Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
234 results about "Electrocardiogram QRS complex" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
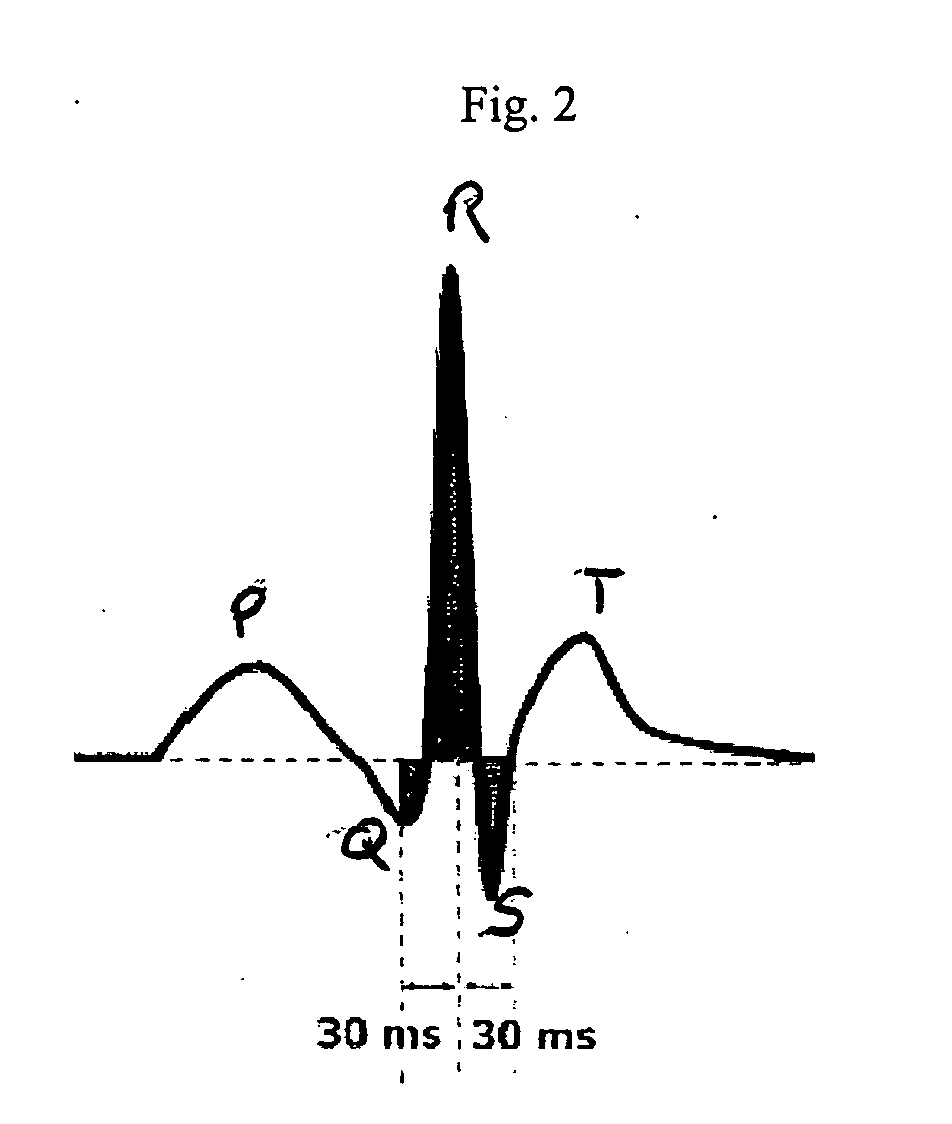
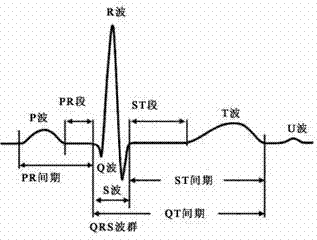
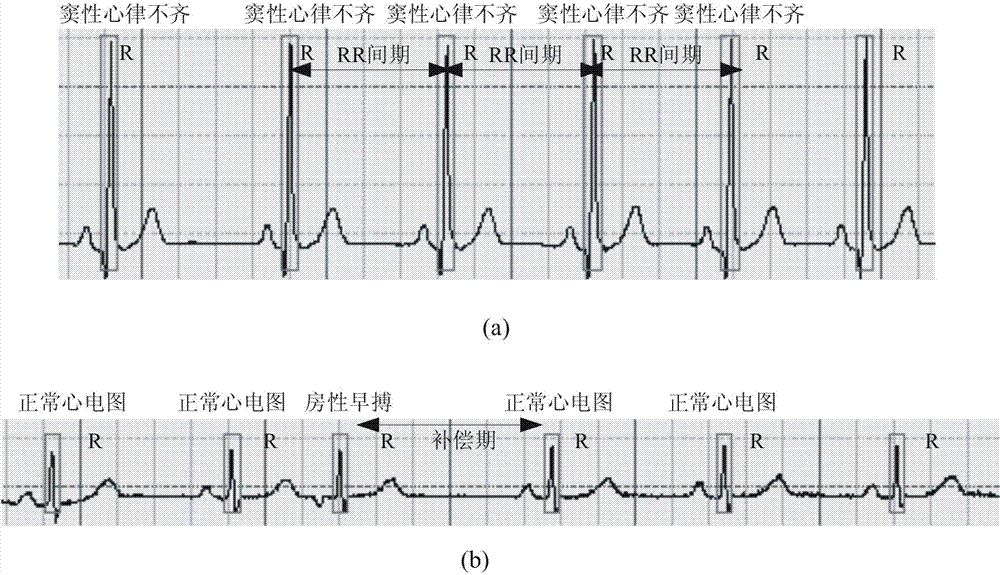
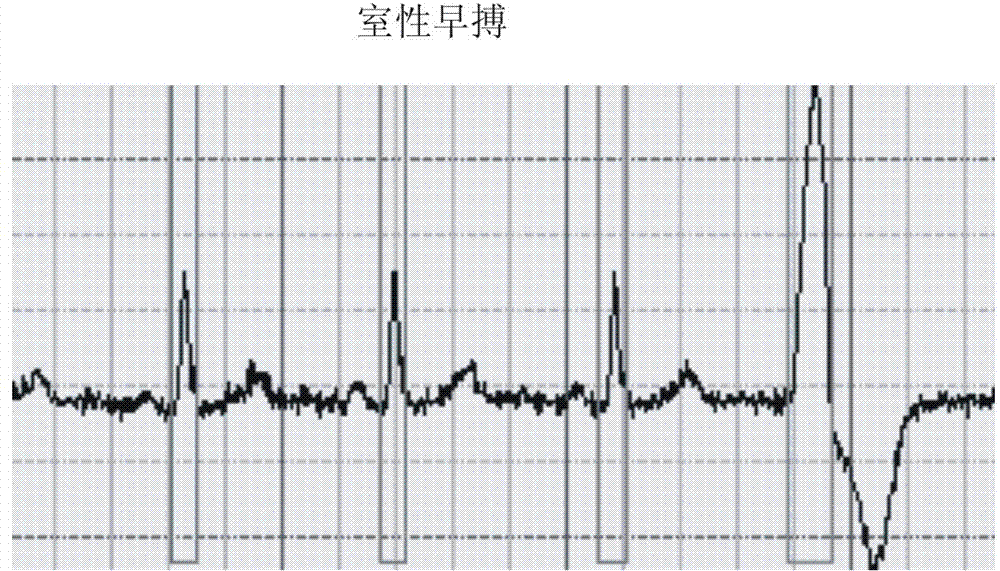
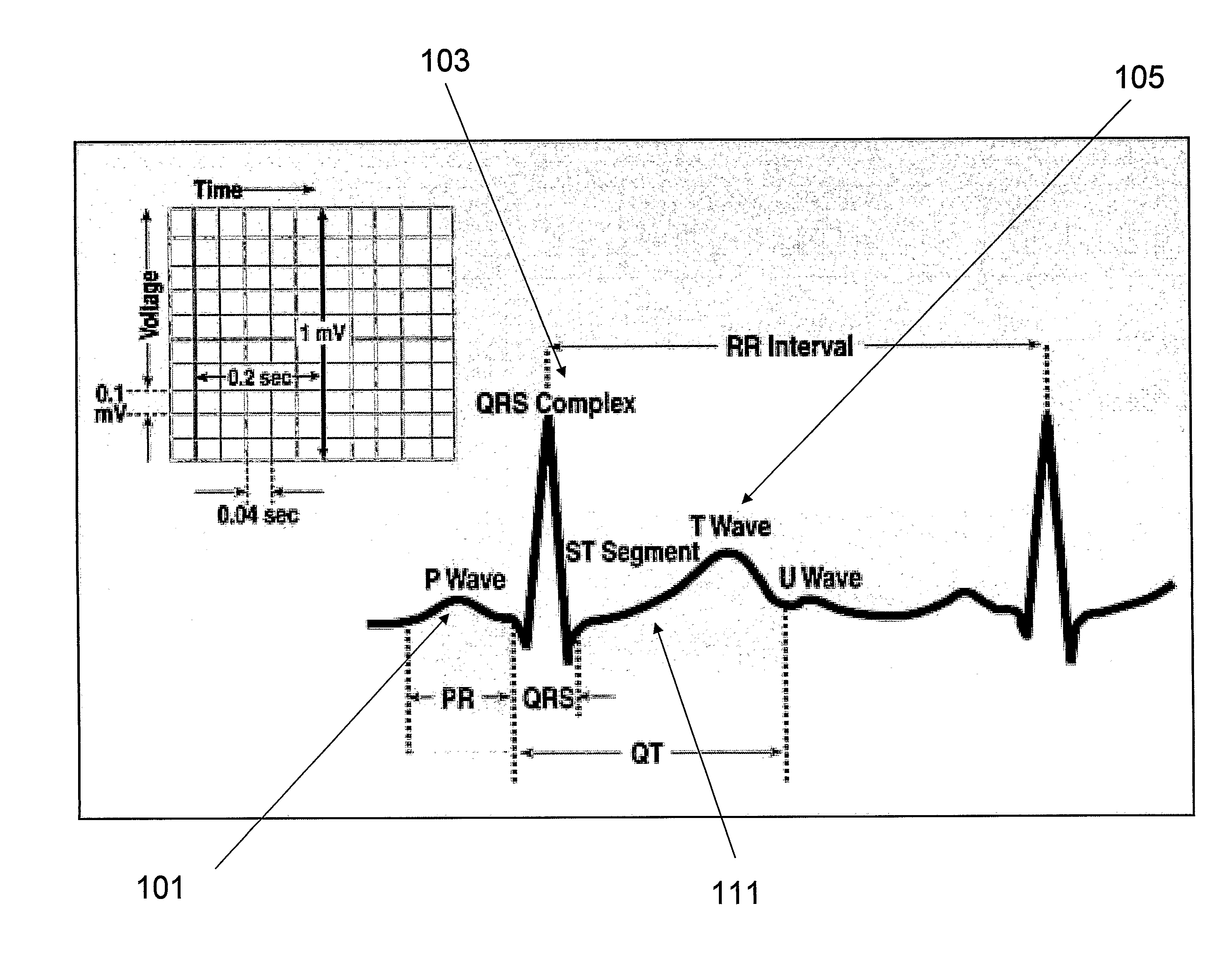
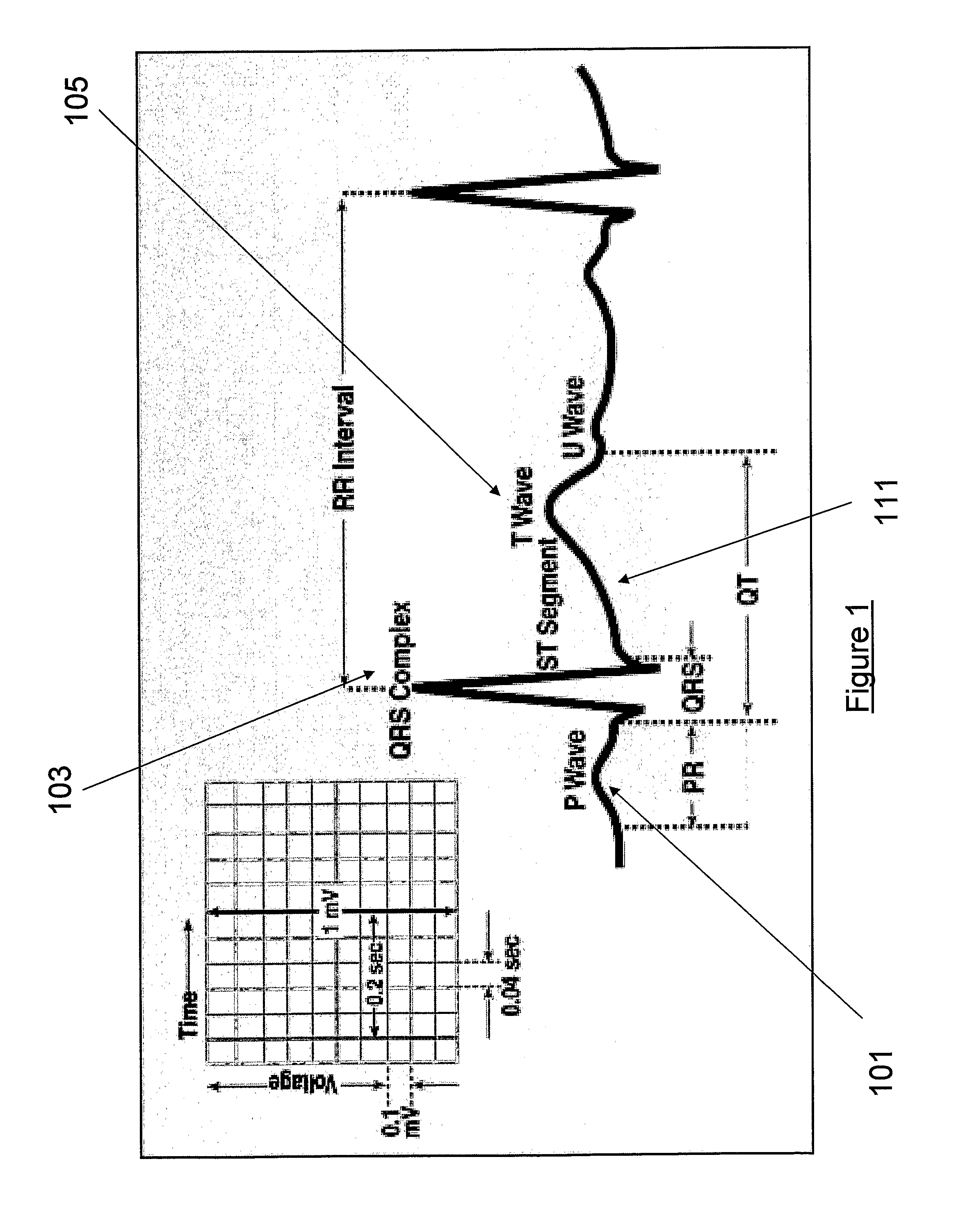
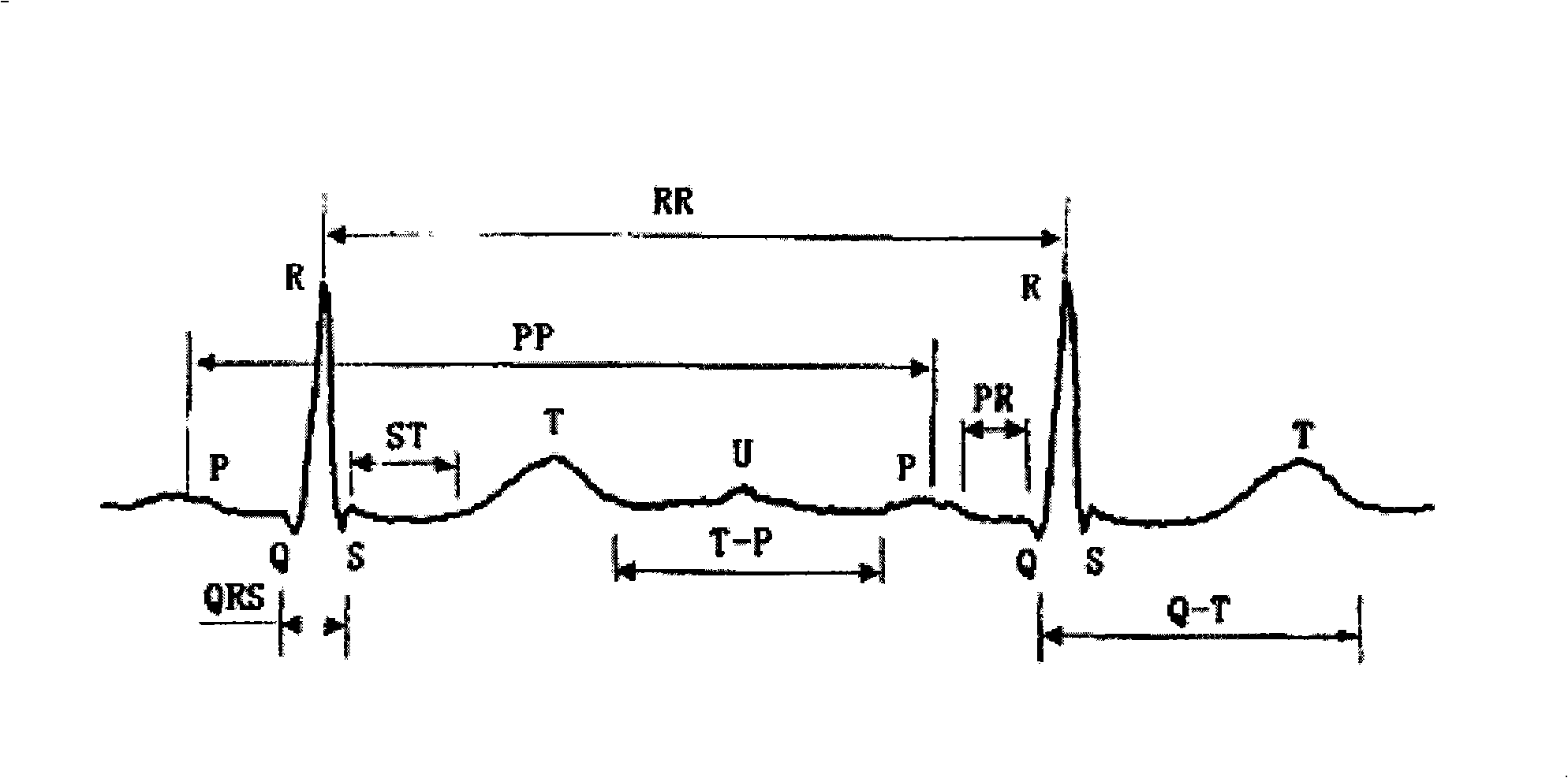
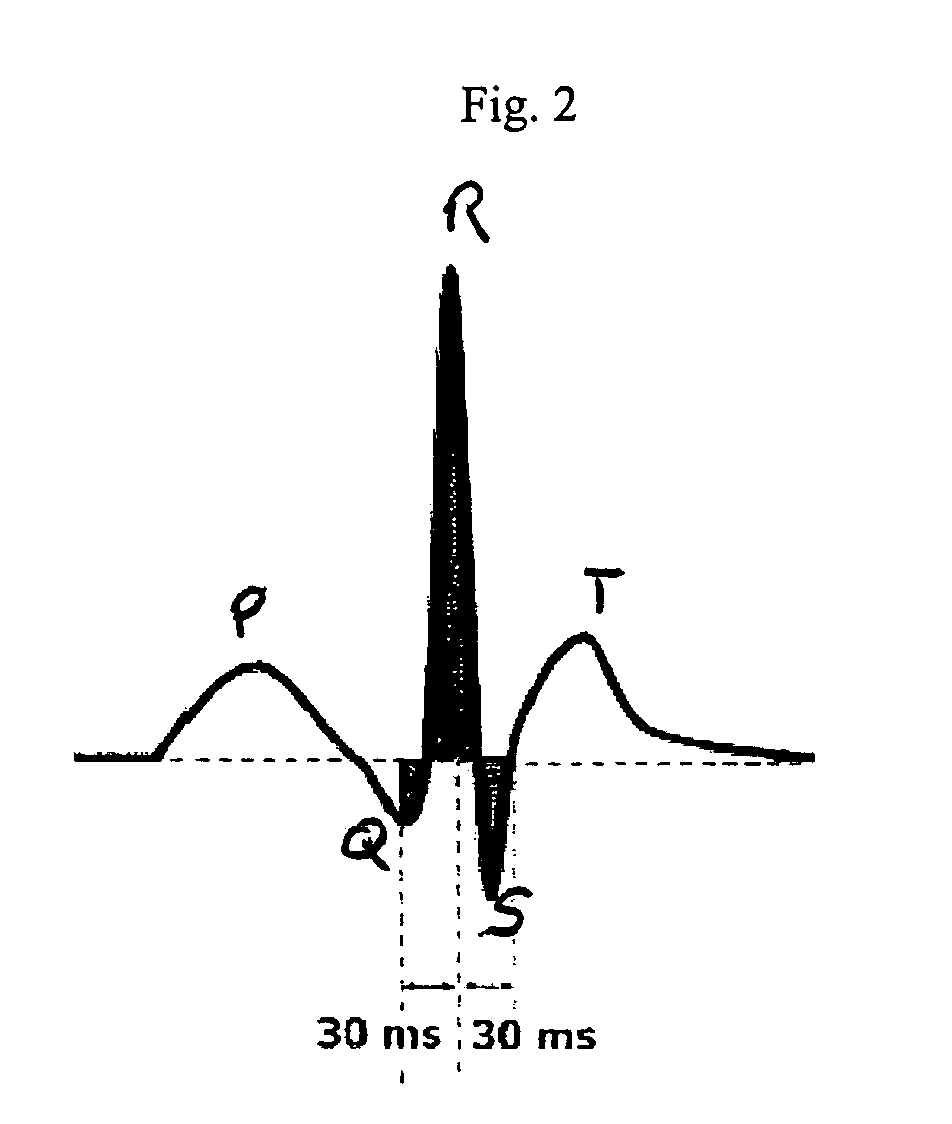
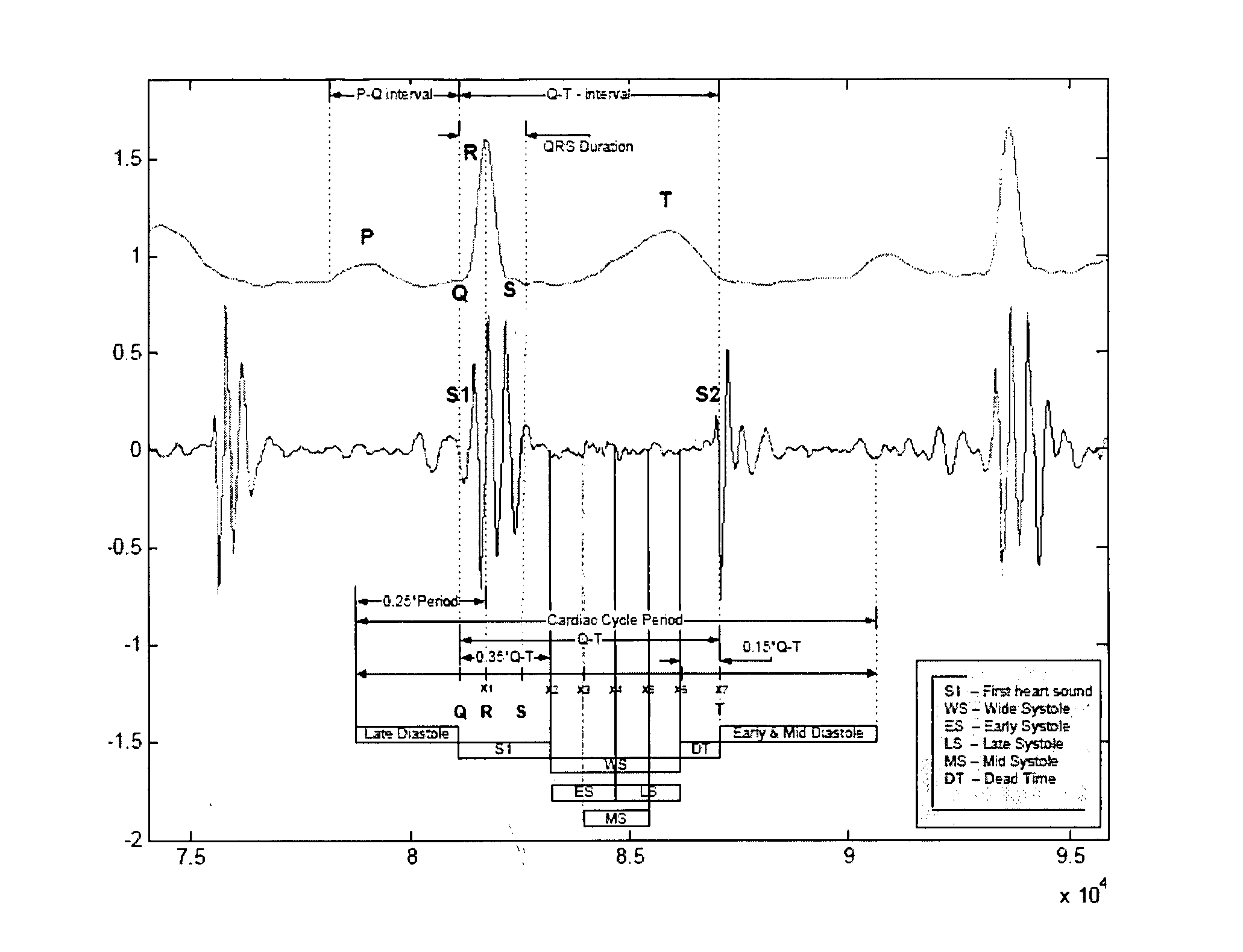
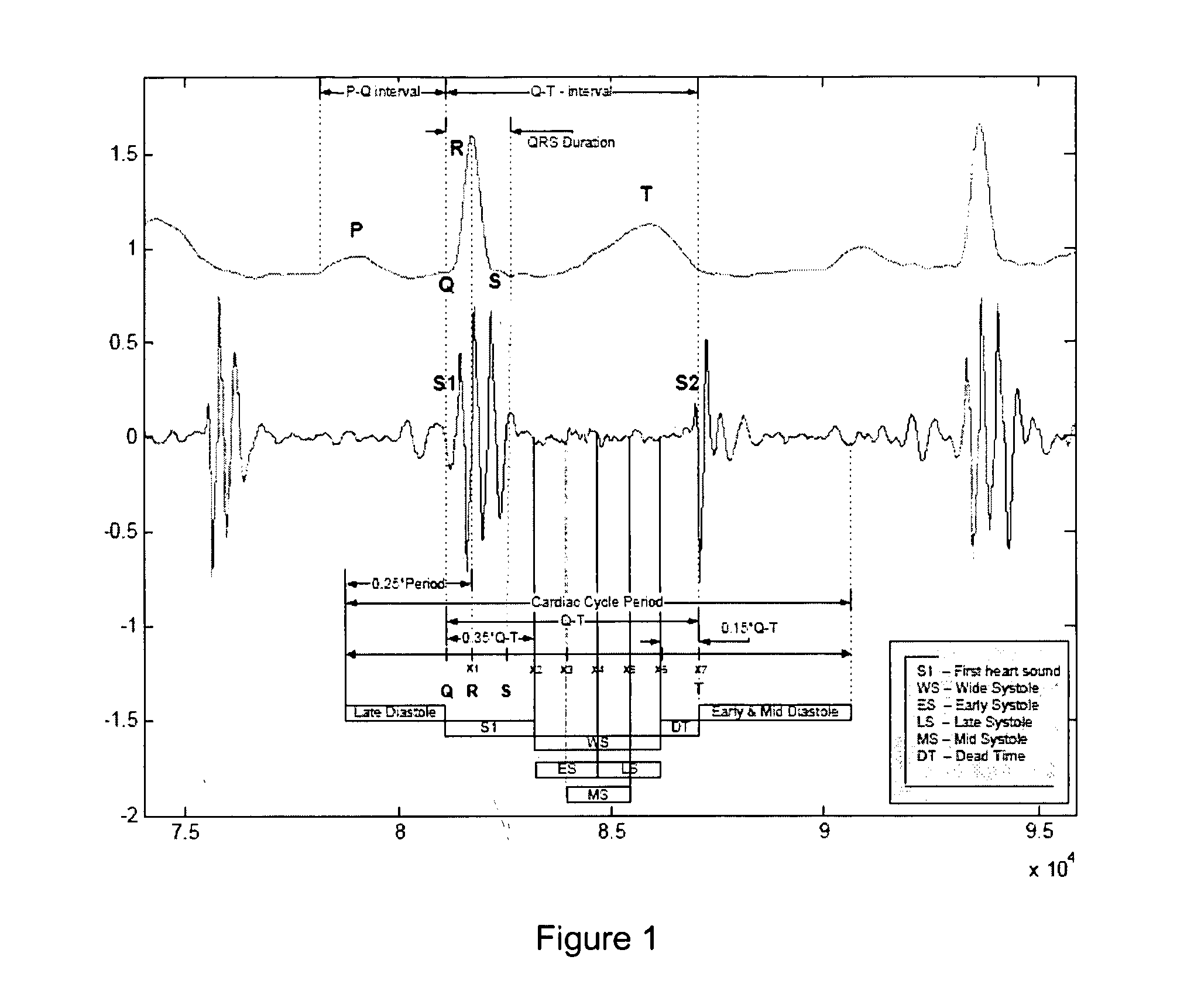
The QRS complex is a name for the combination of three of the graphical deflections seen on a typical electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG). It is usually the central and most visually obvious part of the tracing, in other words, it's the main spike seen on an ECG line.
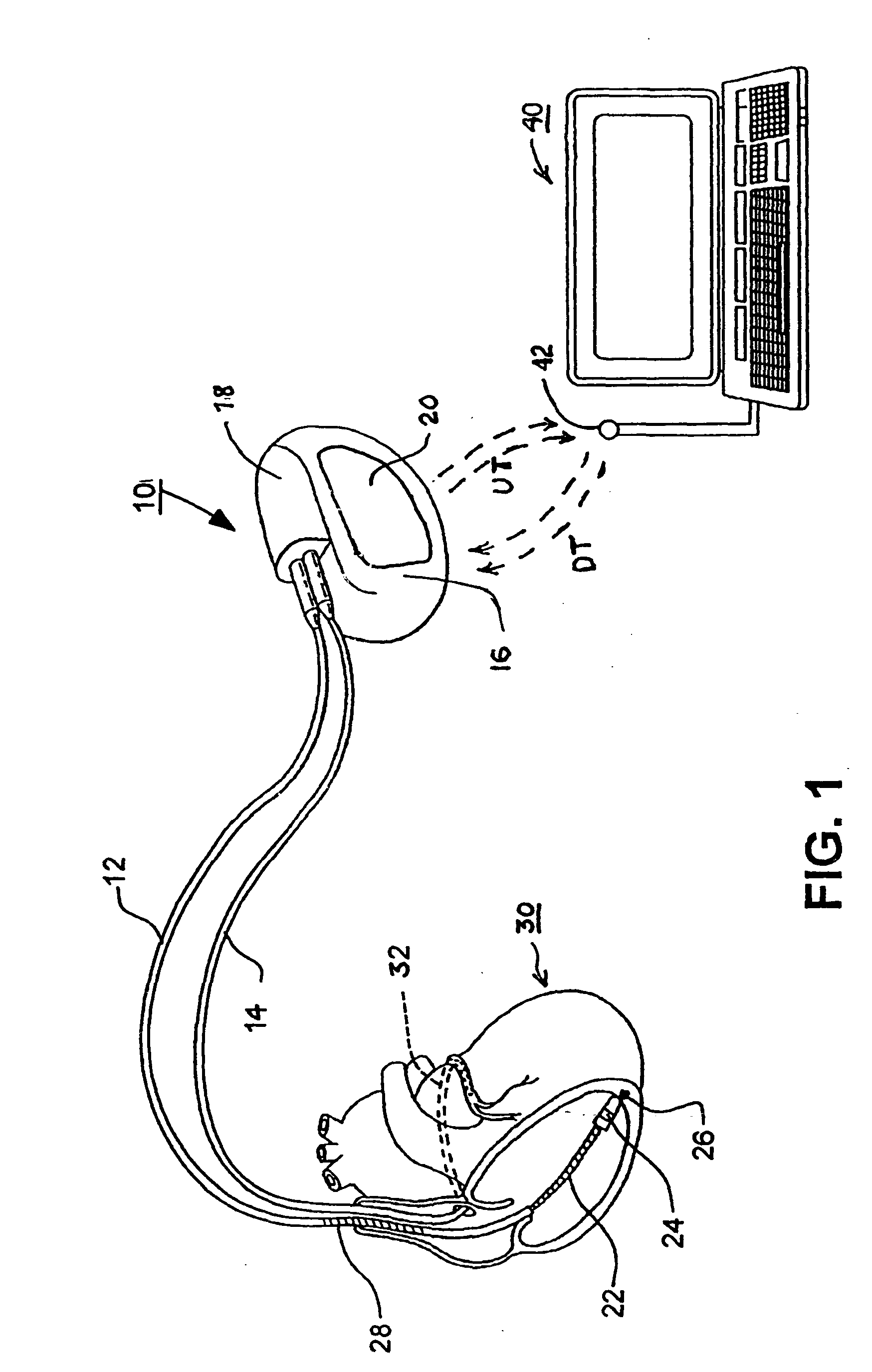
System, software, and method for detection of sleep-disordered breathing using an electrocardiogram
InactiveUS20060041201A1High sensitivityStrong specificityElectrocardiographySensorsEcg signalSleep disordered breathing
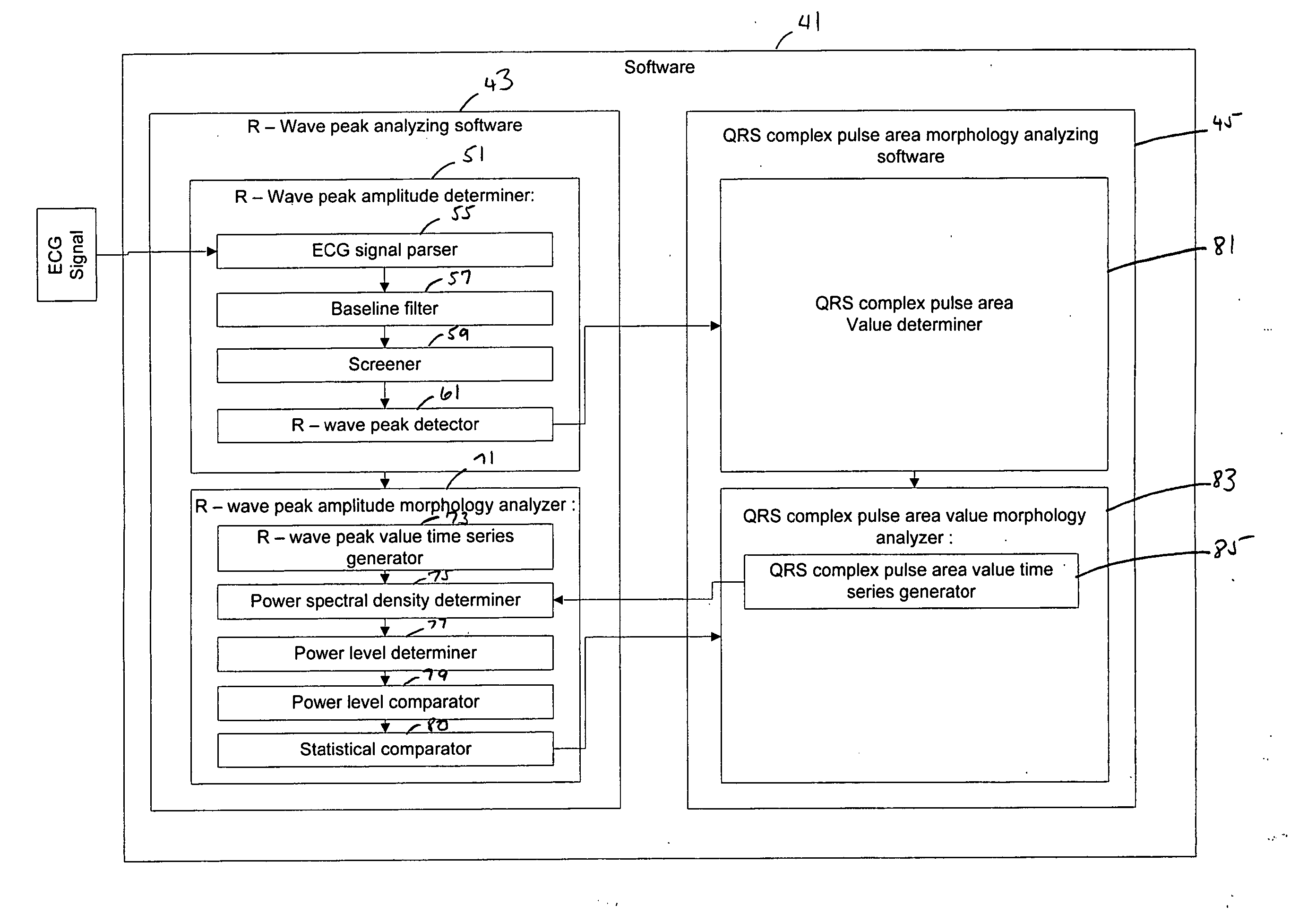
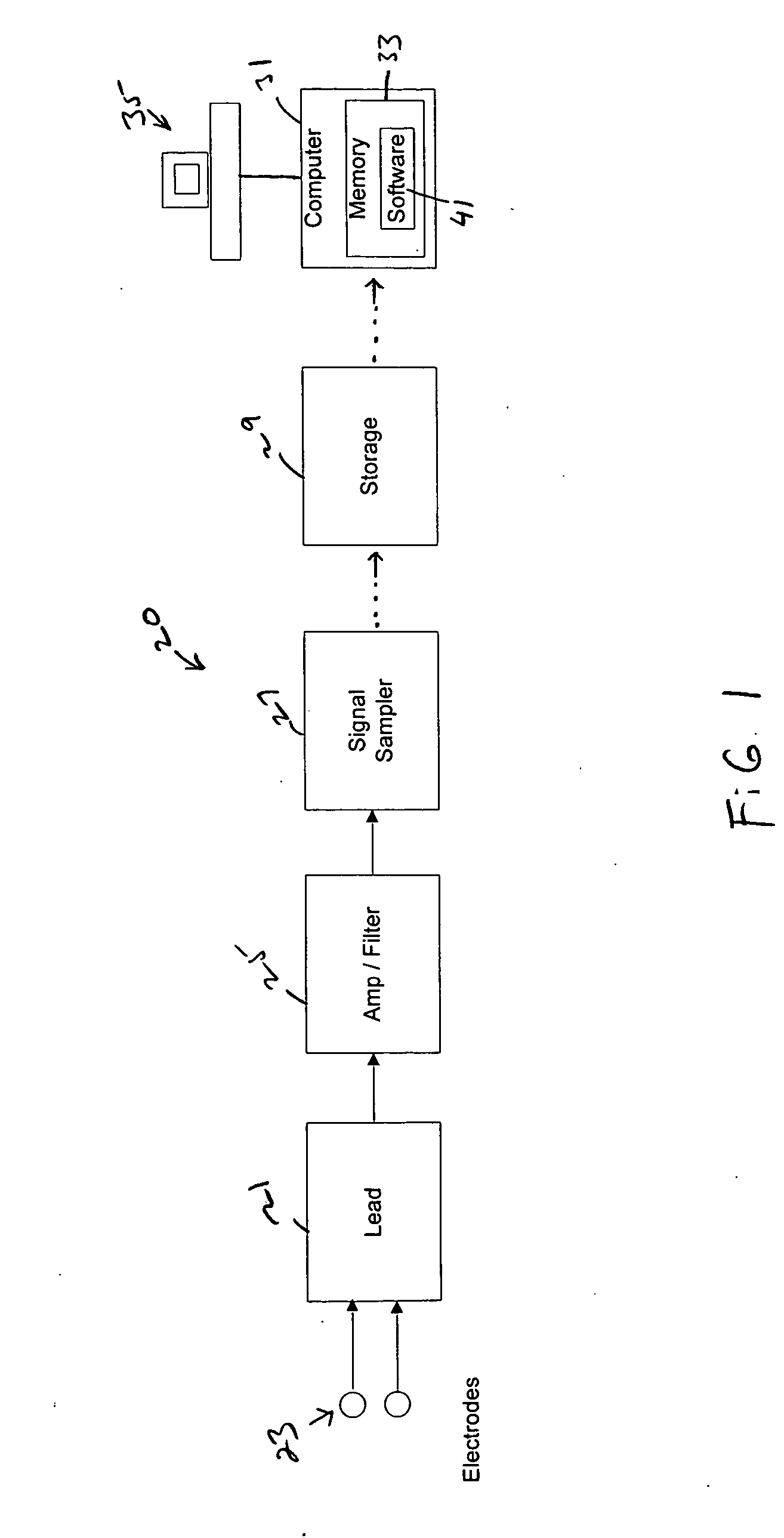
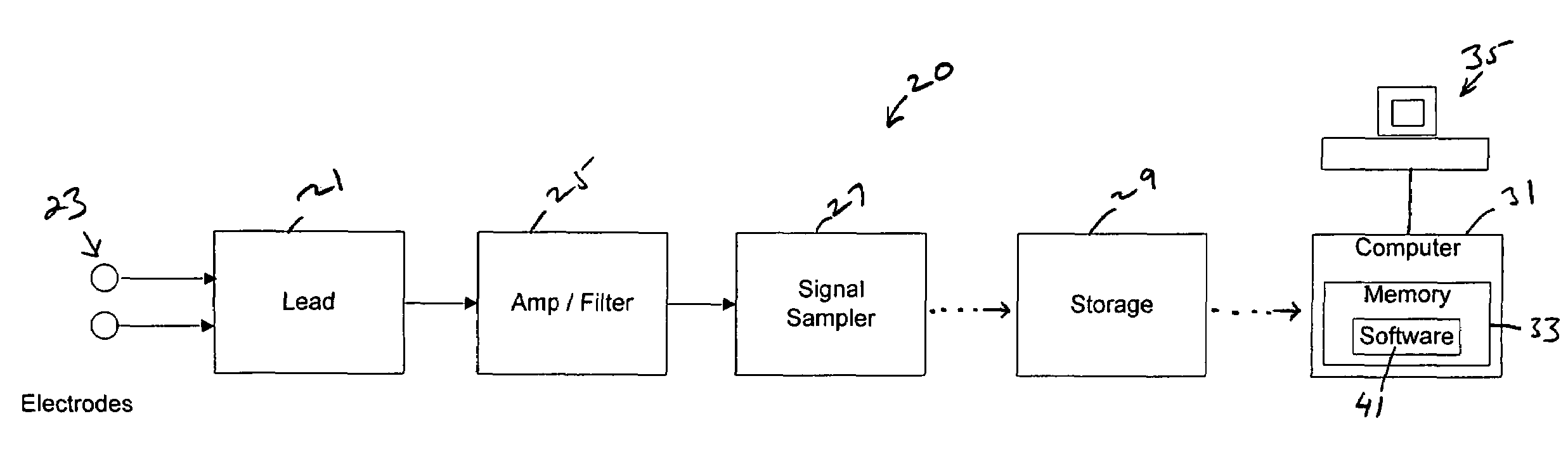
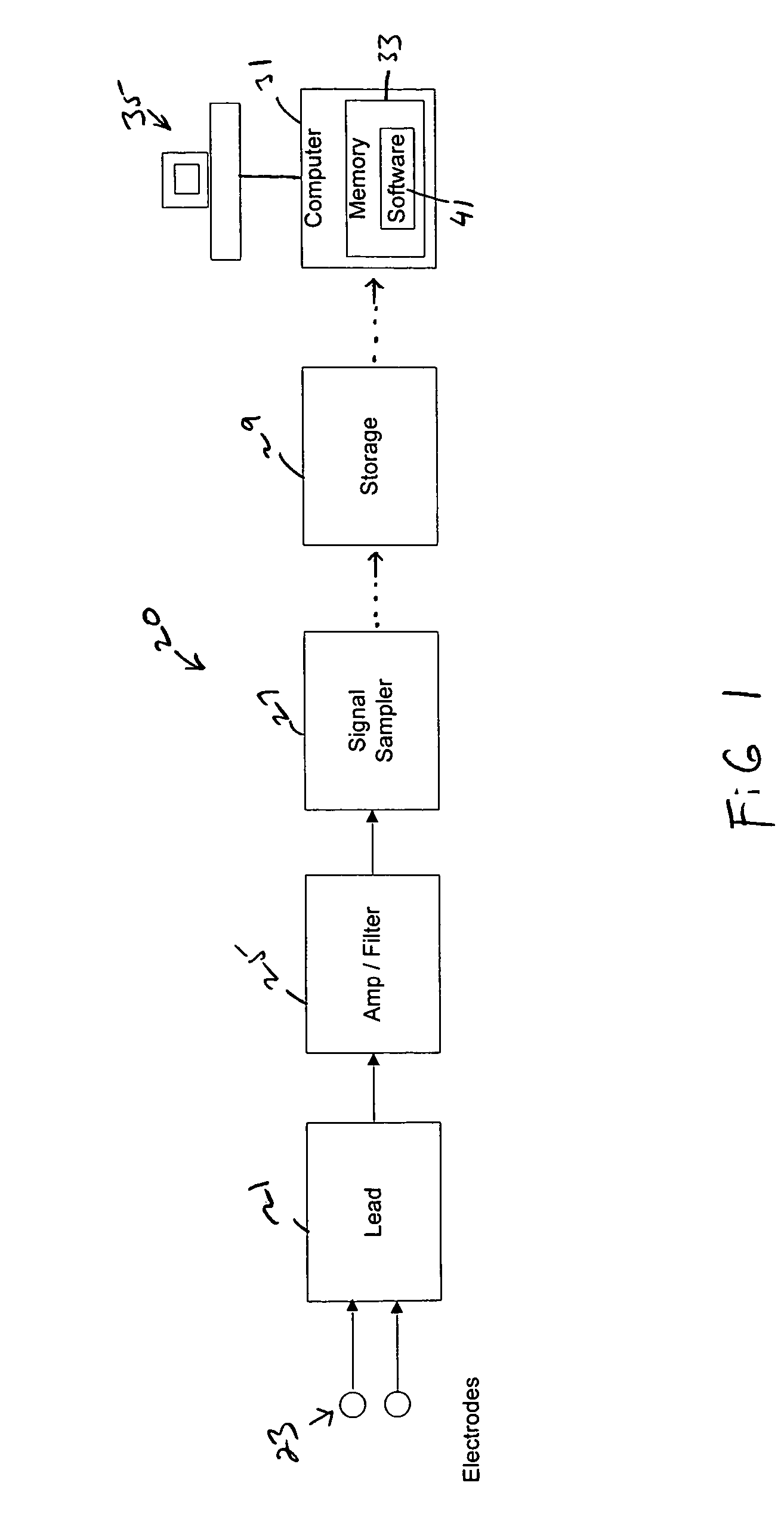
A system to form and store an electrocardiogram (ECG) signal derived from a cardiac electrical signal that includes an apparatus having a pair of the electrodes to connect to a patient to detect the cardiac electrical signal. A signal sampler samples the cardiac electrical signal to form the ECG signal. A data storage device stores the ECG signal. A computer communicates with the data storage device to retrieve the ECG signal for analysis by software stored in the memory of the computer. The software analyzes a morphology of the amplitude of a plurality of R-wave peaks contained within the ECG signal and / or analyzes a morphology of the area of a plurality of QRS complex pulses contained within the ECG signal.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
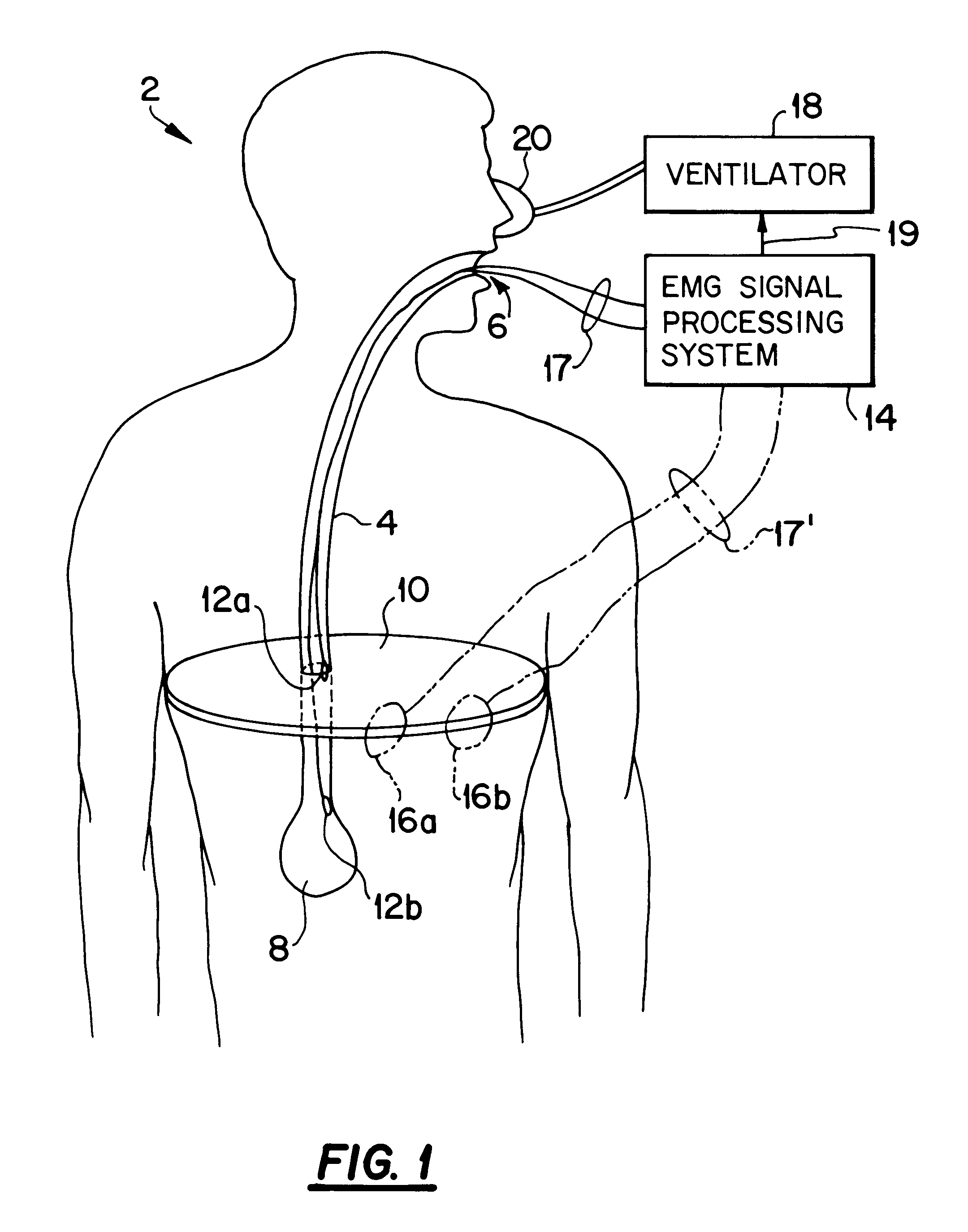
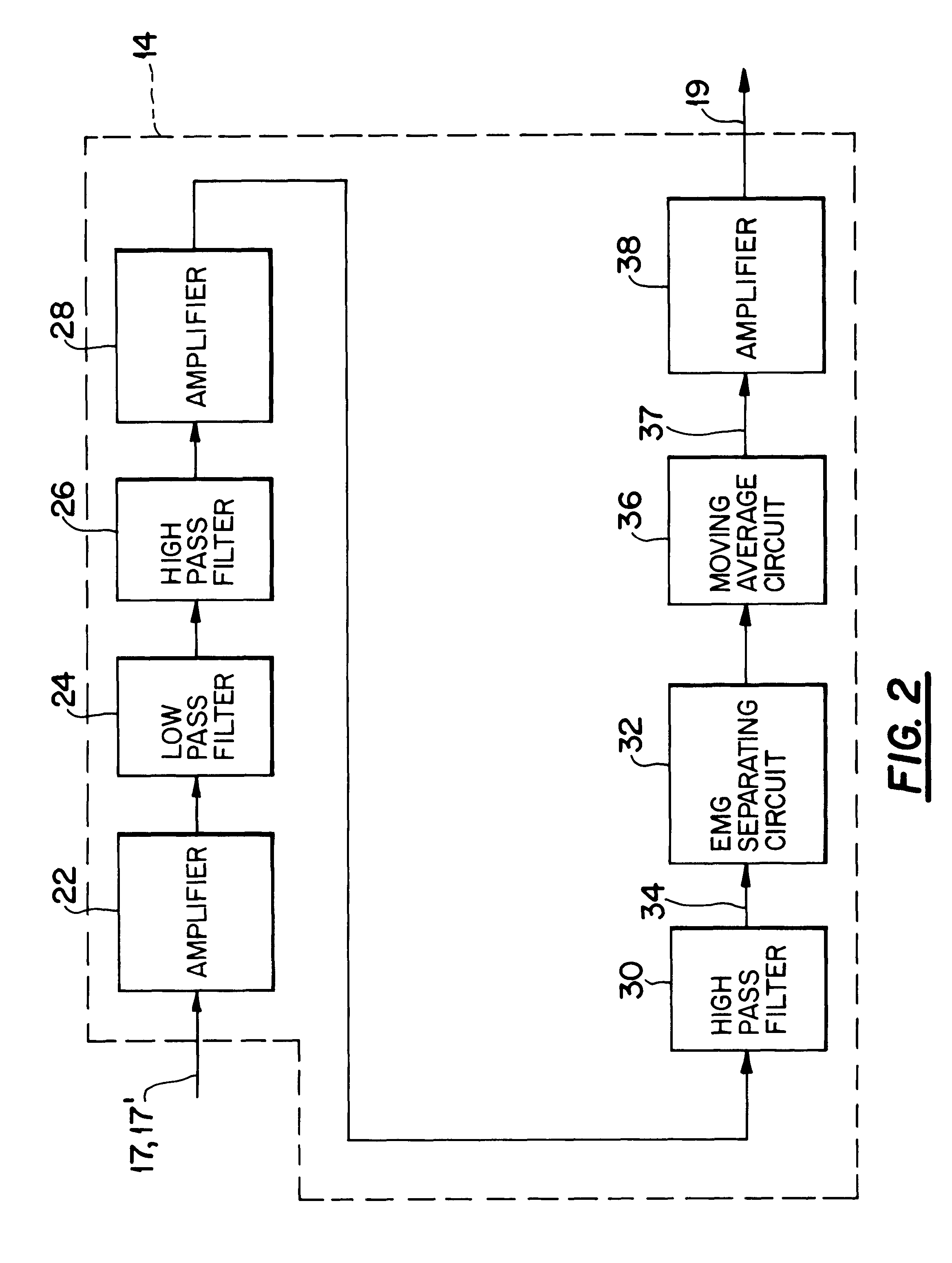
Method and apparatus for producing a model EMG signal from a measured EMG signal
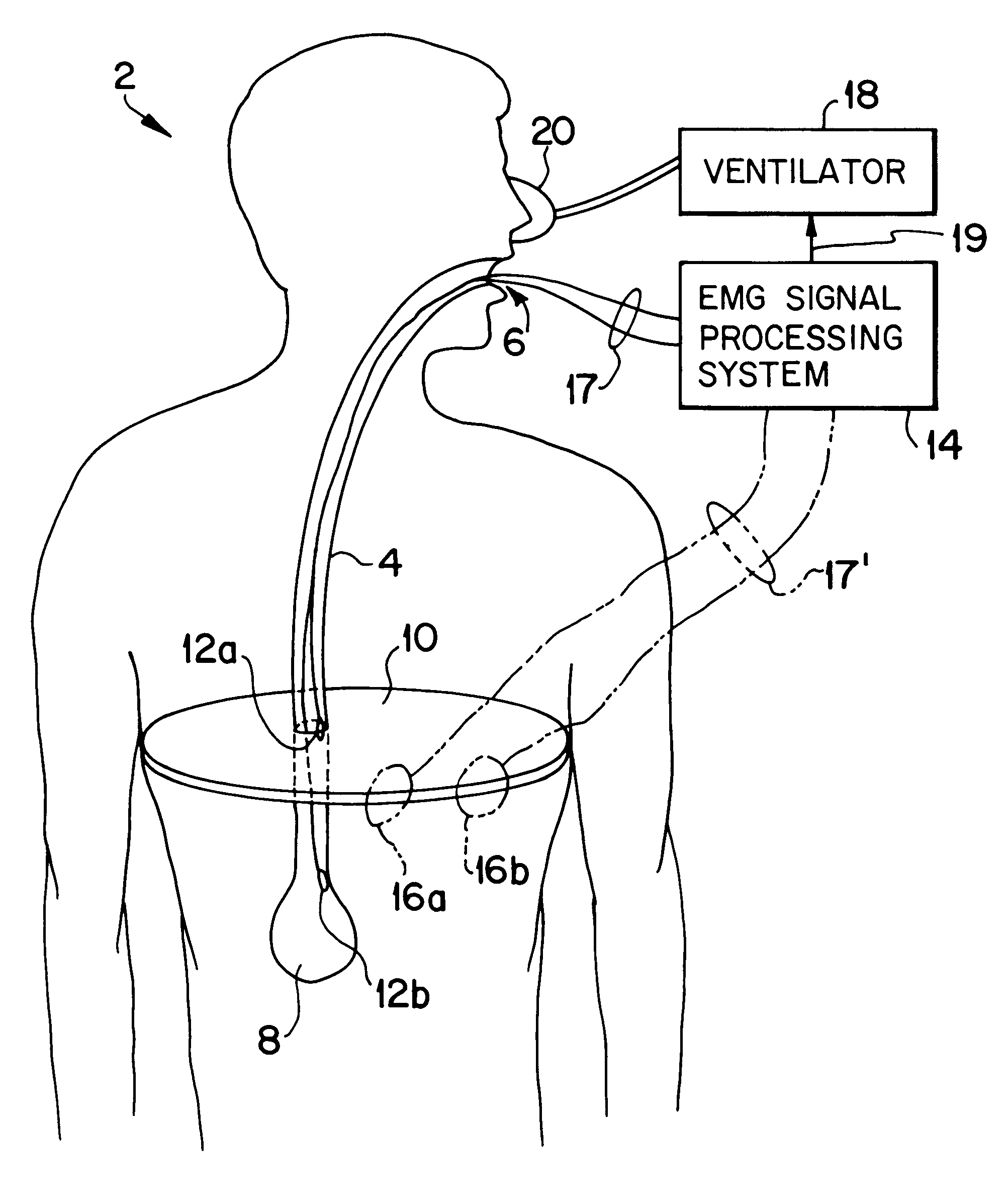
A model EMG signal is produced from a measured EMG signal that includes a patient's EMG signal and ECG signal by processing the measured EMG signal to produce a logic signal that is in a first binary state in the absence of a P wave, a QRS complex and a T wave of an ECG cycle of the measured EMG signal and that is in a second binary state during at least one of the P wave, the QRS complex and the T wave of the ECG cycle. The measured EMG signal is processed to produce a first envelope signal. The model EMG signal is produced as a function of the first envelope signal when the logic signal is in the first binary state and the absence of the first envelope signal when the logic signal is in the second binary state.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
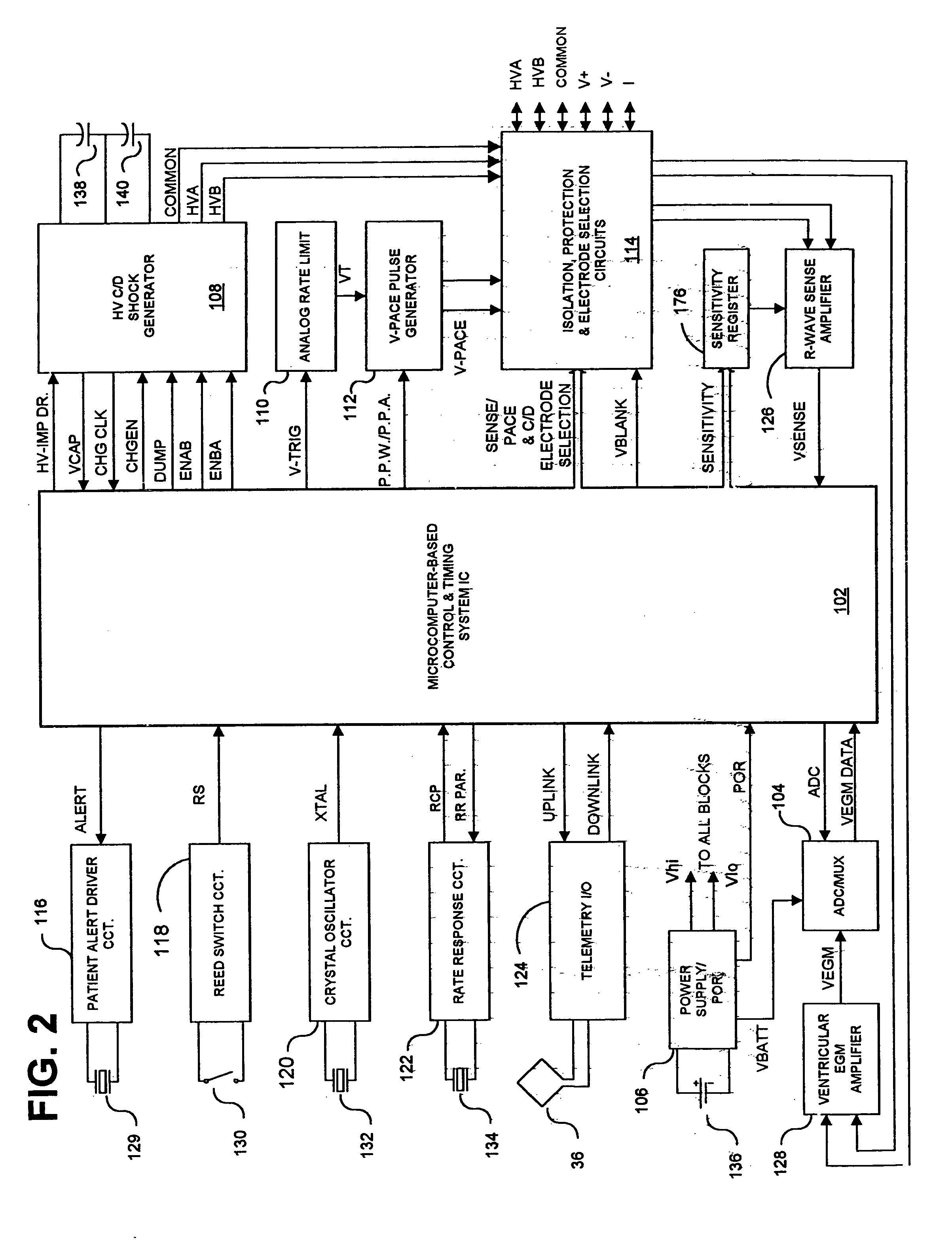
Methods and apparatus for discriminating polymorphic tachyarrhythmias from monomorphic tachyarrhythmias facilitating detection of fibrillation
InactiveUS7076289B2High detection specificityDiscriminationElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsFibrillationComputer science
Systems and methods that improving the specificity of discriminating between a monomorphic tachyarrhythmia and a polymorphic tachyarrhythmia are provided that examine frequency content and baseline information of the EGM as discriminatory signatures. Particular algorithms of the present invention that are employed to determine frequency content of the QRS complexes are titled the Slope Distribution Metric (SDM) algorithm and the Slope Distribution Composite (SDC) algorithm.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Portable ECG monitor and method for atrial fibrillation detection
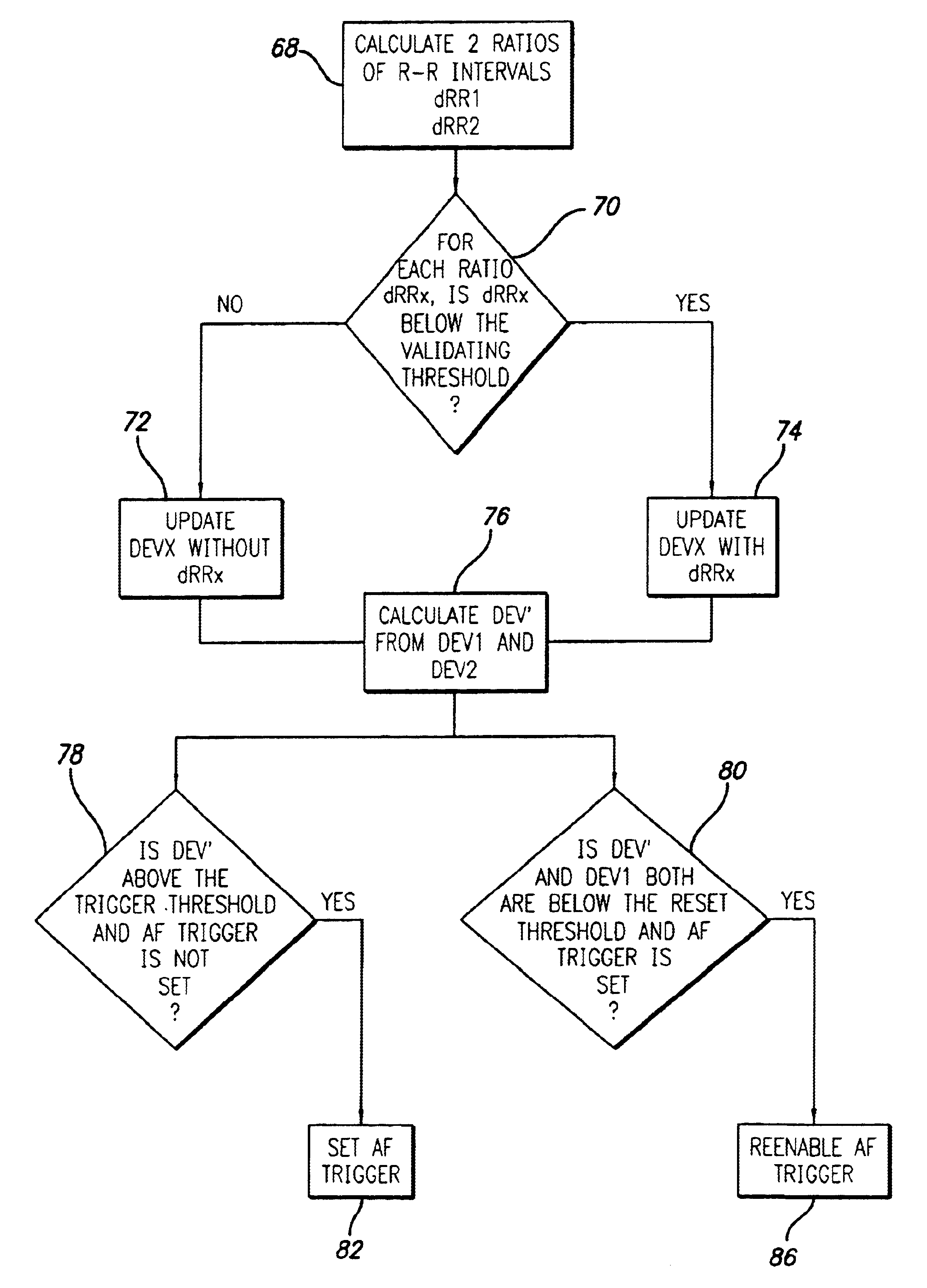
An apparatus and method for detecting an atrial fibrillation through monitoring the R—R intervals of a patient's QRS complexes. Ratios of the current R—R interval are made to previous R—R intervals. Multiple moving averages are taken of the ratio results. The ratios are compared to a validating threshold and if the particular ratio is within a selected range, a moving average is calculated with inclusion of the present R—R interval. If the ratio is outside the range, a moving average is calculated without inclusion of the current R—R interval. The moving averages are combined and this difference average is compared to a trigger threshold. If the difference average exceeds the threshold, an atrial fibrillation is determined to exist, a memory trigger is provided, and the QRS complex data within a selected period of time about the atrial fibrillation event are recorded and removed from overwrite status in the memory. A reset threshold, differing from the trigger threshold, is used and if the difference average falls below the reset threshold, the method and apparatus are re-enabled to record a new AFIB event.
Owner:LIFEWATCH SERVICES
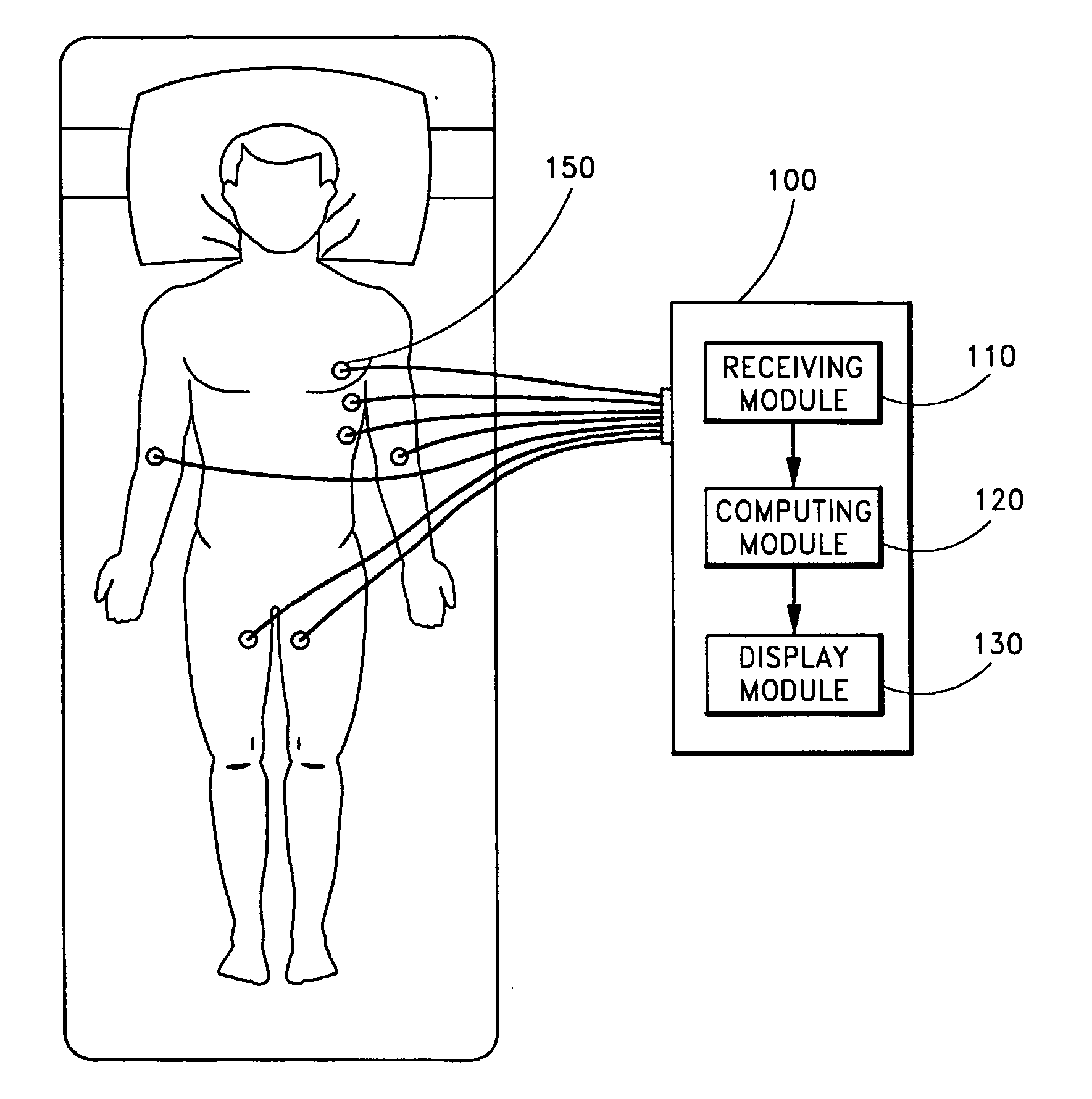
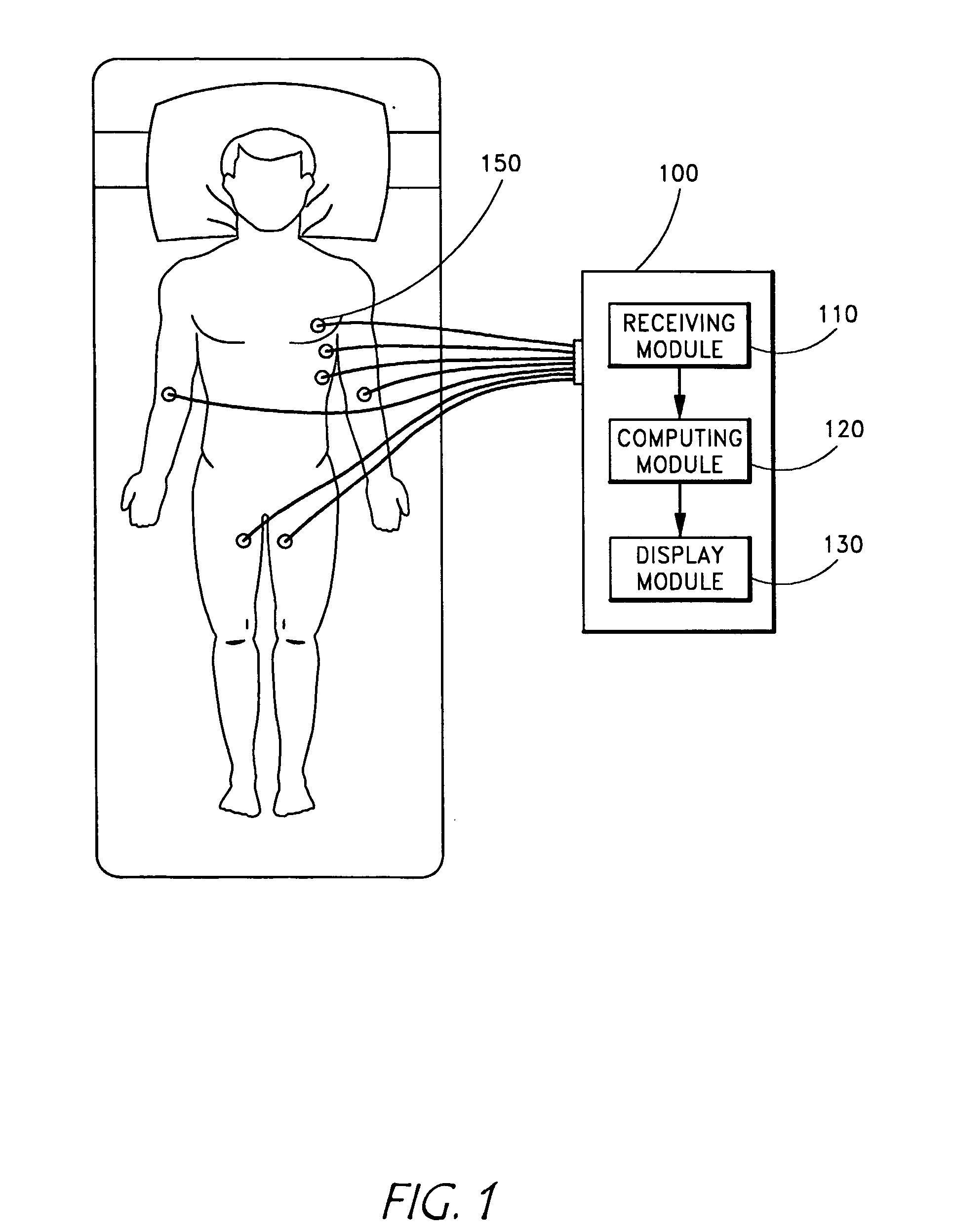
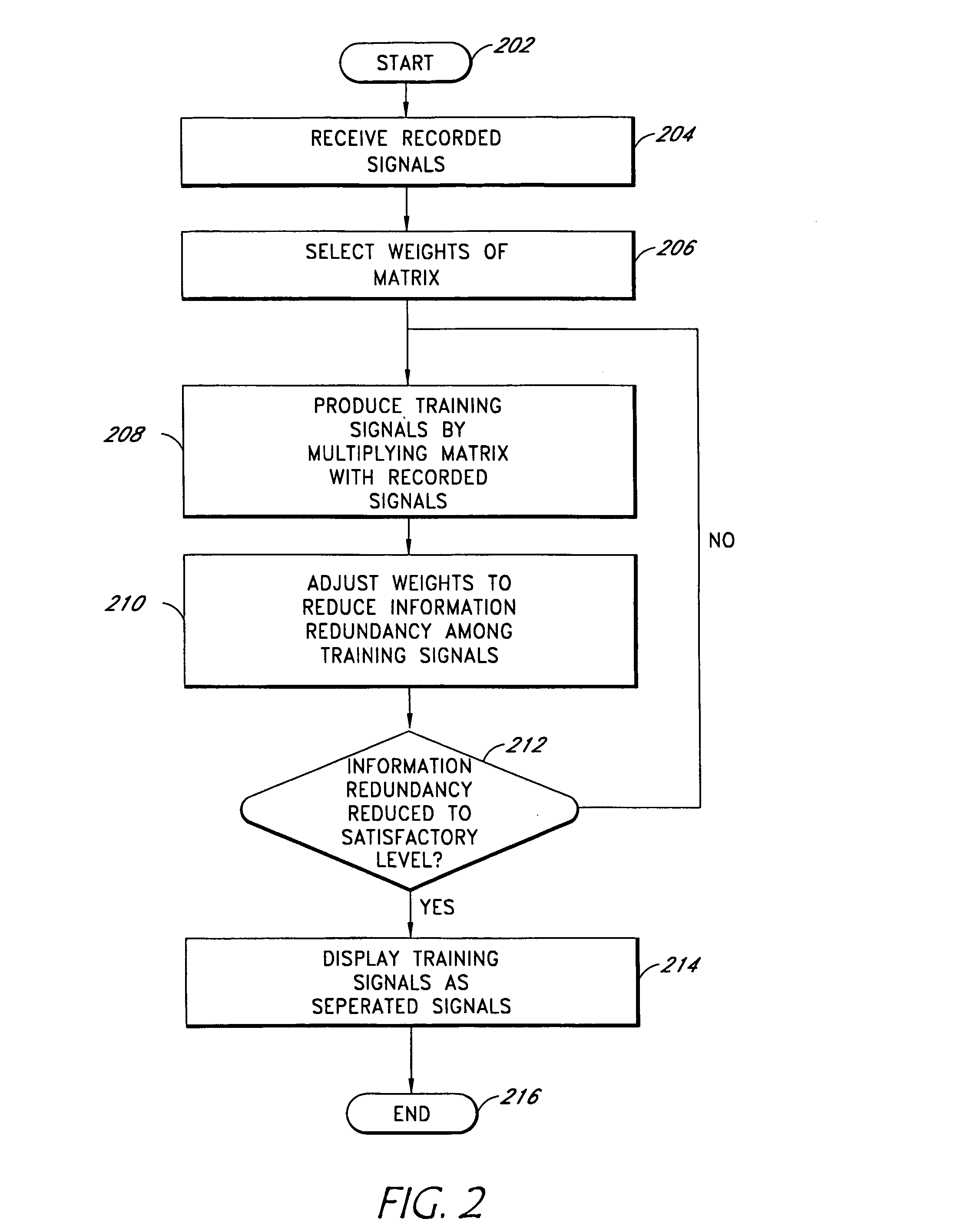
System and method for separating cardiac signals
InactiveUS20050010120A1Quick aimInhibition is effectiveElectrocardiographySensorsCardiac pacemaker electrodePhase space
EKG sensors ((150) are placed on a patient (140) to receive electrocardiogram (EKG) recording signals, which are typically combinations of original signals from different sources, such as pacemaker signals, QRS complex signals, and irregular oscillatory signals that suggest an arrhythmia condition. A computing module (120) uses independent component analysis to separate the recorded EKG signals. The separated signals are displayed to help physicians to analyze heart conditions and to identify probably locations of abnormal heart conditions. At least a portion of the separated signals can be further displayed in a chaos phase space portrait to help detect abnormality in heart conditions.
Owner:SIGMED
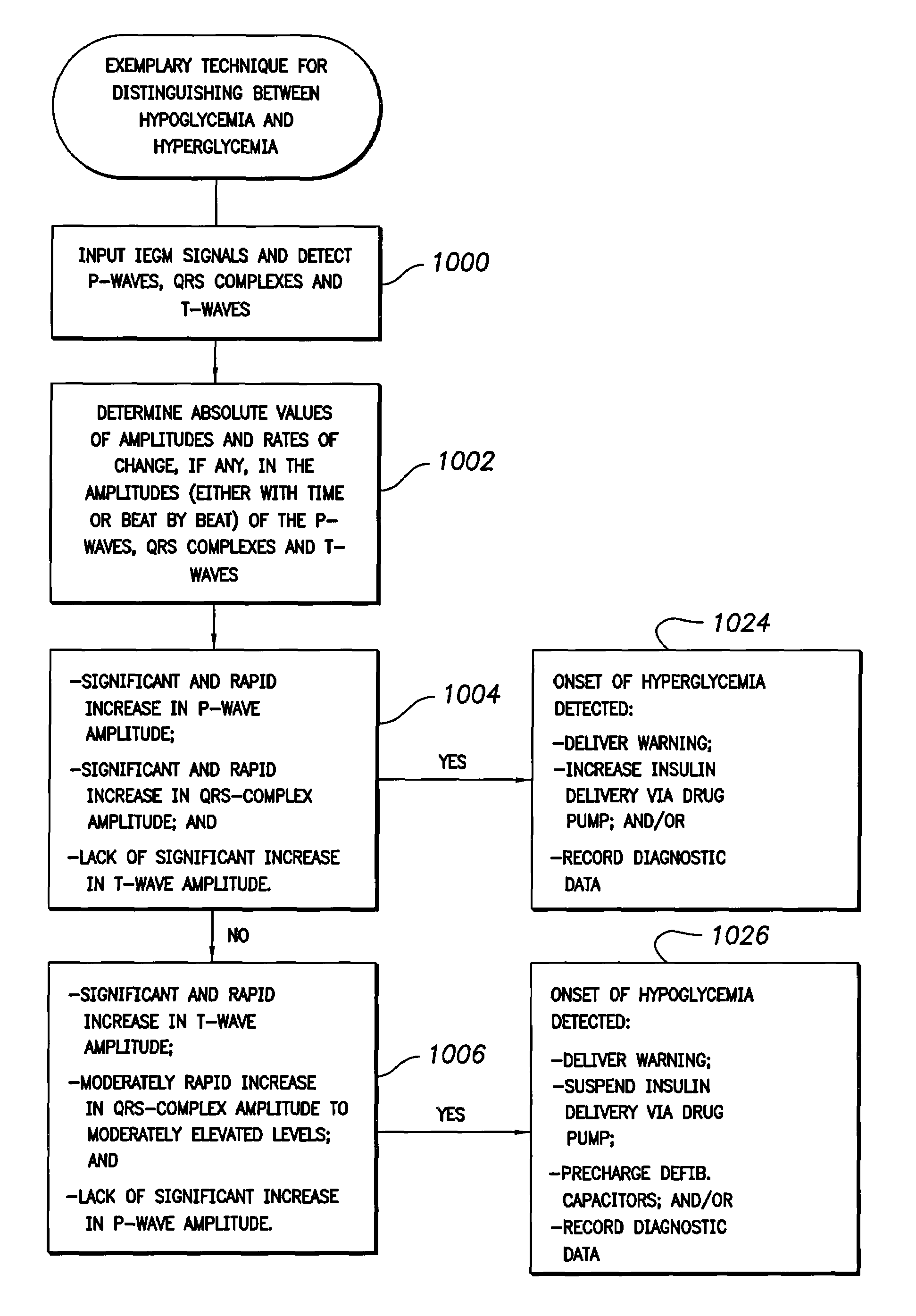
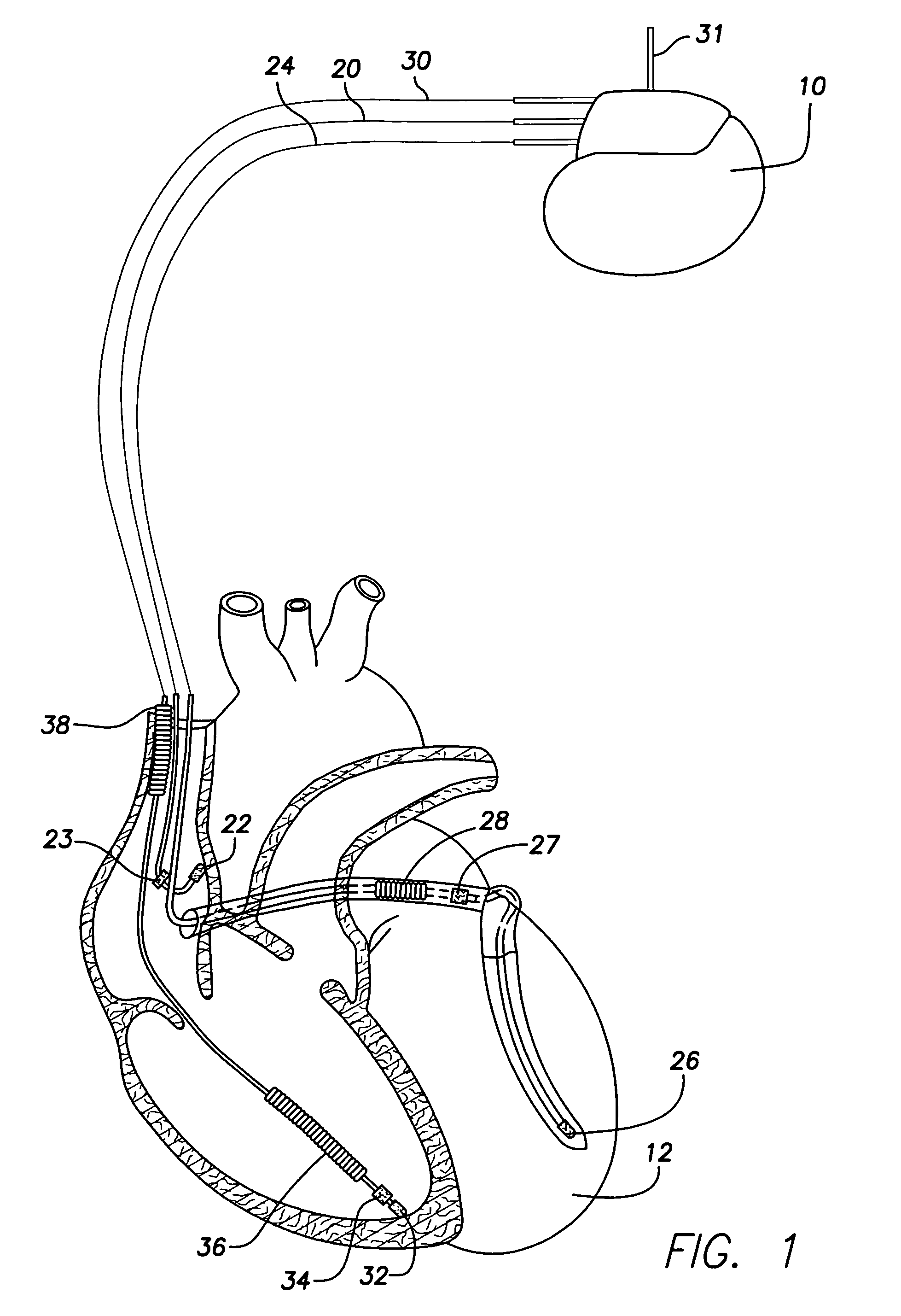
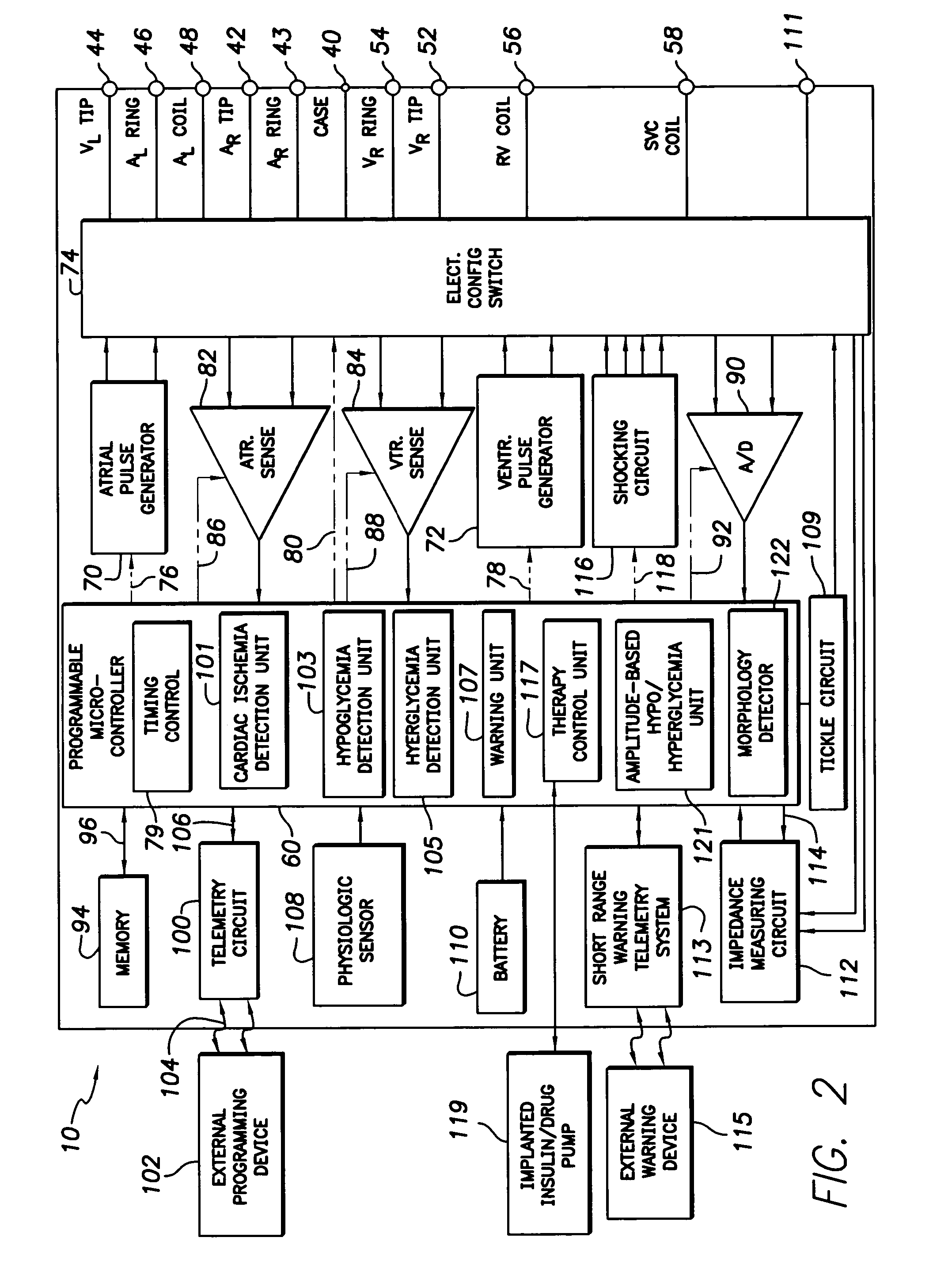
System and method for distinguishing between hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia using an implantable medical device
ActiveUS7524287B2Improve blood sugar controlReduce deliveryElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyAcute hyperglycaemiaT wave
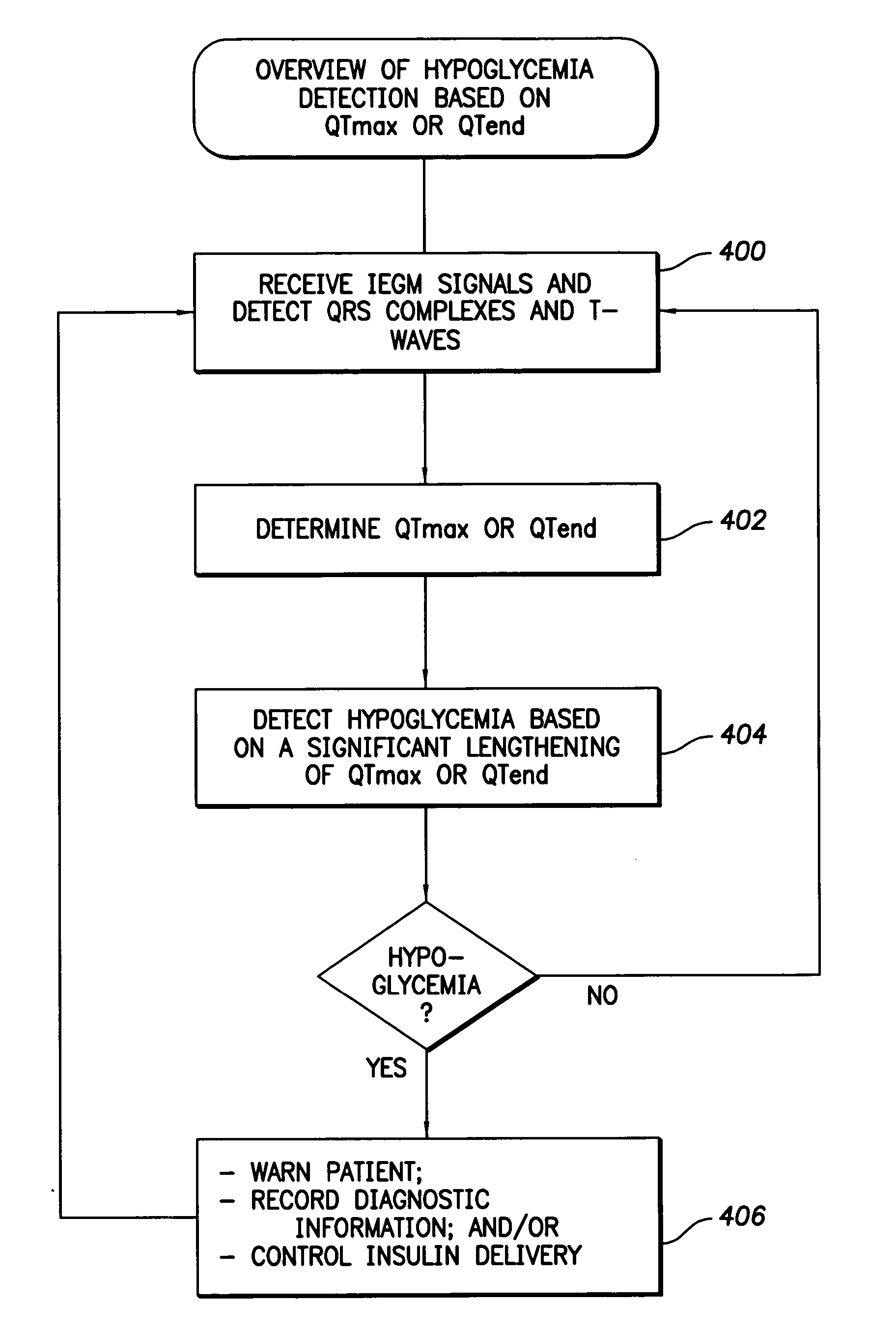
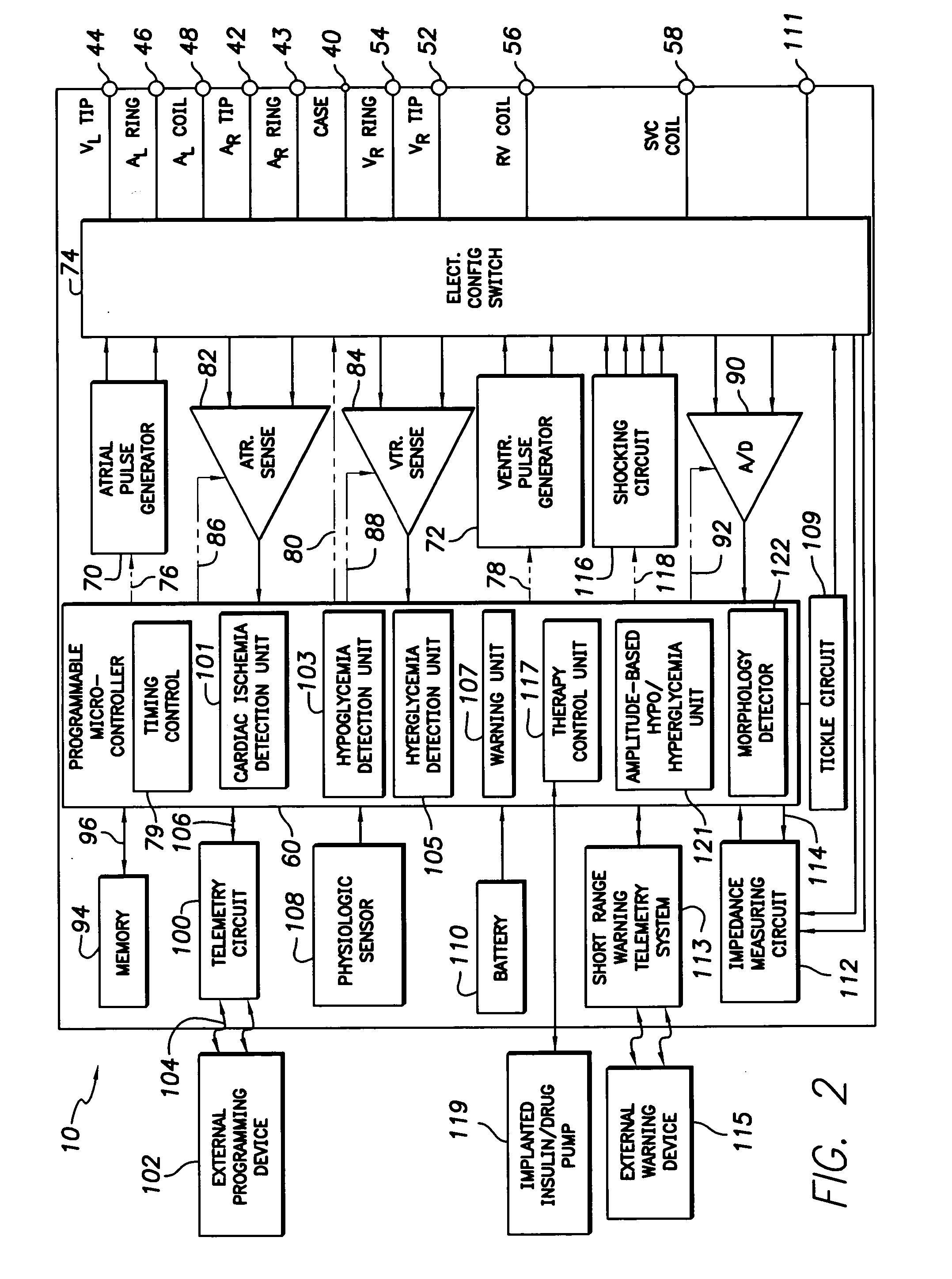
Techniques are described for detecting and distinguishing among ischemia, hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia based on intracardiac electrogram (IEGM) signals. In one technique, these conditions are detected and distinguished based on an analysis of: the interval between the QRS complex and the peak of a T-wave (QTmax), the interval between the QRS complex and the end of a T-wave (QTend), alone or in combination with a change in ST segment elevation. By exploiting QTmax and QTend in combination with ST segment elevation, changes in ST segment elevation caused by hypo / hyperglycemia can be properly distinguished from changes caused by cardiac ischemia. In another technique, hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia are predicted, detected and / or distinguished from one another based on an analysis of the amplitudes of P-waves, QRS-complexes and T-waves within the IEGM. Appropriate warning signals are delivered and therapy is automatically adjusted.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
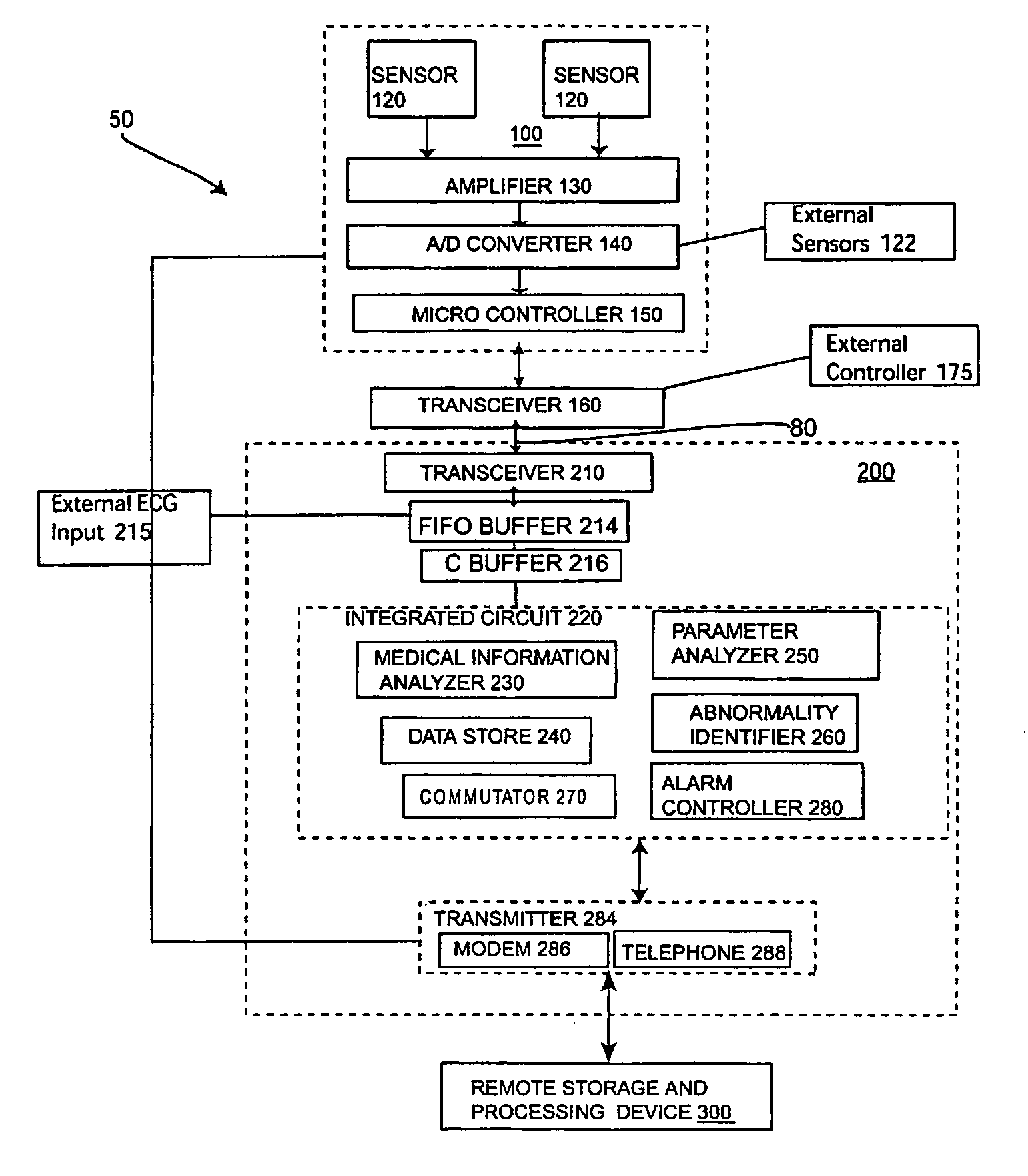
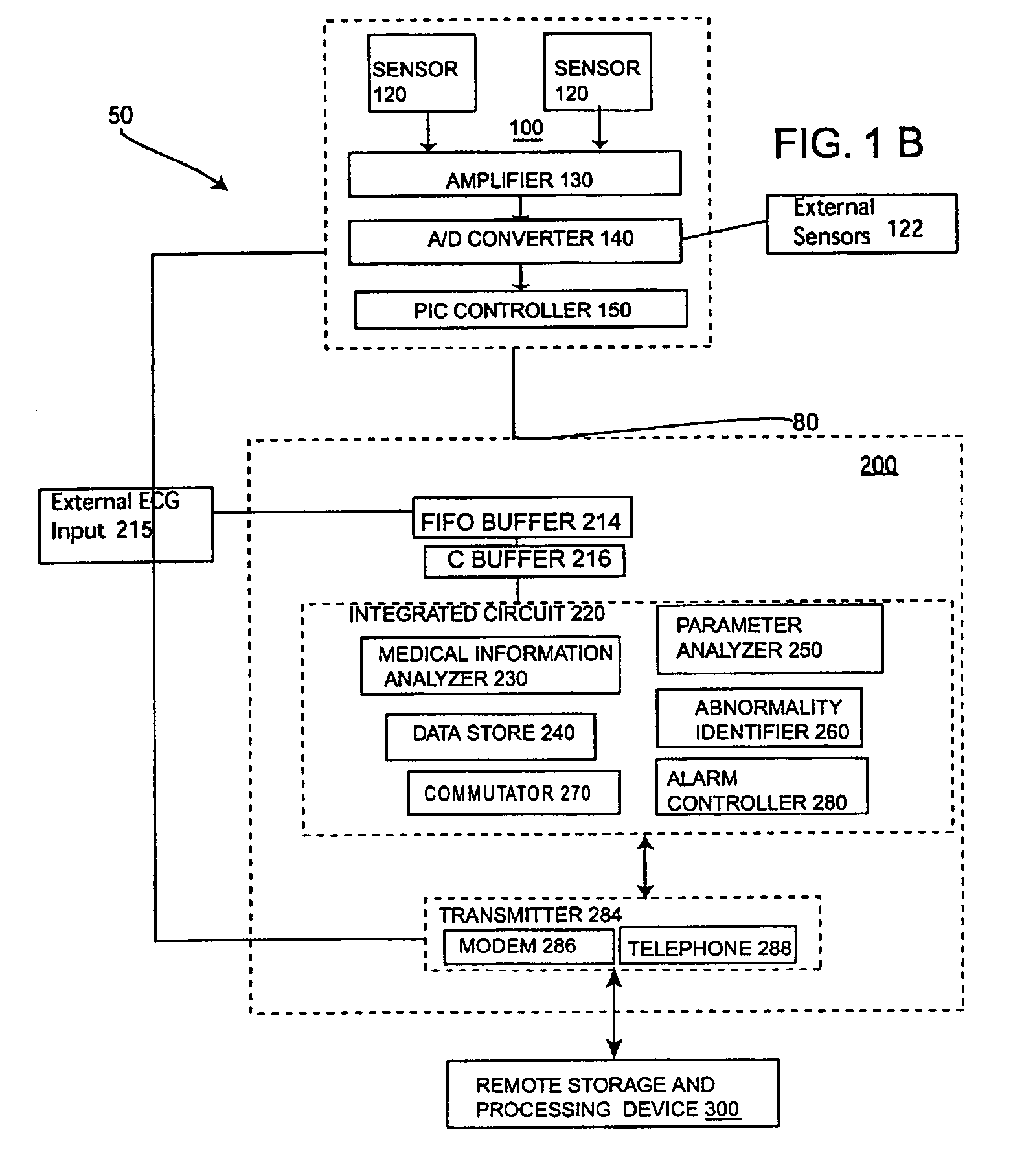
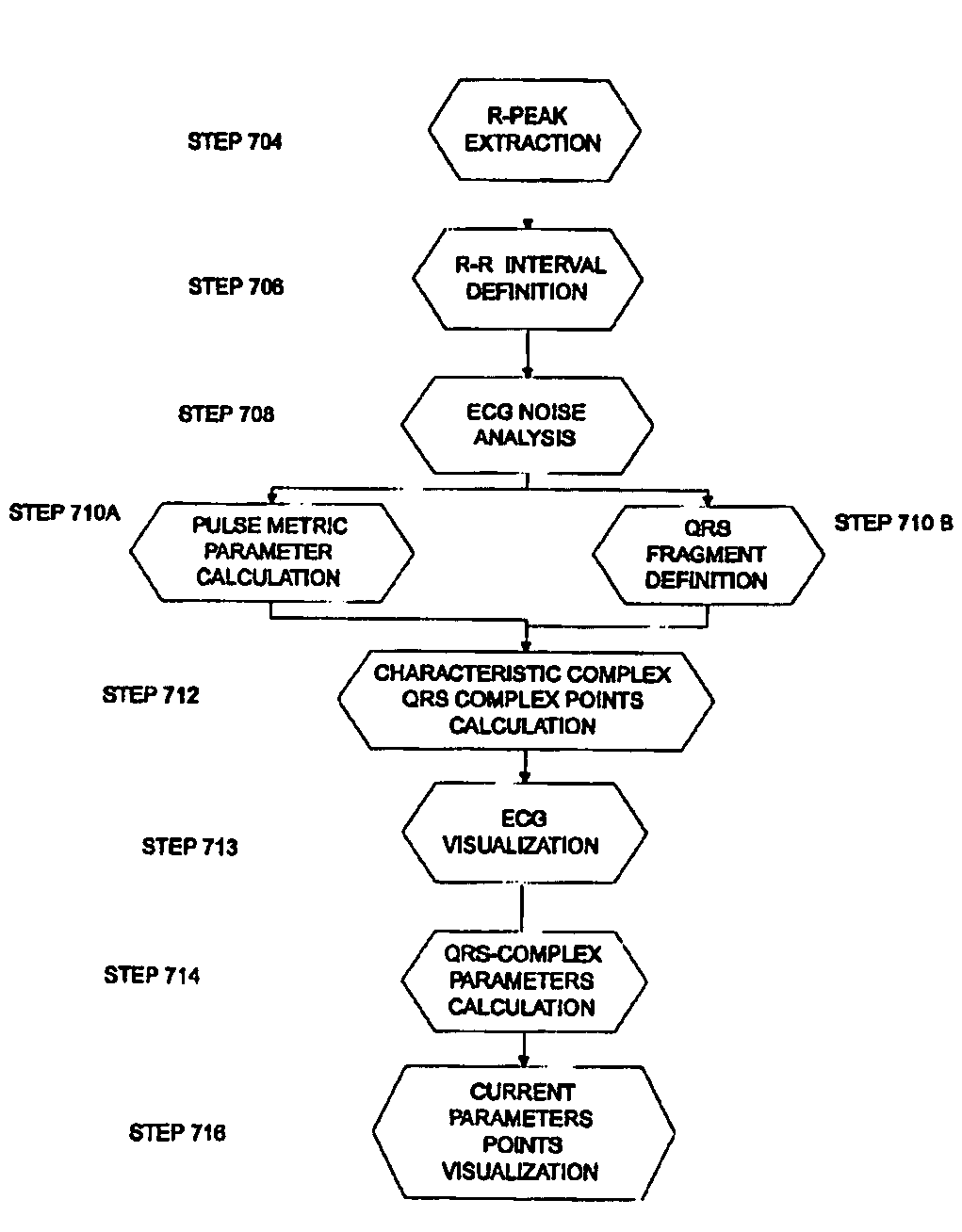
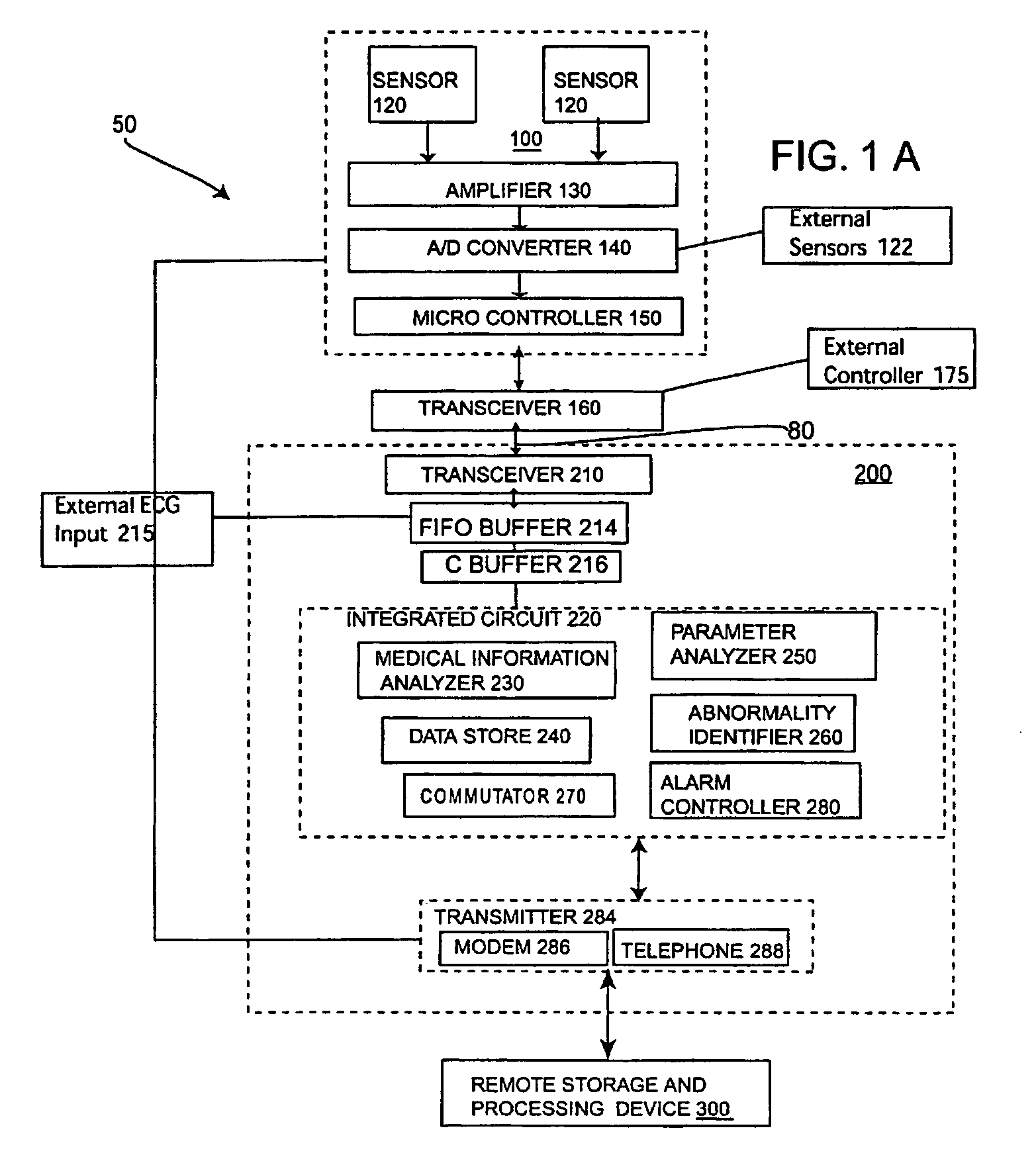
System process for analyzing the medical condition of a user
InactiveUS20050101873A1ElectrocardiographyHealth-index calculationElectrocardiogram QRS complexSystematic process
A device and a process for analyzing a medical condition of a user. This device and process can also be used to predict a future abnormal medical condition of the user. The device includes a portable information-receiving device, an information processing device and a remote storage and processing device. These three devices may be in communication with each other via a wireless communication system. This device can include a GPS system for locating the user when the user is having an abnormal medical condition. The process is designed to take a digital signal from a plurality of ECG sensors on the portable information device and form a QRS wave. One or more points are extracted from this QRS wave are used to form a QRS complex wave. QRS complex waves are used to analyze the medical condition of the user. A plurality of parameters are calculated from these points on the QRS wave. If the medical condition of the user is in an abnormal range then an alarm will sound. However, if the user is not in an abnormal range, then the device may also predict the possibility of a future occurrence of an abnormal medical condition in the user.
Owner:MONEBO TECH
System and method for distinguishing between hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia using an implantable medical device
ActiveUS20060167365A1Improve blood sugar controlReduce deliveryElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyAcute hyperglycaemiaT wave
Techniques are described for detecting and distinguishing among ischemia, hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia based on intracardiac electrogram (IEGM) signals. In one technique, these conditions are detected and distinguished based on an analysis of: the interval between the QRS complex and the peak of a T-wave (QTmax), the interval between the QRS complex and the end of a T-wave (QTend), alone or in combination with a change in ST segment elevation. By exploiting QTmax and QTend in combination with ST segment elevation, changes in ST segment elevation caused by hypo / hyperglycemia can be properly distinguished from changes caused by cardiac ischemia. In another technique, hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia are predicted, detected and / or distinguished from one another based on an analysis of the amplitudes of P-waves, QRS-complexes and T-waves within the IEGM. Appropriate warning signals are delivered and therapy is automatically adjusted.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Methods and apparatus for discriminating polymorphic tachyarrhythmias from monomorphic tachyarrhythmias facilitating detection of fibrillation
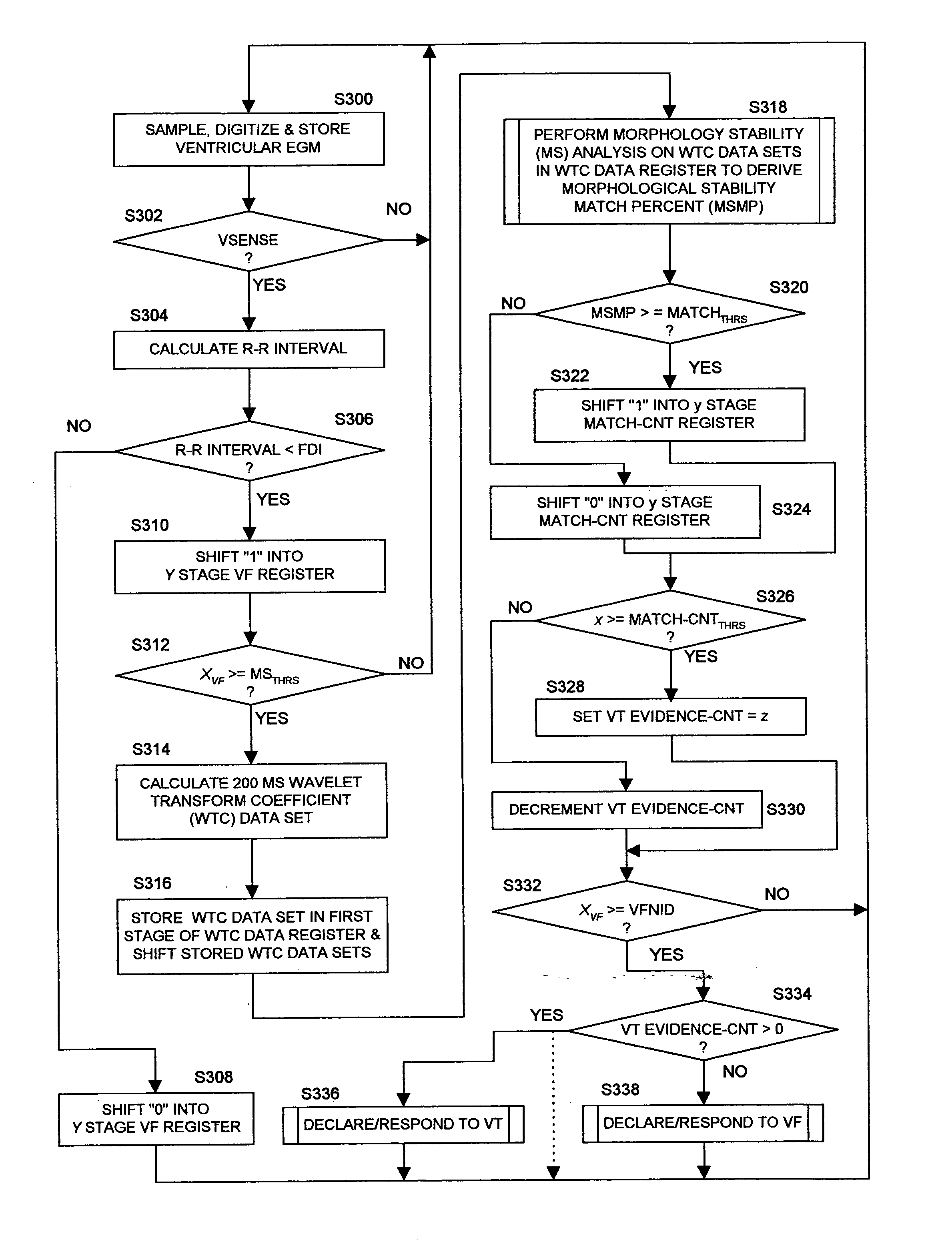
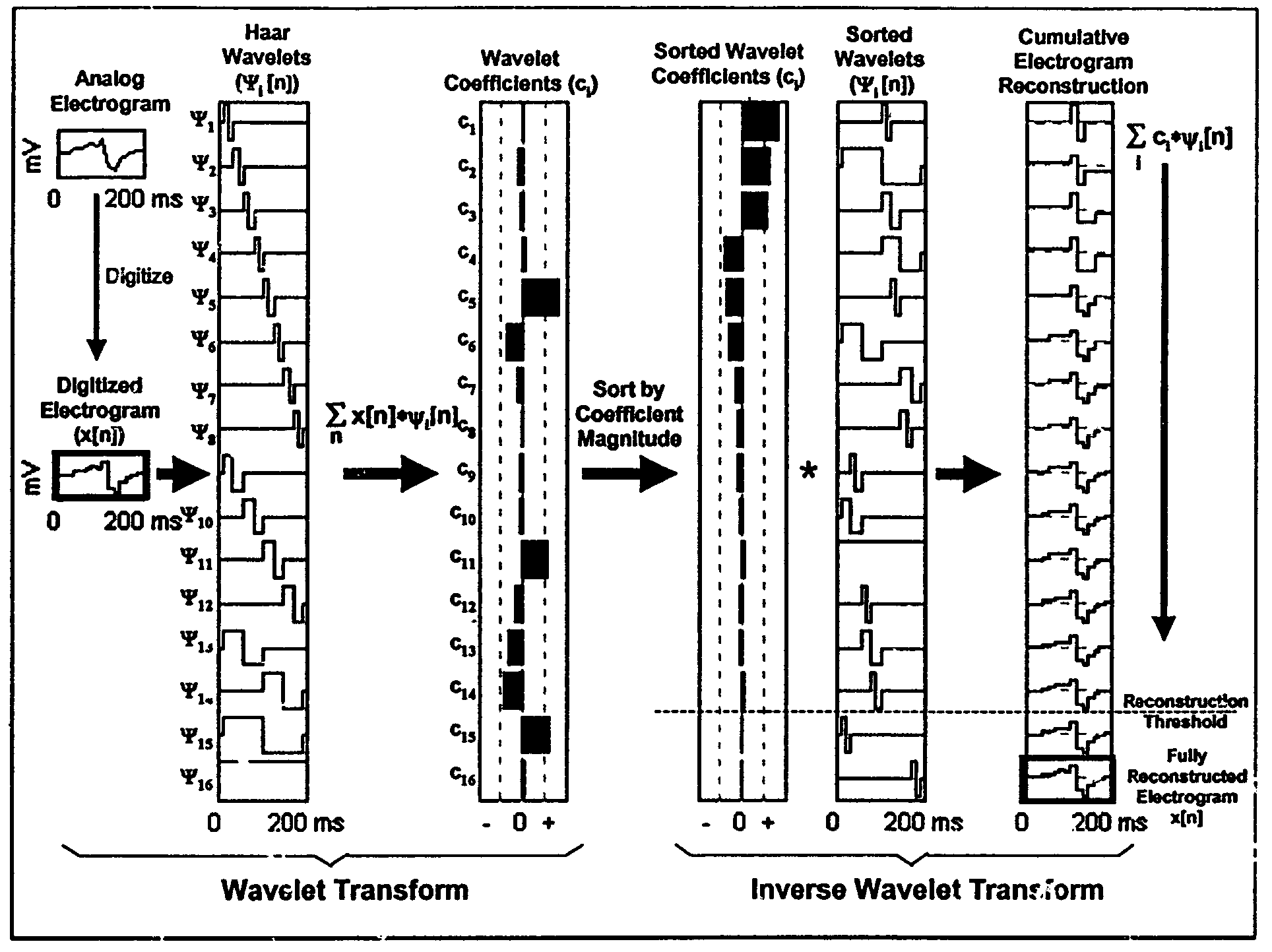
Methods and apparatus are provided for discriminating high rate polymorphic QRS complexes from high rate monomorphic QRS complexes to increase the specificity of detection of polymorphic VT and VF employing wavelet transform signal processing of the QRS complexes are disclosed. Wavelet transforms are applied to the sampled amplitude values of a sequence of QRS complexes to develop wavelet transform coefficient (WTC) data sets. At least selected ones of the WTC data sets are processed and comparisons are made to determine a wavelet match score. A determination is made as a function of the wavelet match scores of the series of successive QRS complexes that characterizes the most recent QRS complex as more or less likely to signify polymorphic VT or VF.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System process for analyzing the medical condition of a user
InactiveUS7289844B2ElectrocardiographyHealth-index calculationInformation processingCommunications system
A device and a process for analyzing a medical condition of a user. This device and process can also be used to predict a future abnormal medical condition of the user. The device includes a portable information-receiving device, an information processing device and a remote storage and processing device. These three devices may be in communication with each other via a wireless communication system. This device can include a GPS system for locating the user when the user is having an abnormal medical condition. The process is designed to take a digital signal from a plurality of ECG sensors on the portable information device and form a QRS wave. One or more points are extracted from this QRS wave are used to form a QRS complex wave. QRS complex waves are used to analyze the medical condition of the user. A plurality of parameters are calculated from these points on the QRS wave. If the medical condition of the user is in an abnormal range then an alarm will sound. However, if the user is not in an abnormal range, then the device may also predict the possibility of a future occurrence of an abnormal medical condition in the user.
Owner:MONEBO TECH
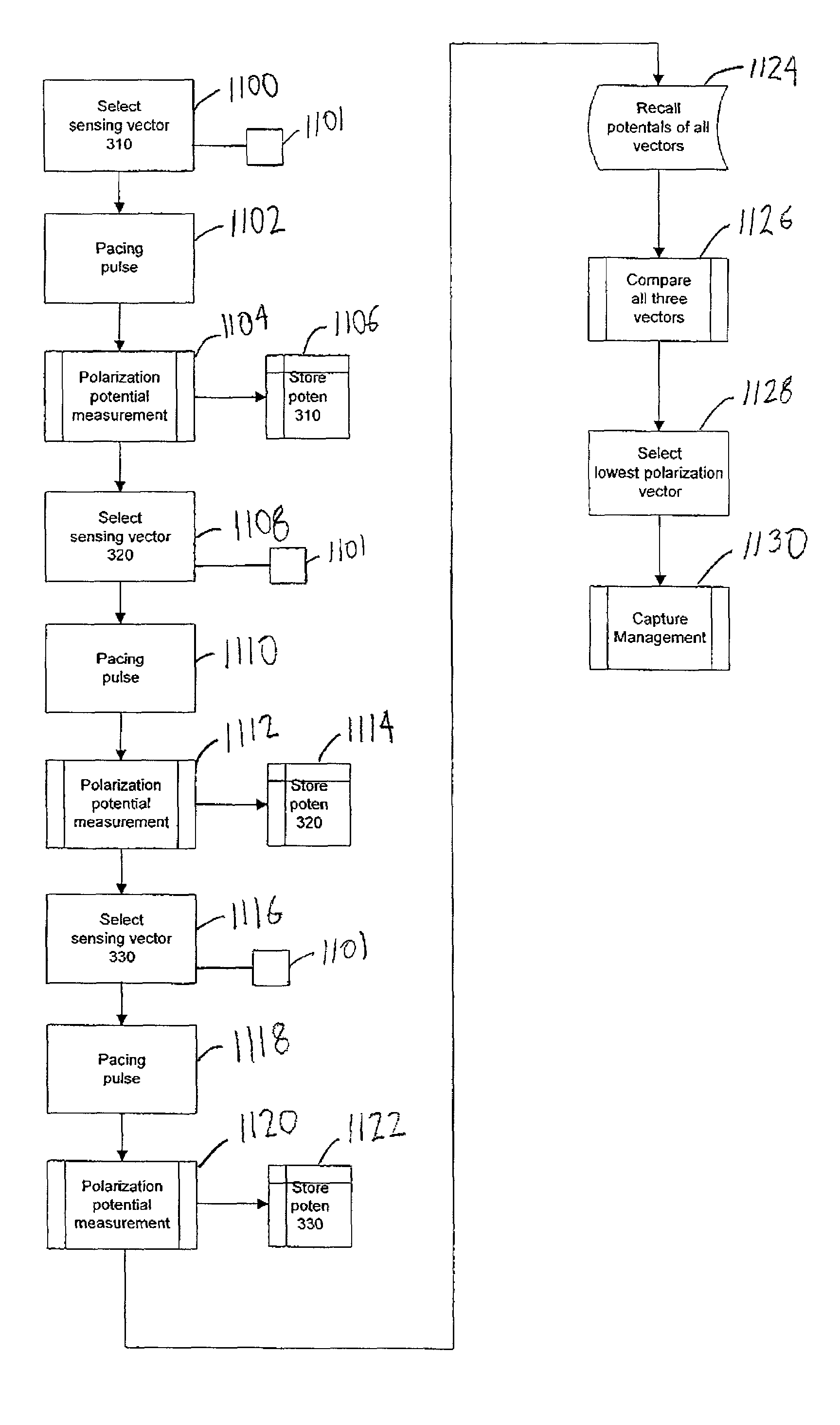
Capture management in multi-site pacing
Methods and apparatus for capture management in multi-chamber pacing are disclosed. In one embodiment, the invention includes determining a combination of electrodes from a plurality of electrodes that yields the lowest polarization potential immediately following delivery of an electrical stimulus to a heart; and performing capture detection using that combination of electrodes. In order to distinguish loss of capture in one ventricle in bi-ventricular pacing, certain embodiments may also include measuring a width of a QRS complex and determining when the width is greater than a predetermined value. A method for detecting single ventricular loss of capture in bi-ventricular pacing is also described utilizing comparison of evoked QRS complex morphology to a predefined waveform.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Automatic electrocardiogram recognition system
InactiveCN103110417AImprove analysis efficiencyPrioritizeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsT waveComputer-aided
The invention discloses an automatic electrocardiogram recognition system. The system comprises an electrocardiogram acquisition device, a wireless / wired network transmission module, an electrocardiogram collection and time domain feature recognizer, an electrocardiogram dominant wave interphase recognizer, an electrocardiogram QRS wave group similarity recognizer and an electrocardiogram queuing recognizer, the electrocardiogram acquisition device inputs acquired data to the electrocardiogram collection and time domain feature recognizer via the transmission module, the electrocardiogram collection and time domain feature recognizer recognizes to obtain positions of peak points of P waves, QRS waves and T waves on a 12-lead, the electrocardiogram dominant wave interphase recognizer recognizes heart rate to obtain normal and abnormal results of the heart rate, the electrocardiogram QRS wave group similarity recognizer recognizes whether an electrocardiogram probably has premature beat or not, and the electrocardiogram queuing recognizer sequences and outputs. The system performs real-time computer-aided analysis of clinically acquired 12-lead electrocardiograms to automatically recognize arrhythmia and premature beat electrocardiograms, and accordingly efficiency of electrocardiogram analysis is improved while a priority processing means is provided for emergency electrocardiograms.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
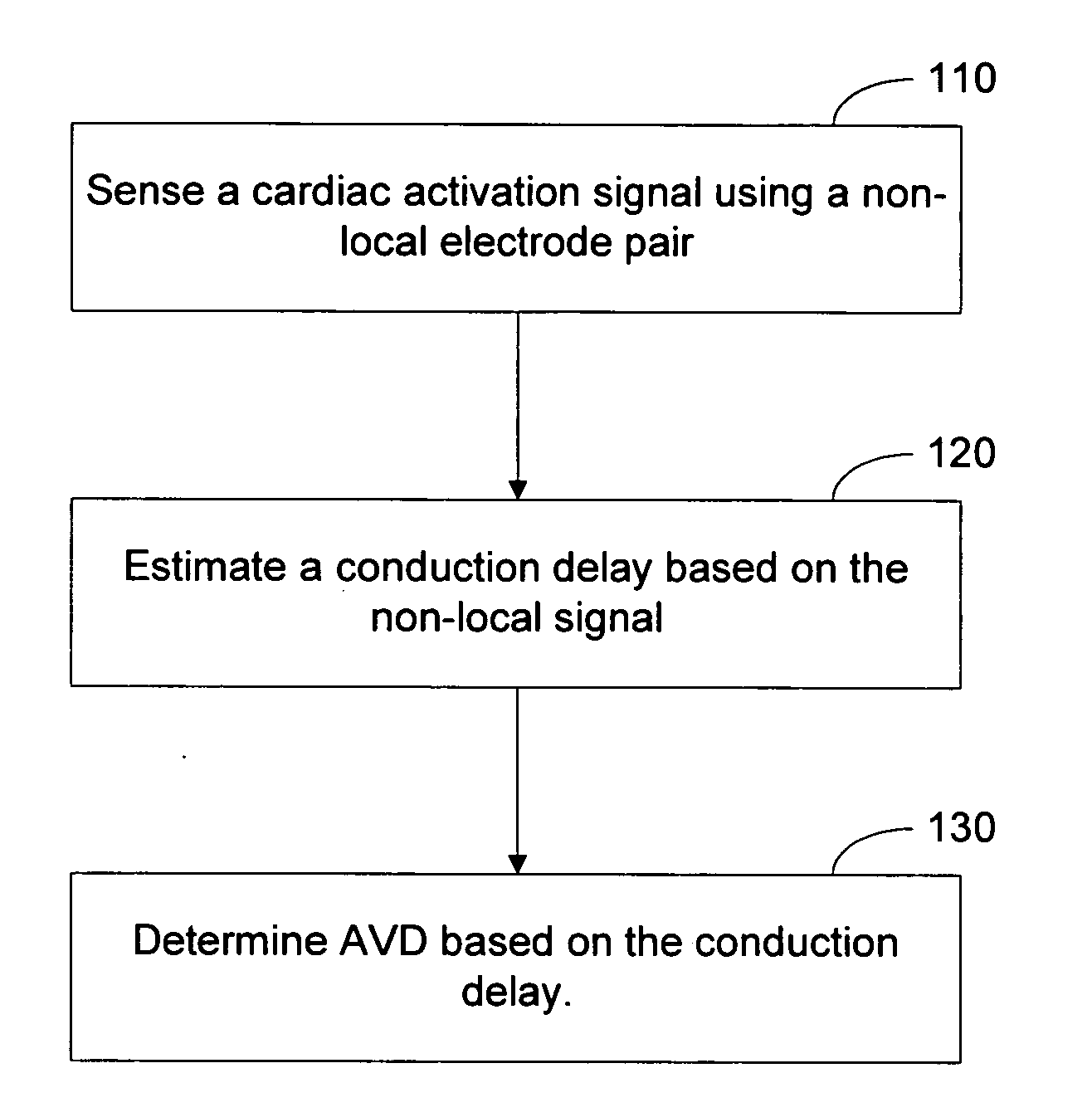
Determination of cardiac pacing parameters based on non-localized sensing
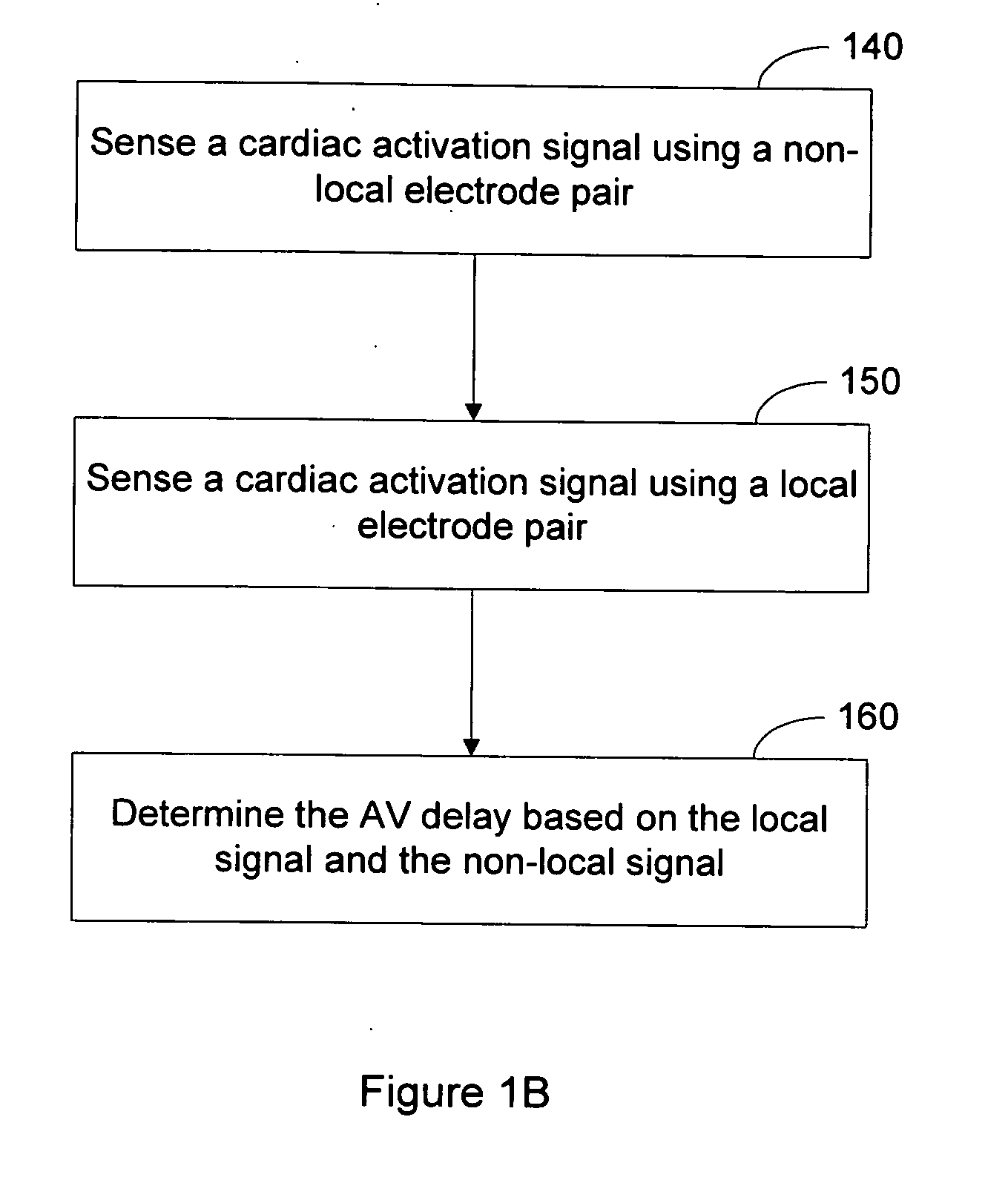
An atrioventricular delay (AVD) for cardiac pacing therapy is determined based, at least in part, on one or more cardiac activation signals sensed using body-implantable electrodes providing non-local sensing. A conduction delay is estimated using a non-local cardiac activation signal and the AVD is determined based on the conduction delay. Estimating the conduction delay may involve measuring a P-wave width or measuring a QRS complex width of the non-local signal. If multiple signals are sensed, the conduction delay may be estimated from a selected signal or may be estimated by forming a representative signal such as through averaging or other methods. The AVD may be determined as a function of the estimated conduction delay.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
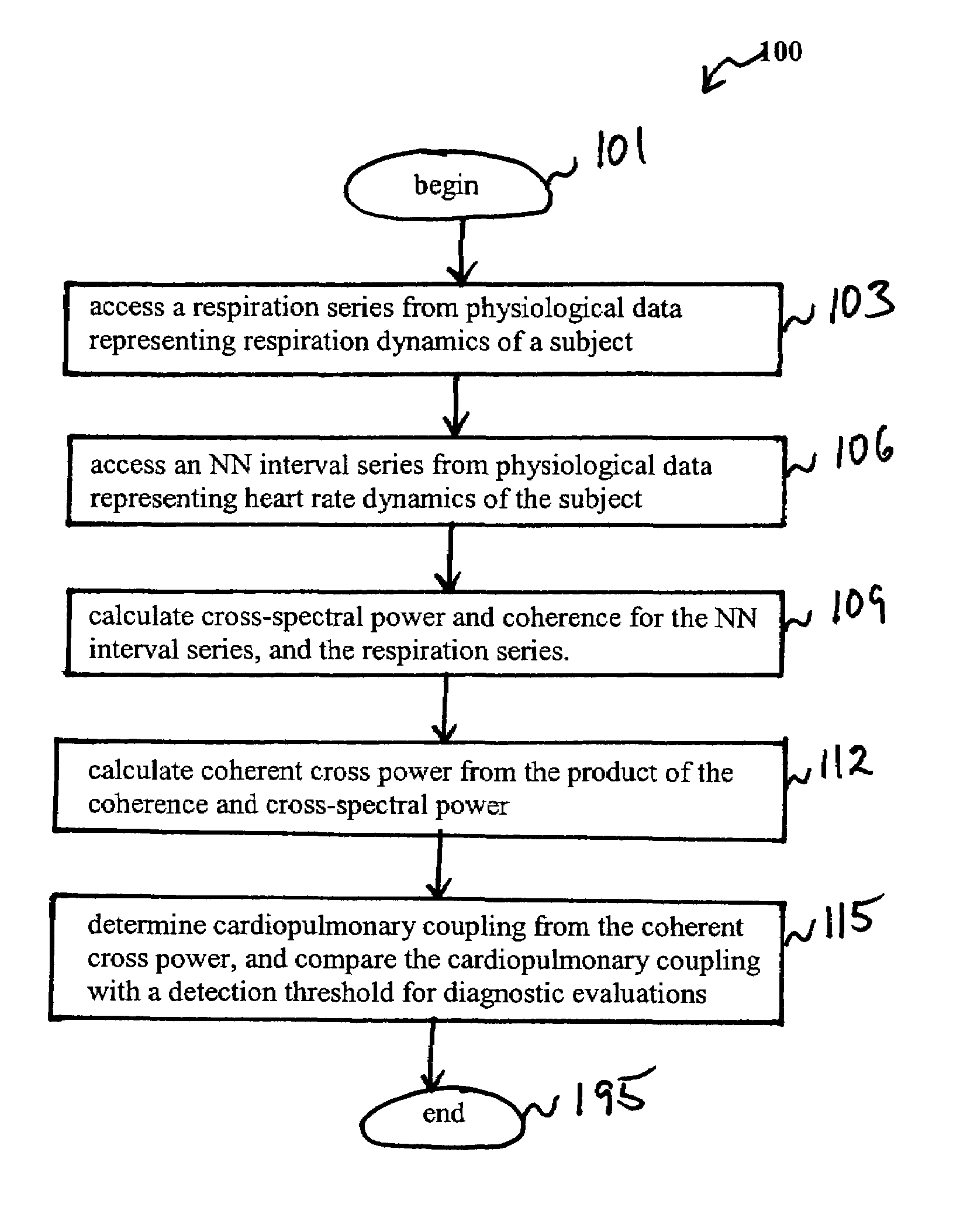
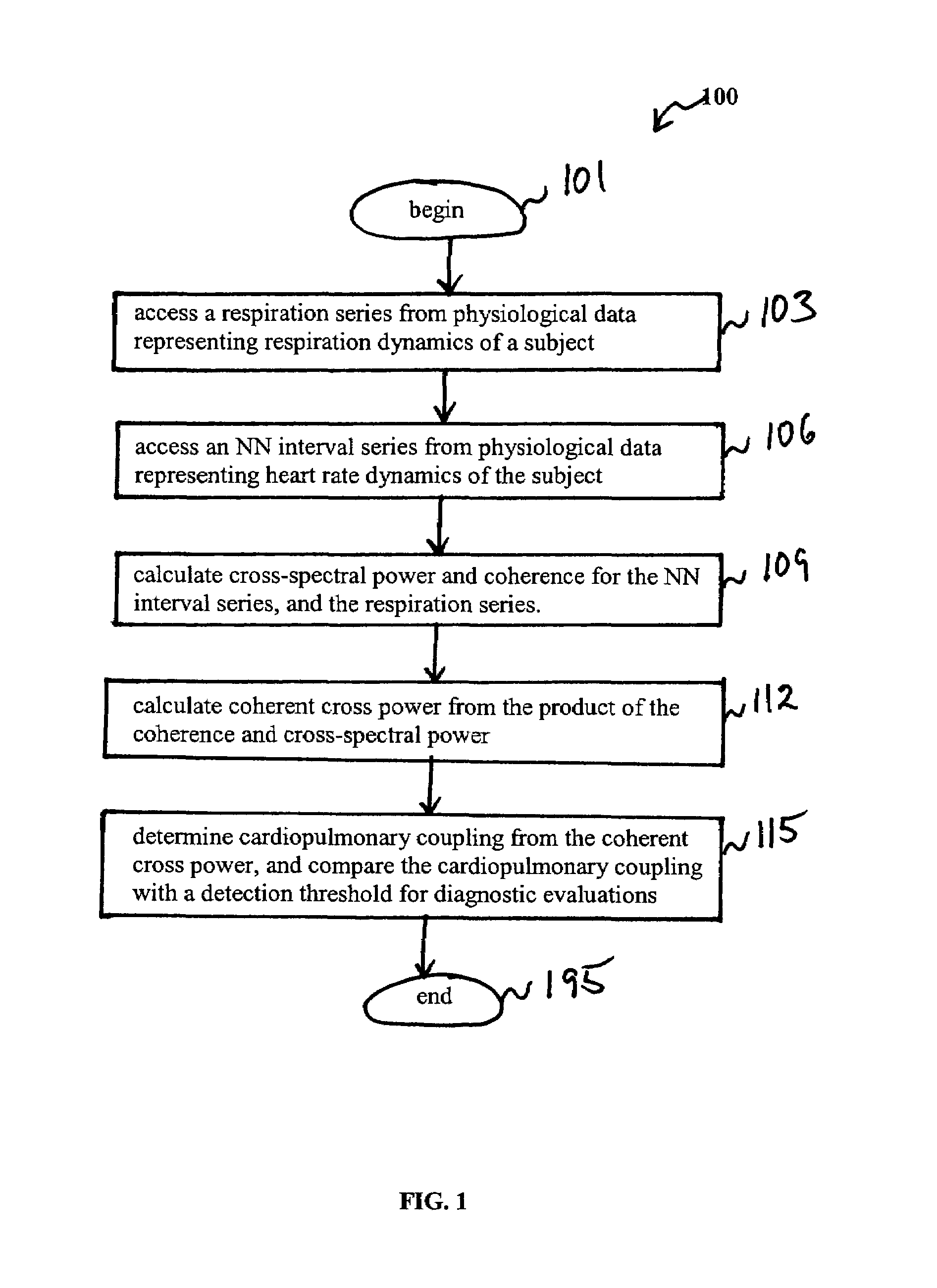
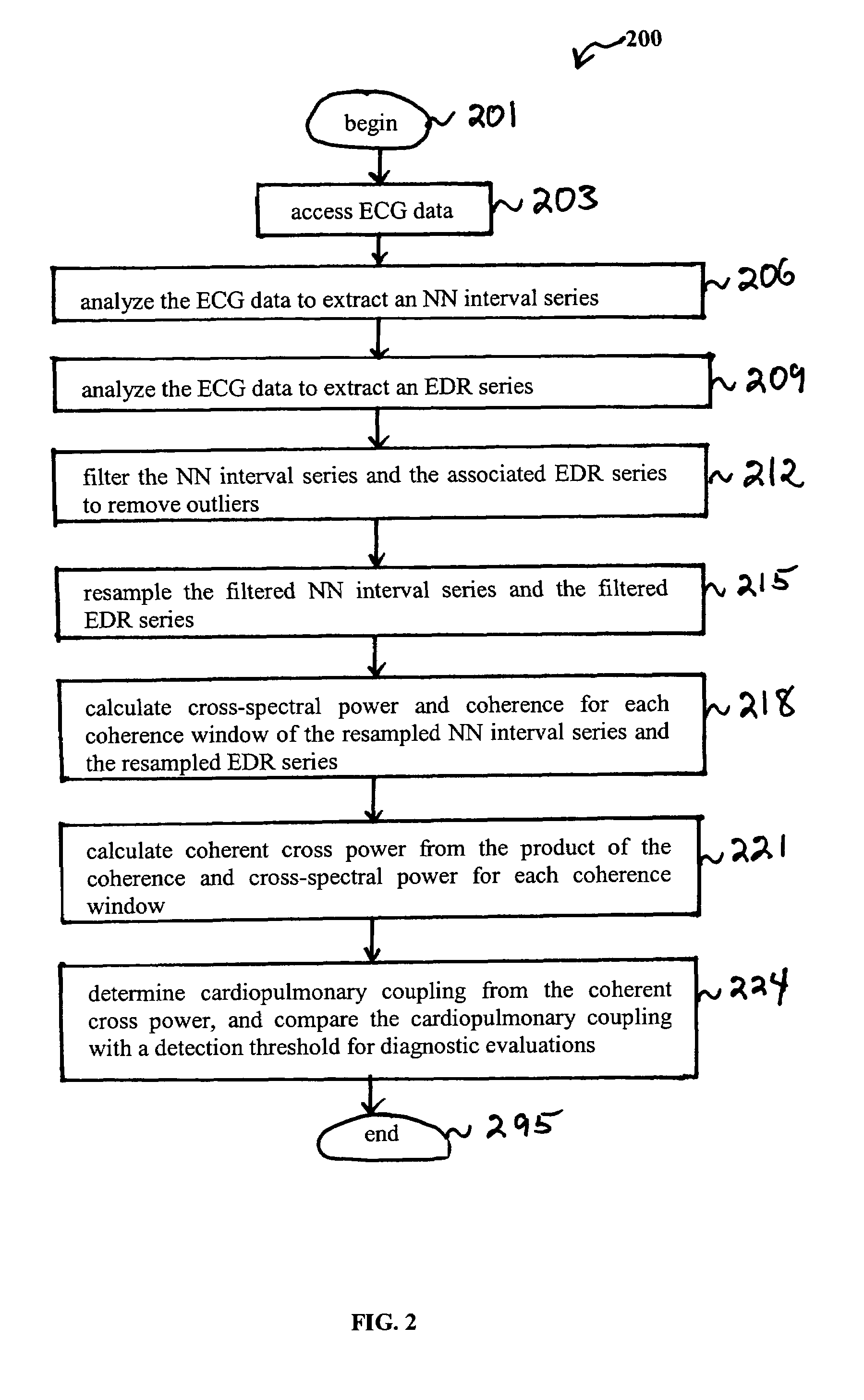
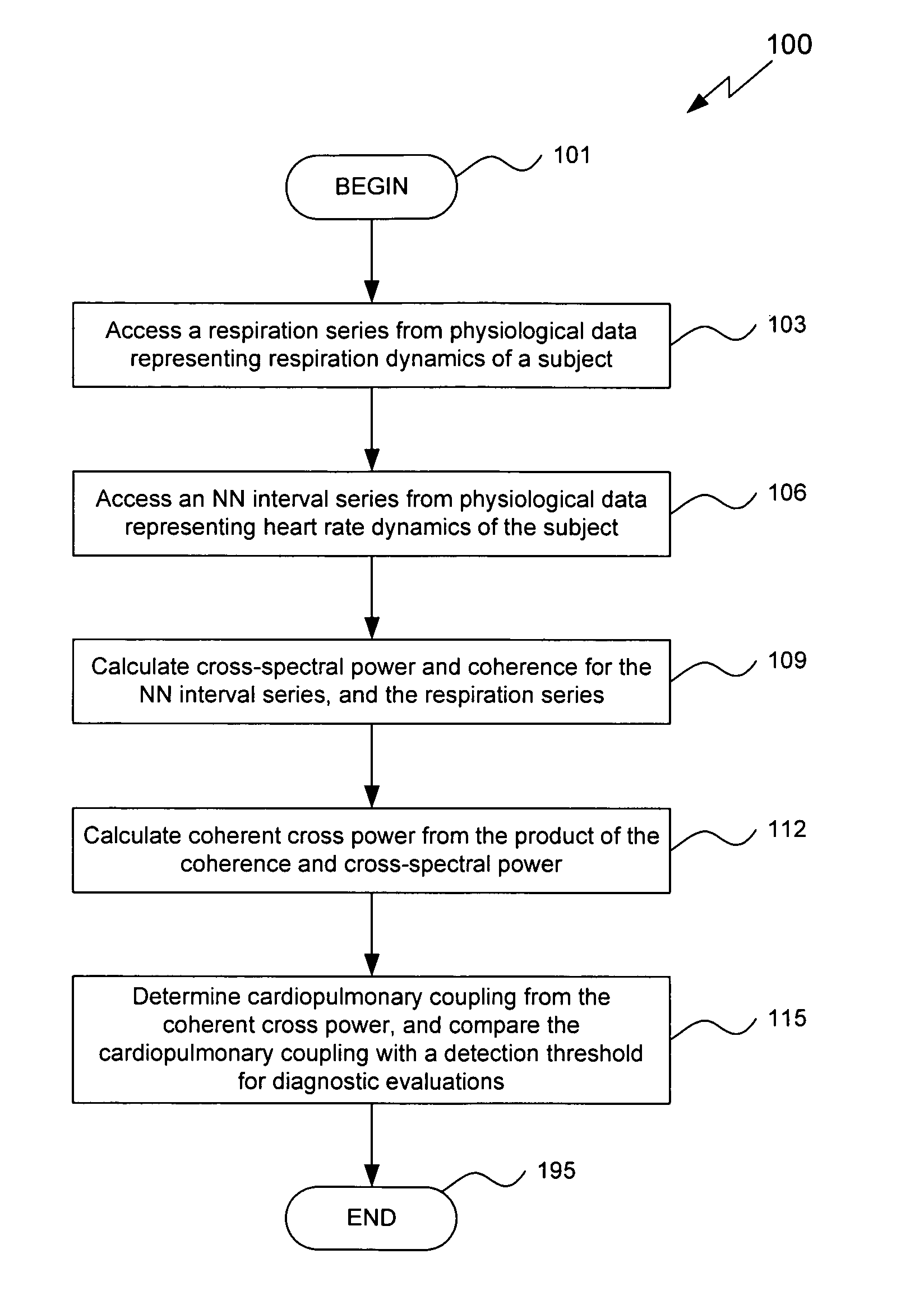
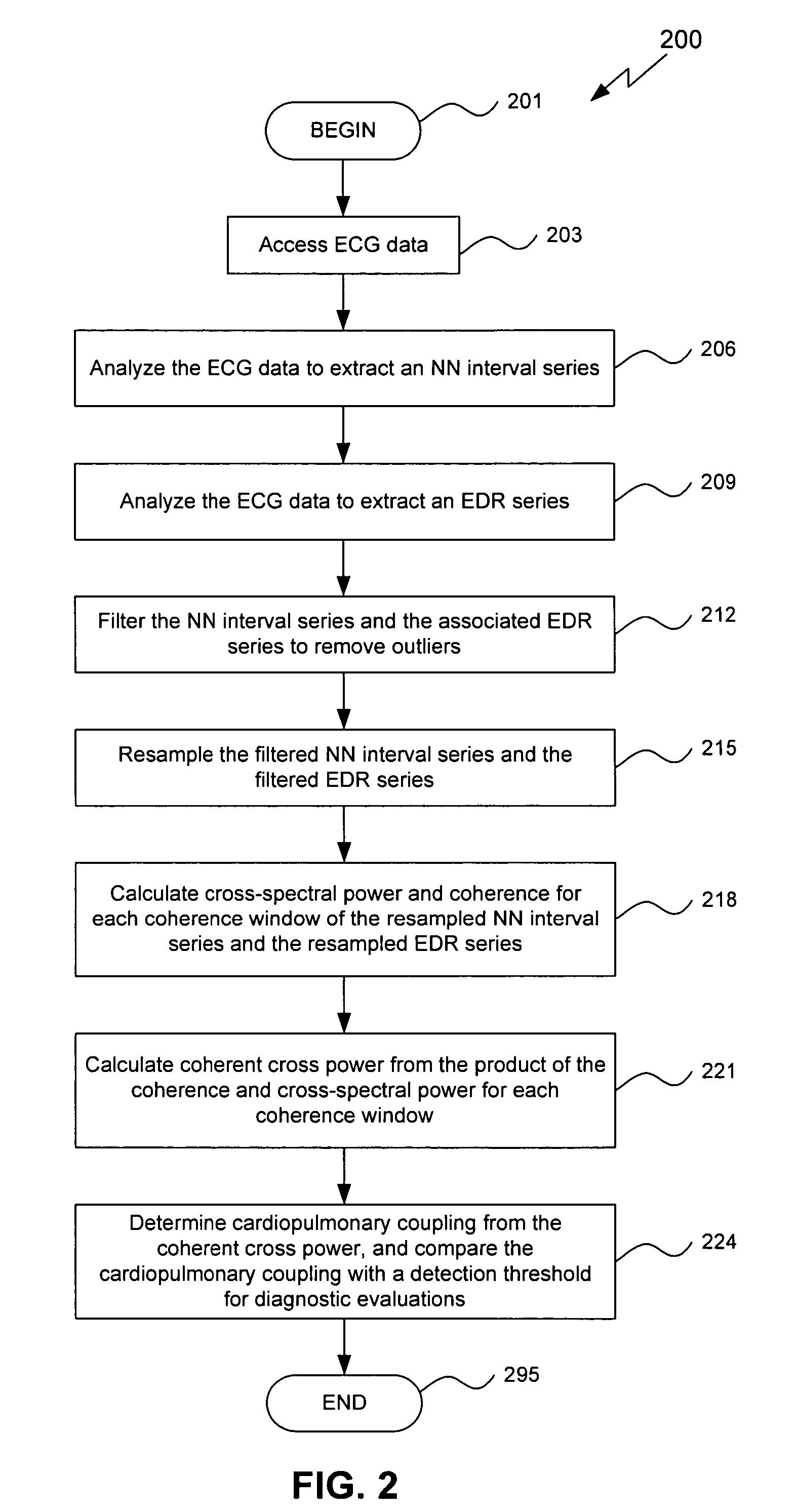
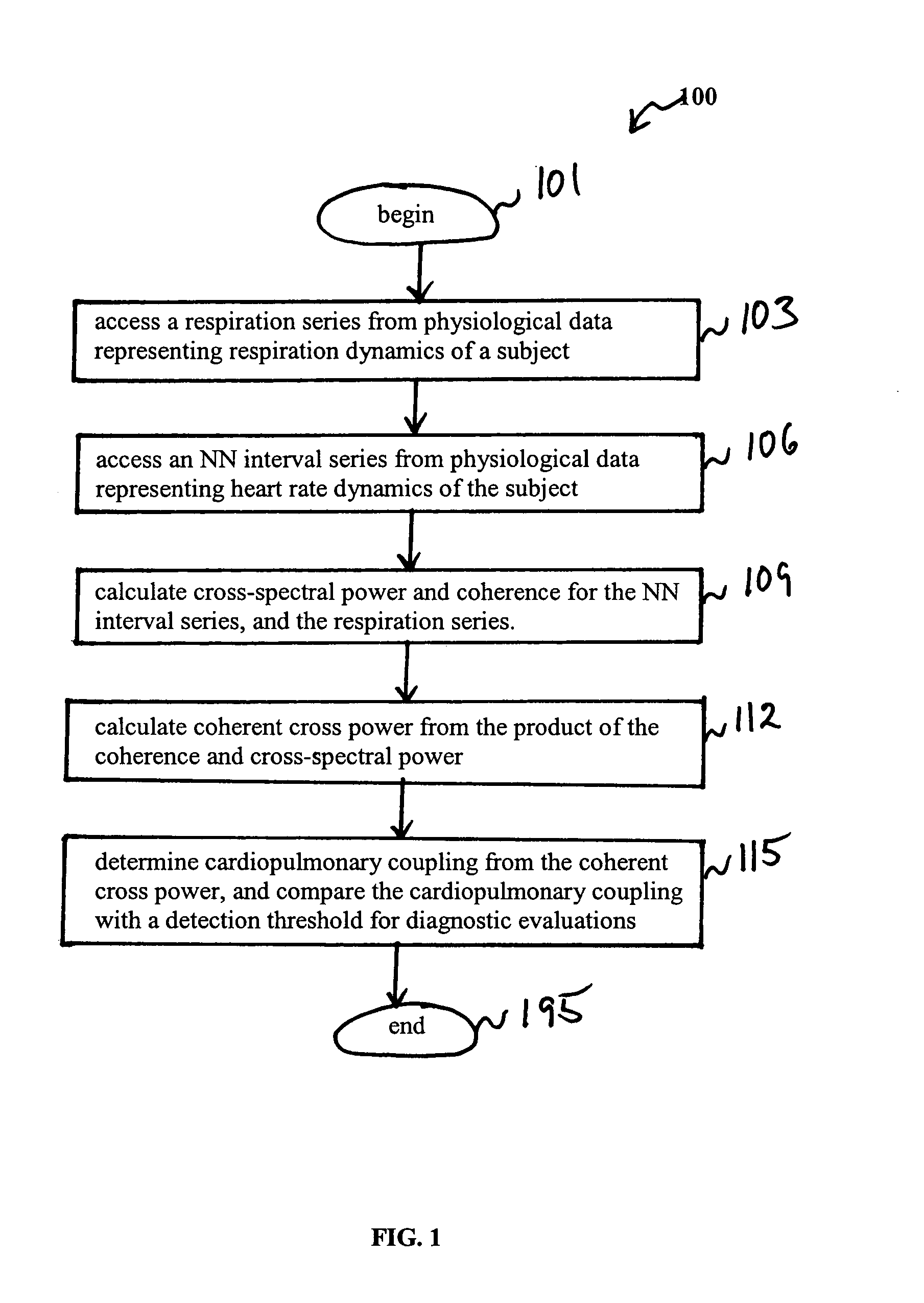
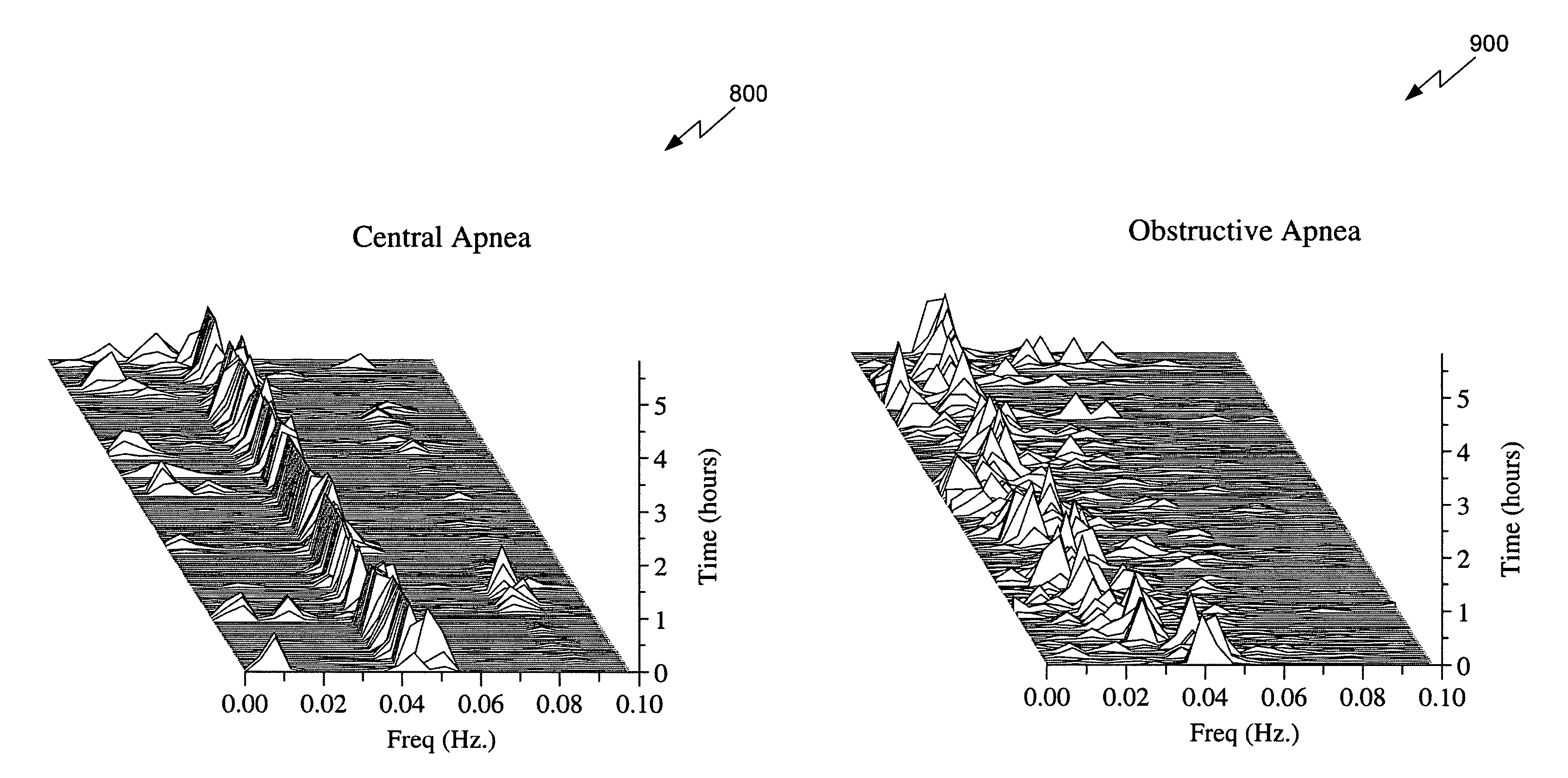
Assessment of sleep quality and sleep disordered breathing based on cardiopulmonary coupling
An assessment of sleep quality and sleep disordered breathing is determined from the cardiopulmonary coupling between two physiological data series. In an embodiment, an R-R interval series is derived from an electrocardiogram (ECG) signal. The normal beats from the R-R interval series are extracted to produce a normal-to-normal (NN) interval series. The amplitude variations in the QRS complex are used to extract to a surrogate respiration signal (i.e., ECG-derived respiration (EDR)) that is associated with the NN interval series. The two series are corrected to remove outliers, and resampled. The cross-spectral power and coherence of the two resampled signals are calculated over a plurality of coherence windows. For each coherence window, the product of the coherence and cross-spectral power is used to calculate coherent cross power. Using the appropriate thresholds for the coherent cross power, the proportion of sleep spent in CAP, non-CAP, and wake and / or REM are determined.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
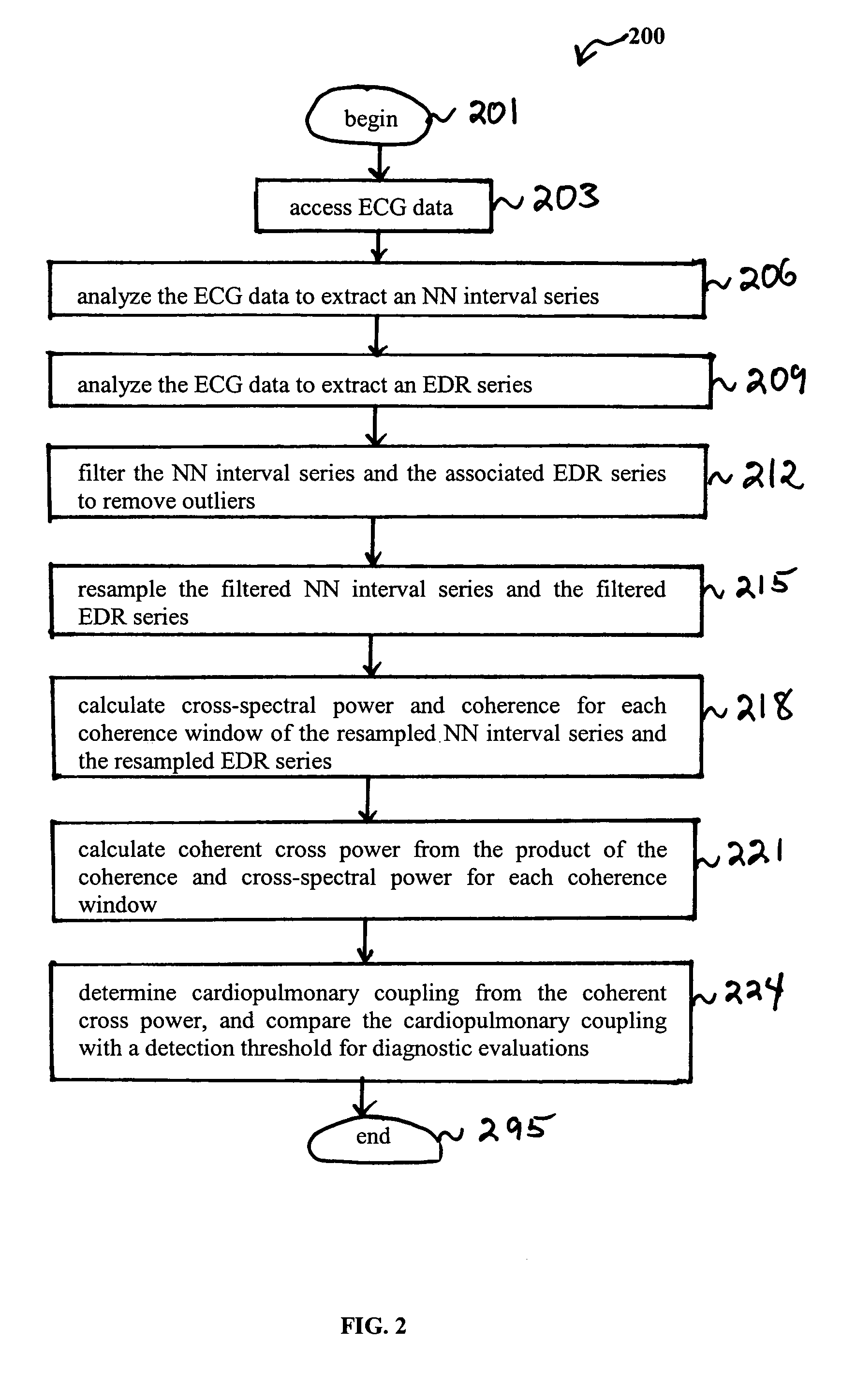
Assessment of sleep quality and sleep disordered breathing based on cardiopulmonary coupling
An assessment of sleep quality and sleep disordered breathing is determined from cardiopulmonary coupling between two physiological data series. An R-R interval series is derived from an electrocardiogram (ECG) signal. The normal beats from the R-R interval series are extracted to produce a normal-to-normal interval series. The amplitude variations in the QRS complex are used to extract a surrogate respiration signal (i.e., ECG-derived respiration) associated with the NN interval series. The two series are corrected to remove outliers, and resampled. The cross-spectral power and coherence of the two resampled signals are calculated over a plurality of coherence windows. For each coherence window, the product of the coherence and cross-spectral power is used to calculate coherent cross-power. Using the appropriate thresholds for the coherent cross-power, the proportion of sleep spent in CAP, non-CAP, and wake and / or REM are determined. Coherent cross-power can be applied to differentiate obstructive from non-obstructive disease, and admixtures of the same.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
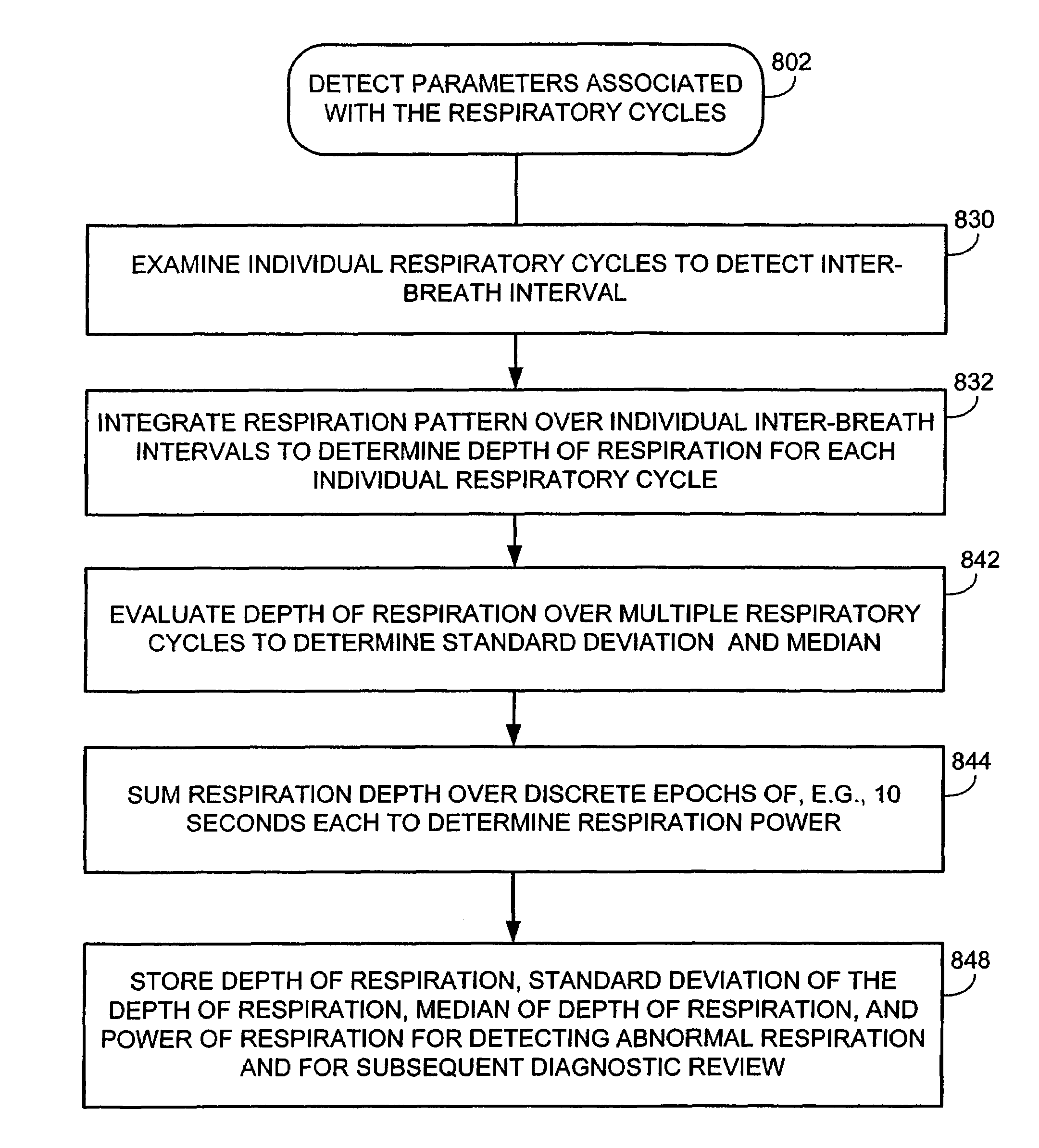
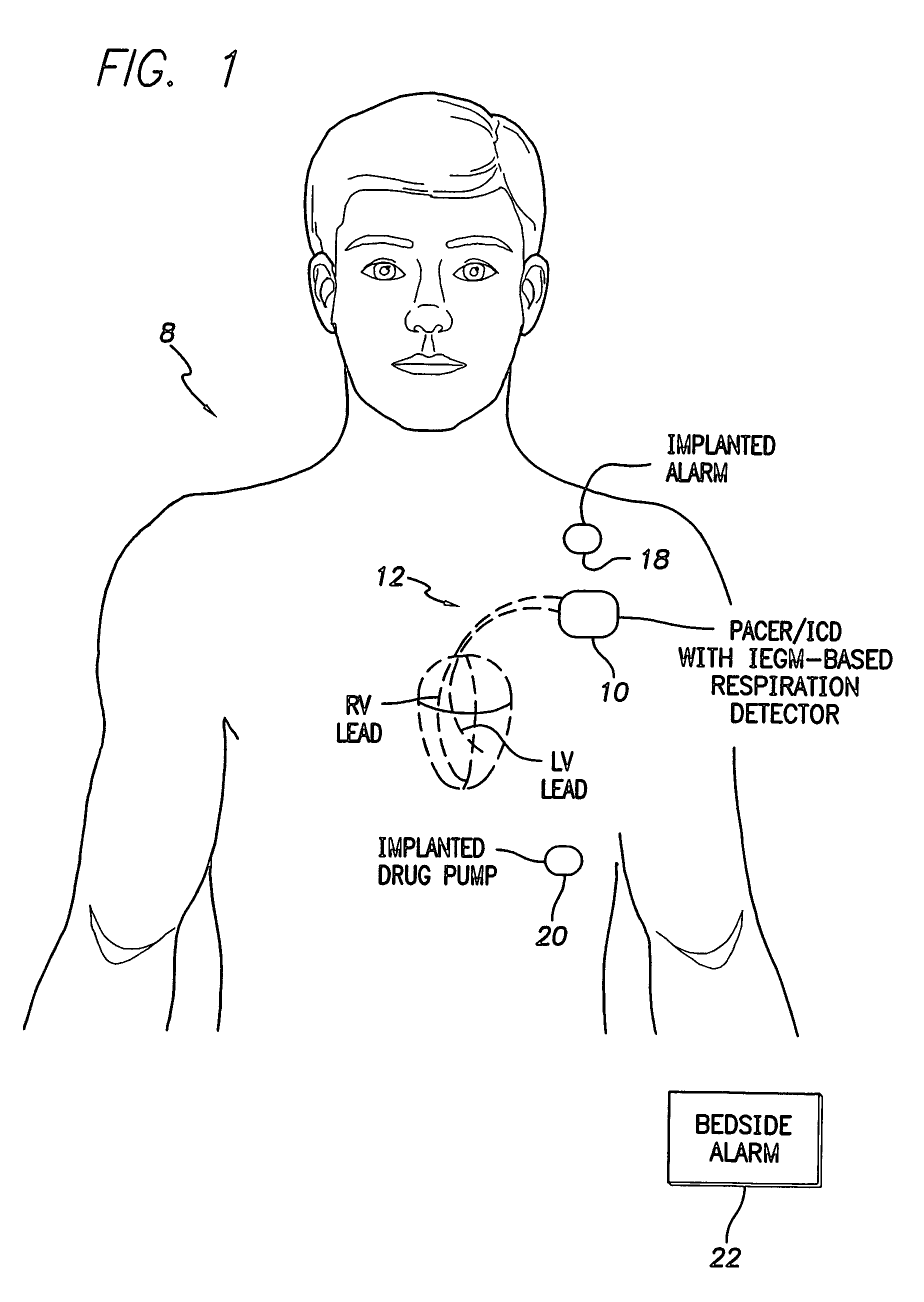
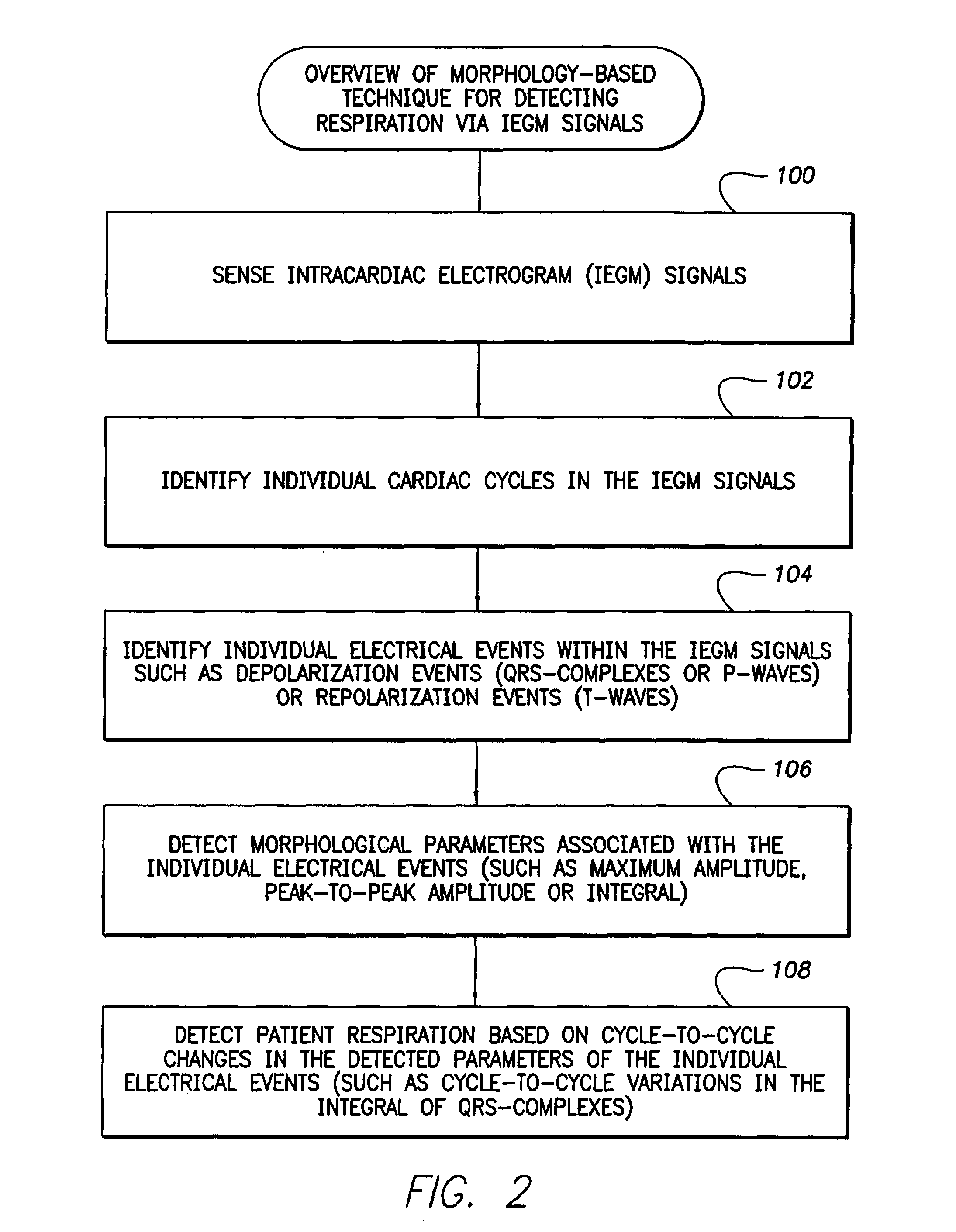
System and method for detecting abnormal respiration via respiratory parameters derived from intracardiac electrogram signals
Techniques are provided for tracking patient respiration based upon intracardiac electrogram (IEGM) signals or other electrical cardiac signals. Briefly, respiration patterns are detected based upon cycle-to-cycle changes in morphological features associated with individual electrical events with the IEGM signals. For example, slight changes in the peak amplitudes of QRS-complexes, P-waves or T-waves are tracked to identify cyclical variations representative of patient respiration. Alternatively, the integrals of the morphological features of the individual events may be calculated for use in tracking respiration. In any case, once respiration patterns have been identified, episodes of abnormal respiration, such as apnea, hyperpnea, nocturnal asthma, or the like, may be detected and therapy automatically delivered. In particular, techniques for detecting abnormal respiration based on various respiratory parameters derived from the IEGM—such as respiration depth and respiration power—are described.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Assessment of sleep quality and sleep disordered breathing based on cardiopulmonary coupling
An assessment of sleep quality and sleep disordered breathing is determined from the cardiopulmonary coupling between two physiological data series. In an embodiment, an R-R interval series is derived from an electrocardiogram (ECG) signal. The normal beats from the R-R interval series are extracted to produce a normal-to-normal (NN) interval series. The amplitude variations in the QRS complex are used to extract to a surrogate respiration signal (i.e., ECG-derived respiration (EDR)) that is associated with the NN interval series. The two series are corrected to remove outliers, and resampled. The cross-spectral power and coherence of the two resampled signals are calculated over a plurality of coherence windows. For each coherence window, the product of the coherence and cross-spectral power is used to calculate coherent cross power. Using the appropriate thresholds for the coherent cross power, the proportion of sleep spent in CAP, non-CAP, and wake and / or REM are determined.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Methods and apparatus for discriminating polymorphic tachyarrhythmias from monomorphic tachyarrhythmias facilitating detection of fibrillation
InactiveUS7103405B2High detection specificityFast conductionElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsHigh rateFibrillation
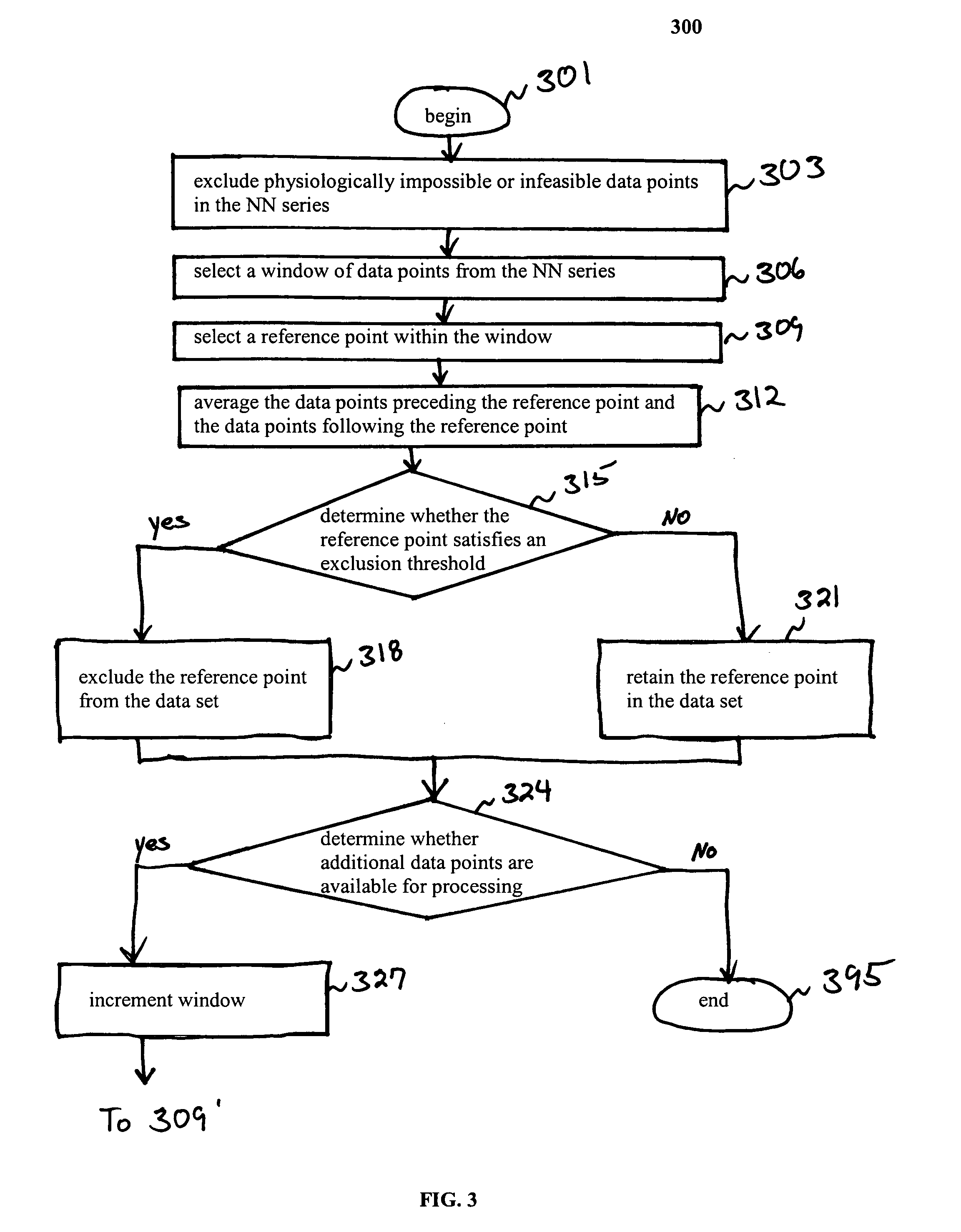
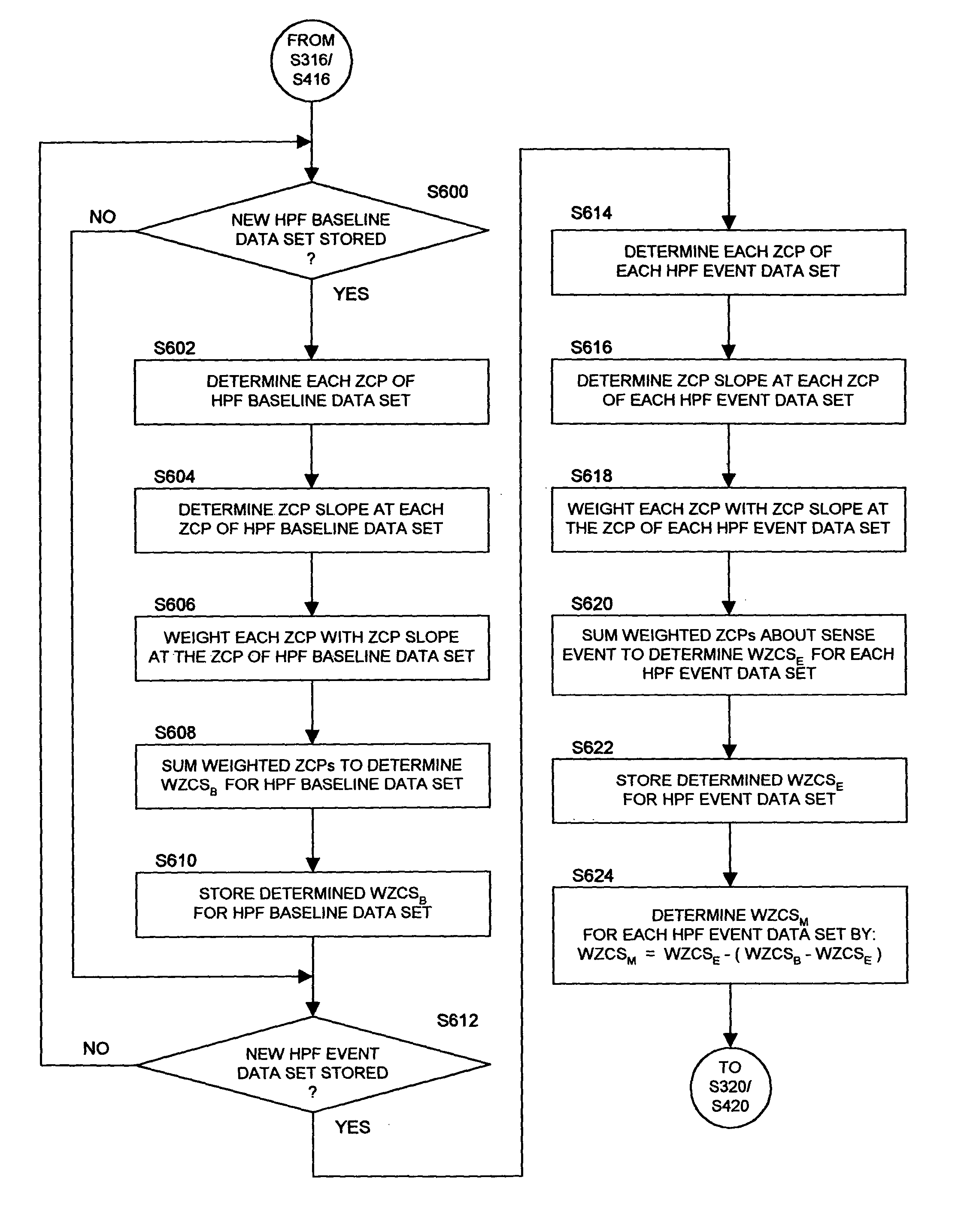
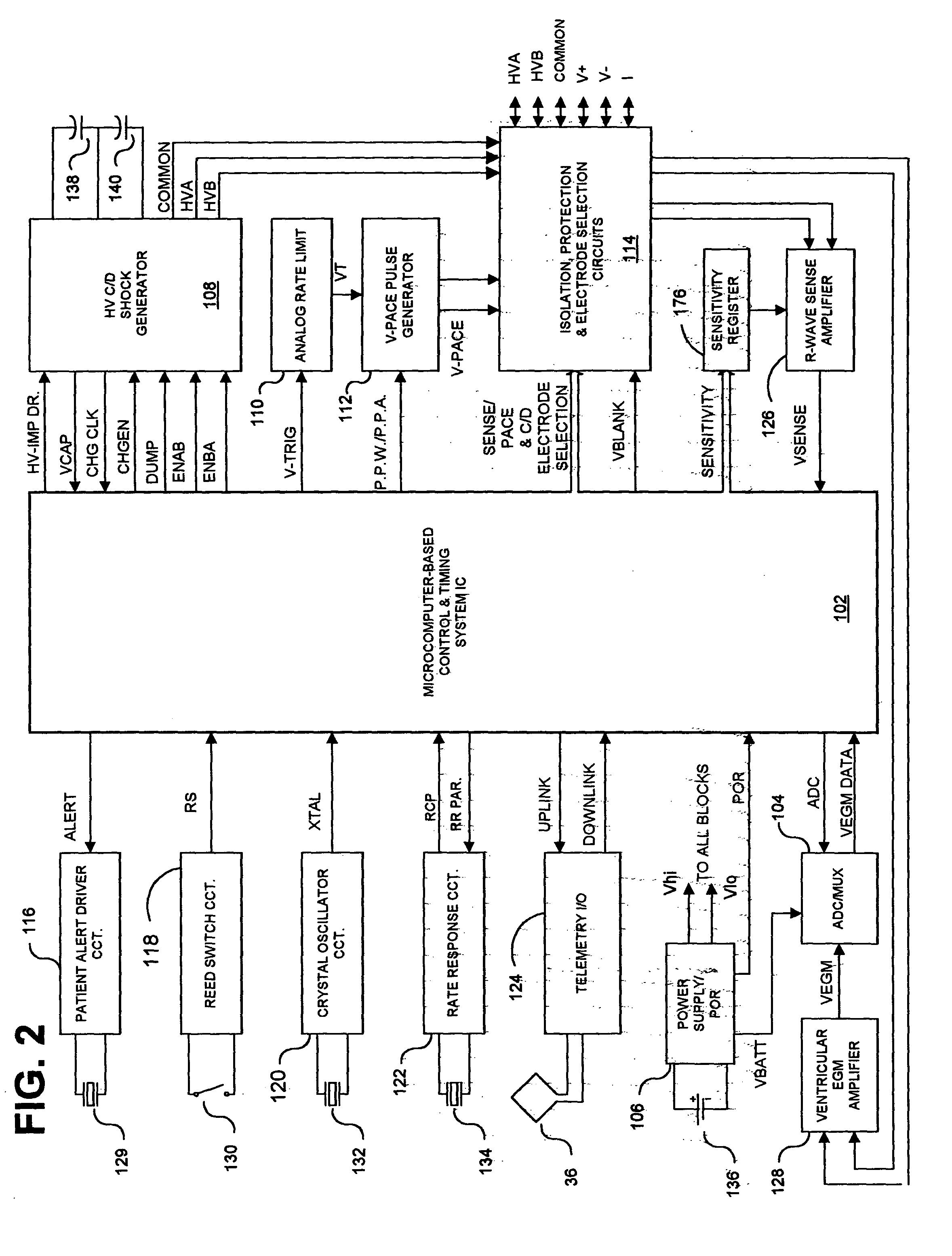
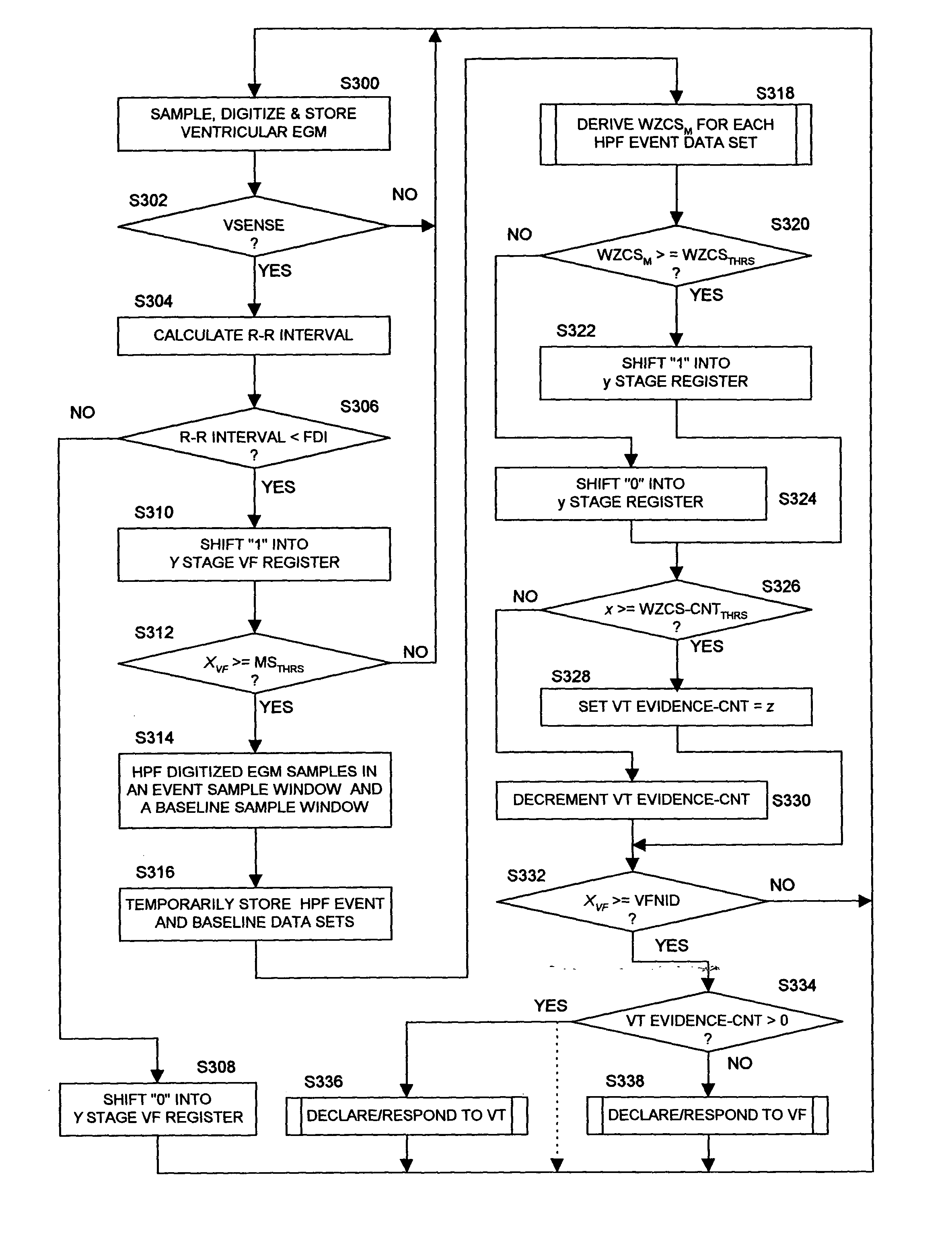
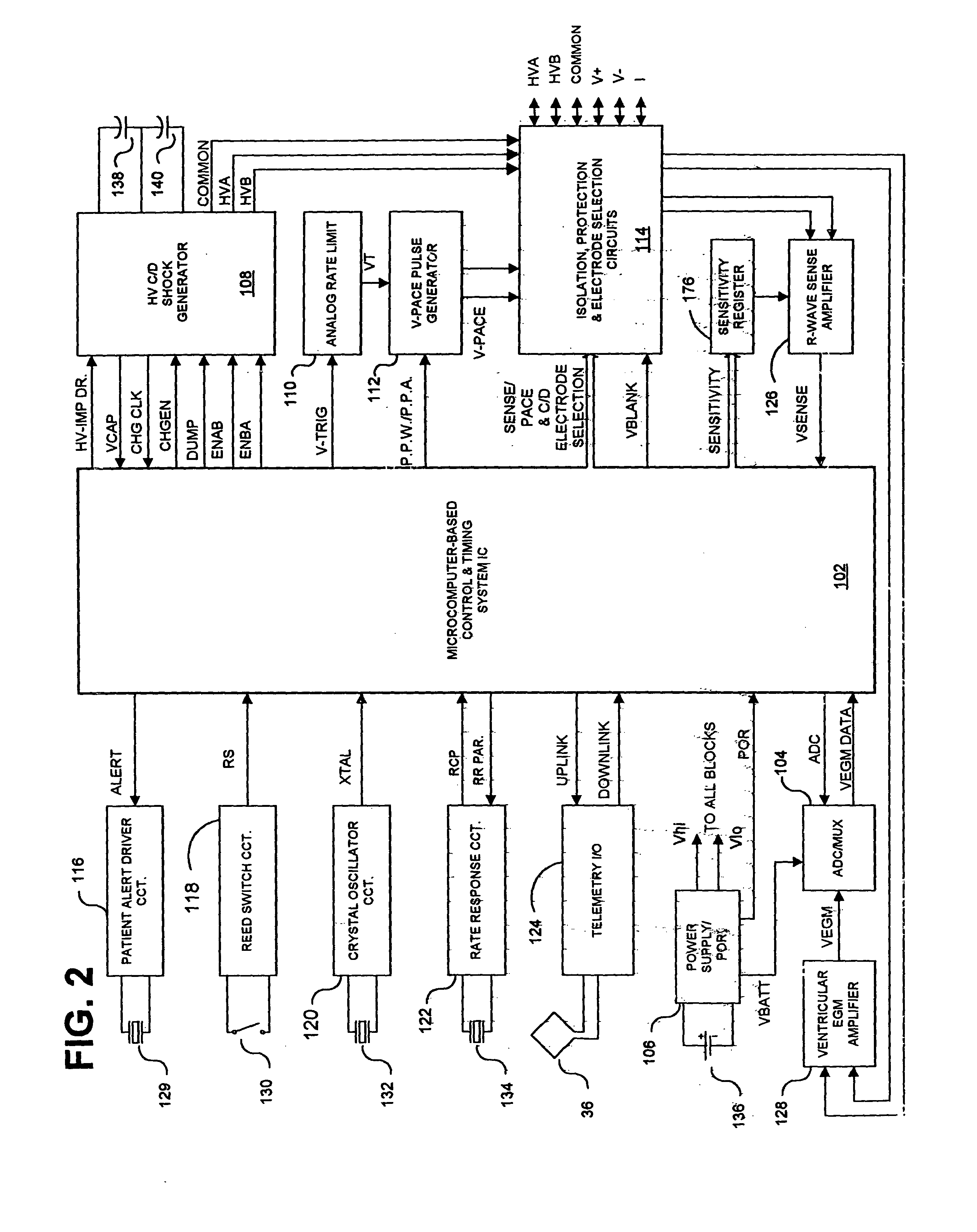
Systems and methods employing a weighted zero crossing sum metric (WZCSM) derived from the EGM that improves the specificity of discriminating between a monomorphic tachyarrhythmia and a polymorphic tachyarrhythmia are provided that examine frequency content and baseline information of the EGM as discriminatory signatures are disclosed. In preferred embodiments, high rate polymorphic QRS complexes are discriminated from high rate monomorphic QRS complexes to increase the specificity of detection of polymorphic VT and VF. Zero crossing points (ZCPs) and weighted ZCP slopes of the high pass filtered EGM signal in baseline and sense event windows are identified. The weighted ZCPs of the baseline window are summed to provide a baseline WZCSB, and the weighted ZCPs of the VSENSE event window are summed to provide a VSENSE event WZCSE. A WZCSM is derived from the VSENSE event WZCSE and the baseline WZCSB that is compared to a threshold.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods and apparatus for discriminating polymorphic tachyarrhythmias from monomorphic tachyarrhythmias facilitating detection of fibrillation
ActiveUS7130677B2High detection specificityStrong specificityElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsData setHigh rate
Methods and apparatus are provided for discriminating high rate polymorphic QRS complexes from high rate monomorphic QRS complexes to increase the specificity of detection of polymorphic VT and VF employing wavelet transform signal processing of the QRS complexes are disclosed. Wavelet transforms are applied to the sampled amplitude values of a sequence of QRS complexes to develop wavelet transform coefficient (WTC) data sets. At least selected ones of the WTC data sets are processed and comparisons are made to determine a wavelet match score. A determination is made as a function of the wavelet match scores of the series of successive QRS complexes that characterizes the most recent QRS complex as more or less likely to signify polymorphic VT or VF.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apparatus and Method for Analysis of High Frequency Qrs Complexes
An apparatus for QRS waveform quantifying, comprising: an input unit, for receiving one or more high frequency (HF) range QRS complexes from one or more ECG leads, a primary analyzer, for calculating a primary index from the high frequency (HF) range QRS complex, and a secondary analyzer, connected after the primary analyzer, for deriving a secondary index from the primary index, thereby to provide a quantification of QRS complexes.
Owner:BSP MEDICAL LTD
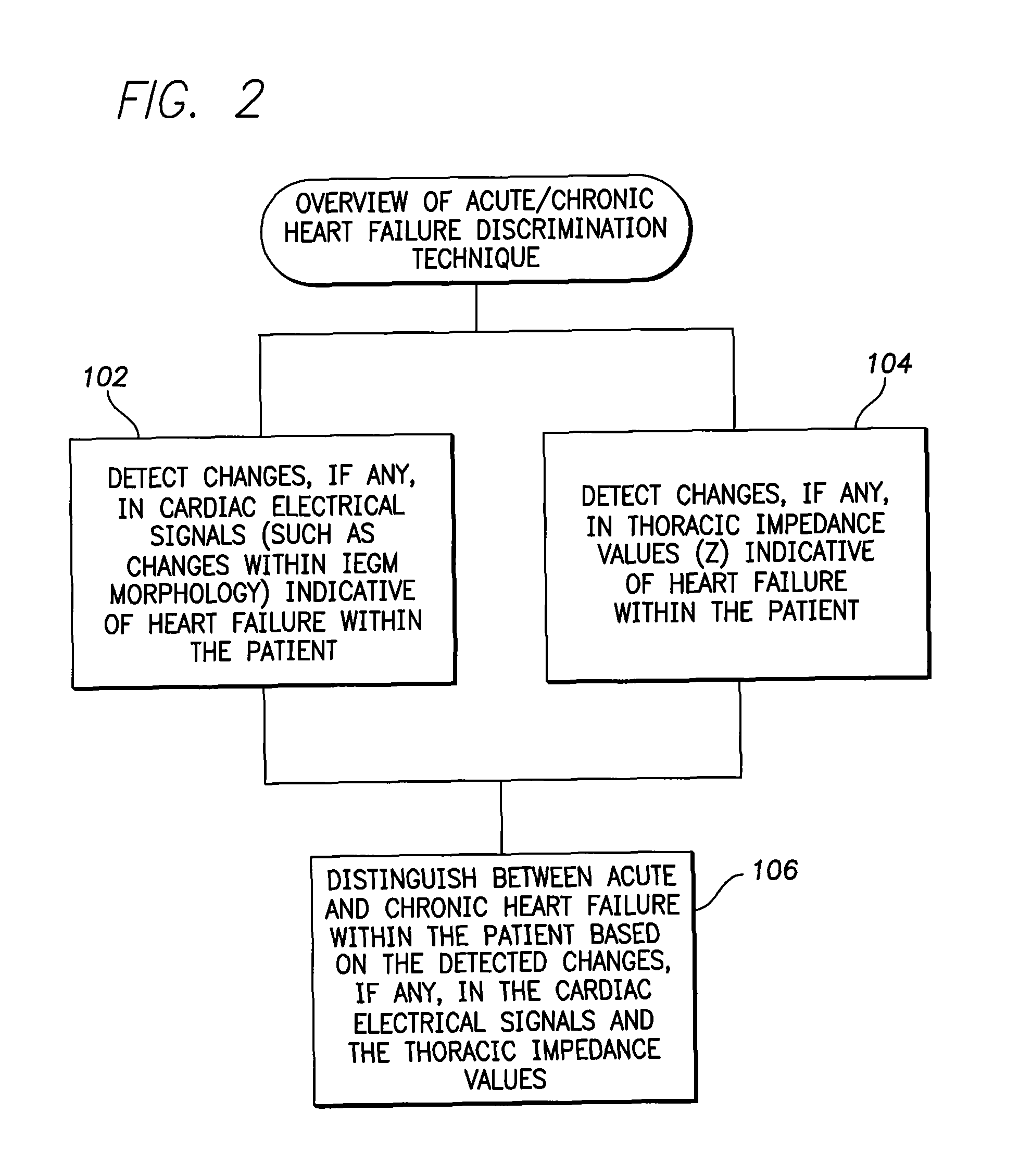
System and method for discriminating acute and chronic heart failure using an implantable medical device
InactiveUS7899522B1Immediate corrective actionElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyImplanted deviceMedical device
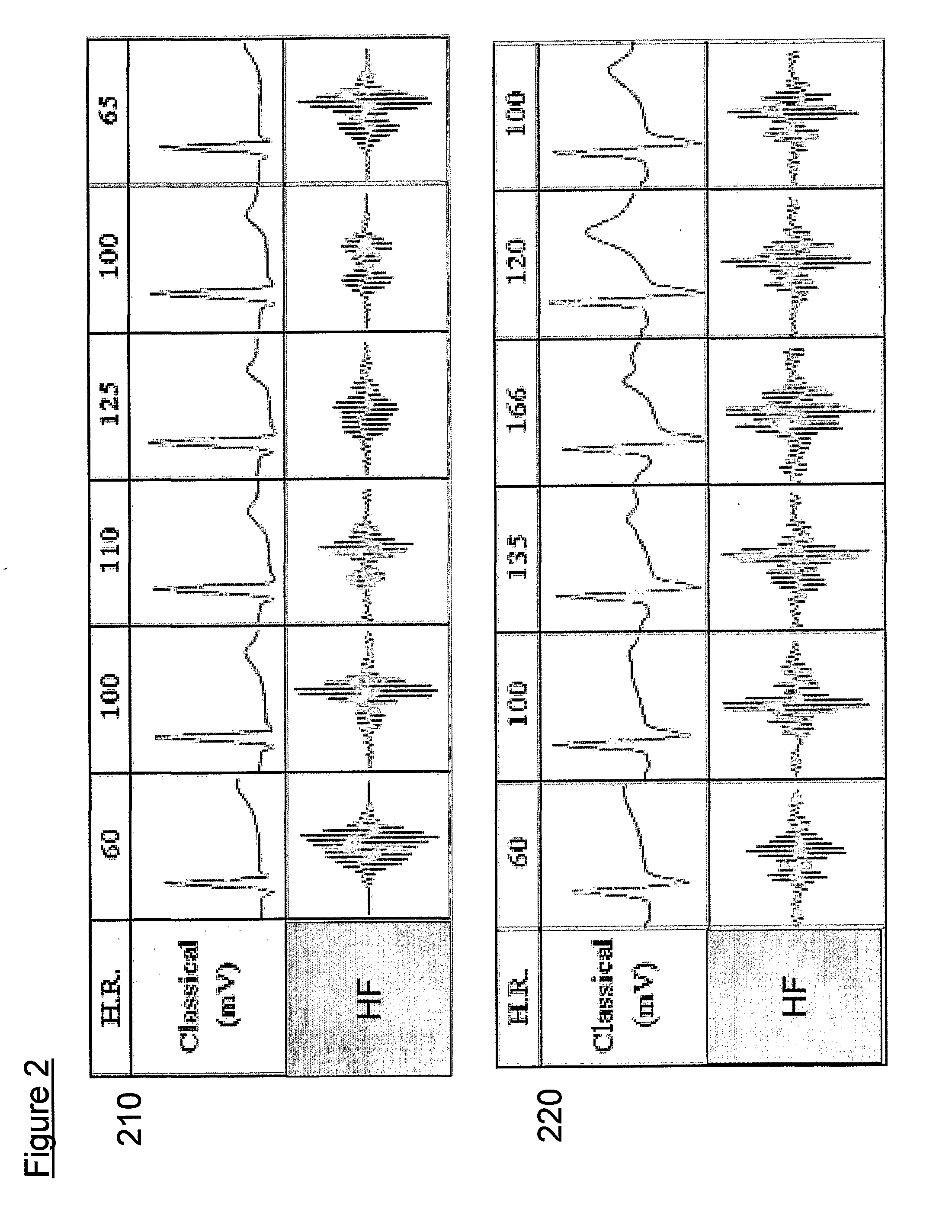
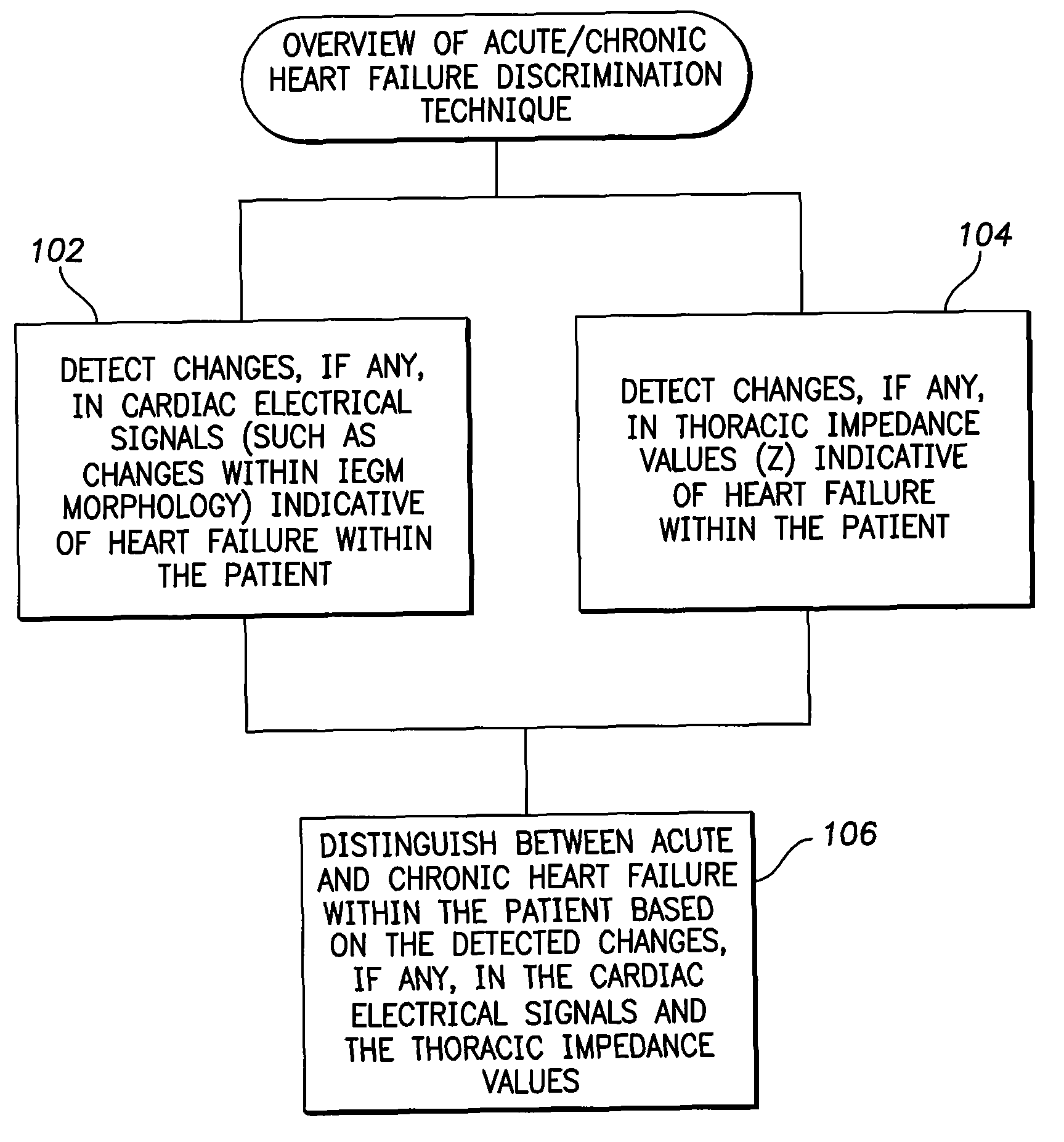
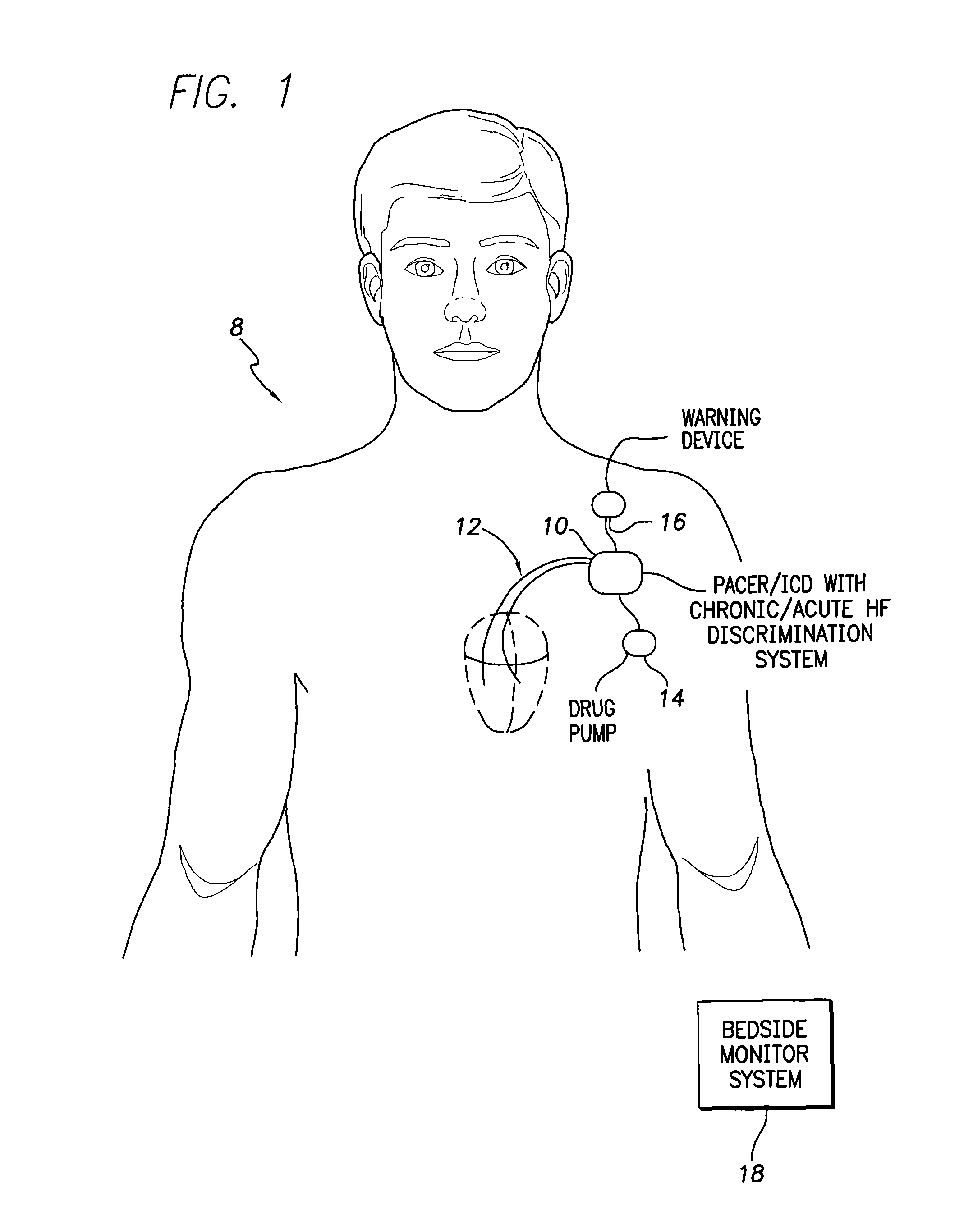
Techniques are provided for evaluating heart failure within a patient. In one example, the implantable device detects a decrease, if any, in selected morphological parameters derived from the intracardiac electrogram (IEGM) that are indicative of possible heart failure, such as paced depolarization integrals (PDI) or peak-to-peak amplitudes of QRS-complexes. The device also detects a decrease, if any, in transthoracic impedance, which is also indicative of possible heart failure. Acute heart failure is indicated if there is a decrease in the morphological IEGM parameters but no significant decrease in transthoracic impedance. Chronic heart failure is indicated if there is a decrease in transthoracic impedance but no significant decrease in the morphological IEGM parameters. If both transthoracic impedance and the morphological IEGM parameters are found to be decreasing significantly, the device issues a warning of severe heart failure.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Nonlinear method and apparatus for electrocardiogram pacemaker signal filtering
InactiveUS20050234361A1Overcome limitationsProvide benefitsElectrocardiographyDigital technique networkNonlinear methodsEcg signal
Signal “peak” and “valley” removal properties of mathematical morphology operators are exploited in a method and apparatus for detecting, removing, or improving fidelity of pacemaker signal components of the Electrocardiogram (ECG) at sampling rates well below the pacemaker signal Nyquist rate. The method works for the wide variability in pacemaker signal amplitude, width, firing frequency, and other characteristics encountered in practice, and it works for malfunctioning pacemakers that may fire at any point relative to the QRS complex of the ECG signal. Filtering operations require minimal digital storage and are computationally inexpensive (no multiplications), mainly involving “maximum” and “minimum” type signal detections over a finite time history of the input signal. This implies that the method can be inexpensively implemented on small instruments in either hardware or software. The method may also be used to estimate the height and polarity of the pacemaker voltage spike, even though the base sampling period may be longer than the width of the spike.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
Methods and apparatus for discriminating polymorphic tachyarrhythmias from monomorphic tachyarrhythmias facilitating detection of fibrillation
ActiveUS8332022B2High detection specificityStrong specificityElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyHigh rateData set
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for electrocardiogram recognition and specification
InactiveCN101268938AReduce workloadHigh ECG feature recognition accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsClassification methodsDiagnostic instrument
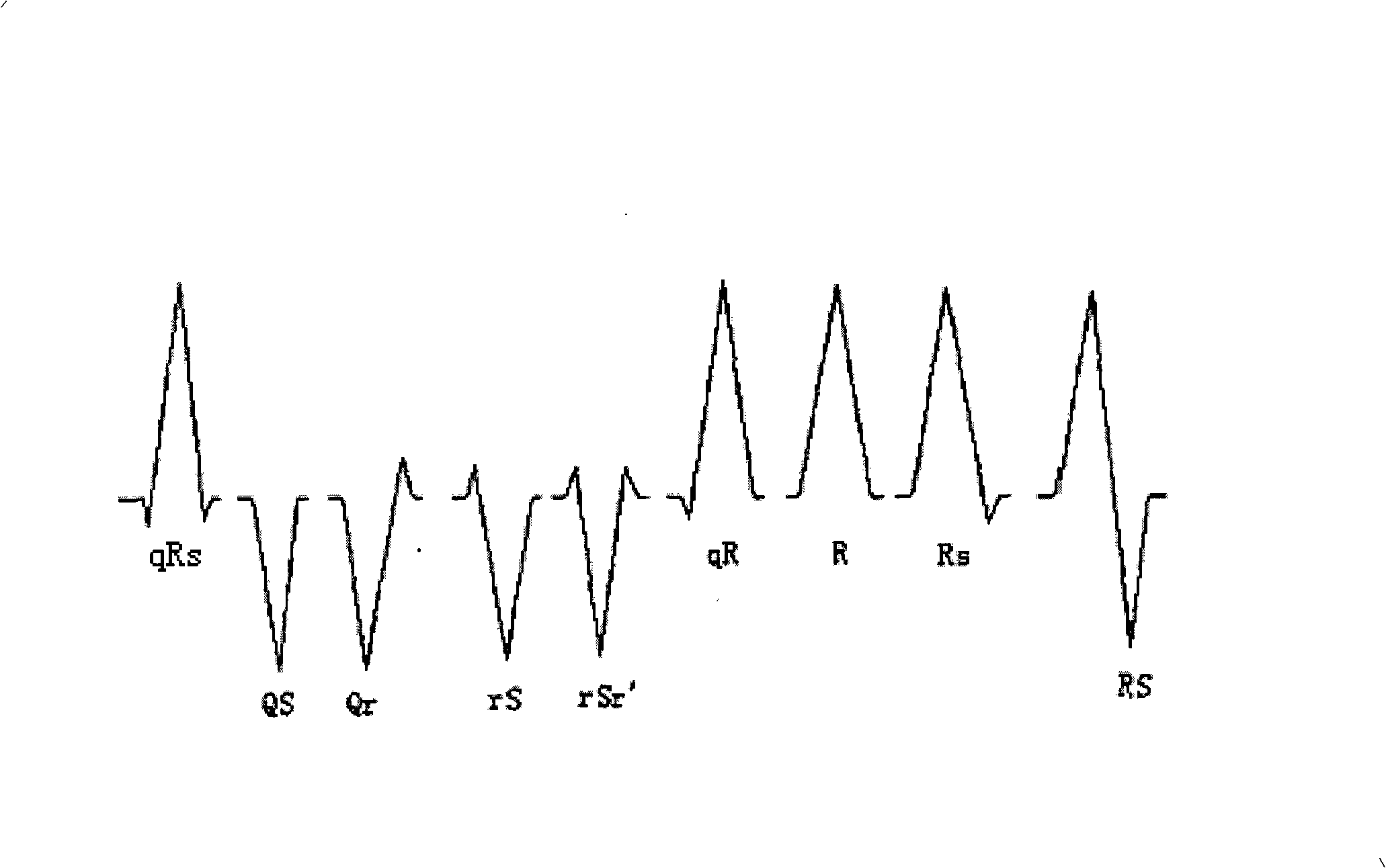
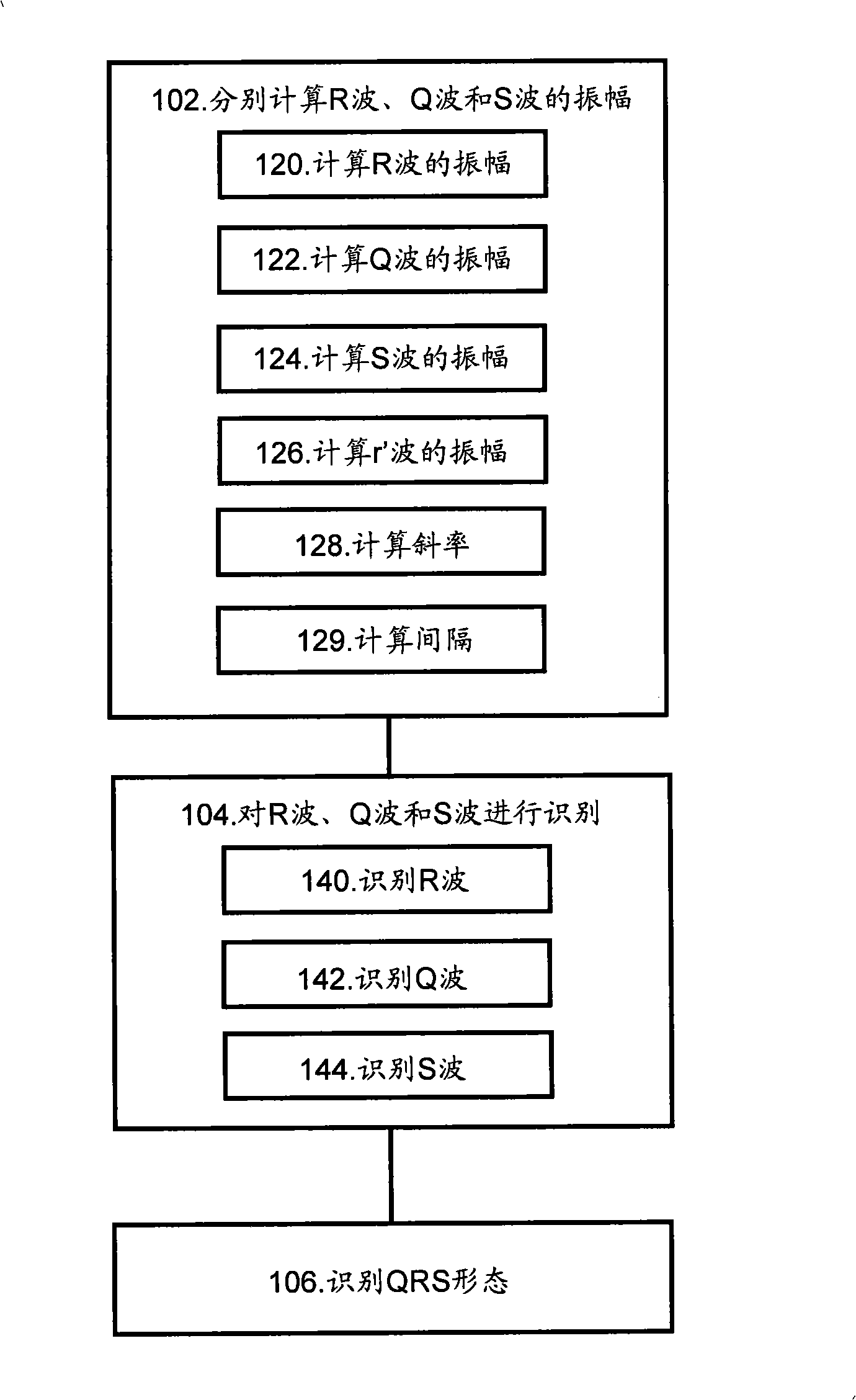
The invention discloses a method which is used for the recognition and the classification of an ECG and a device thereof. The method and the device obtain a QRS wave group queue obtained by an ECG diagnostic instrument, thereby being capable of obtaining the starting point, the end point, the slope and the R wave position of each QRS wave, the amplitude and the direction of the Q wave, the R wave and the S wave, the interval of two adjacent R waves, the form model of the QRS wave and the incisure and the slurring of the QRS wave and so on. The invention also discloses a mode classification method which is used for the ECG diagnostic instrument and fully borrows ideas from the thought processes of experts. The invention is the method and the device which realize the effective characteristic recognition and the mode classification of the ECG by fewer operations.
Owner:董军 +1
Implantable electroporation therapy device and method for using same
ActiveUS20050096584A1Undesirable side-effectImprove treatment outcomesElectrotherapyMedical devicesAbnormal tissue growthElectroporation therapy
IMDs and methods are provided for electroporation treatment of subcutaneous tumors. In some embodiments, IMDs of the present invention may store and introduce chemotherapy drugs into the body prior to electroporation therapy. High frequency stimulation of tissue in or around the tumor may also be provided to increase tissue temperature prior to electroporation therapy. Still further, delivery of the electroporation therapy may be synchronized with cardiac qRs complex to avoid impeding normal cardiac rhythm. Algorithms to suspend therapy in the event of edema may also be incorporated.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System, software, and method for detection of sleep-disordered breathing using an electrocardiogram
InactiveUS7343198B2High sensitivityStrong specificityElectrocardiographySensorsEcg signalSleep disordered breathing
A system to form and store an electrocardiogram (ECG) signal derived from a cardiac electrical signal that includes an apparatus having a pair of the electrodes to connect to a patient to detect the cardiac electrical signal. A signal sampler samples the cardiac electrical signal to form the ECG signal. A data storage device stores the ECG signal. A computer communicates with the data storage device to retrieve the ECG signal for analysis by software stored in the memory of the computer. The software analyzes a morphology of the amplitude of a plurality of R-wave peaks contained within the ECG signal and / or analyzes a morphology of the area of a plurality of QRS complex pulses contained within the ECG signal.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Medical decision support system
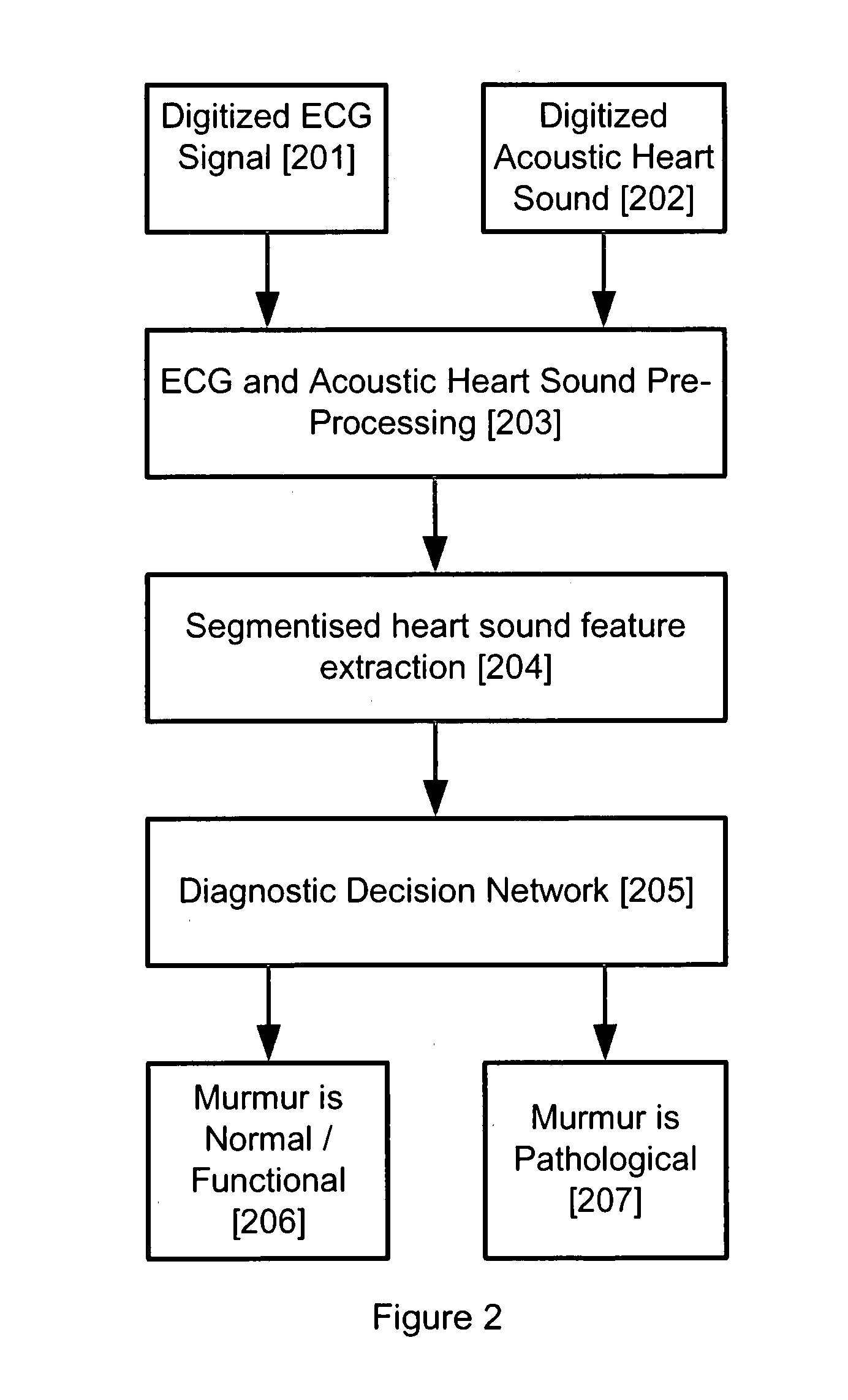
A process for pre-processing recorded and digitised heart sounds and corresponding digitised ECG signals is provided. The pre-processed signals (203) are suitable for input into an automatic decision support system implemented by means of a diagnostic decision network (205), used for diagnosing and differentiation between normal / functional (206) and pathological (207) heart murmurs, particularly in paediatric patients. The process includes identifying or predicting locations of individual heart beats within the heart sound signal, identifying the positions of the S1 and S2 heart pulses within the respective heart beats, predicting and identifying the locations and durations of the systole and diastole segments of the heart beats (302), determining if segmentation of the heart sound signal is possible based on the selected and isolated heart beats (305), and the segmentation of the respective heart beats into segments for allowing better feature extraction. The invention also provides a process for detecting the QRS complex of an ECG signal for optimizing the number of heart beat cycles detected.
Owner:DIACOUSTIC MEDICAL DEVICES
Assessment of sleep quality and sleep disordered breathing based on cardiopulmonary coupling
An assessment of sleep quality and sleep disordered breathing is determined from cardiopulmonary coupling between two physiological data series. An R-R interval series is derived from an electrocardiogram (ECG) signal. The normal beats from the R-R interval series are extracted to produce a normal-to-normal interval series. The amplitude variations in the QRS complex are used to extract a surrogate respiration signal (i.e., ECG-derived respiration) associated with the NN interval series. The two series are corrected to remove outliers, and resampled. The cross-spectral power and coherence of the two resampled signals are calculated over a plurality of coherence windows. For each coherence window, the product of the coherence and cross-spectral power is used to calculate coherent cross-power. Using the appropriate thresholds for the coherent cross-power, the proportion of sleep spent in CAP, non-CAP, and wake and / or REM are determined. Coherent cross-power can be applied to differentiate obstructive from non-obstructive disease, and admixtures of the same.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Methods and apparatus for discriminating polymorphic tachyarrhythmias from monomorphic tachyarrhythmias facilitating detection of fibrillation
Systems and methods that improving the specificity of discriminating between a monomorphic tachyarrhythmia and a polymorphic tachyarrhythmia are provided that examine frequency content and baseline information of the EGM as discriminatory signatures are disclosed. Particular algorithms of the present invention that are employed to determine frequency content of the QRS complexes are titled the Slope Distribution Metric (SDM) algorithm and the Slope Distribution Composite (SDC) algorithm.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods and apparatus for discriminating polymorphic tachyarrhythmias from monomorphic tachyarrhythmias facilitating detection of fibrillation
Systems and methods employing a weighted zero crossing sum metric (WZCSM) derived from the EGM that improves the specificity of discriminating between a monomorphic tachyarrhythmia and a polymorphic tachyarrhythmia are provided that examine frequency content and baseline information of the EGM as discriminatory signatures are disclosed. In preferred embodiments, high rate polymorphic QRS complexes are discriminated from high rate monomorphic QRS complexes to increase the specificity of detection of polymorphic VT and VF. Zero crossing points (ZCPs) and weighted ZCP slopes of the high pass filtered EGM signal in baseline and sense event windows are identified. The weighted ZCPs of the baseline window are summed to provide a baseline WZCSB, and the weighted ZCPs of the VSENSE event window are summed to provide a VSENSE event WZCSE. A WZCSM is derived from the VSENSE event WZCSE and the baseline WZCSB that is compared to a threshold.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com