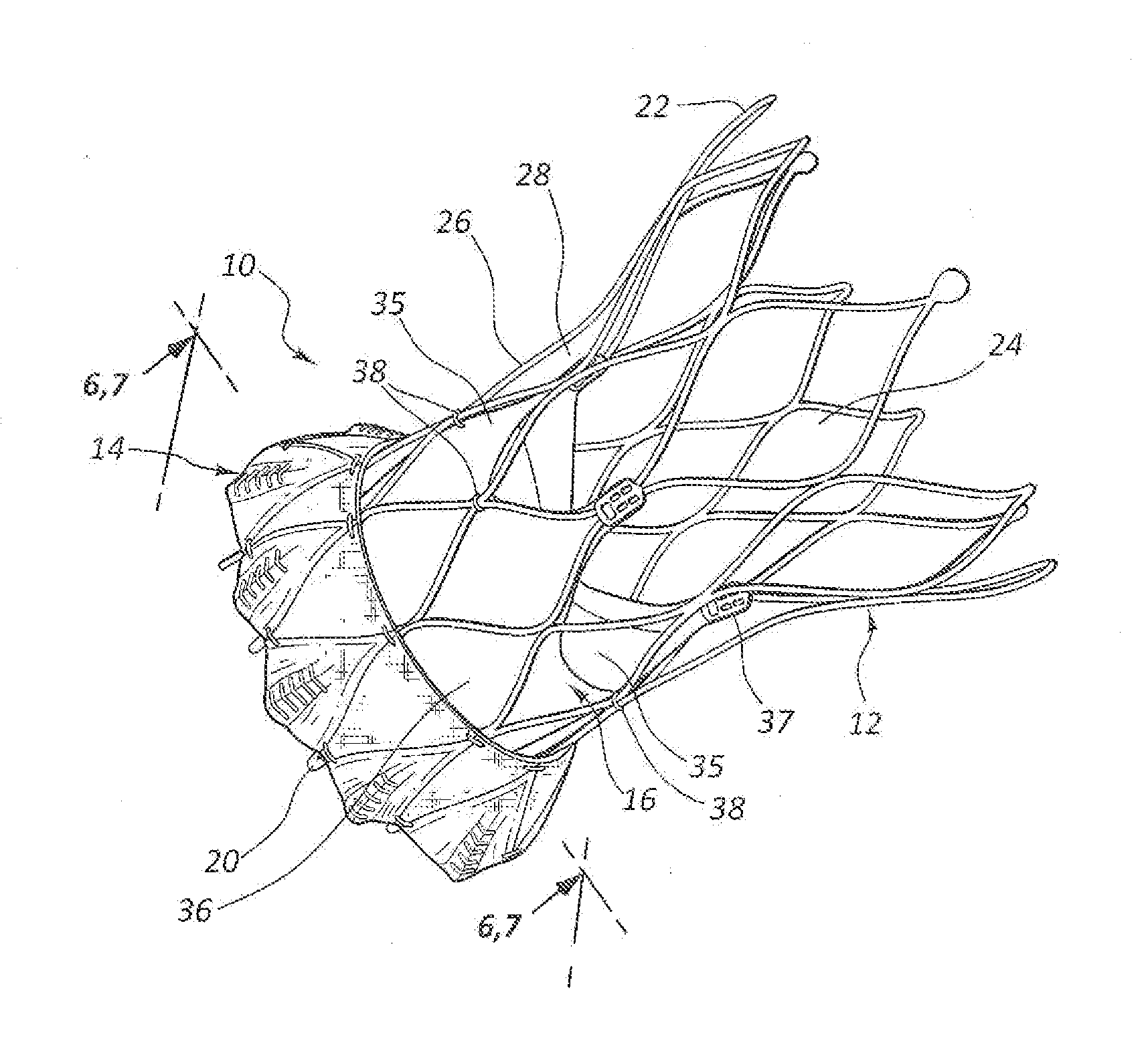
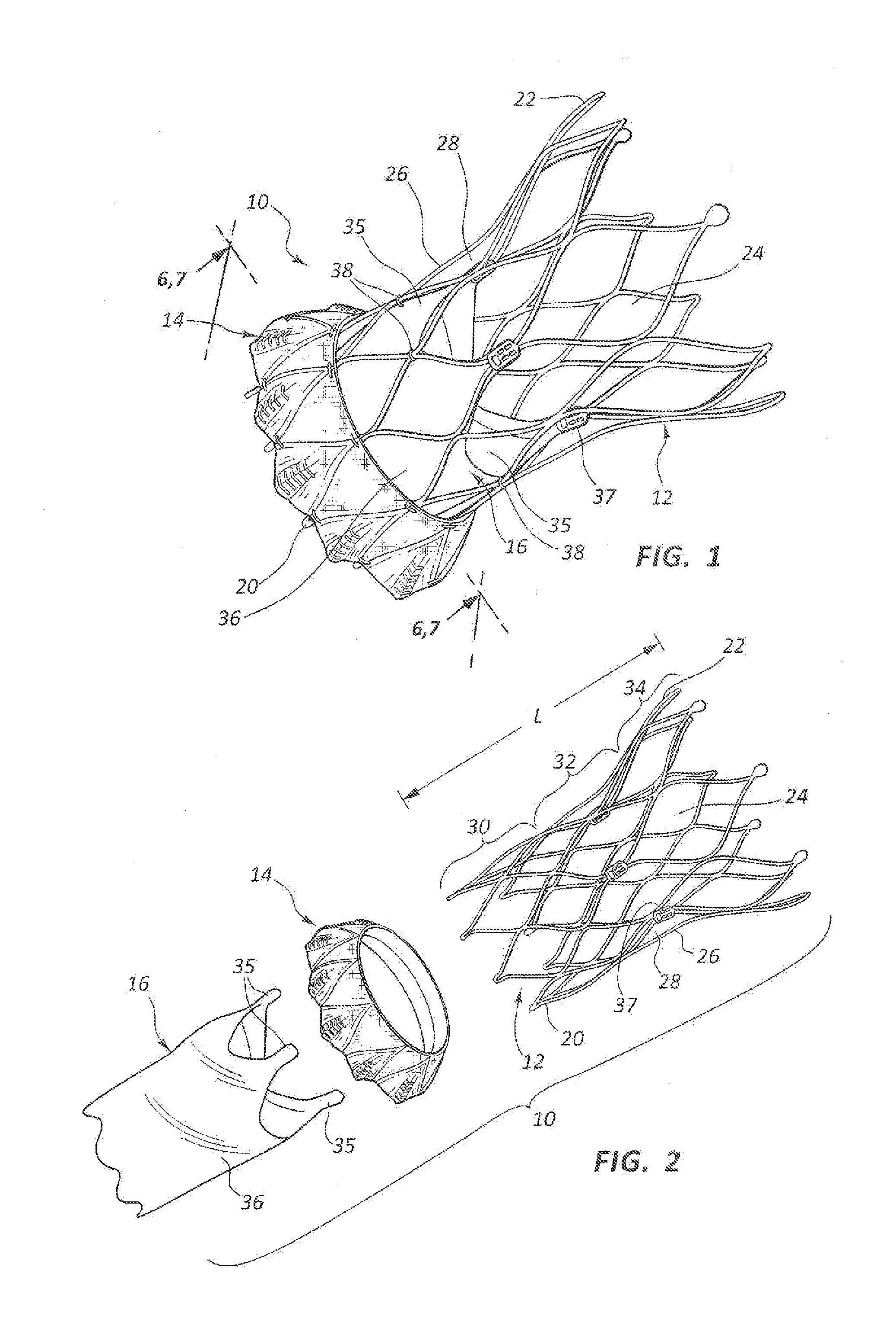
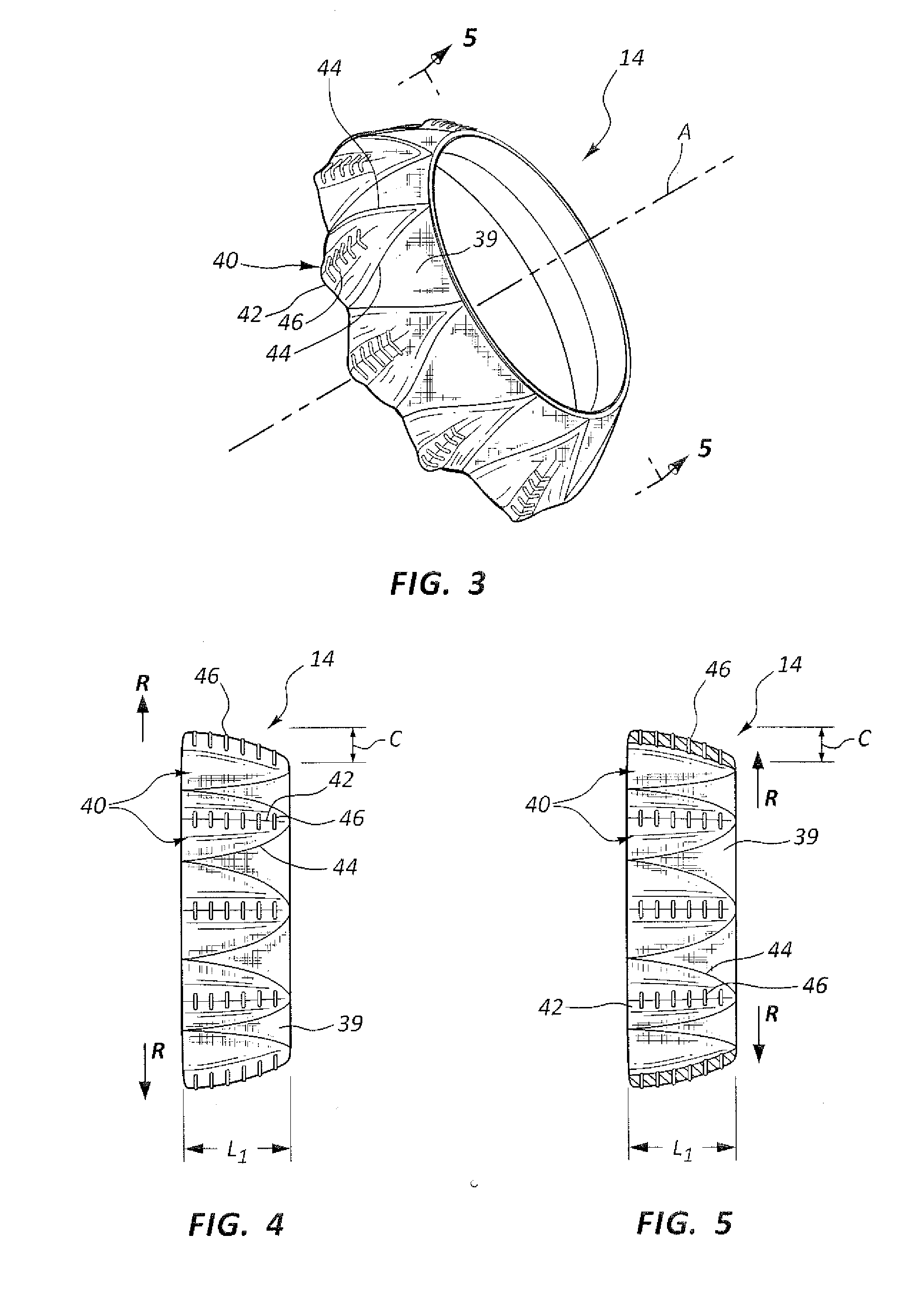
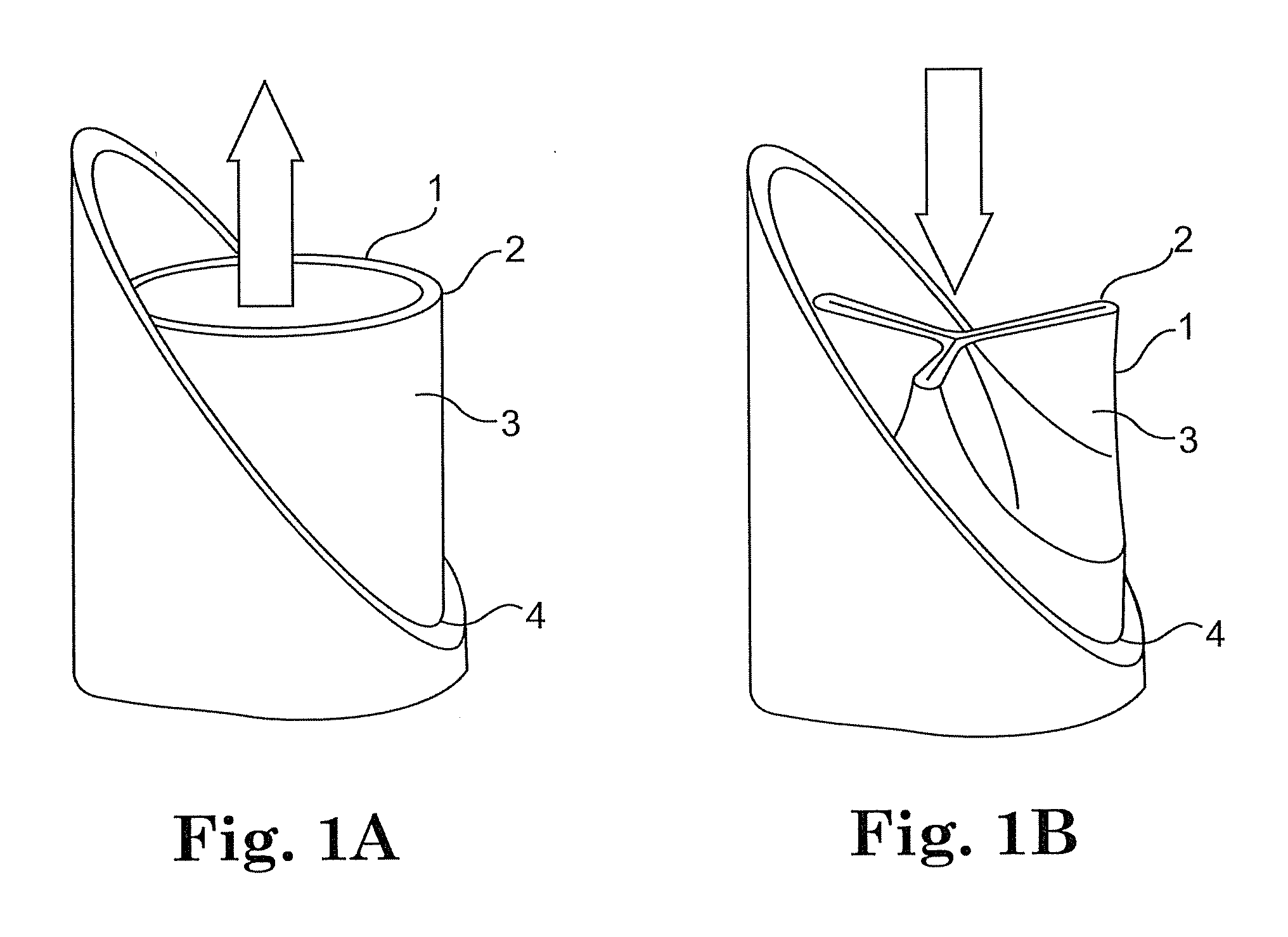
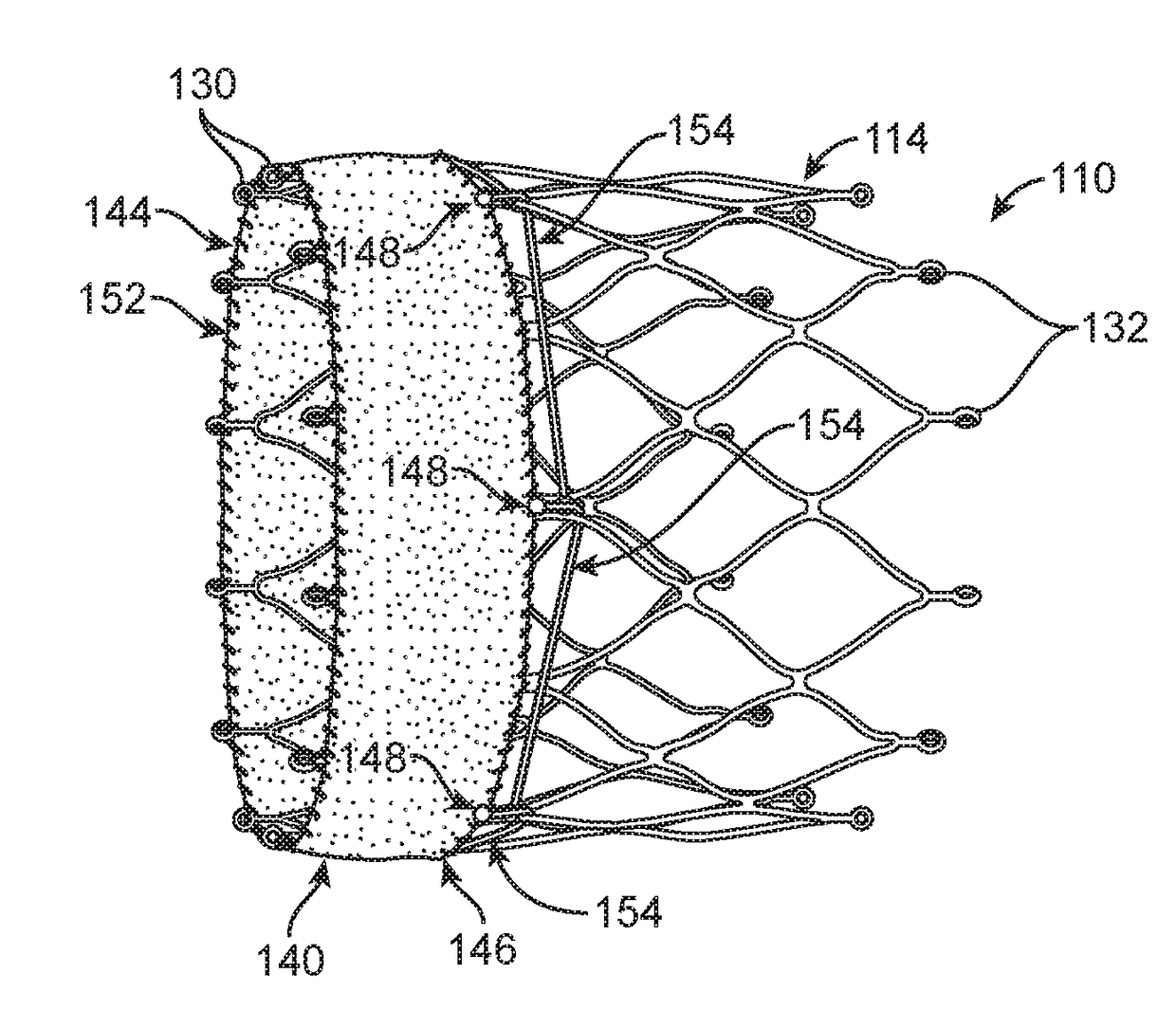
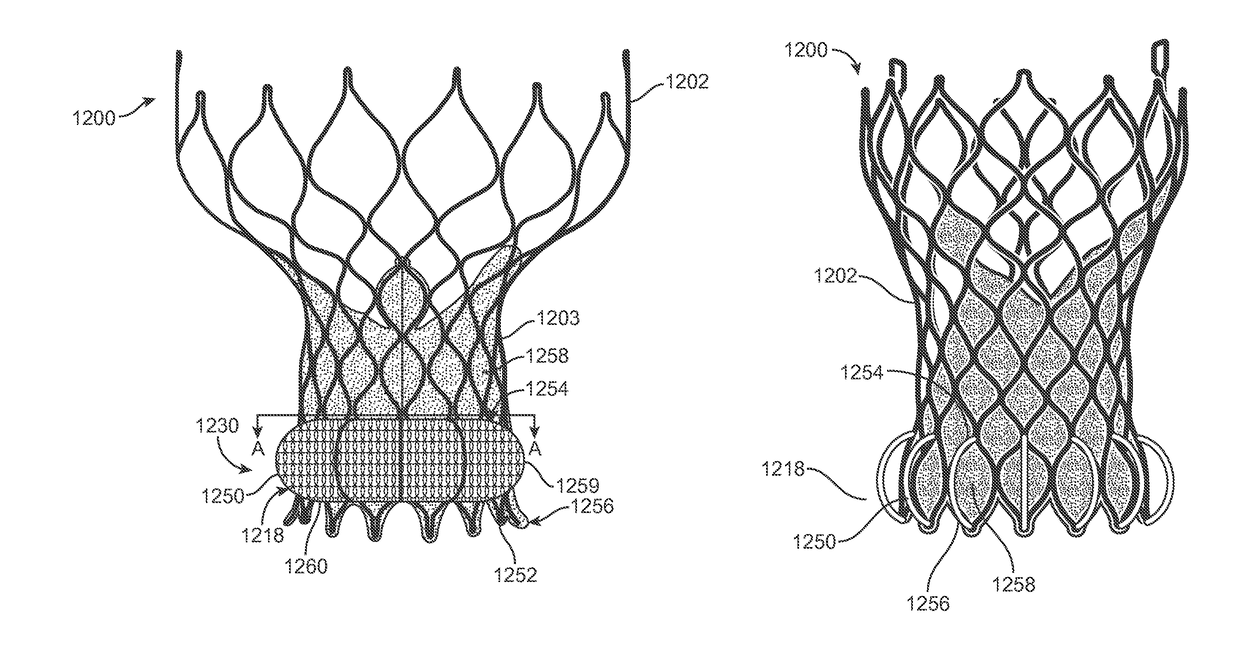
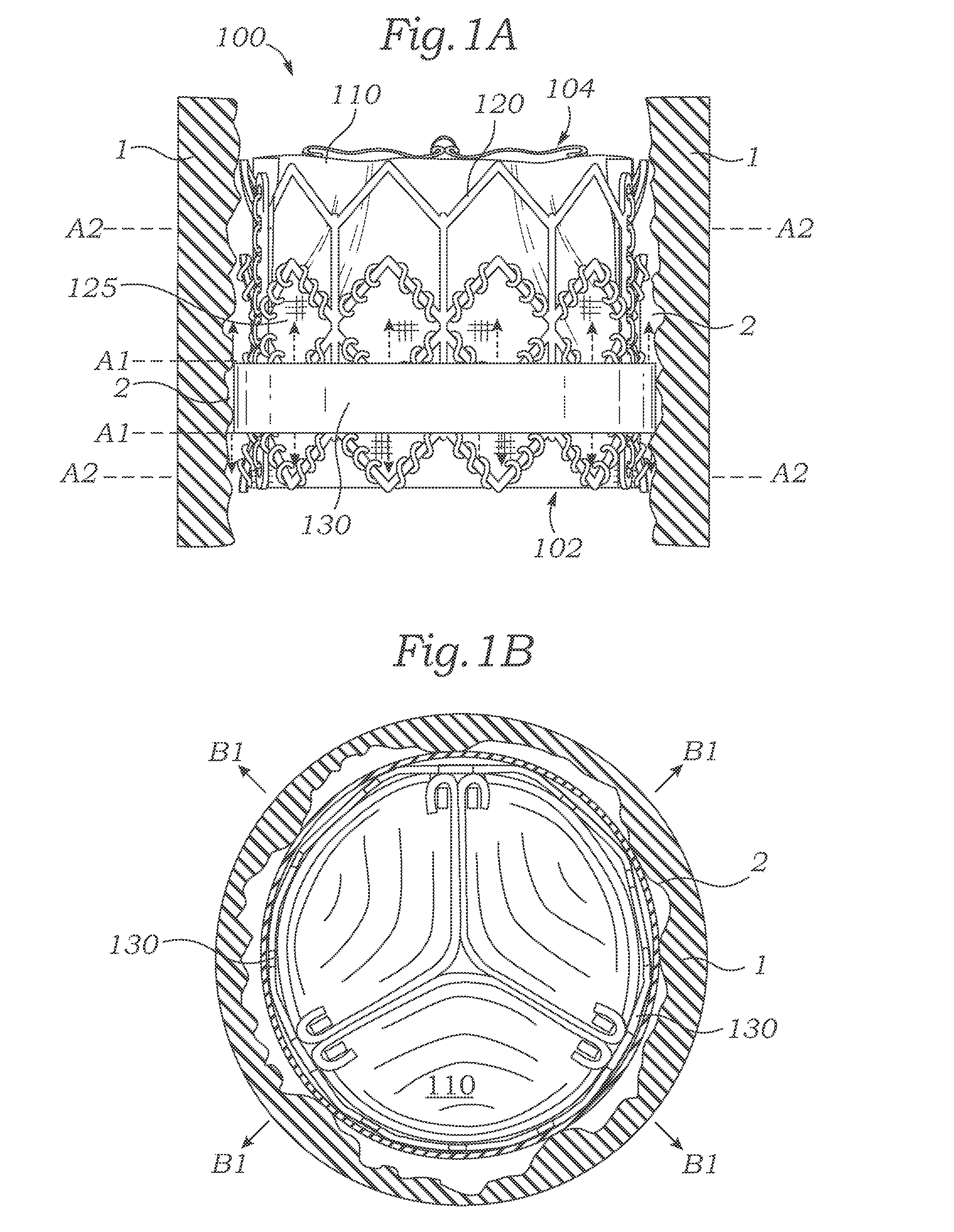
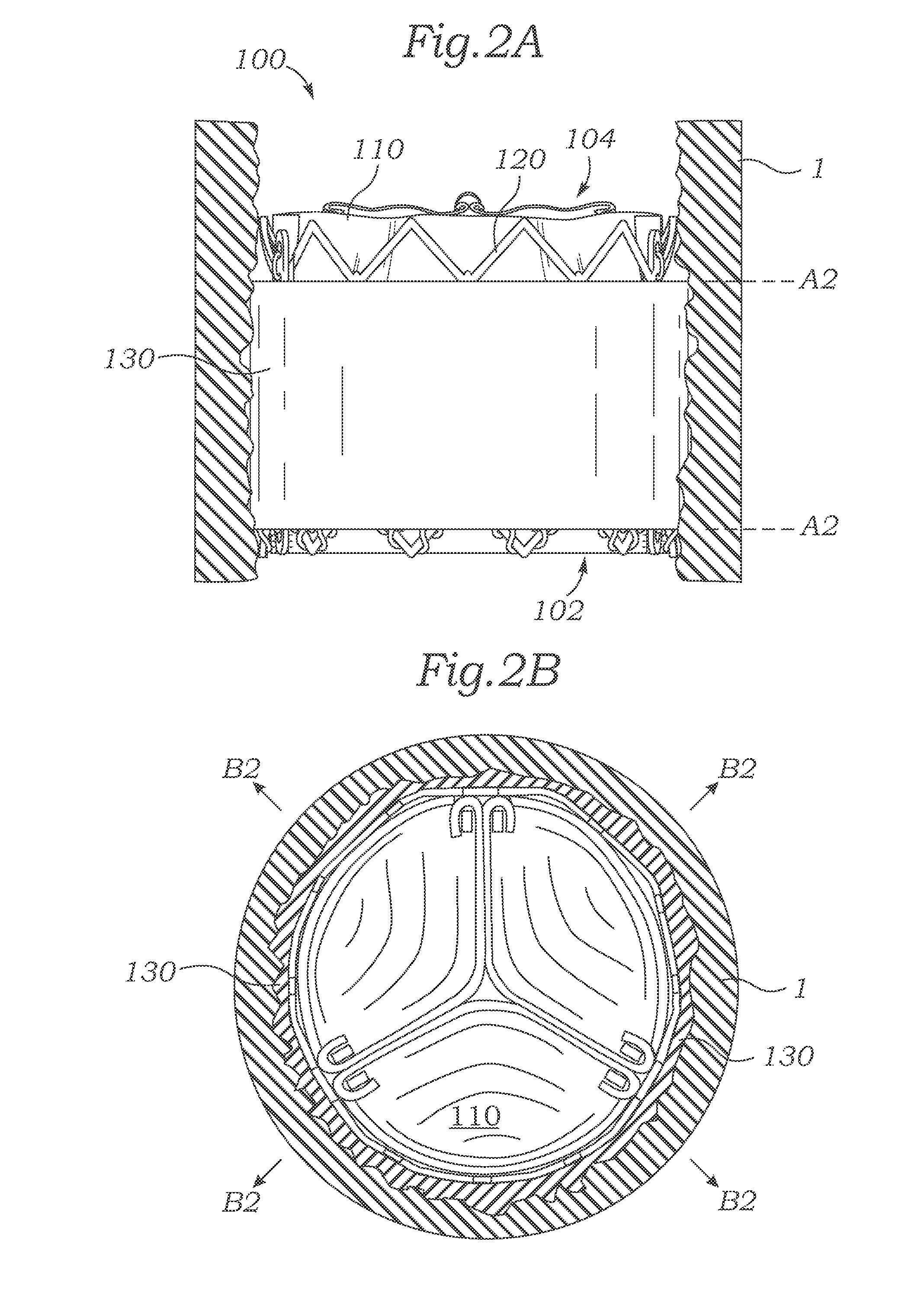
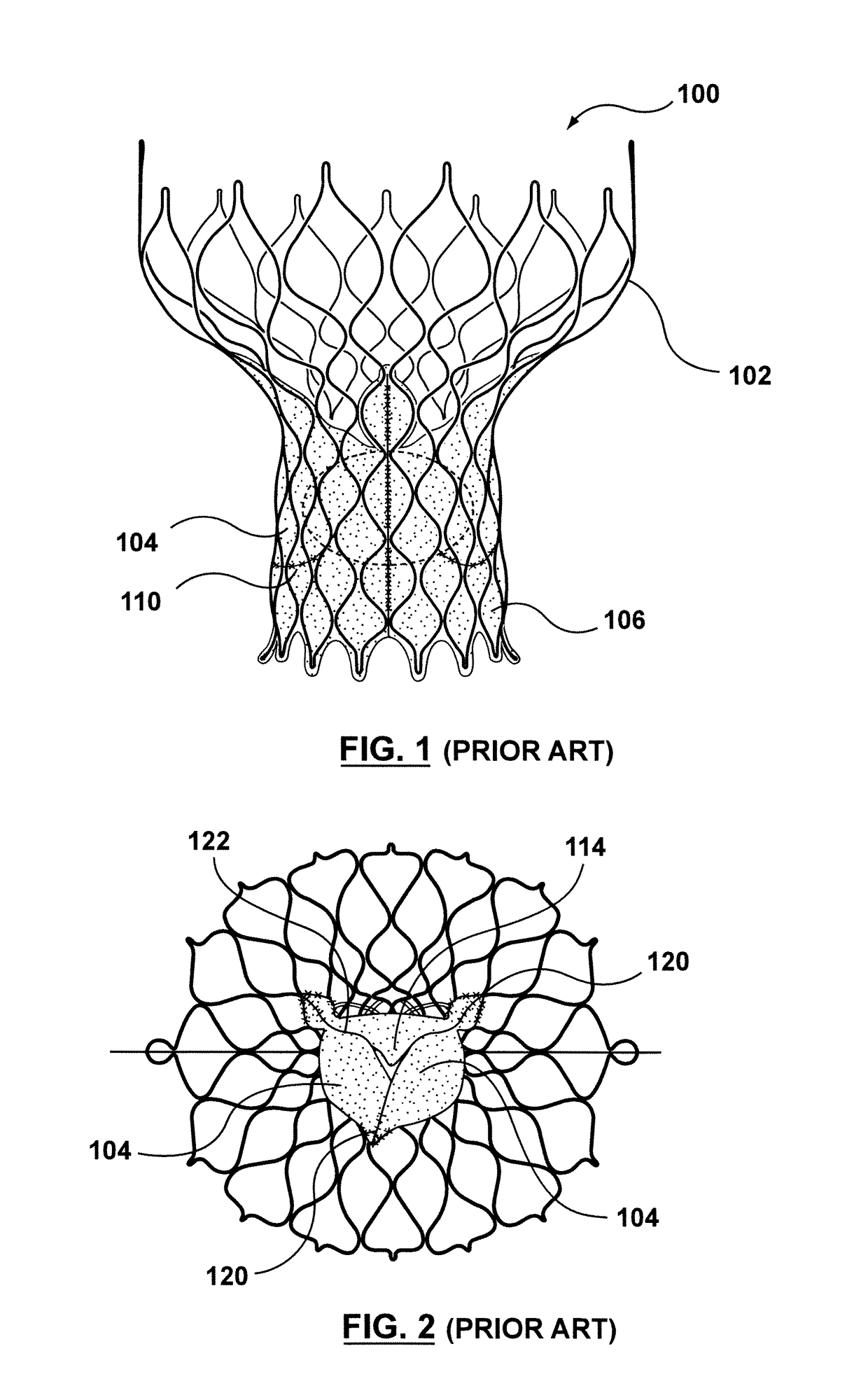
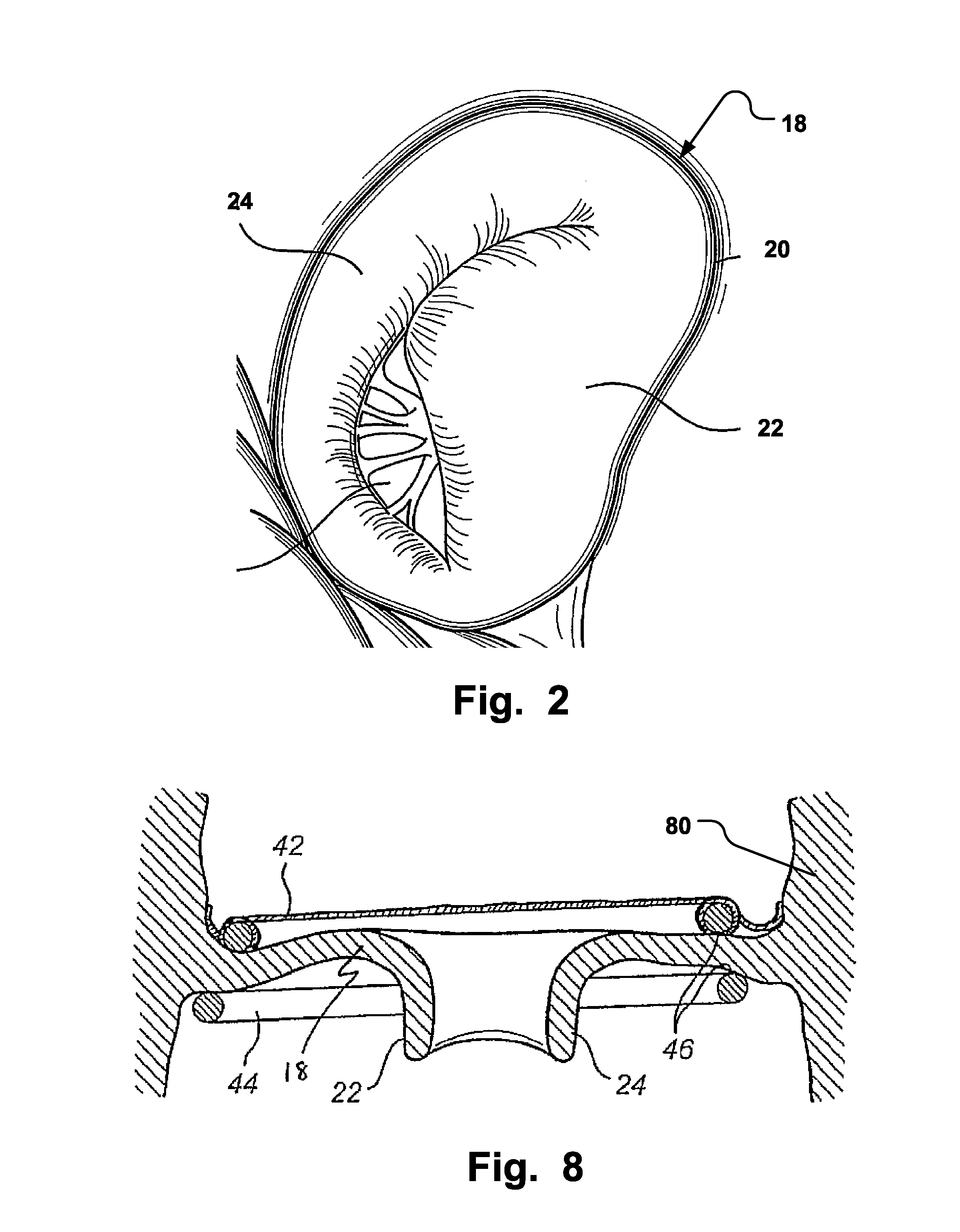
A valve prosthesis includes one or more anti-paravalvular leakage components coupled to a stent. The anti-paravalvular leakage component may encircle the stent and include a radially expandable control ring coupled to an unattached edge of a flexible skirt which extends the unattached skirt edge outwardly away from the stent and against the native heart valve to form an open-ended annular pocket around the stent. The anti-paravalvular leakage component may encircle the perimeter of the stent and include a flexible skirt having opposing edges coupled to the stent to form one or more enclosed compartments around the stent. Each compartment includes a one-way valve which allows for blood flow into the compartment but prevents blood flow out of the compartment. The anti-paravalvular leakage component may be at least one flap that is coupled to an inner surface of the stent and formed of a flexible material moveable by blood flow.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
Methods and systems for reducing paravalvular leakage in heart valves
InactiveUS20100168844A1Reducing paravalvular leakageIncrease opportunitiesHeart valvesParavalvular leakageCuff
A replacement valve comprises a valve body having an inflow end, an outflow end, and a valve support structure, and a valve cuff surrounding the inflow end of the valve body. The valve support structure surrounds the valve body, and the valve cuff is coupled to the valve support structure. The valve cuff includes a skirt portion and at least one flange coupled to and protruding from the skirt portion, the at least one flange forming a seal around the inflow end of the valve body.
Owner:MEDTRONIC 3F THERAPEUTICS
Method for implanting prosthetic valve
Owner:TRUELEAF MEDICAL LTD
Anti-Paravalvular Leakage Component for a Transcatheter Valve Prosthesis
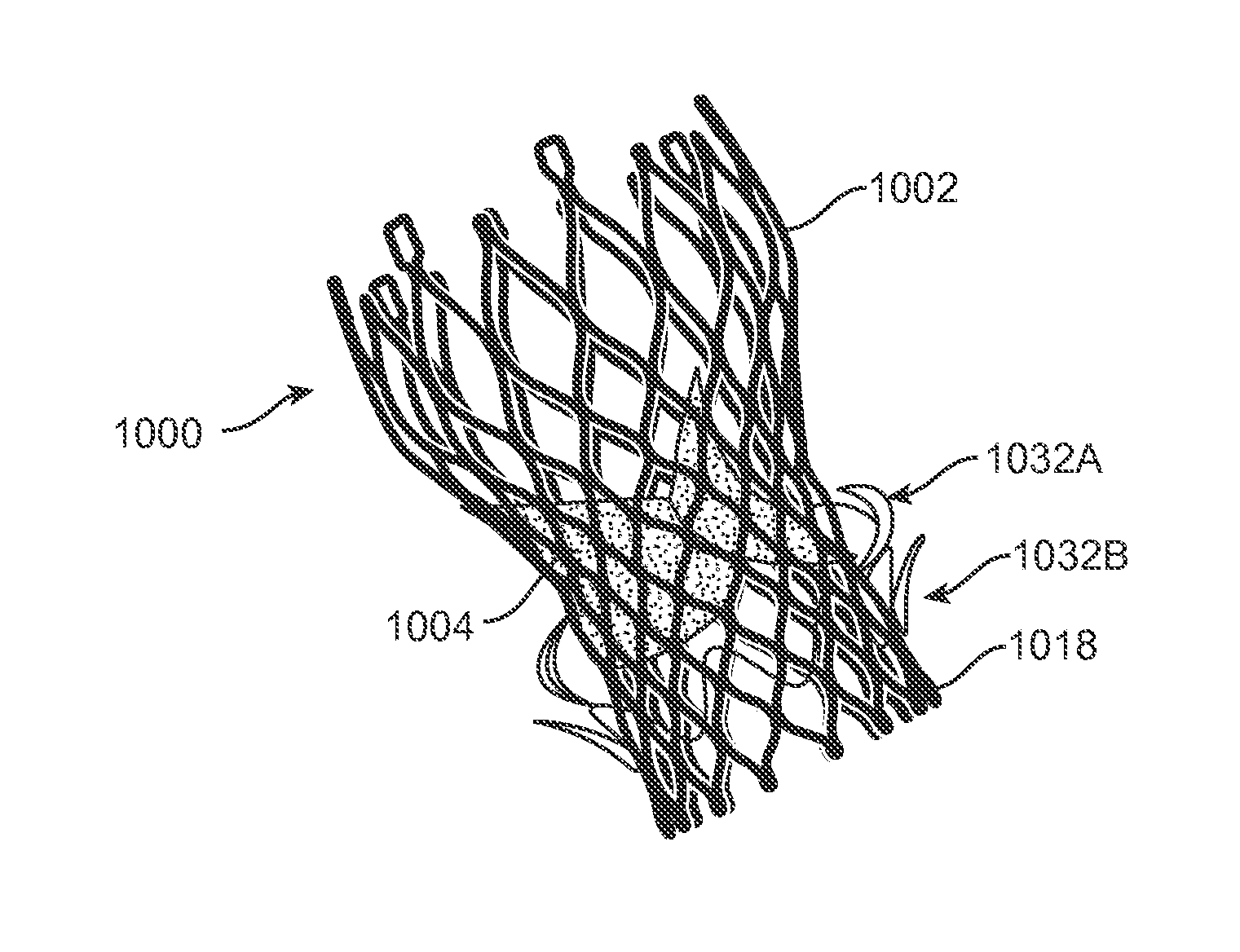
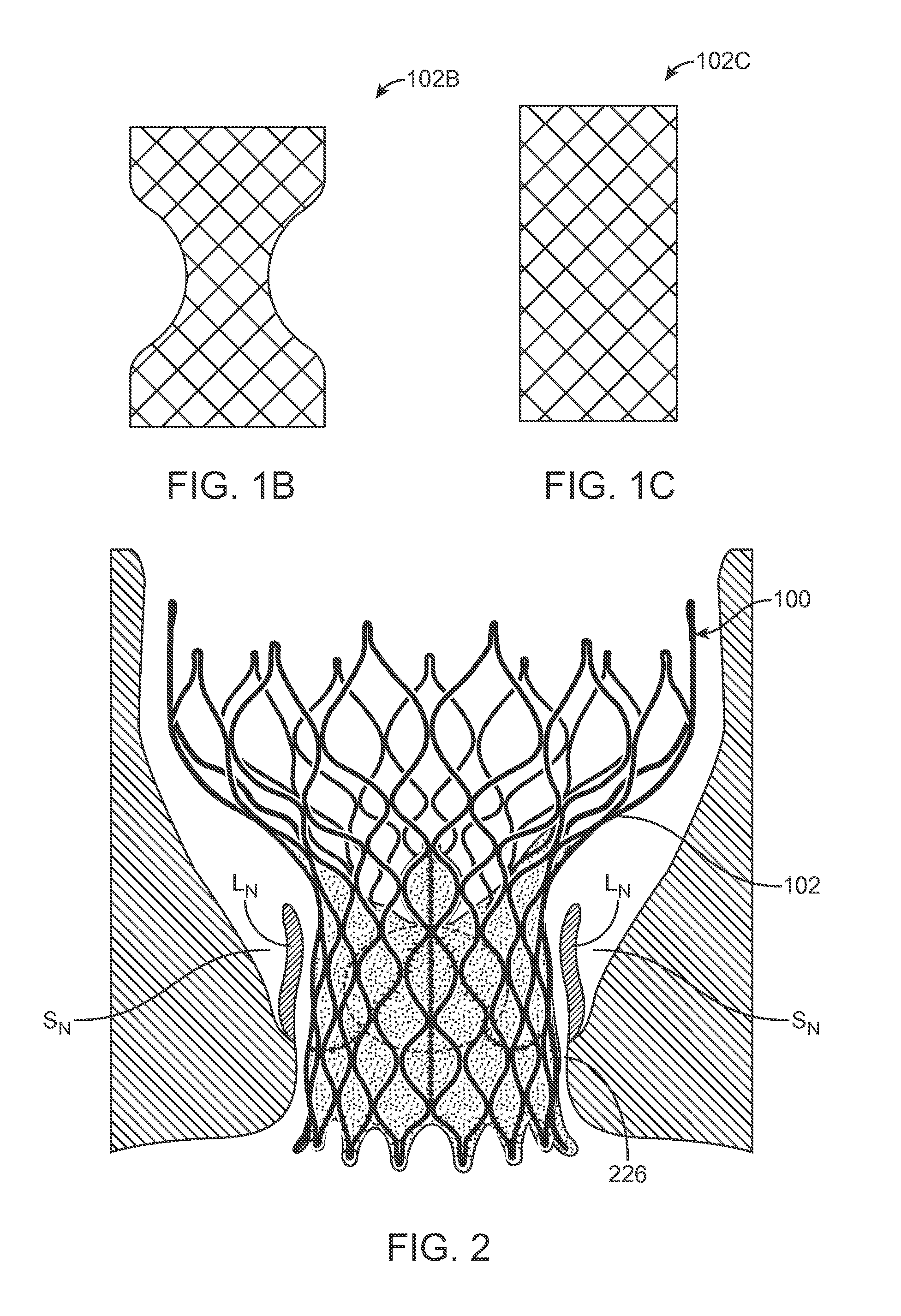
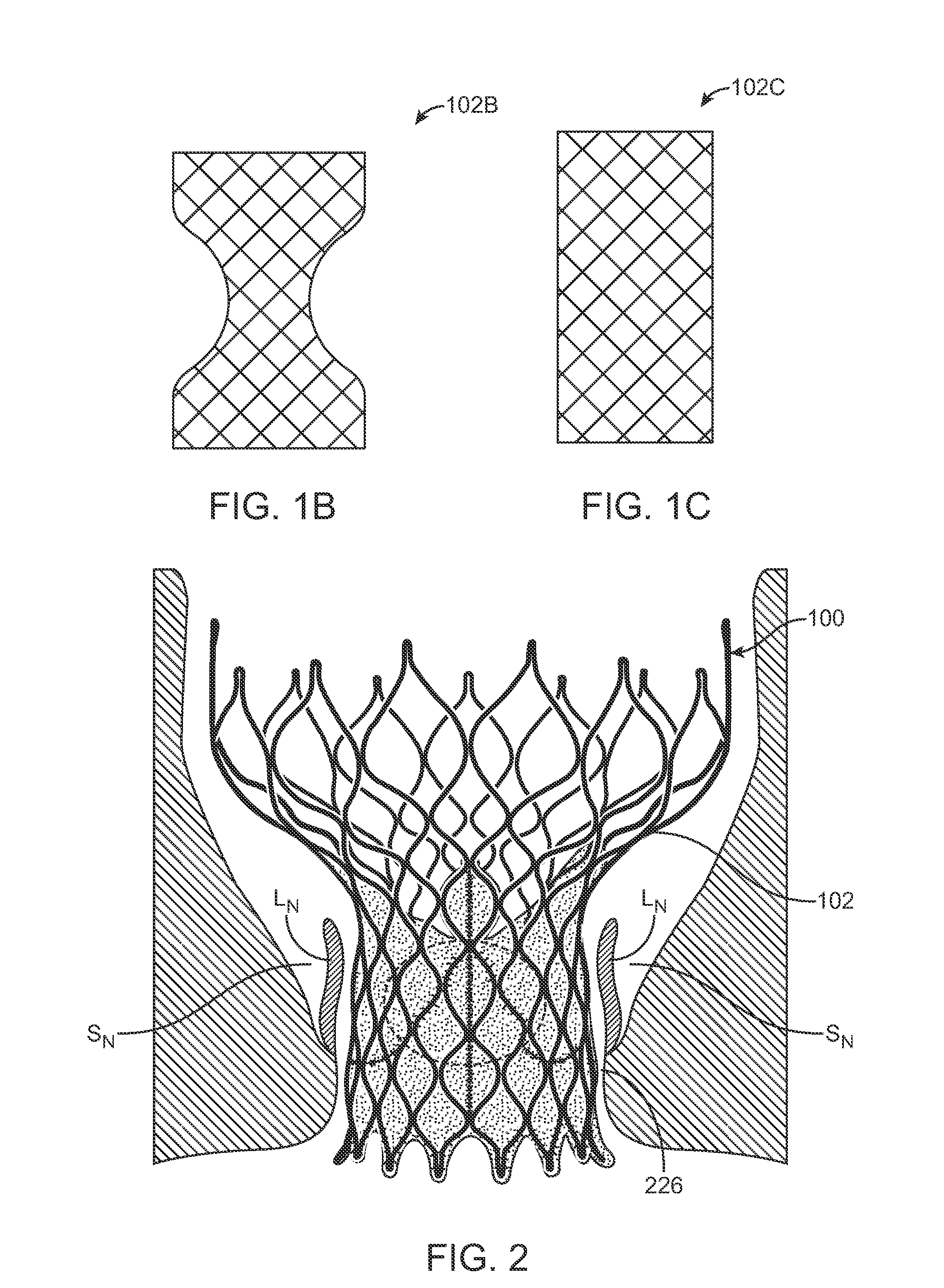
A transcatheter valve prosthesis includes an expandable tubular stent, a prosthetic valve within the stent, and an anti-paravalvular leakage component coupled to and encircling the stent which includes a plurality of self-expanding struts and an annular sealing membrane. Each strut has a first end coupled to a distal end of the stent and a second end not coupled to the stent. Each anti-paravalvular leakage component is moveable between a compressed configuration and a deployed configuration. In the compressed configuration, each strut extends distally away from the distal end of the stent. In the deployed configuration, each strut extends proximally away from the distal end of the stent. In an embodiment hereof, the deployed strut has a C-shape and is twisted such that the C-shape lies in a plane substantially along or tangential with the outer surface of the stent. In another embodiment hereof, the deployed strut is rolled-up and extends radially away from the outer surface of the stent.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Anti-paravalvular leakage component for a transcatheter valve prosthesis
A transcatheter valve prosthesis includes an expandable tubular stent, a prosthetic valve within the stent, and an anti-paravalvular leakage component coupled to and encircling the stent which includes a plurality of self-expanding struts and an annular sealing membrane. Each strut has a first end coupled to a distal end of the stent and a second end not coupled to the stent. Each anti-paravalvular leakage component is moveable between a compressed configuration and a deployed configuration. In the compressed configuration, each strut extends distally away from the distal end of the stent. In the deployed configuration, each strut extends proximally away from the distal end of the stent. In an embodiment hereof, the deployed strut has a C-shape and is twisted such that the C-shape lies in a plane substantially along or tangential with the outer surface of the stent. In another embodiment hereof, the deployed strut is rolled-up and extends radially away from the outer surface of the stent.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Anti-Paravalvular Leakage Component for a Transcatheter Valve Prosthesis
A transcatheter valve prosthesis includes an expandable tubular stent, a prosthetic valve within the stent, and an anti-paravalvular leakage component coupled to and encircling the tubular stent. The anti-paravalvular leakage component includes a radially-compressible annular scaffold, which is a sinusoidal patterned ring of self-expanding material, and an impermeable membrane extending over the annular scaffold. The anti-paravalvular leakage component has an expanded configuration in which at least segments of the annular scaffold curve radially away from the tubular stent. Alternatively, the anti-paravalvular leakage component includes a plurality of self-expanding segments and an annular sealing element coupled to inner surfaces of the segments. The anti-paravalvular leakage component has an expanded configuration in which the segments curve radially away from the tubular stent and the annular sealing element is positioned between an outer surface of the tubular stent and inner surfaces of the segments. The segments may be orthogonal or oblique to the outer surface of the tubular stent.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
Transcatheter Valve Prosthesis and a Concurrently Delivered Sealing Component
ActiveUS20140236287A1Prevent paravalvular leakagePrevent leakageHeart valvesParavalvular leakageCatheter
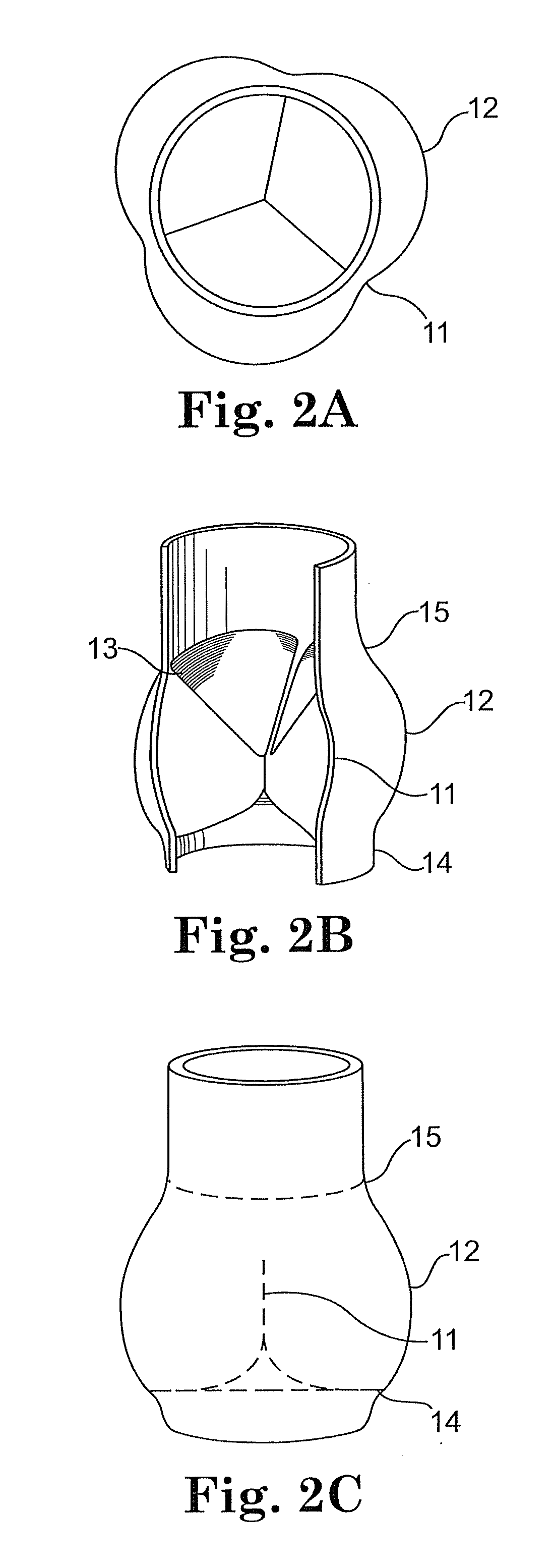
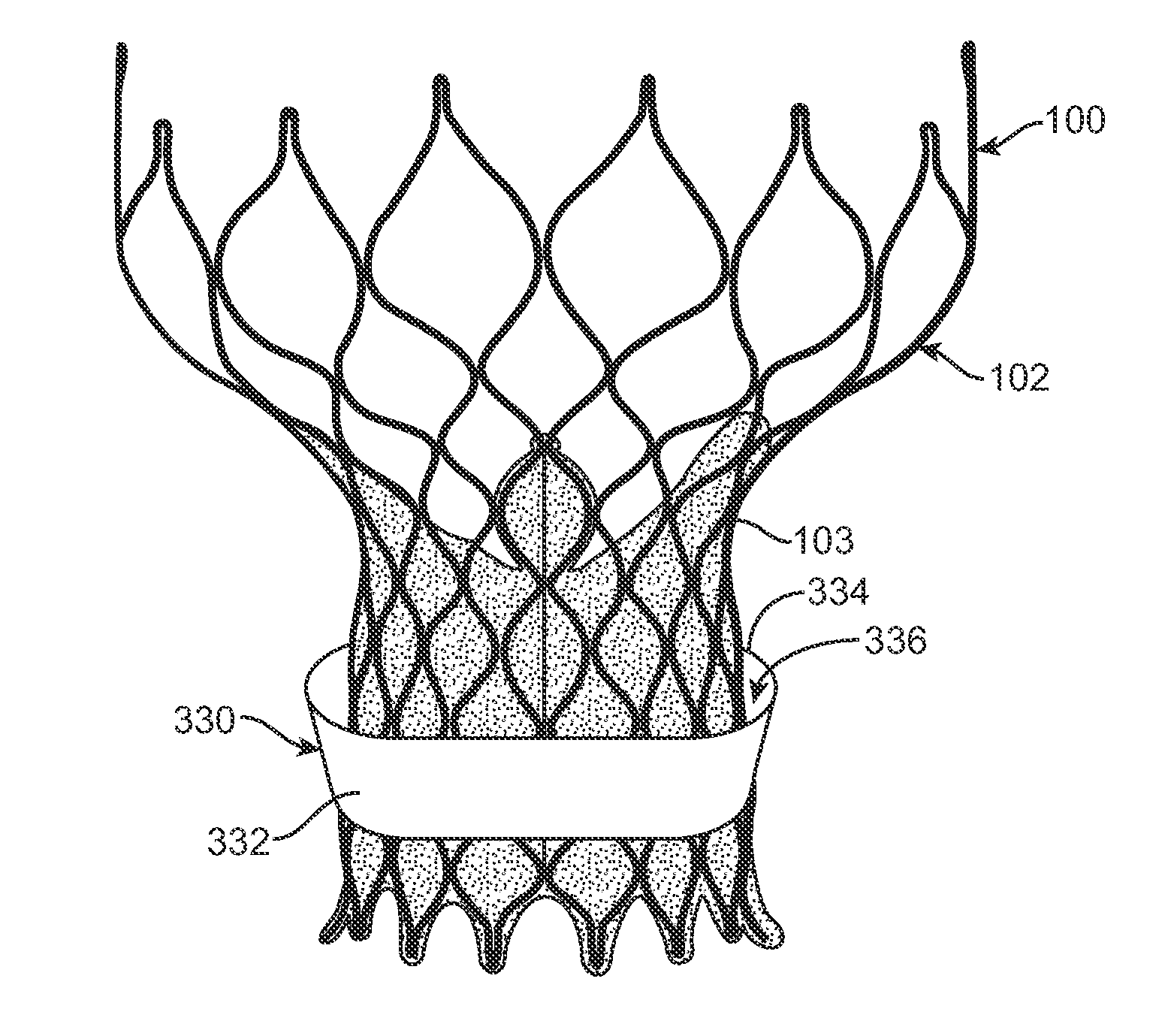
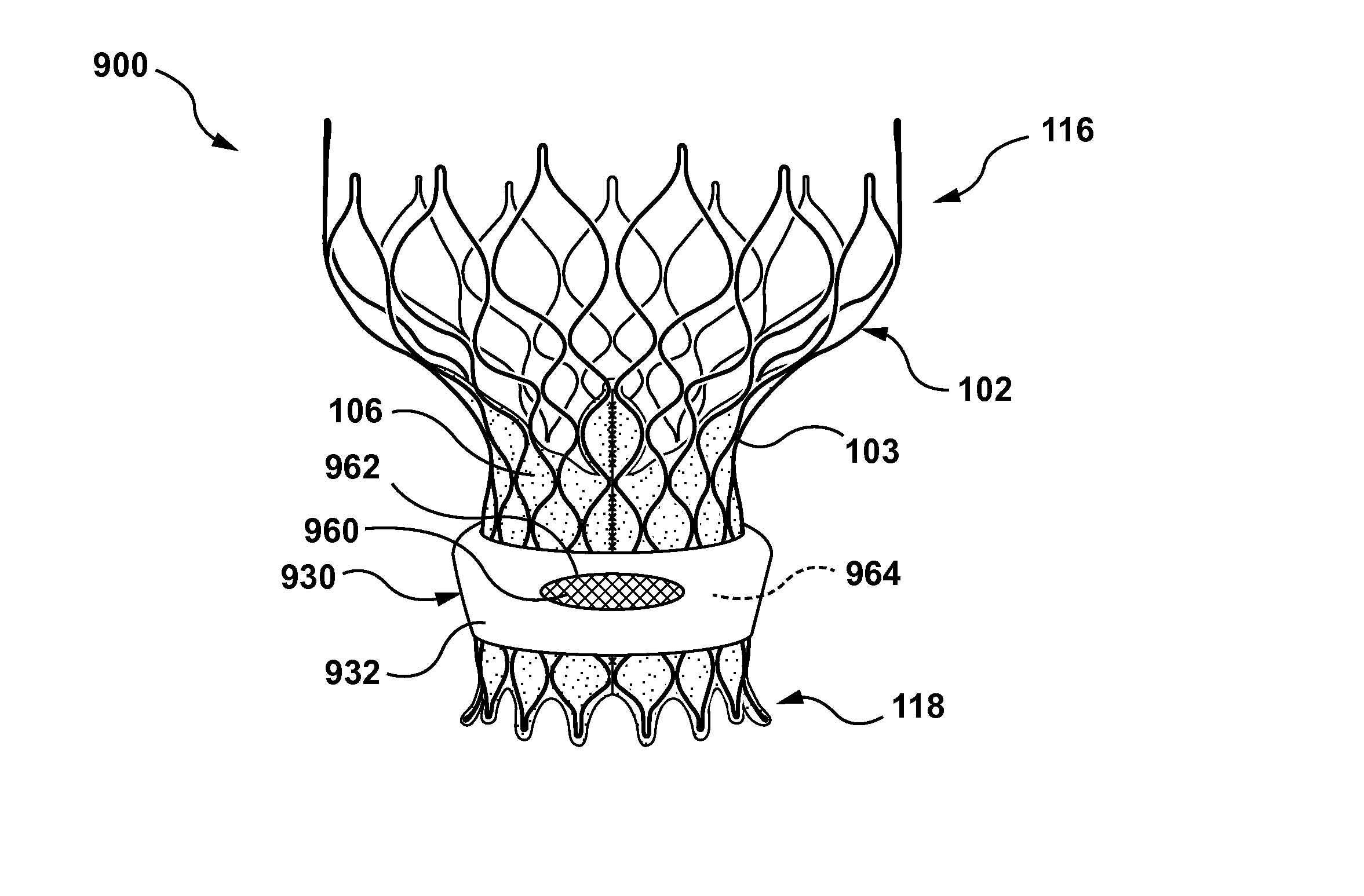
A method of preventing paravalvular leakage includes concurrent delivery of a heart valve prosthesis and an annular sealing component. During delivery, the sealing component is moved from a first position to a second position of the heart valve prosthesis which is longitudinally spaced apart from the first position of the heart valve prosthesis. The sealing component is secured around the heart valve prosthesis at the second position by a contoured outer surface of the heart valve prosthesis. The sealing component may be a flexible ring or may be a cylindrical flexible sleeve having a plurality of ribs longitudinally extending over the cylindrical sleeve. The ribs operate to deploy the sealing component such that at least a portion of the cylindrical sleeve buckles outwardly away from the outer surface of the heart valve prosthesis.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
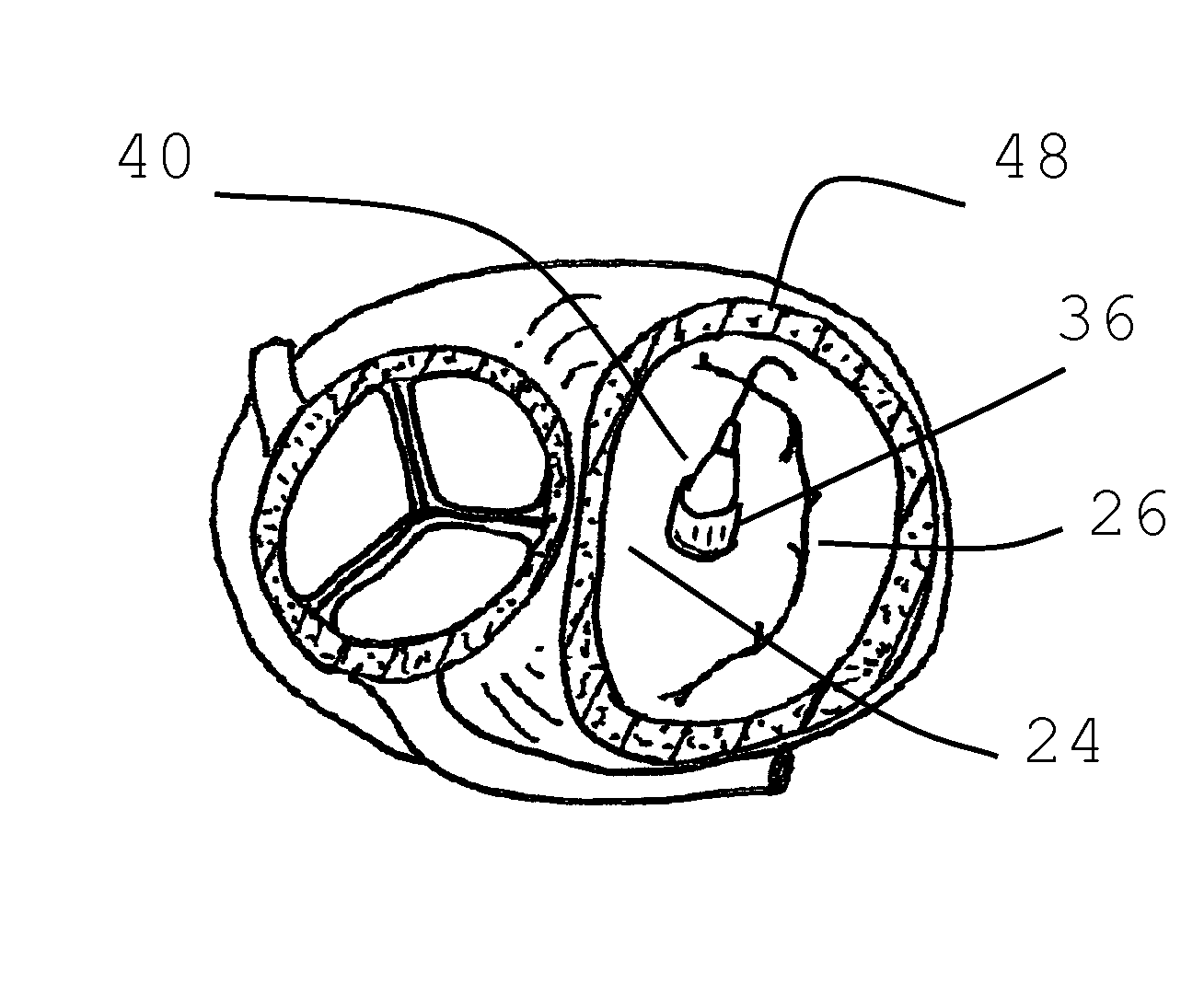
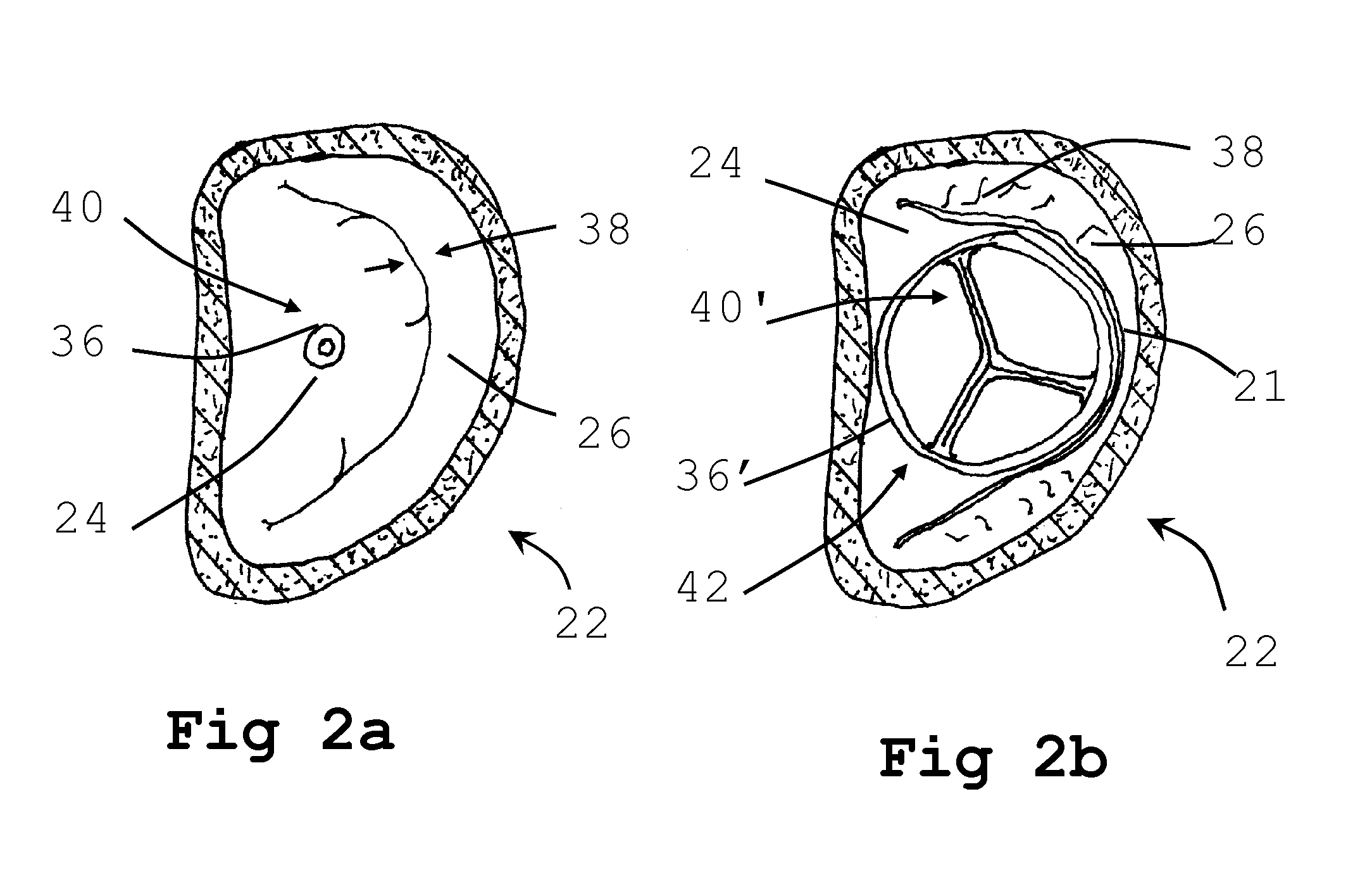
Arrangement, a loop-shaped support, a prosthetic heart valve and a method of repairing or replacing a native heart valve
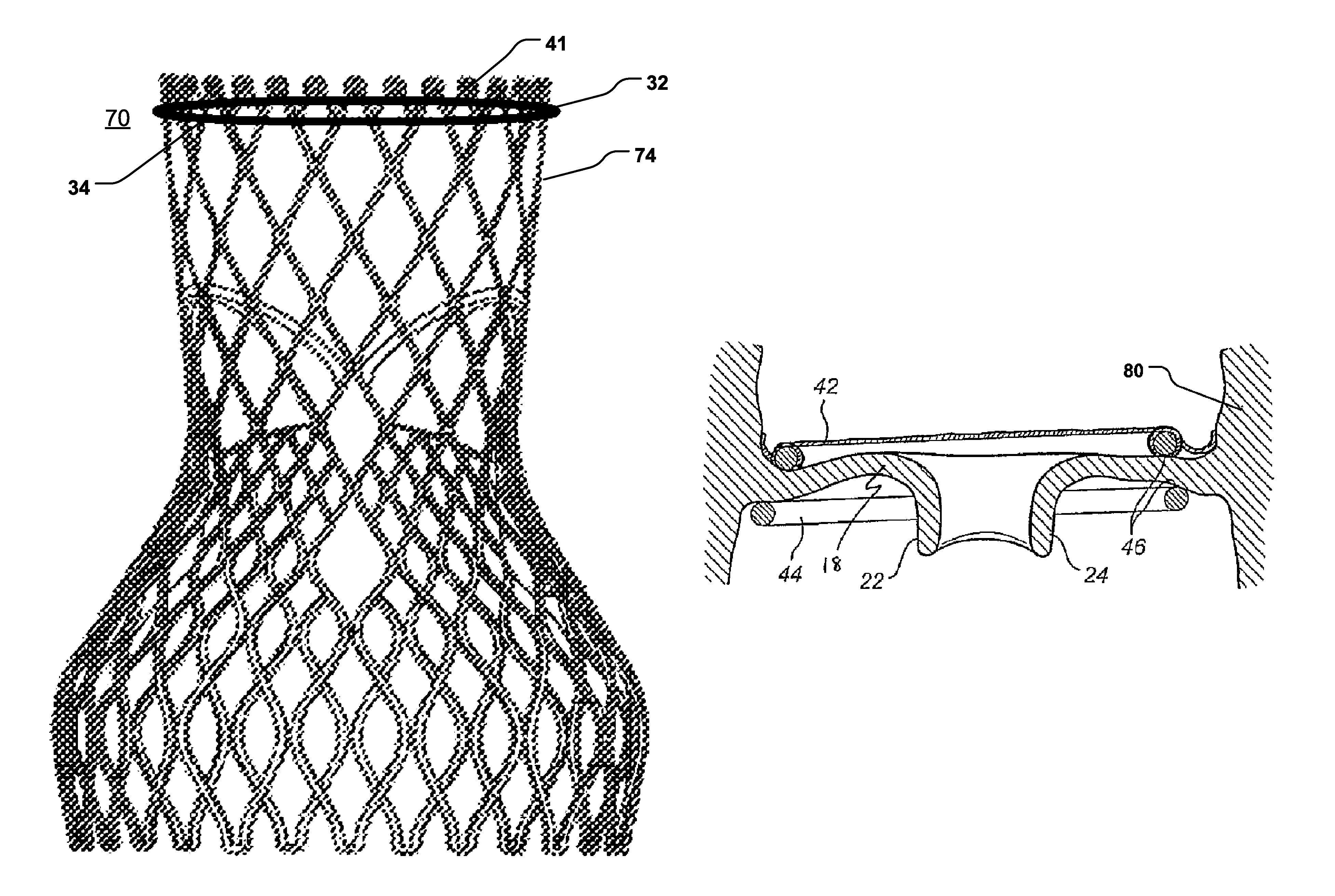
ActiveUS9474599B2Leakage and regurgitationEnabling minimally invasive and percutaneous replacement or repairAnnuloplasty ringsParavalvular leakageProsthesis
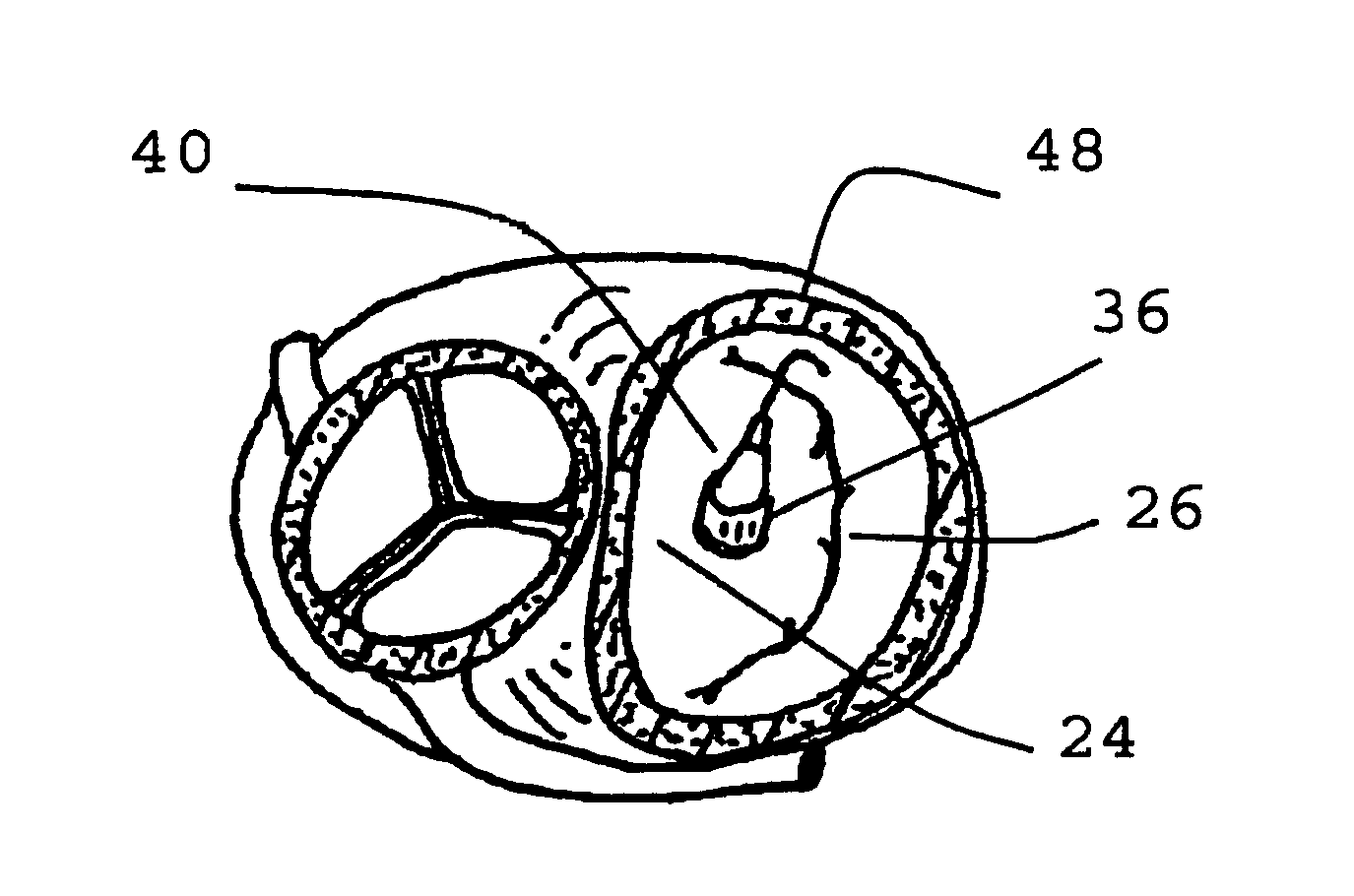
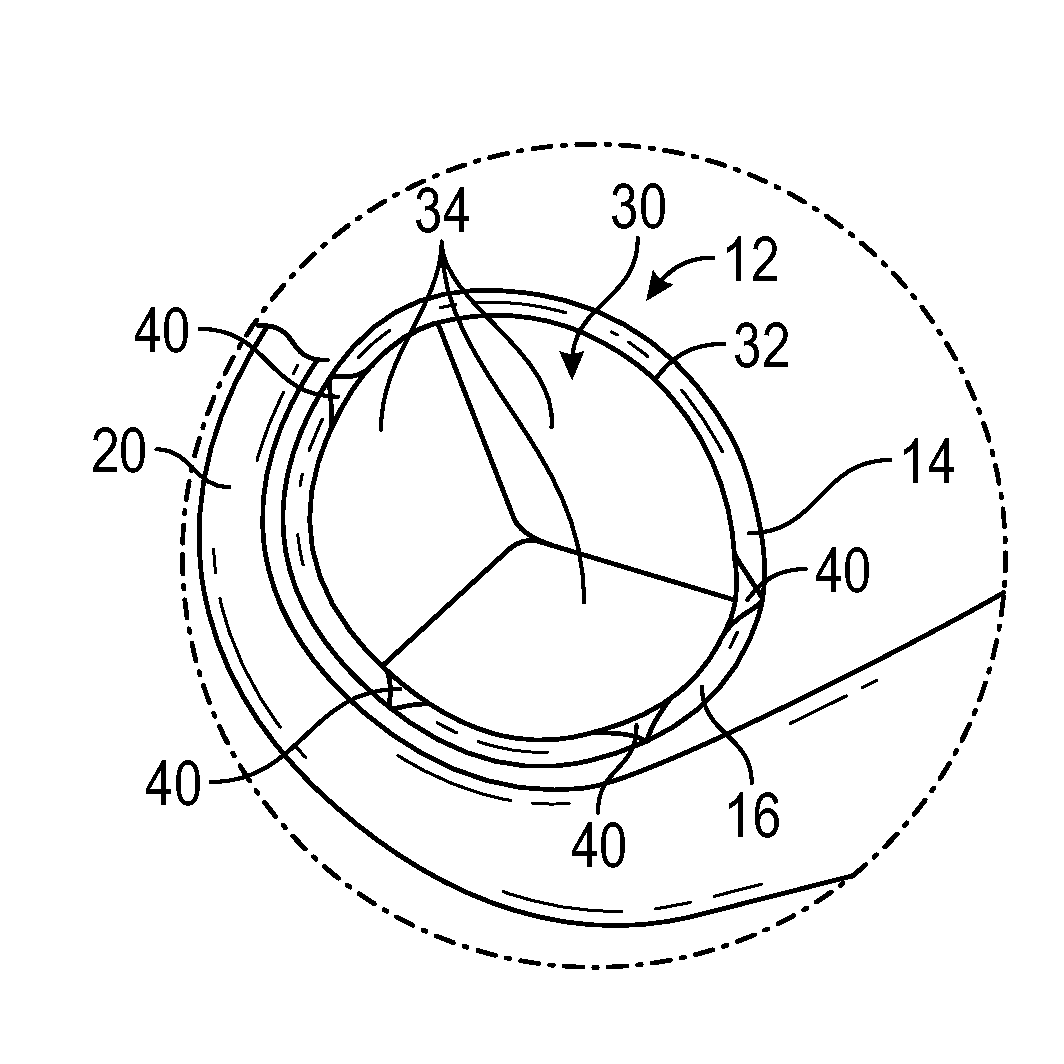
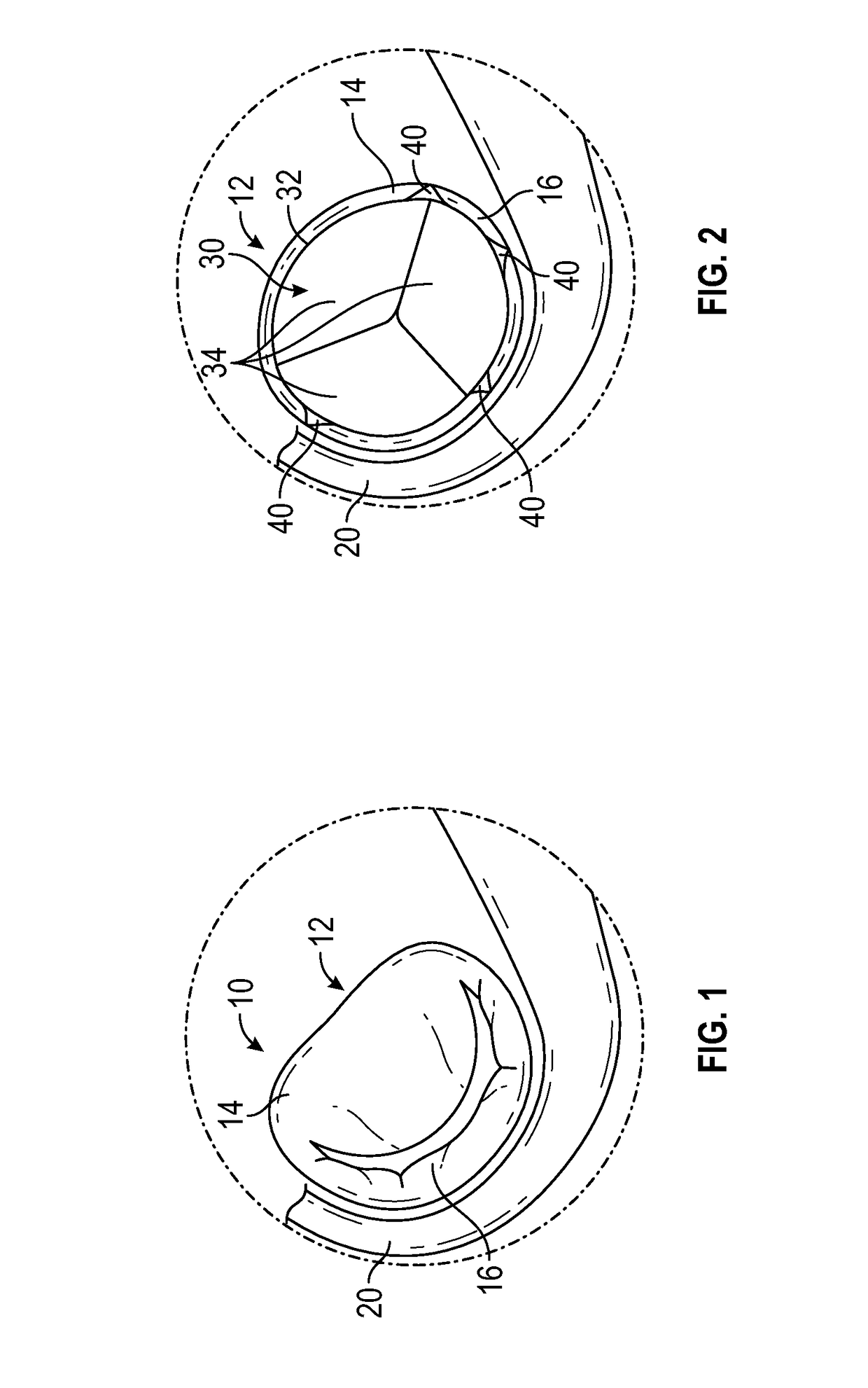
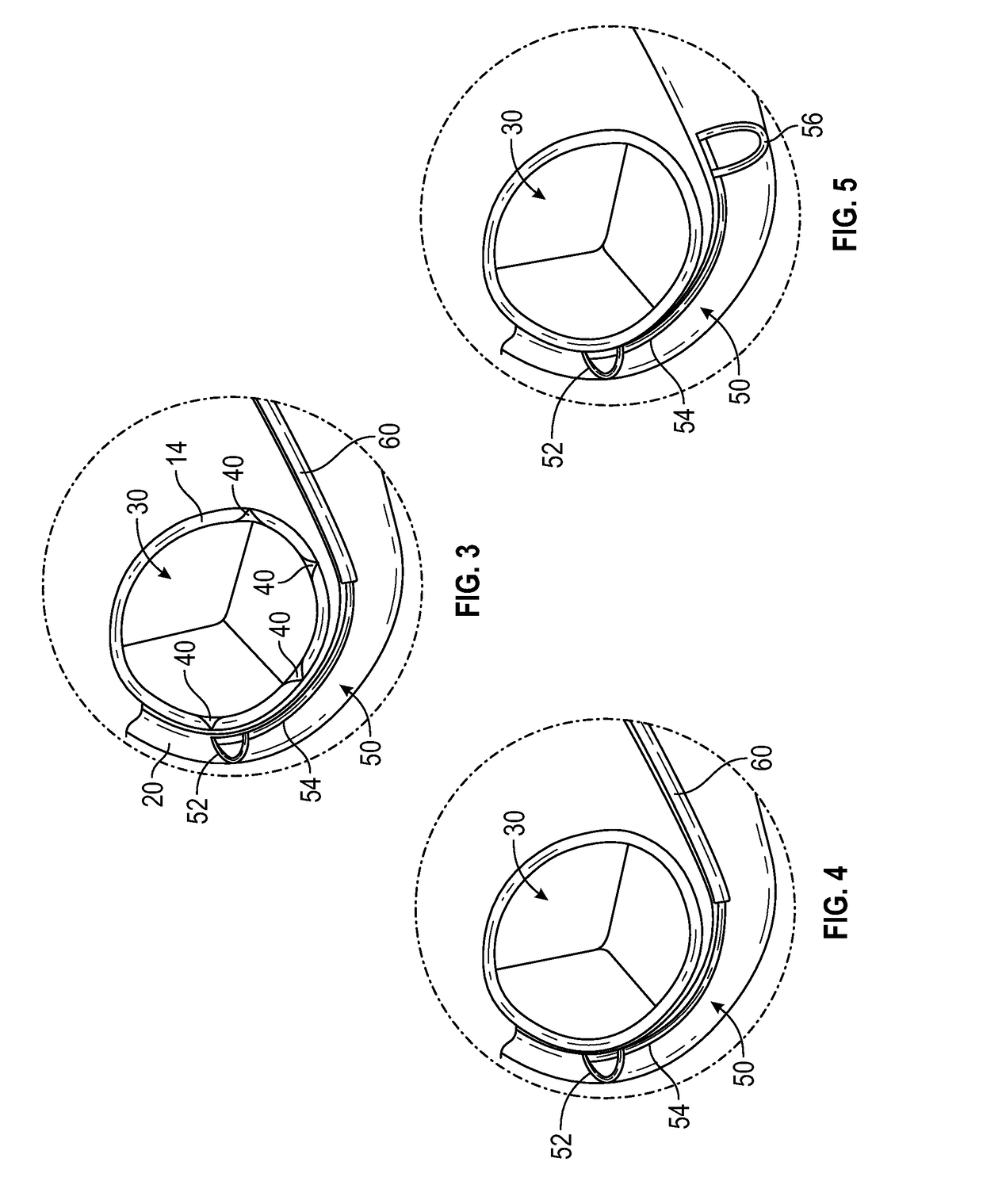
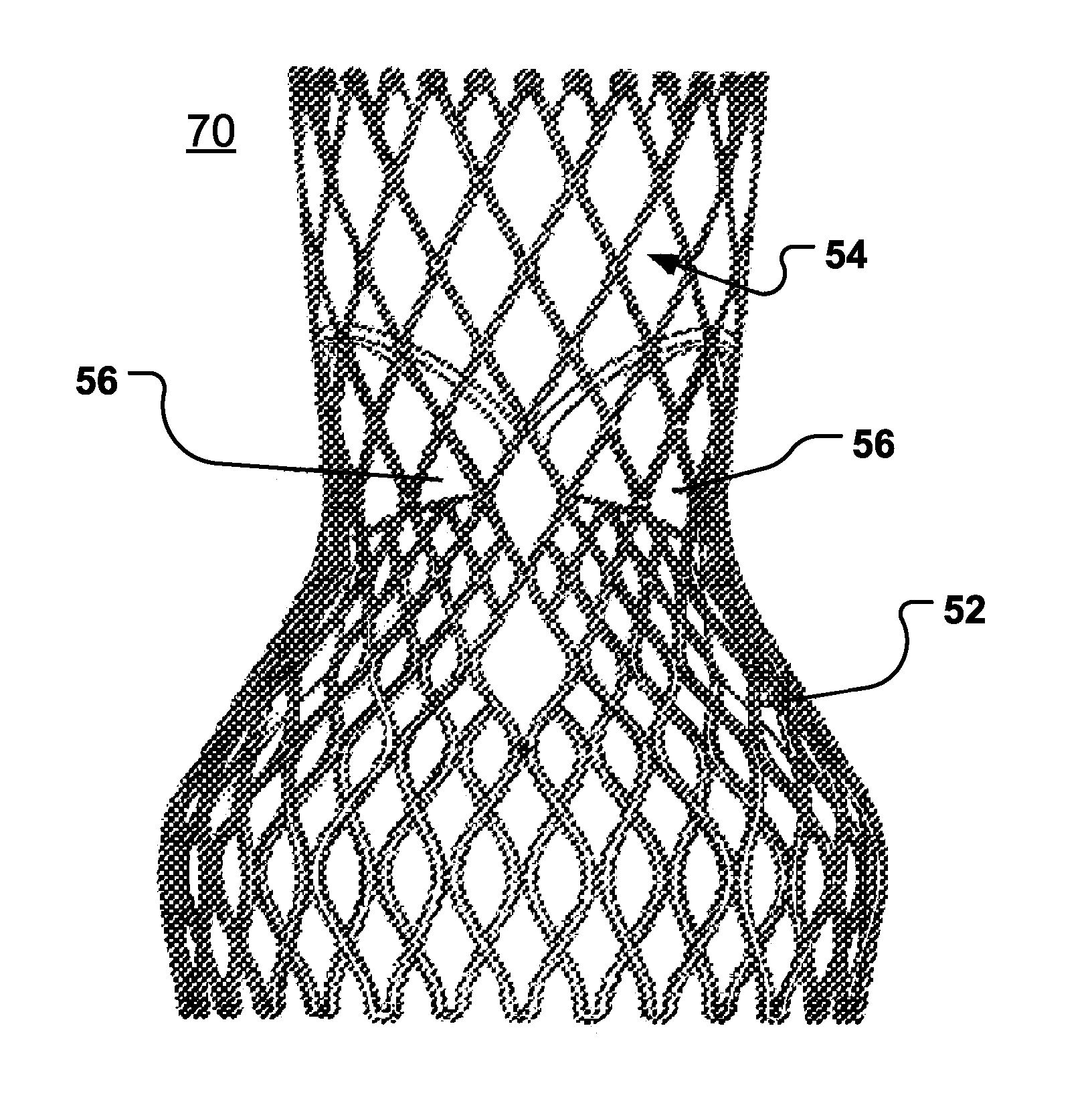
The present disclosure relates to an arrangement, a loop-shaped support, a prosthetic heart valve and a method of repairing or replacing a native heart valve. With the method or the arrangement, leakage or regurgitation between a prosthetic heart valve and the surrounding valve tissue is prevented. In one embodiment, an arrangement for replacement or repair of a native heart valve is provided, which comprises a loop-shaped support (41) and a prosthetic heart valve (70) and wherein an outer segment (32) of the loop-shaped support (41) is positionable towards surrounding valve tissue of a native heart valve and wherein an outer surface (74) of the prosthetic heart valve (70) is positionable towards an inner segment (34) of the loop-shaped support (41) so as to prevent paravalvular leakage or regurgitation between the prosthetic heart valve (70) and the surrounding valve tissue of the native heart valve.
Owner:MEDTENTIA INT LTD OY
Method of Treating Paravalvular Leakage After Prosthetic Valve Implantation
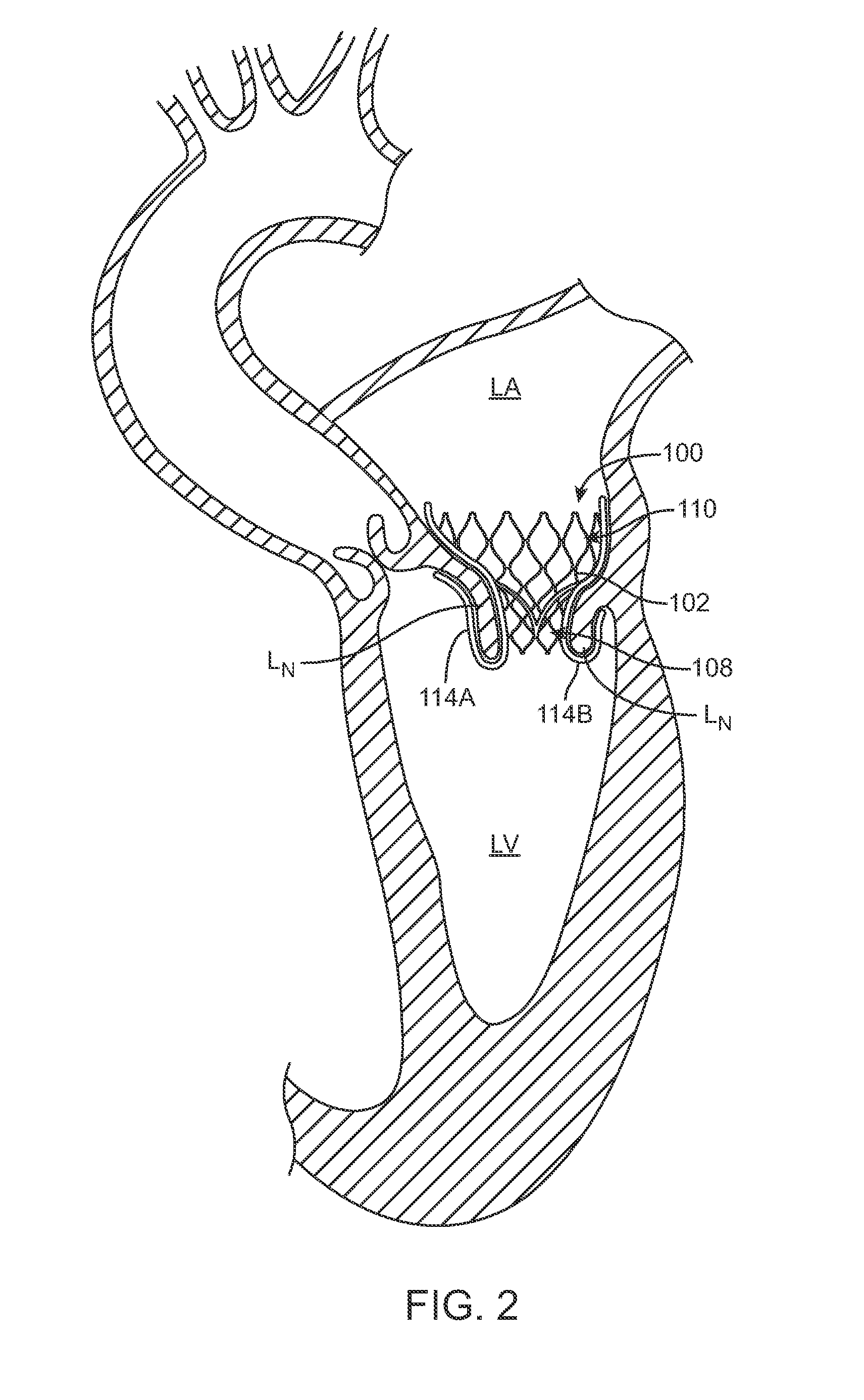
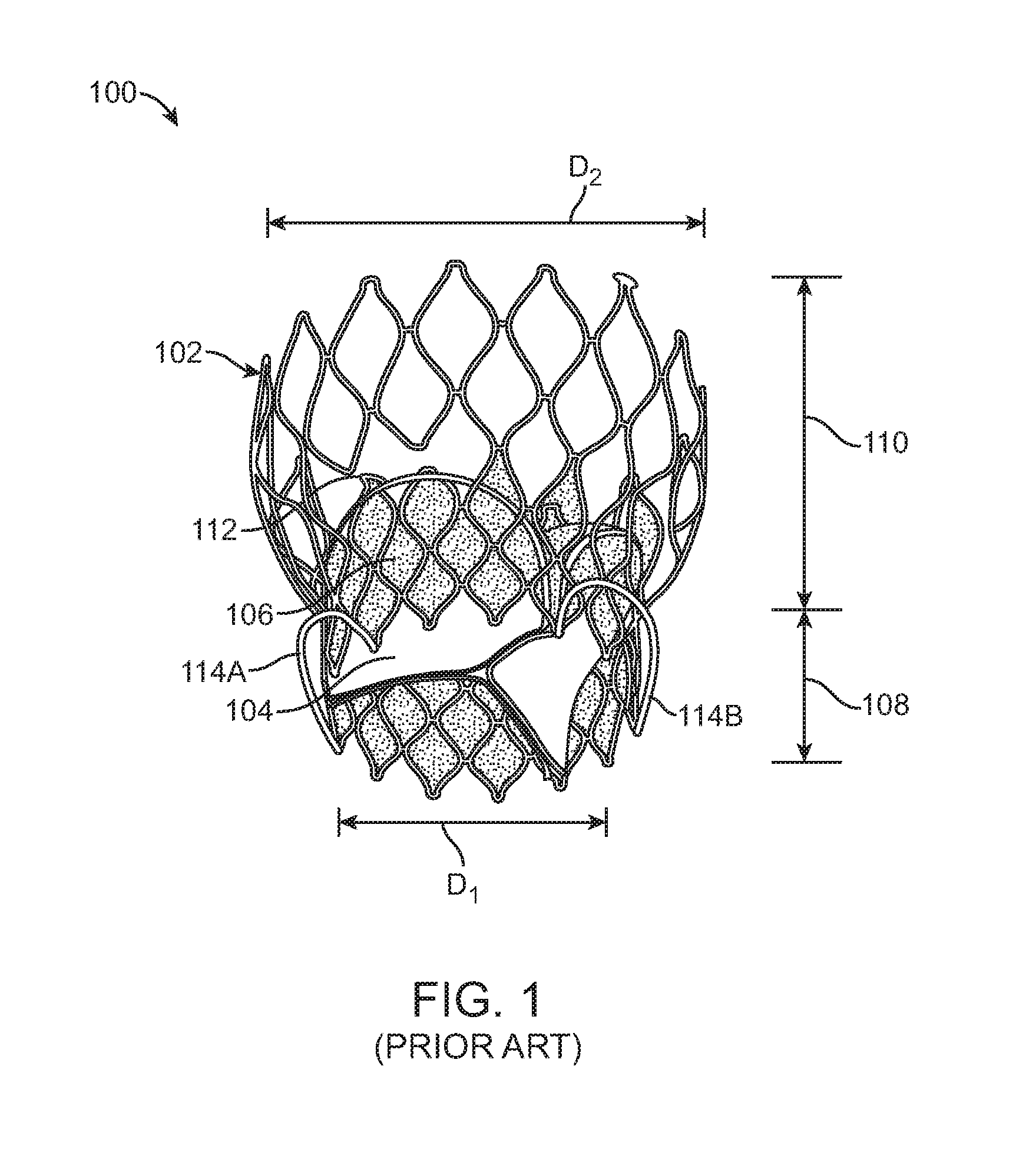
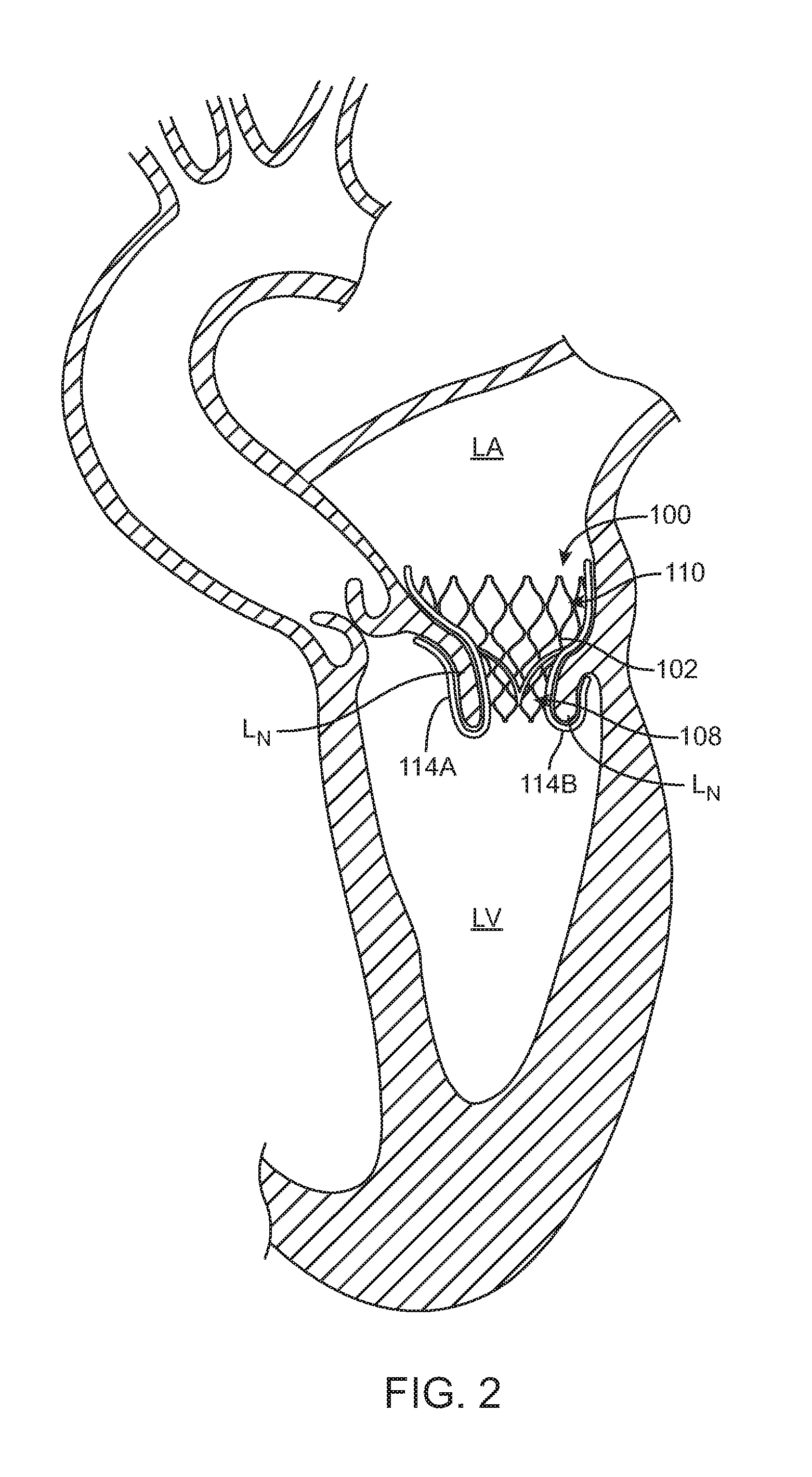
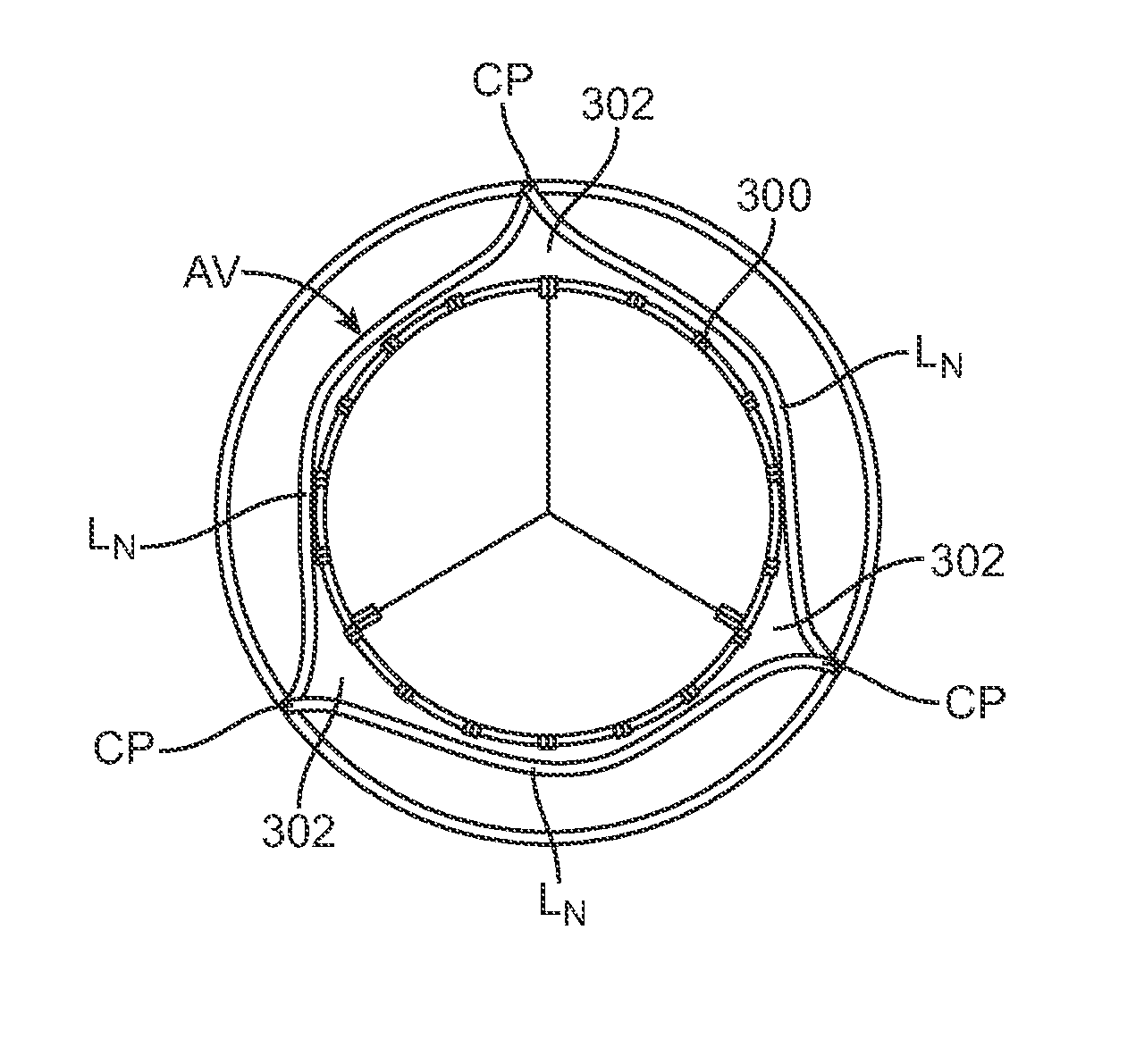
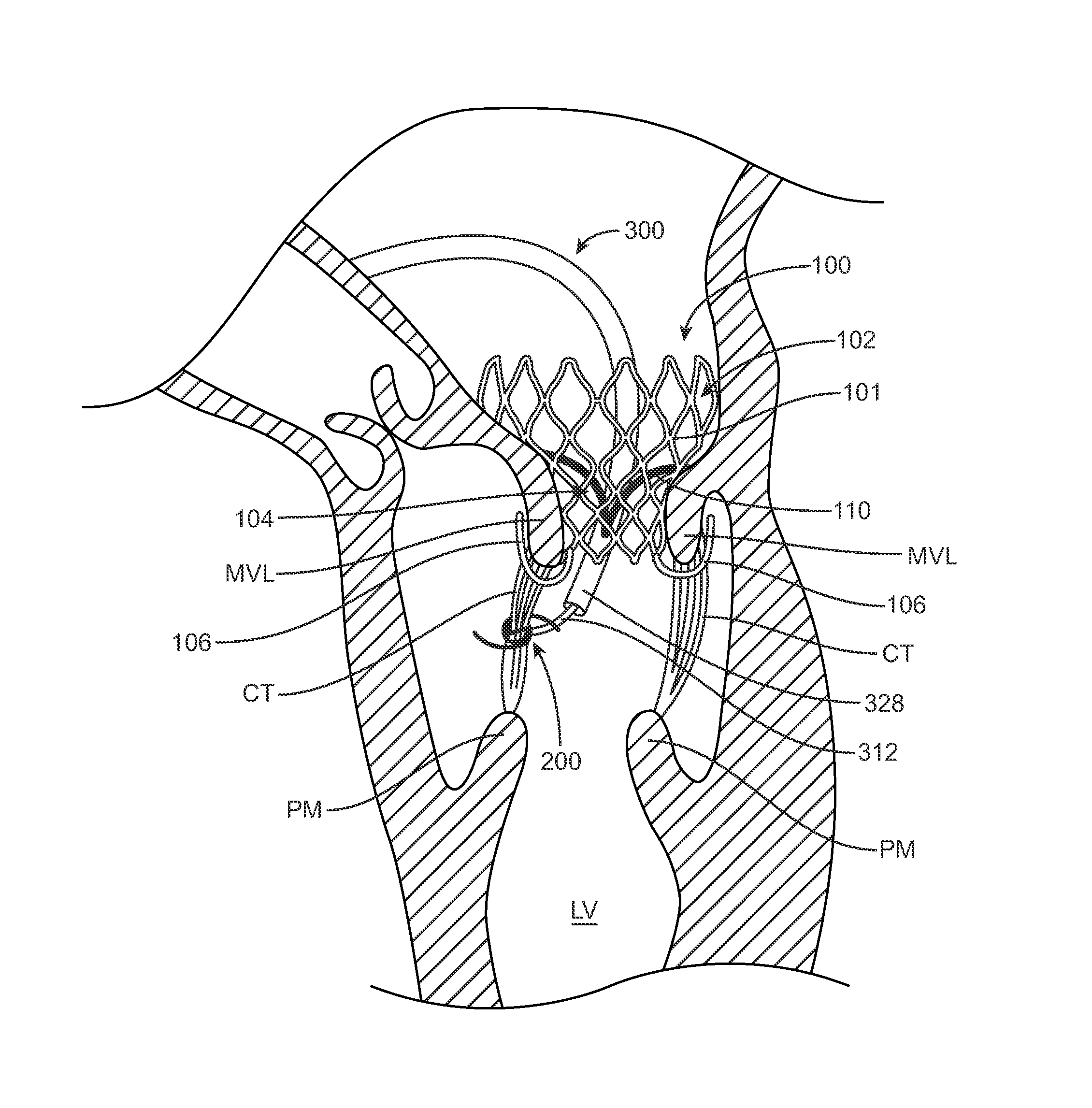
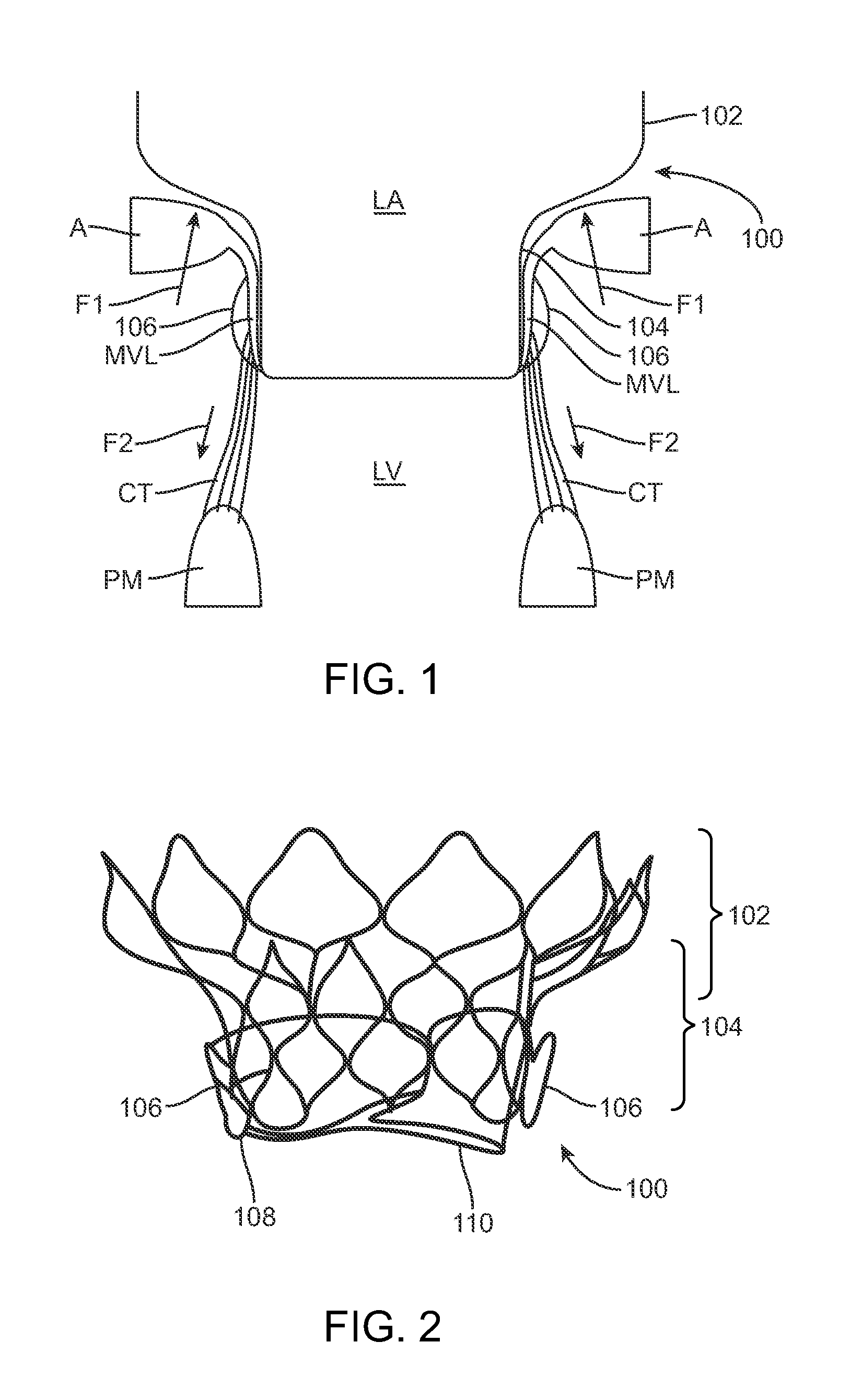
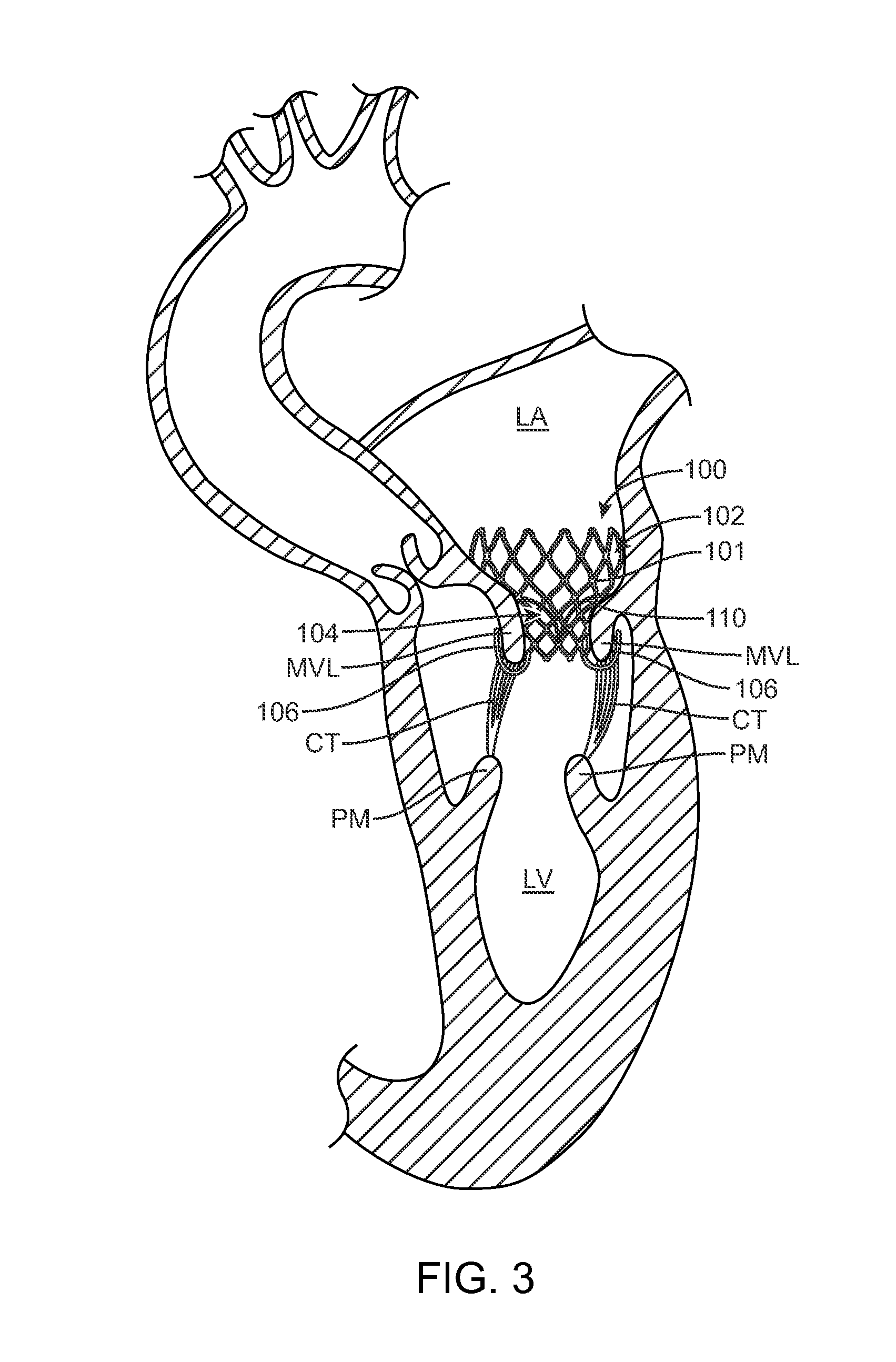
A method for treating paravalvular leakage at a location of a stented prosthetic valve includes the steps of delivering a clip to a location adjacent chordae tendinae of a native valve, and deploying the clip such that the clip captures at least some of the chordae tendinae of the native valve, thereby increasing tension in the captured chordae tendinae. The clip is delivered to the location in a collapsed stated and is released from a sheath convert to an undeflected or relaxed state. After the clip is released from the sheath, the clip is rotated to capture the chordae tendinae. The clip is then released from the delivery system and the delivery system is retracted.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
Anti-Paravalvular Leakage Component for a Transcatheter Valve Prosthesis
A transcatheter valve prosthesis includes an expandable tubular stent, a prosthetic valve within the stent, and an anti-paravalvular leakage component coupled to and encircling the tubular stent. The anti-paravalvular leakage component includes a radially-compressible annular scaffold, which is a sinusoidal patterned ring of self-expanding material, and an impermeable membrane extending over the annular scaffold. The anti-paravalvular leakage component has an expanded configuration in which at least segments of the annular scaffold curve radially away from the tubular stent. Alternatively, the anti-paravalvular leakage component includes a plurality of self-expanding segments and an annular sealing element coupled to inner surfaces of the segments. The anti-paravalvular leakage component has an expanded configuration in which the segments curve radially away from the tubular stent and the annular sealing element is positioned between an outer surface of the tubular stent and inner surfaces of the segments.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
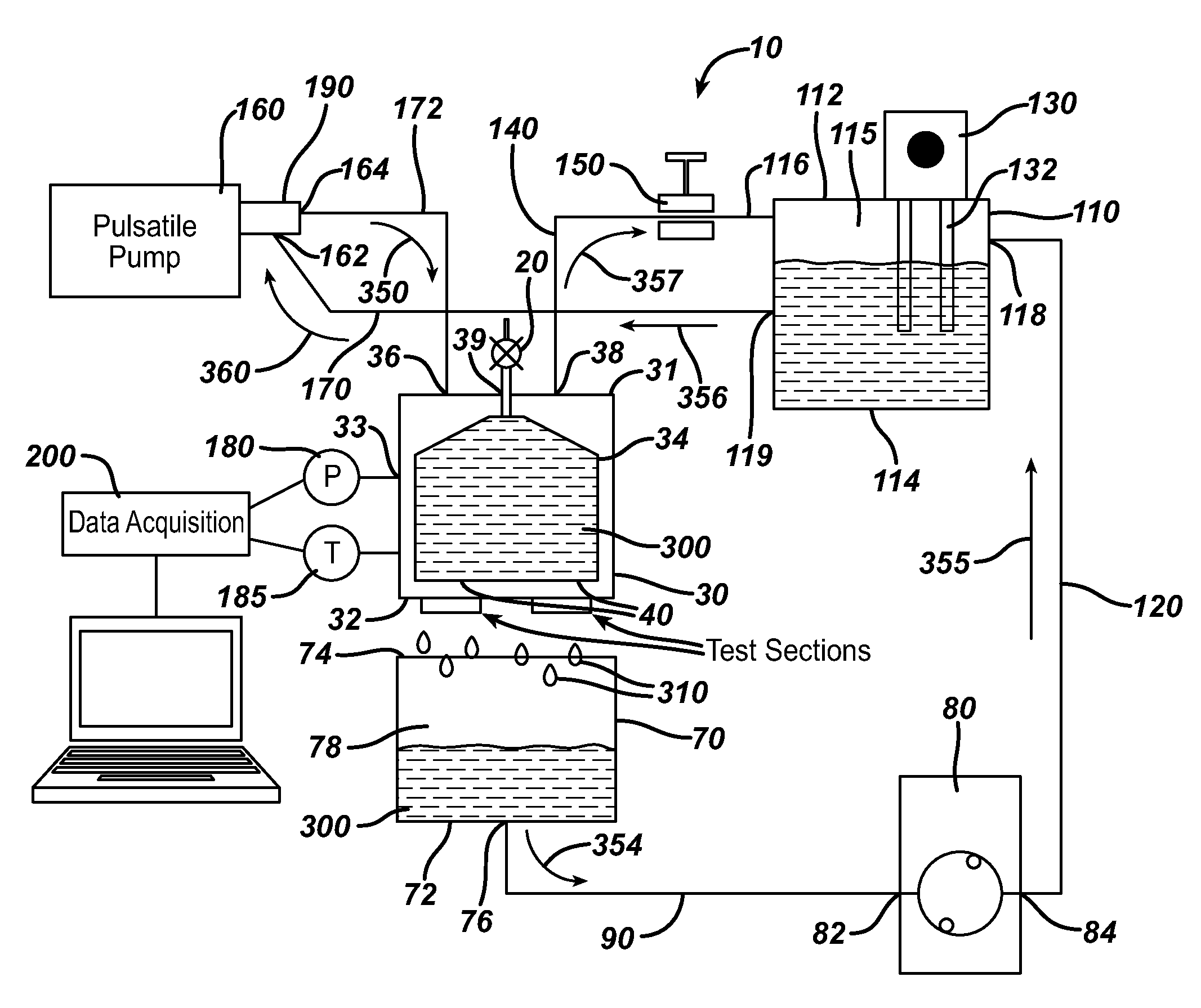
Paravalvular leak test apparatus and method
An apparatus and method for measuring paravalvular leakage from a prosthetic heart valve in vitro. The apparatus has a pulse chamber pressure vessel and a pulsatile pump. The sewing ring of a prosthetic heart valve is mounted to a mounting member which is affixed to the pressure chamber, and paravalvular leakage from the heart valve is collected and measured.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Method for implanting prosthetic valve
ActiveUS9326852B2Inhibiting natural separatingAvoid separationBalloon catheterHeart valvesParavalvular leakageVALVE PORT
A method for implanting a prosthetic valve apparatus in a novel location which replaces the function of a native diseased valve after an Alfieri procedure. The prosthetic valve apparatus includes a one way valve and an expandable valve seating. anchoring and securing apparatus in a newly created orifice near or at the center of the anterior valve leaflet. The prosthetic valve apparatus also causes the sealing of the native valve and thus results in a solution for paravalvular leakage and regurgitation.
Owner:TRUELEAF MEDICAL LTD
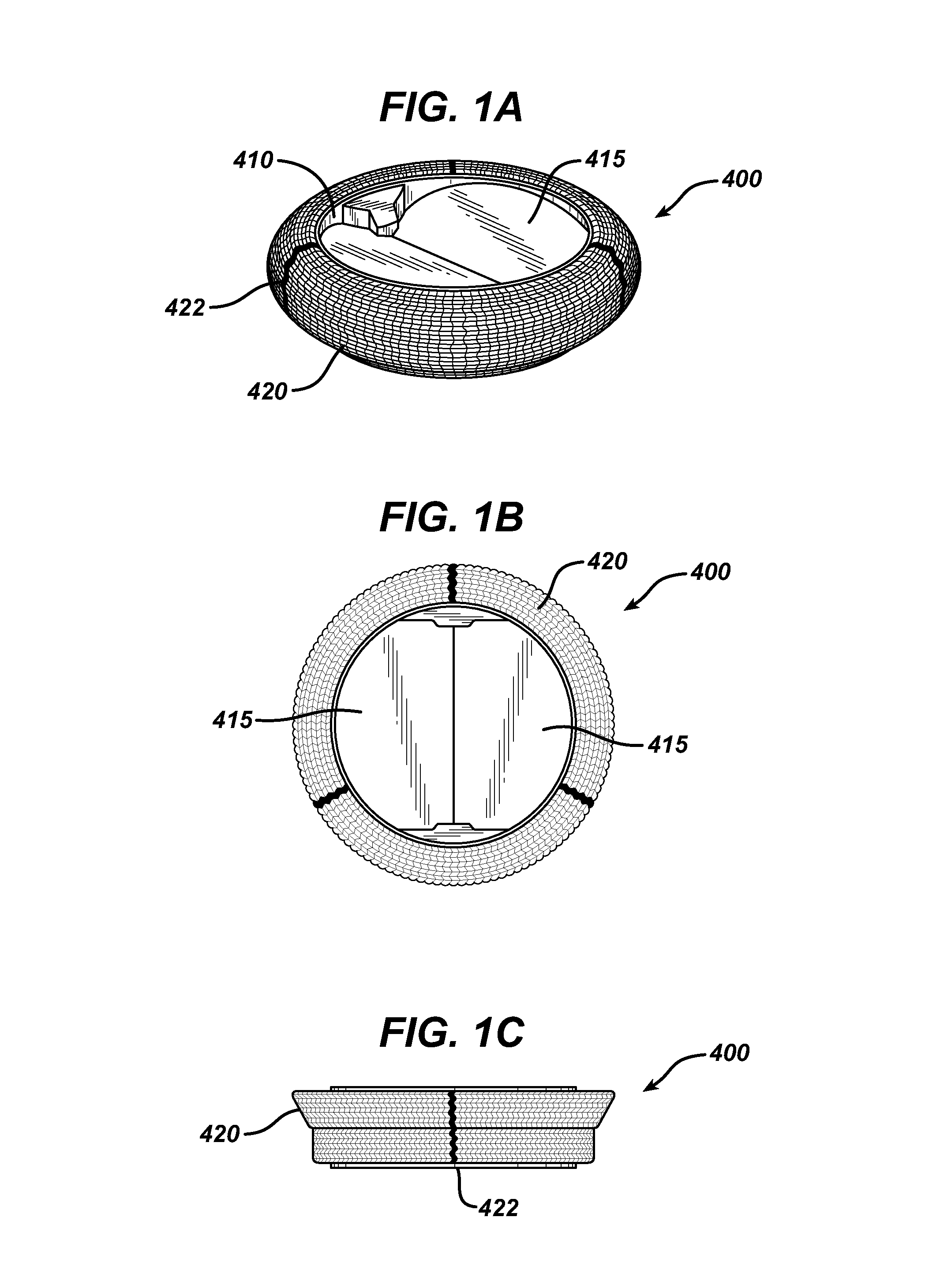
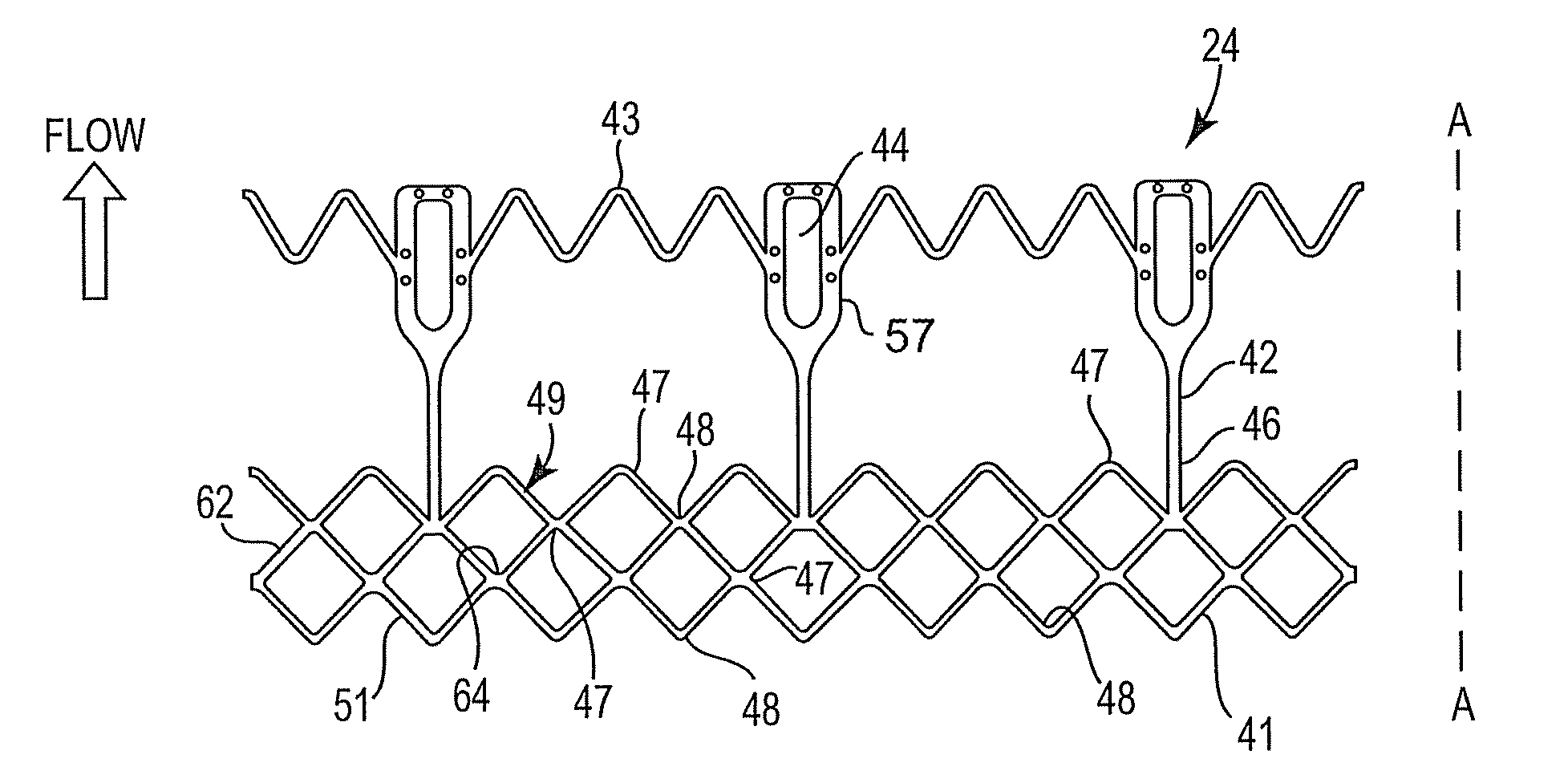
Puckering Seal for Reduced Paravalvular Leakage
A heart valve assembly includes a heart valve, a self-expandable and collapsible stent, and a sealing member. The stent includes an inflow end and an outflow end and is configured to support the heart valve internally. The sealing member is connected to and extends circumferentially around the stent. The sealing member includes a plurality of radially outward extending protrusions comprising a fold of material of the sealing member.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Anchoring structure with concave landing zone
ActiveUS20100100176A1Reducing paravalvular leakageIncrease opportunitiesHeart valvesParavalvular leakageLanding zone
A method and device for reducing paravalvular leakage upon implantation of a replacement heart valve is provided. The valve assembly includes a tissue or bioprosthetic heart valve attached to an anchoring structure. The anchoring structure includes an inlet rim that is substantially C-shaped in cross section to form a concave landing zone. The anchoring structure self-seats when implanted in the sinus of a patient with the proximal and distal ends of the C-shaped inlet rim pushed against the aorta to effectively prevent paravalvular leakage.
Owner:MEDTRONIC PS MEDICAL
Methods and Devices for Repairing and/or Preventing Paravalvular Leakage Post-Implantation of a Valve Prosthesis
ActiveUS20140114402A1Prevent leakageBalloon catheterHeart valvesParavalvular leakagePost implantation
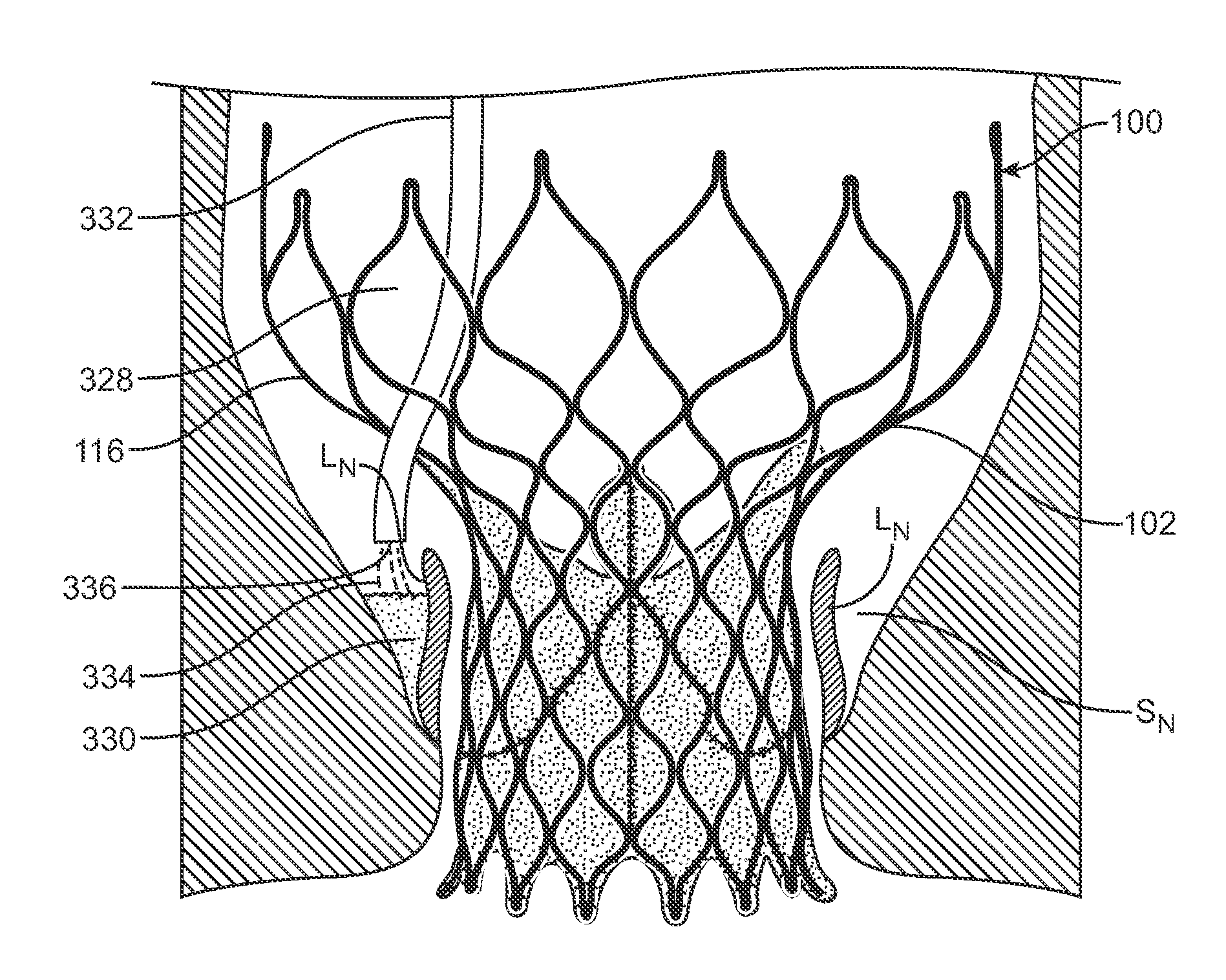
Devices and methods for delivering a sealing element post-implantation of valve prosthesis that functions to occlude or fill gaps present between the valve prosthesis and the native valve tissue, thereby reducing, minimizing, or eliminating leaks there through. In a first method, an injectable material is placed within a native valve sinus to form a sealing element that presses native valve leaflets against an outer surface of a heart valve prosthesis. In a second method, an injectable sealing material or a preformed annular sealing component is positioned between the outer surface or perimeter of a heart valve prosthesis and native heart valve tissue. In a third method, a preformed sealing element or component is placed within a heart valve prosthesis to press the prosthesis against native valve tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
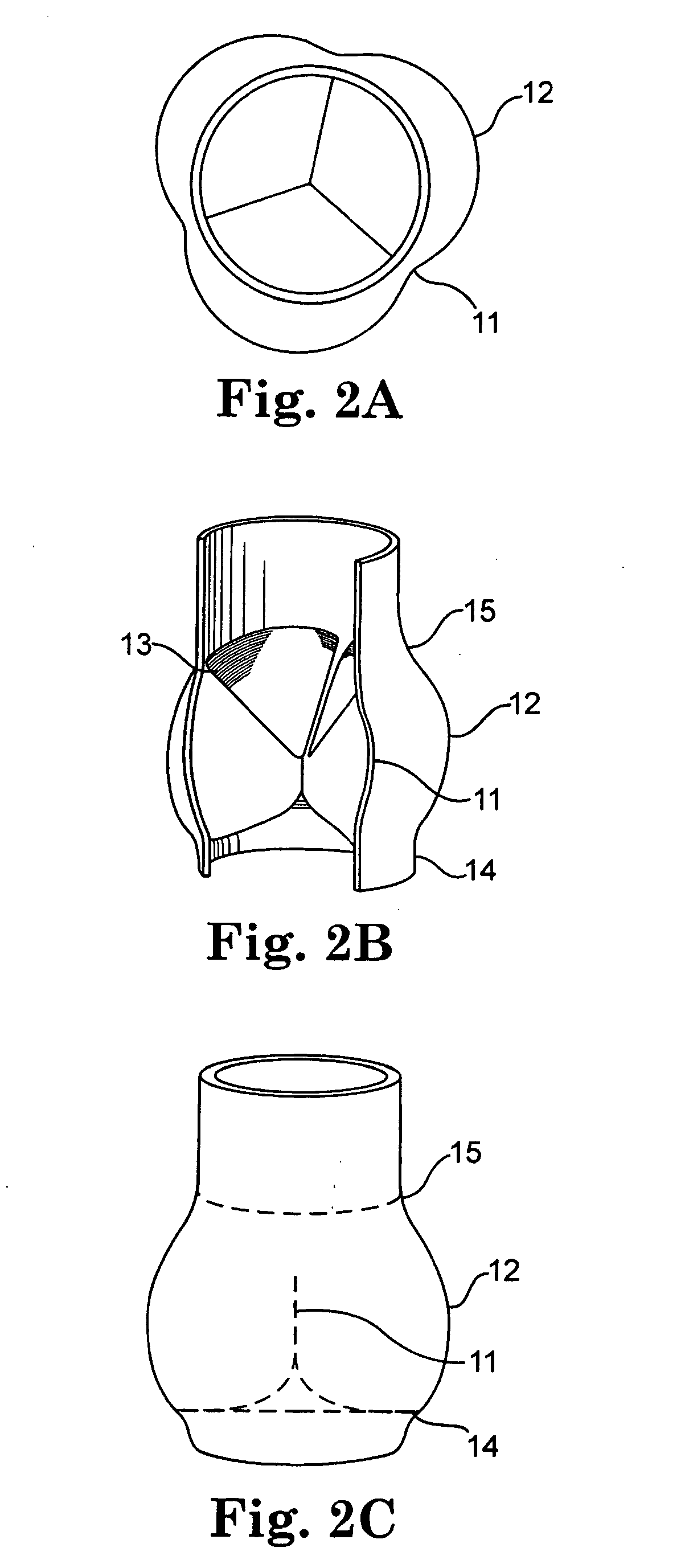
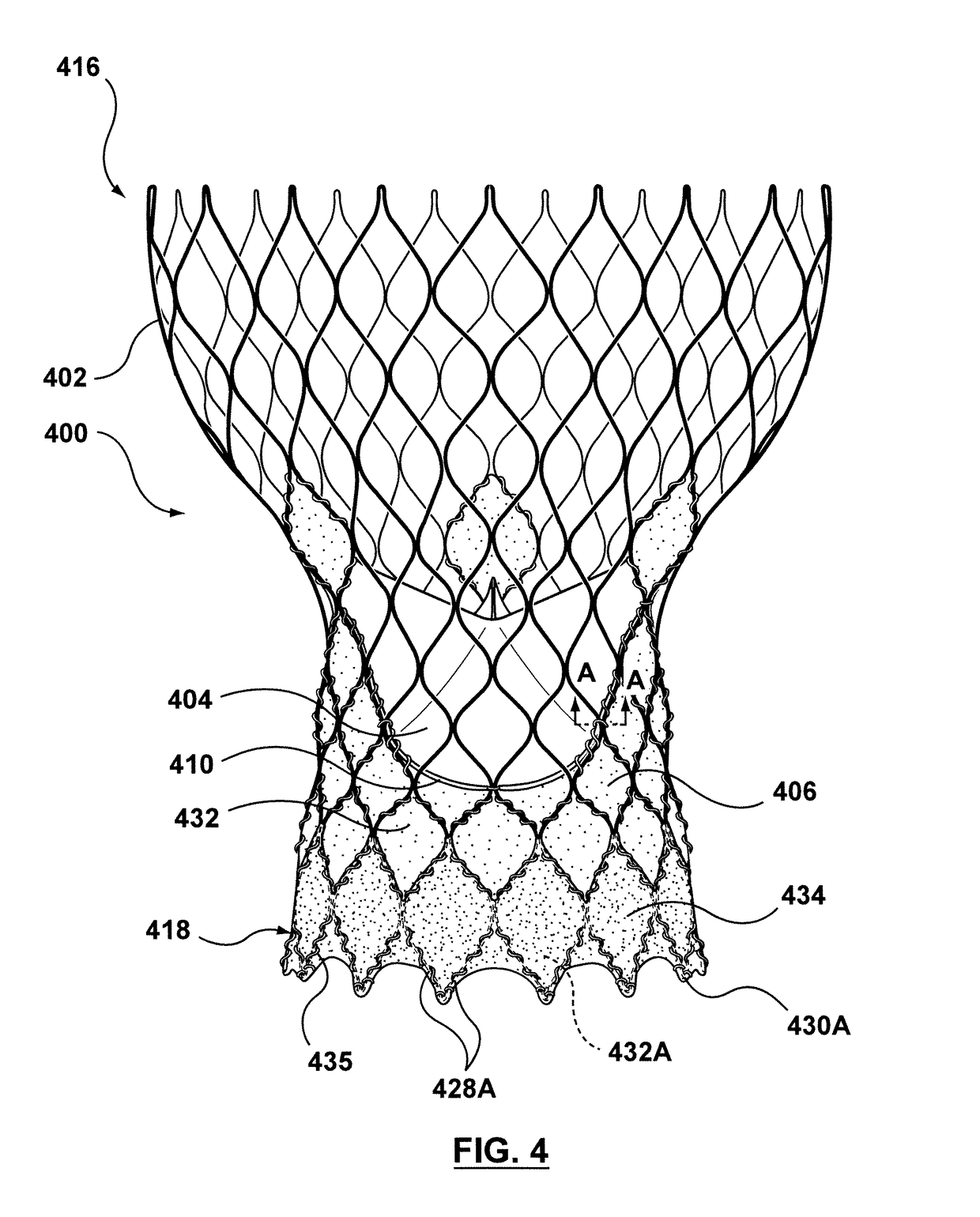
Transcatheter valve prosthesis having an external skirt for sealing and preventing paravalvular leakage
A transcatheter valve prosthesis including a tubular stent includes an interior skirt or skirt portion is coupled to and covers an inner circumferential surface of the stent, and an exterior skirt or skirt portion is coupled to and covers an outer circumferential surface of the stent. A prosthetic valve component is disposed within and secured to the interior skirt or skirt portion. The interior and exterior skirts or skirt portions may overlap to form a double layer of skirt material on the stent, or may be portions of a skirt that do not overlap such that only a single layer of skirt material covers the stent. When the stent is in at least the compressed configuration, at least one endmost crown may be positioned radially inwards with respect to the remaining endmost crowns formed at the inflow end of the stent in order to accommodate the exterior skirt.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Devices for treating paravalvular leakage and methods use thereof
InactiveUS20160256269A1Shortened proximalLow elongationSuture equipmentsHeart valvesParavalvular leakageDistal portion
An aspect of the present teachings includes a method of percutaneously treating a paravalvular leakage. In a preferred embodiment, the method includes providing an anchor having an elongate anchor member and a tensioning member, positioning the anchor through a paravalvular leakage, deploying the anchor wherein at least a part of the distal portion of the elongate anchor member is on one side of the paravalvular leakage, and applying tension to the tensioning member so that at least a part of the distal portion of the elongate anchor member transitions from the elongate configuration to the shortened configuration. Another aspect of the present teachings includes a device that can be used in a method of percutaneously treating a paravalvular leakage.
Owner:MITRALIGN INC
Transcatheter valve prosthesis and a concurrently delivered sealing component
A method of preventing paravalvular leakage includes concurrent delivery of a heart valve prosthesis and an annular sealing component. During delivery, the sealing component is moved from a first position to a second position of the heart valve prosthesis which is longitudinally spaced apart from the first position of the heart valve prosthesis. The sealing component is secured around the heart valve prosthesis at the second position by a contoured outer surface of the heart valve prosthesis. The sealing component may be a flexible ring or may be a cylindrical flexible sleeve having a plurality of ribs longitudinally extending over the cylindrical sleeve. The ribs operate to deploy the sealing component such that at least a portion of the cylindrical sleeve buckles outwardly away from the outer surface of the heart valve prosthesis.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Transcatheter Valve Prosthesis Having a Variable Shaped Cross-Section for Preventing Paravalvular Leakage
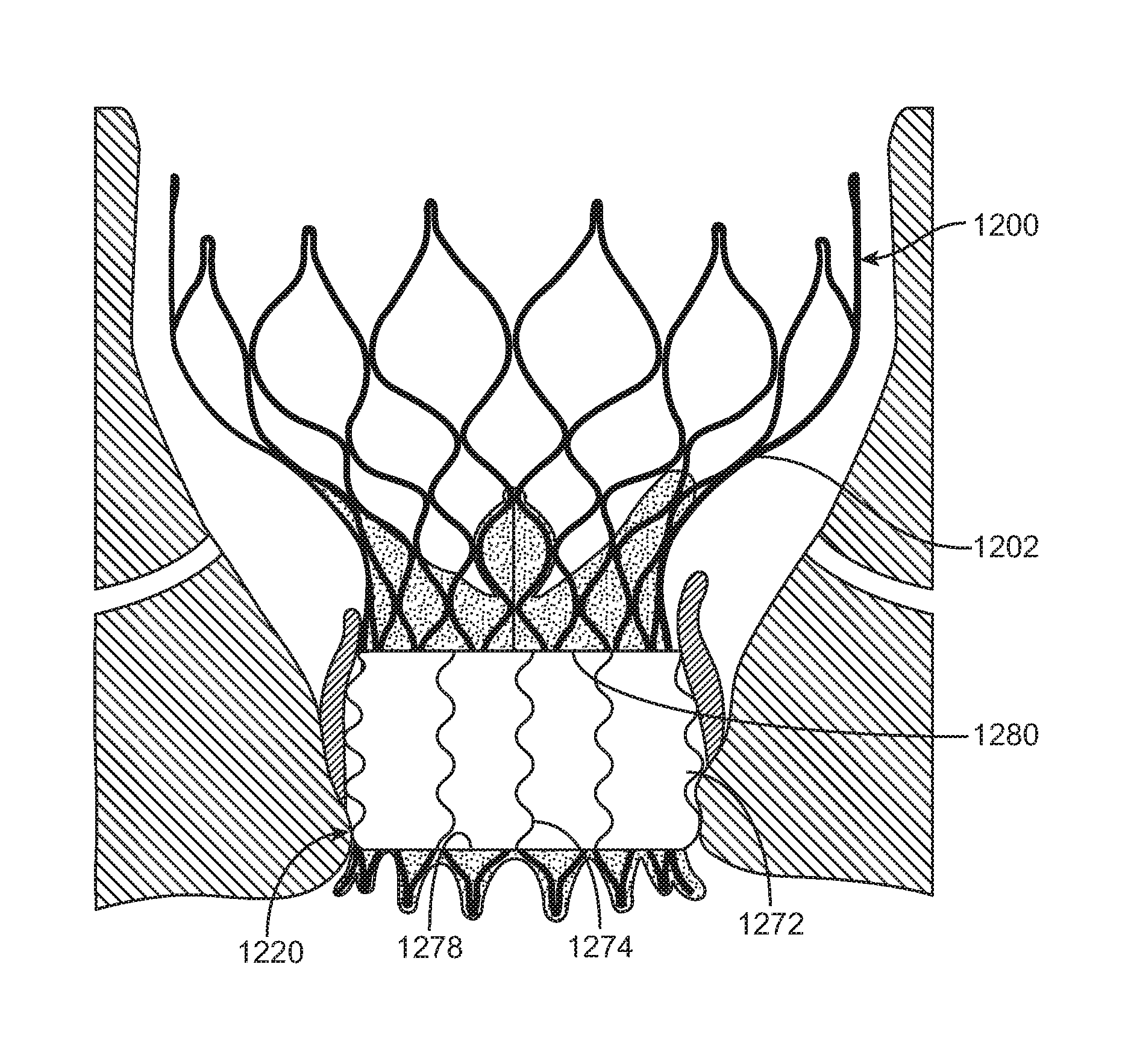
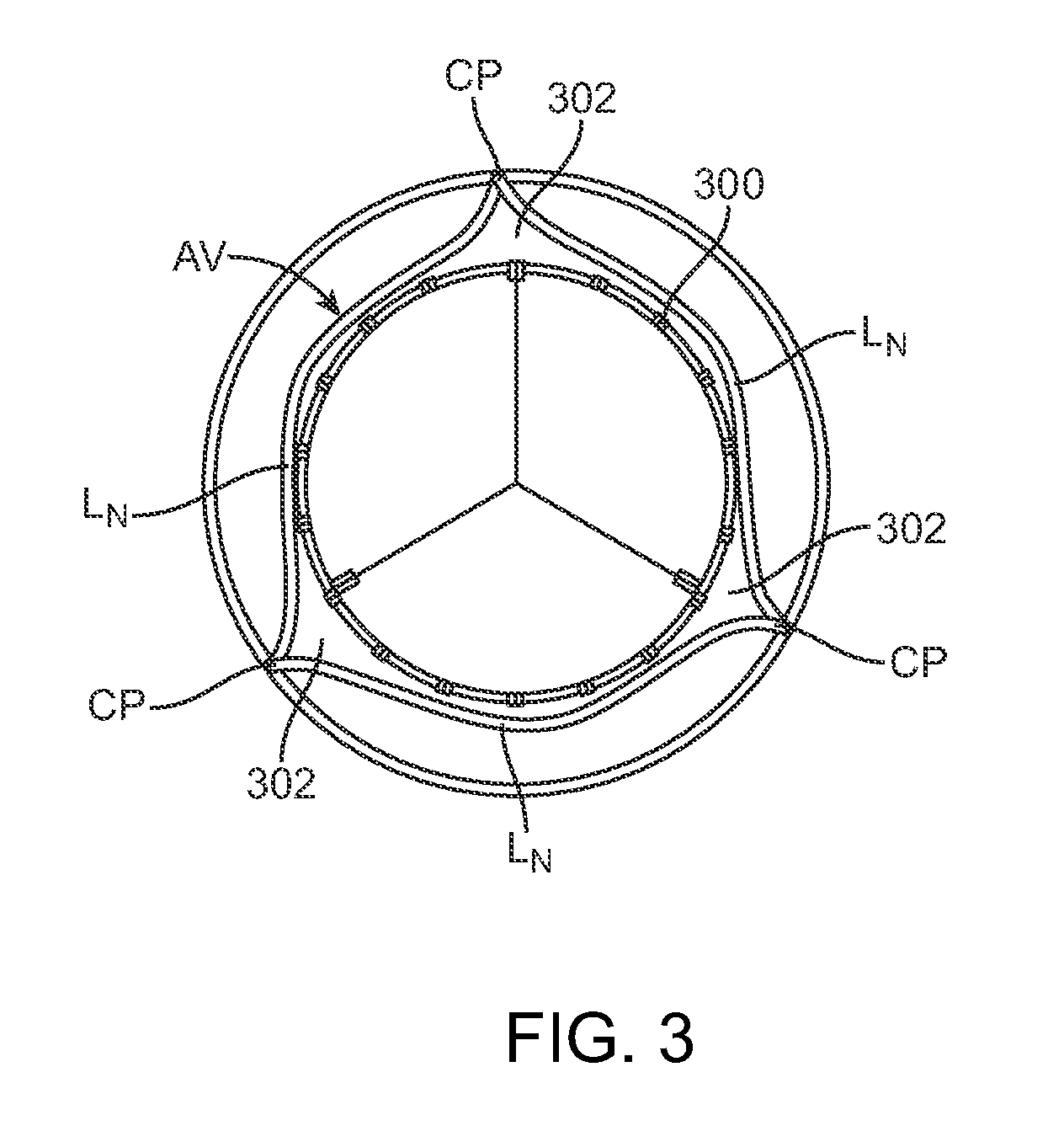
A transcatheter valve prosthesis includes a self-expanding tubular stent component and a prosthetic valve disposed within and secured to the stent component. The tubular stent component has a proximal portion, a distal portion, and an intermediate portion between the proximal and distal portions. In a compressed delivery configuration, the tubular stent component has a generally circular cross-section along its length. In an expanded deployed configuration, the proximal and distal portions have a generally circular cross-section while the intermediate portion of the stent component has a generally triangular cross-section with three vertexes that are configured to project into three commissural points of a native valve when the valve prosthesis is implanted in situ. The generally triangular transverse cross-section of the valve prosthesis is formed by pulling or extending selected or particular struts of the stent component radially outwards and then applying heat to heat-set the stent component in the deployed configuration.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Stented prosthetic heart valve having wrap and methods of delivery and deployment
ActiveUS20170273784A1Effectively reduce stasisNot increase profileHeart valvesProsthetic valveParavalvular leakage
Systems and methods of delivering and deploying a stented prosthetic heart valve having a wrap that is automatically deployed to prevent or mitigate paravalvular leakage. In various embodiments, during transcatheter delivery of the stented prosthetic heart valve, the wrap is extends beyond a stent frame of the stented prosthetic heart valve so that the profile of the stented prosthetic heart valve is not increased during delivery. The disclosed embodiments are arranged and configured so that upon expansion of a stent frame of the stented prosthetic heart valve, a plurality of elongated members automatically pull the wrap distally into a deployed arrangement.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Anti-paravalvular leakage component for a transcatheter valve prosthesis
A transcatheter valve prosthesis includes an expandable tubular stent, a prosthetic valve within the stent, and an anti-paravalvular leakage component coupled to and encircling the tubular stent. The anti-paravalvular leakage component includes a radially-compressible annular scaffold, which is a sinusoidal patterned ring of self-expanding material, and an impermeable membrane extending over the annular scaffold. The anti-paravalvular leakage component has an expanded configuration in which at least segments of the annular scaffold curve radially away from the tubular stent. Alternatively, the anti-paravalvular leakage component includes a plurality of self-expanding segments and an annular sealing element coupled to inner surfaces of the segments. The anti-paravalvular leakage component has an expanded configuration in which the segments curve radially away from the tubular stent and the annular sealing element is positioned between an outer surface of the tubular stent and inner surfaces of the segments. The segments may be orthogonal or oblique to the outer surface of the tubular stent.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
Bioprosthetic heart valves having adaptive seals to minimize paravalvular leakage
InactiveUS20150122687A1Simple to provideSurgical furnitureHeart valvesParavalvular leakageCardiology
A packaged bioprosthetic heart valve comprising a bioprosthetic heart valve, an adaptive seal and a package. The bioprosthetic heart valve comprises an at least partially dehydrated biological tissue leaflet structure coupled to a supporting frame. The bioprosthetic heart valve has a periphery, an inflow portion, and an outflow portion. The adaptive seal is coupled to the bioprosthetic heart valve around at least a portion of the periphery. The adaptive seal comprises an expandable material that expands after exposure to an initiating condition. The bioprosthetic heart valve and the adaptive seal is stored and contained within the package, which does not contain a liquid storage solution in contact with the bioprosthetic heart valve and the adaptive seal.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Anti-paravalvular leakage components for a transcatheter valve prosthesis
A valve prosthesis includes one or more anti-paravalvular leakage components coupled to a stent. The anti-paravalvular leakage component may encircle the stent and include a radially expandable control ring coupled to an unattached edge of a flexible skirt which extends the unattached skirt edge outwardly away from the stent and against the native heart valve to form an open-ended annular pocket around the stent. The anti-paravalvular leakage component may encircle the perimeter of the stent and include a flexible skirt having opposing edges coupled to the stent to form one or more enclosed compartments around the stent. Each compartment includes a one-way valve which allows for blood flow into the compartment but prevents blood flow out of the compartment. The anti-paravalvular leakage component may be at least one flap that is coupled to an inner surface of the stent and formed of a flexible material moveable by blood flow.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
Anchoring structure with concave landing zone
A method and device for reducing paravalvular leakage upon implantation of a replacement heart valve is provided. The valve assembly includes a tissue or bioprosthetic heart valve attached to an anchoring structure. The anchoring structure includes an inlet rim that is substantially C-shaped in cross section to form a concave landing zone. The anchoring structure self-seats when implanted in the sinus of a patient with the proximal and distal ends of the C-shaped inlet rim pushed against the aorta to effectively prevent paravalvular leakage.
Owner:MEDTRONIC PS MEDICAL
Method of treating paravalvular leakage after prosthetic valve implantation
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
Transcatheter valve prosthesis having an external skirt for sealing and preventing paravalvular leakage
A transcatheter valve prosthesis including a tubular stent includes an interior skirt or skirt portion is coupled to and covers an inner circumferential surface of the stent, and an exterior skirt or skirt portion is coupled to and covers an outer circumferential surface of the stent. A prosthetic valve component is disposed within and secured to the interior skirt or skirt portion. The interior and exterior skirts or skirt portions may overlap to form a double layer of skirt material on the stent, or may be portions of a skirt that do not overlap such that only a single layer of skirt material covers the stent. When the stent is in at least the compressed configuration, at least one endmost crown may be positioned radially inwards with respect to the remaining endmost crowns formed at the inflow end of the stent in order to accommodate the exterior skirt.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Methods and devices for repairing and/or preventing paravalvular leakage post-implantation of a valve prosthesis
Devices and methods for delivering a sealing element post-implantation of valve prosthesis that functions to occlude or fill gaps present between the valve prosthesis and the native valve tissue, thereby reducing, minimizing, or eliminating leaks there through. In a first method, an injectable material is placed within a native valve sinus to form a sealing element that presses native valve leaflets against an outer surface of a heart valve prosthesis. In a second method, an injectable sealing material or a preformed annular sealing component is positioned between the outer surface or perimeter of a heart valve prosthesis and native heart valve tissue. In a third method, a preformed sealing element or component is placed within a heart valve prosthesis to press the prosthesis against native valve tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Transcatheter valve prostheses having a sealing component formed from tissue having an altered extracellular matrix
A transcatheter valve prosthesis including a sealing component formed from a tissue having an altered extracellular matrix. The altered extracellular matrix includes at least one weakened connection such that the tissue is configured to swell or expand upon contact with a fluid. The altered extracellular matrix does not reduce compressibility of the tissue such that the delivery profile of the transcatheter valve prosthesis is not adversely affected. The tissue having an altered extracellular matrix transforms from a compressed state for delivery within a vasculature to an expanded state in situ when blood infiltrates or flows within the at least one weakened connection. The sealing component in the expanded state conforms to the geometry of the native valve tissue, thereby preventing paravalvular leakage at the implantation site.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Methods and devices for reducing paravalvular leakage
ActiveUS20180256330A1Reduce curvatureIncrease the curvatureAnnuloplasty ringsParavalvular leakageCoronary sinus
Methods and devices for reducing paravalvular leakage associated with a replacement mitral valve. The methods can include monitoring for paravalvular leakage between a replacement mitral valve and tissue proximate the mitral valve annulus; if a sufficient amount of paravalvular leakage is observed, deploying a tissue reshaping device at least partially within a coronary sinus; remodeling coronary sinus tissue with the tissue reshaping device to remodel at least one of mitral valve annulus tissue, at least one mitral valve leaflet, and left atrium tissue in an attempt to reduce the paravalvular leakage; and monitoring for a reduction in paravalvular leakage after the remodeling step.
Owner:CARDIAC DIMENSIONS
Arrangement, A Loop-Shaped Support, A Prosthetic Heart Valve And A Method Of Repairing Or Replacing A Native Heart Valve
ActiveUS20150039082A1Leakage and regurgitationBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsParavalvular leakageProsthesis
The present disclosure relates to an arrangement, a loop-shaped support, a prosthetic heart valve and a method of repairing or replacing a native heart valve. With the method or the arrangement, leakage or regurgitation between a prosthetic heart valve and the surrounding valve tissue is prevented. In one embodiment, an arrangement for replacement or repair of a native heart valve is provided, which comprises a loop-shaped support (41) and a prosthetic heart valve (70) and wherein an outer segment (32) of the loop-shaped support (41) is positionable towards surrounding valve tissue of a native heart valve and wherein an outer surface (74) of the prosthetic heart valve (70) is positionable towards an inner segment (34) of the loop-shaped support (41) so as to prevent paravalvular leakage or regurgitation between the prosthetic heart valve (70) and the surrounding valve tissue of the native heart valve.
Owner:MEDTENTIA INT LTD OY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com