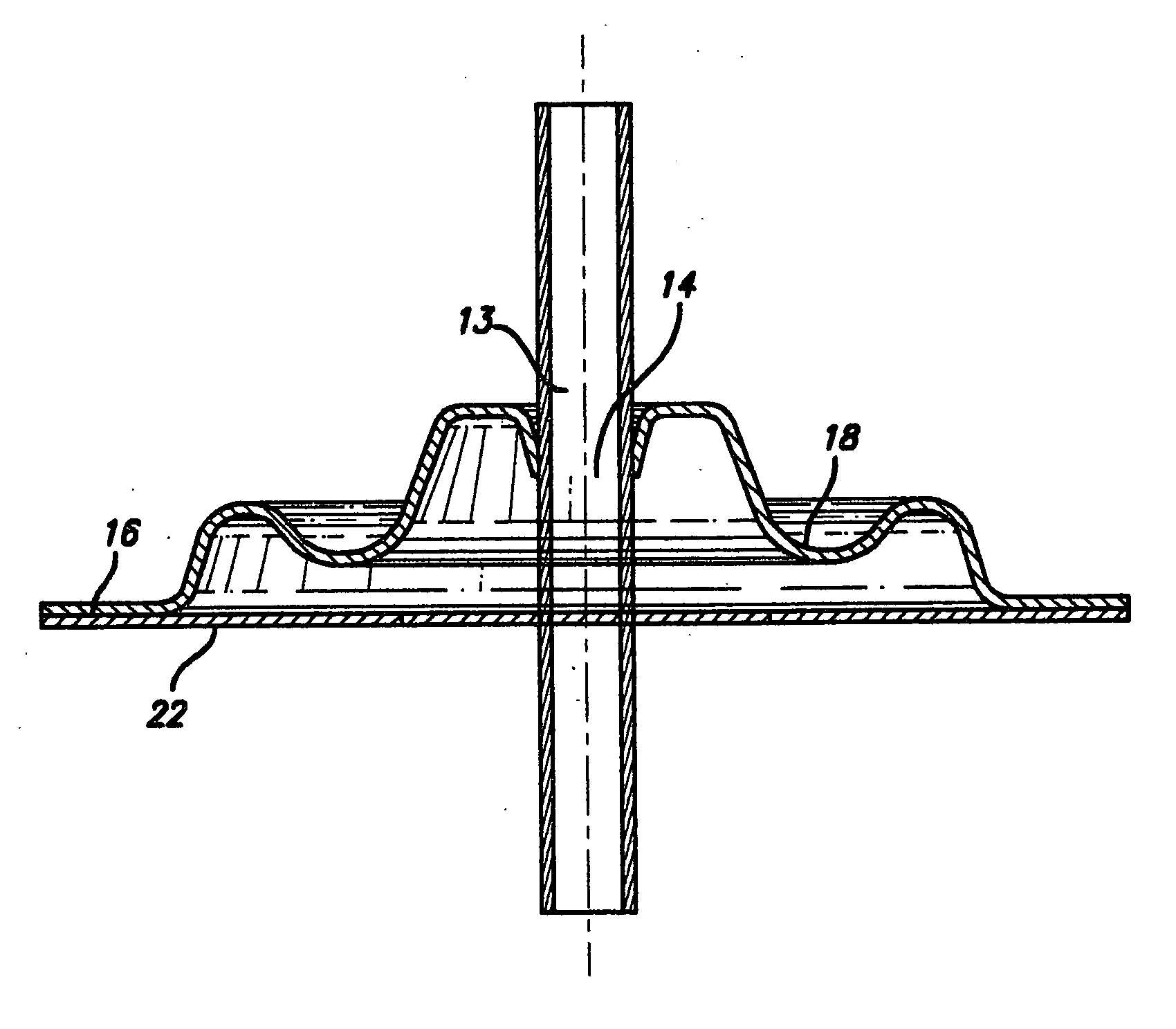
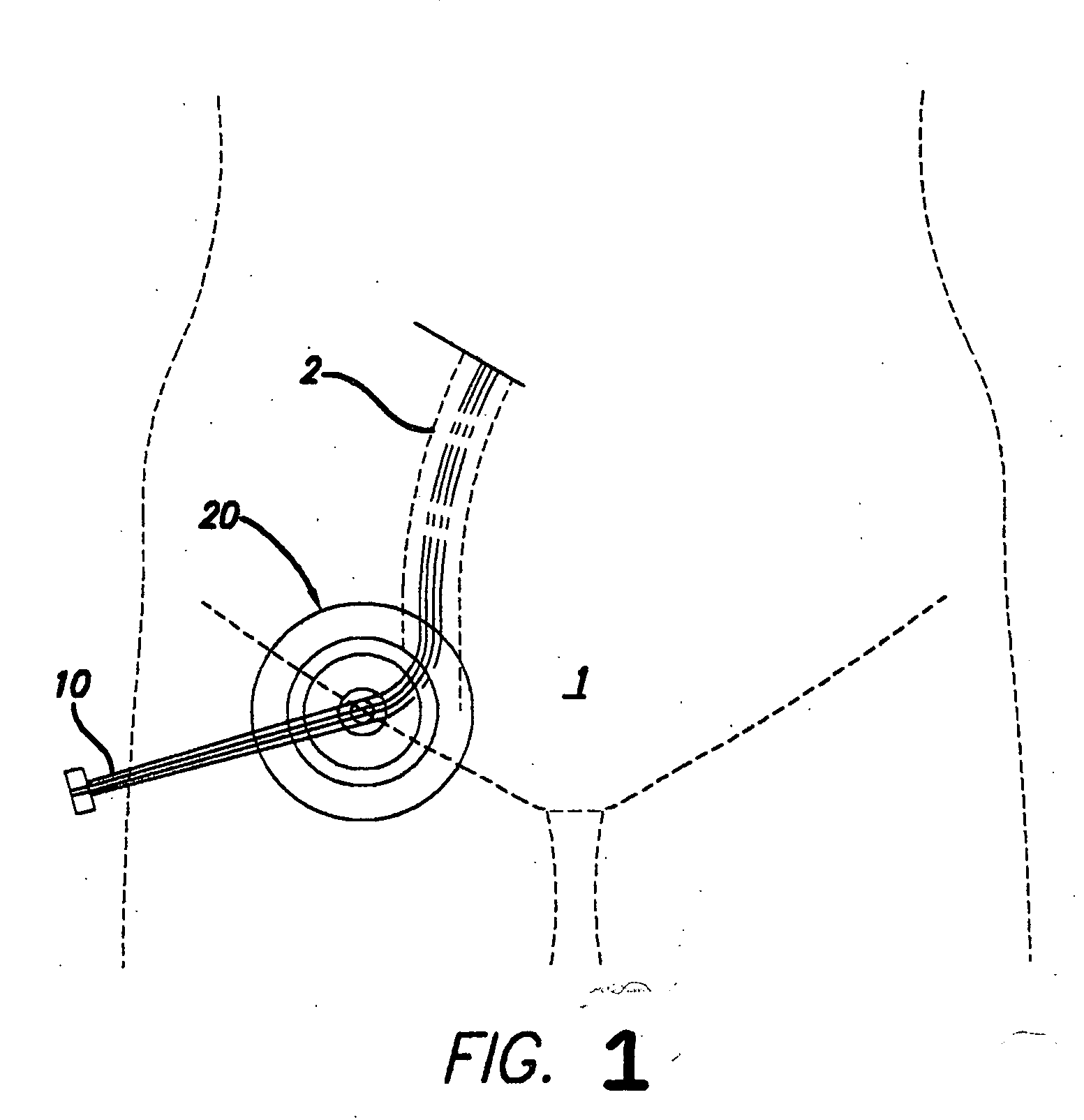
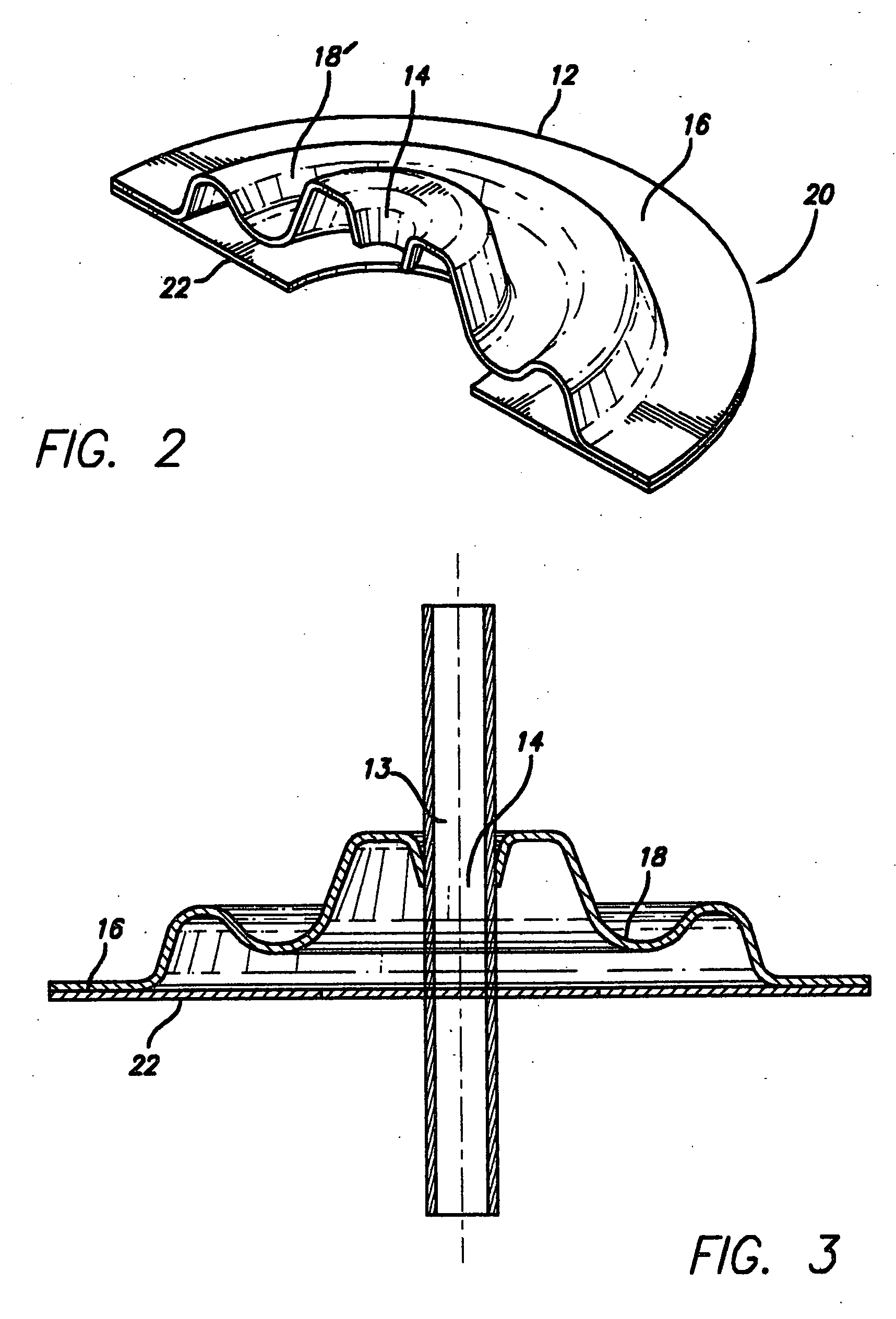
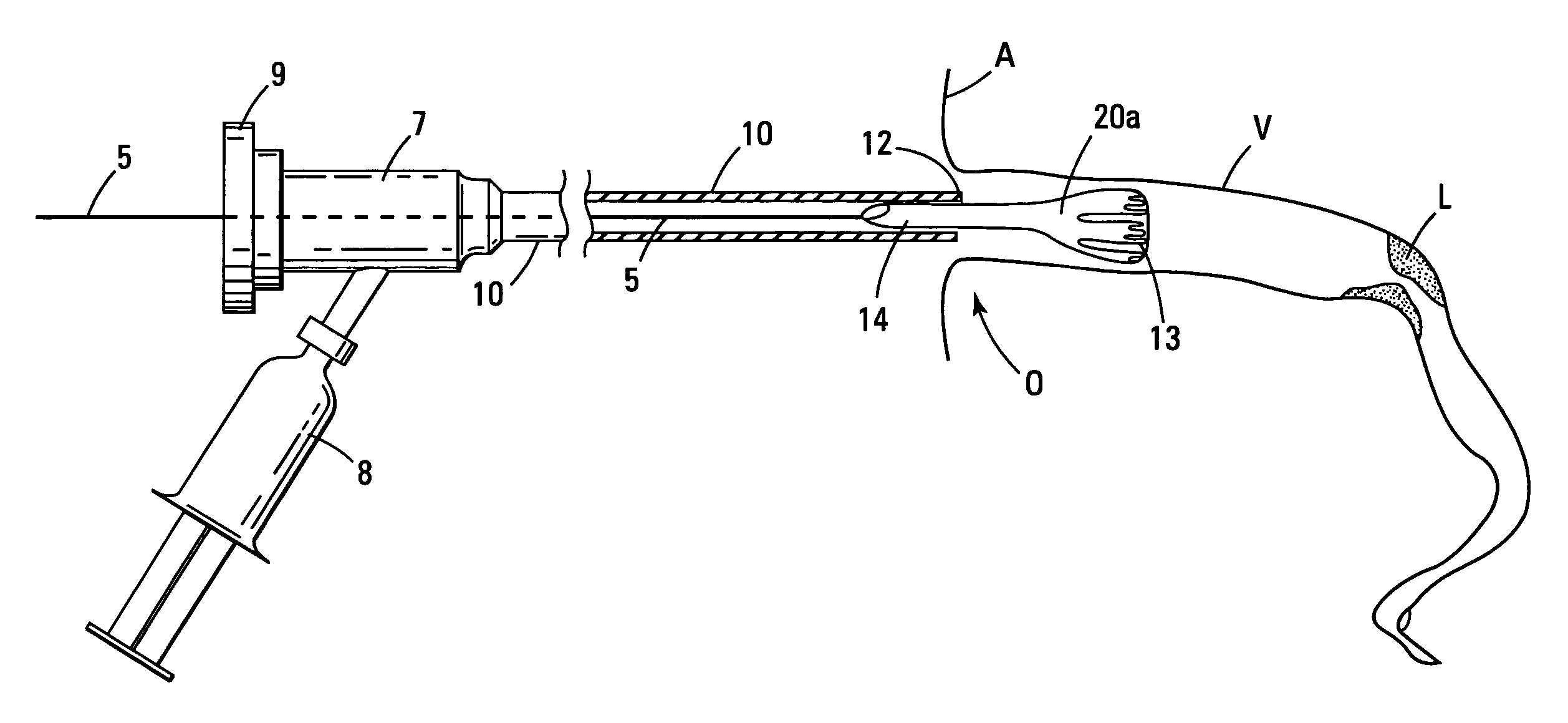
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
93 results about "Endovascular surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
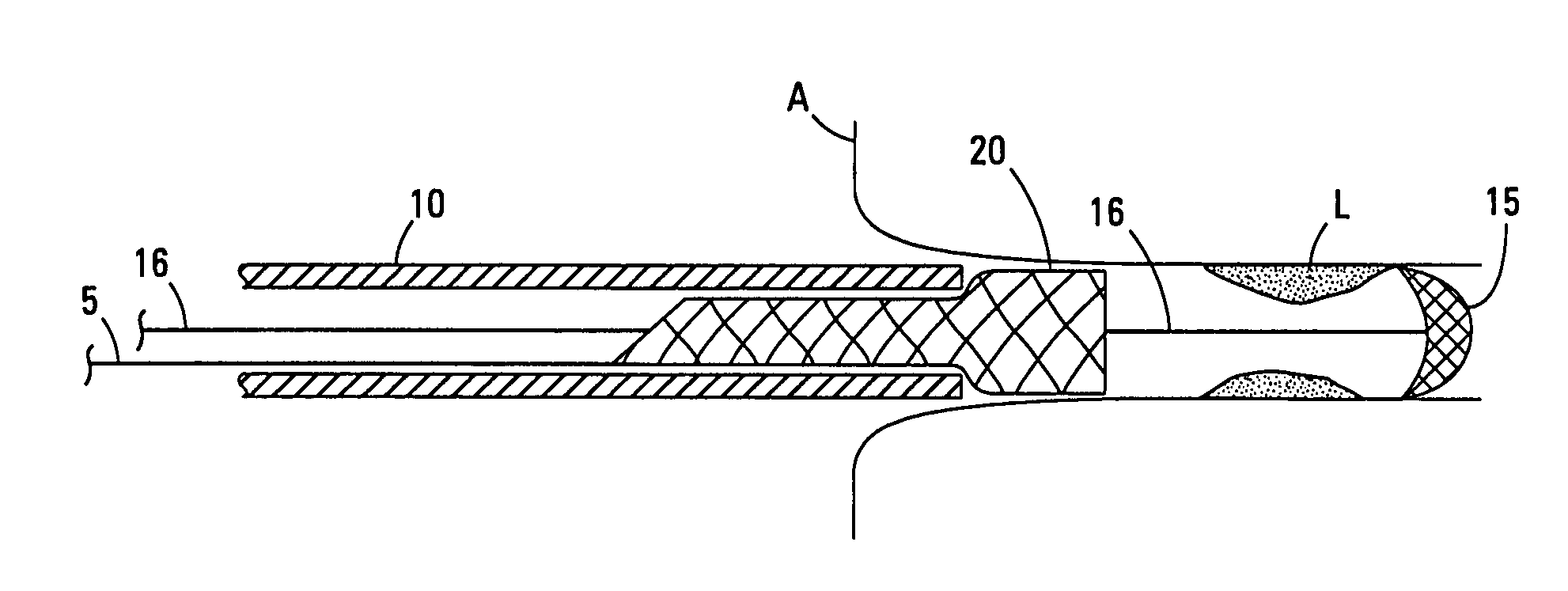
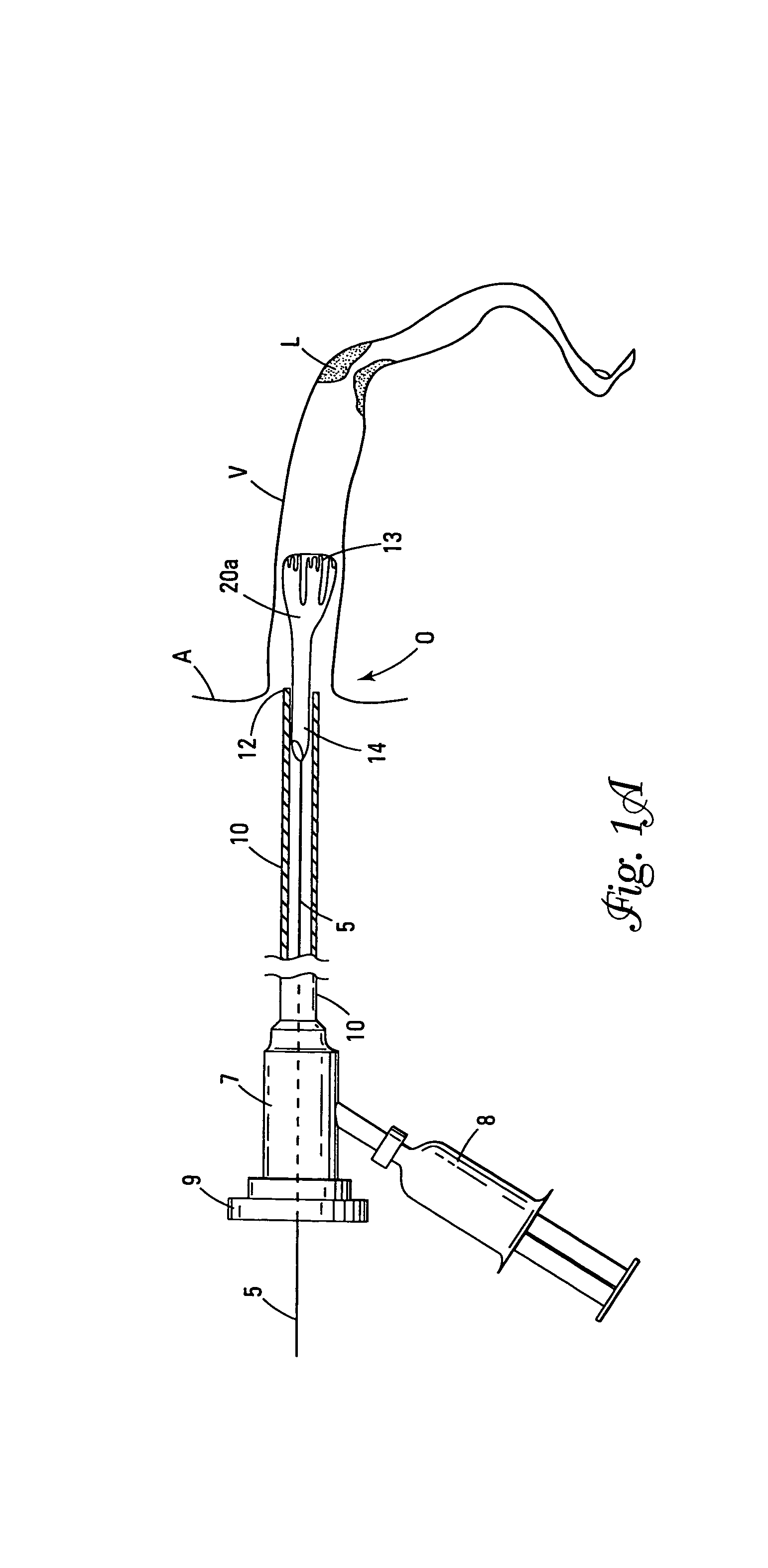
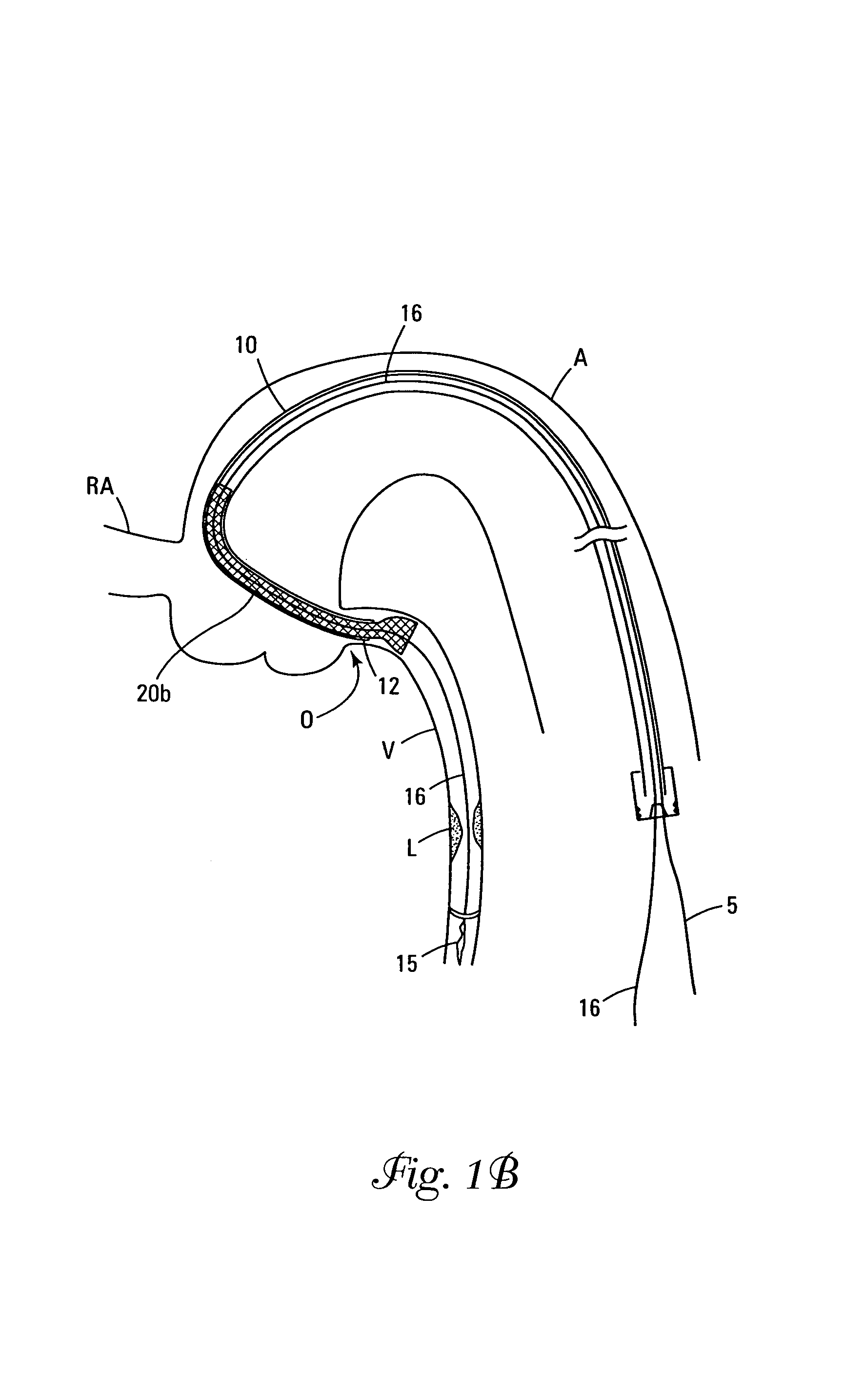
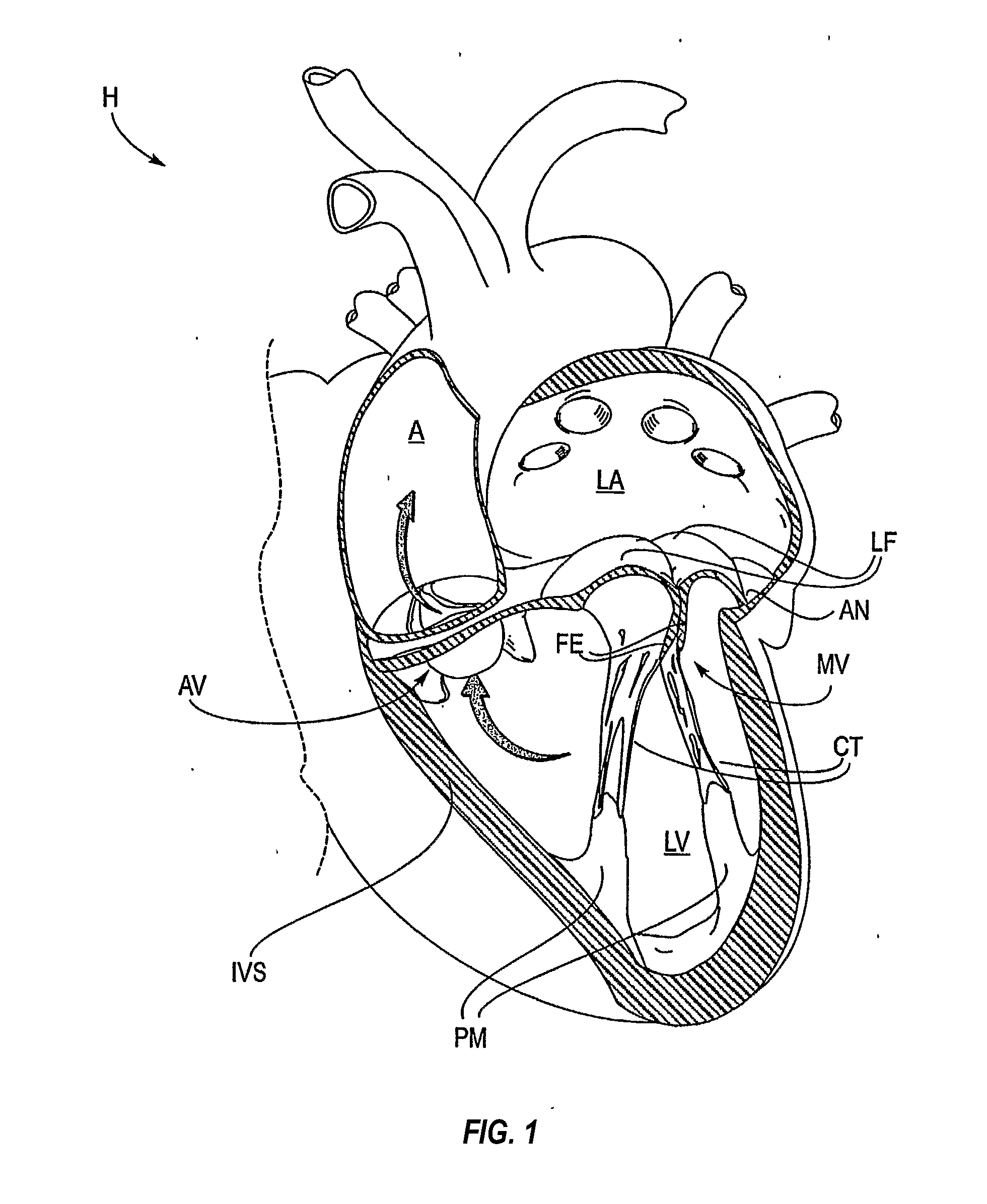
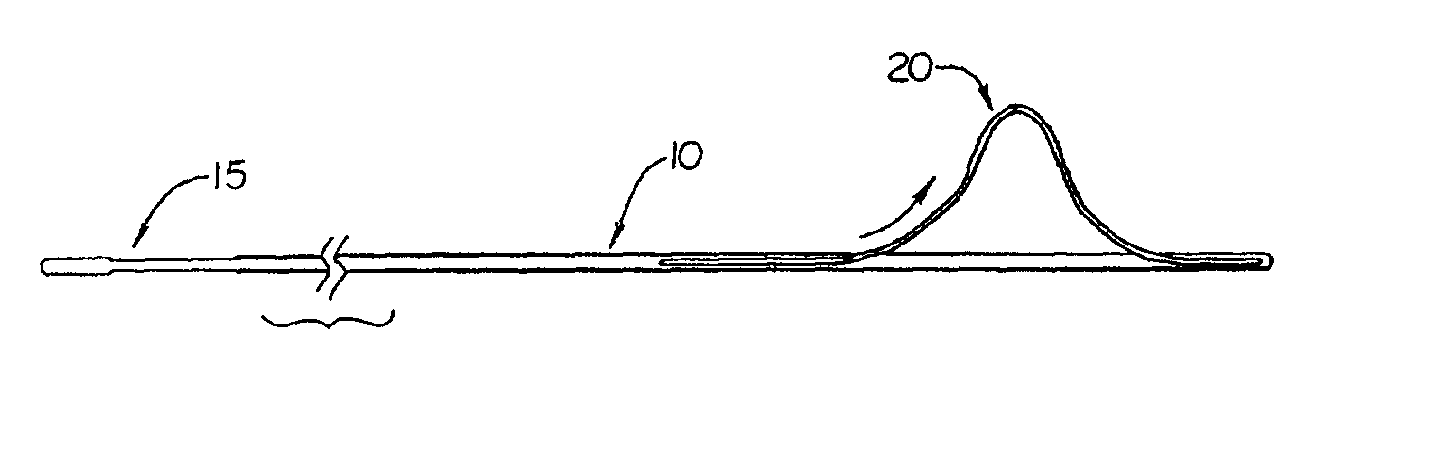
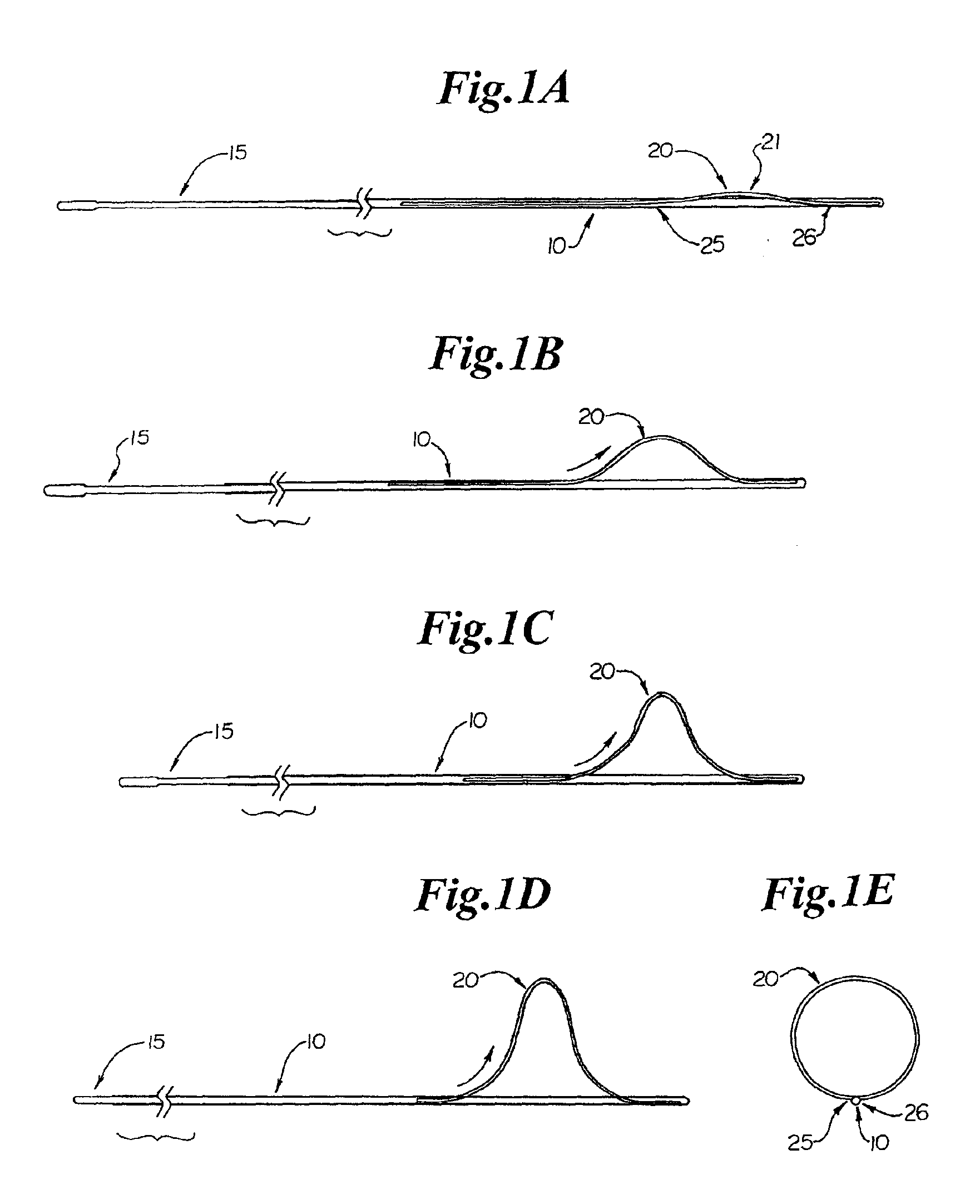
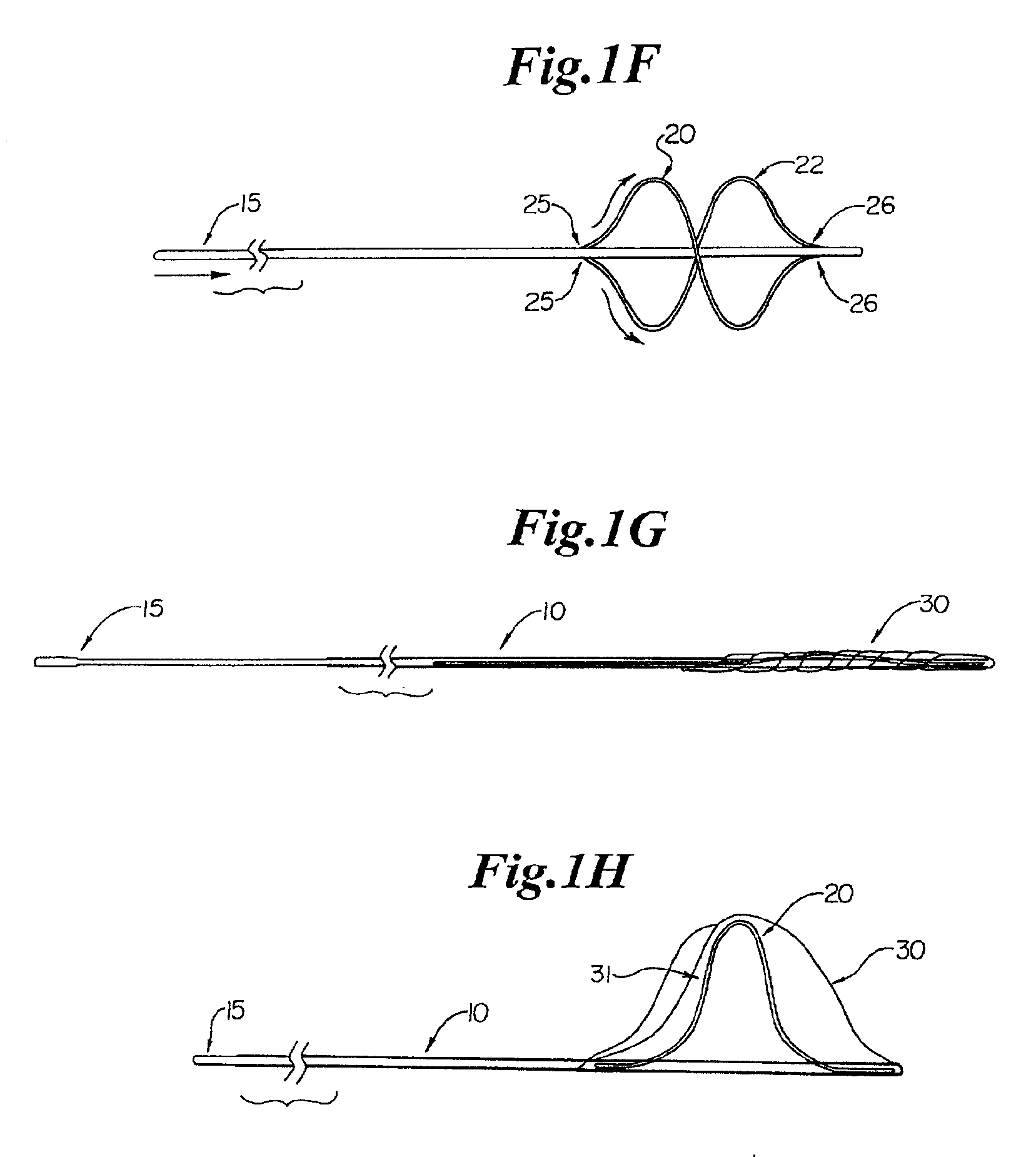
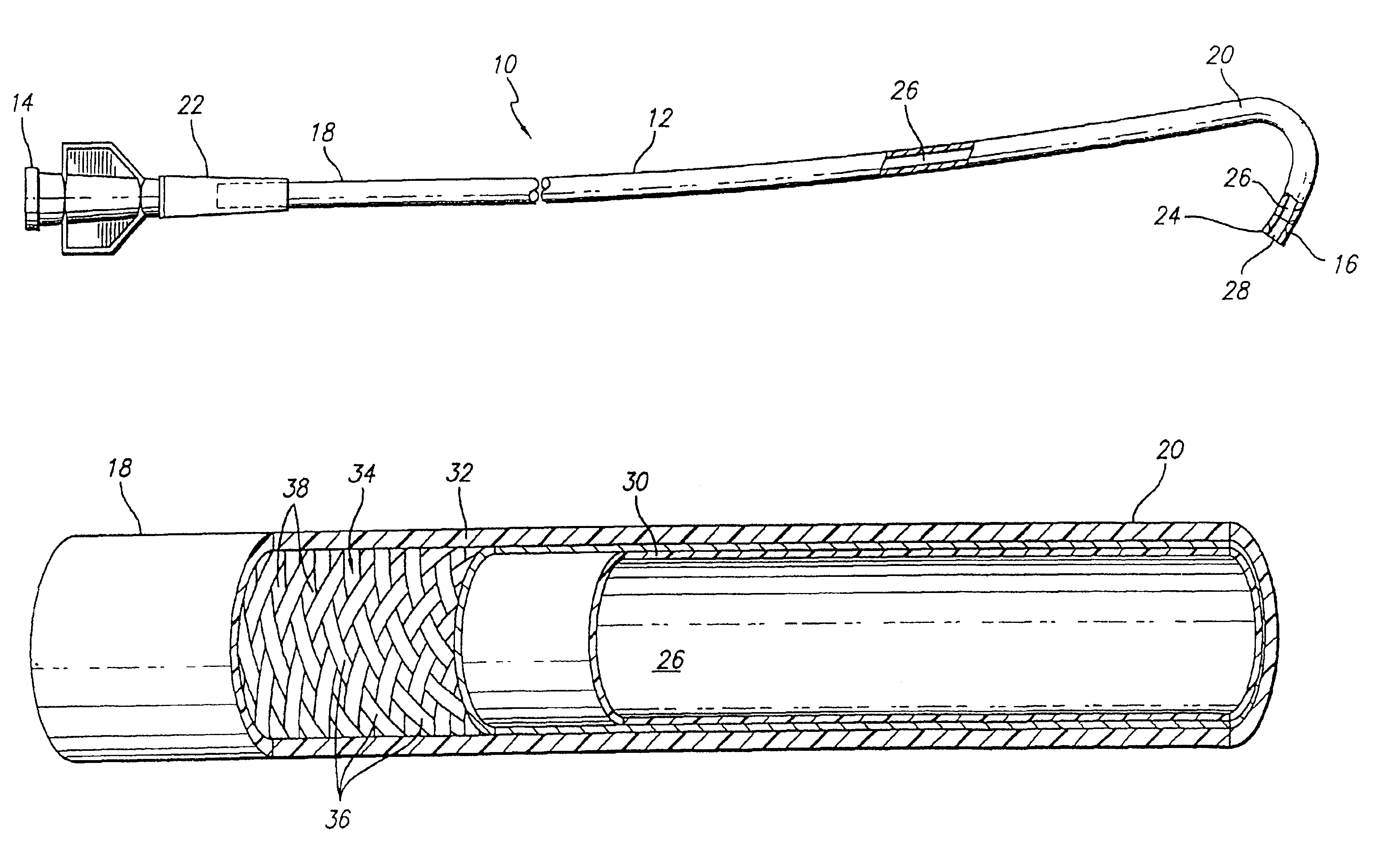
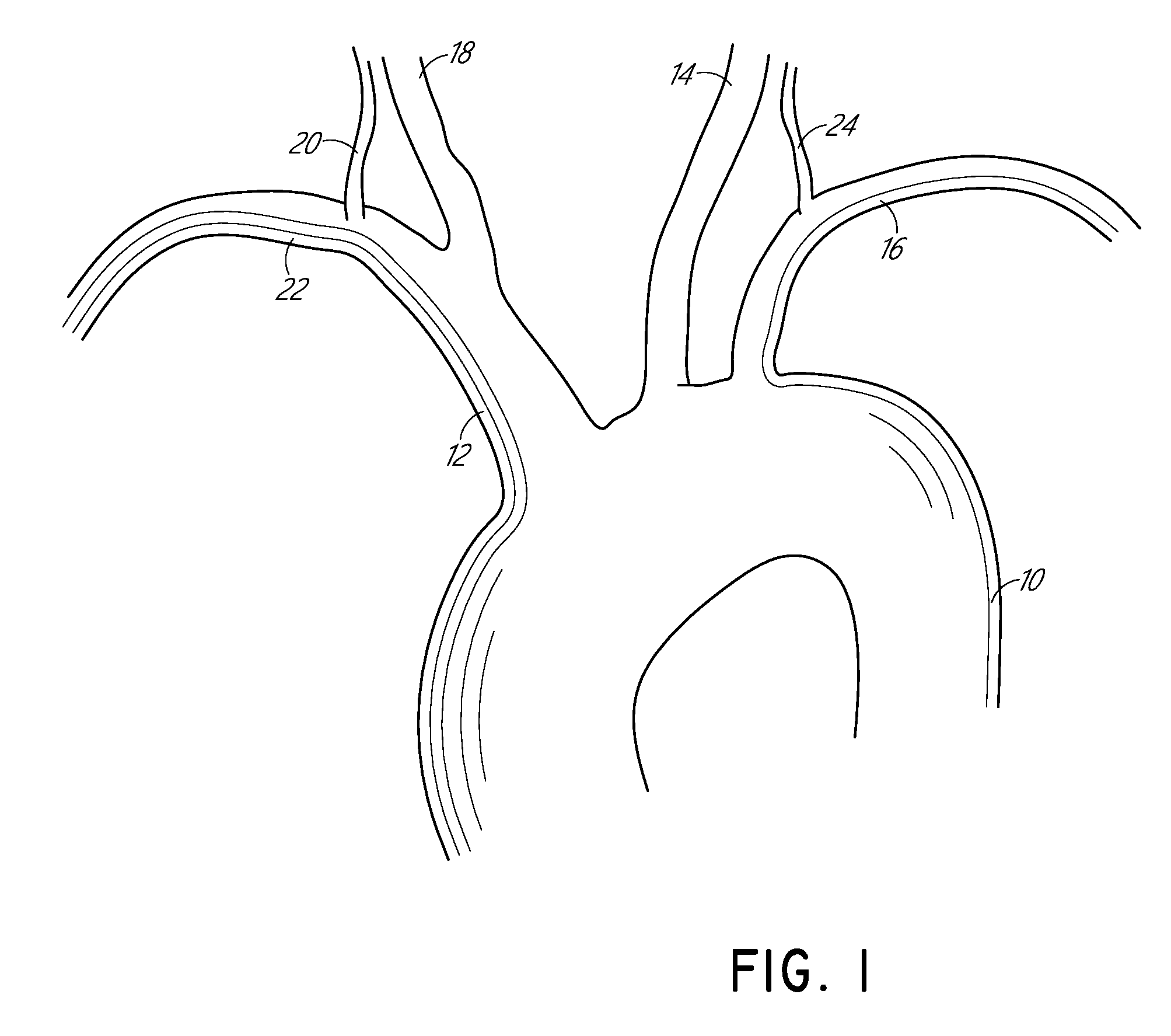
Endovascular surgery is a form of minimally invasive surgery that was designed to access many regions of the body via major blood vessels. Endovascular techniques were originally pioneered for diagnostic purposes by radiologists. Basic techniques involve the introduction of a catheter percutaneously into a large blood vessel. Typically the blood vessel chosen is the femoral artery or a vein found near the groin. Access to the femoral artery for example, is required for coronary, carotid, and cerebral angiographic procedures. The catheter is injected with a radio-opaque dye that can be seen on live X-ray or fluoroscopy. As the dye courses through the blood vessels, characteristic images are seen by experienced viewers and can assist in the diagnosis of diseases such as atherosclerosis, vascular trauma, or aneurysms. In recent years, however, the development of intravascular balloons, stents and coils have allowed for new therapies as alternatives to traditional surgeries such as Coronary artery bypass surgery, carotid endarterectomy and aneurysm clipping.
Cardiac valve procedure methods and devices
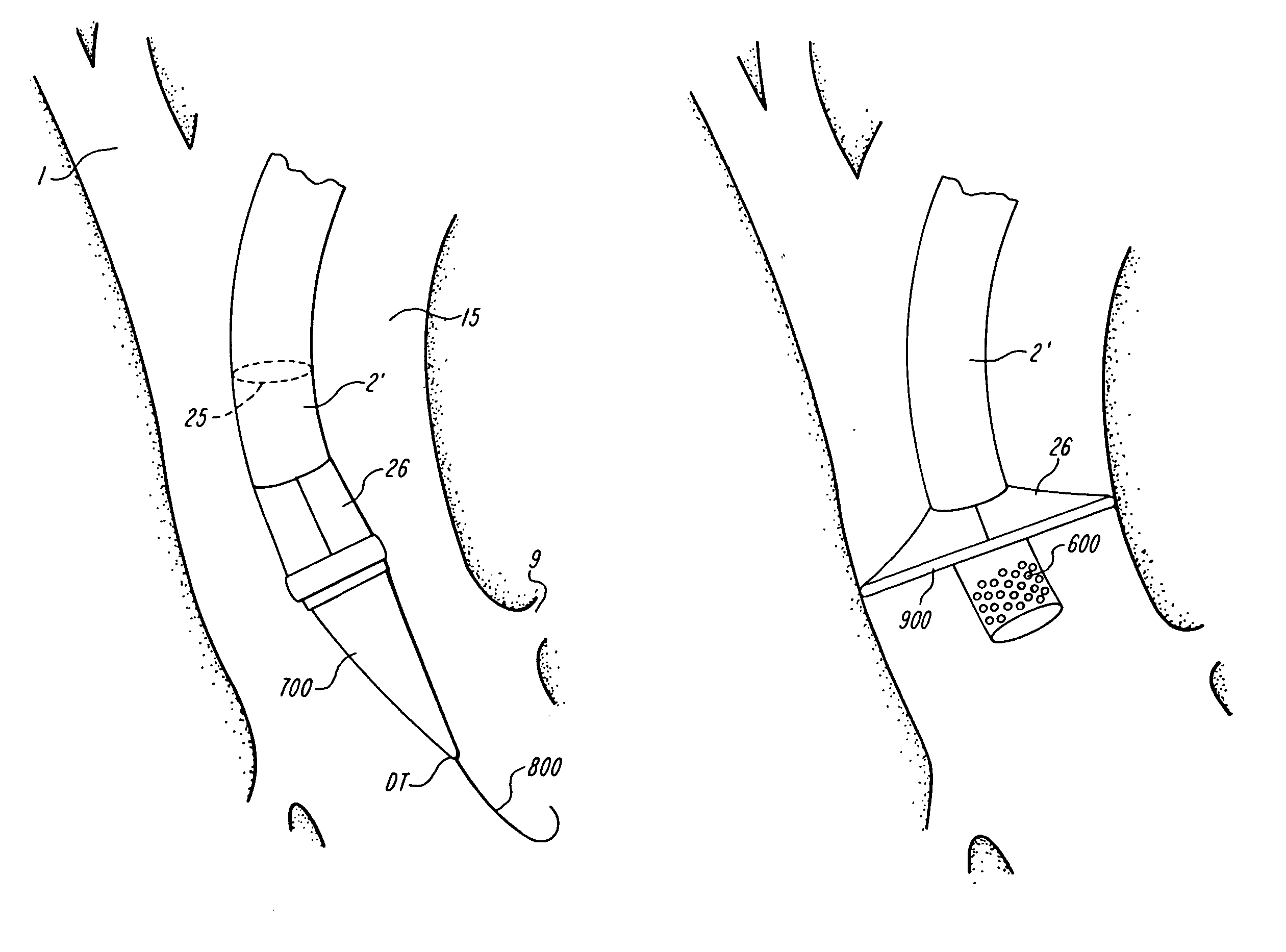
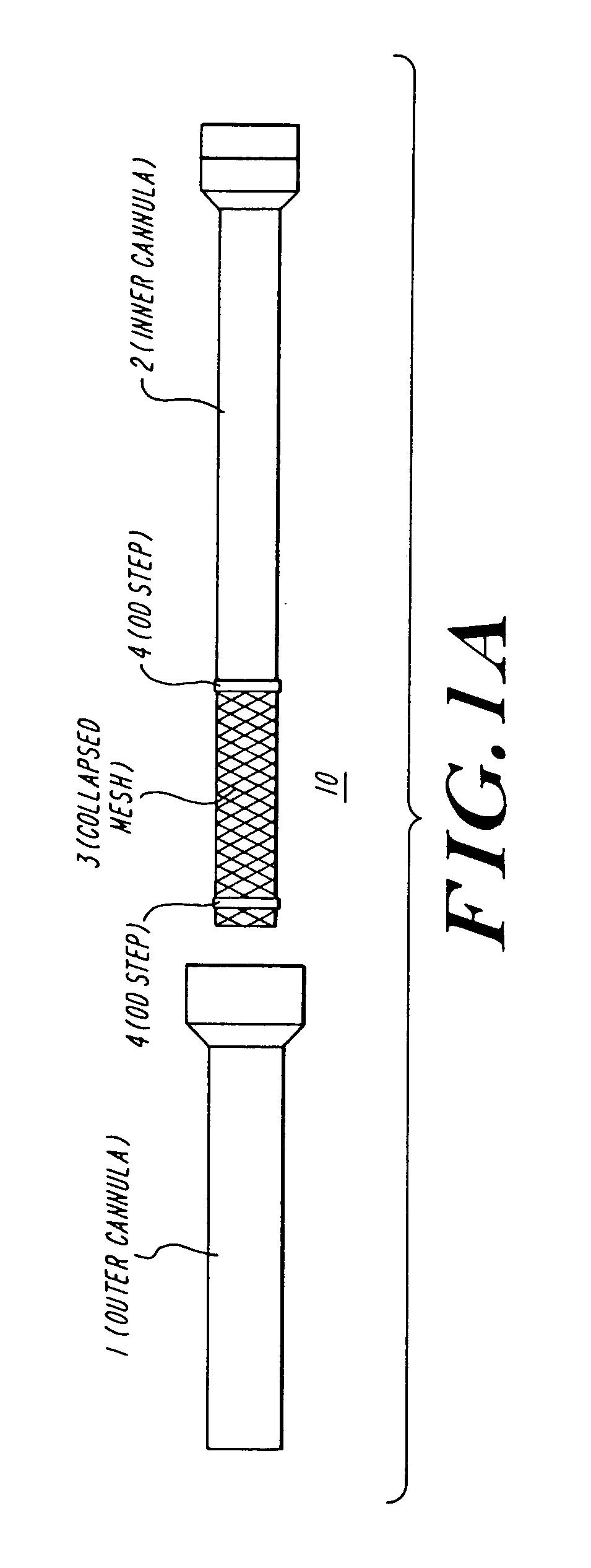
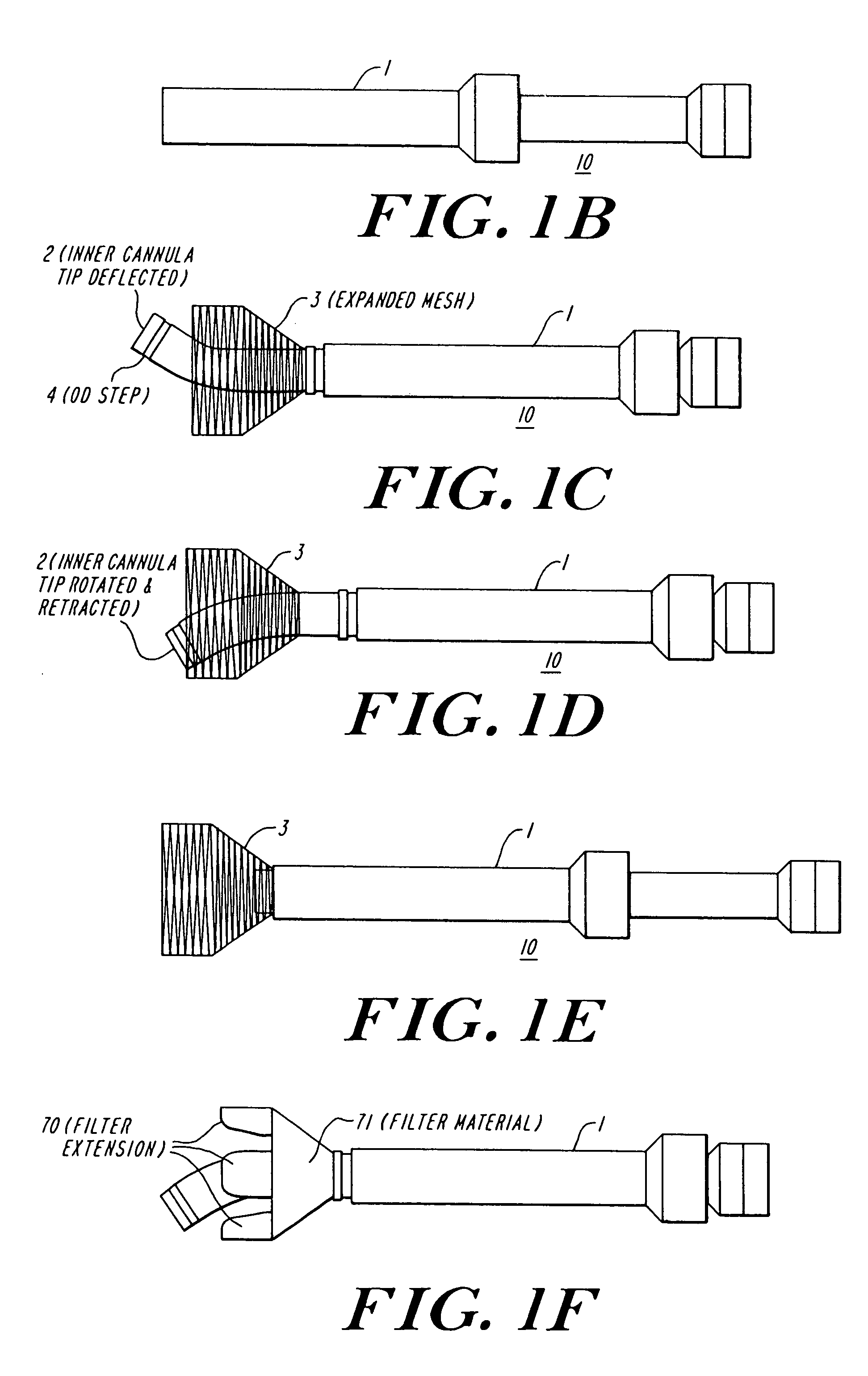
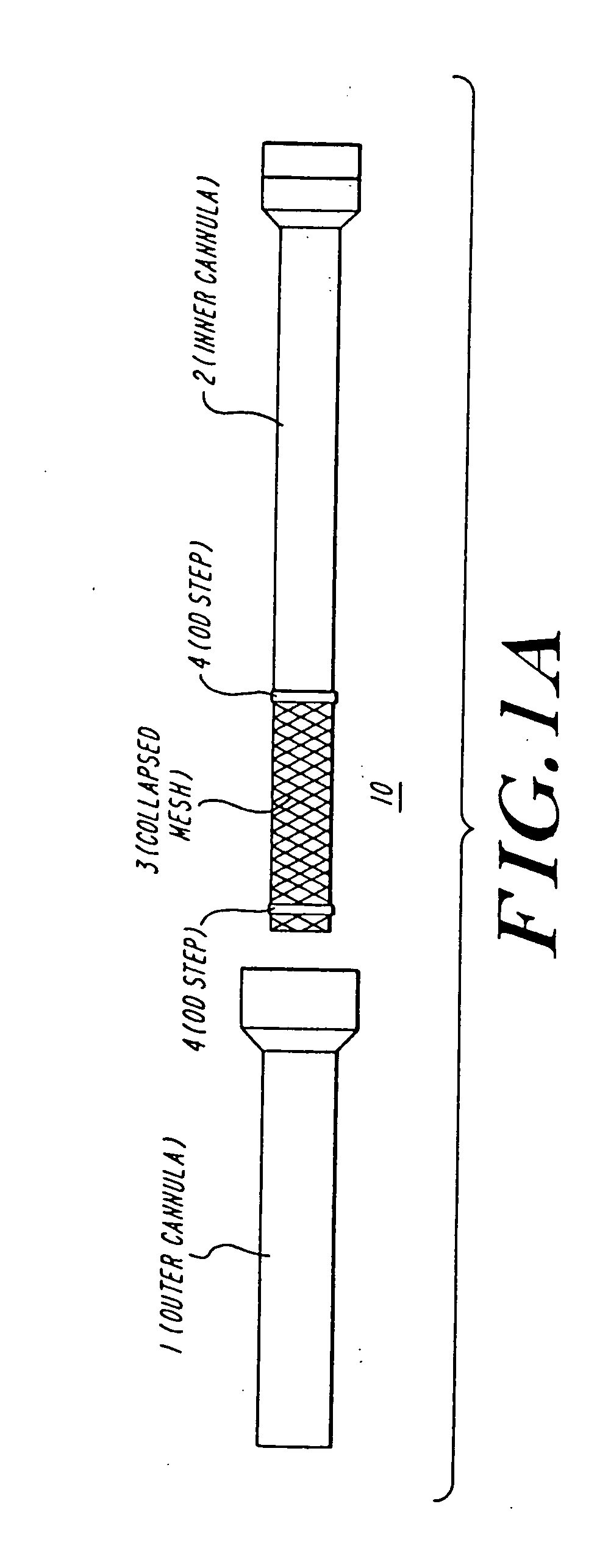
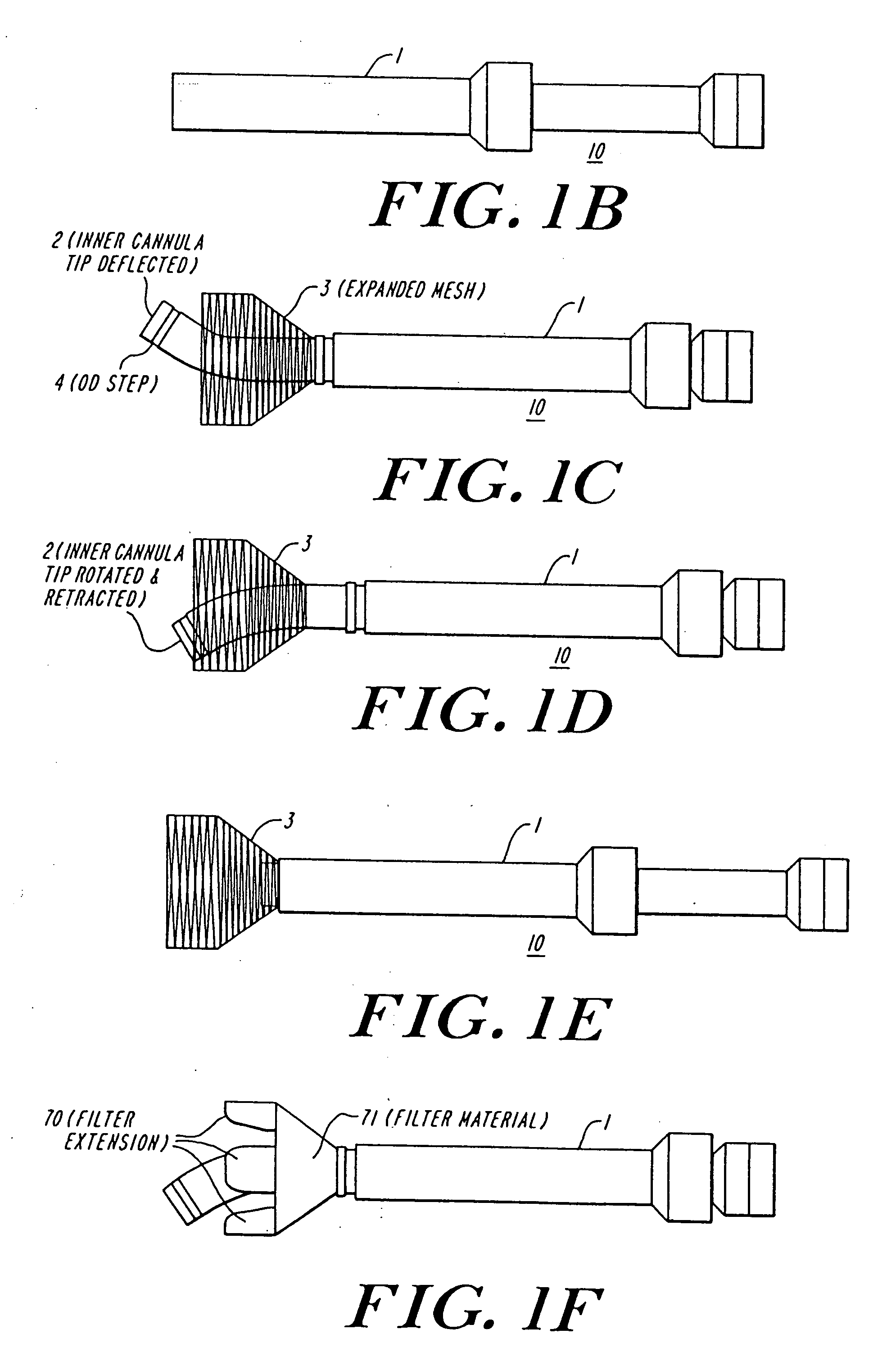
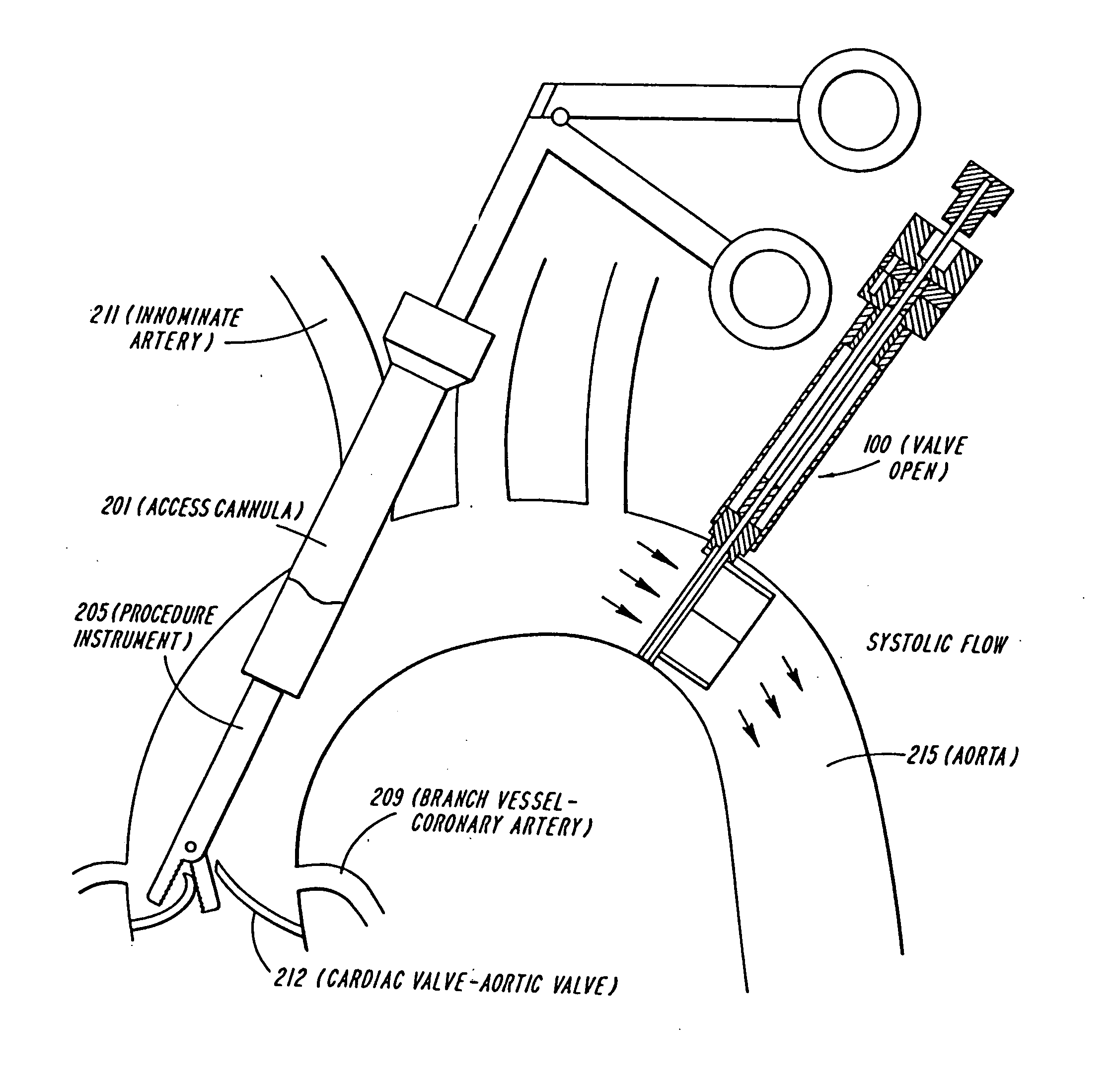
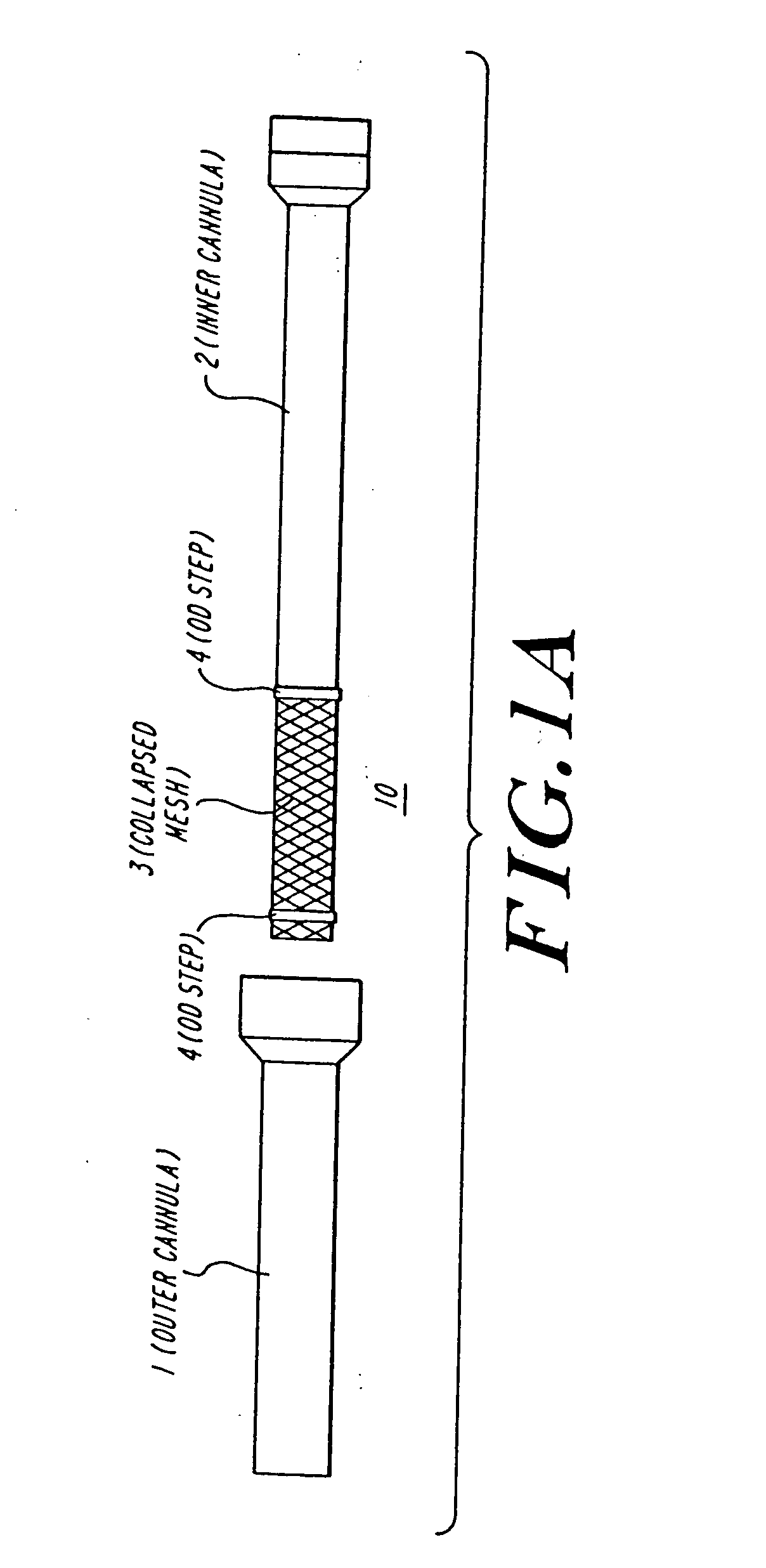
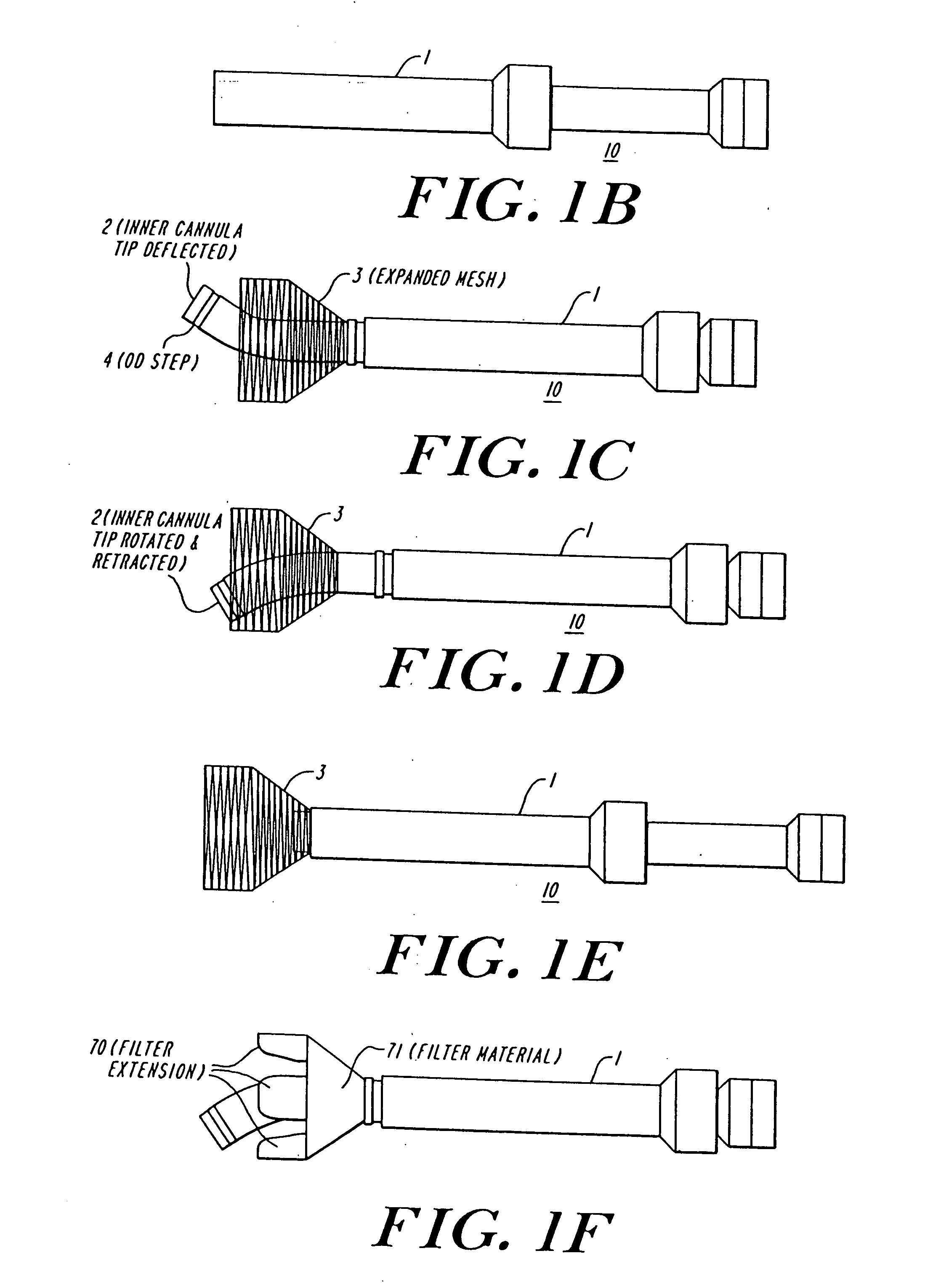
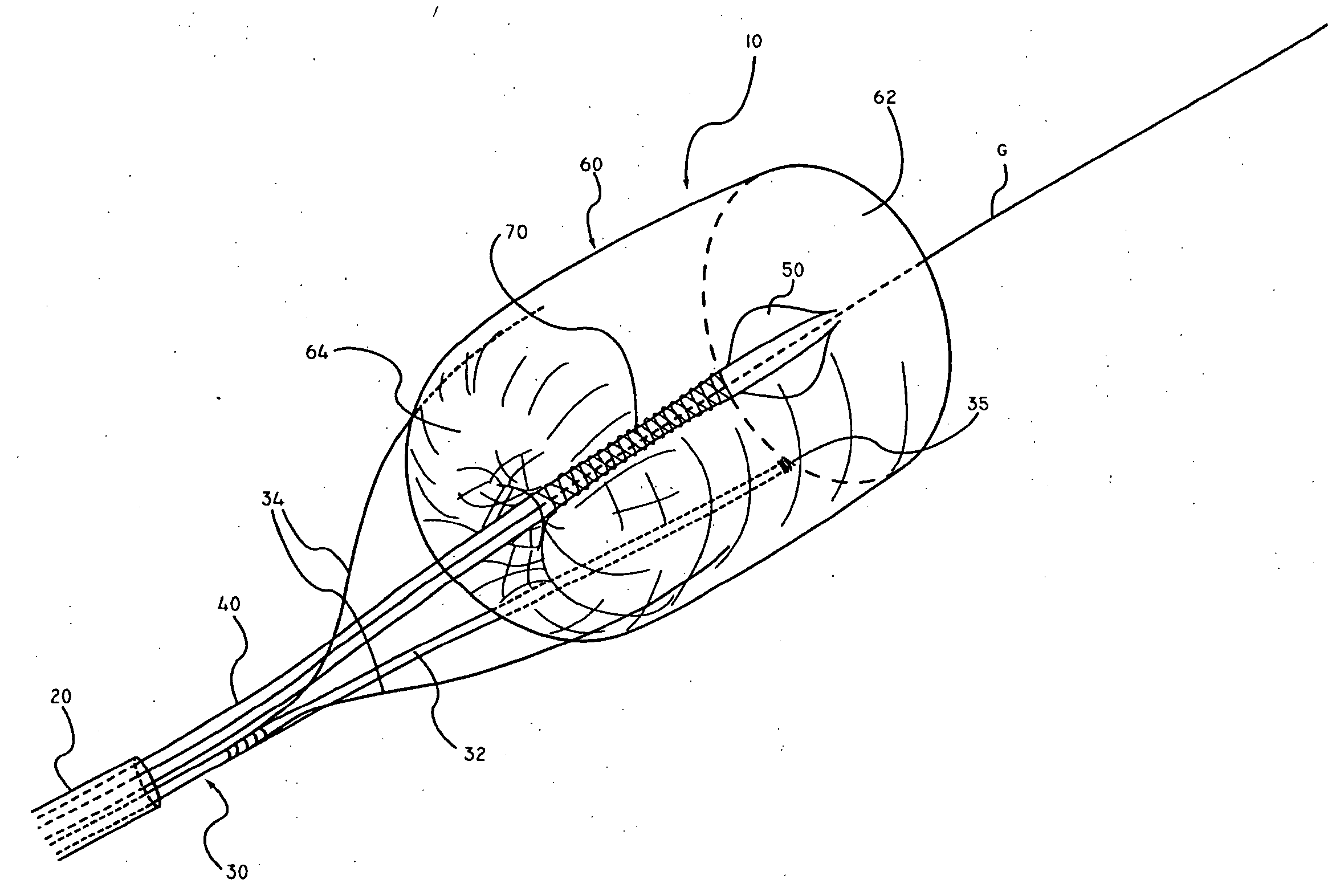
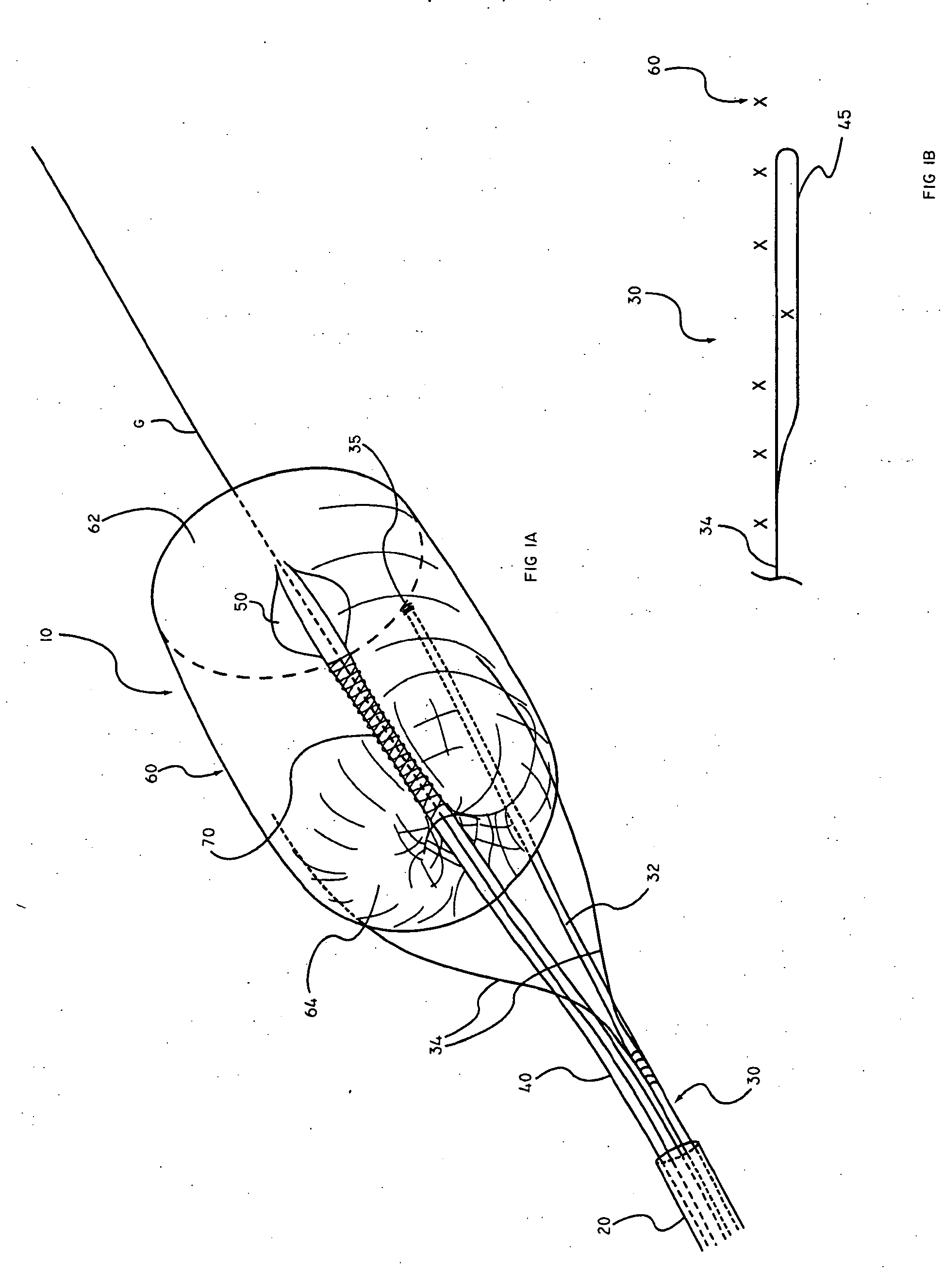
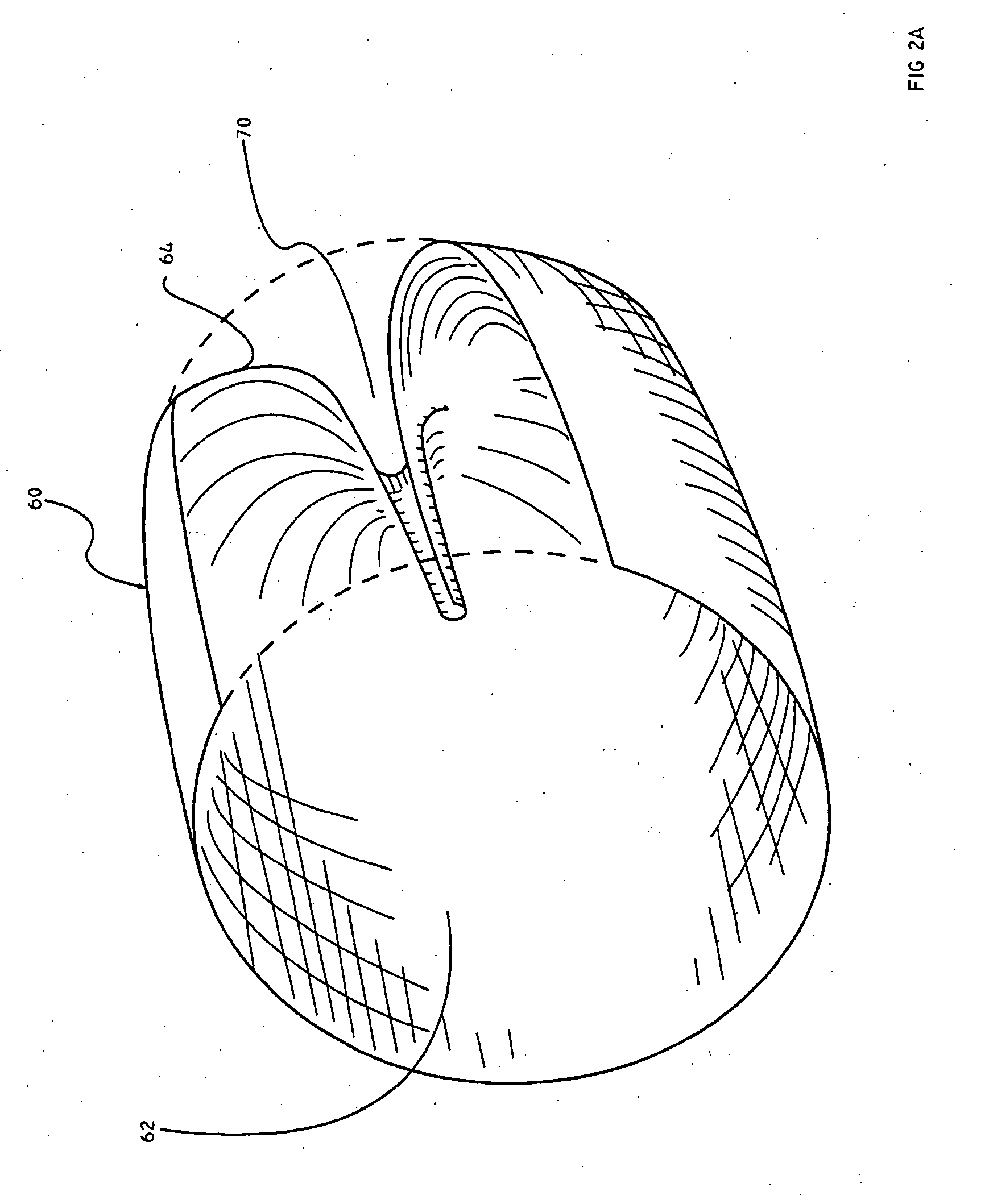
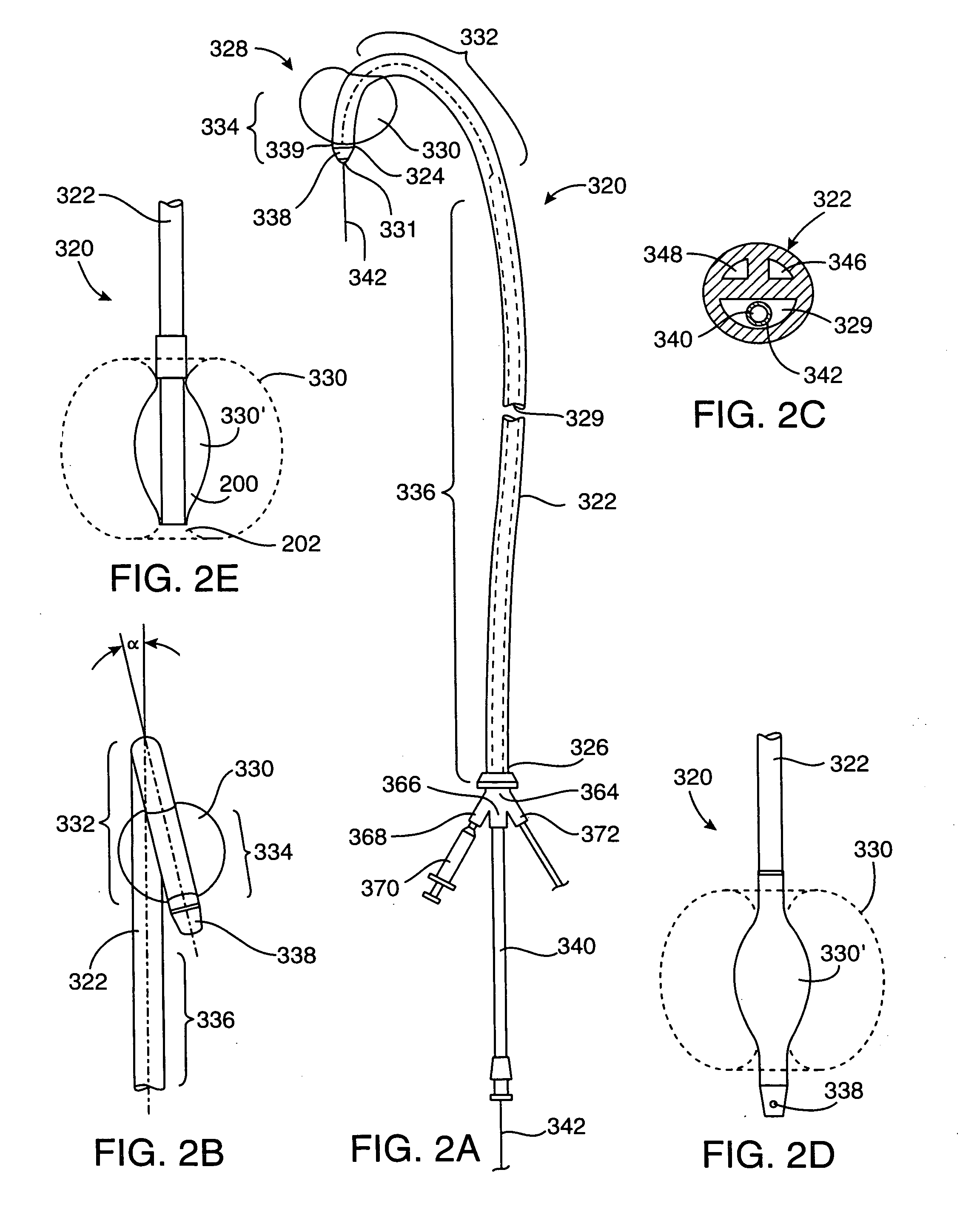
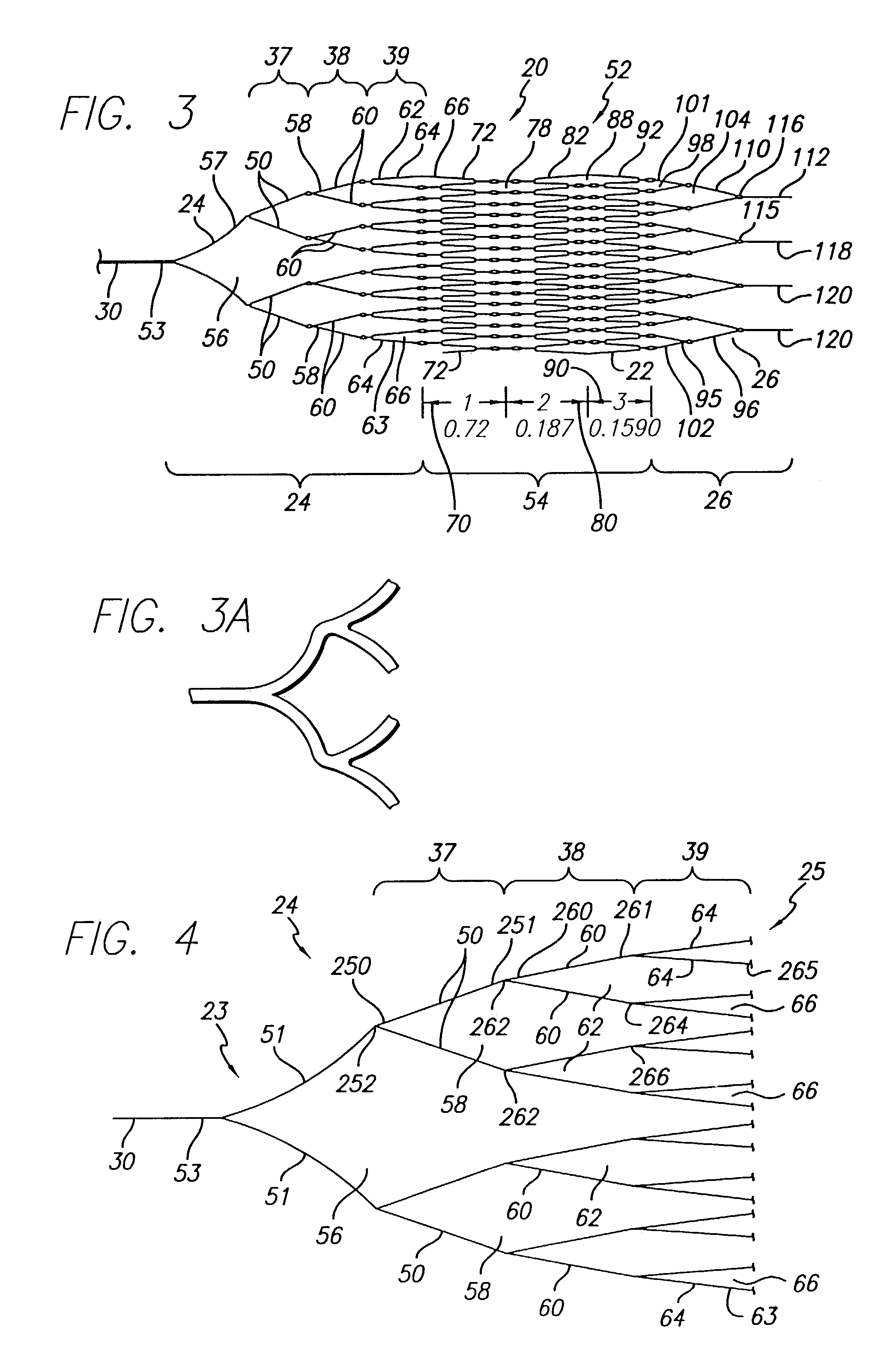
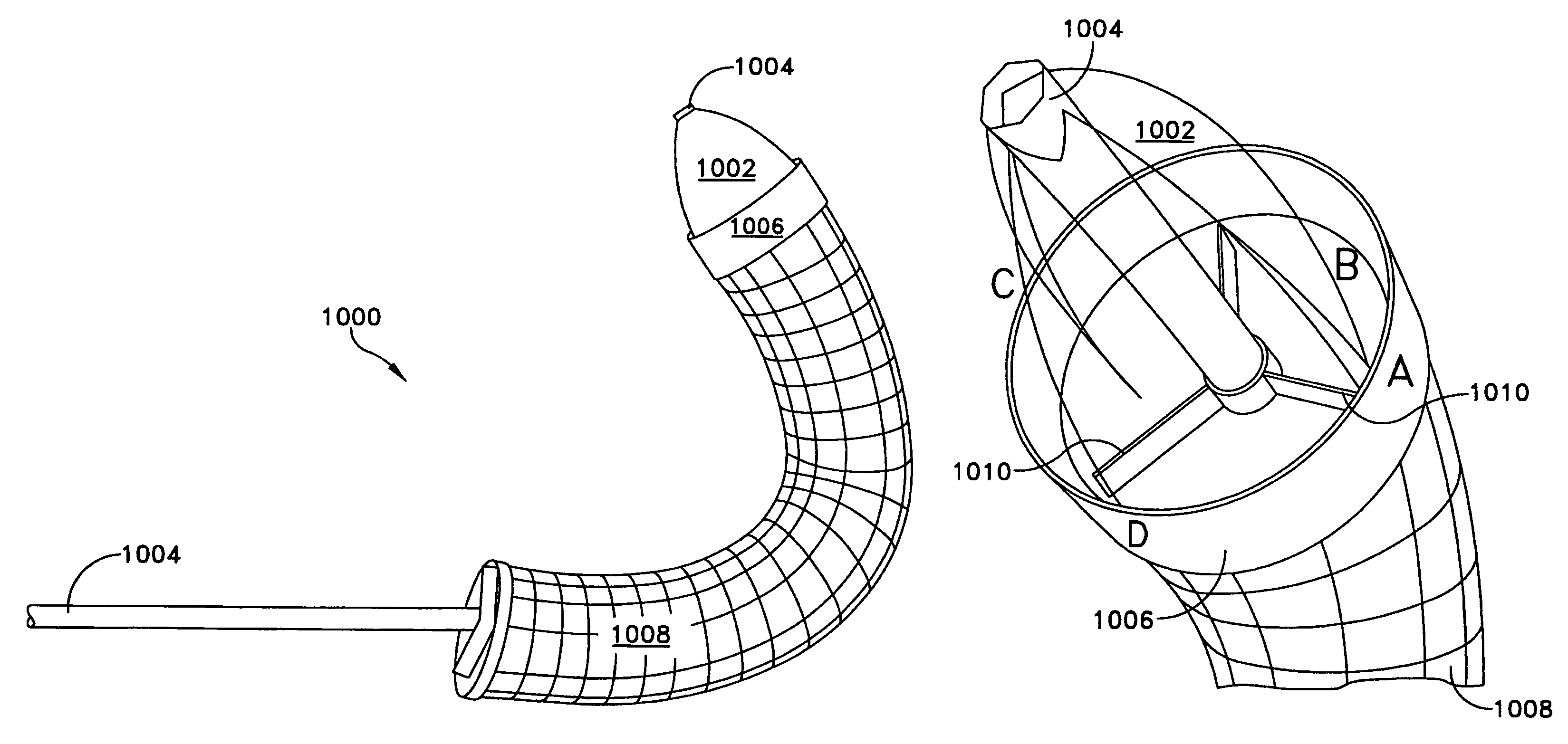
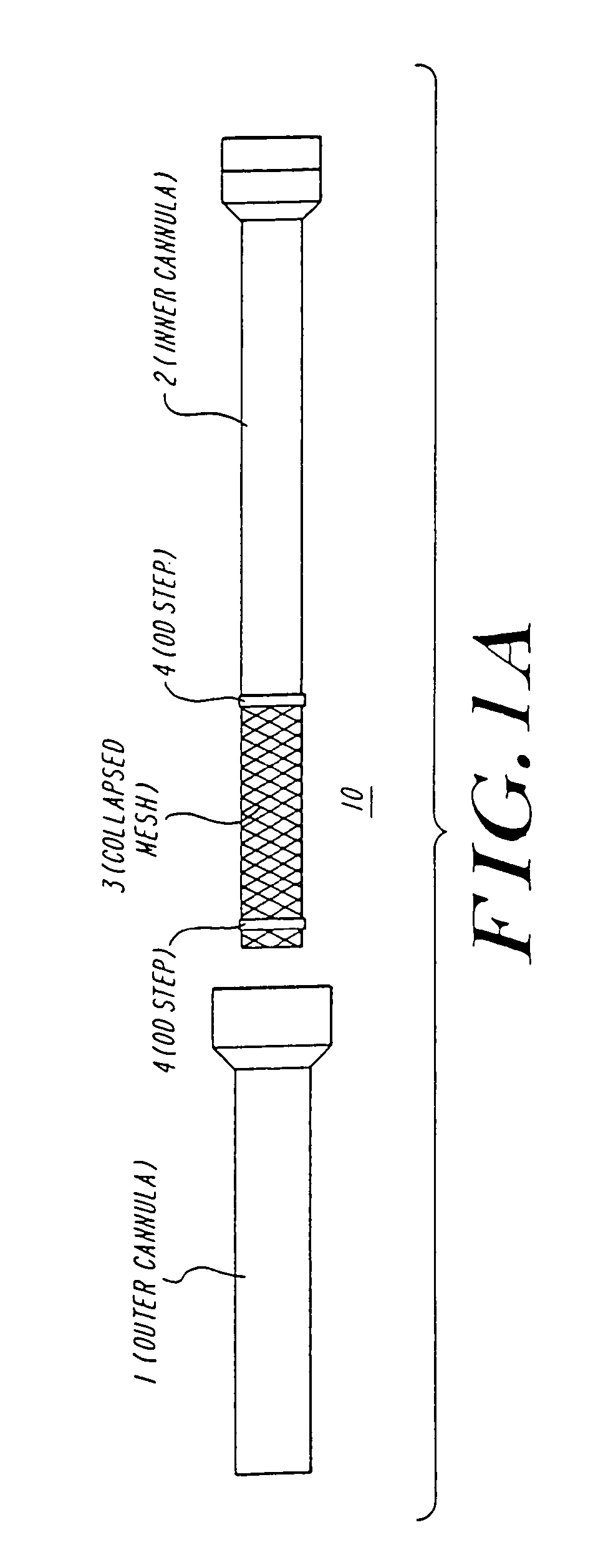
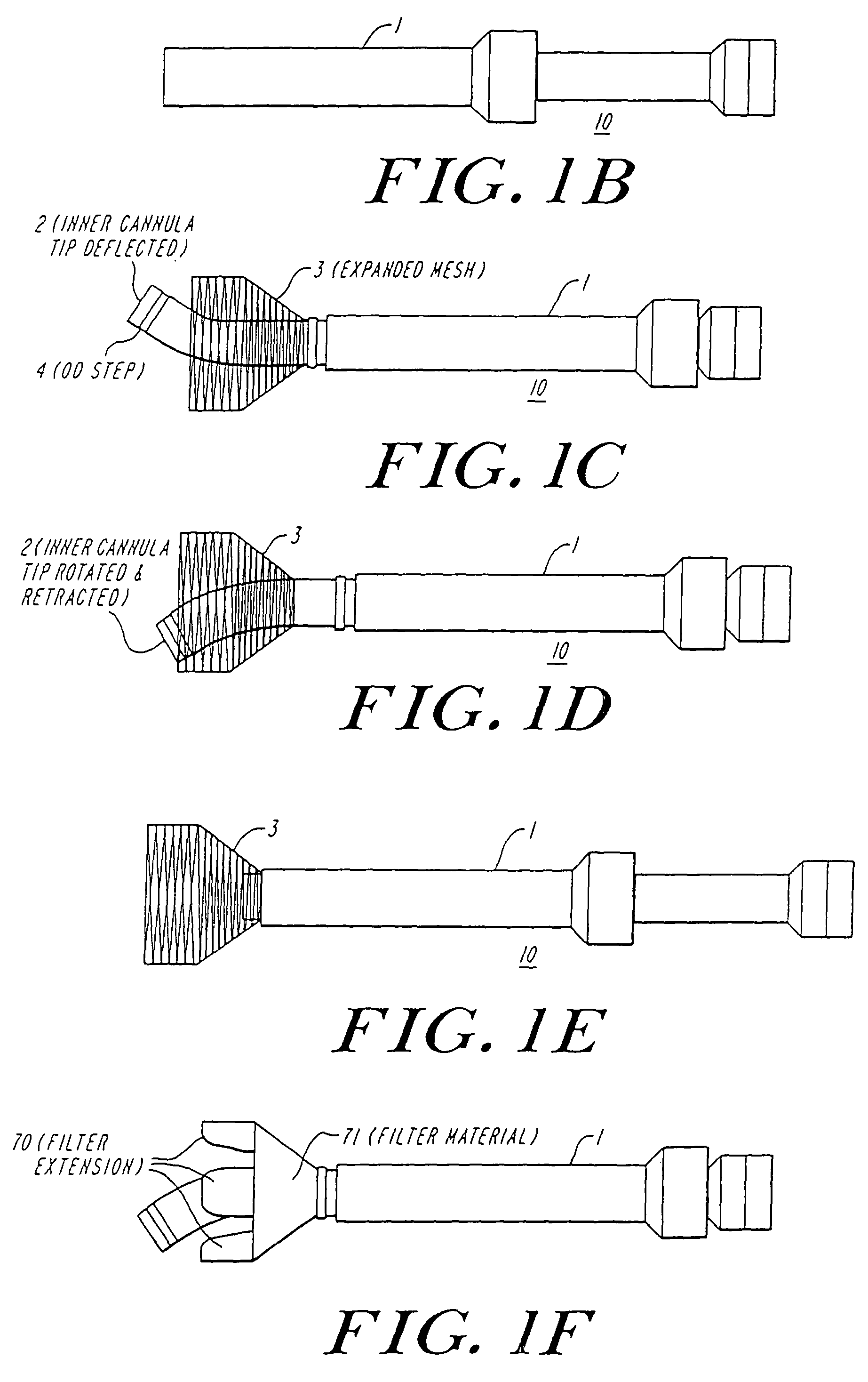
The present invention discloses devices and methods for performing intravascular procedures with out cardiac bypass. The devices include various embodiments of temporary filter devices, temporary valves, and prosthetic valves.The temporary filter devices have one or more cannulae which provide access for surgical tools for effecting repair of the cardiac valves. A cannula may have filters of various configurations encircling the distal region of the cannula, which prevent embolitic material from entering the coronary arteries and aorta.The temporary valve devices may also have one or more cannulae which guide the insertion of the valve into the aorta. The valve devices expand in the aorta to occupy the entire flow path of the vessel. In one embodiment, the temporary valve is a disc of flexible, porous, material that acts to filter blood passing therethrough. A set of valve leaflets extend peripherally from the disc. These leaflets can alternately collapse to prevent blood flow through the valve and extend to permit flow.The prosthetic valves include valve fixation devices which secure the prosthetic valve to the wall of the vessel. In one embodiment, the prosthetic valves have at least one substantially rigid strut, at least two expandable fixation rings located about the circumference of the base of the apex of the valve, and one or more commissures and leaflets. The prosthetic valves are introduced into the vascular system a compressed state, advanced to the site of implantation, expanded and secured to the vessel wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Cardiac valve procedure methods and devices
The present invention discloses devices and methods for performing intravascular procedures with out: cardiac bypass. The devices include various embodiments of temporary filter devices, temporary valves, and prosthetic valves. The temporary filter devices have one or more cannulae which provide access for surgical tools for effecting repair of the cardiac valves. A cannula may have filters of various configurations encircling the distal region of the cannula, which prevent embolitic material from entering the coronary arteries and aorta. The temporary valve devices may also have one or more cannulae which guide the insertion of the valve into the aorta. The valve devices expand in the aorta to occupy the entire flow path of the vessel. In one embodiment, the temporary valve is a disc of flexible, porous, material that acts to filter blood passing therethrough. A set of valve leaflets extend peripherally from the disc. These leaflets can alternately collapse to prevent blood flow through the valve and extend to permit flow. The prosthetic valves include valve fixation devices which secure the prosthetic valve to the wall of the vessel. In one embodiment, the prosthetic valves have at least one substantially rigid strut, at least two expandable fixation rings located about the circumference of the base of the apex of the valve, and one or more commissures and leaflets. The prosthetic valves are introduced into the vascular system a compressed state, advanced to the site of implantation, expanded and secured to the vessel wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Cardiac valve procedure methods and devices
The present invention discloses devices and methods for performing intravascular procedures with out cardiac bypass. The devices include various embodiments of temporary filter devices, temporary valves, and prosthetic valves. The temporary filter devices have one or more cannulae which provide access for surgical tools for effecting repair of the cardiac valves. A cannula may have filters of various configurations encircling the distal region of the cannula, which prevent embolitic material from entering the coronary arteries and aorta. The temporary valve devices may also have one or more cannulae which guide the insertion of the valve into the aorta. The valve devices expand in the aorta to occupy the entire flow path of the vessel. In one embodiment, the temporary valve is a disc of flexible, porous, material that acts to filter blood passing therethrough. A set of valve leaflets extend peripherally from the disc. These leaflets can alternately collapse to prevent blood flow through the valve and extend to permit flow. The prosthetic valves include valve fixation devices which secure the prosthetic valve to the wall of the vessel. In one embodiment, the prosthetic valves have at least one substantially rigid strut, at least two expandable fixation rings located about the circumference of the base of the apex of the valve, and one or more commissures and leaflets. The prosthetic valves are introduced into the vascular system a compressed state, advanced to the site of implantation, expanded and secured to the vessel wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apparatus and methods for intravascular embolic protection
The present invention provides intravascular embolic protection apparatus including a blood filter element having an accommodating passageway adapted to permit passage of a procedure device therethrough and to substantially seal against passage of particles between the embolic protection apparatus and the procedure device by accommodating to a size and shape of the procedure device. Furthermore, the present invention provides a method of performing an endovascular procedure on a patient including the steps of delivering an embolic protection apparatus to a location within a vascular lumen of the patient; passing a procedure device through an accommodating passageway of the apparatus, the accommodating passageway accommodating to a size and shape of the procedure device; performing the endovascular procedure; and removing the procedure device from the patient.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Device to create proximal stasis
A method and system of performing an intravascular procedure at a treatment site in a vessel of a patient. A device creates a seal to prevent the flow of blood during the treatment of vascular disease. A seal may be formed between the distal inside diameter of a sheath or catheter such as a guide catheter as well as within a vessel, such as an artery or vein. An elongated device having a distal portion extending from the catheter and having a fluid impermeable membrane disposed about at least the distal end of the device is used to seal the vessel. The system includes a device to occlude blood flow and a distal protection device to filter or remove embolic debris.
Owner:EV3
System and methods for performing endovascular procedures
InactiveUS20060058775A1Procedure is complicatedEasy to controlStentsGuide needlesExtracorporeal circulationAtherectomy
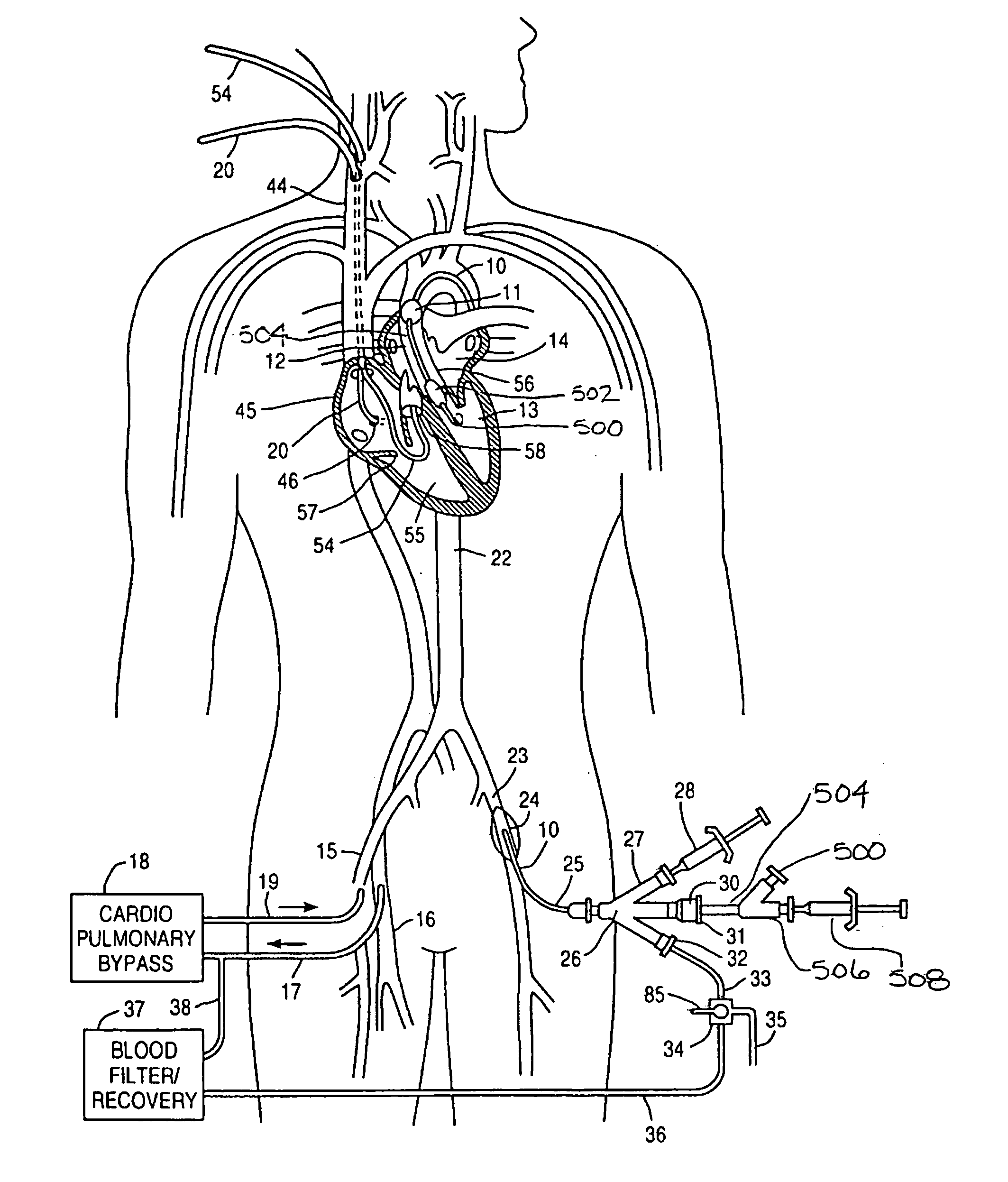
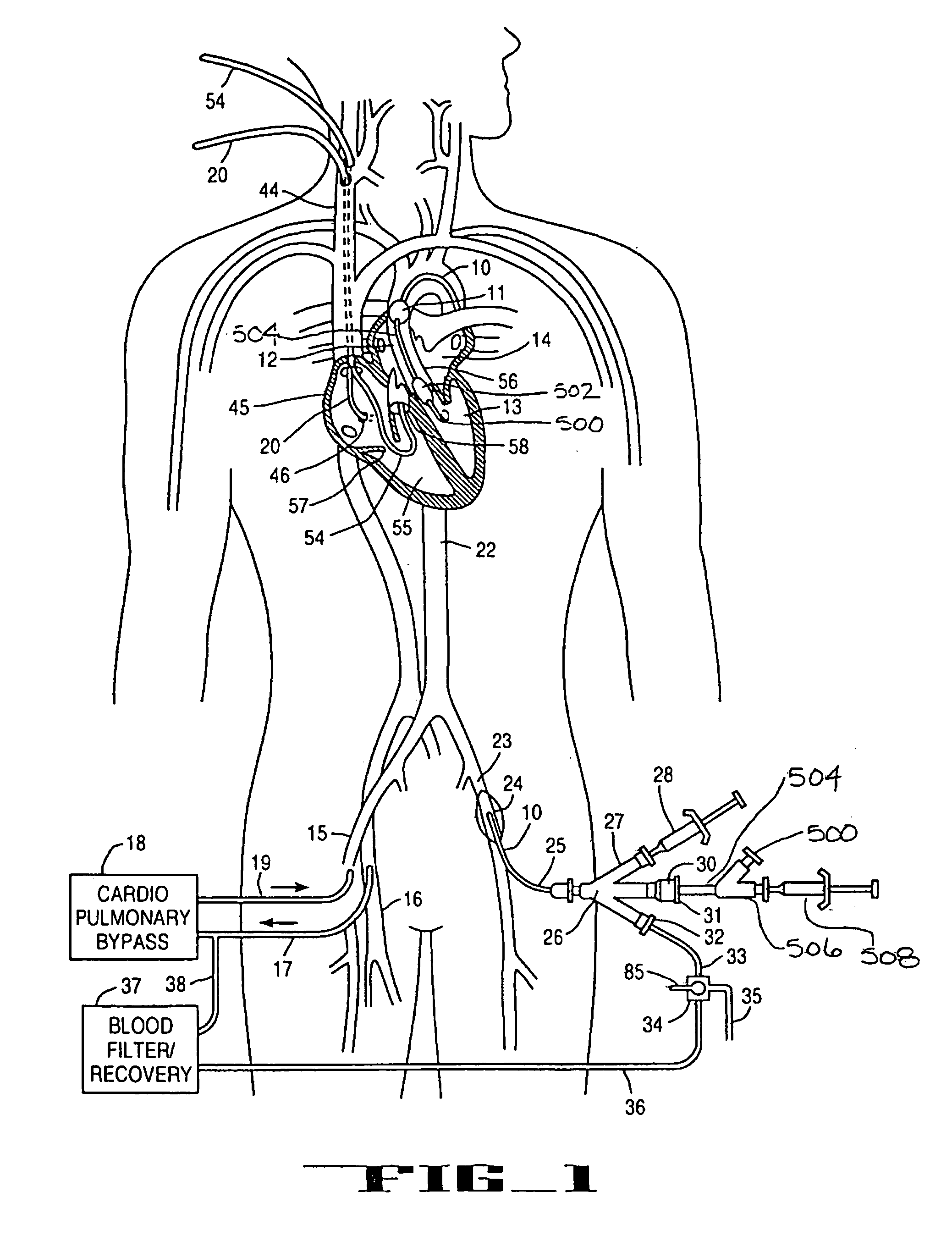
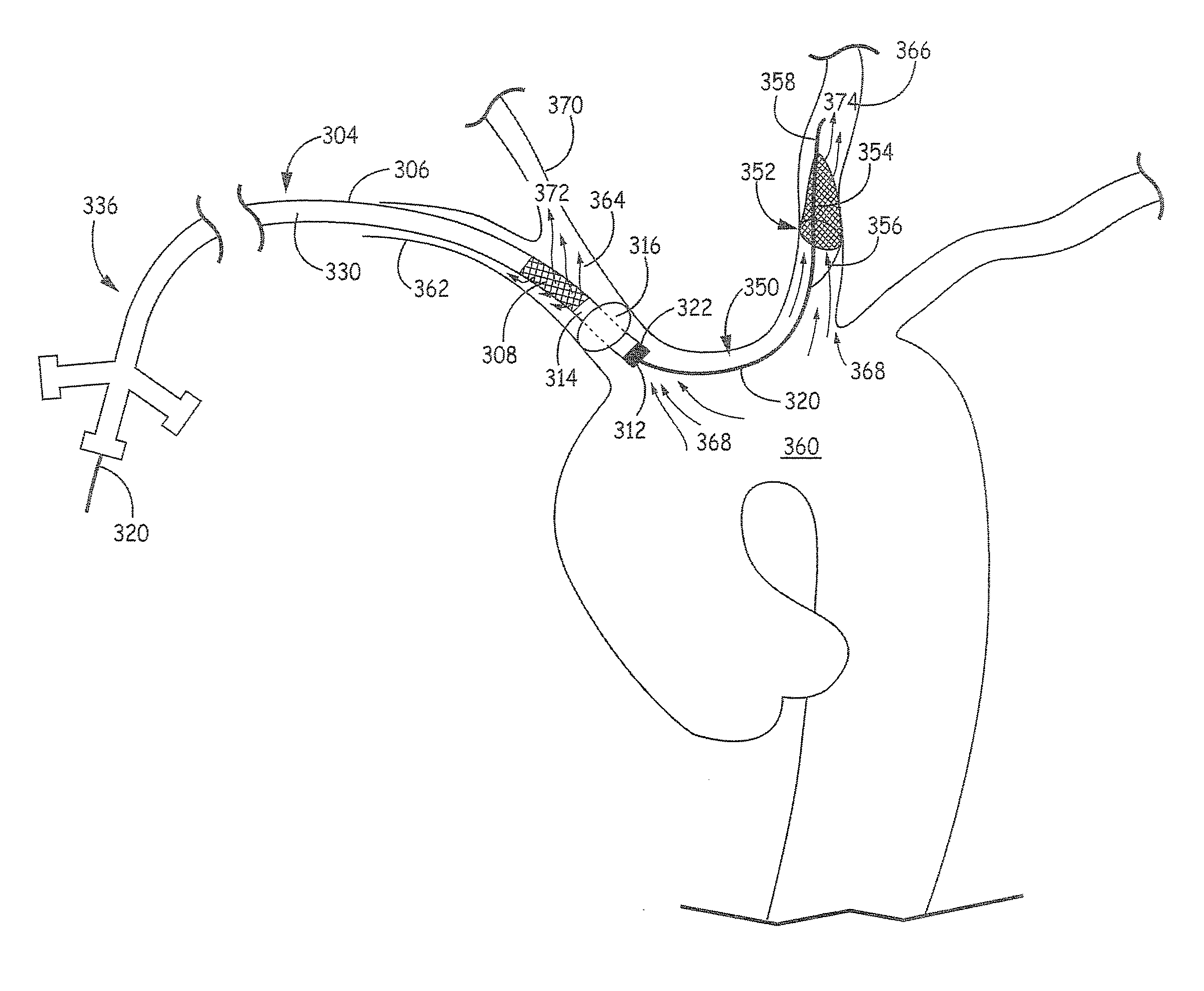
A system for inducing cardioplegic arrest and performing an endovascular procedure within the heart or blood vessels of a patient. An endoaortic partitioning catheter has an inflatable balloon which occludes the ascending aorta when inflated. Cardioplegic fluid may be infused through a lumen of the endoaortic partitioning catheter to stop the heart while the patient's circulatory system is supported on cardiopulmonary bypass. One or more endovascular devices are introduced through an internal lumen of the endoaortic partitioning catheter to perform a diagnostic or therapeutic endovascular procedure within the heart or blood vessels of the patient. Surgical procedures such as coronary artery bypass surgery or heart valve replacement may be performed in conjunction with the endovascular procedure while the heart is stopped. Embodiments of the system are described for performing: fiberoptic angioscopy of structures within the heart and its blood vessels, valvuloplasty for correction of valvular stenosis in the aortic or mitral valve of the heart, angioplasty for therapeutic dilatation of coronary artery stenoses, coronary stenting for dilatation and stenting of coronary artery stenoses, atherectomy or endarterectomy for removal of atheromatous material from within coronary artery stenoses, intravascular ultrasonic imaging for observation of structures and diagnosis of disease conditions within the heart and its associated blood vessels, fiberoptic laser angioplasty for removal of atheromatous material from within coronary artery stenoses, transmyocardial revascularization using a side-firing fiberoptic laser catheter from within the chambers of the heart, and electrophysiological mapping and ablation for diagnosing and treating electrophysiological conditions of the heart.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Embolic filter
InactiveUS7004955B2Maintaining and restoring patencyImprove the immunitySurgeryDilatorsEndovascular surgeryBiomedical engineering
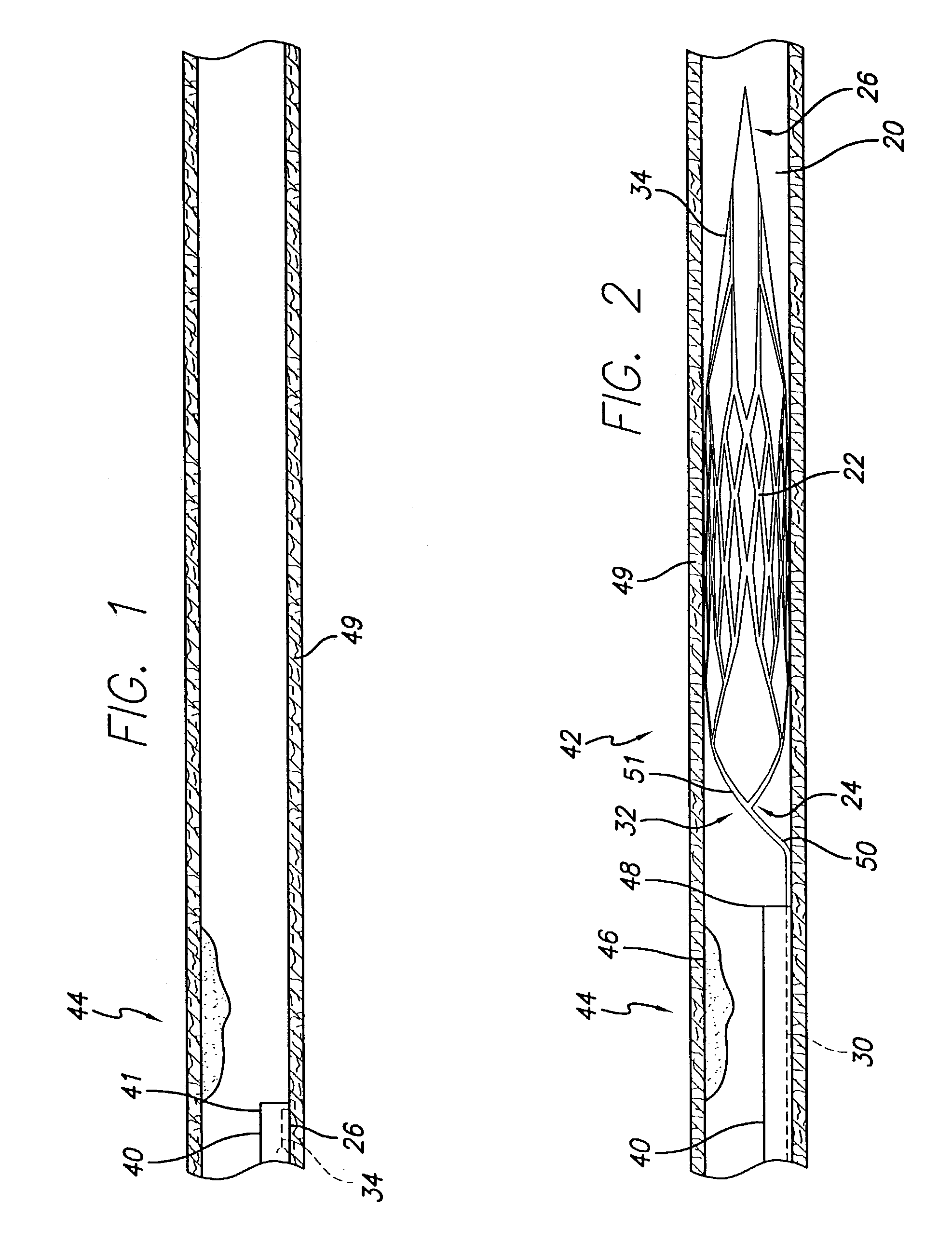
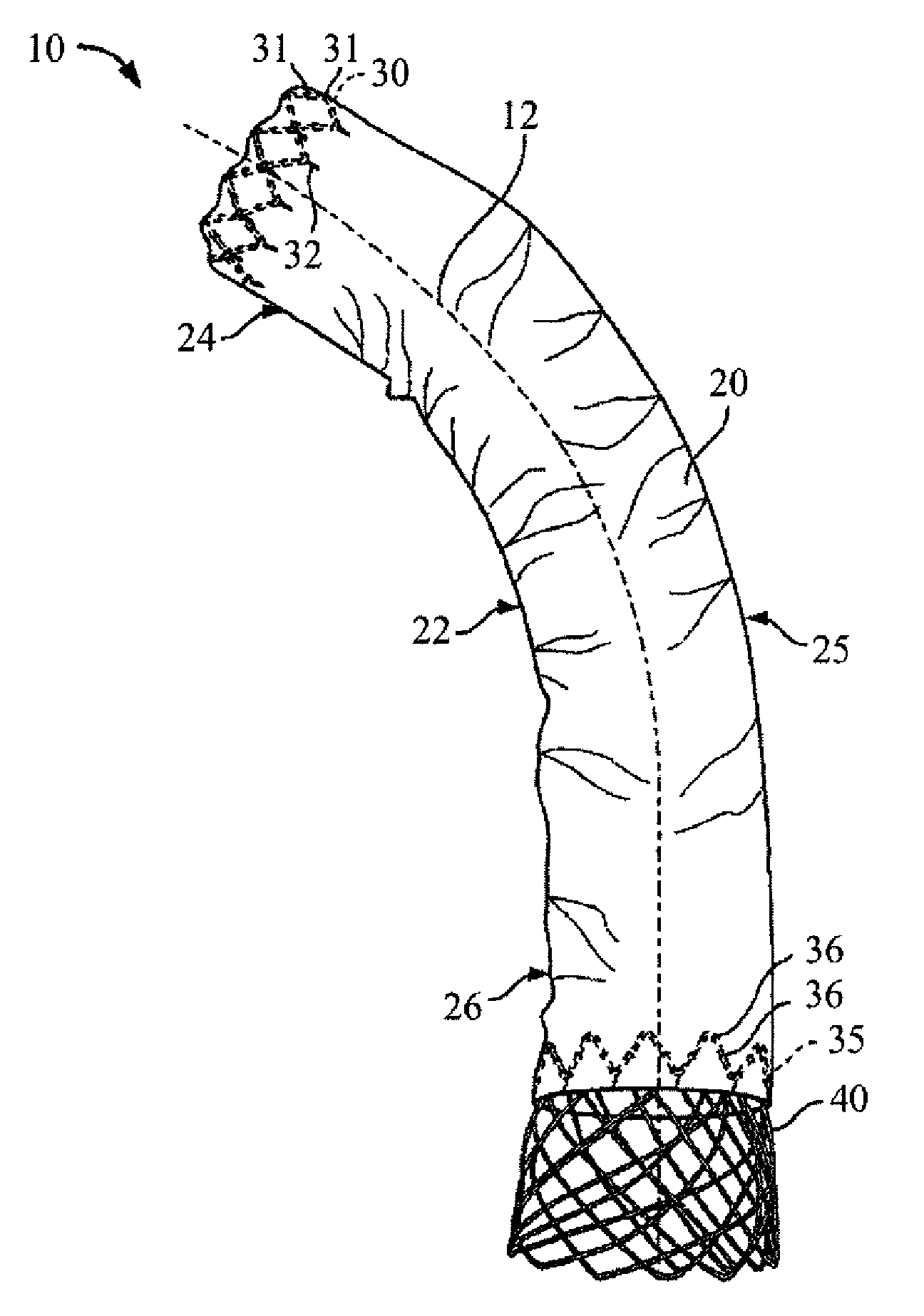
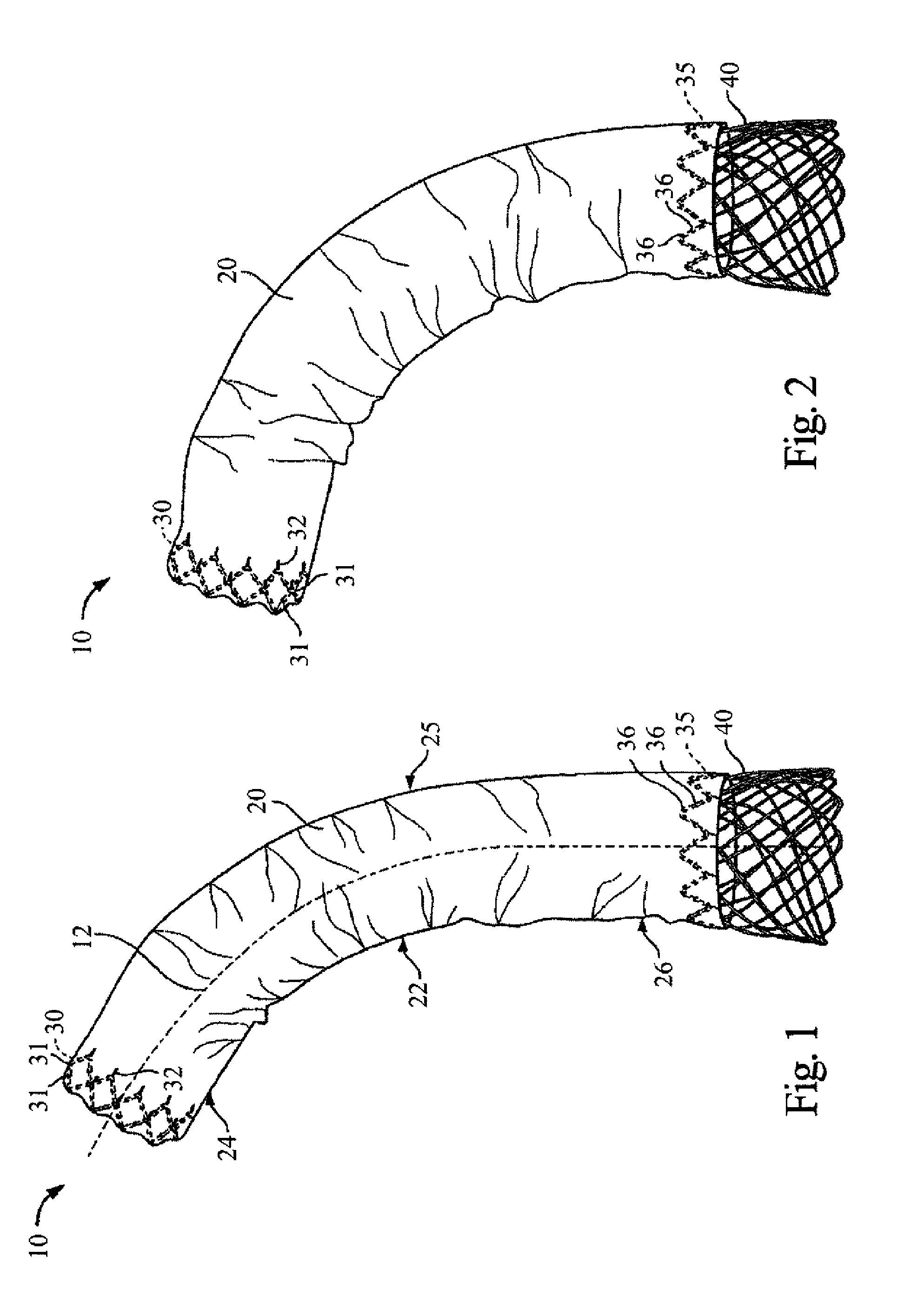
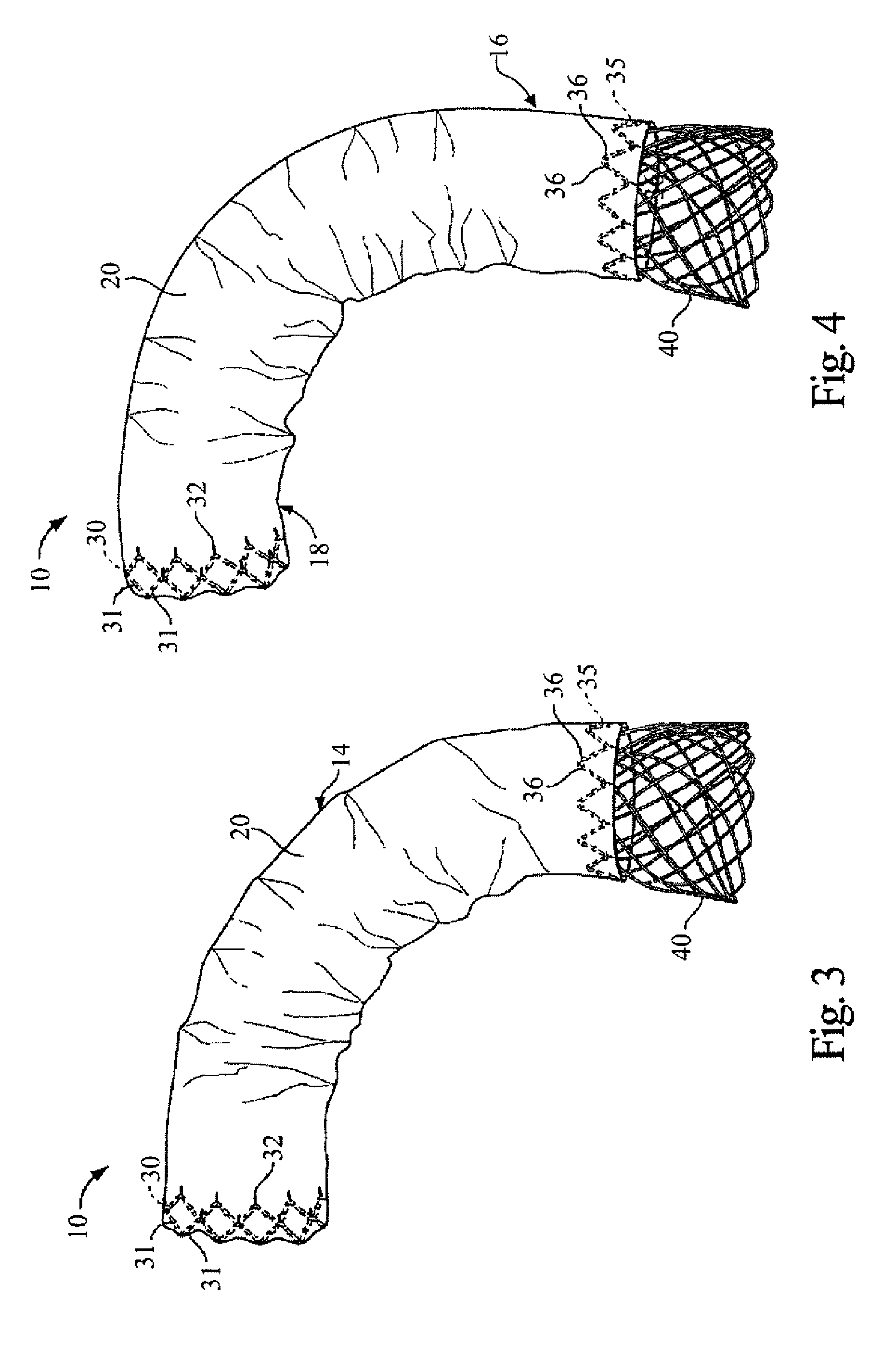
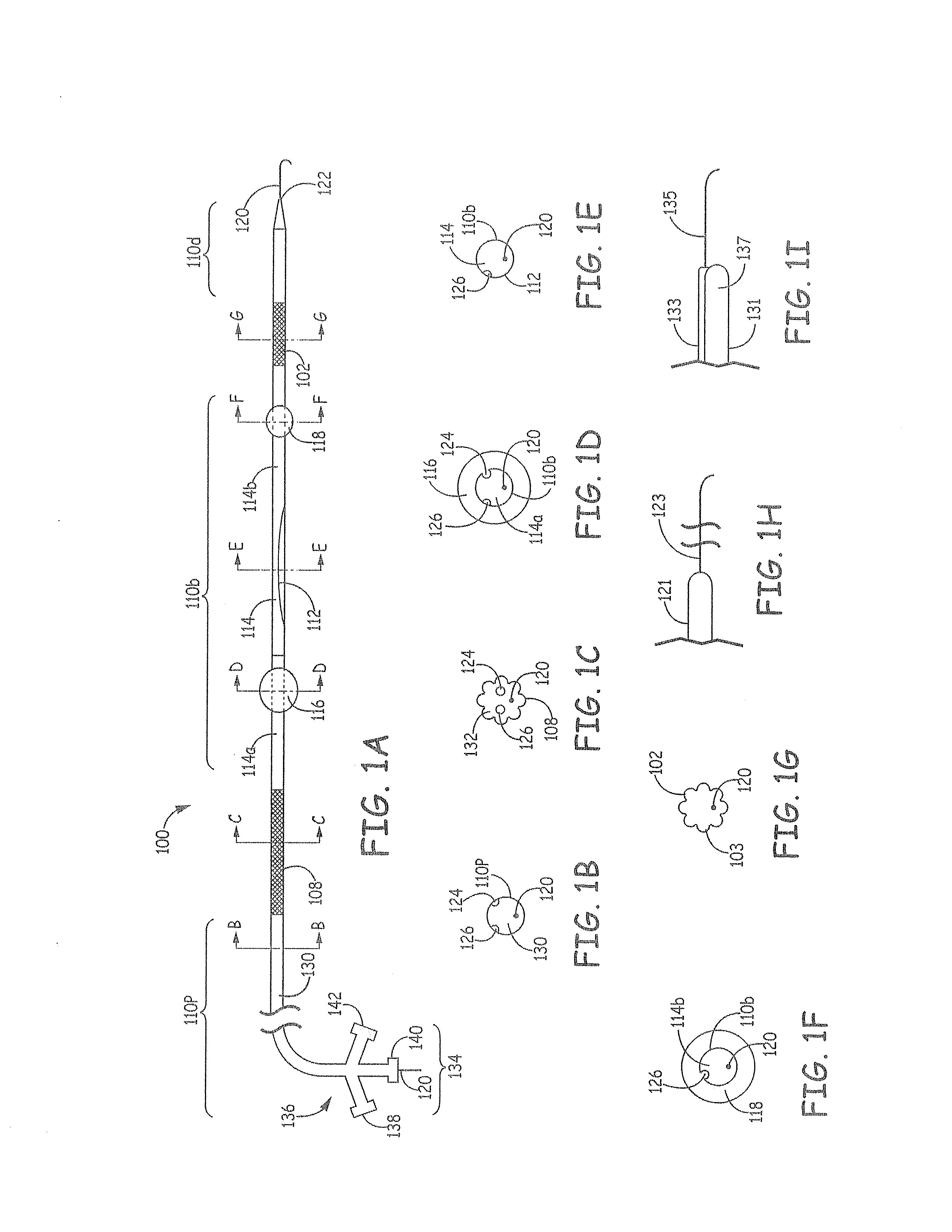
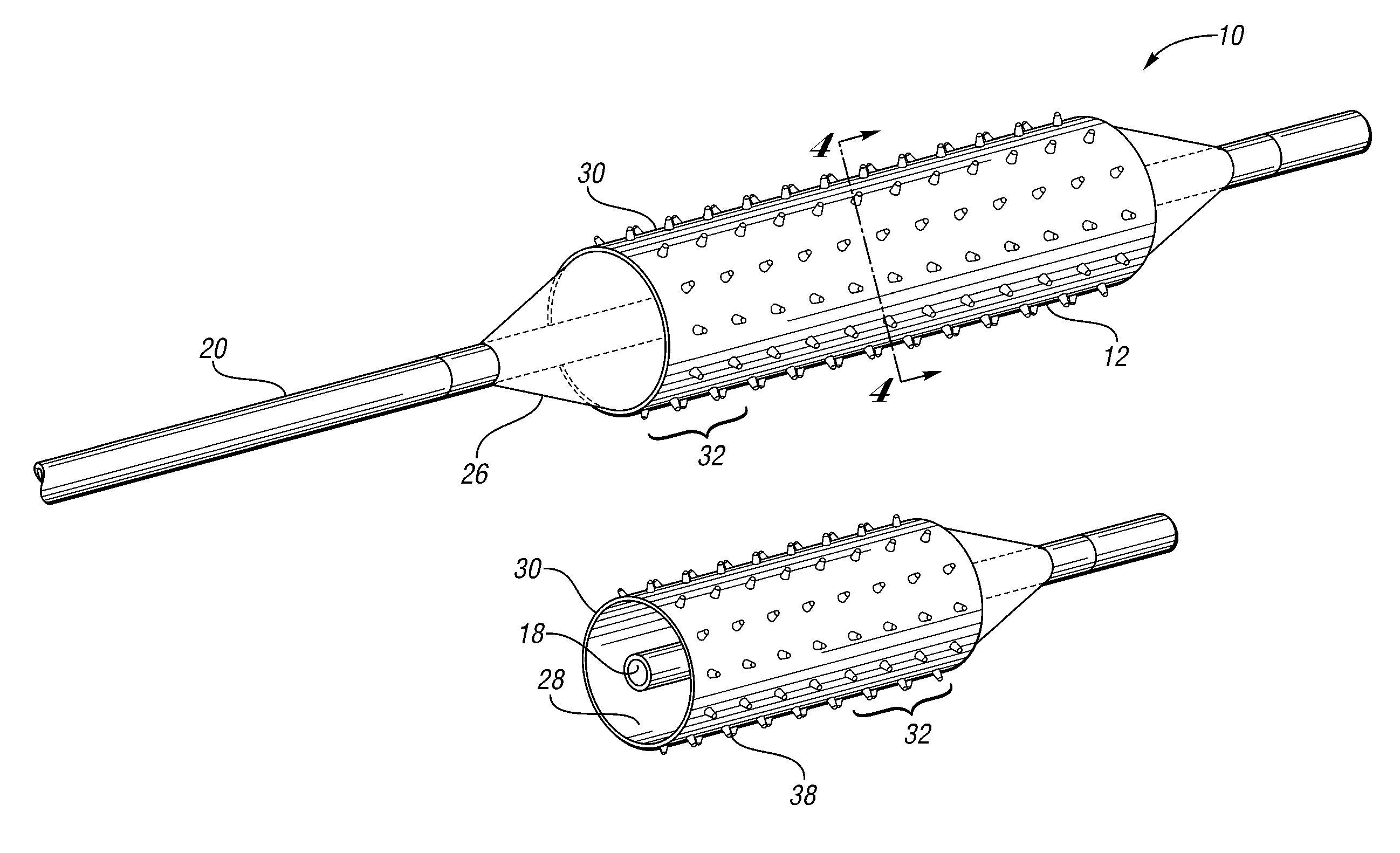
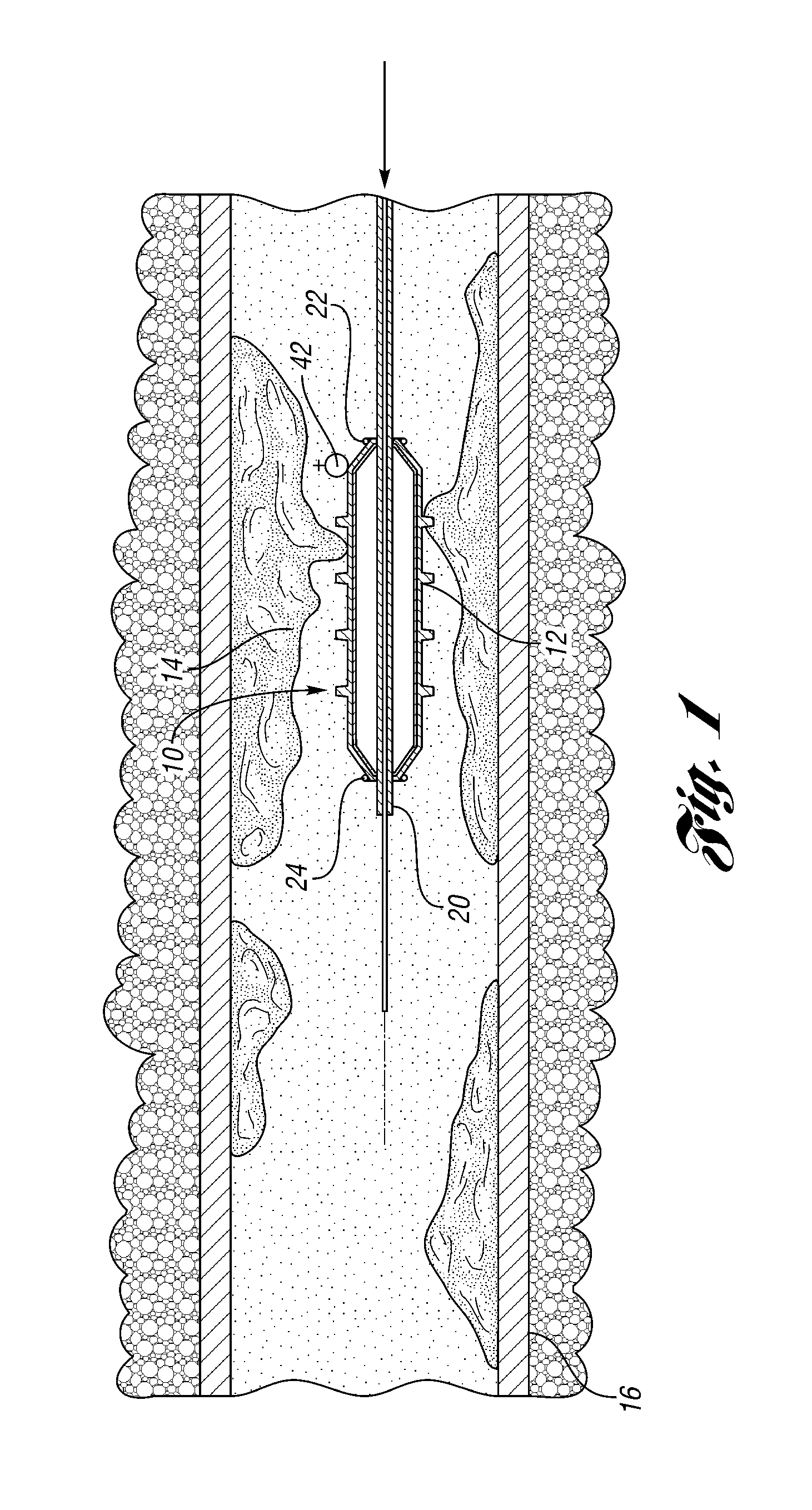
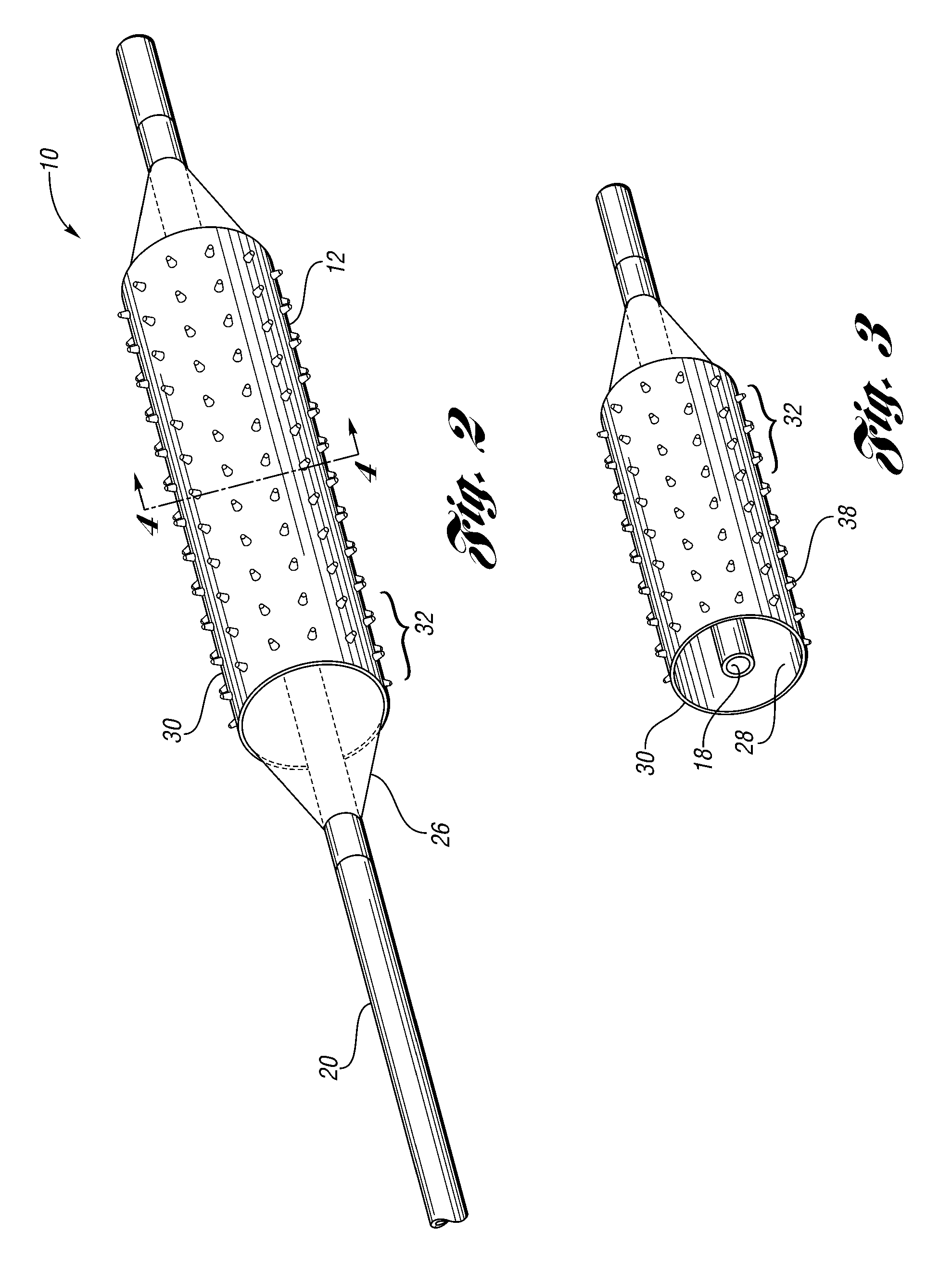
An intravascular filter device for use in capturing debris which may occur as a result of an intravascular procedure. The filter device includes a proximal section, a distal section and a mid-section. The mid-section includes three rings configured in a sixteen apices alternating V-pattern. The filter device specifically embodies structure that provides enhanced radial opening and angular resistance to collapse in its expanded state. While, in its compressed state the filter device provides an extremely small compressed profile giving it the desired ability to be delivered into very small vessels of the human vasculature.
Owner:ENDOVASCULAR TECH
Mitral valve fixation device removal devices and methods
ActiveUS20150257883A1Easy accessSuture equipmentsHeart valvesEndovascular surgeryMitral valve leaflet
Procedures may be performed on the heart after the installation of a mitral valve fixation device. In order to prepare the heart for such procedures, the fixation device may be removed or disabled in minimally invasive ways (e.g., through an endovascular procedure), without requiring open access to the heart. The fixation device may be partitioned so that one portion may remain attached to each leaflet of the mitral valve. In another example, the leaflets may be cut along the edges of the distal element(s) of the fixation device, so as to cut the fixation device from the leaflet(s). Systems and devices for performing such procedures endovascularly are disclosed. Fixation devices with improved access to a release harness are also disclosed.
Owner:EVALVE
Stent for Endovascular Procedures
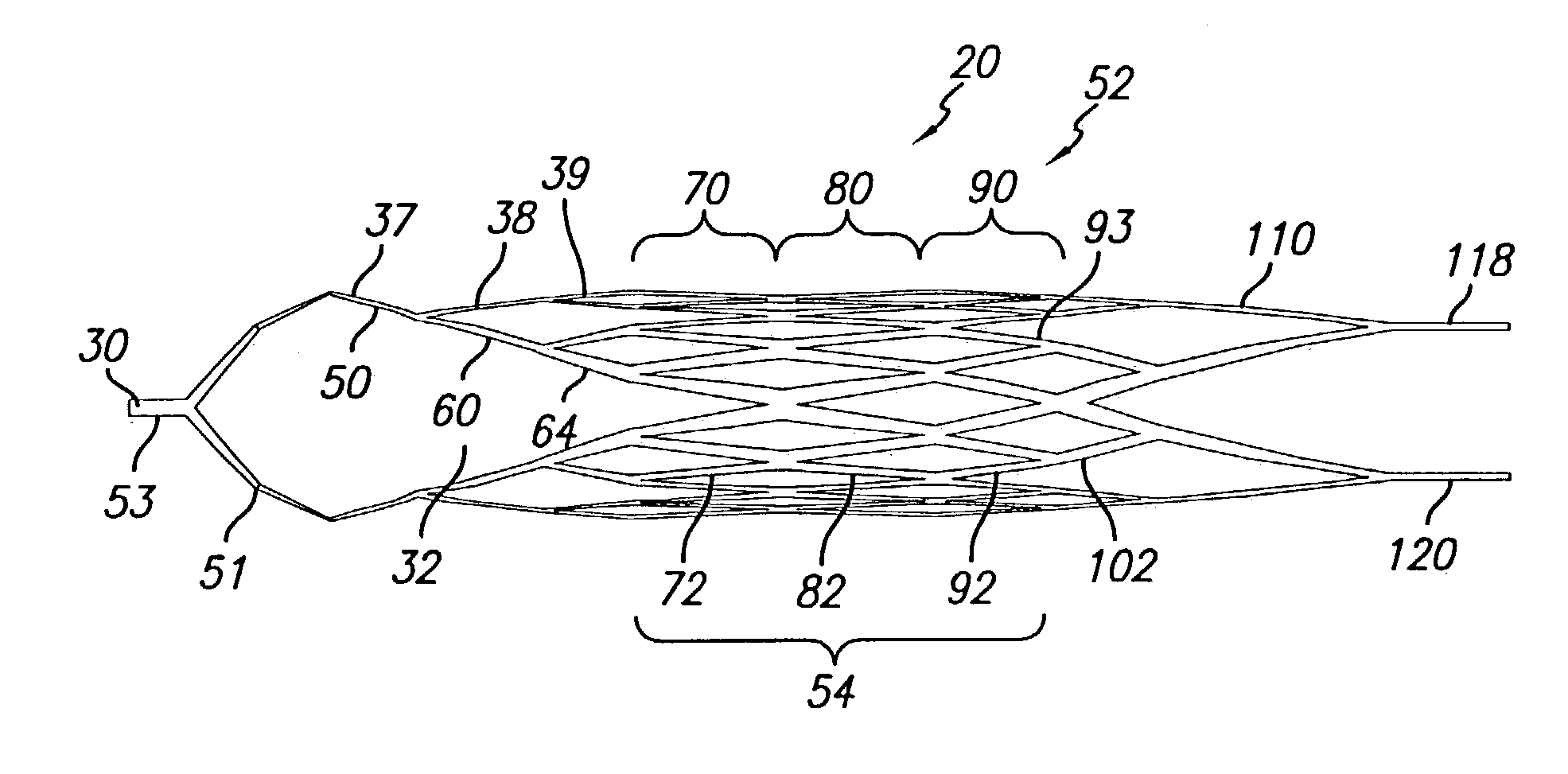
A stent graft for deploying a stent graft at a lesion site is provided. The stent graft comprises a tubular graft and a support stent, at least a portion of which lies within the tubular graft. The graft has a proximal end and a distal end. The support stent has a proximal end and a distal end, and comprises at least one wire forming a first helical wire portion having a first translational direction about an axis of the support stent and a second helical wire portion having a second translational direction about the axis opposite the first translational direction. When the support stent is in a compressed delivery configuration, the support stent has a first length, and when the support stent is in an expanded deployed configuration, the support stent has a second length which is less than the first length. When in the delivery configuration, the support stent is attached to the graft only at or near the proximal end of the graft.
Owner:VASCULAR INNOVATIONS
Endovascular device for application of prosthesis with sutures
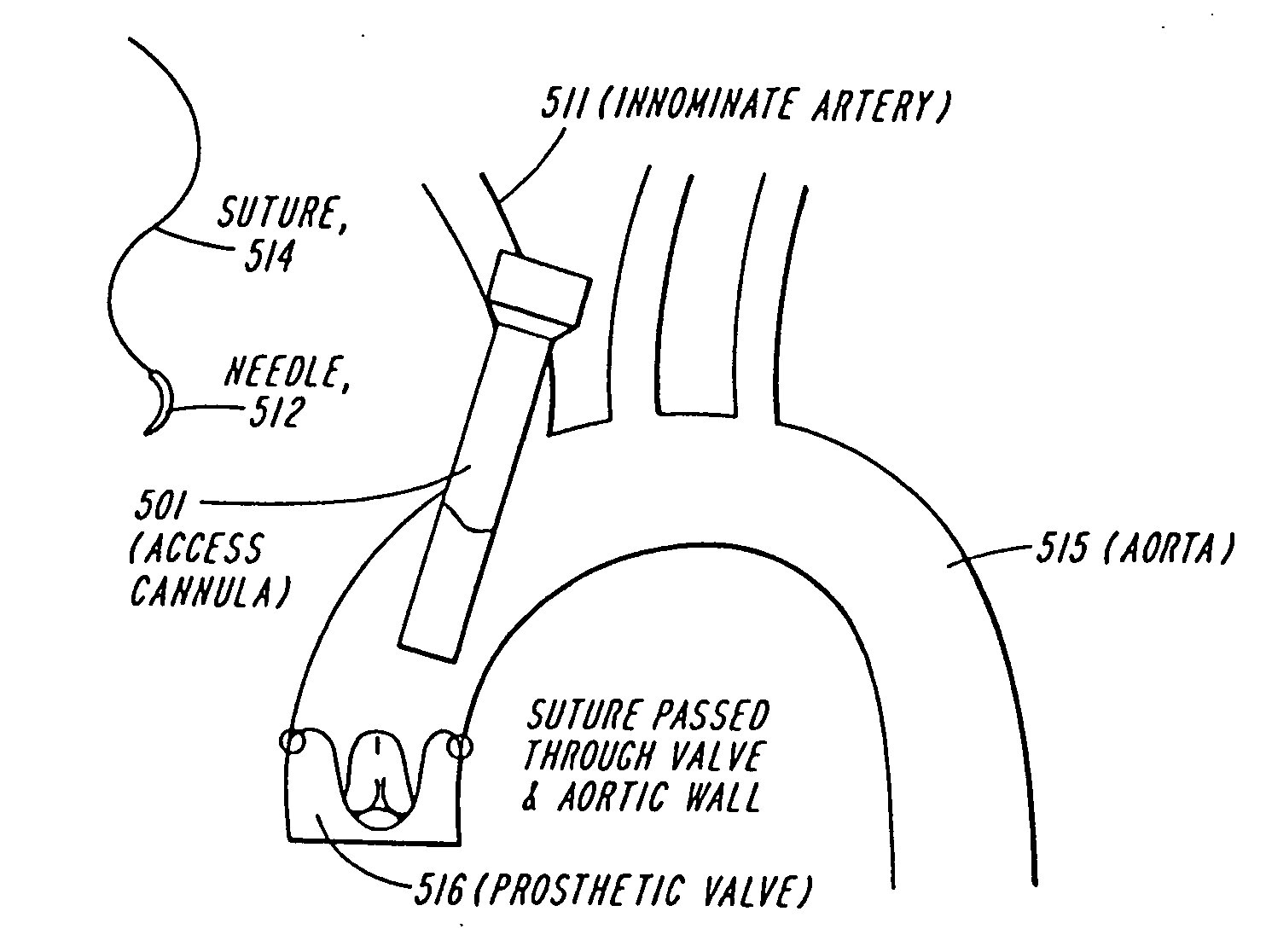
An endovascular surgical device is disclosed for attaching an endovascular prosthesis to a vascular wall. The device includes a tubular member and an applicator device. The tubular member has longitudinal bands separated by slots that are configured to expand upon being placed in compression. The applicator device has a distal end with a rotary head for applying sutures. A portion of the suture is at least partially positioned in the rotary head. A method is described that includes positioning a prosthesis and an endovascular device within a portion of vascular wall that requires reinforcing or repairing. The tubular part is expanded, forcing the prosthesis and vascular wall to expand. The applicator device applies the suture to attach the prosthesis to the vascular wall. Additional sutures can be applied by removing the applicator device, attaching a second suture and repositioning the applicator device to attach a second suture.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
System and method for intraoperative guidance of stent placement during endovascular interventions
A method for guiding stent deployment during an endovascular procedure includes providing a virtual stent model of a real stent that specifies a length, diameter, shape, and placement of the real stent. The method further includes projecting the virtual stent model onto a 2-dimensional (2D) DSA image of a target lesion, manipulating a stent deployment mechanism to navigate the stent to the target lesion while simultaneously acquiring real-time 2D fluoroscopic images of the stent navigation, and overlaying each fluoroscopic image on the 2D DSA image having the projected virtual stent model image, where the 2D fluoroscopic images are acquired from a C-arm mounted X-ray apparatus, and updating the projection of the virtual stent model onto the fluoroscopic images whenever a new fluoroscopic image is acquired or whenever the C-arm is moved, where the stent is aligned with the virtual stent model by aligning stent end markers with virtual end markers.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
Endovascular guidewire filter and methods of use
InactiveUS6936059B2Avoid accidental displacementAssist in removingSurgeryDilatorsVeinEndovascular surgery
A filter device for temporary placement of a filter in an artery or vein is disclosed. The devices include (1) an elongate tubular member having a single or double side-wire loop, (2) an elongate member having a filter bonded to a circular rim joined by a plurality of tethers and an independently moveable tether, and (3) an elongate member having a parachute filter joined by a plurality of flexible struts. The filter conforms to the interior of a vessel wall when expanded and contracts to a consistent diameter without bunching when stowed. The filter devices may act as guidewires for guiding a therapeutic catheter to a region of interest within a vessel. Methods of using the filter device to entrap and remove embolic material from a vessel during endovascular procedures are also disclosed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Expanded UHMWPE for guiding catheter liners and other lubricious coatings
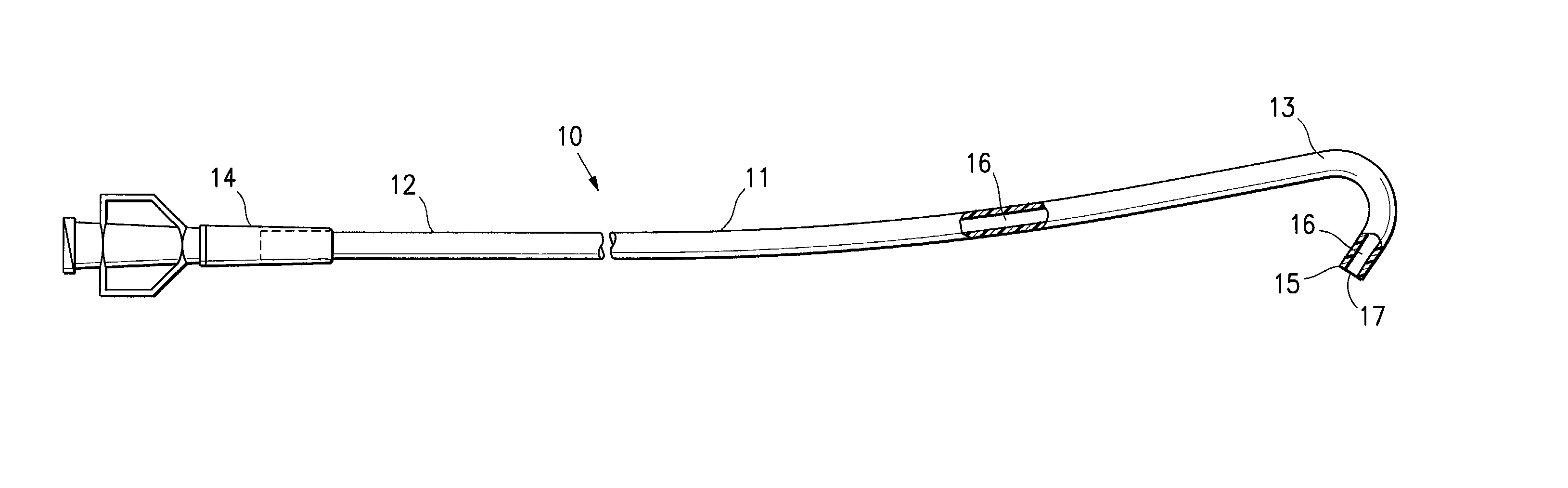
An intraluminal catheter, such as a guiding catheter, employed for intravascular procedures and having an inner liner formed of expanded Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) is disclosed. The expanded UHMWPE is microporous and has an oriented microstructure structure characterized by nodes interconnected by fibrils. The inner liner formed of expanded UHMWPE is very thin to maximize the inner lumen diameter and has excellent mechanical properties.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Distal protection apparatus with improved wall apposition
InactiveUS20060149313A1Easy loadingPrevent thrombosisSurgeryDilatorsEndovascular surgeryEmbolization material
In accordance with the present invention, a distal protection and embolic material retrieval device with improved apposition to both large and small vessel walls of varying geometries for enhancing the filtering of embolic material during intravascular procedures while allowing for the passage of blood is provided. The device includes a filter basket designed to maximize apposition of the filtering portion to that of the vessel wall and may include struts which provide circumferential support to the filtering membrane and thereby minimizing or eliminating in-folding of the filter basket. Thin film materials may also be utilized for the filtering membrane of the filter basket. In addition one can incorporate biological and / or pharmaceutical agents in combination with the present invention.
Owner:ARGUELLO EDWARD +3
Devices and methods for the controlled formation and closure of vascular openings
InactiveUS20080208213A1Easy to createOptimally apposeSurgical staplesWound clampsEndovascular surgeryImplanted device
The present invention includes systems, devices and methods for percutaneously forming an aperture within a tissue structure or vessel and closing the aperture in a manner which optimizes hemostasis and healing. The invention in one aspect includes implantable devices which are used to seal the tissue aperture upon closure of the aperture after a percutaneous or endovascular procedure.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
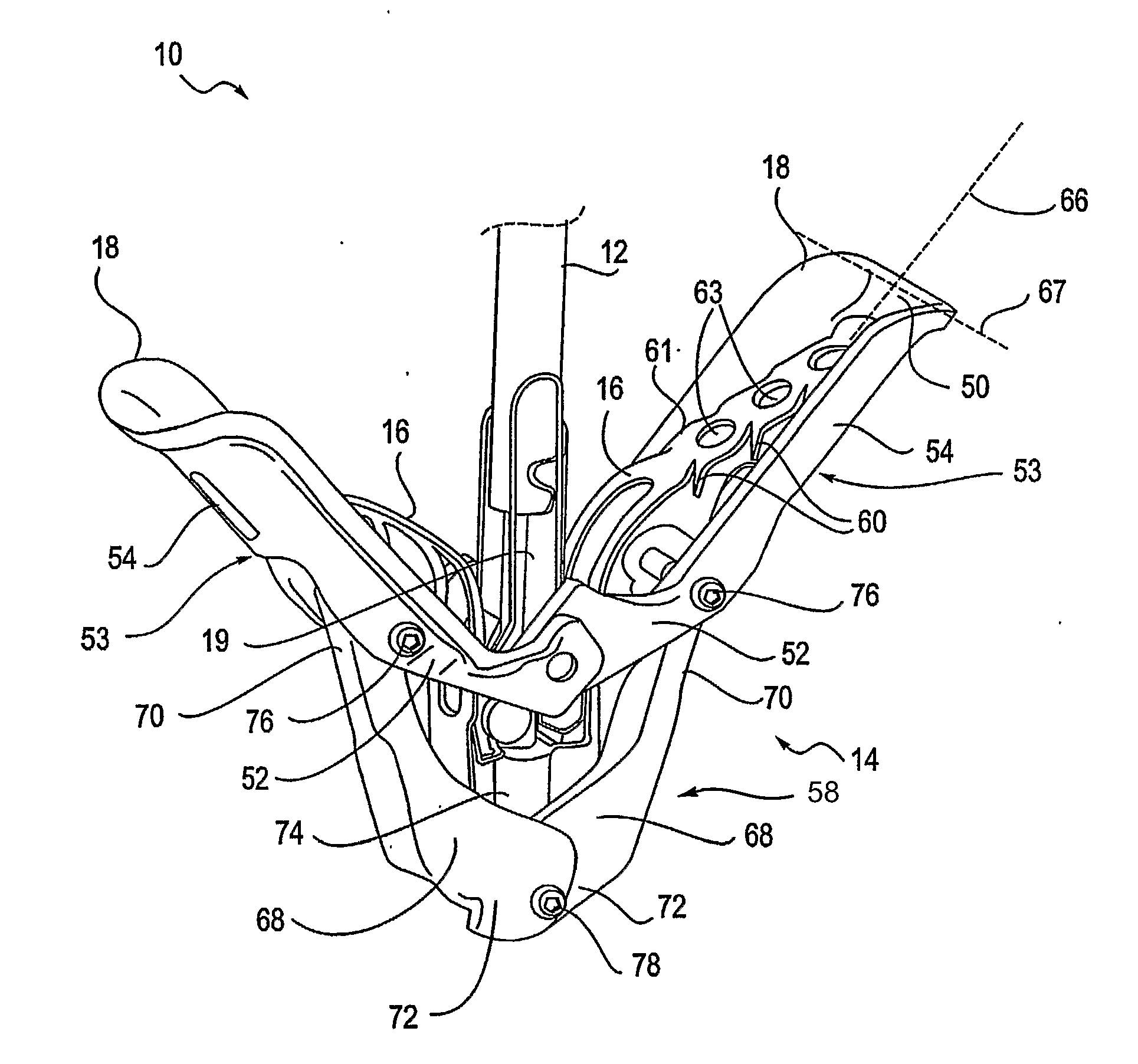
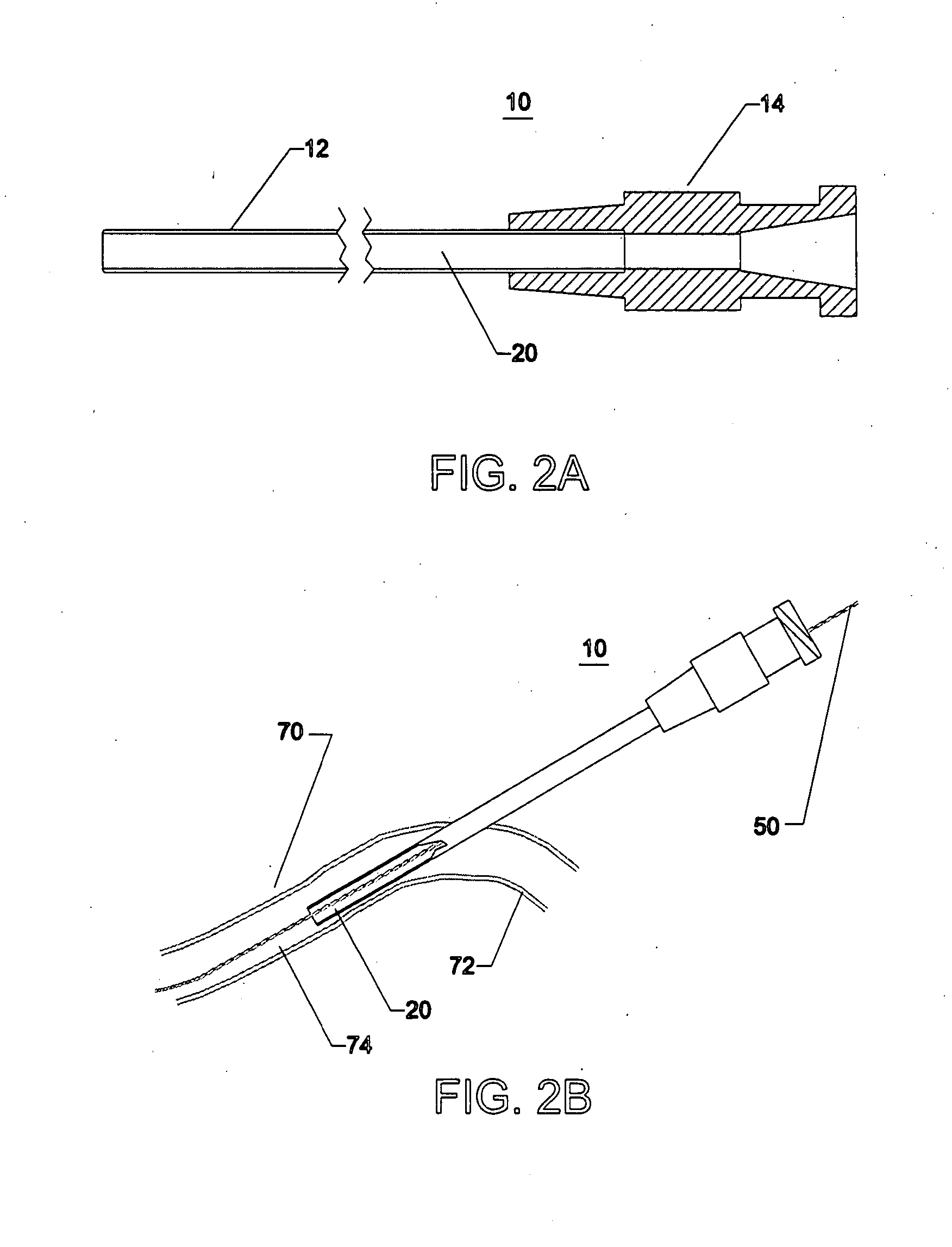
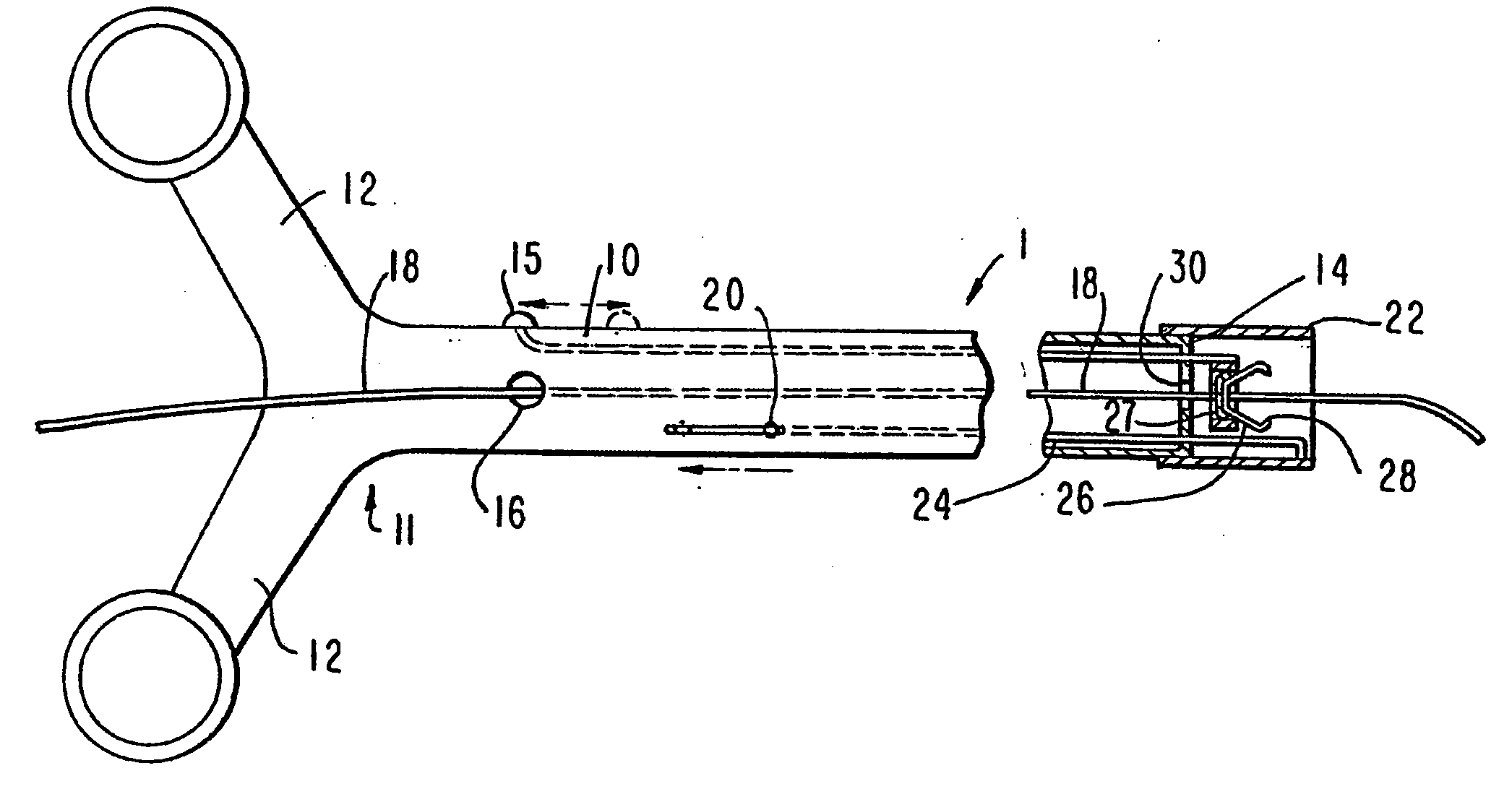
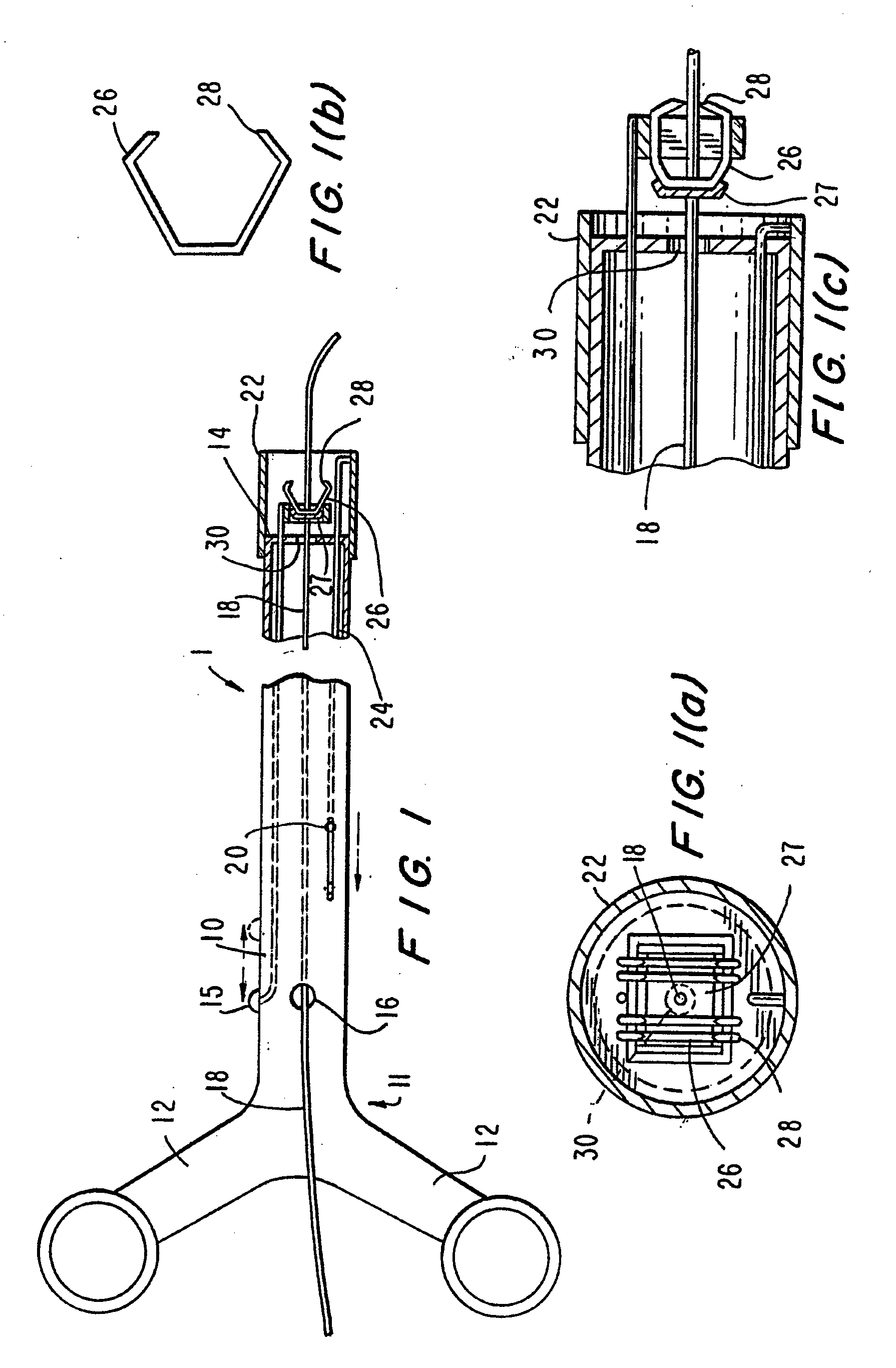
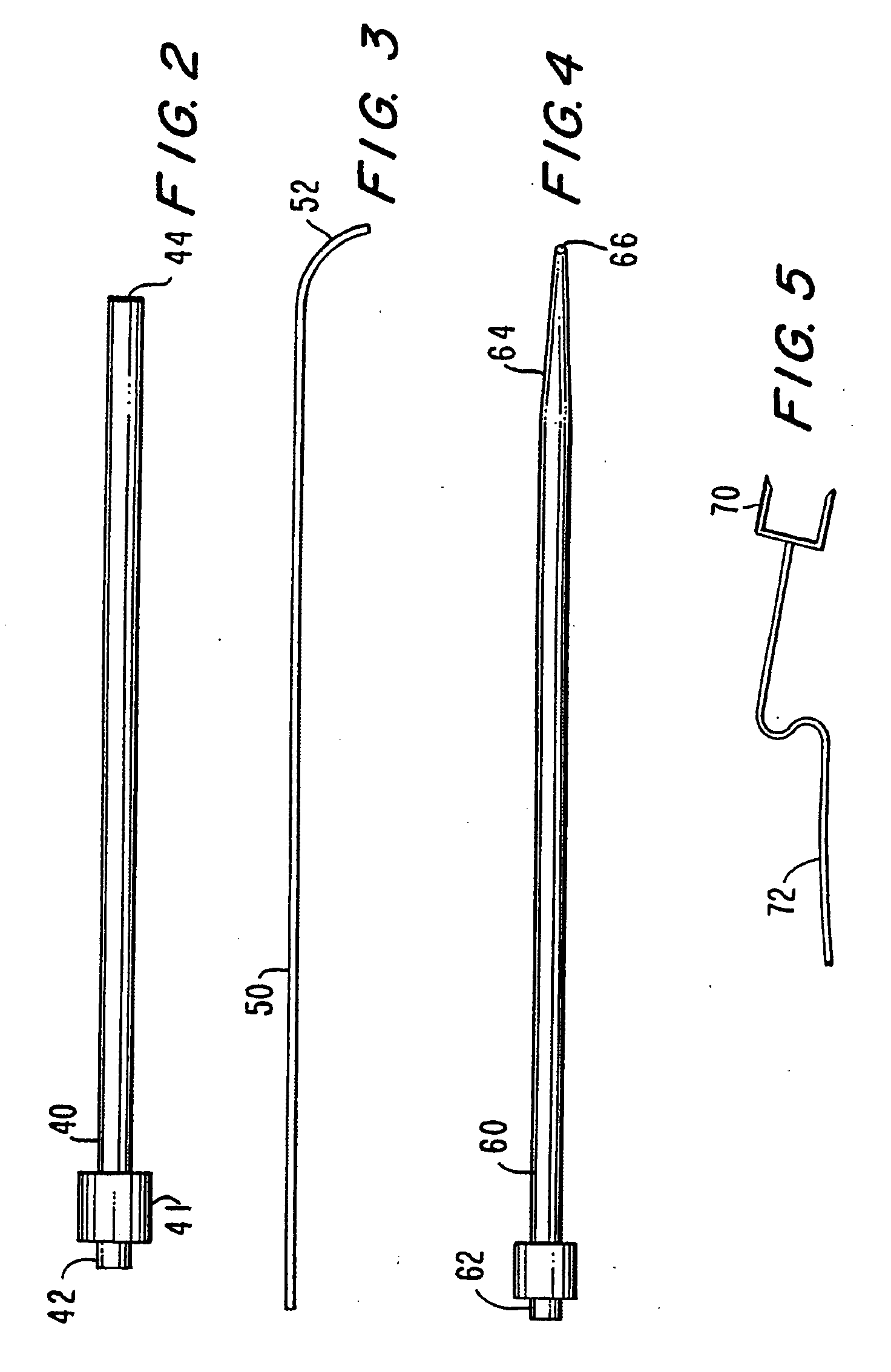
Endovascular surgical method
An endovascular surgical method comprises the steps of (1) incising a patient to gain access to the interior of a selected blood vessel, (2) inserting a cannula through an aperture formed in a sealing member comprising an elastomeric membrane having an aperture for receiving the cannula, an elongated wall portion surrounding the aperture, an outer flange region, an expandable bellowed intermediate portion between the flange region and the elongated wall portion, and a layer of adhesive on the bottom surface of the flange region, (3) orienting the membrane so that the bottom surface of the flange region contacts the patient's skin when the cannula is inserted through the incision, the aperture and cannula being relatively sized to form a tight fit and seal around the cannula, and (4) perform surgery from within the selected blood vessel by inserting and withdrawing surgical instruments through the cannula to so that the intermediate membrane portion resiliently supports the cannula for movement against its elongated wall portion without transmitting stress to the flange portion that would cause the flange portion to pull away from the patient's skin.
Owner:MCLUCAS BRUCE
Device to create proximal stasis
A method and system of performing an intravascular procedure at a treatment site in a vessel of a patient. A device creates a seal to prevent the flow of blood during the treatment of vascular disease. A seal may be formed between the distal inside diameter of a sheath or catheter such as a guide catheter as well as within a vessel, such as an artery or vein. An elongated device having a distal portion extending from the catheter and having a fluid impermeable membrane disposed about at least the distal end of the device is used to seal the vessel. The system includes a device to occlude blood flow and a distal protection device to filter or remove embolic debris.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Delivery system with helical shaft
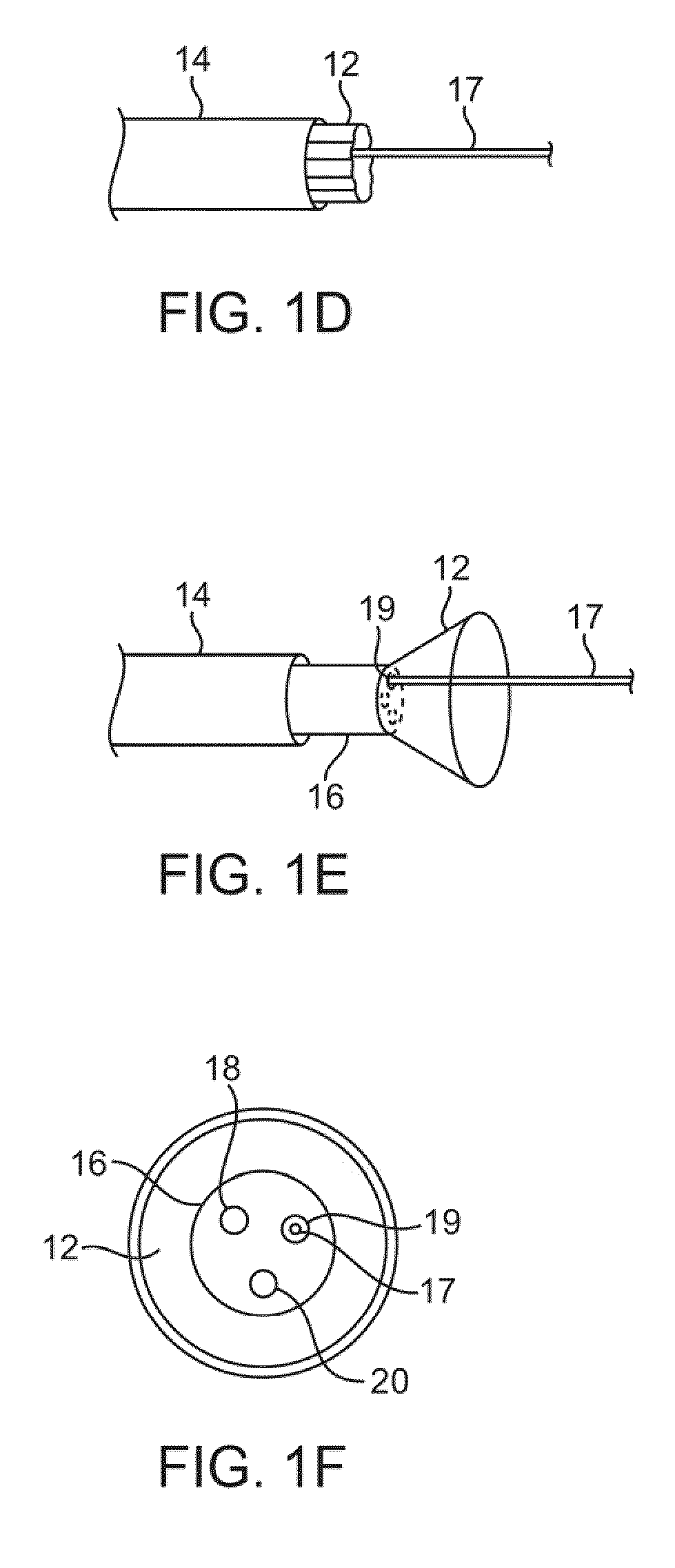
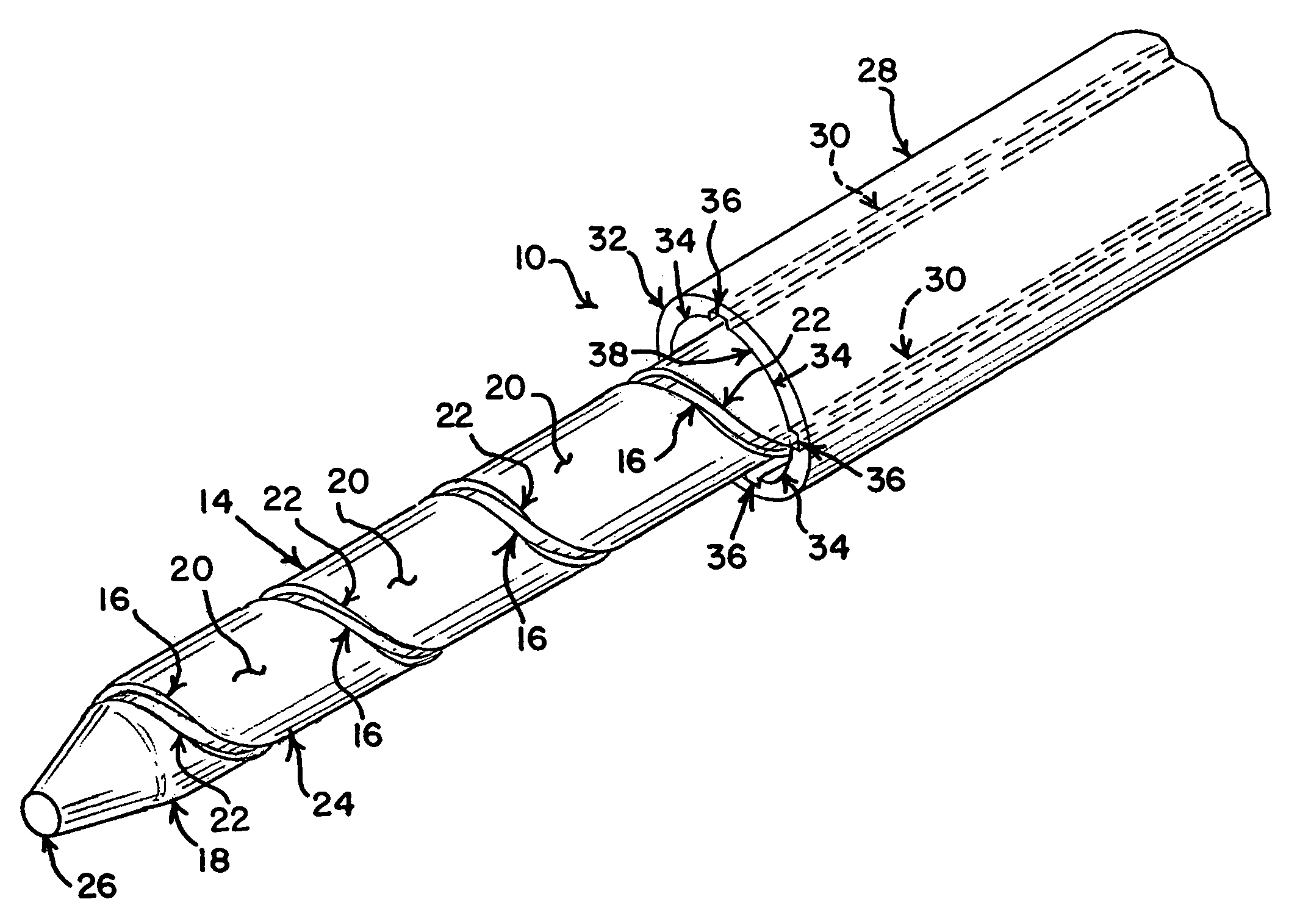
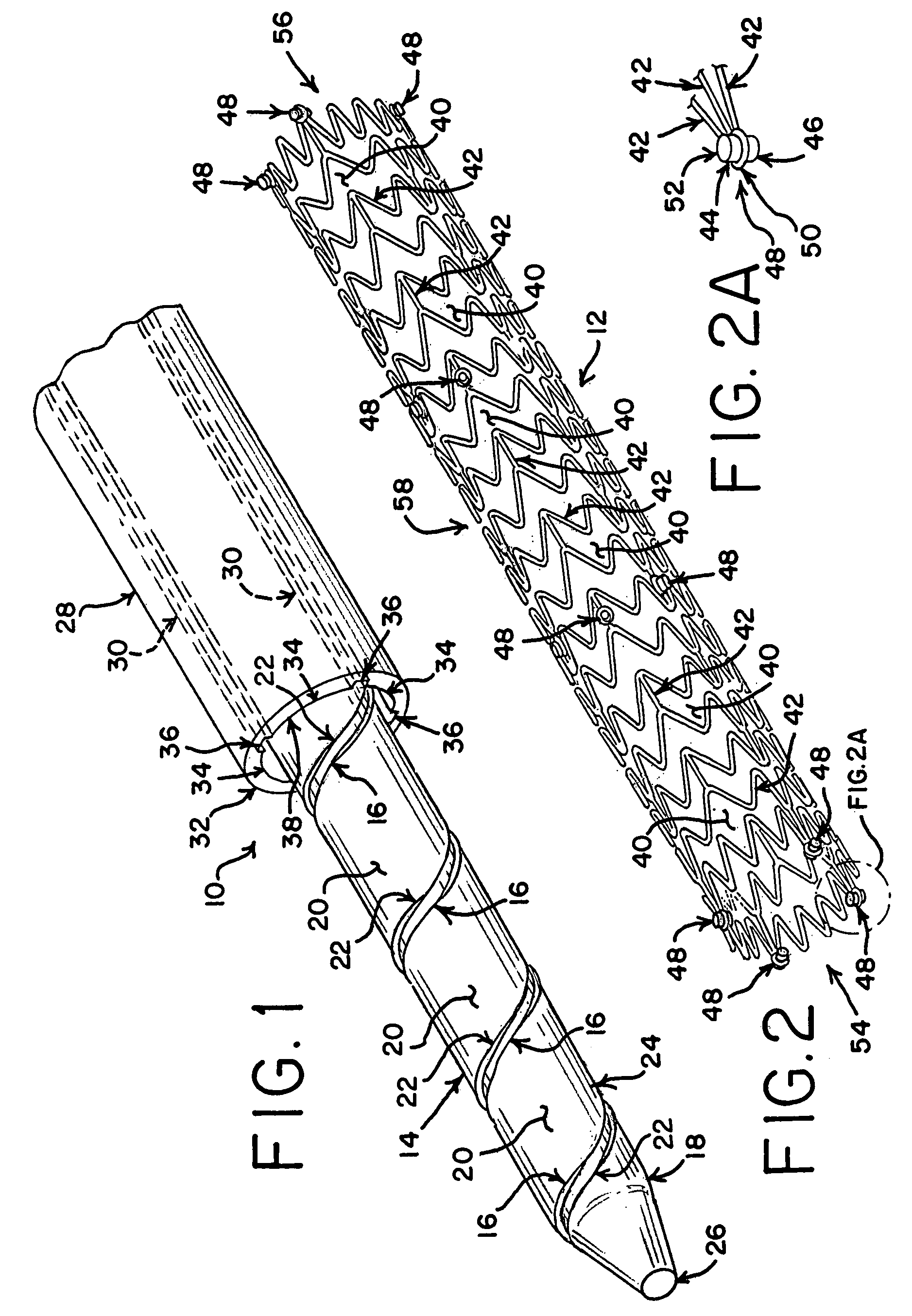
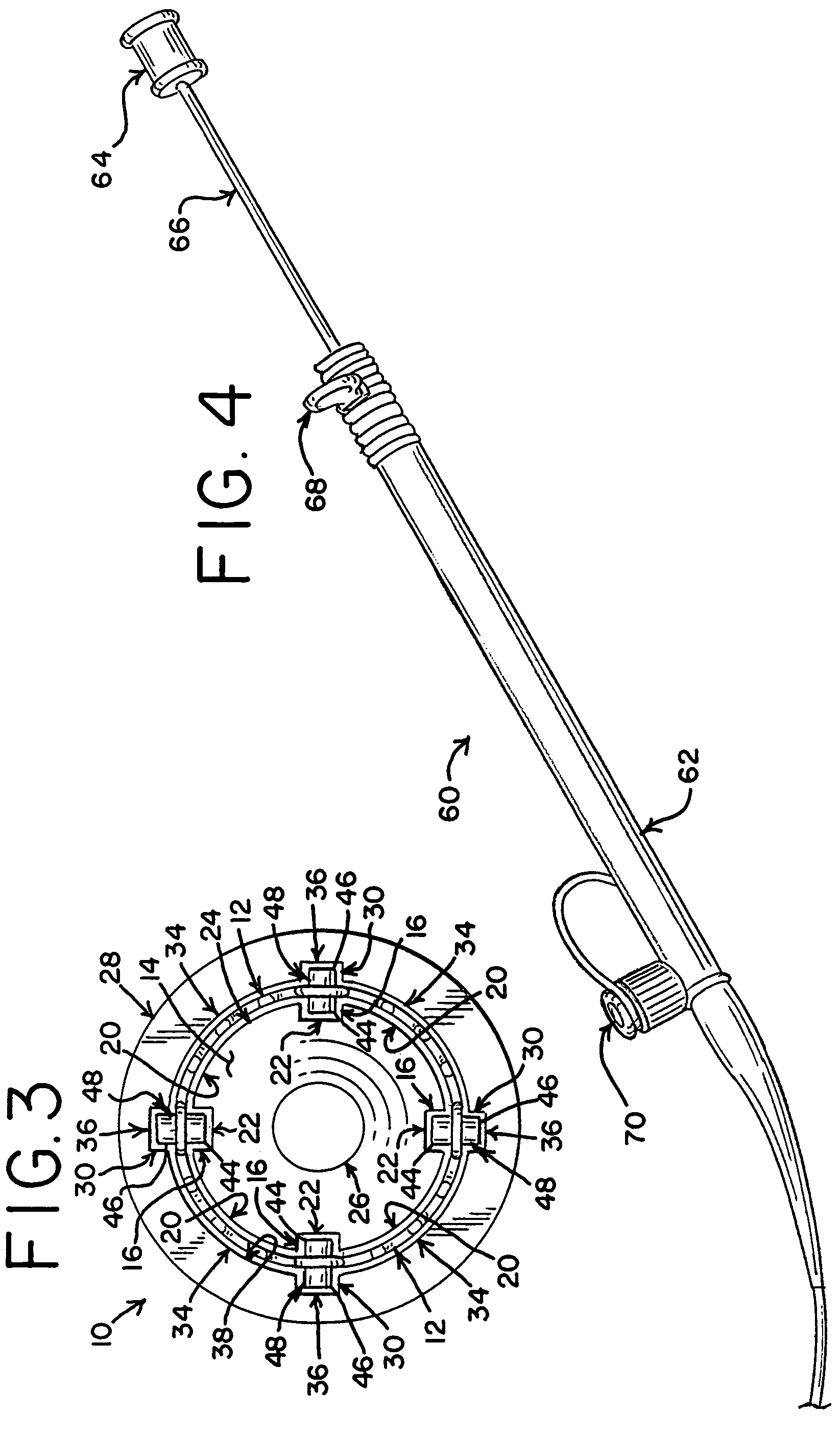
A delivery system is provided for releasing a medical device within a body cavity. The delivery system may be used in an intravascular procedure to implant a self-expandable stent. A helical structure on the shaft of the delivery system engages the inner surface of the stent. As a result, the stent may be released by rotating the shaft relative to the stent which pushes the stent forward from the distal end of the shaft.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Endovascular guidewire filter and methods of use
ActiveUS20050159774A1Tight stowagePrevent accidental releaseCannulasDilatorsVeinEndovascular surgery
A filter device for temporary placement of a filter in an artery or vein is disclosed. The devices include (1) an elongate tubular member having a single or double side-wire loop, (2) an elongate member having a filter bonded to a circular rim joined by a plurality of tethers and an independently moveable tether, and (3) an elongate member having a parachute filter joined by a plurality of flexible struts. The filter conforms to the interior of a vessel wall when expanded and contracts to a consistent diameter without bunching when stowed. The filter devices may act as guidewires for guiding a therapeutic catheter to a region of interest within a vessel. Methods of using the filter device to entrap and remove embolic material from a vessel during endovascular procedures are also disclosed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Stabilization of visualization catheters
ActiveUS8131350B2Improve the immunityFacilitate intravascular procedure and treatment of tissueSurgeryEndoscopesEndovascular surgeryCatheter
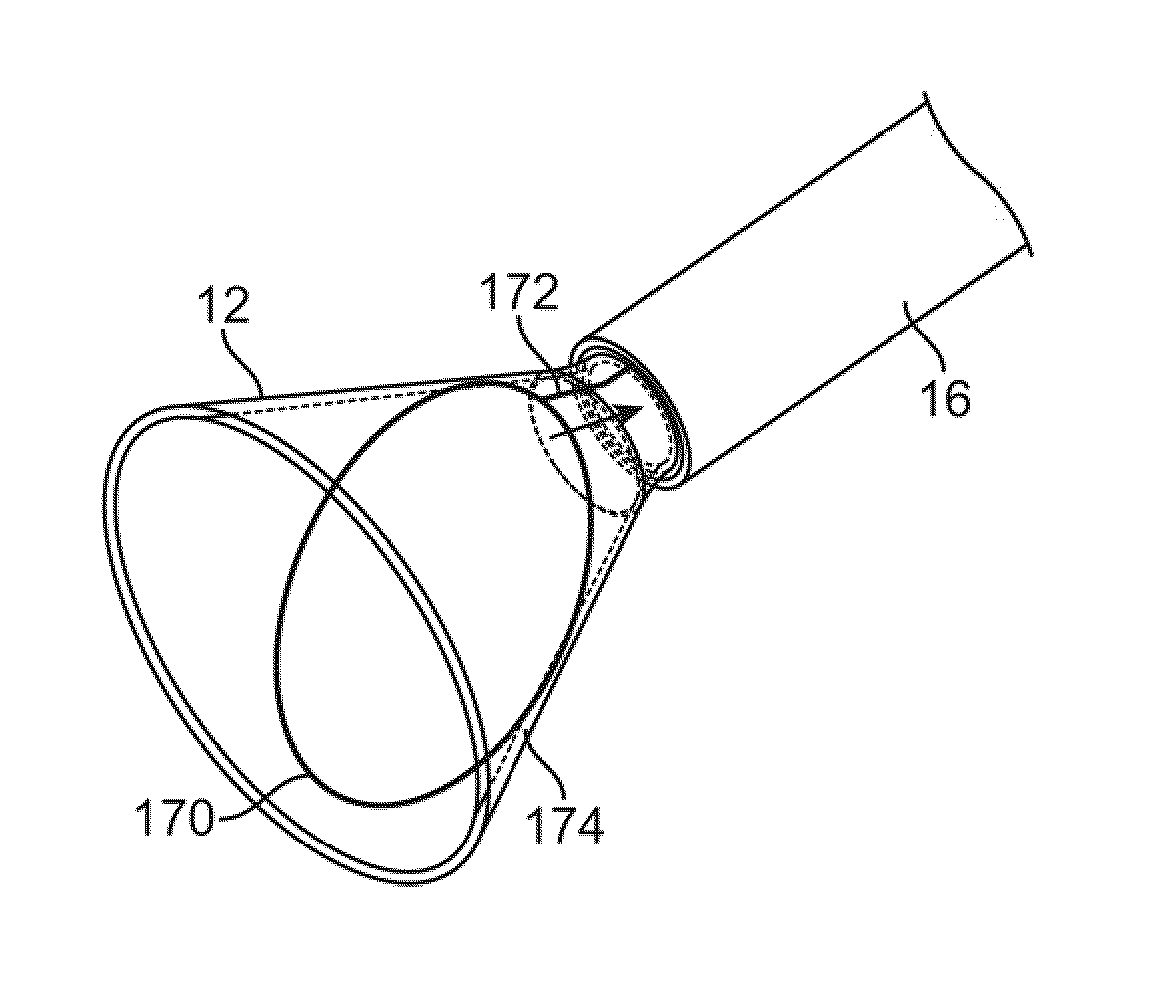
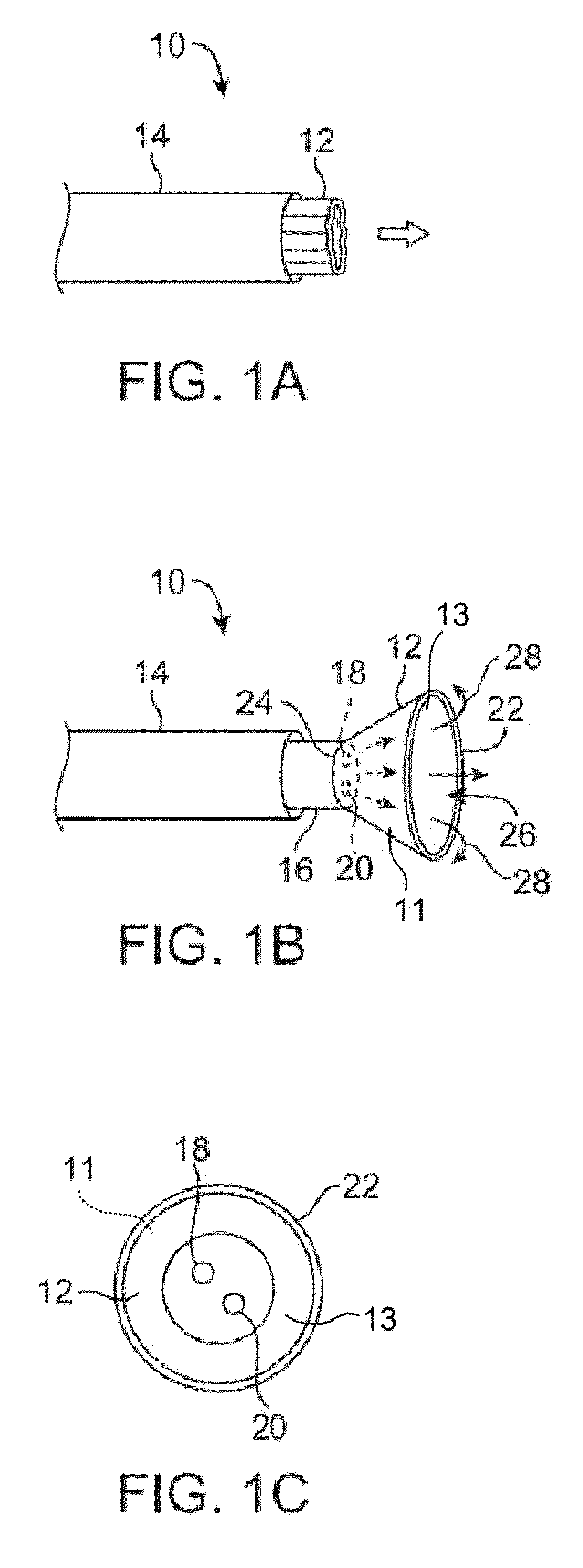
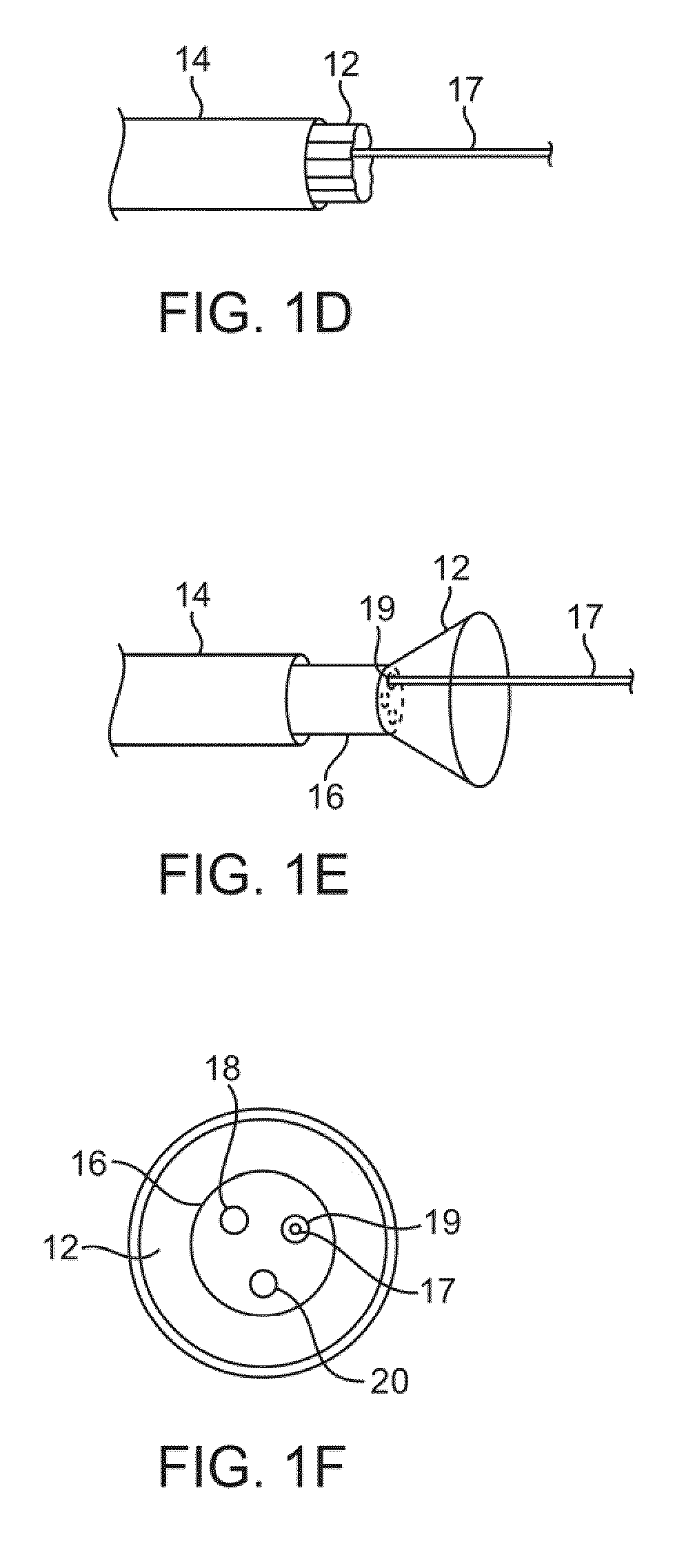
Systems for the stabilization of visualization catheters are described herein which facilitate the deployment and retraction of an imaging hood from a catheter. Such systems may include a deployment catheter and an imaging hood having one or more structural elements which may be integrated or advanced into the hood independently of the hood itself. Moreover, additional features such as rapid exchange ports may be integrated along the hood or along the catheter proximal to the hood to facilitate intravascular procedures and treatments.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
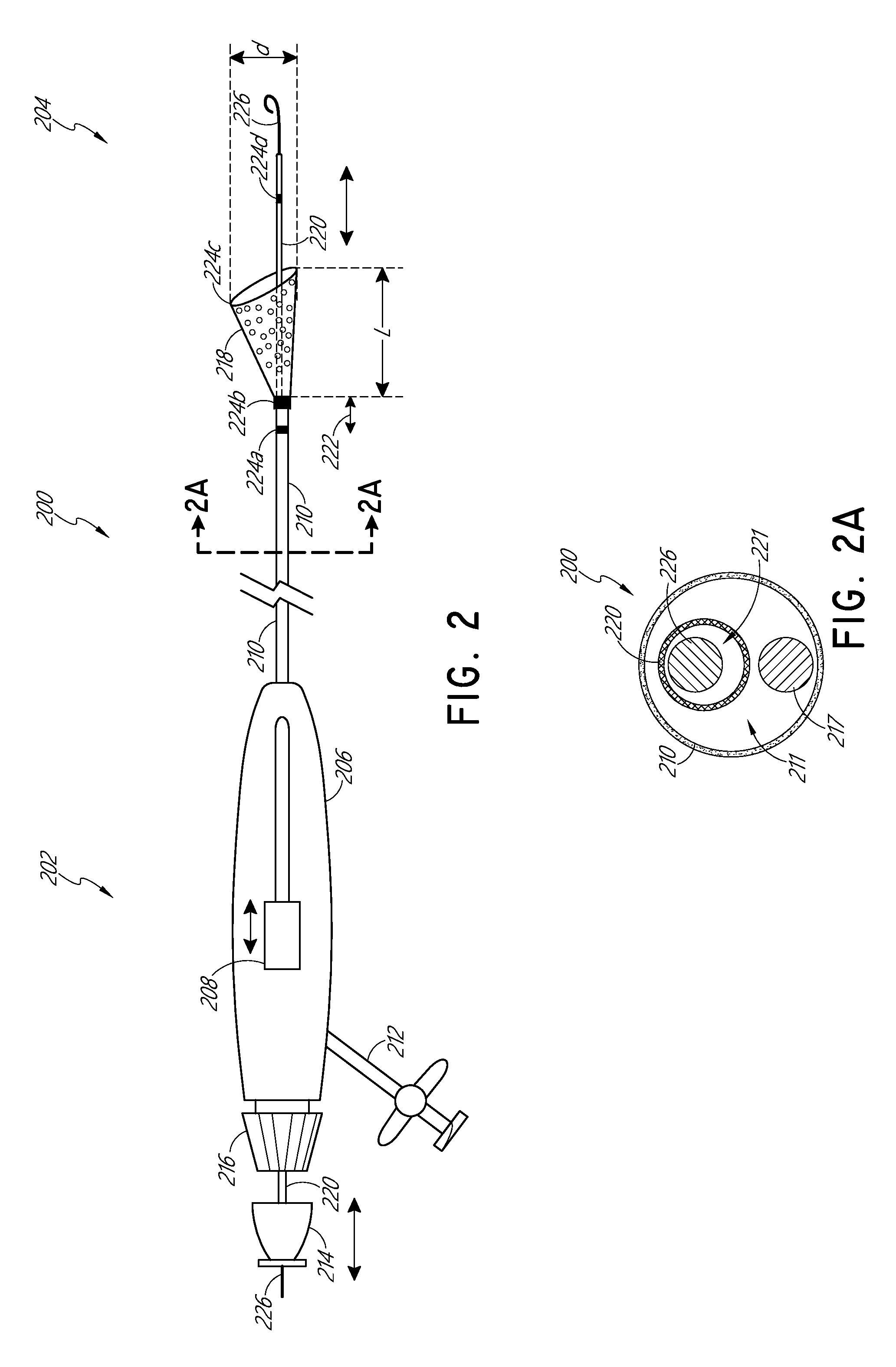
Aortic arch filtration system for carotid artery protection
Filtration systems with integrated filter element(s) forming portions of the wall of the filtration catheter are disclosed. The filtration catheters disclosed herein are designed to be used alone or in conjunction with another filter device to provide embolic protection of both carotid arteries. Occlusive element such as balloon is placed on the exterior of the filtration catheter to redirect blood flow in the vessels during the filtration process as well as to help anchor the filtration catheter inside the vessel. The integrated filter element(s) does not require collapsing thus significantly reduces the complexity of the filtration system retrieval process and the chances of releasing emboli back into the blood stream. The compact design of the filtration systems makes them particularly suitable for embolic protection during endovascular procedures on or close to the heart.
Owner:LUMEN BIOMEDICAL
Catheter with enhanced reinforcement
InactiveUS20020072729A1Minimizes supportThinner polymer layerCatheterIntravenous devicesMedicineAdhesive
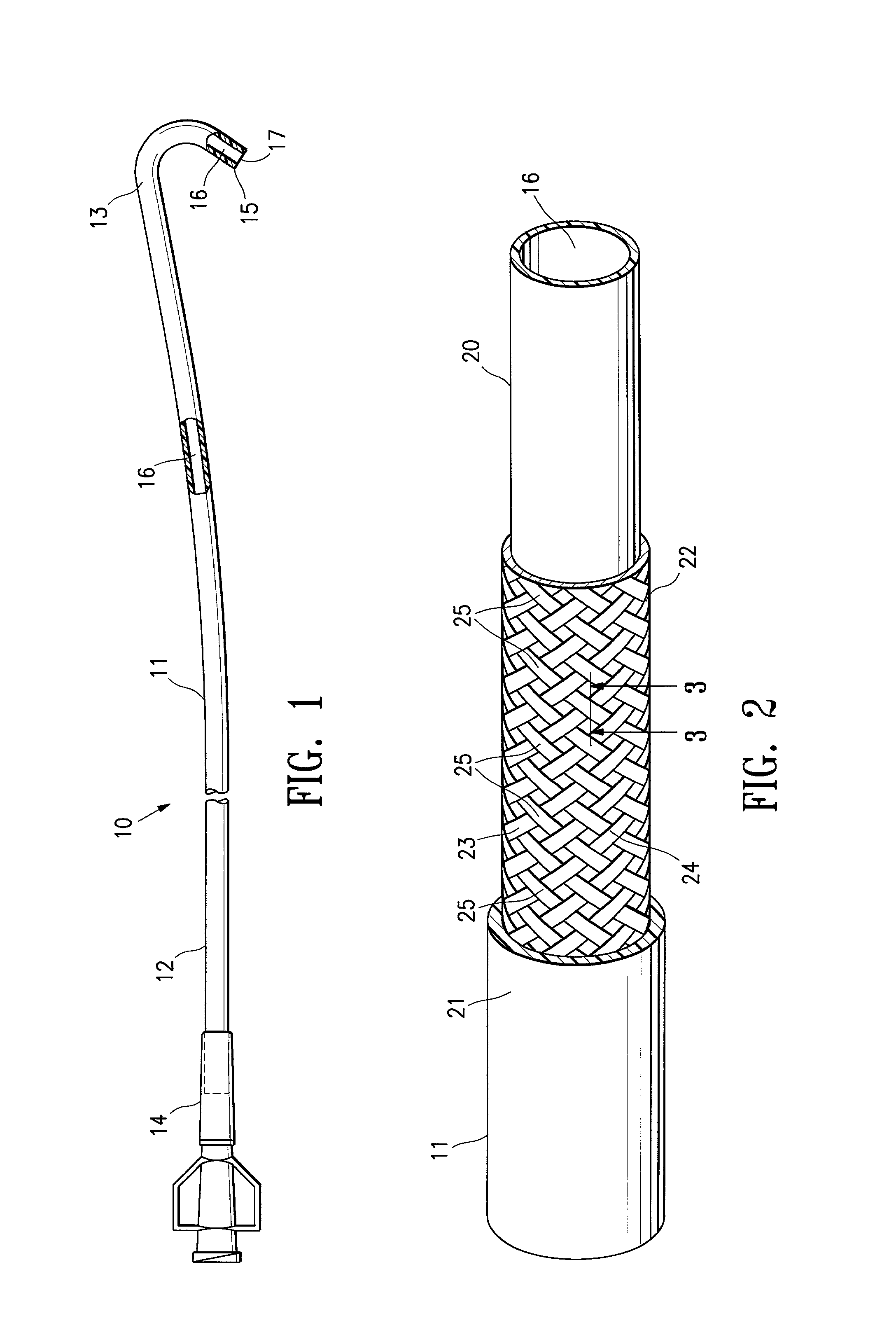
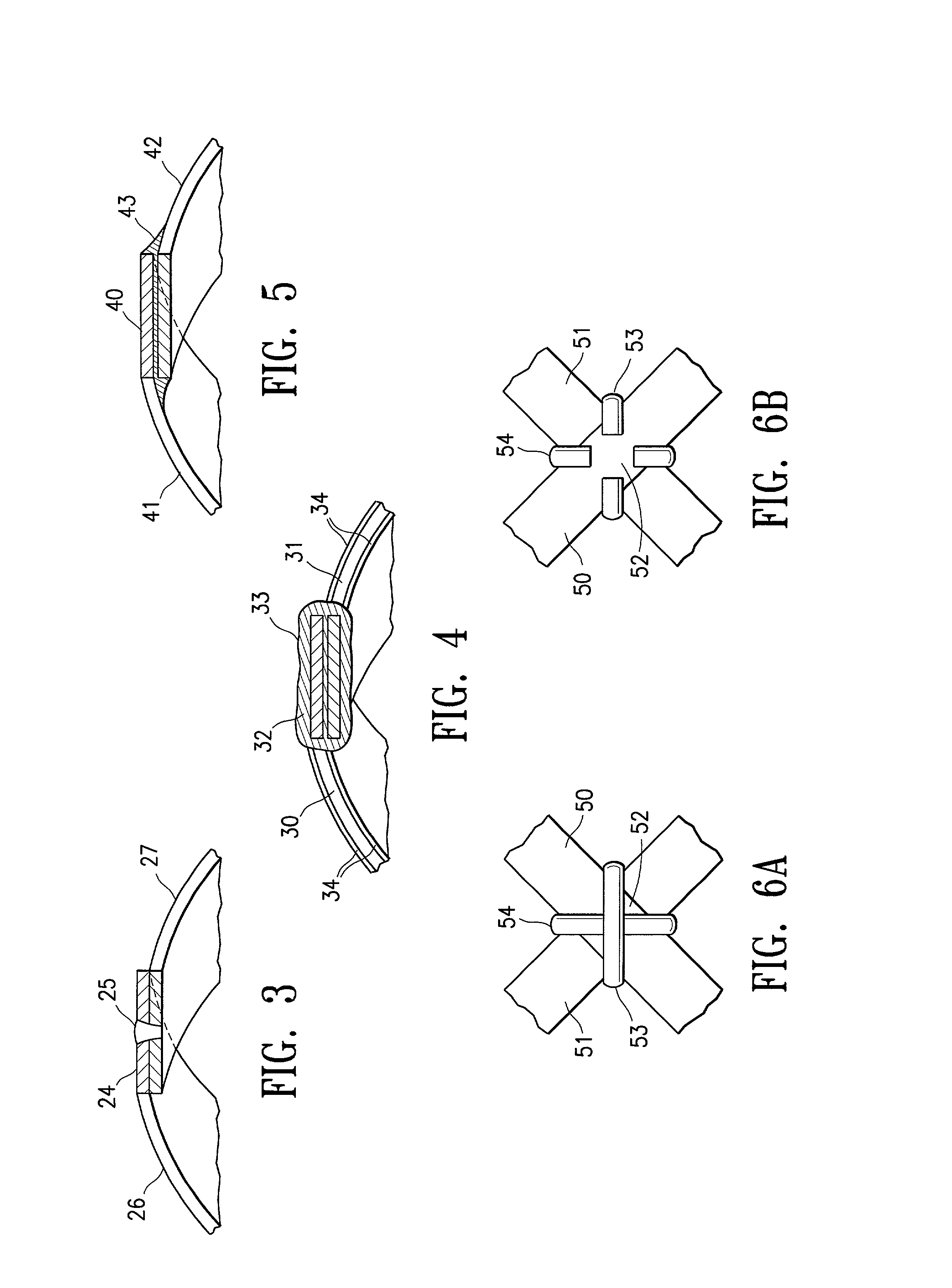
An intracorporeal catheter such as a guiding catheter employed for intravascular procedures which generally has an elongated catheter shaft with a polymeric wall with a multistrand reinforcing structure wherein the strands at a plurality of cross point locations of the reinforcing structure are secured together to hold at least part of the braided reinforcing structure in a desired shape for utilization. The strands may be metallic or polymeric or mixtures thereof. The strands can be secured together at the cross points thereof by a variety of ways. In one embodiment a plurality of the strands forming the reinforcing structure are formed of metal and are provided with a coating of solder so that the strands can be secured together by applying heat to the strands at the cross point locations to melt the solder and allow a solidified solder connection between the strands to be formed upon cooling while holding at least the portion of the reinforcing structure having secured cross points while holding the portion of the reinforcing structure in the desire shape. Other embodiment involve other methods of securing the strands at the cross points including welding, brazing, adhesives or mechanical connections.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Mitral valve fixation device removal devices and methods
ActiveUS20170143330A1Easy accessSuture equipmentsHeart valvesEndovascular surgeryMitral valve leaflet
Procedures may be performed on the heart after the installation of a mitral valve fixation device. In order to prepare the heart for such procedures, the fixation device may be removed or disabled in minimally invasive ways (e.g., through an endovascular procedure), without requiring open access to the heart. The fixation device may be partitioned so that one portion may remain attached to each leaflet of the mitral valve. In another example, the leaflets may be cut along the edges of the distal element(s) of the fixation device, so as to cut the fixation device from the leaflet(s). Systems and devices for performing such procedures endovascularly are disclosed. Fixation devices with improved access to a release harness are also disclosed.
Owner:EVALVE
Method and apparatus for percutaneous wound sealing
InactiveUS20080046005A1Surgical veterinaryWound clampsPolyethylene glycolInterventional neuroradiology
Owner:NEOMEND INC
Endovascular Flexible Stapling Device
The present invention concerns a flexible stapling device (1). More particularly, this invention concerns a flexible endovascular stapling device (1) for an intavascular procedure such as patent foramen ovale closure, which is designed to avoid open heart surgery by permitting the closure of the defect utilizing a stapling means (26) which is positioned by using a flexible shaft / guidewire system.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Cardiac valve procedure methods and devices
Devices and methods for performing intravascular procedures without cardiac bypass include embodiments of temporary filter devices, temporary valves, and prosthetic valves. The temporary filter devices have a cannula which provides access for surgical tools for effecting repair of cardiac valves. The cannula may have filters which prevent embolitic material from entering the coronary arteries and aorta. The valve devices may also have a cannula for insertion of the valve into the aorta. The valve devices expand in the aorta to occupy the entire flow path of the vessel and operate to prevent blood flow and to permit flow through the valve. The prosthetic valves include valve fixation devices which secure the prosthetic valve to the wall of the vessel. The prosthetic valves are introduced into the vascular system in a compressed state, advanced to the site of implantation, and expanded and secured to the vessel wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Catheter system with balloon-mounted plaque-modifying elements
Owner:KASSAB KUGHN ENDOVASCULAR DEVICES
Stabilization of visualization catheters
ActiveUS20090275842A1Improve the immunityFacilitate intravascular procedureSurgeryEndoscopesEndovascular surgeryBlood vessel
Systems for the stabilization of visualization catheters are described herein which facilitate the deployment and retraction of an imaging hood from a catheter. Such systems may include a deployment catheter and an imaging hood having one or more structural elements which may be integrated or advanced into the hood independently of the hood itself. Moreover, additional features such as rapid exchange ports may be integrated along the hood or along the catheter proximal to the hood to facilitate intravascular procedures and treatments.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Delivery system with helical shaft
A delivery system is provided for releasing a medical device within a body cavity. The delivery system may be used in an intravascular procedure to implant a self-expandable stent. A helical structure on the shaft of the delivery system engages the inner surface of the stent. As a result, the stent may be released by rotating the shaft relative to the stent which pushes the stent forward from the distal end of the shaft.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Vascular filters, deflectors, and methods
Vascular filters and deflectors and methods for filtering bodily fluids. A blood filtering assembly can capture embolic material dislodged or generated during an endovascular procedure to inhibit or prevent the material from entering the cerebral vasculature. A blood deflecting assembly can deflect embolic material dislodged or generated during an endovascular procedure to inhibit or prevent the material from entering the cerebral vasculature.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com