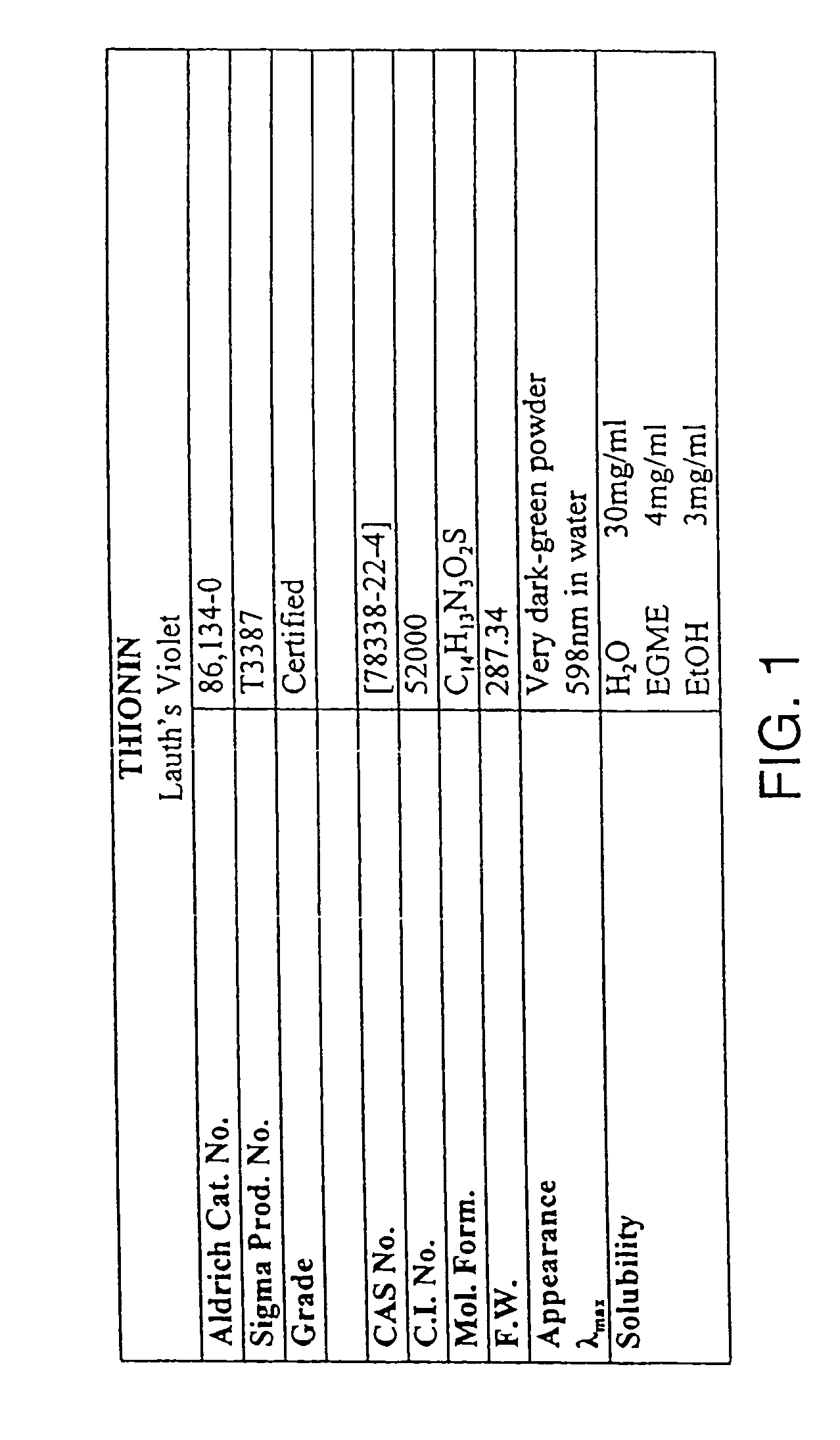
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Cytology sample" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
However, cytology samples may be prepared in other ways, including cytocentrifugation. Different types of smear tests may also be used for cancer diagnosis. In this sense, it is termed a cytologic smear. Cytopathology is frequently, less precisely, called cytology, which means "the study of cells".
Nanoparticle conjugates
InactiveUS20060246524A1Easy to detectMaterial nanotechnologyPowder deliveryIn situ hybridisationOrganic chemistry
Conjugate compositions are disclosed that include a specific-binding moiety covalently coupled to a nanoparticle through a heterobifunctional polyalkyleneglycol linker. In one embodiment, a conjugates is provided that includes a specific-binding moiety and a fluorescent nanoparticle coupled by a heterobifunctional PEG linker. Fluorescent conjugates according to the disclosure can provide exceptionally intense and stable signals for immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization assays on tissue sections and cytology samples, and enable multiplexing of such assays.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Antibody conjugates
InactiveUS20060246523A1Easy to detectIntense stainingHybrid immunoglobulinsHydrolasesIn situ hybridisationAntibody conjugate
Antibody / signal-generating moiety conjugates are disclosed that include an antibody covalently linked to a signal-generating moiety through a heterobifunctional polyalkyleneglycol linker. The disclosed conjugates show exceptional signal-generation in immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization assays on tissue sections and cytology samples. In one embodiment, enzyme-metallographic detection of nucleic acid sequences with hapten-labeled probes can be accomplished using the disclosed conjugates as a primary antibody without amplification.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Antibody conjugates
ActiveUS20090176253A1Easy to detectHigh activityHydrolasesEnzyme stabilisationIn situ hybridisationAntibody conjugate
Antibody / signal-generating moiety conjugates are disclosed that include an antibody covalently linked to a signal-generating moiety through a heterobifunctional polyalkyleneglycol linker. The disclosed conjugates show exceptional signal-generation in immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization assays on tissue sections and cytology samples. In one embodiment, enzyme-metallographic detection of nucleic acid sequences with hapten-labeled probes can be accomplished using the disclosed conjugates as a primary antibody without amplification.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Layered device with capture regions for cellular analysis
InactiveUS7214477B1Easy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingCellular architectureElectrophoresis
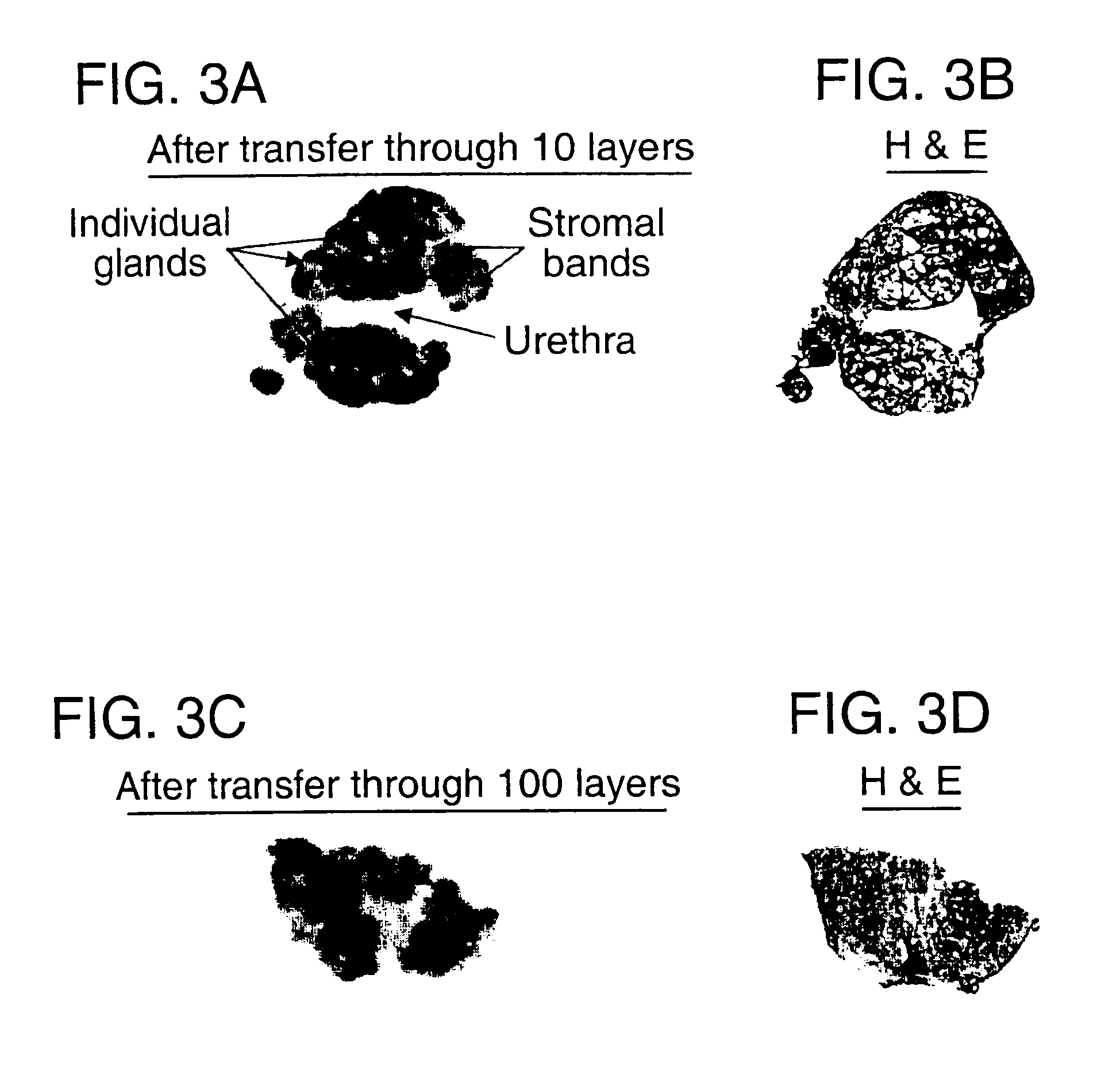
The present invention involves methods, systems, and devices for analyzing a biological material, such as a cellular or other specimen. The method includes placing the specimen on a substrate having different capture regions, such as contiguous layers, wherein the different capture regions of the substrate contain different identification molecules, and transferring components of the specimen through the capture regions under conditions that allow the components to interact with different identification molecules in the different regions of the substrate. The components of the specimen can be transferred through the different layers (or other regions) of the substrate by capillary action of a solution moving through the cellular specimen or by electrophoresis. The transfer of components of the specimen through the substrate may occur while maintaining a geometric correspondence to the specimen, such as the cytoarchitecture of a cellular specimen, for example by moving the components through parallel layers having positions that correspond to positions within the specimen. When the cellular architecture of the specimen is maintained, a correlation between the different identification molecules and the components of the cellular specimens may be made. The analysis can occur with one or more different discrete (for example cellular) specimens on a surface of the substrate. Examples of cellular specimens include, but are not limited to tissue sections, particularly tumor tissue sections. The cellular specimen can also include cultured cells or a cytology sample. Cytostat tissue sections cut slightly thicker than usual, that is about 25 to about 50 μm, improves the ability to detect molecules of moderate and low level abundance.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Antibody conjugates
ActiveUS8658389B2Easy to detectHigh activityHydrolasesChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAntibody conjugateNucleic acid sequencing
Antibody / signal-generating moiety conjugates are disclosed that include an antibody covalently linked to a signal-generating moiety through a heterobifunctional polyalkyleneglycol linker. The disclosed conjugates show exceptional signal-generation in immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization assays on tissue sections and cytology samples. In one embodiment, enzyme-metallographic detection of nucleic acid sequences with hapten-labeled probes can be accomplished using the disclosed conjugates as a primary antibody without amplification.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Nanoparticle conjugates
InactiveUS20090181398A1Easy to detectMaterial nanotechnologyPowder deliveryOrganic chemistryFluorescent nanoparticles
Conjugate compositions are disclosed that include a specific-binding moiety covalently coupled to a nanoparticle through a heterobifunctional polyalkyleneglycol linker. In one embodiment, a conjugates is provided that includes a specific-binding moiety and a fluorescent nanoparticle coupled by a heterobifunctional PEG linker. Fluorescent conjugates according to the disclosure can provide exceptionally intense and stable signals for immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization assays on tissue sections and cytology samples, and enable multiplexing of such assays.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
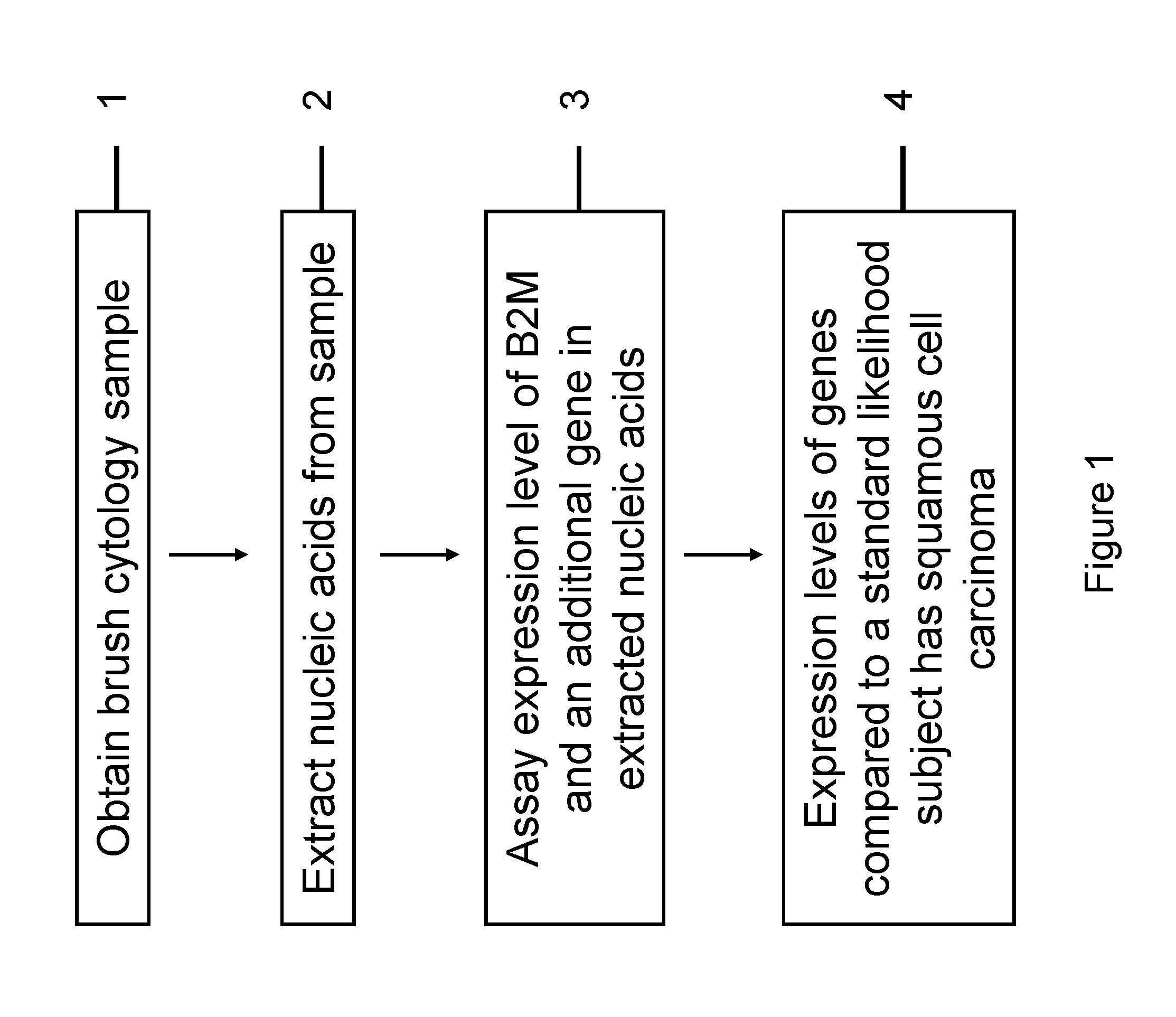
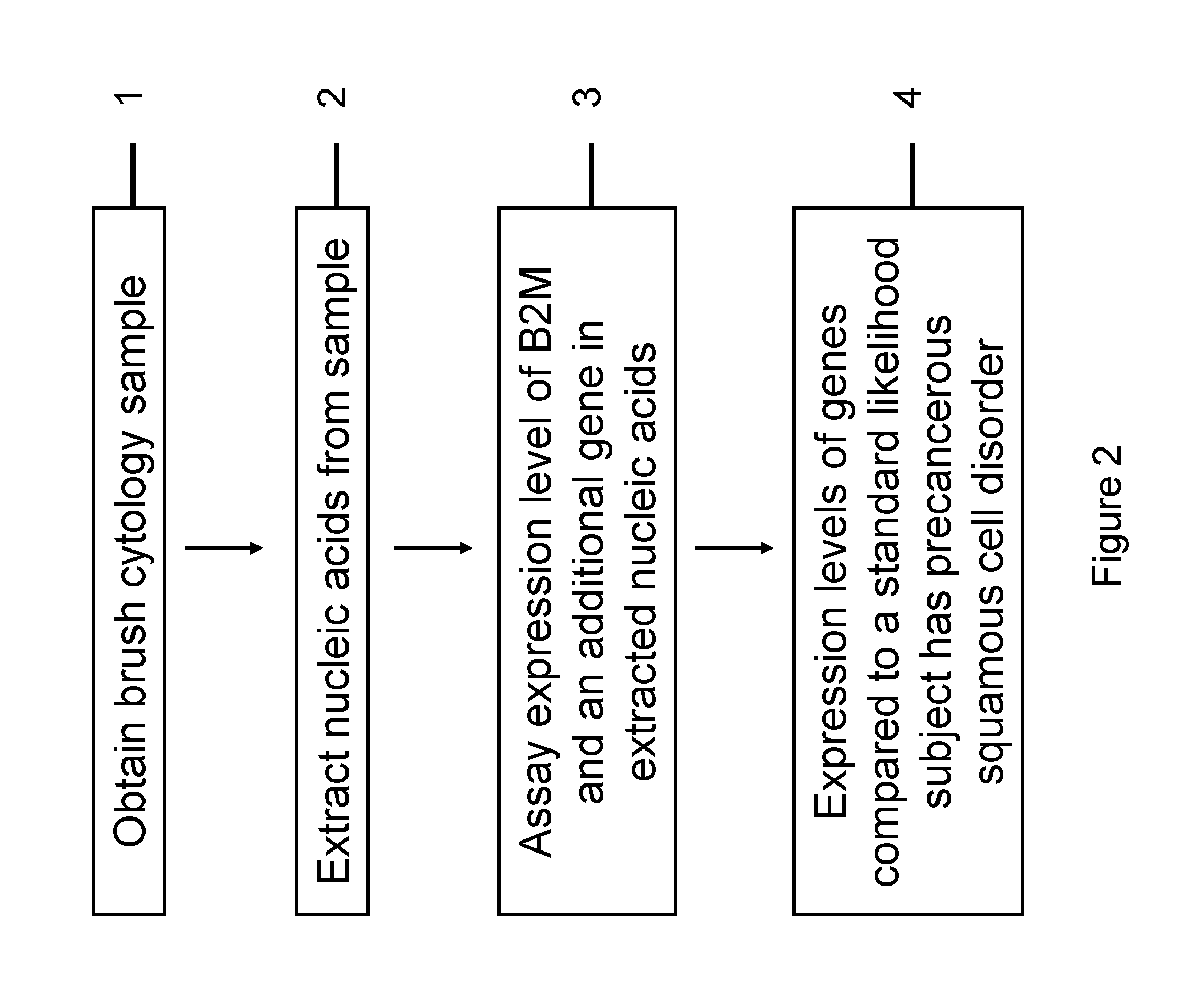
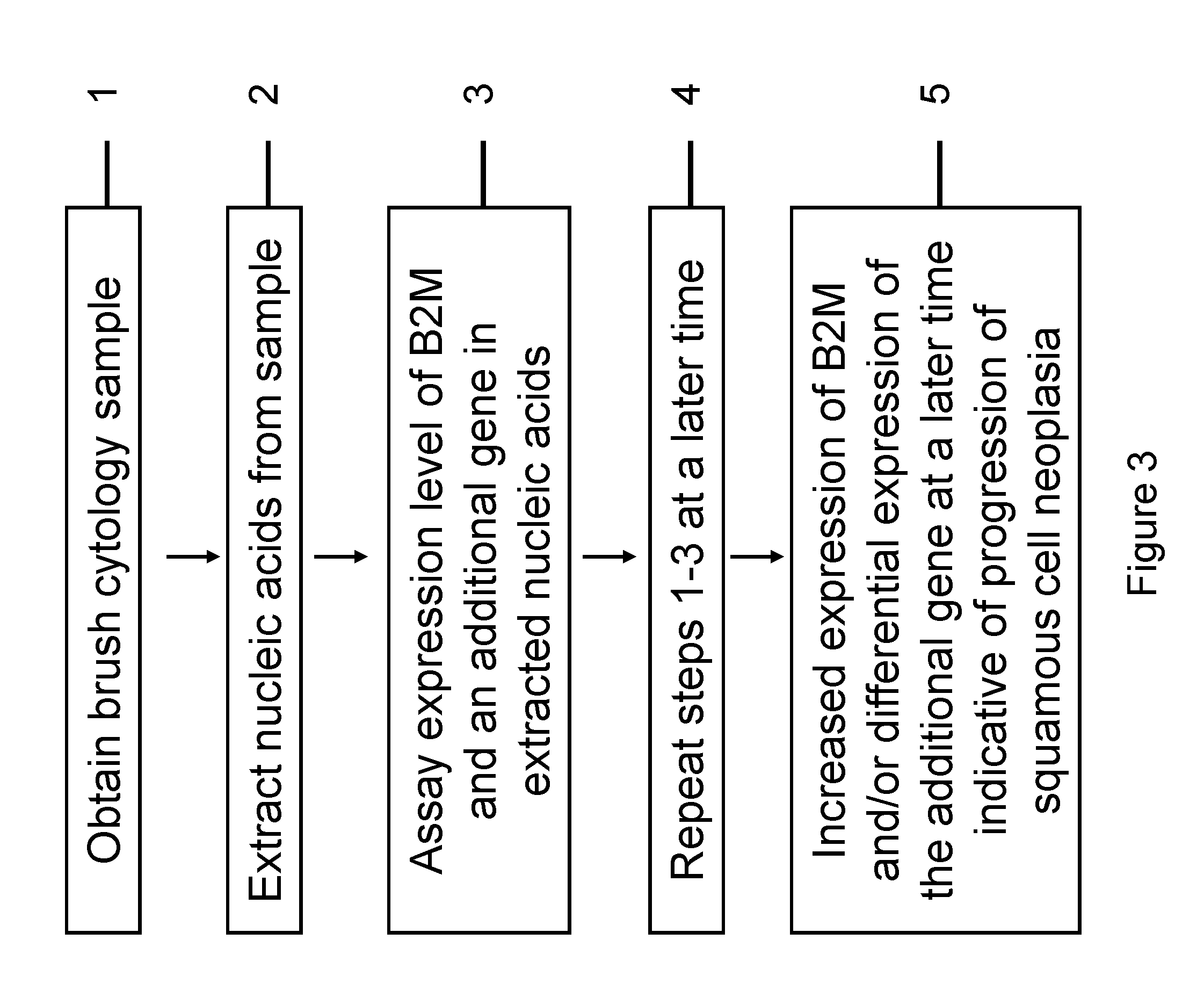
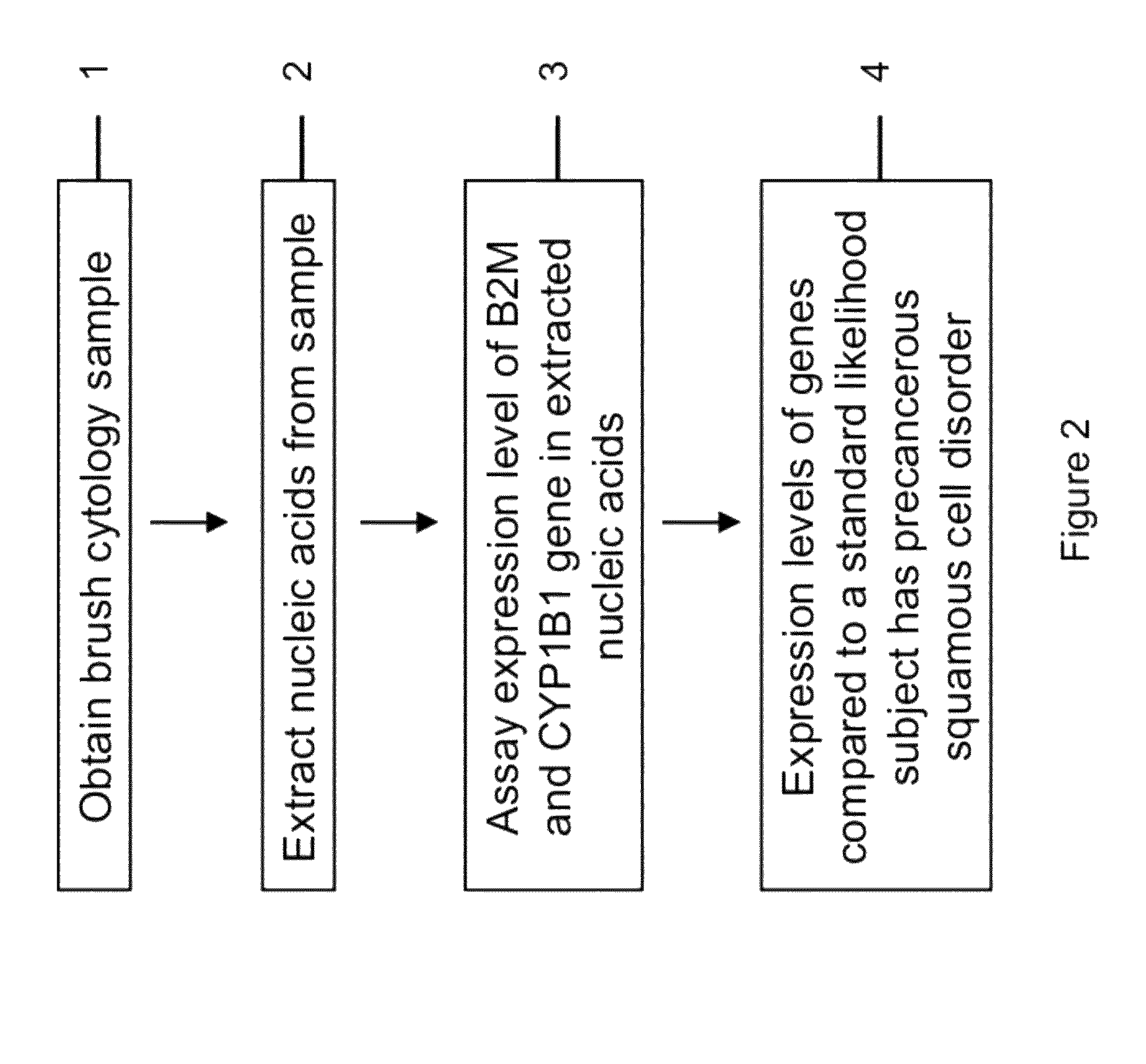
RNA from cytology samples to diagnose disease
InactiveUS20120231468A1Monitor progressMicrobiological testing/measurementSquamous CarcinomasWhite blood cell
The invention relates to methods and kits for detecting the likelihood that a subject has cancer, e.g., squamous cell carcinoma, by assaying the expression levels of tumor associated genes. More specifically, the expression levels of nucleic acids or proteins can be assayed in the tumor associated genes, e.g., over-expression of beta-2 microgobulin (B2M), keratin 17 (KRT17), interleukin 8 (IL8), or annexin A2 (ANXA2), and under-expression of cytochrome p450 1B1 (CYP1B1) or laminin gamma-2 (LAMC2) can be indicative of the likelihood a subject has squamous cell carcinoma or a precancerous squamous cell disorder. The expression levels compared to standards can be indicative of the likelihood a subject has squamous cell carcinoma. The expression levels of B2M, CYP1B1, KRT17, IL8, ANXA2, or LAMC2 can also be repeatedly assayed to monitor the progression of a squamous cell neoplasia.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
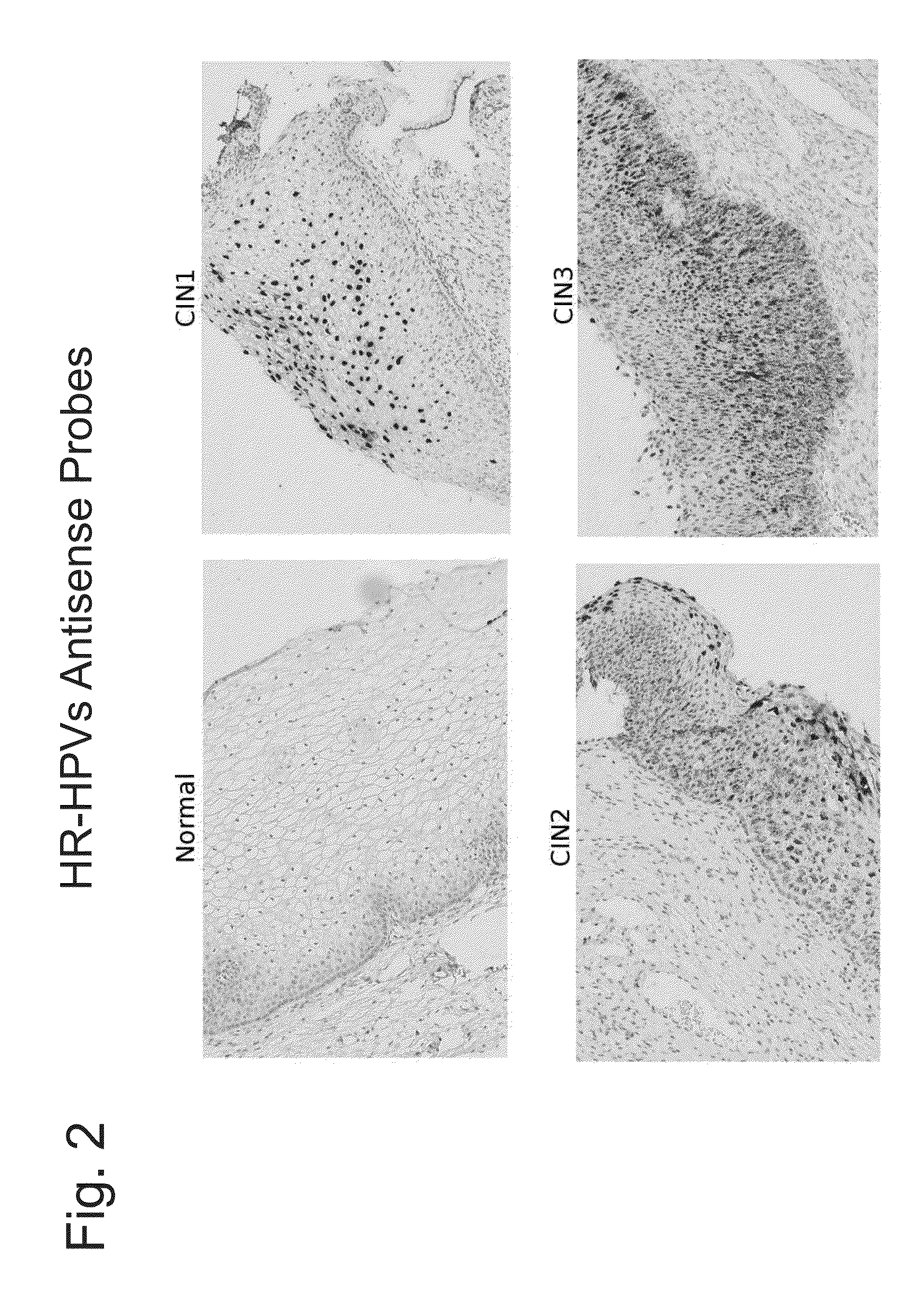
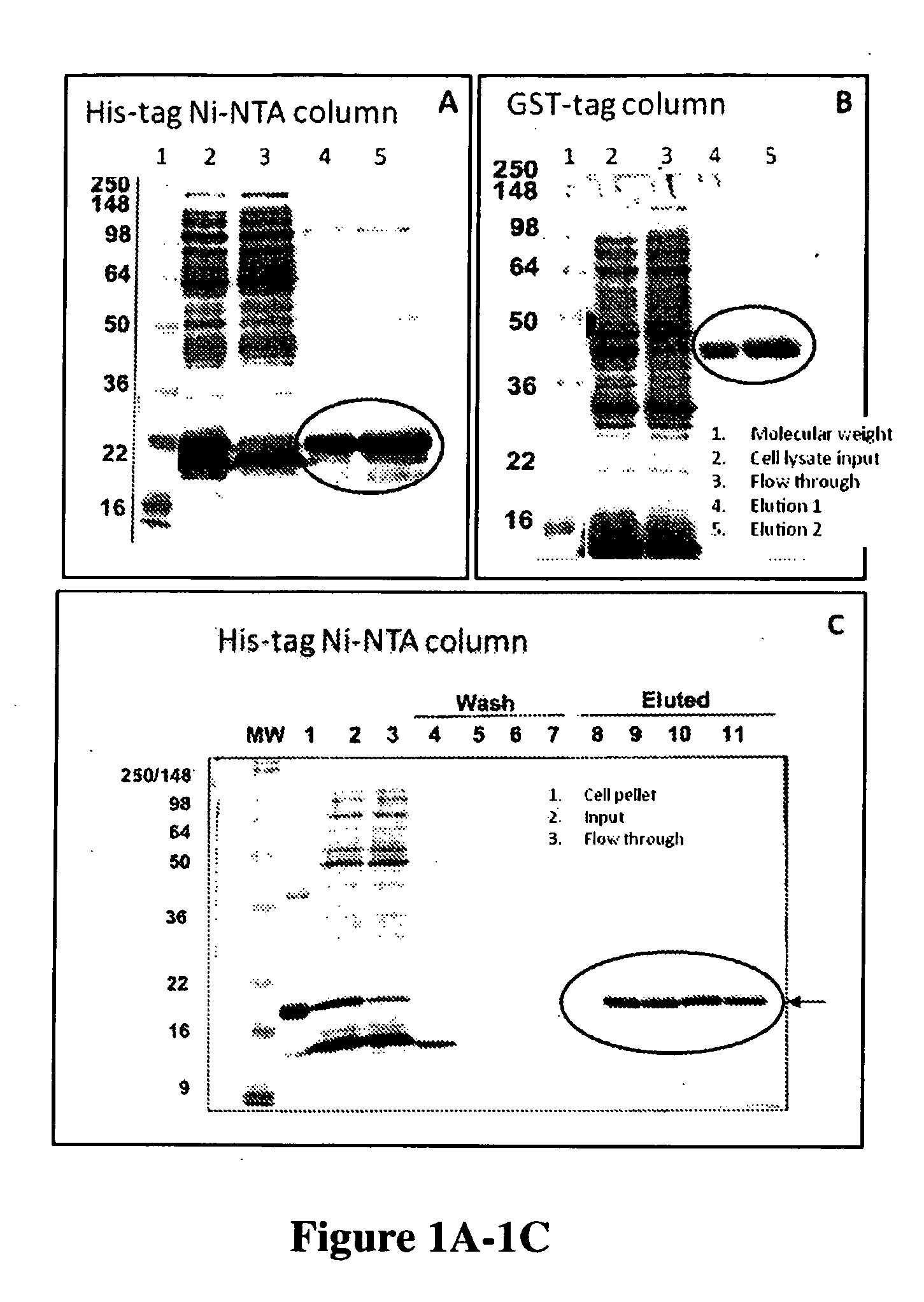
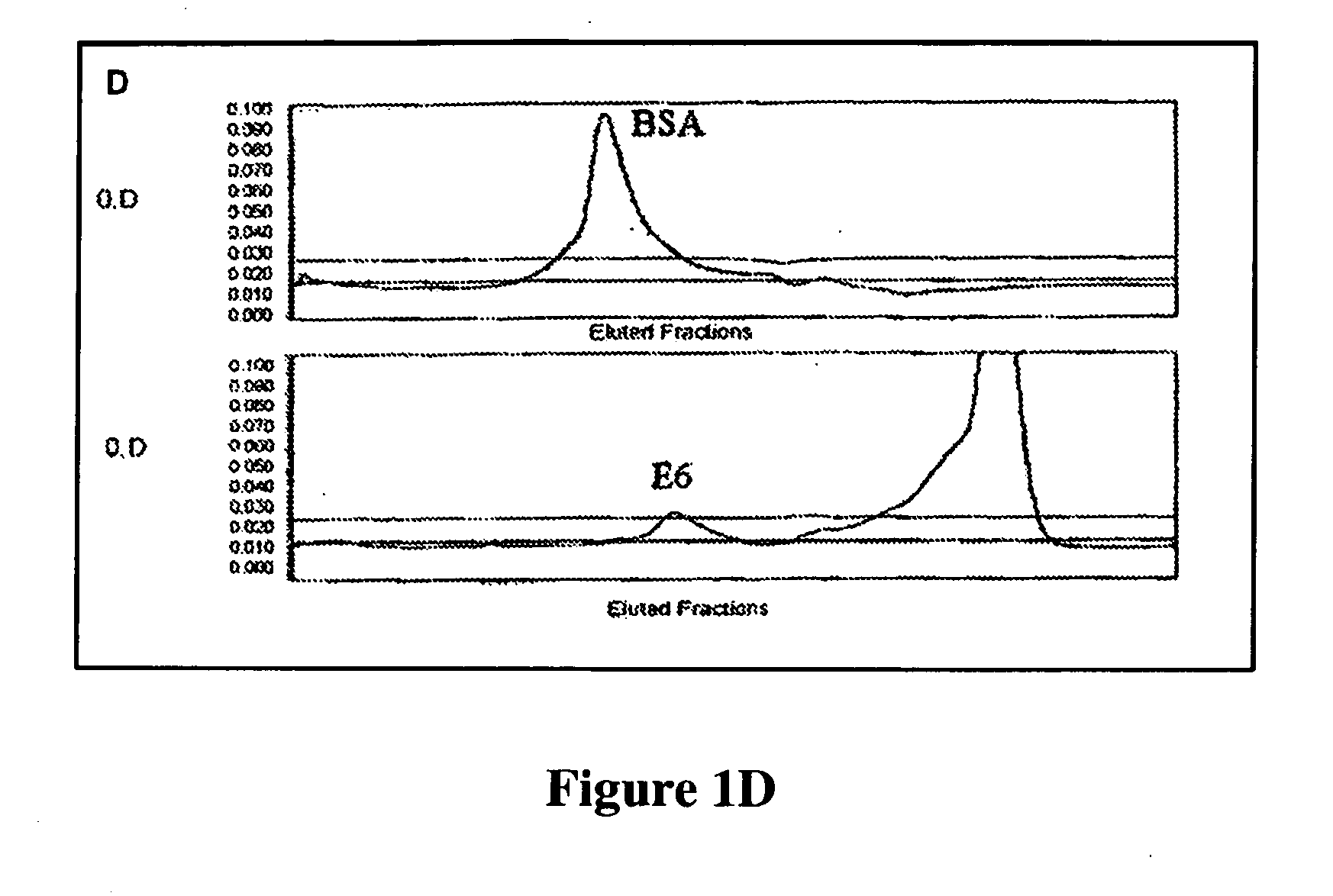
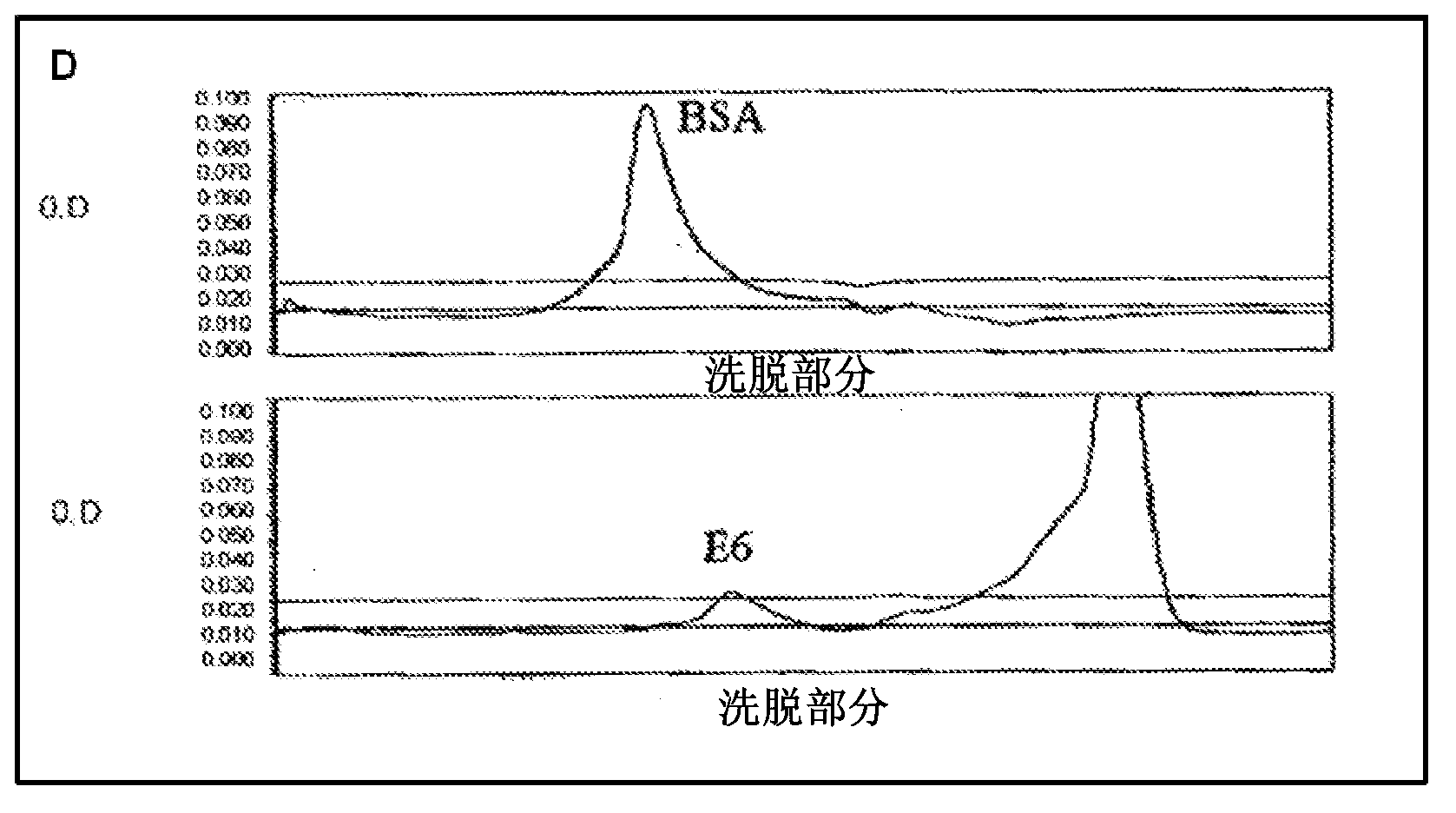
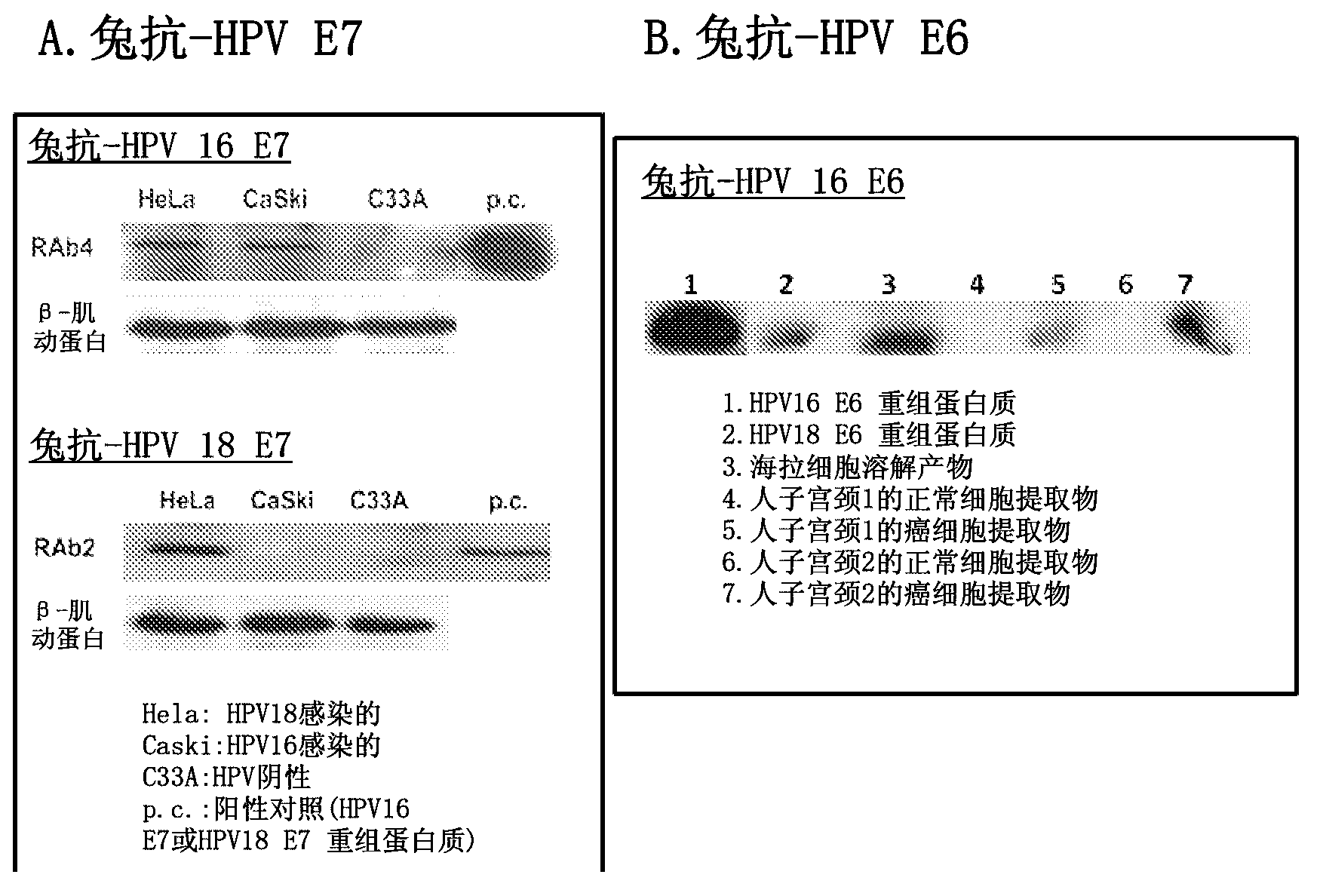
Differentiation between transient and persistent high-risk HPV infection by in situ hybridization
InactiveUS20140357509A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningIn situ hybridisationCervical tissue
The invention relates to methods of categorizing a cervical tissue or cytology sample by performing an in situ hybridization assay using an antisense E6 or E7 probe on a cervical tissue sample, wherein the antisense E6 or E7 probe can simultaneously detect HPV DNA and HPV RNA; detecting the presence of HPV nucleic acid; and categorizing the cervical tissue sample based on HPV nucleic acid expression.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL DIAGNOSTICS INC
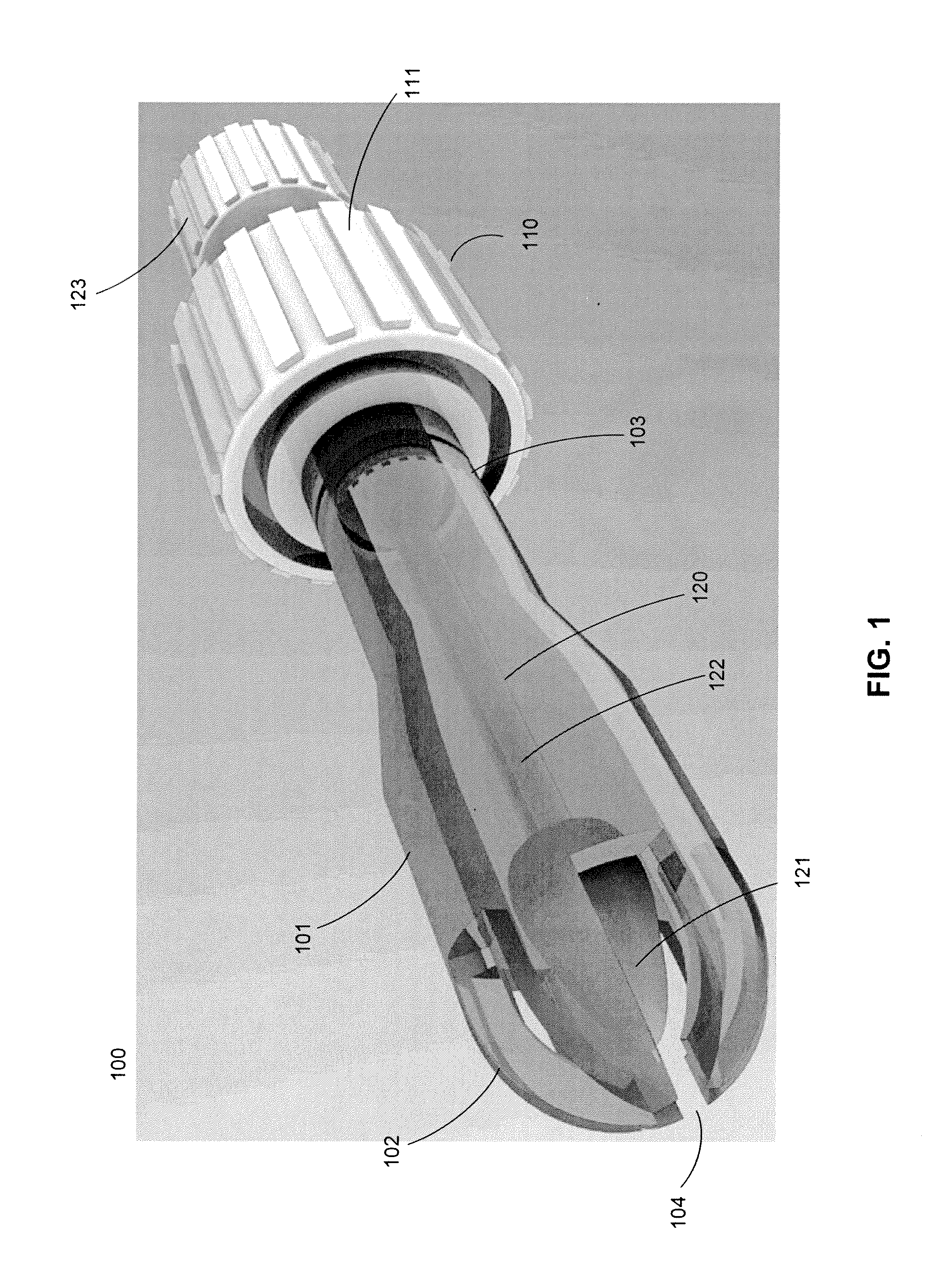
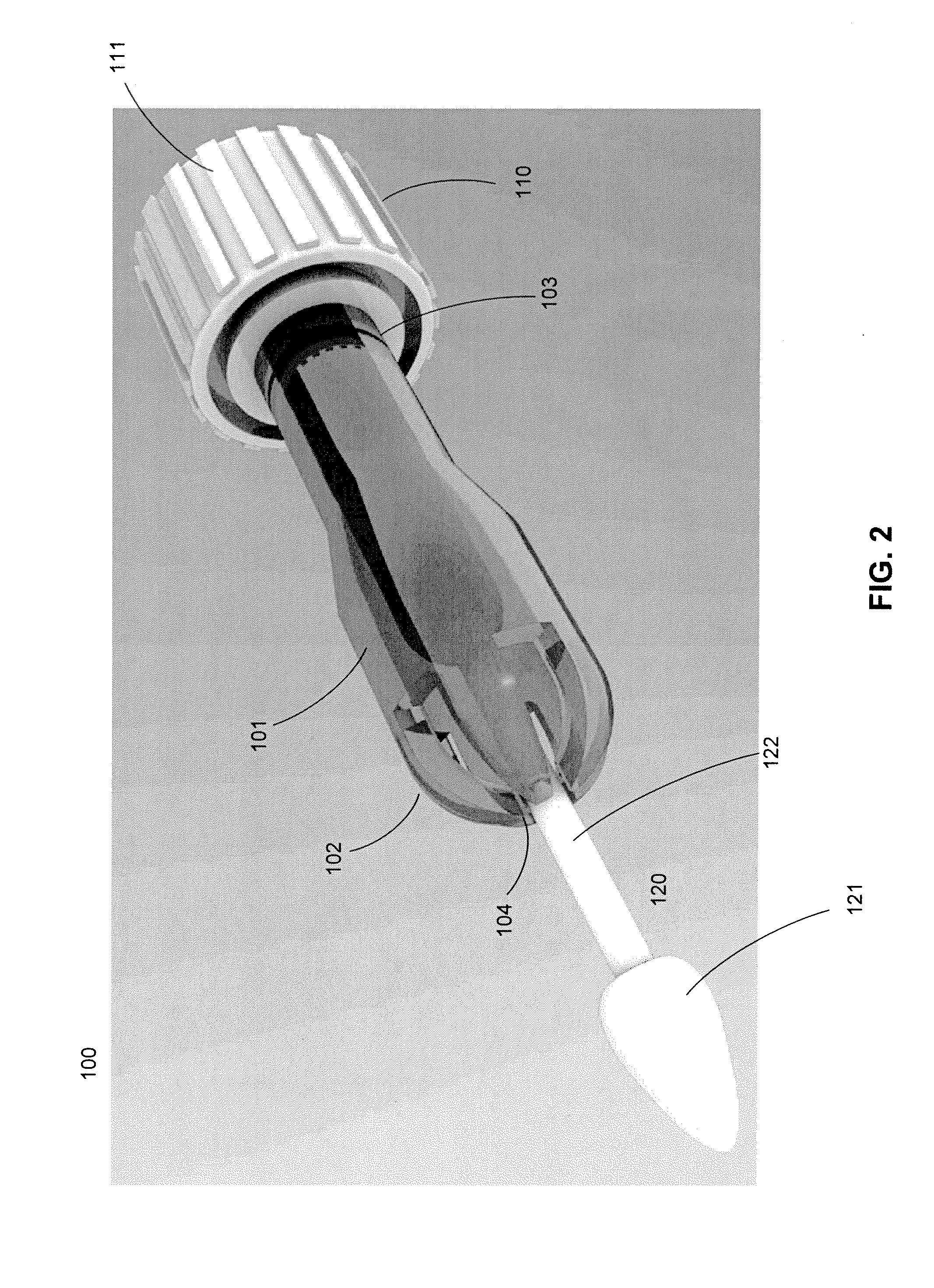
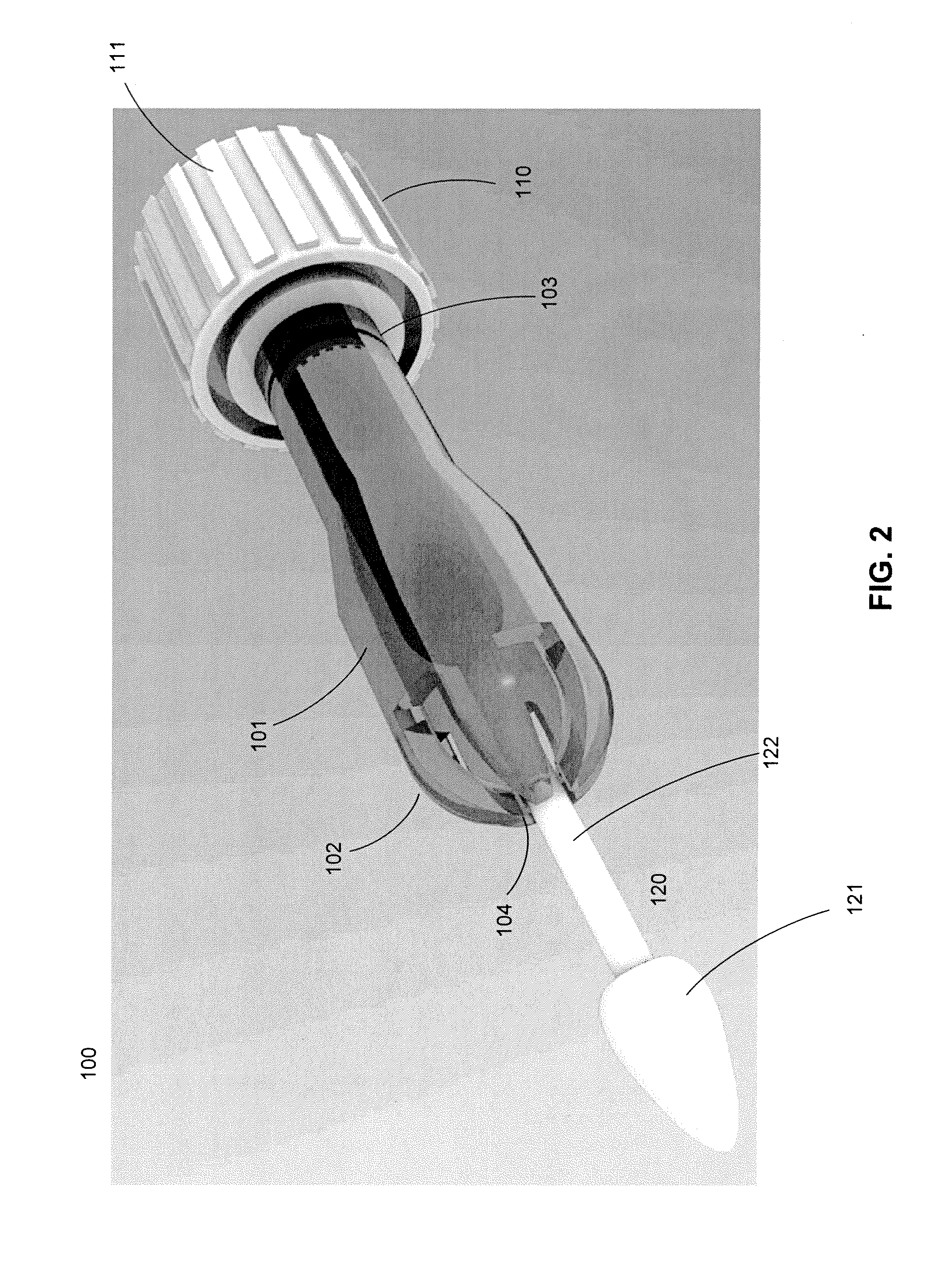
Cytological cell sample collection, storage, and transport device
A cytological cell sample collection, storage, and transport device is disclosed. The device comprises a sheath, a collection assembly, a base, and a containment vial. The collection assembly is slidably coupled to the base to expose a swab head comprising the collection assembly. The containment vial is configured to enclose the sheath and collection assembly within the internal volume defined by the containment vial and the base.
Owner:IN HINDSIGHT
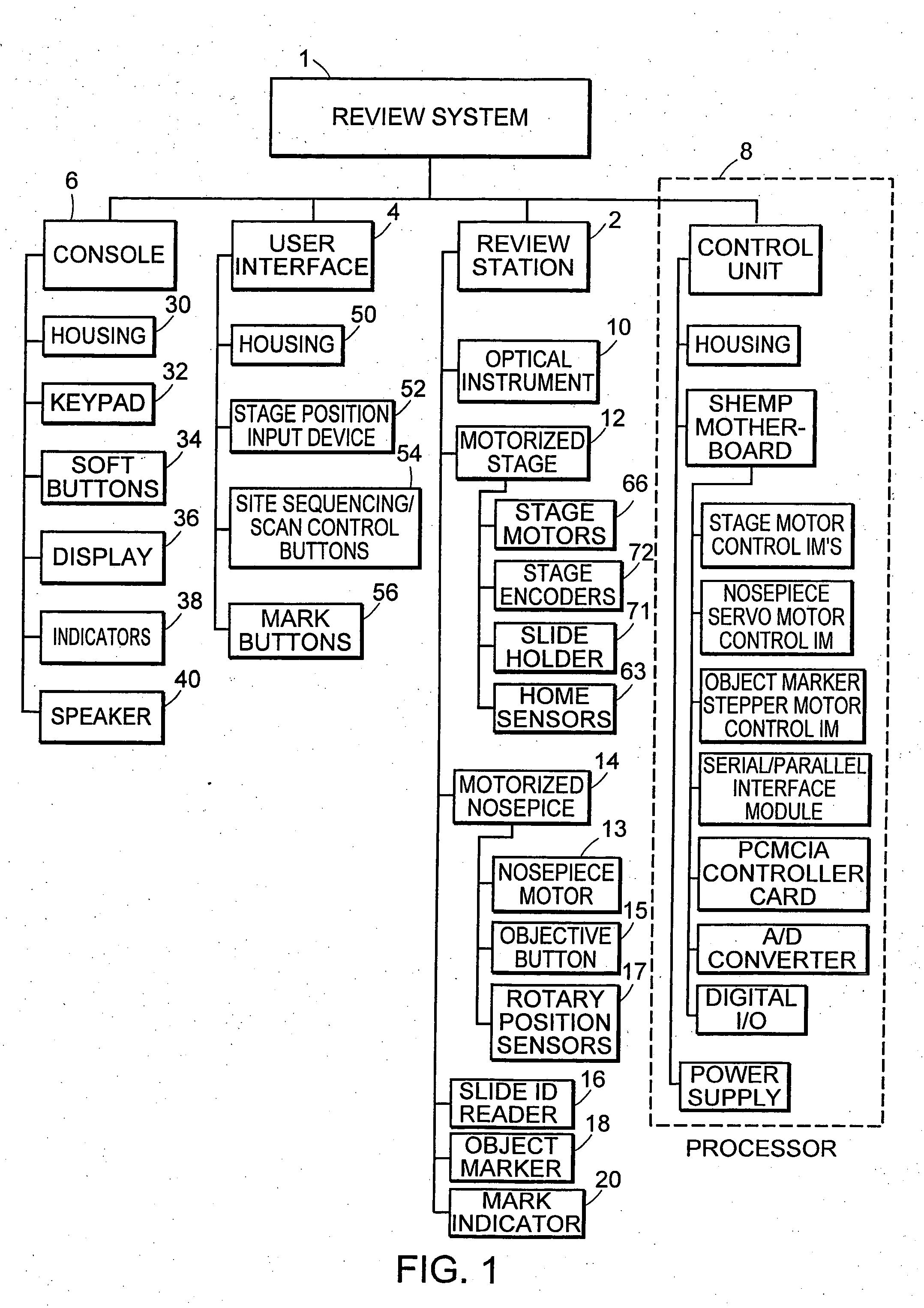
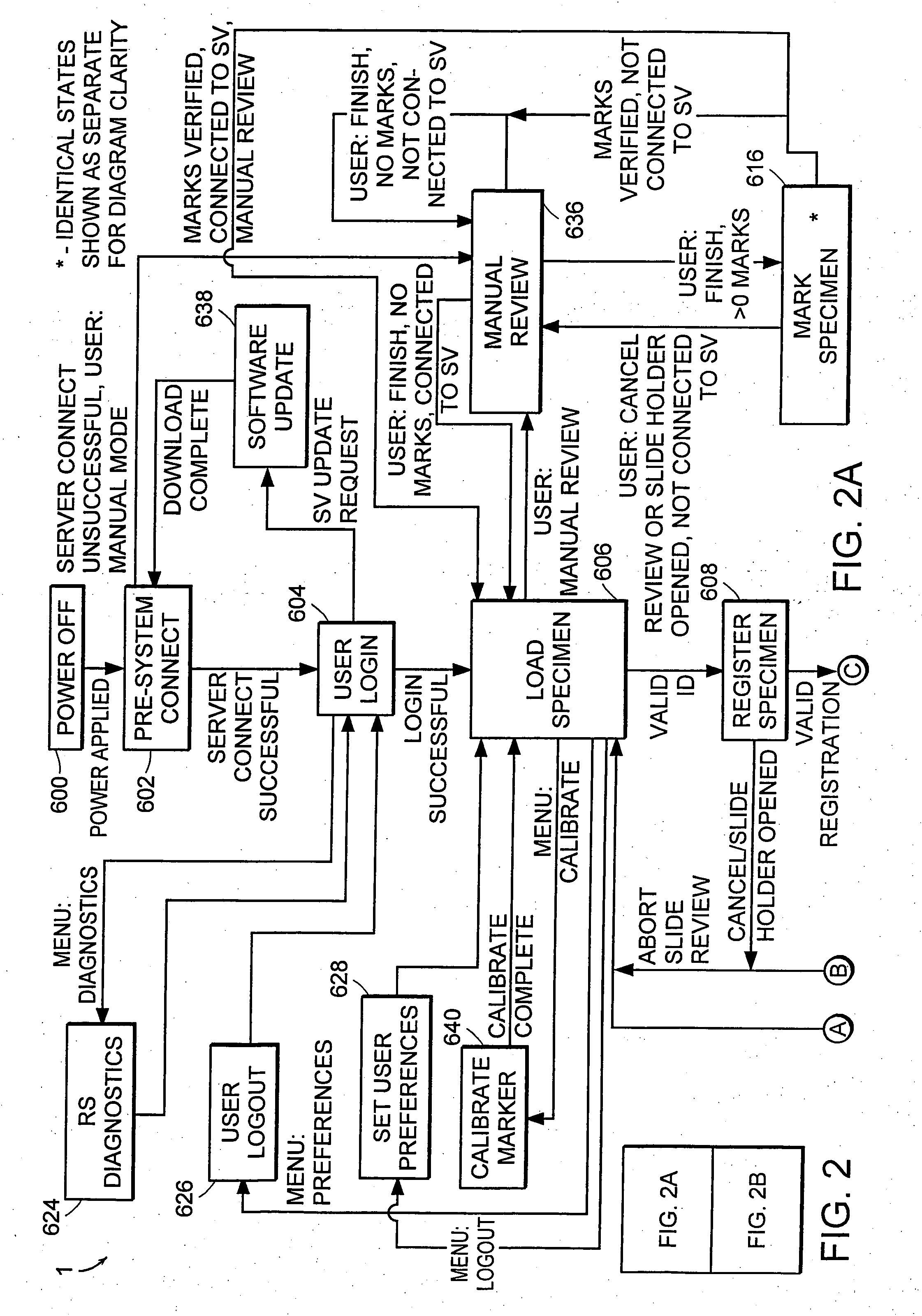
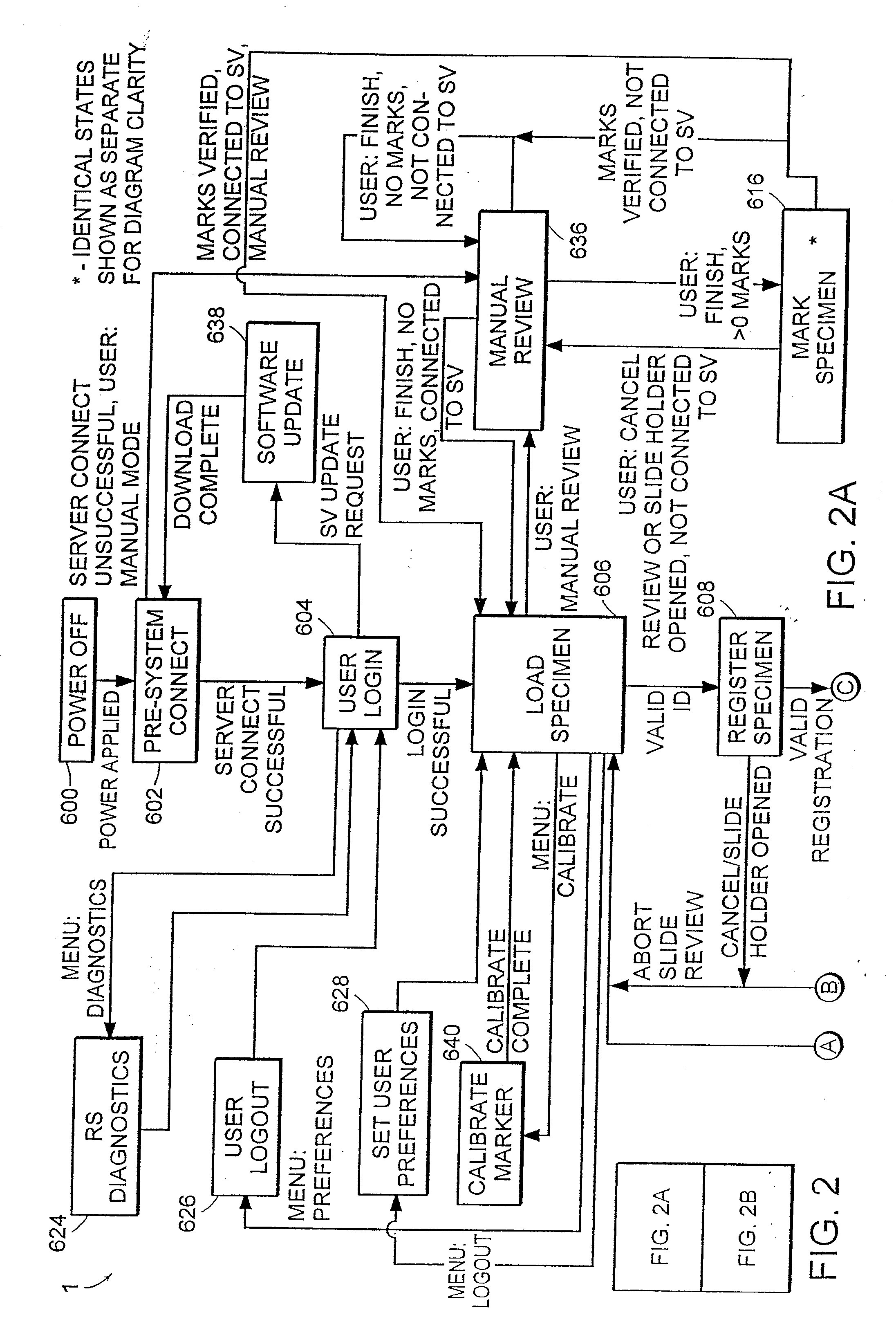
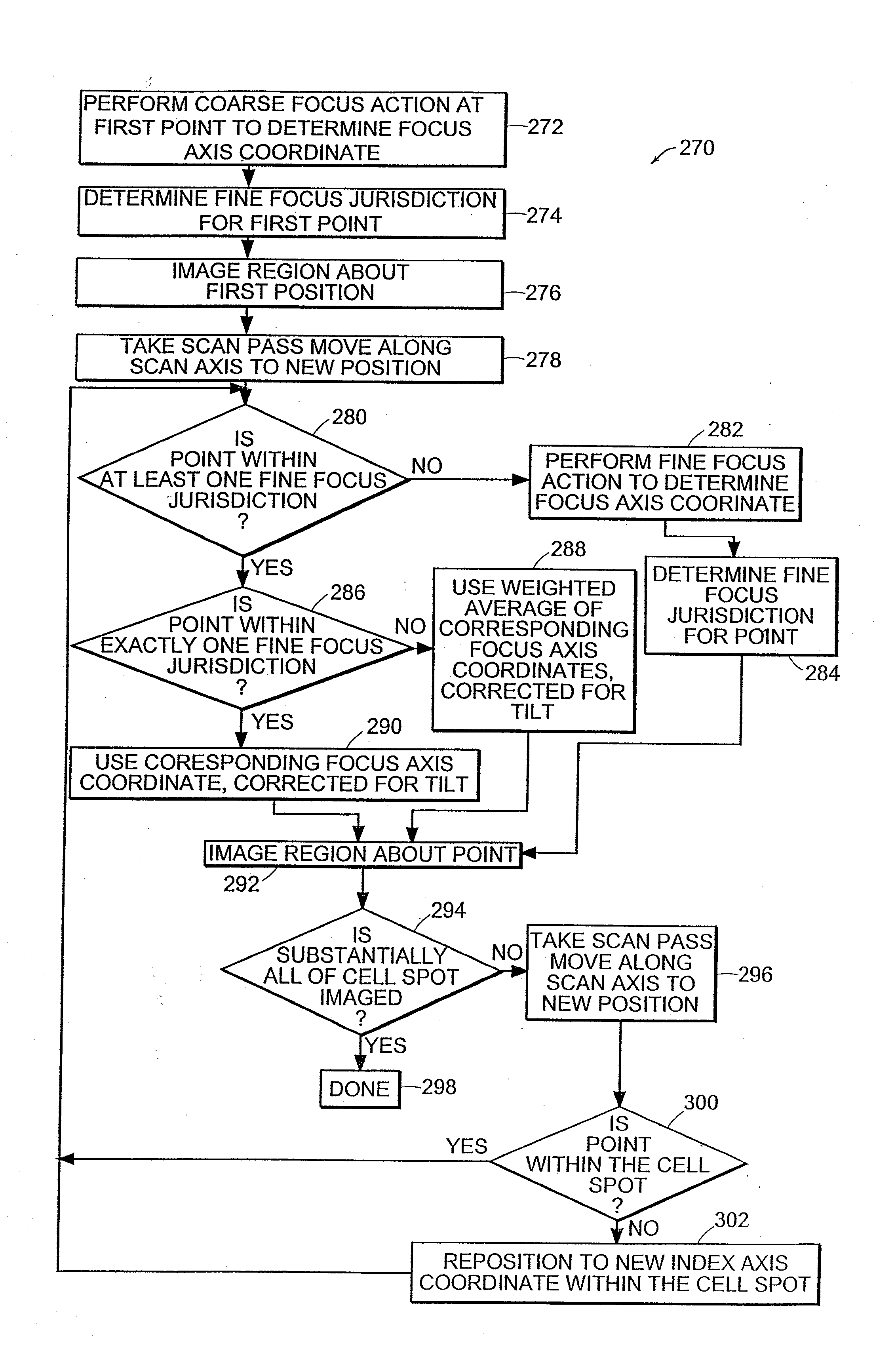
Cytological imaging systems and methods
InactiveUS20060077538A1Efficient preparationAddressing slow performanceImage enhancementImage analysisComputer scienceImage system
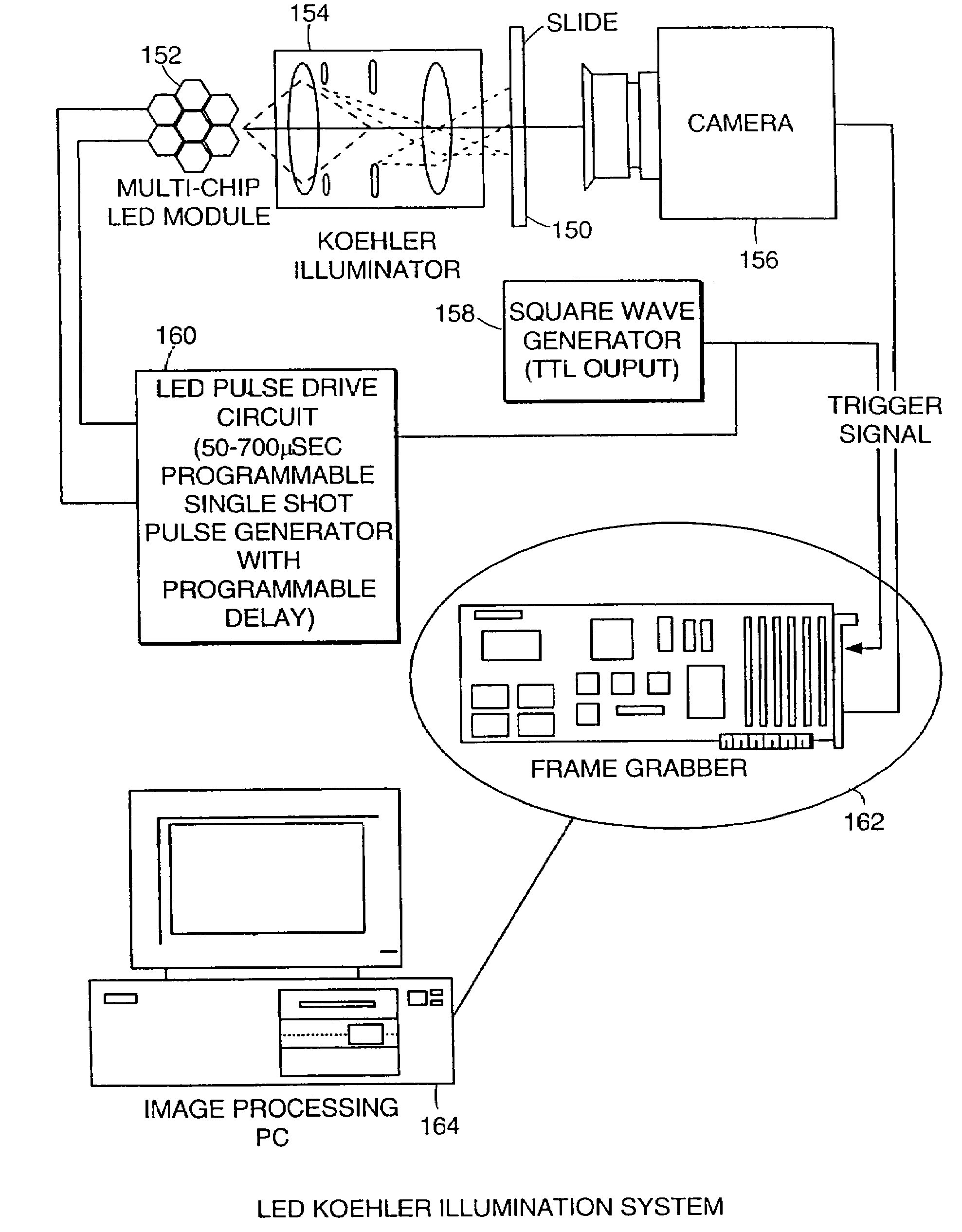
The present invention relates to the analysis of specimens. Specifically, the invention relates to methods and apparatus for reviewing specimen slides, including apparatus for holding the slides. The invention also relates to an automatic focusing method for an imaging system and methods for accommodating vibration in the imaging system. In particular, the methods and apparatus may be applied to the automated analysis of cytological specimen slides.
Owner:CYTYC CORP
Cytological imaging systems and methods
InactiveUS20080013812A1Efficiently and accurately imagesSave stepsImage enhancementImage analysisComputer scienceImage system
The present invention relates to the analysis of specimens. Specifically, the invention relates to methods and apparatus for reviewing specimen slides, including apparatus for holding the slides. The invention also relates to an automatic focusing method for an imaging system and methods for accommodating vibration in the imaging system. In particular, the methods and apparatus may be applied to the automated analysis of cytological specimen slides.
Owner:CYTYC CORP
Cytological imaging systems and methods
InactiveUS20080013168A1Efficiently and accurately imagesSave stepsImage enhancementImage analysisComputer scienceImage system
Owner:CYTYC CORP
High throughput cell-based HPV immunoassays for diagnosis and screening of HPV-associated cancers
ActiveUS20120282595A1High throughput assayLow detection sensitivityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementInfected cellProstasomes
Methods for quantifying an HPV protein expression in a clinical sample are disclosed. The quantifying methods include the process for obtaining the clinical sample. Such a clinical sample is consisted of a population of cells that are susceptible to infection by an HPV. The quantifying methods also include the process for depositing the clinical sample into a container. The clinical sample is contacted with the first antibody that specifically binds to an HPV protein which is expressed by an HPV-infected cell under a condition that promotes specific binding of the first antibody to the HPV protein expressed by the population of cells. The methods further include the process for quantifying the specific binding of the first antibody and thereby quantifying the HPV protein expression in the clinical sample. The assay provides an objective test to identify patients with high-grade precursor from cytology samples before biopsy.
Owner:HEER MEDICAL TECH DEV CO LTD
Cytological imaging systems and methods
InactiveUS20080018994A1Efficiently and accurately imagesSave stepsImage enhancementImage analysisComputer scienceImage system
The present invention relates to the analysis of specimens. Specifically, the invention relates to methods and apparatus for reviewing specimen slides, including apparatus for holding the slides. The invention also relates to an automatic focusing method for an imaging system and methods for accommodating vibration in the imaging system. In particular, the methods and apparatus may be applied to the automated analysis of cytological specimen slides.
Owner:CYTYC CORP
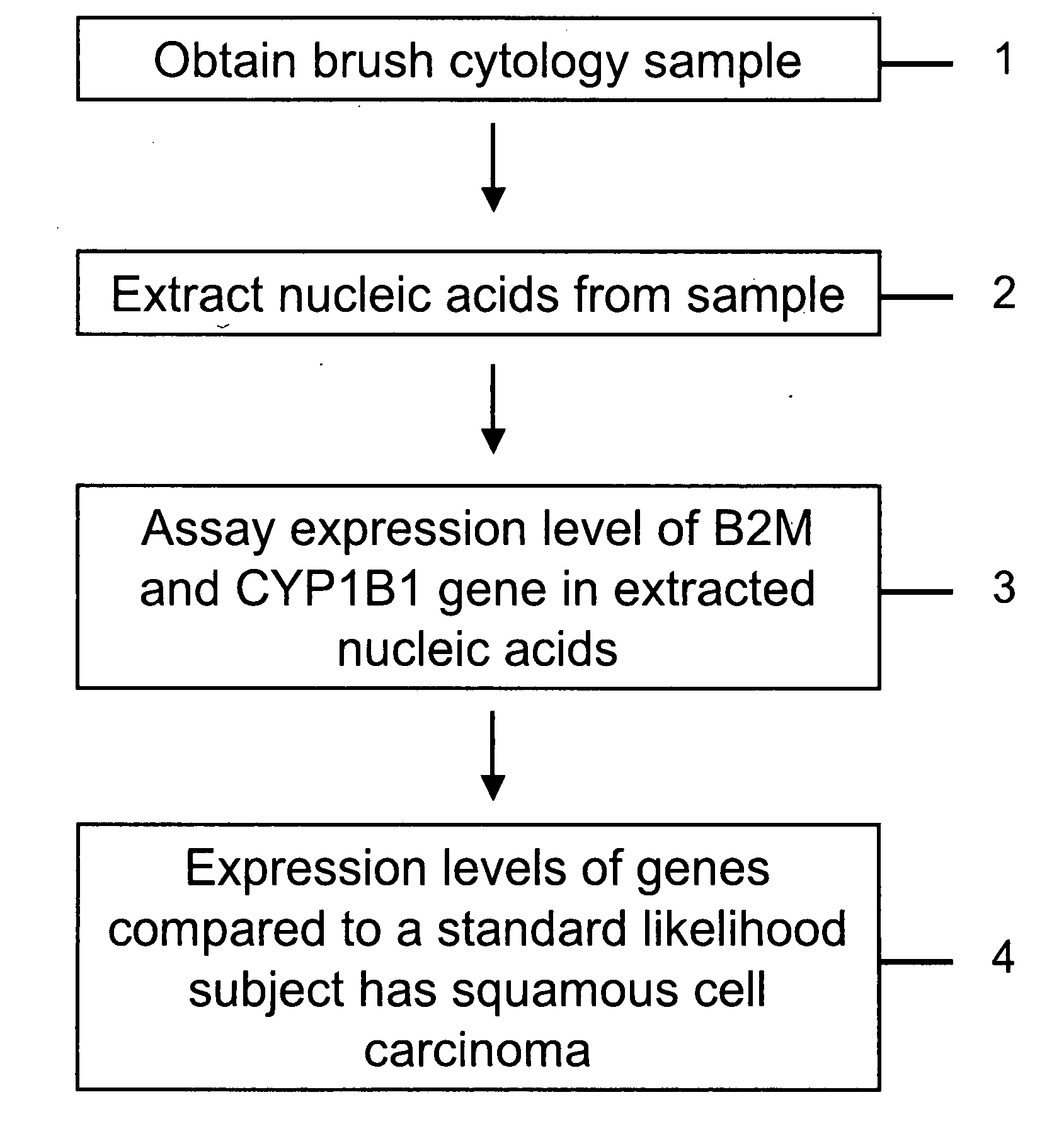
RNA from cytology samples to diagnose disease
The invention relates to methods and kits for detecting the likelihood that a subject has cancer, e.g., squamous cell carcinoma, by assaying the expression levels of tumor associated genes. More specifically, the expression levels of nucleic acids or proteins can be assayed in the tumor associated genes, e.g., beta-2 microgobulin (B2M) and cytochrome p450 1B1 (CYP1B1). The expression levels compared to standards can be indicative of the likelihood a subject has squamous cell carcinoma. For example, over-expression of B2M and under-expression of CYP1B1 can be indicative of the likelihood a subject has squamous cell carcinoma. Also, over-expression of B2M and over-expression of CYP1B1 can be indicative of the likelihood a subject has a precancerous squamous cell disorder. The expression levels of B2M and CYP1B1 can also be repeatedly assayed to monitor the progression of a squamous cell neoplasia.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
RNA From Cytology Samples To Diagnose Disease
The invention relates to methods and kits for detecting the likelihood that a subject has cancer, e.g., squamous cell carcinoma, by assaying the expression levels of tumor associated genes. More specifically, the expression levels of nucleic acids or proteins can be assayed in the tumor associated genes, e.g., beta-2 microgobulin (B2M) and cytochrome p450 1B1 (CYP1B1). The expression levels compared to standards can be indicative of the likelihood a subject has squamous cell carcinoma. For example, over-expression of B2M and under-expression of CYP1B1 can be indicative of the likelihood a subject has squamous cell carcinoma. Also, over-expression of B2M and over-expression of CYP1B1 can be indicative of the likelihood a subject has a precancerous squamous cell disorder. The expression levels of B2M and CYP1B1 can also be repeatedly assayed to monitor the progression of a squamous cell neoplasia.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
High throughput cell-based HPV immunoassays for diagnosis and screening of HPV-associated cancers
ActiveCN102822672AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisInfected cellCell based
Owner:HEER MEDICAL TECH DEV CO LTD
Cytological imaging system and method
InactiveUS20080278707A1Wasted heatWasted lightImage analysisPreparing sample for investigationCytoplasmic partBiology
Owner:CYTYC CORP
Cytological imaging system and method
InactiveUS7411664B2Less heatWasted heatImage analysisPreparing sample for investigationCytoplasmic partBiology
The present invention relates to the analysis of cytological material. Specifically, the invention relates to stains and methods of producing the stains, methods of staining cells for cytological or histological analysis to contrast the nuclear portion of the cell from the cytoplasmic portion, and systems and methods for illuminating a cytological sample. The analysis can be automated or manual.
Owner:CYTYC CORP
Treatment device for treating histological or cytological samples
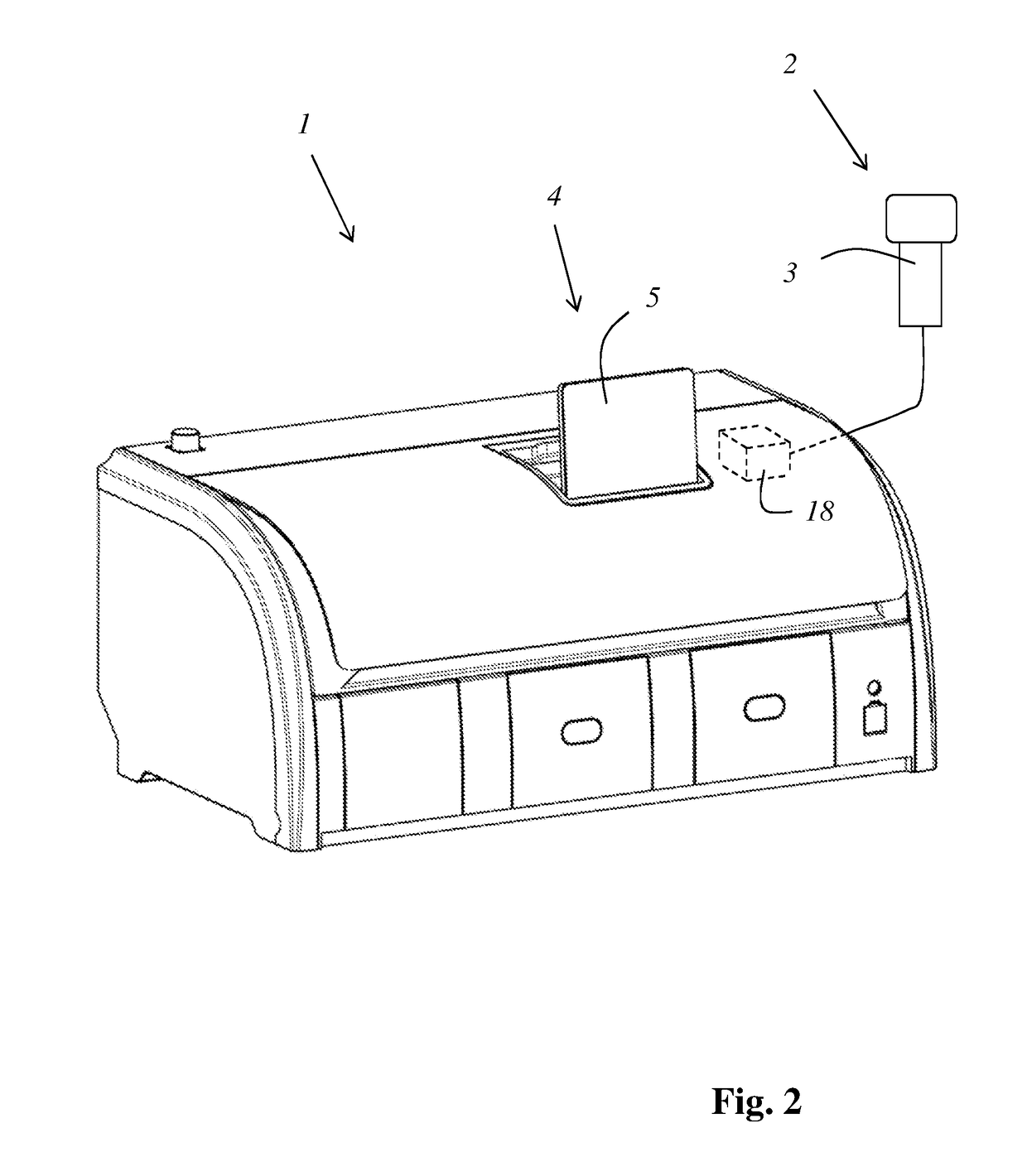
ActiveUS20180003600A1Simple treatmentRisk of errorPreparing sample for investigationLogisticsPsychiatryHistology
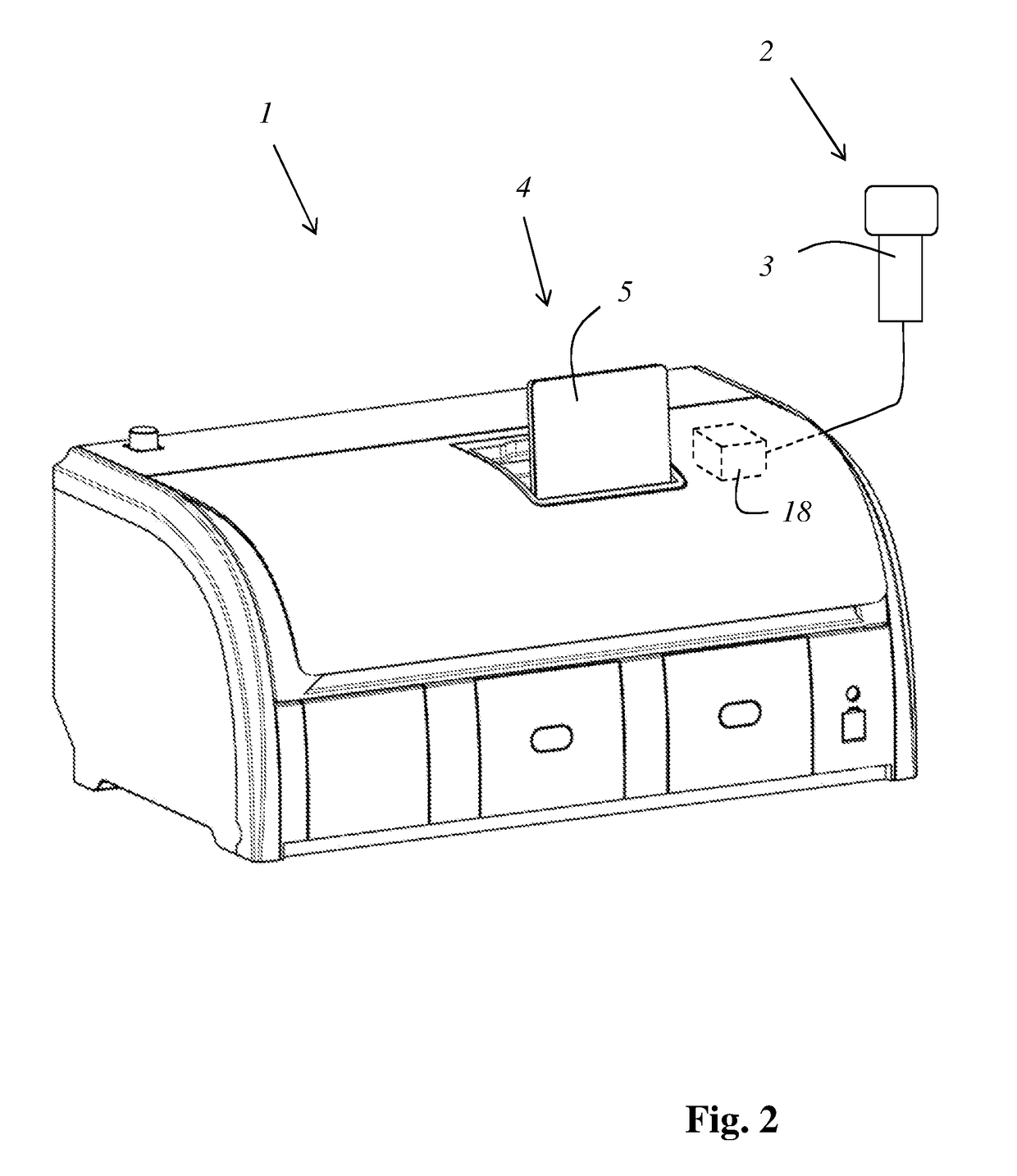
A treatment device (1) for treating histological or cytological samples has a plurality of containers (6) for different treatment agents and a detection apparatus (2) for detecting a code which unequivocally identifies a type of a treatment agent or a type of a group of treatment agents from a package or replacement container of a treatment agent or group of treatment agents. The device furthermore has an evaluation apparatus (18) that, based on a detected code, ascertains which of the containers is or are to be replenished or replaced, and an indicating apparatus (4) which communicates to a user the ascertained container (6) or containers (6) that is or are to be replenished or replaced. The indicating apparatus may include a display (5) presenting a schematic image of the plurality of containers (6) with image(s) of each ascertained container being marked, and / or a light source (15) that illuminates each ascertained container.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST NUSSLOCH
Systems and kits for preparing cytology samples for examination
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Treatment device for treating histological or cytological samples
ActiveUS10151673B2Simple treatmentRisk of incorrectPreparing sample for investigationLogisticsDisplay devicePsychiatry
A treatment device (1) for treating histological or cytological samples has a plurality of containers (6) for different treatment agents and a detection apparatus (2) for detecting a code which unequivocally identifies a type of a treatment agent or a type of a group of treatment agents from a package or replacement container of a treatment agent or group of treatment agents. The device furthermore has an evaluation apparatus (18) that, based on a detected code, ascertains which of the containers is or are to be replenished or replaced, and an indicating apparatus (4) which communicates to a user the ascertained container (6) or containers (6) that is or are to be replenished or replaced. The indicating apparatus may include a display (5) presenting a schematic image of the plurality of containers (6) with image(s) of each ascertained container being marked, and / or a light source (15) that illuminates each ascertained container.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST NUSSLOCH
System and kit for preparing a cytological sample for examination
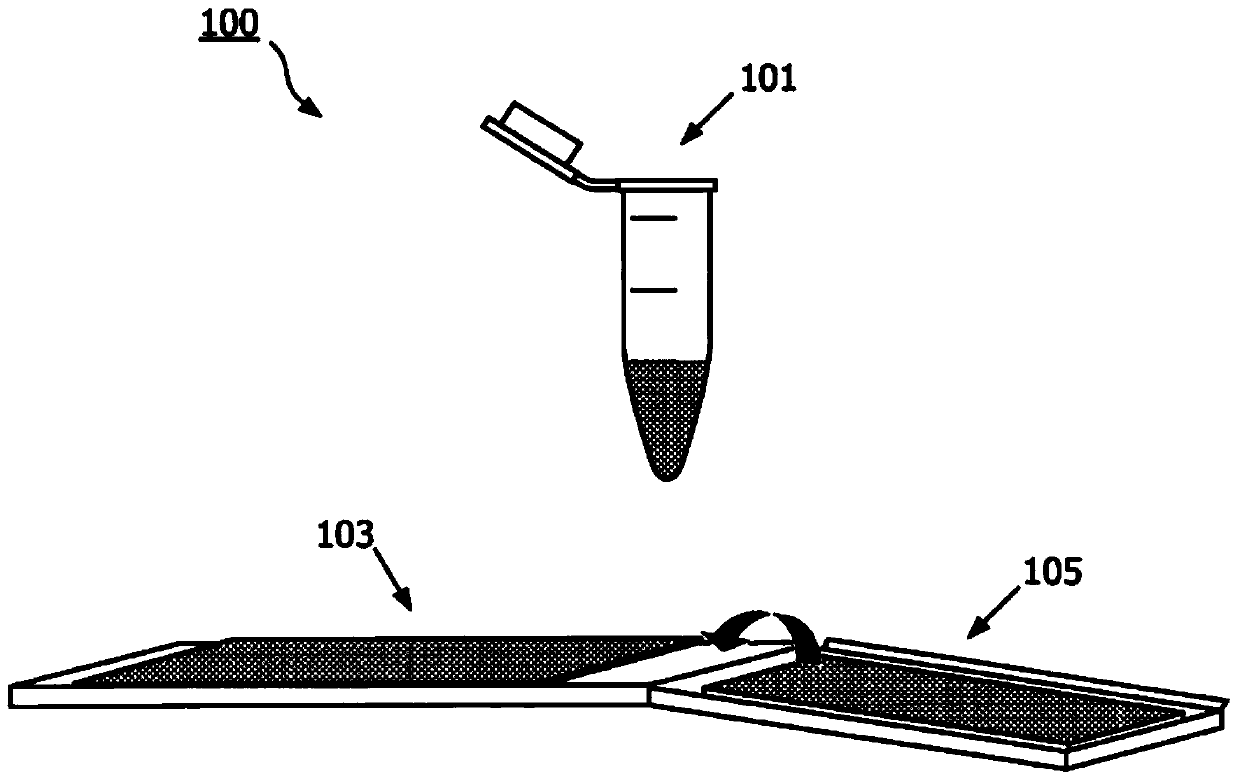
ActiveCN103827654APH conditions are easy to controlPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingBiologyCytology sample
The present invention is related to a system or kit for preparing a cytological sample for examination, which comprises a fixative for fixing cells comprised in said sample, a cell surface modifier for modification of the surface of cells comprised in said sample, a first sample support meanshaving at least two sides, and a second sample support means having at least two sides, wherein on at least one side of at least one of the support means a cytoplasmic stain or a nuclear stain is deposited (Fig. 1).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method for detection of cells in a cytological sample having at least one anomaly
ActiveUS20210012088A1Inaccurate analysisEarly diagnosisCharacter and pattern recognitionColor/spectral properties measurementsAnalytical chemistryCell
Disclosed is a method for detecting cells having at least one anomaly in a cytological sample on the basis of at least one first digitised digitised-electron-microscopy image of the sample.
Owner:OFFICE NAT DETUD & DE RECH AEROSPATIALES
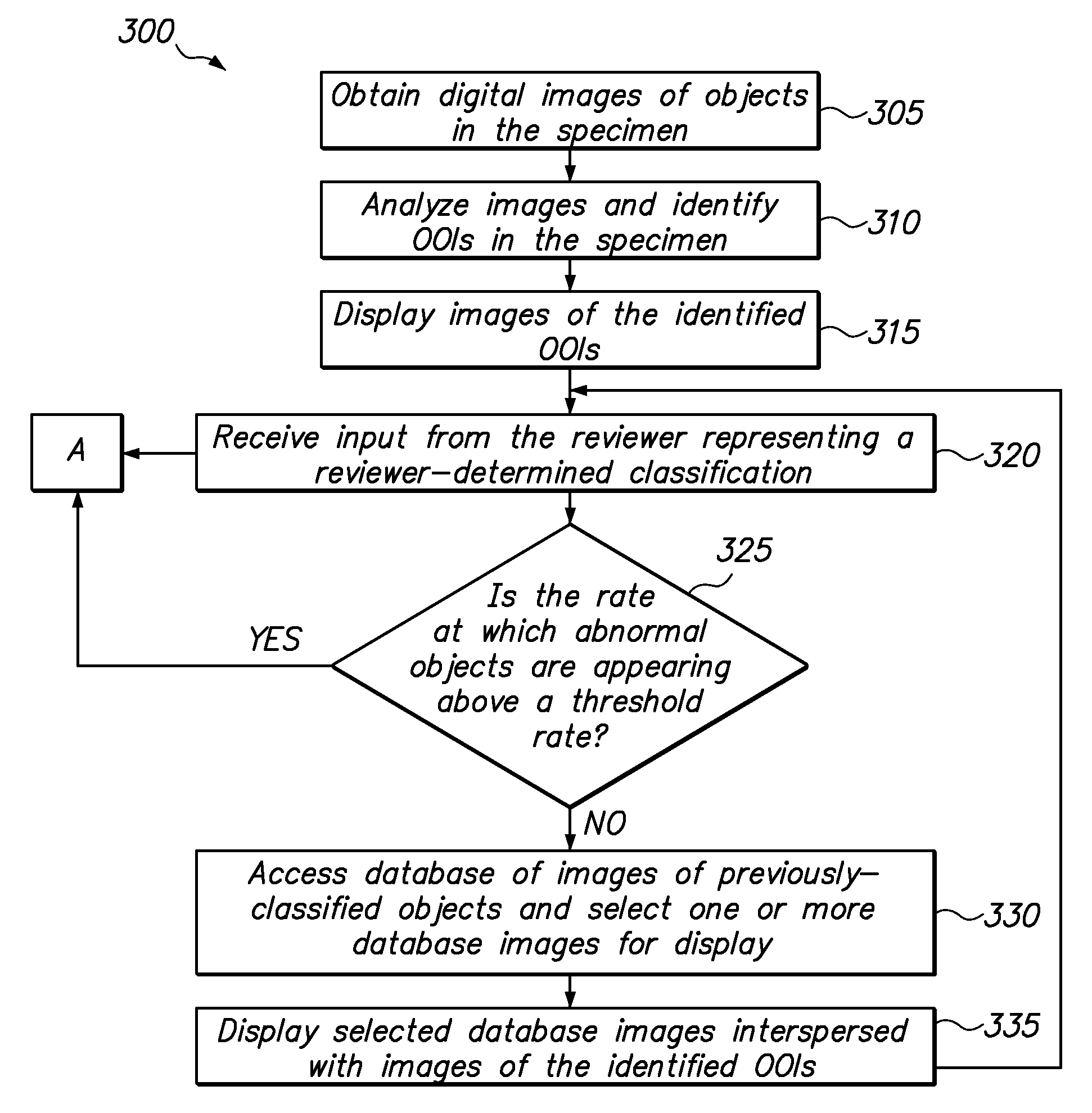
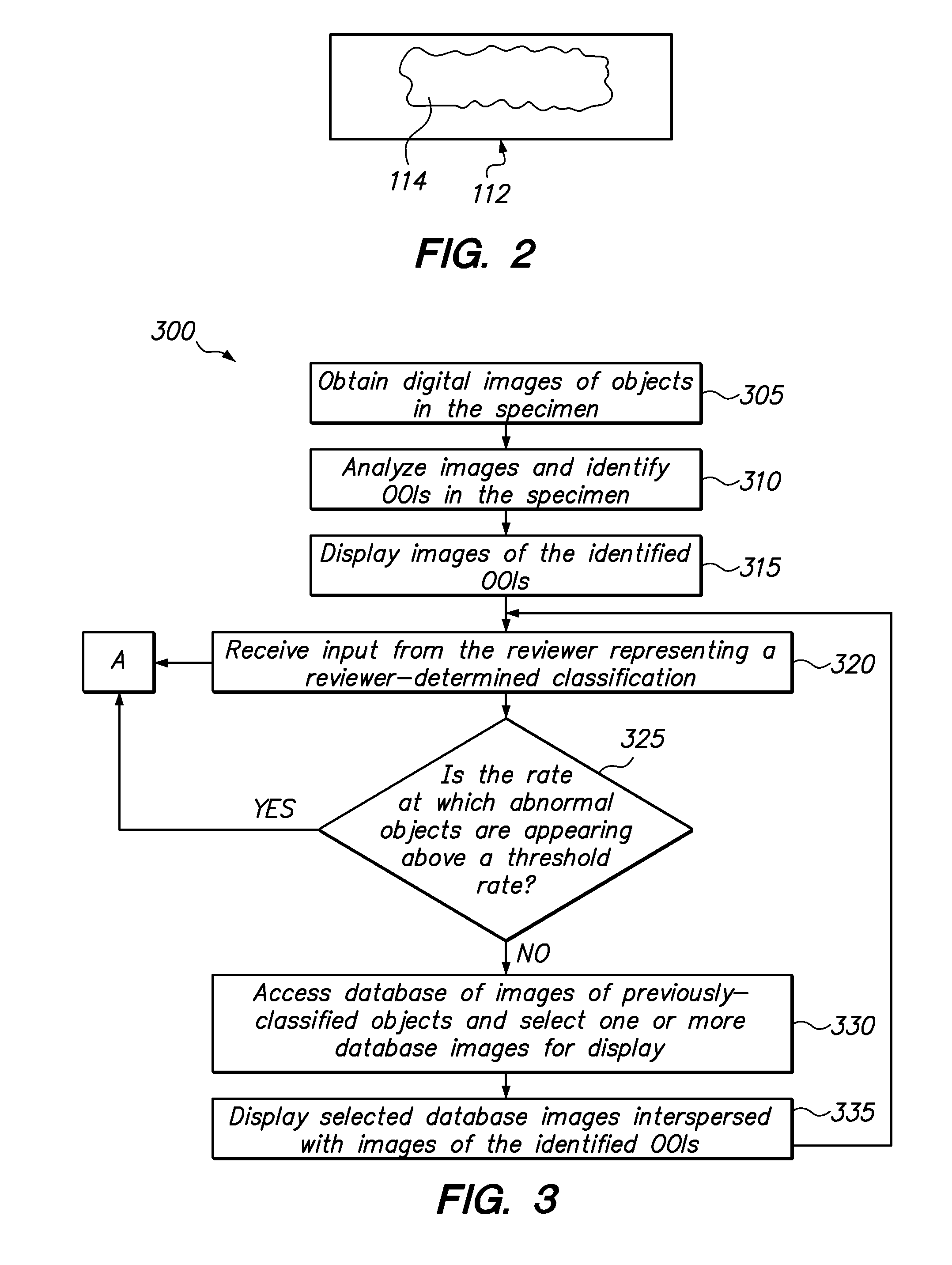
Method for automatically seeding previously-classified images among images of objects of interest from a specimen
ActiveUS8983166B2High frequencyData visualisationComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionComputer-aidedSample image
A computer-assisted method of classifying cytological samples, includes using a processor to analyze images of cytological samples and identify cytological objects of interest within the sample images, wherein the processor (i) displays images of identified cytological objects of interest from the sample images to a reviewer, (ii) accesses a database of images of previously classified cytological objects, and (iii) displays to the reviewer, interspersed with the displayed images of the identified objects of interest from the sample images, one or more images obtained from the database of images of previously-classified objects.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
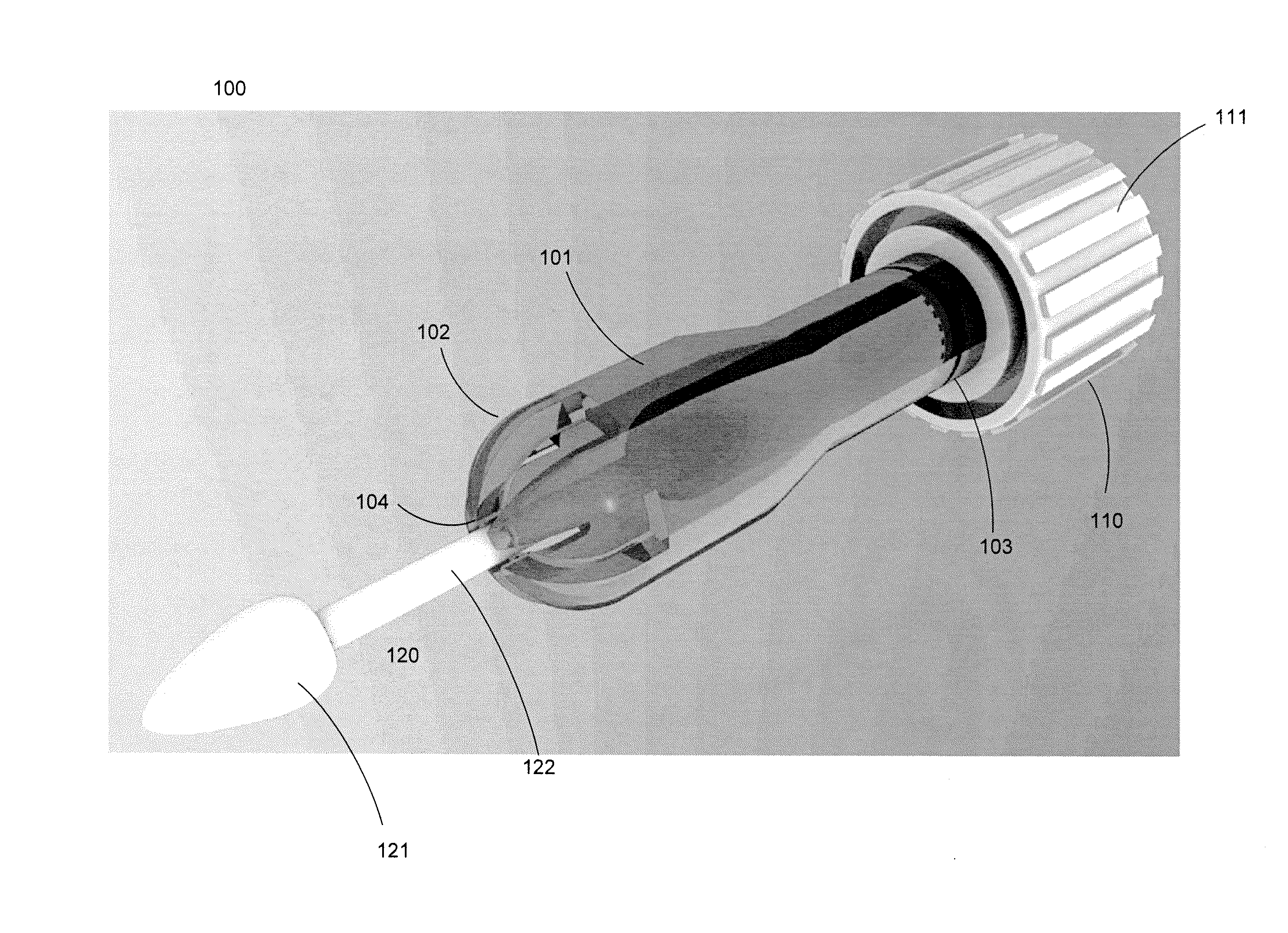
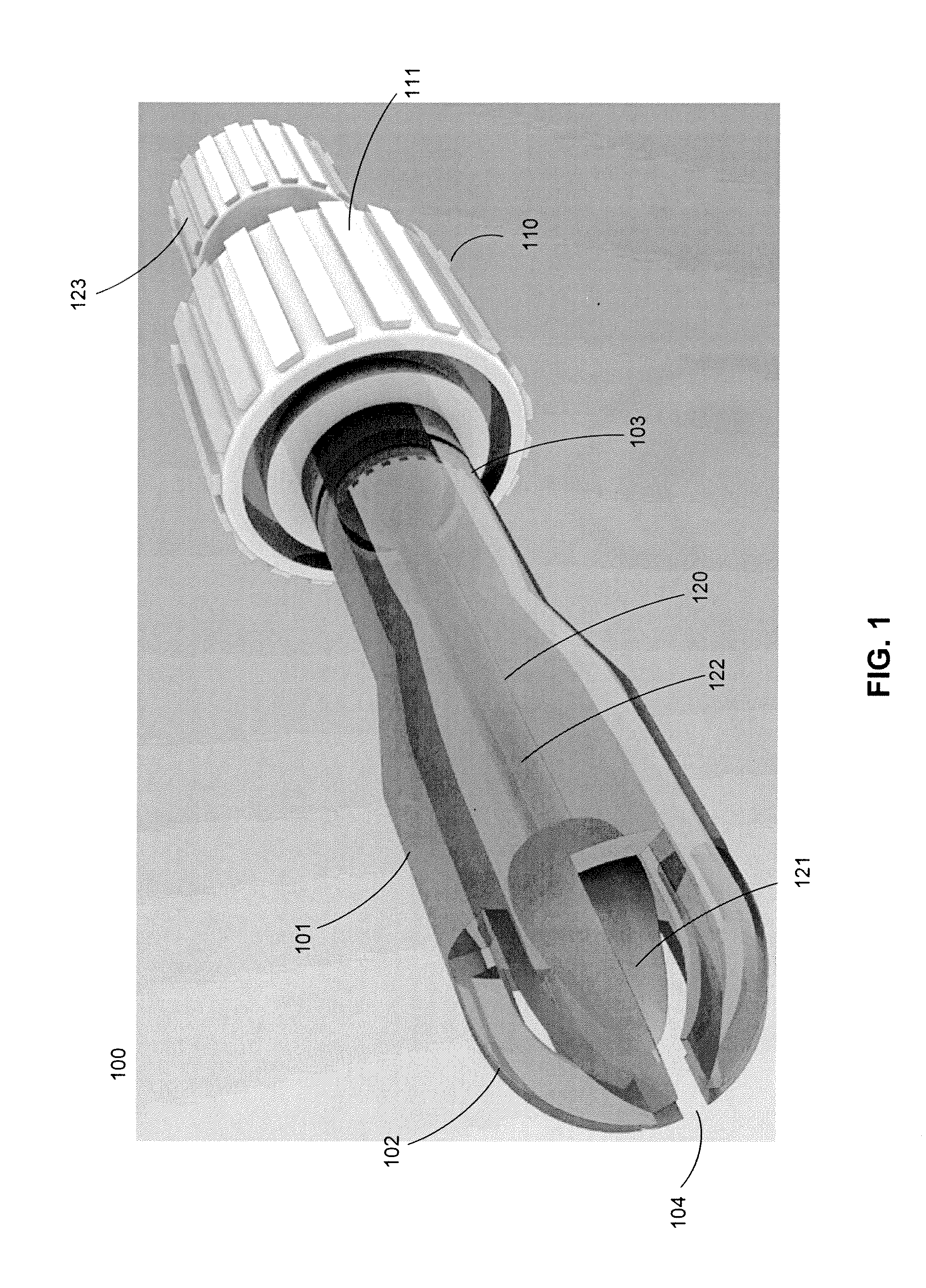
Cytological cell sample collection, storage, and transport device
A cytological cell sample collection, storage, and transport device is disclosed. The device comprises a sheath, a collection assembly, a base, and a containment vial. The collection assembly is slidably coupled to the base to expose a swab head comprising the collection assembly. The containment vial is configured to enclose the sheath and collection assembly within the internal volume defined by the containment vial and the base.
Owner:IN HINDSIGHT
A manual method for depositing a sample directly onto a slide for liquid based cytology
An efficient manual method for preparing a cytology sample for staining. According to the method, a biological sample is provided, wherein the biological sample is a liquid-based cytology sample. A slide is placed in a holder adapted for receiving the slide. The slide is pre-coated with a composition that will cause cells to adhere to the slide. A settling chamber is placed over said slide and thesettling chamber is locked onto the holder. The settling chamber has openings in both proximate and distal ends. The opening in the distal end of the settling chamber is positioned over the slide such that the slide is interposed between the holder and the settling chamber and the slide is in fluid communication with the settling chamber. A density reagent is then dispensed into the settling chamber. The liquid-based cytology sample is then dispensed into the settling chamber over the reagent. The assembly formed by the holder, slide and settling chamber (and its liquid contents) is placed ina centrifuge. The assembly is centrifuged for less than 5 minutes at a rotation force of less than 500g. The density reagent and the liquid thereover are decanted from the settling chamber. The settling chamber is removed from over the slide. The slide is removed from the holder for staining.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Direct immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry methods
InactiveCN112236677AHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMultiplexCytochemistry
Owner:贵州美鑫达医疗科技有限公司
Additive for accelerating hybridization
ActiveUS11021739B2Shorten the timeFast and low-costMicrobiological testing/measurementDextranDiagnosis laboratory
The present invention describes an additive for accelerating hybridization comprising: a) an aqueous solution of sodium dextran sulphate, b) a salt, c) a buffer system, d) a strong mineral base possibly mixed with at least one polar aprotic solvent, or at least one polar aprotic solvent.The additive described herein enables a reduction in the time required to perform the investigations with molecular probes on histological and cytological samples; the possibility of applying it to the protocol already in use in the routine practices of various laboratories in order to reduce the working time of histological and cytological samples for investigations with molecular probes, with no organisational impacts on the operators' work, enabling a more rapid diagnostic response for the patient and offering the possibility of using the additive described herein without formamide.
Owner:ALMA MATER STUDIORUM UNIV DI BOLOGNA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com