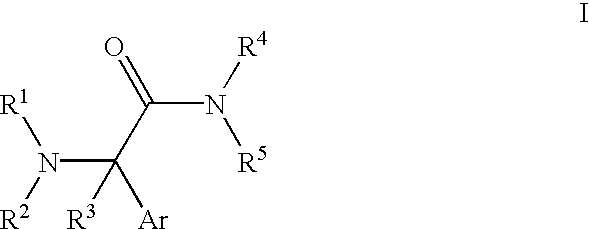
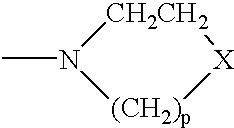
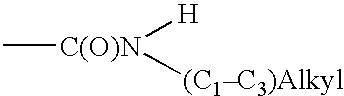
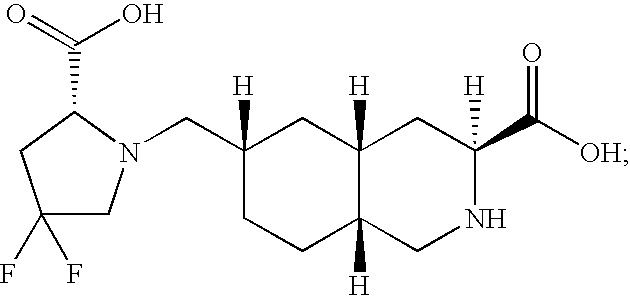
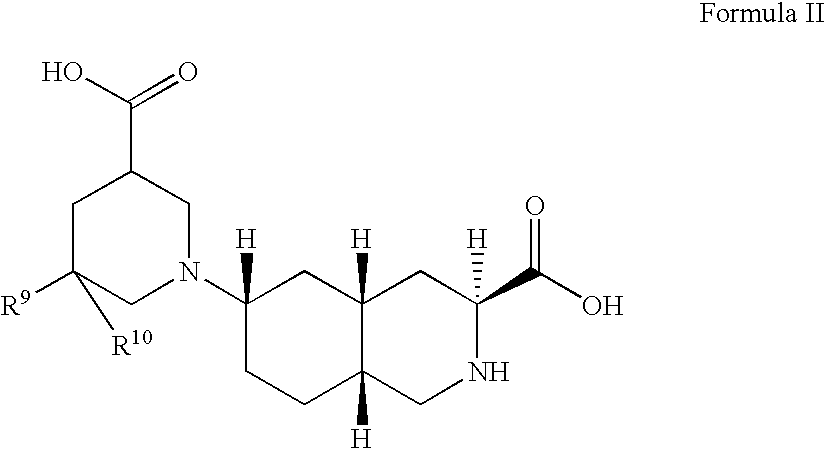
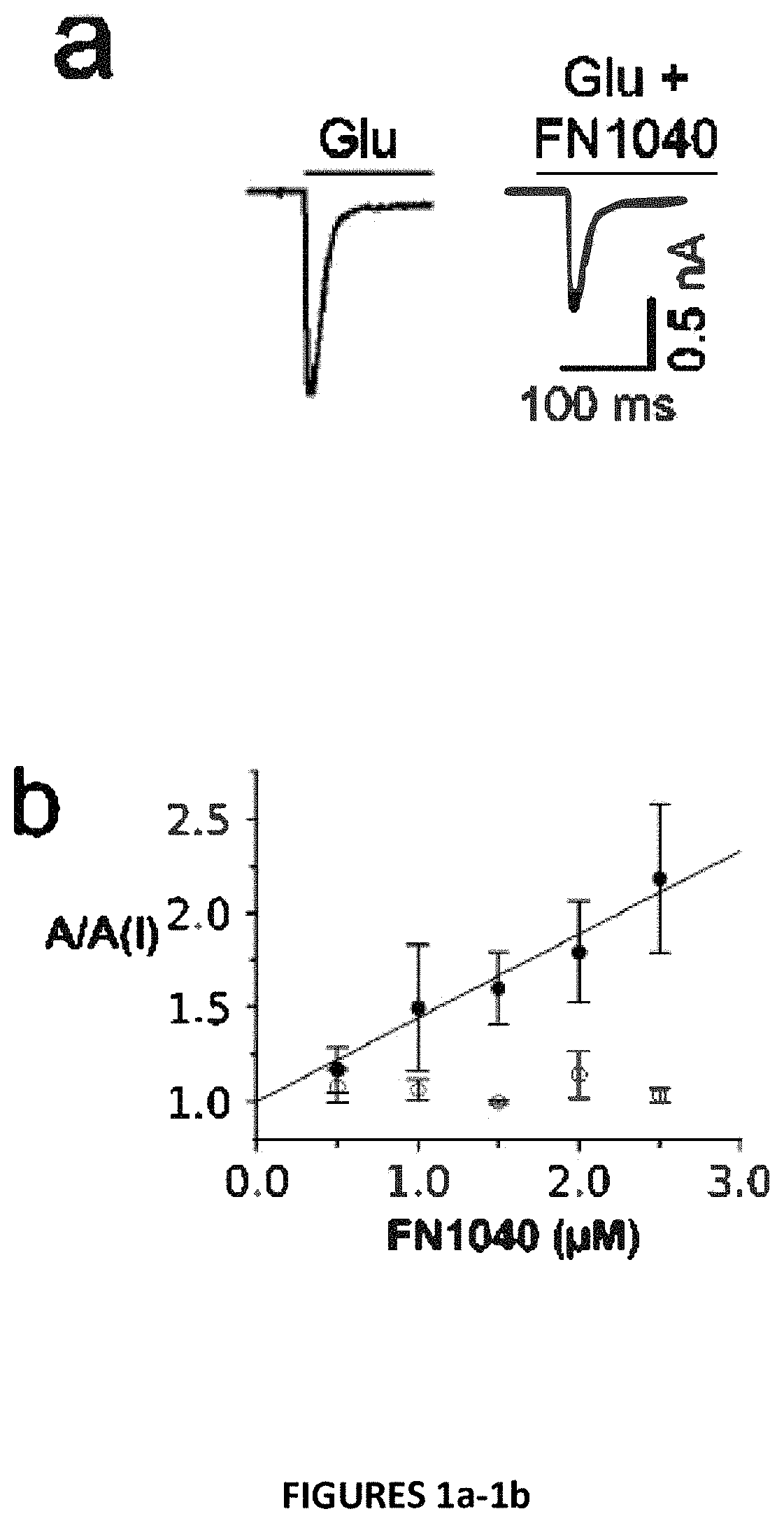
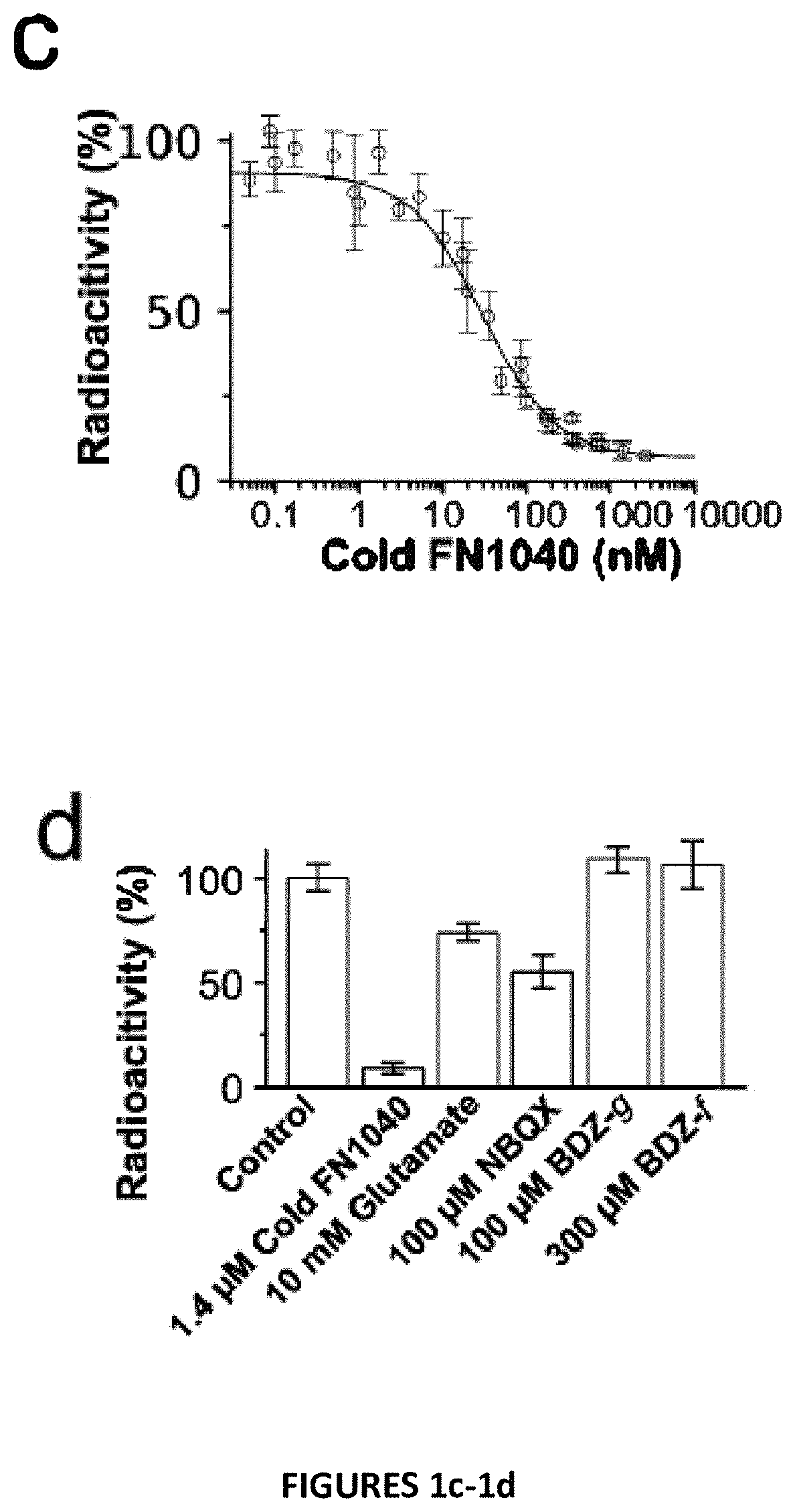
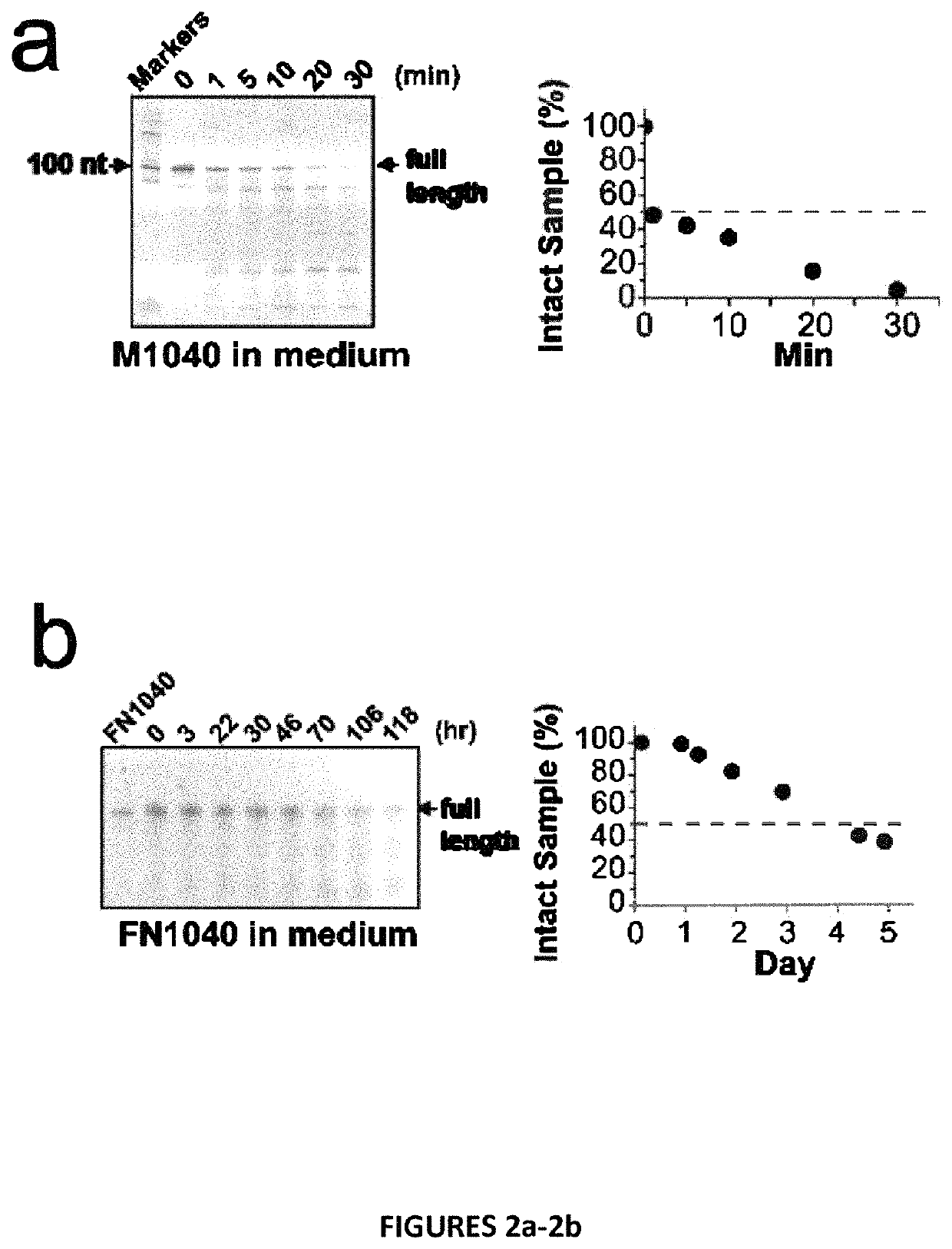
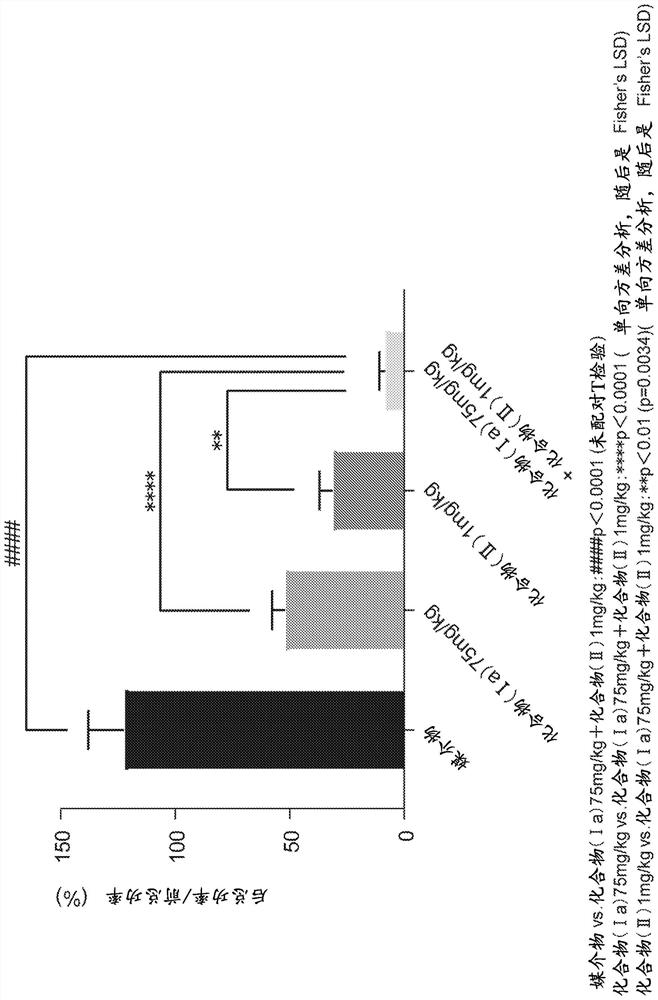
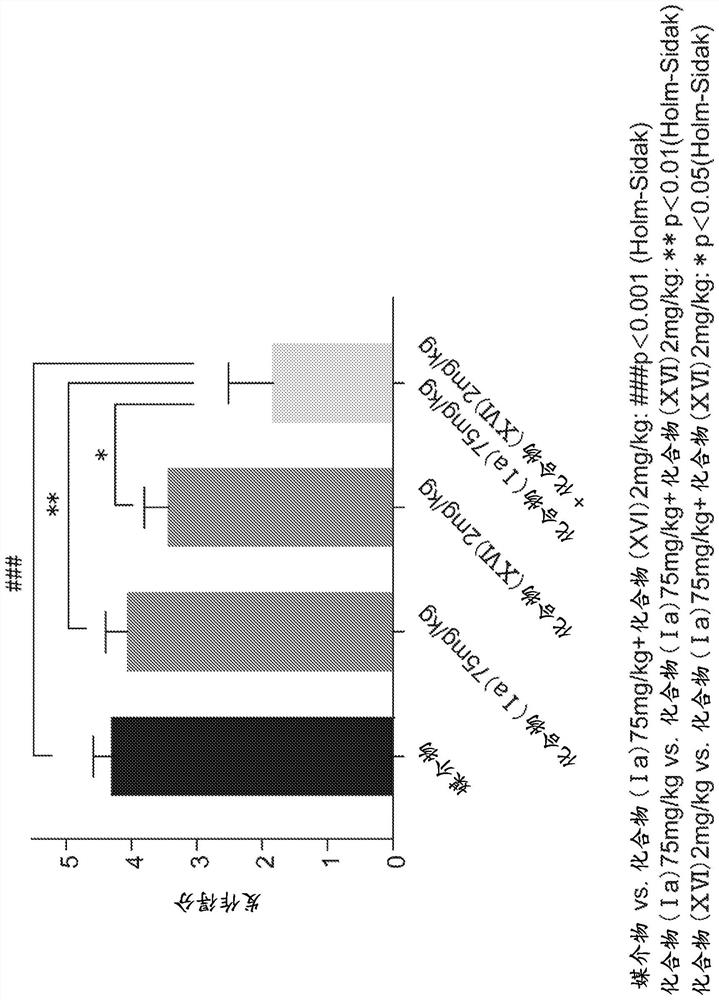
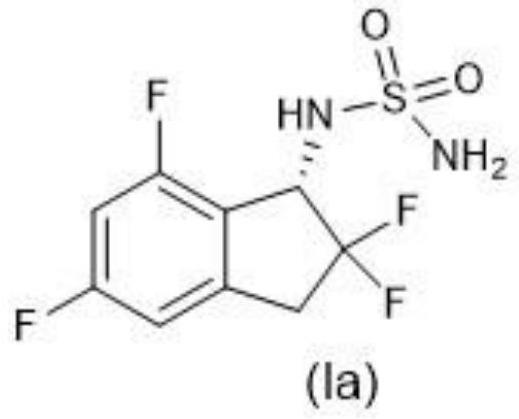
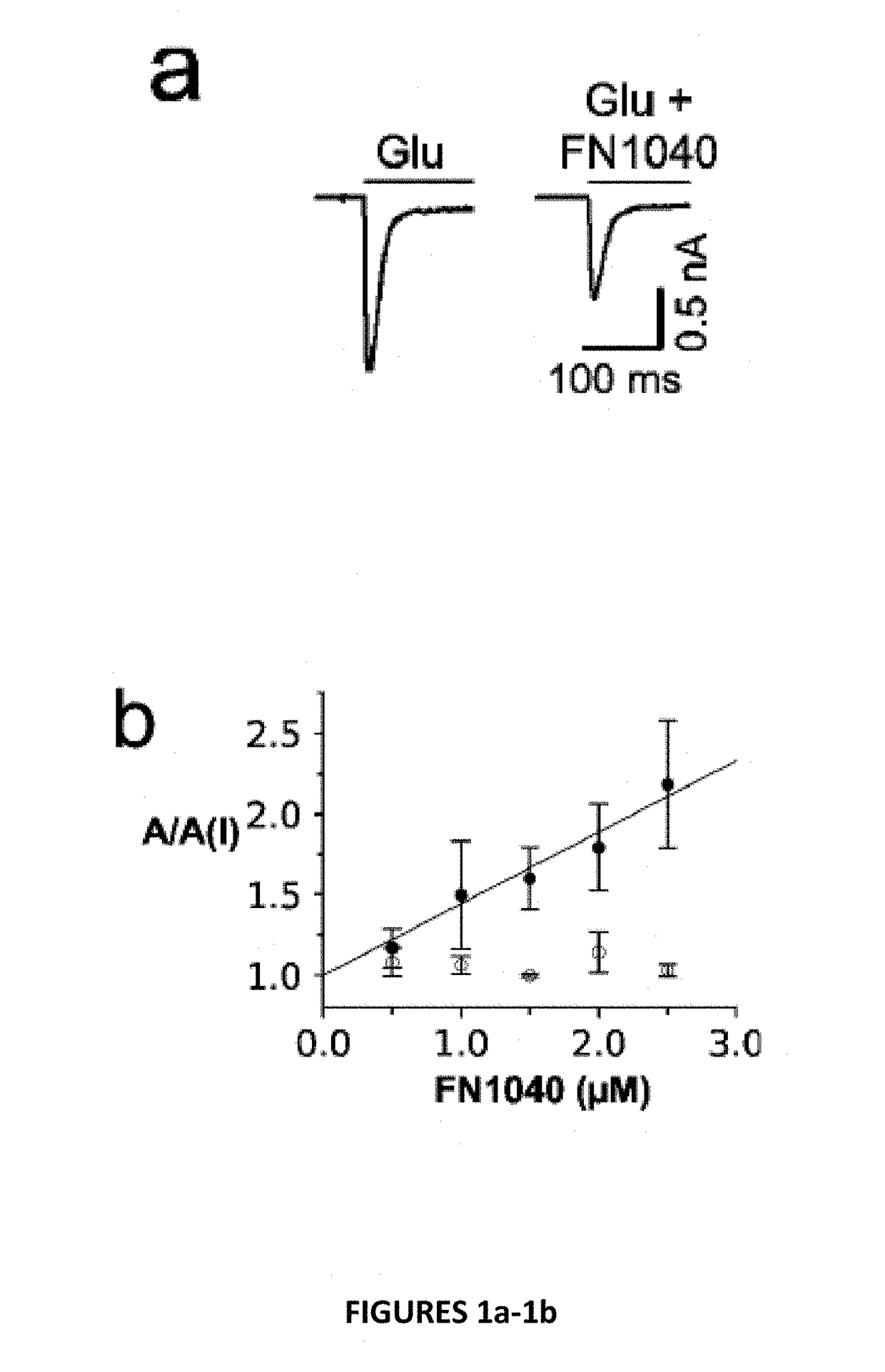
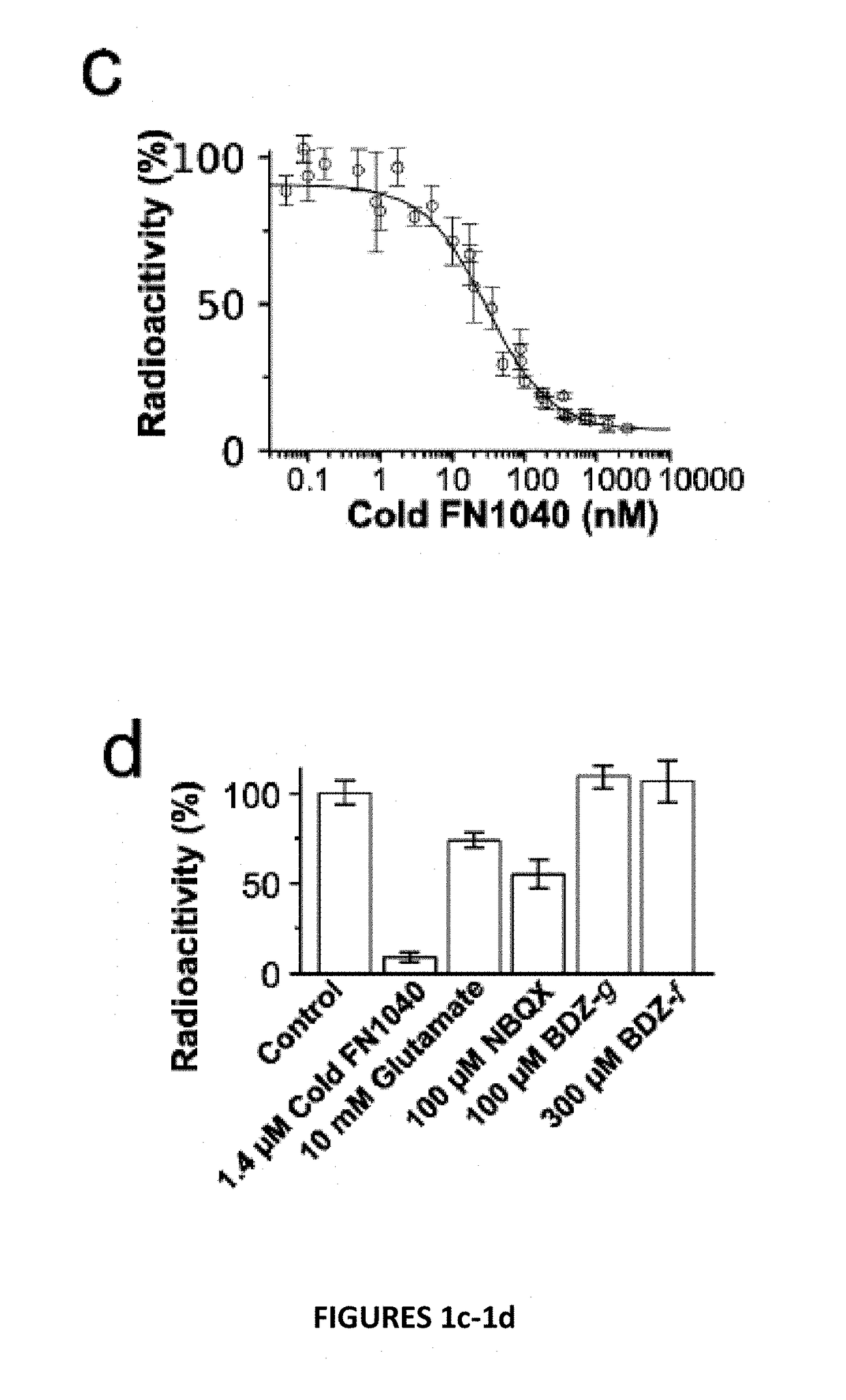
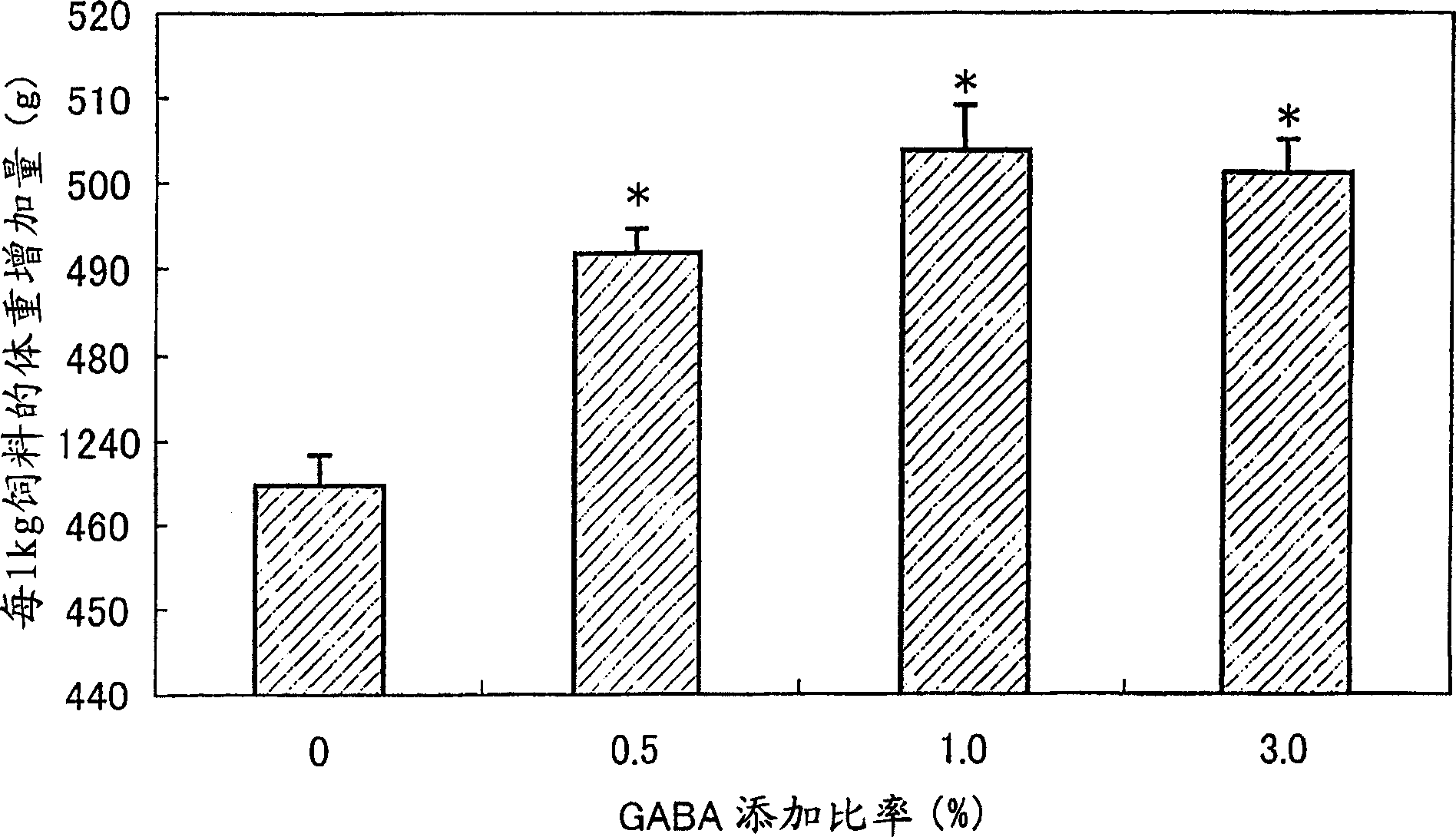
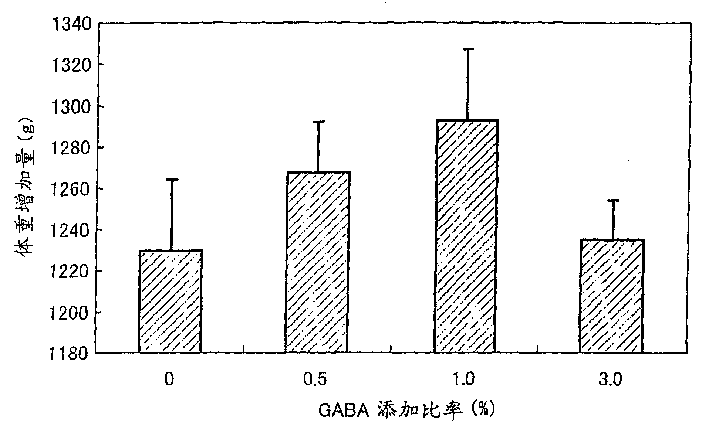
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Glutamate receptor antagonist" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An excitatory amino acid receptor antagonist, or glutamate receptor antagonist, is a chemical substance which antagonizes one or more of the glutamate receptors.
Method for treating tension-type headache
Tension-type headache is treated by interacting smith neuronal transmission in relation to pain in connection with headache in a way which prevents or decreases sensitization of second order nociceptive neurons. In particular, treatment is performed by administration of an effective amount of a substance which prevents or decreases central sensitization. Important examples of such substances are substances which interact with glutamate neurotransmission, such as glutamate receptor antagonists, such as NMDA receptor antagonists, such as MK-801 or Amitriptylline or Imipramine or Desipramine or Mirtazaprine or Venlafaxine. Other examples are substances which interact with nitric oxide, such as nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitors, such as L-NMMA or L-NAME or L-NIO or L-NNA. According to a broader aspect of the invention tension-type headache is treated by administration of substances which are effective in preventing or decreasing pain in connection with tension-type headache, such as the substances mentioned above. An additional aspect of the invention relates to treatment of tension-type headache by administration of substances which substantially inhibit the activity of nitric oxide synthase (NOS), such as NOS inhibitors, such as L-NMMA or L-NAME or L-NIO or L-NNA.
Owner:NEURAXON INC
Methods of treating tardive dyskinesia and other movement disorders
InactiveUS7498361B2Decreases postsynaptic responseSpread the wordBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsNR1 NMDA receptorAcamprosate
The present invention describes a novel treatment for movement disorders, including tardive dyskinesia, tic disorders, Tourette's syndrome, and blepharospasm, and other focal dystonias. The treatment of the present invention utilizes agents that simultaneously act as NMDA-type glutamate receptor antagonists and GABA-A receptor agonists. Preferably these two activities are characteristic of a single agent, for example acamprosate. Alternatively, separate agents having these activities can be combined and administered together. The invention also provides a third agent that acts as a non-competitive NMDA-receptor blocking agent or ion channel blocker that augments the effect of the primary treatment. A particularly preferred ion channel blocking agent is magnesium. Alternatively, magnesium can be administered alone for prevention and treatment of movement disorders.
Owner:SYNCHRONEURON
Glutamate receptor antagonists and methods of use
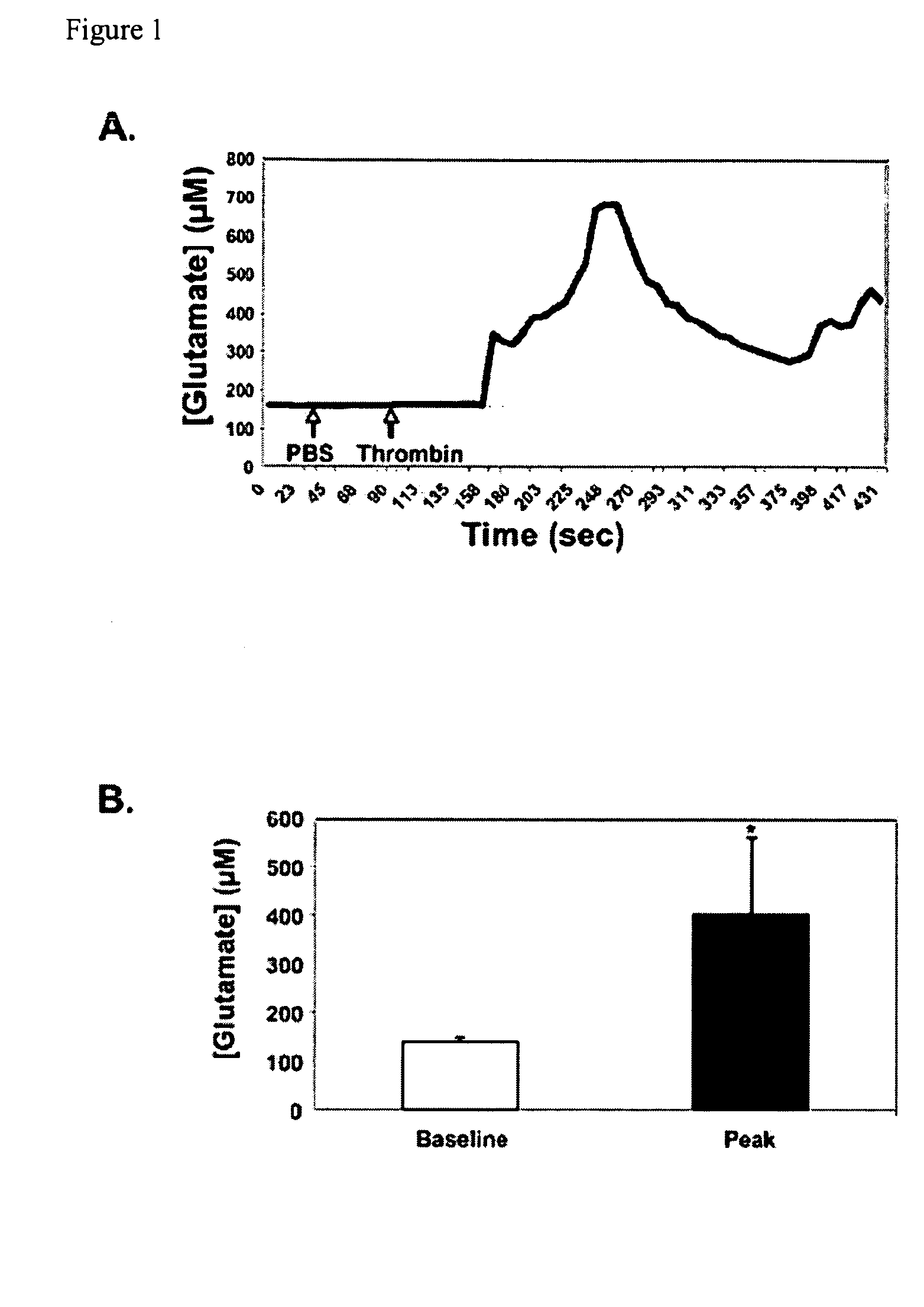
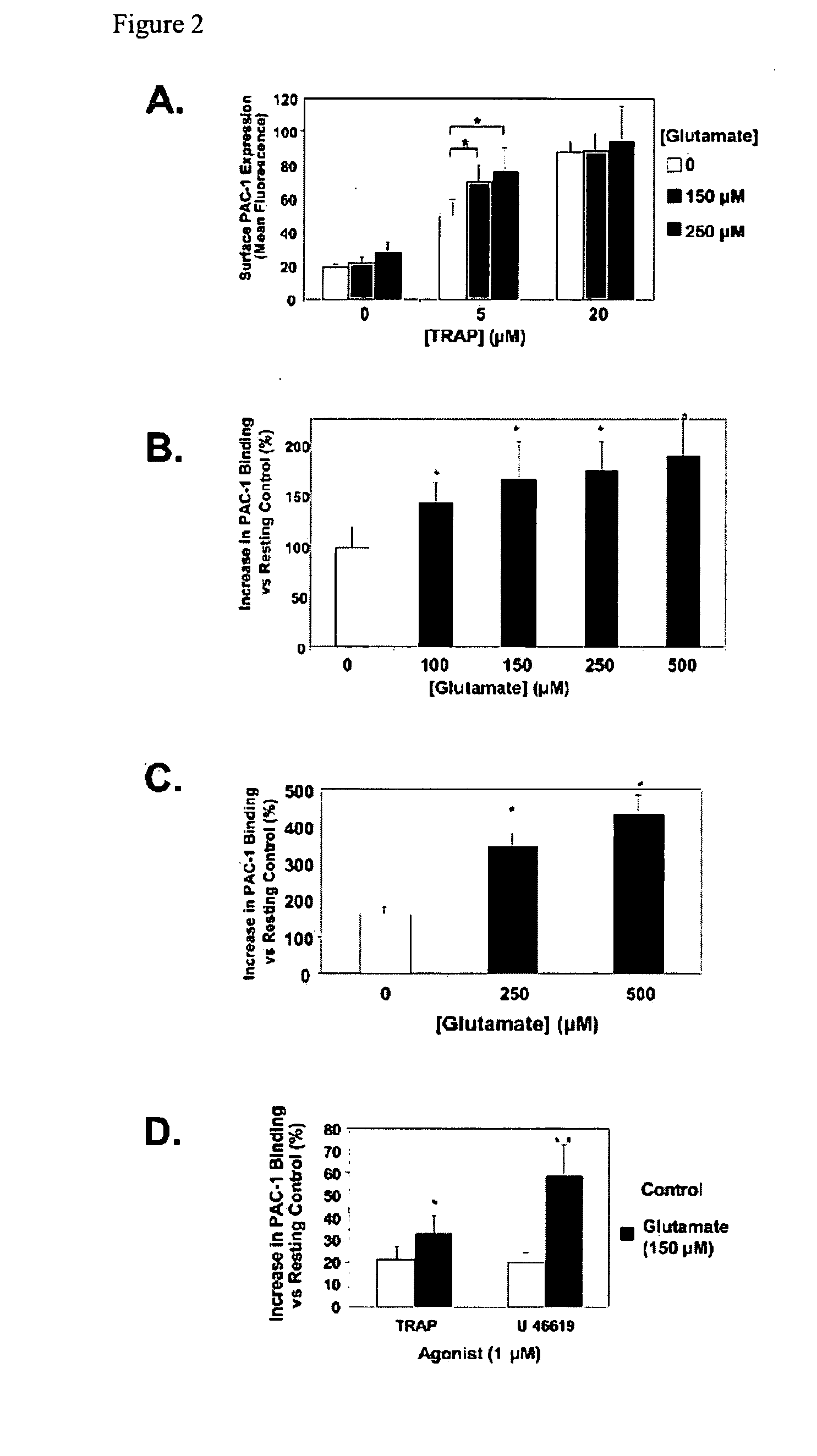
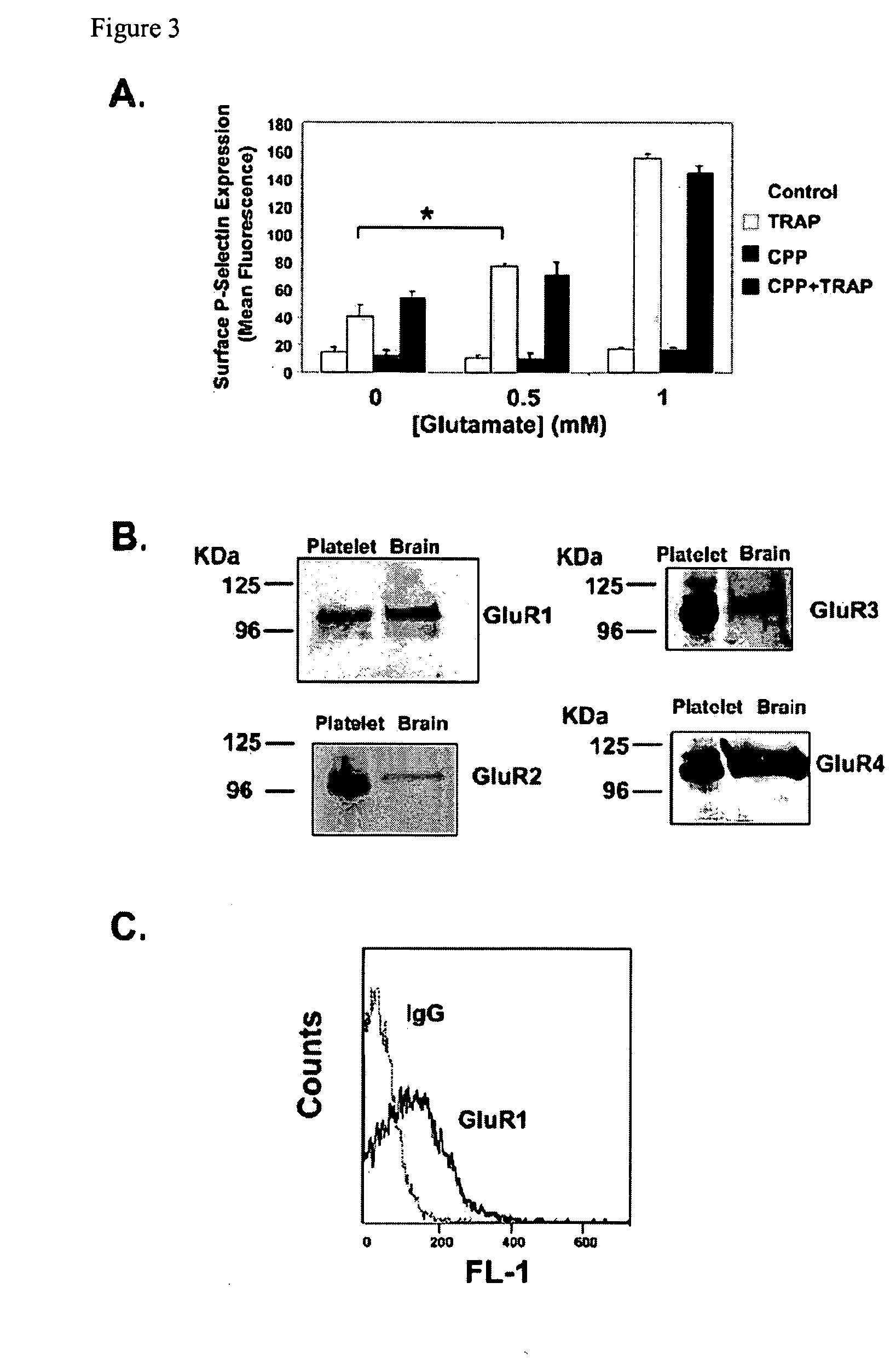
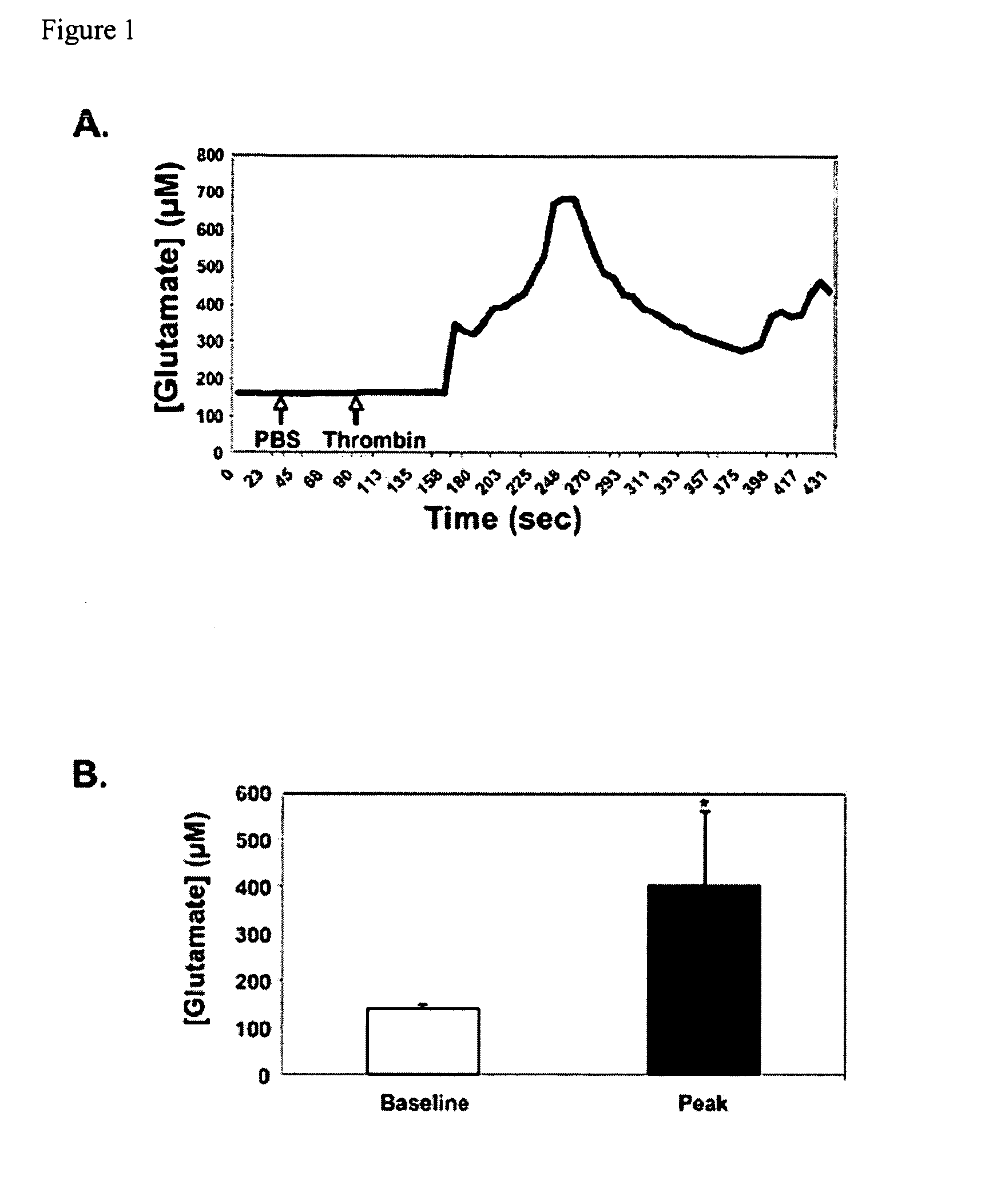
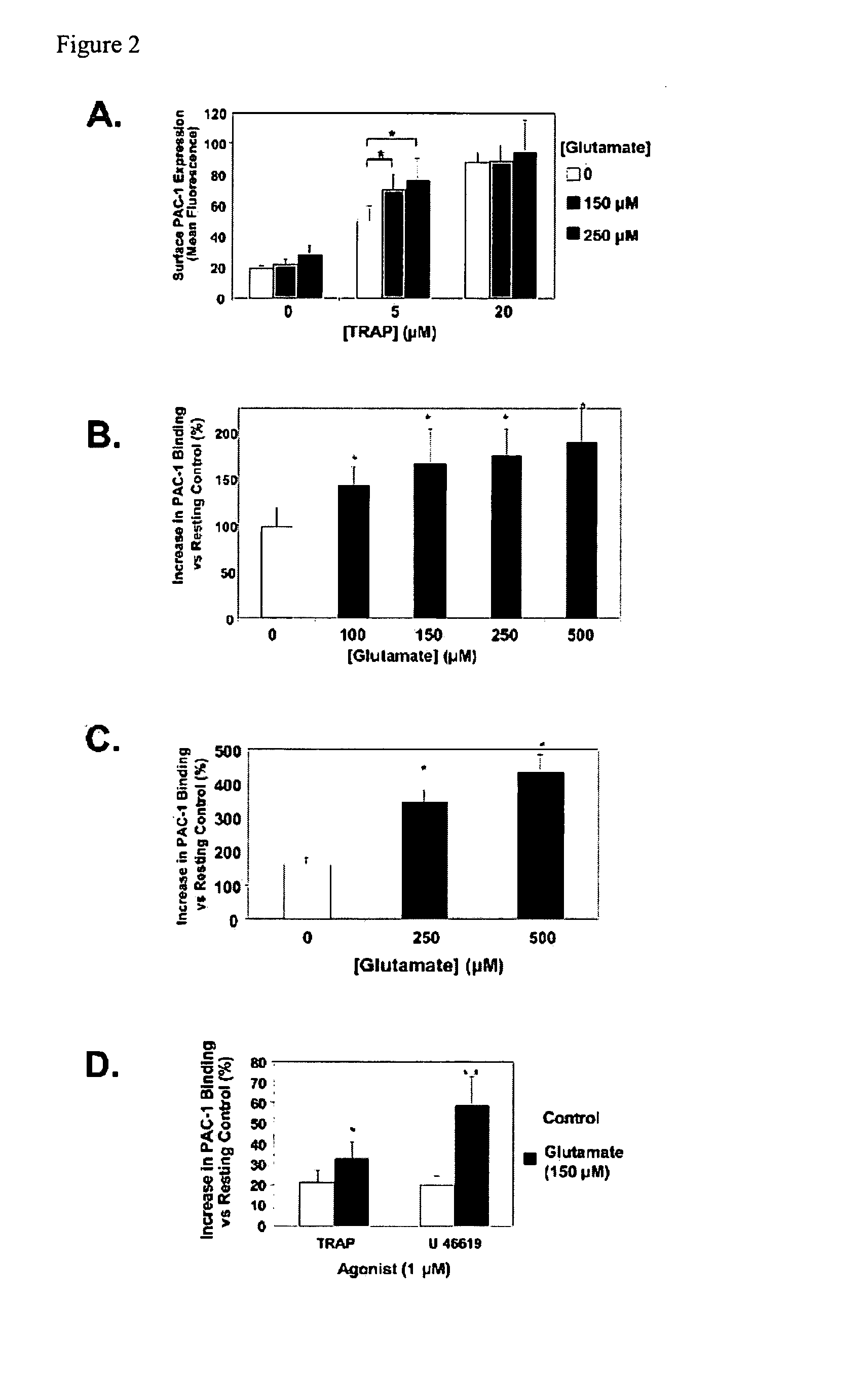
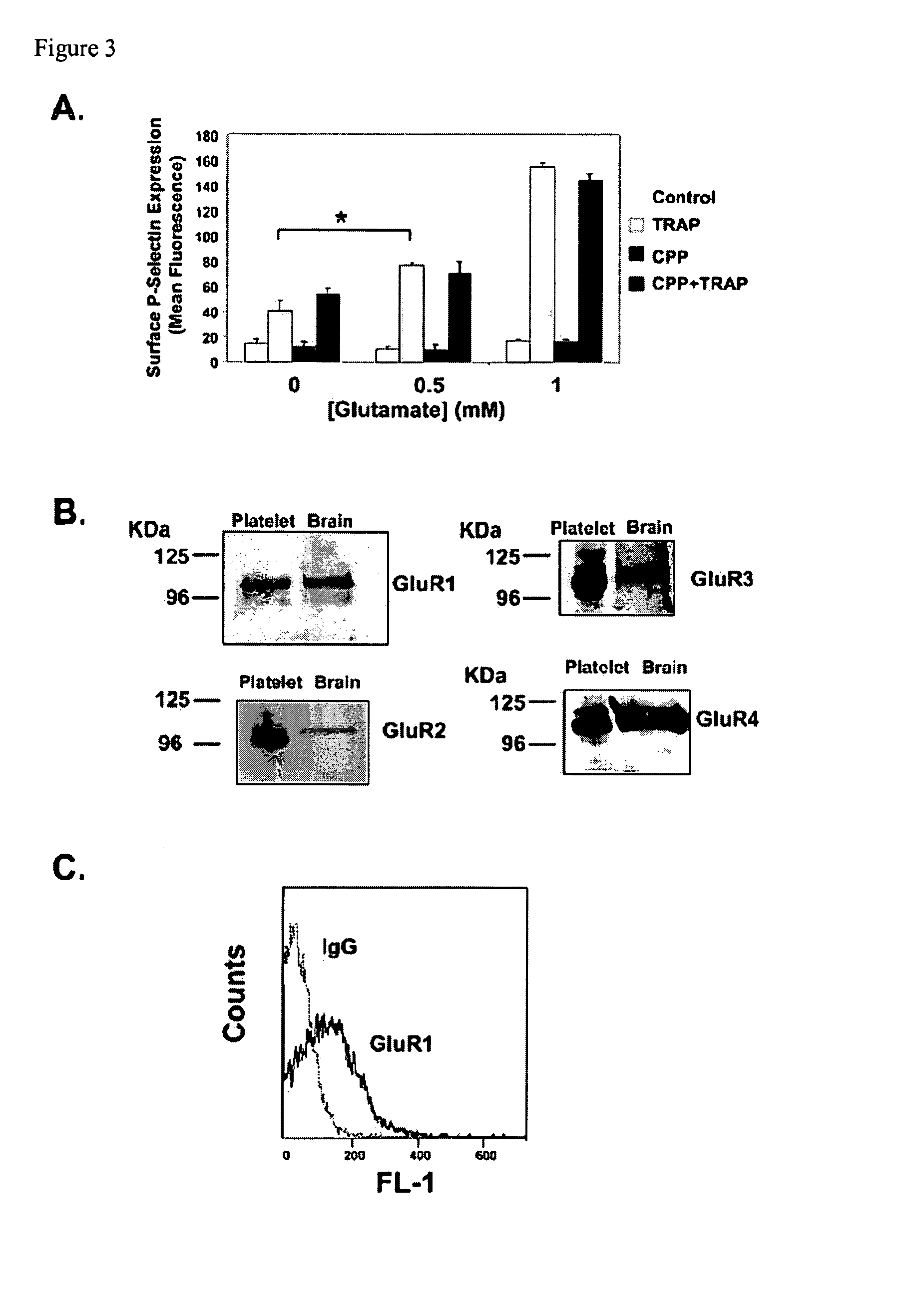
ActiveUS20100196354A1Modulate platelet activityModulate thrombosisCompound screeningBiocidePlateletGlutamate receptor antagonist
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for modulating platelet activity by inhibiting or activating glutamate receptors. The invention further relates to preventing or treating thrombotic diseases.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Compositions and methods employing NMDA antagonists for achieving an anesthetic-sparing effect
InactiveUS20090061024A1Enhanced cardiopulmonaryReduce concentrationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideGlutamate receptor antagonistReceptor antagonist
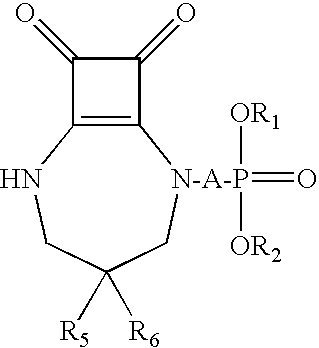
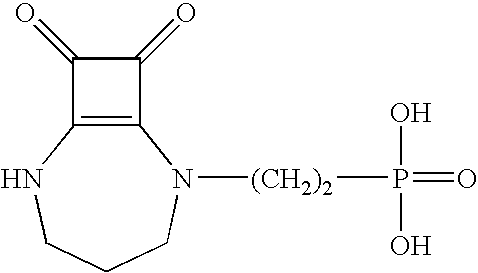
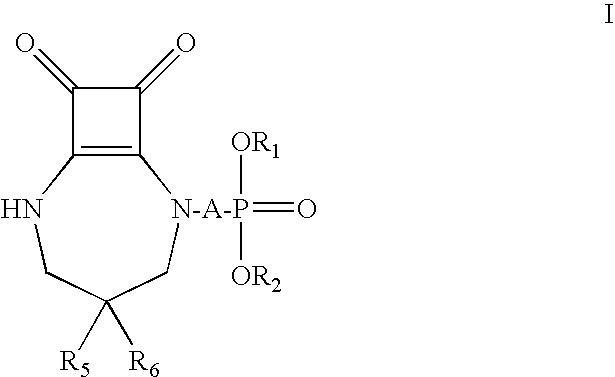
Provided herein are compositions, combinations, and methods comprising NMDA antagonists including, but not limited to, NMDA glutamate receptor antagonists such as [2-(8,9-dioxo-2,6-diazabicyclo[5.2.0]non-1-(7)-en-2-yl)alkyl]phosphonic acid and derivatives thereof, which are effective in reducing the amount of anesthetic required to maintain anesthesia (i.e. to achieve an anesthetic-sparing effect).
Owner:WYETH LLC
Methods of treating tardive dyskinesia and other movement disorders
InactiveUS20060128802A1Enhances GABA-A transmissionDecreased cellular responseBiocideAnimal repellantsNR1 NMDA receptorAcamprosate
The present invention describes a novel treatment for movement disorders, including tardive dyskinesia, tic disorders, Tourette's syndrome, and blepharospasm, and other focal dystonias. The treatment of the present invention utilizes agents that simultaneously act as NMDA-type glutamate receptor antagonists and GABA-A receptor agonists. Preferably these two activities are characteristic of a single agent, for example acamprosate. Alternatively, separate agents having these activities can be combined and administered together. The invention also provides a third agent that acts as a non-competitive NMDA-receptor blocking agent or ion channel blocker that augments the effect of the primary treatment. A particularly preferred ion channel blocking agent is magnesium. Alternatively, magnesium can be administered alone for prevention and treatment of movement disorders.
Owner:SYNCHRONEURON
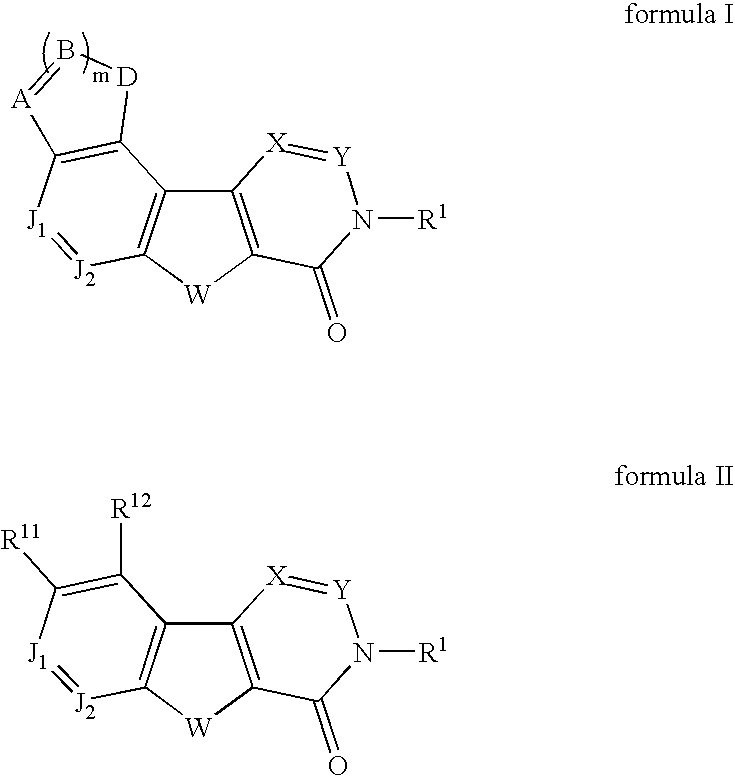
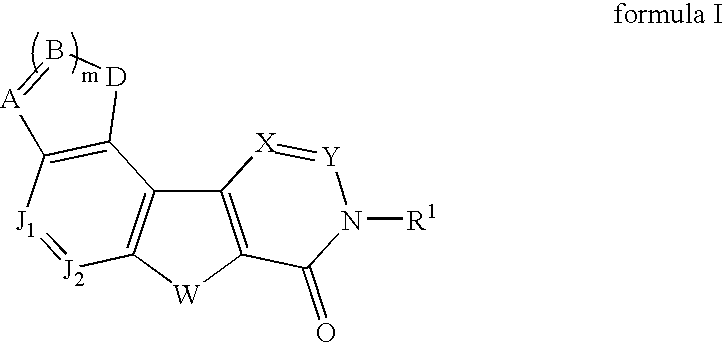
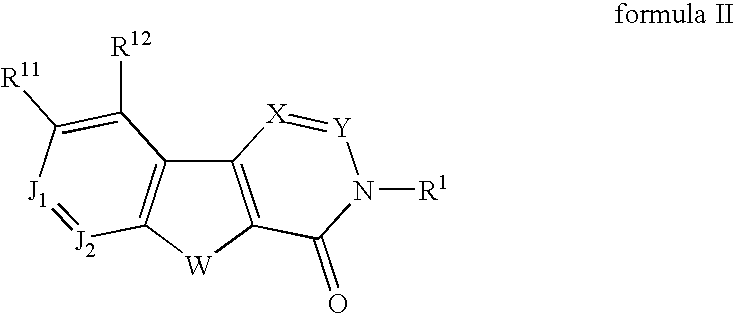
Fused tetracyclic mglur1 antagonists as therapeutic agents
In its many embodiments, the present invention provides tetracyclic compounds of formula I or formula II (wherein the various moieties are as defined herein) useful as metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR) antagonists, particularly as selective metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 antagonists, pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds, and methods of treatment using the compounds and compositions to treat diseases associated with metabotropic glutamate receptor (e.g., mGluR1) such as, for example, pain, migraine, anxiety, urinary incontinence and neurodegenerative diseases such Alzheimers disease.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
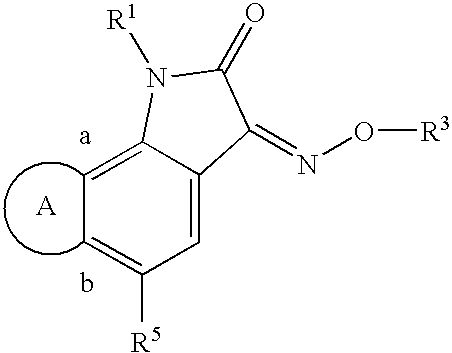
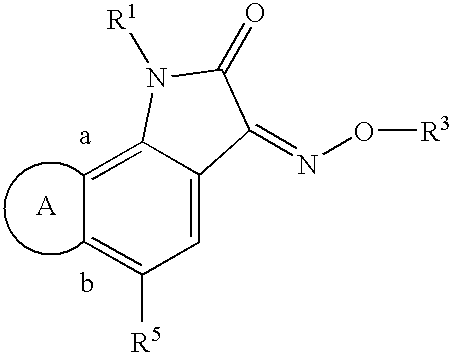
Indole-2,3-dione-3-oxime derivatives
Indole-2,3-dione-3-oxime derivatives, for instance compounds represented by the formulaare capable of antagonizing the effect of excitatory amino acids, such as glutamate. Also disclosed are methods of preparing the compounds, pharmaceutical compositions comprising them, and methods of treatment of disorders or diseases which are responsive to excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists.
Owner:NEUROSEARCH AS
Heteropolycyclic compounds and their use as metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists
Compounds of formula (II), wherein X, Y, and Z are independently selected from N, O, S, C, and CO, and at least one of X, Y, and Z is a heteroatom; Ar1 and Ar2 are independently selected from heterocycles base or fused heterocyclyl and aryl groups; the compounds act as metallotropic glutamate receptor antagonists and can be used to treat neurological diseases and disorders.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists for treating central nervous system disease
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
New itch treatment using a combination of neurokinin-1, gastrin releasing peptide, and glutamate receptor antagonists
InactiveUS20150320827A1Avoid spreadingReduce excitementBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGastrin-releasing peptideNK1 receptor antagonist
Methods, and compositions are provided for inhibition of histamine and non-histamine dependent itch signal transmission or scratch behavior. In one aspect, the present invention further comprises administering to the subject an inhibitor of histamine-dependent itch signal transmission. In some cases, the inhibitor of histamine independent itch signal transmission comprises an NK-1 receptor antagonist or the inhibitor of histamine independent itch signal transmission comprises a GRP receptor antagonist. In some cases, the method comprises administering two inhibitors of histamine independent itch signal transmission. For example, the inhibitors of histamine independent itch signal transmission can comprise an NK-1 receptor antagonist and a GRP receptor antagonist. In another embodiment, the invention provides a method of treating itch comprising administering to a subject suffering from itch an NK-1 receptor antagonist, a GRP receptor antagonist.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Heteropolycyclic compounds and their use as metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists
Compounds of formula (II), wherein X, Y, and Z are independently selected from N, O, S, C, and CO, and at least one of X, Y, and Z is a heteroatom; Ar 1 and Ar 2 Independently selected from heterocyclyl or fused heterocyclyl and aryl groups; the compounds act as metallotropic glutamate receptor antagonists and are useful in the treatment of neurological diseases and disorders. ∴
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Model for neurodegenerative diseases involving amyloid accumulation
The present invention provides brain cells, such as normal brain cells, apolipoprotein E deficient brain cells, or apoE4 containing brain cells, that are treated with a compound which can modulate integrins and / or integrin receptors to produce increased sequestration of and / or accumulation of and / or uptake of Aβ, and / or changes in cathepsin D content and / or lysosomal dysfunction, and / or microglia activation in the brain cells. The present invention also provides methods for producing such cells and methods for using the cells for screening an agent or substance that modulates the sequestration of and / or accumulation of and / or uptake of Aβ, and / or lysosomal dysfunction, and / or changes in cathepsin D content and / or microglia activation in the brain cells. The method further provides a new therapeutic target, antagonism of glutamate receptors, for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases which are characterized by inter alia, abnormal amyloid uptake and / or accumulation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
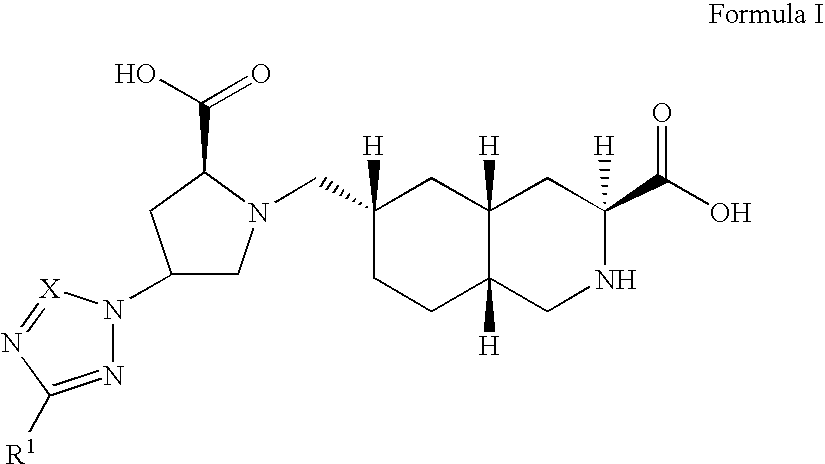
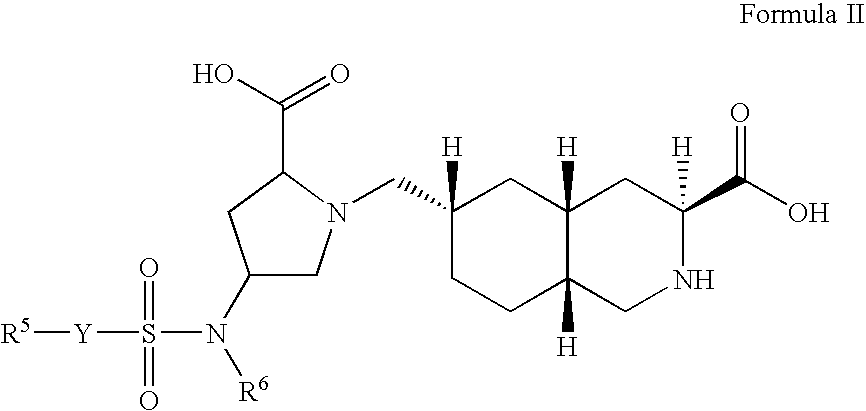
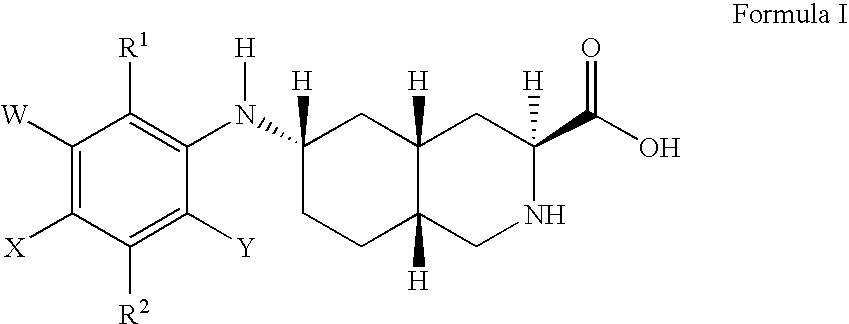
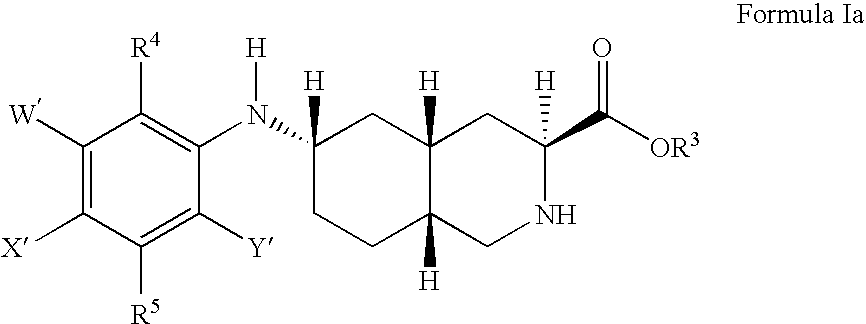
Excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists
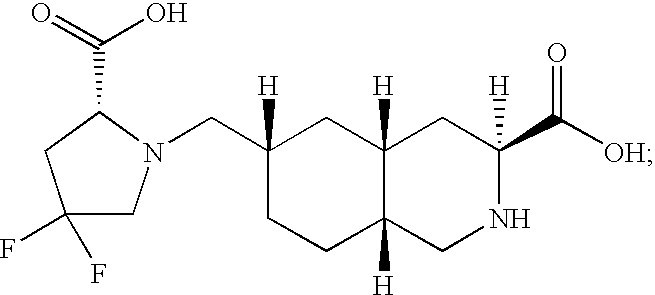
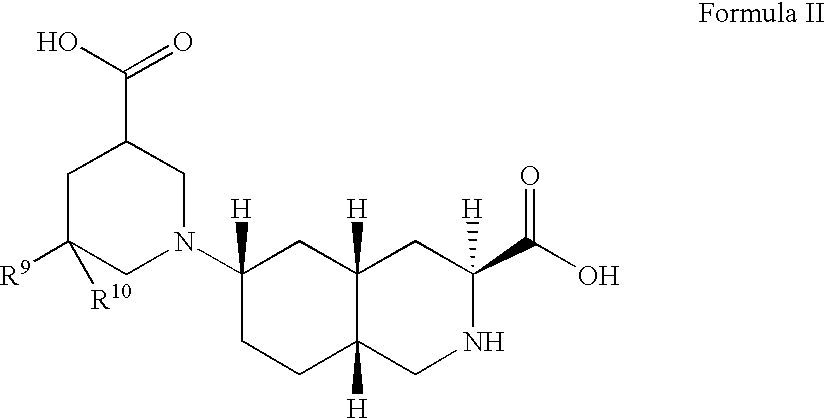
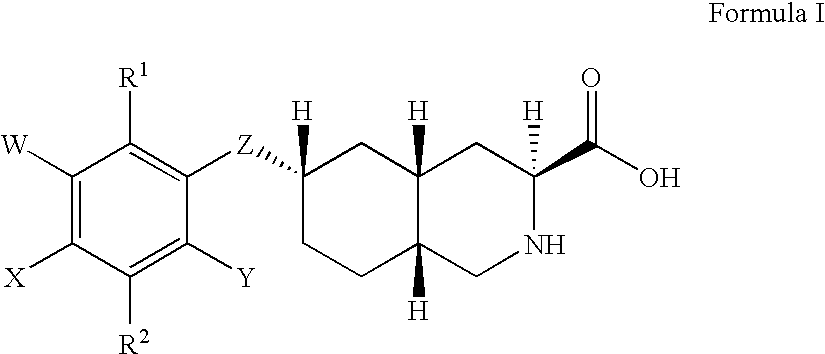
The present invention provides novel compounds of Formula I or Formula II, or the pharmaceutically acceptable salts or prodrugs thereof, pharmaceutical compositions comprising an effective amount of a compound of Formula I or Formula II in combination with a suitable carrier, diluent, or excipient, and methods for treating neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases, particularly pain and migraine.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Glutamate receptor antagonists and methods of use
ActiveUS8603980B2Modulate platelet activityImprove the level ofBiocideCompound screeningPlateletGlutamate receptor antagonist
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for modulating platelet activity by inhibiting or activating glutamate receptors. The invention further relates to preventing or treating thrombotic diseases.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists
The present invention provides novel compounds of Formula I or Formula II, or the pharmaceutically acceptable salts or prodrugs thereof, pharmaceutical compositions comprising an effective amount of a compound of Formula I or Formula II in combination with a suitable carrier, diluent, or excipient, and methods for treating neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases, particularly pain and migraine.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Ntranasal dantrolene administration for treatment of alzheimer's disease
PendingUS20220354827A1Reduce releaseImproving and slowing declineOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderRyanodine receptorSynaptogenesis
Methods for inhibiting impaired neurogenesis and / or synaptogenesis in neurons in a subject with or suspected of having Alzheimer's Disease (AD), methods for improving and / or slowing the decline of cognitive function after onset of neuropathology and cognitive dysfunction, which neuropathology and cognitive dysfunction are caused by AD, methods for improving and / or slowing the decline of memory before onset of symptoms of AD, methods for increasing concentration and duration of dantrolene in the brain, and methods for improving and / or slowing the decline of memory after onset of symptoms of AD, the methods comprising intranasally administering to a subject in need thereof an amount of a pharmaceutical composition comprising dantrolene effective to inhibit over-activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMVDA) receptor and / or ryanodine receptor (RyR). Methods further comprise administering a therapeutically effective amount of a glutamate receptor antagonist to the subject.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Determining the effect of a substance on sequestration, uptake, and accumulation of amyloid in brain cells
InactiveUS7186521B2Avoiding characteristicApolipeptidesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroglial cell activationLysosome
The present invention provides brain cells, such as normal brain cells, apolipoprotein E deficient brain cells, or apoE4 containing brain cells, that are treated with a compound which can modulate integrins and / or integrin receptors to produce increased sequestration of and / or accumulation of and / or uptake of Aβ, and / or changes in cathepsin D content and / or lysosomal dysfunction, and / or microglia activation in the brain cells. The present invention also provides methods for producing such cells and methods for using the cells for screening an agent or substance that modulates the sequestration of and / or accumulation of and / or uptake of Aβ, and / or lysosomal dysfunction, and / or changes in cathepsin D content and / or microglia activation in the brain cells. The method further provides a new therapeutic target, antagonism of glutamate receptors, for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases which are characterized by inter alia, abnormal amyloid uptake and / or accumulation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Epilepsy treatment agent
ActiveUS20210000771A1Remarkable antiepileptic effectUseful in therapyNervous disorderAmide active ingredientsDihydropyridineSulfanilamide
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Chemically modified AMPA receptor RNA aptamers
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
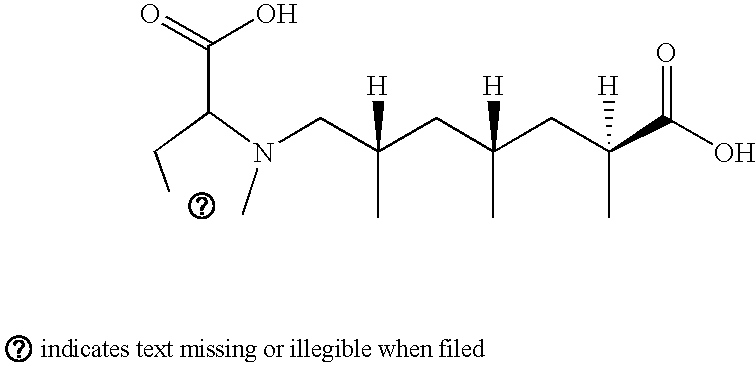
Amino acid derivatives of substituted quinexaline 2,3-dione derivatives as glutamate receptor antagonists
A novel series of substituted quinoxaline 2,3-diones useful as neuroprotective agents are taught. Novel intermediates, processes of preparation, and pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds are also taught. The compounds are glutamate antagonists and are useful in the treatment of stroke, cerebral ischemia, or cerebral infarction resulting from thromboembolic or hemorrhagic stroke, cerebral vasospasms, hypoglycemia, cardiac arrest, status epilepticus, perinatal asphyxia, anoxia, Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's diseases.
Owner:WARNER-LAMBERT CO
Epilepsy treatment agent
PendingCN111801096ASignificant antiepileptic effectNervous disorderAmide active ingredientsPhenyl groupPharmacology
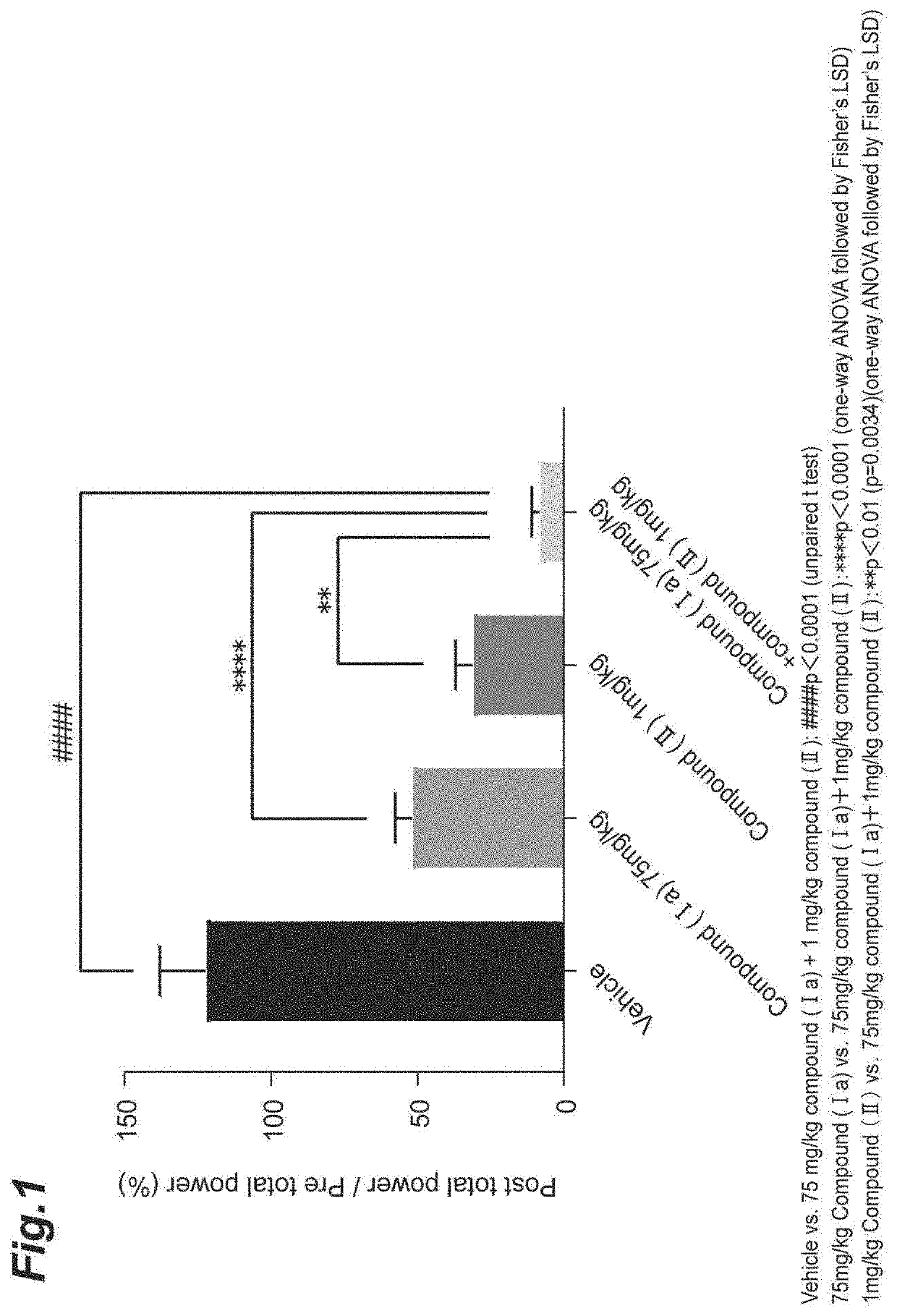
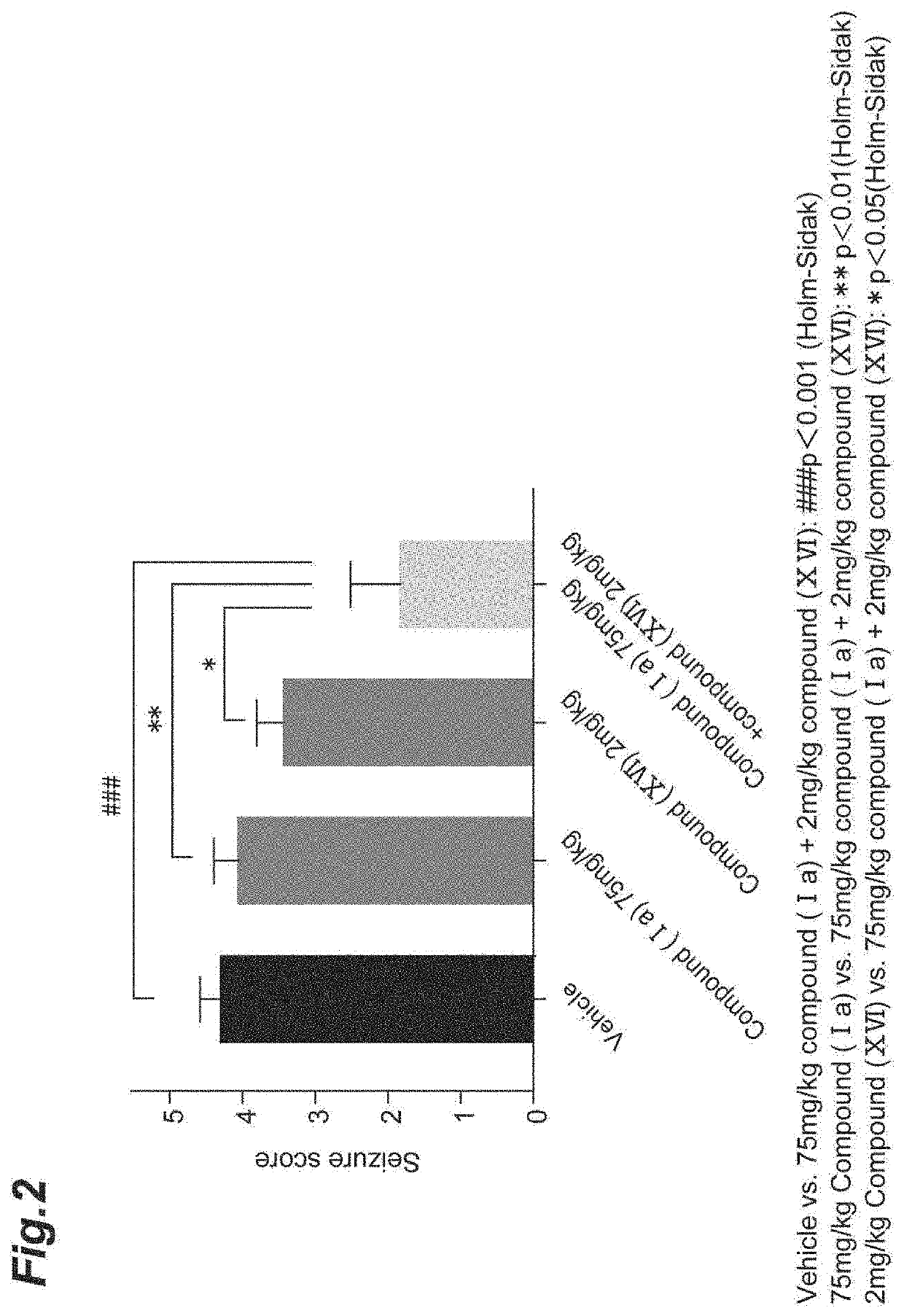
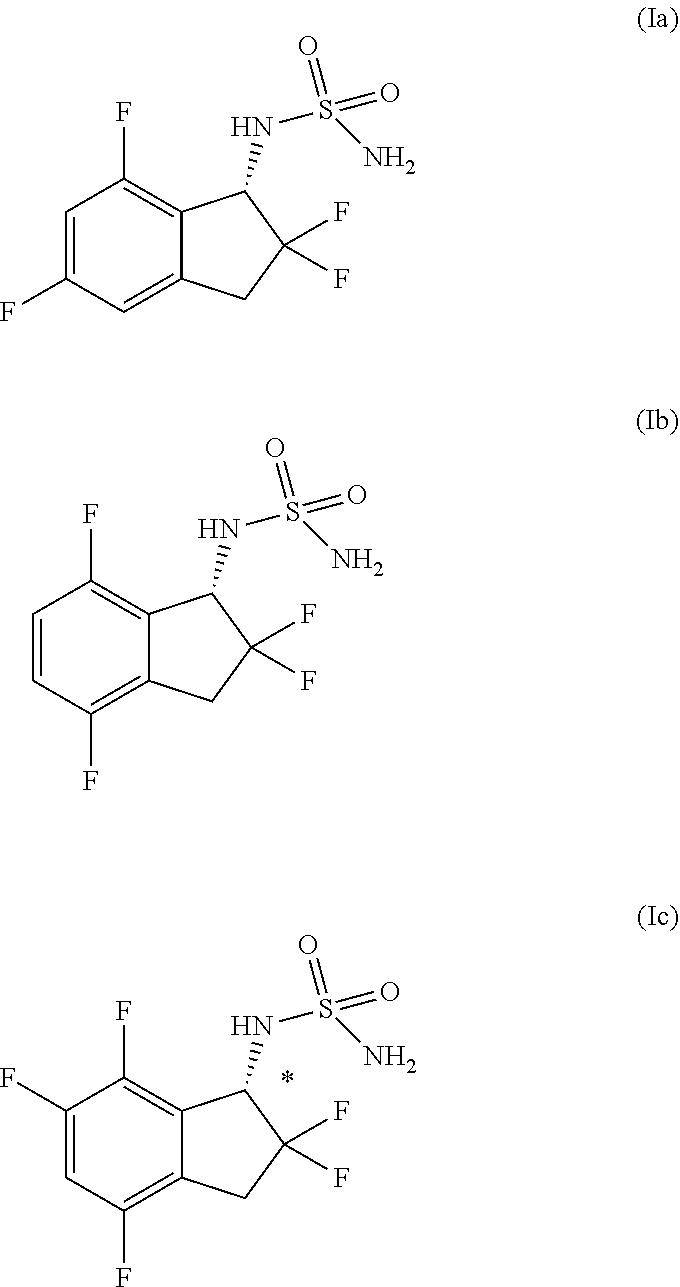
Provided is a combination agent that combines N-[(1S)-2,2,5,7-tetrafluoro-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-yl]sulfamide with an AMPA-type glutamate receptor antagonist such as 3-(2-cyanophenyl)-5-(2-pyridyl)-1-phenyl-1,2-dihydropyridine-2-one or 2-fluoro-6-(3-fluoro-8-oxo-7-(pyridin-3-yl)-7,8-dihydro-6H-pyrano[3,2-b:5,4-b']dipyridin-9-yl]benzonitrile and that can be possibly used as an epilepsy treatment agent.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Chemically modified ampa receptor RNA aptamers
Disclosed is an RNA aptamer, a synthetic oligonucleotide of 2′-fluoro-modified A, U, and C nucleotides, with improved stability compared to its unmodified counterpart. Like the unmodified aptamer, however, the modified version is a potent glutamate receptor antagonist. Additionally, the RNA aptamers described herein are water soluble by nature, and generally exhibit nano- to micromolar potency making them potential therapeutic agents for the treatment of neurological disorders involving glutamate receptor activity.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
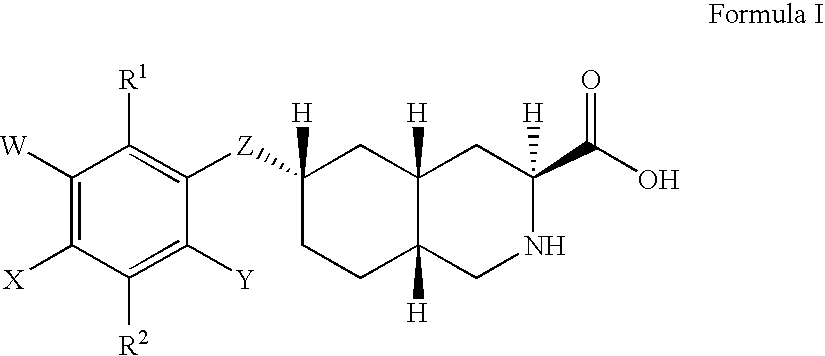
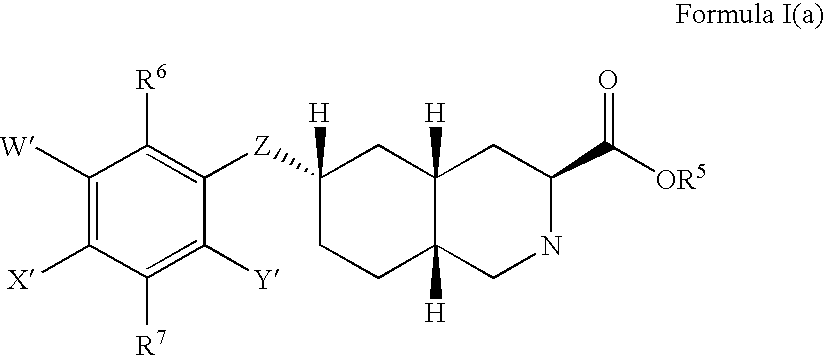
Excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists
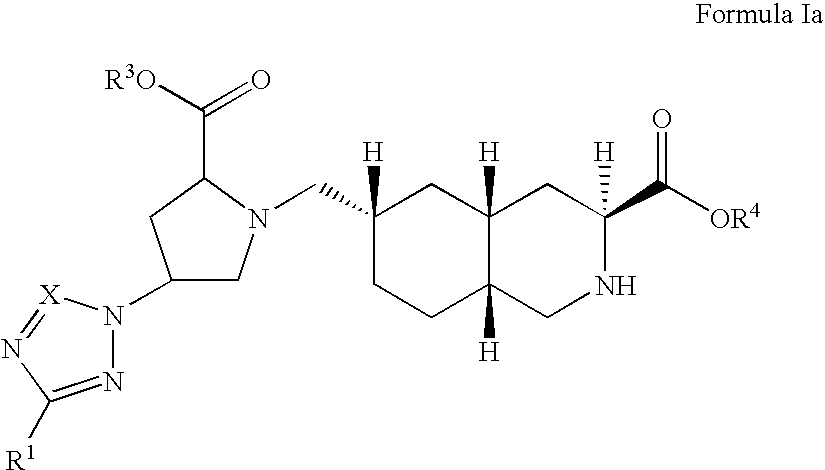
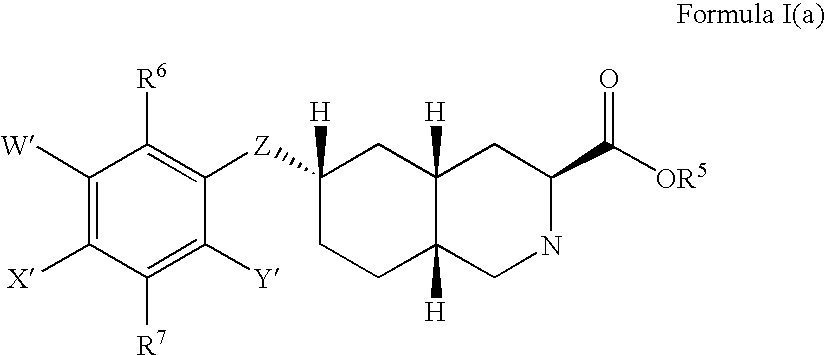
The present invention provides novel compounds of Formula (I) and Formula (I(a)), or the pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof; methods for treating neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases, particularly pain and migraine, comprising administering a compound of Formula (I) or Formula (I(a)); and processes for preparing compounds of Formula (I) or Formula (I(a)).
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Method of fattening poultry
InactiveCN1617676AEffective in fatteningImprove efficiencyMetabolism disorderAnimal feeding stuffGlutamate receptor antagonistNeuron
The present invention provides a method for fattening poultry, which is characterized by administering a substance that inhibits motor neurons. Specifically, it provides administration of a substance selected from the group consisting of GABAB receptor agonists, GABAA receptor agonists, substances that enhance the action of GABAA receptors, and kainate-type glutamate receptor antagonists, or a combination thereof , or a method of fattening poultry by administering feed containing these substances or a composition thereof to poultry.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists
InactiveUS6855725B2Treating and preventing migraineBiocideNervous disorderMigraineGlutamate receptor antagonist
The present invention provides compounds of Formula I or Formula II, or the pharmaceutically acceptable salts or prodrugs thereof, pharmaceutical compositions comprising compounds or Formula I or Formula II, and methods for treating neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases, particularly migraine.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists
InactiveUS20060100237A1Treating and preventing painTreating and preventing and migraineBiocideOrganic chemistryNeuro-degenerative diseaseGlutamate receptor antagonist
The present invention provides novel compounds of Formula (I) and Formula (I(a)), or the pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof; methods for treating neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases, particularly pain and migraine, comprising administering a compound of Formula (I) or Formula (I(a)); and processes for preparing compounds of Formula (I) or Formula (I(a)).
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists
The present invention provides novel compounds of Formula (I), or the pharmaceutically acceptable salts or prodrugs thereof, and methods for treating neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases, particularly pain and migraine.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
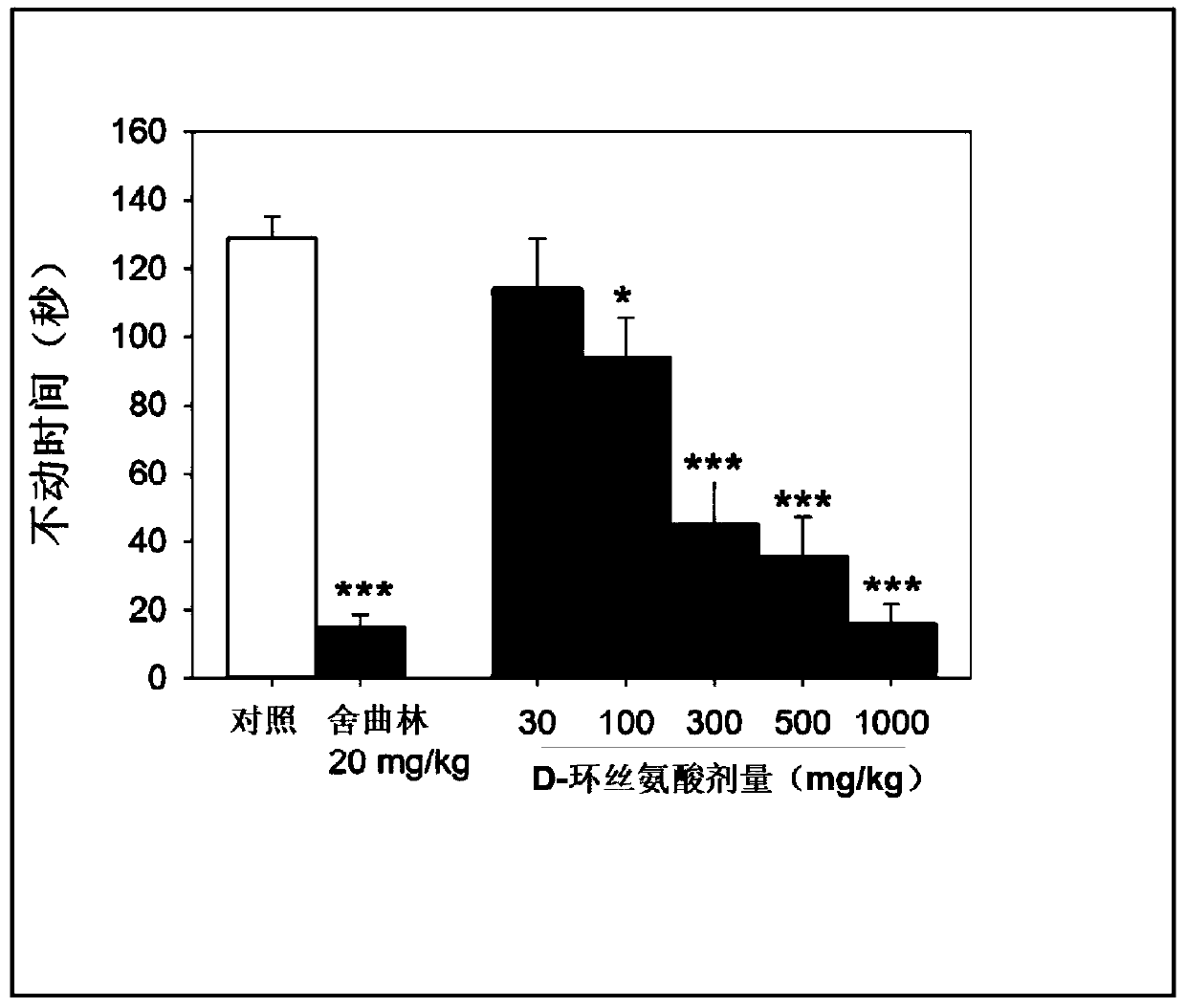
Combined therapy for n-methyl-d-aspartic acid receptor antagonist-responsive neuropsychiatric disorders
PendingCN110996947ANervous disorderHydroxy compound active ingredientsCompulsive disordersAspartic acid receptors
Described herein are compositions, including an oral dosage regimen, for the treatment of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor-related neuropsychiatric disorders such as depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder and that includes an N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor antagonist, such as D-cycloserine formulated to produce plasma levels in excess of 25 microgram / mL, combined with more recently developed antidepressants.
Owner:格莱泰施有限责任公司
Itch treatment using a combination of neurokinin-1, gastrin releasing peptide, and glutamate receptor antagonists
InactiveUS20180221435A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsGastrin-releasing peptideNK1 receptor antagonist
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Intranasal Dantroline Administration For The Treatment Of Alzheimer Disease
Methods for inhibiting impaired neurogenesis and / or synaptic occurrence in neurons of a subject suffering from or suspected of having Alzheimer's disease (AD), methods for ameliorating and / or slowing down a decline in cognitive function following the onset of neuropathology and cognitive dysfunction caused by AD, and methods for improving and / or slowing down a decline in cognitive function following the onset of neuropathology and cognitive dysfunction caused by AD. Methods for ameliorating and / or slowing memory decline prior to the onset of symptoms of AD, methods for increasing the concentration and duration of dantroline in the brain, and methods for ameliorating and / or slowing memory decline after the onset of symptoms of AD, comprising intranasally administering to a subject in need thereof an amount of a pharmaceutical composition, the pharmaceutical composition comprises dantrolin which is effective in inhibiting the excessive activation of the N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) receptor and / or the raney receptor (RyR). The method further comprises administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a glutamate receptor antagonist.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com