Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
133 results about "Bone humerus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
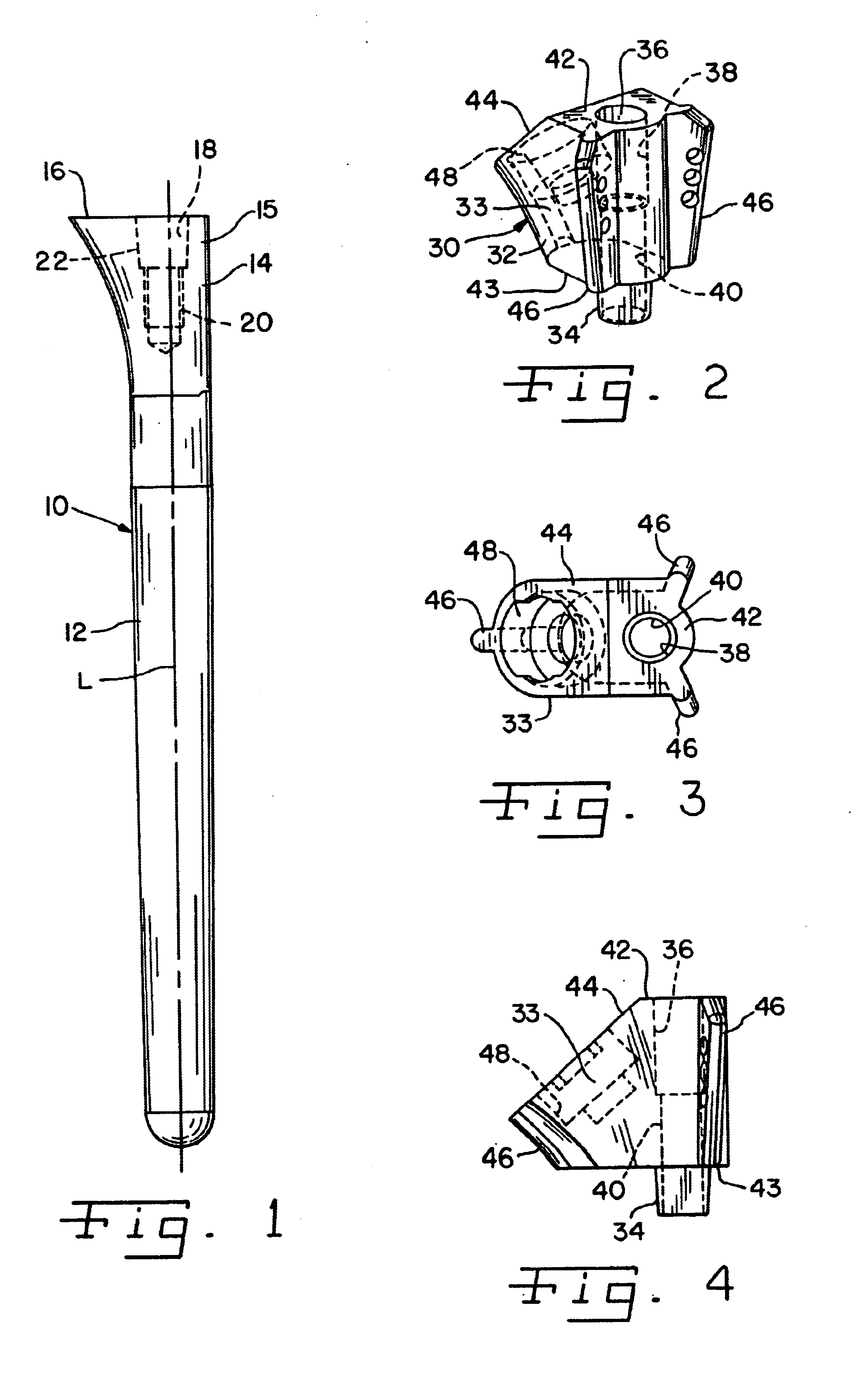
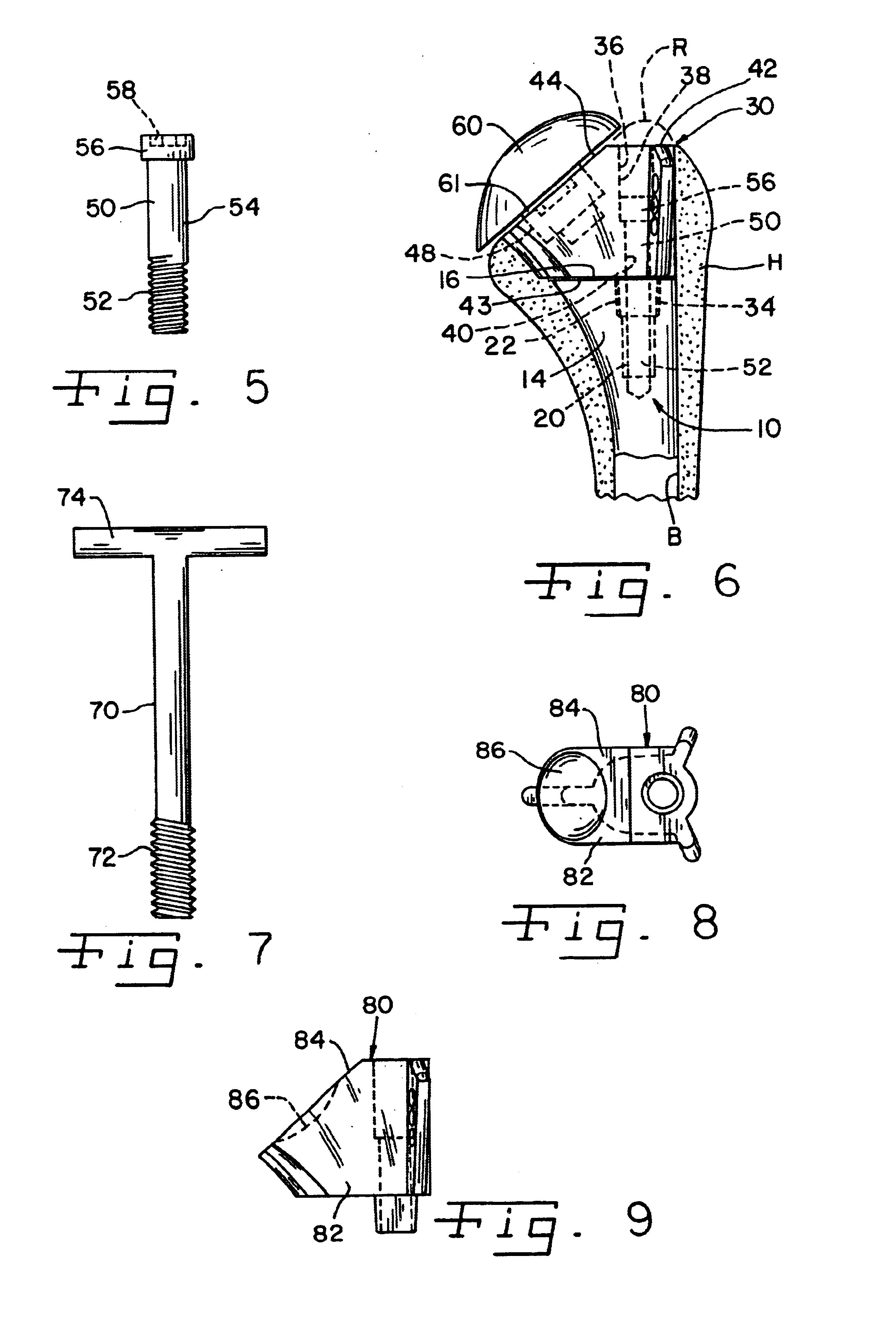
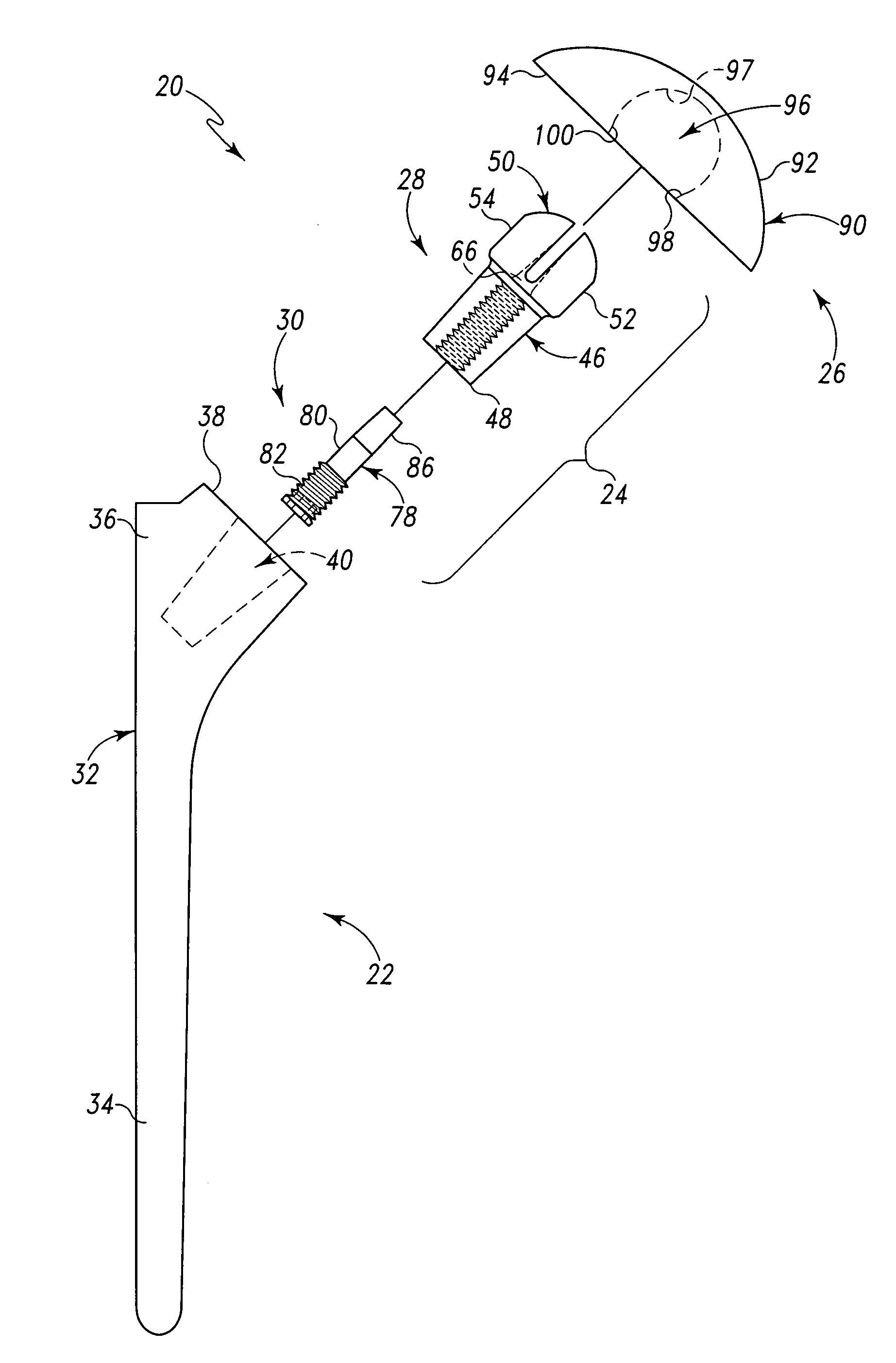
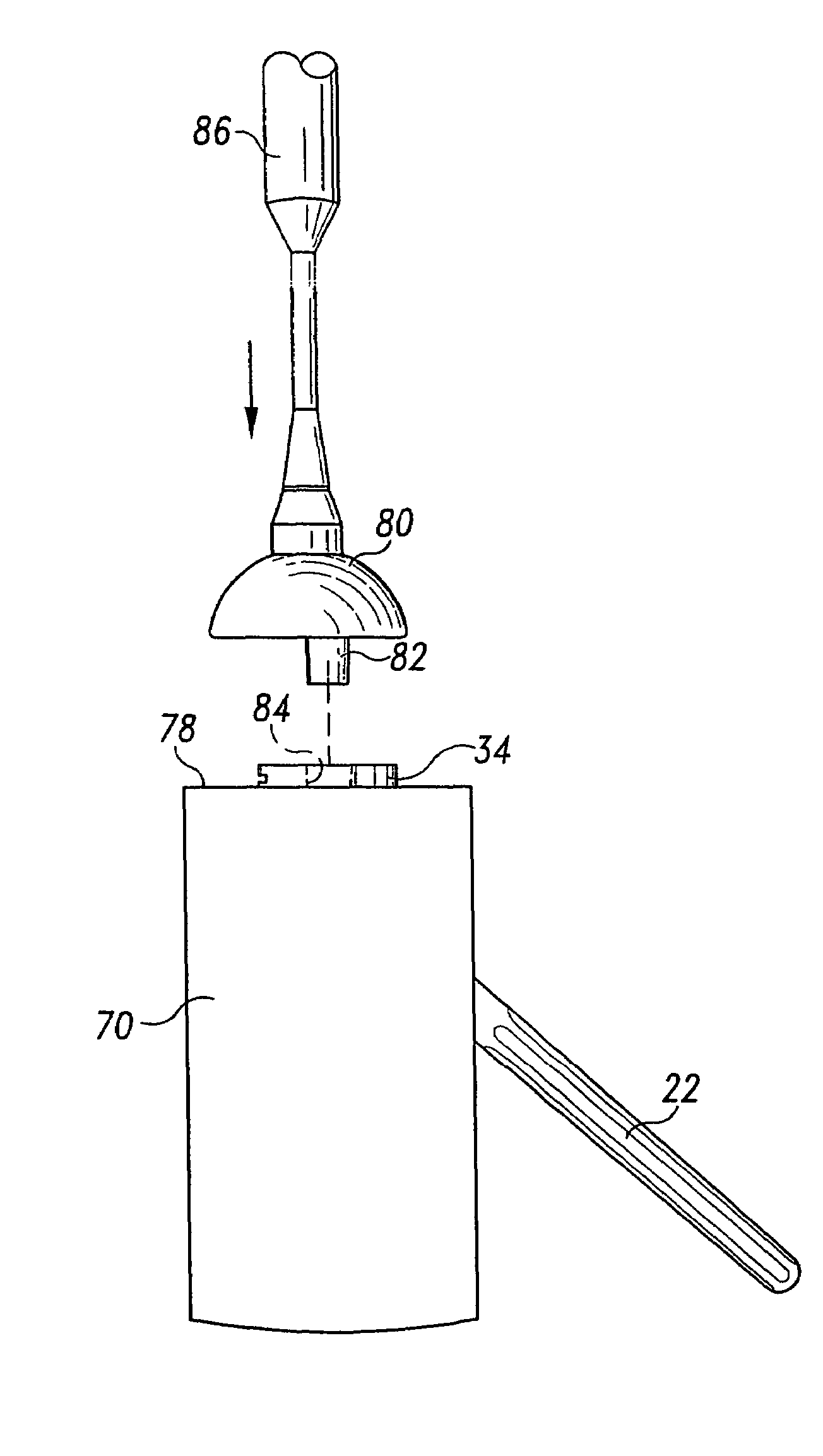
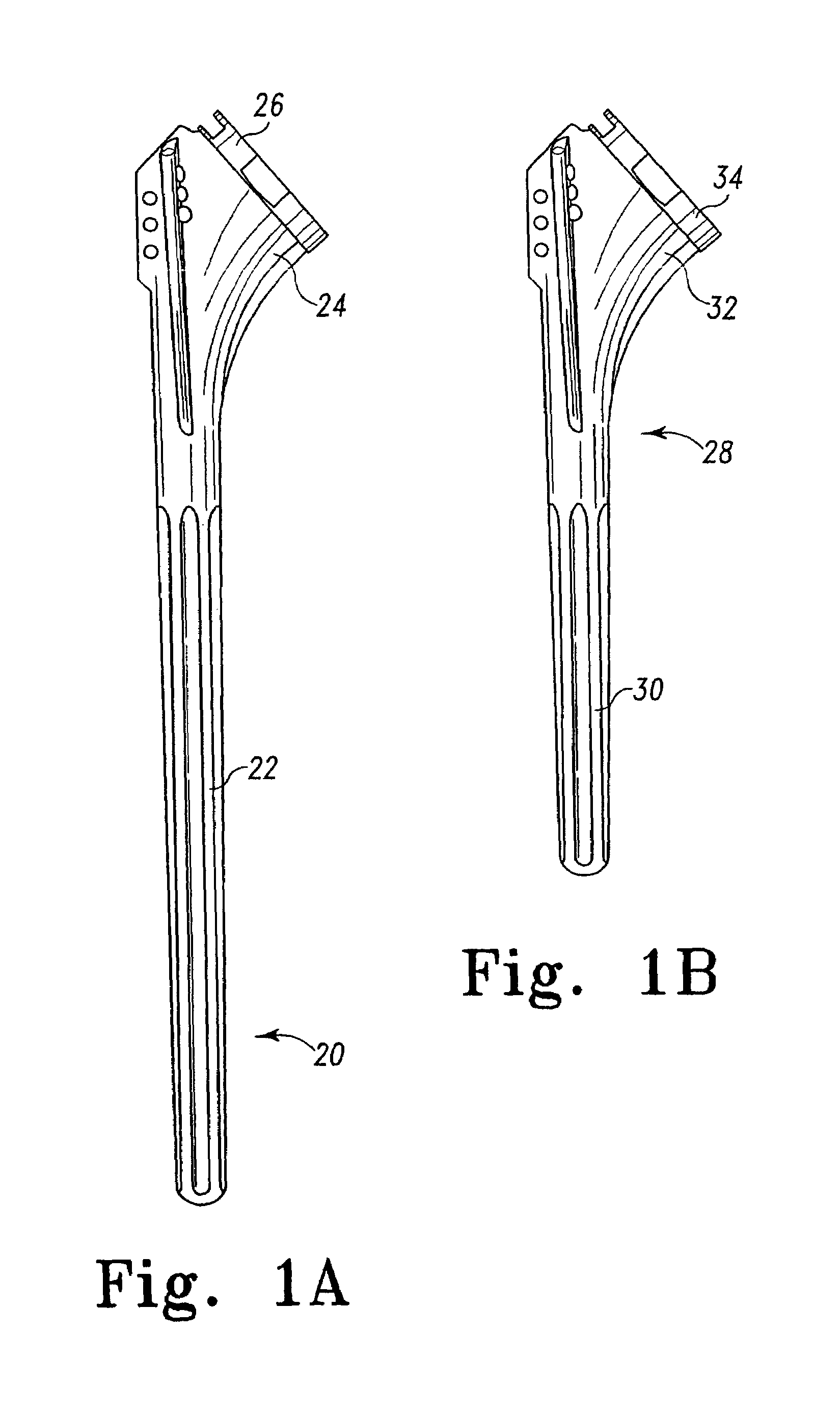
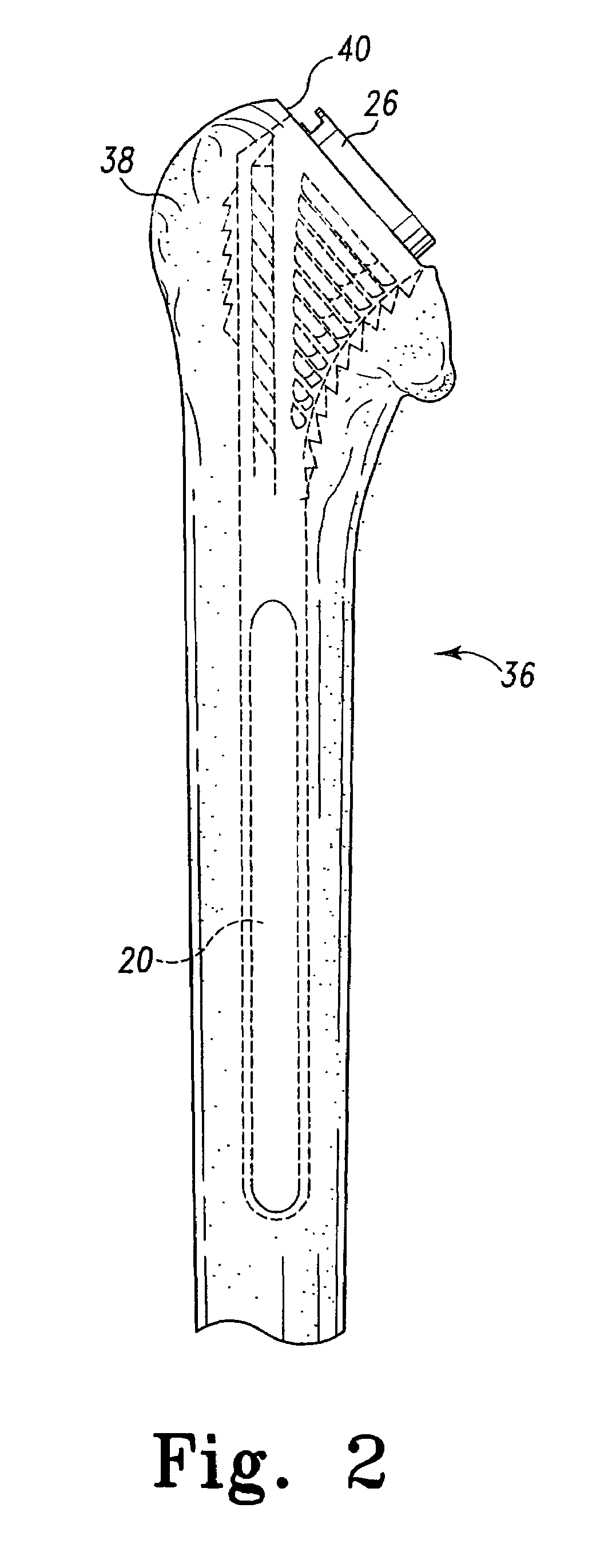
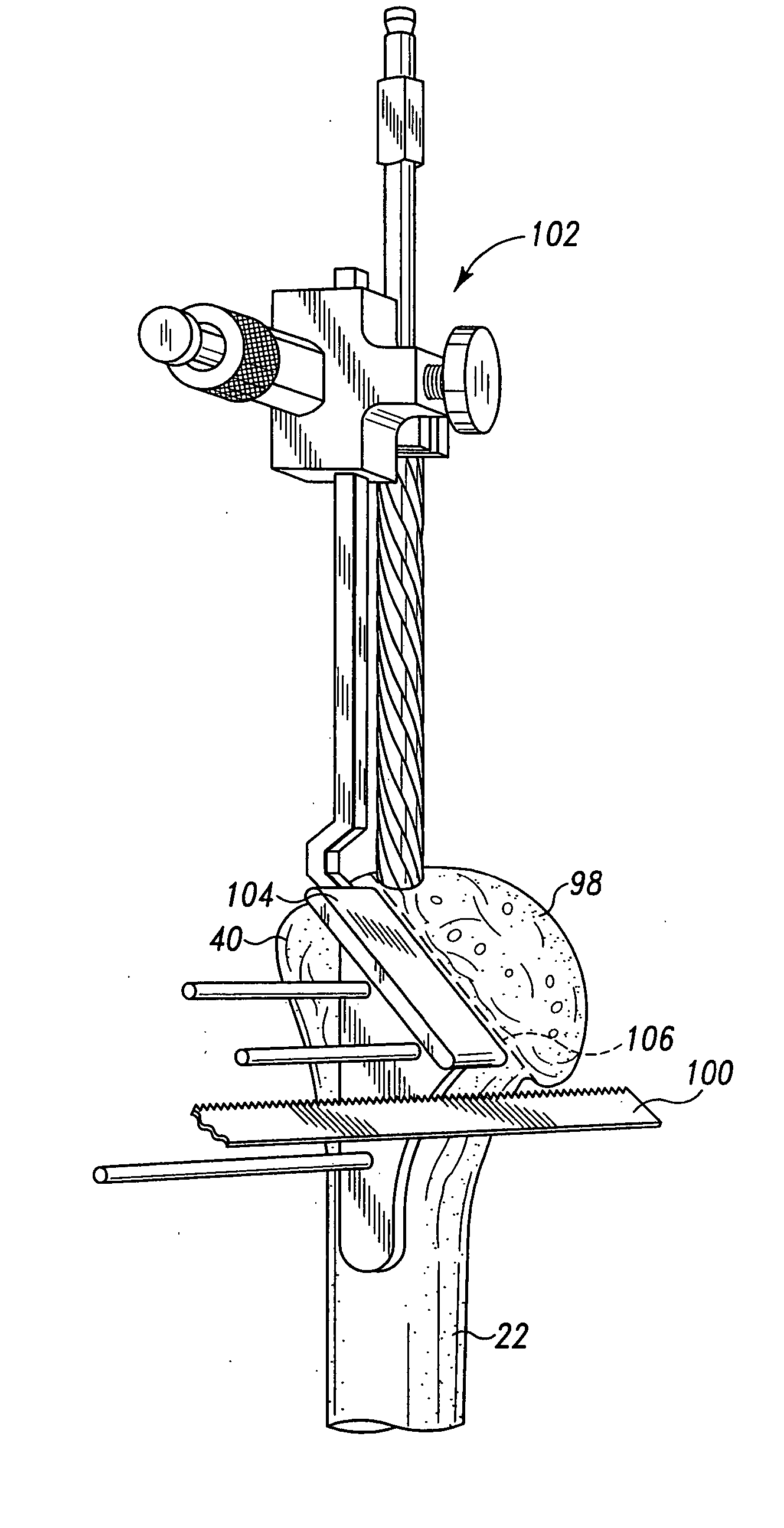
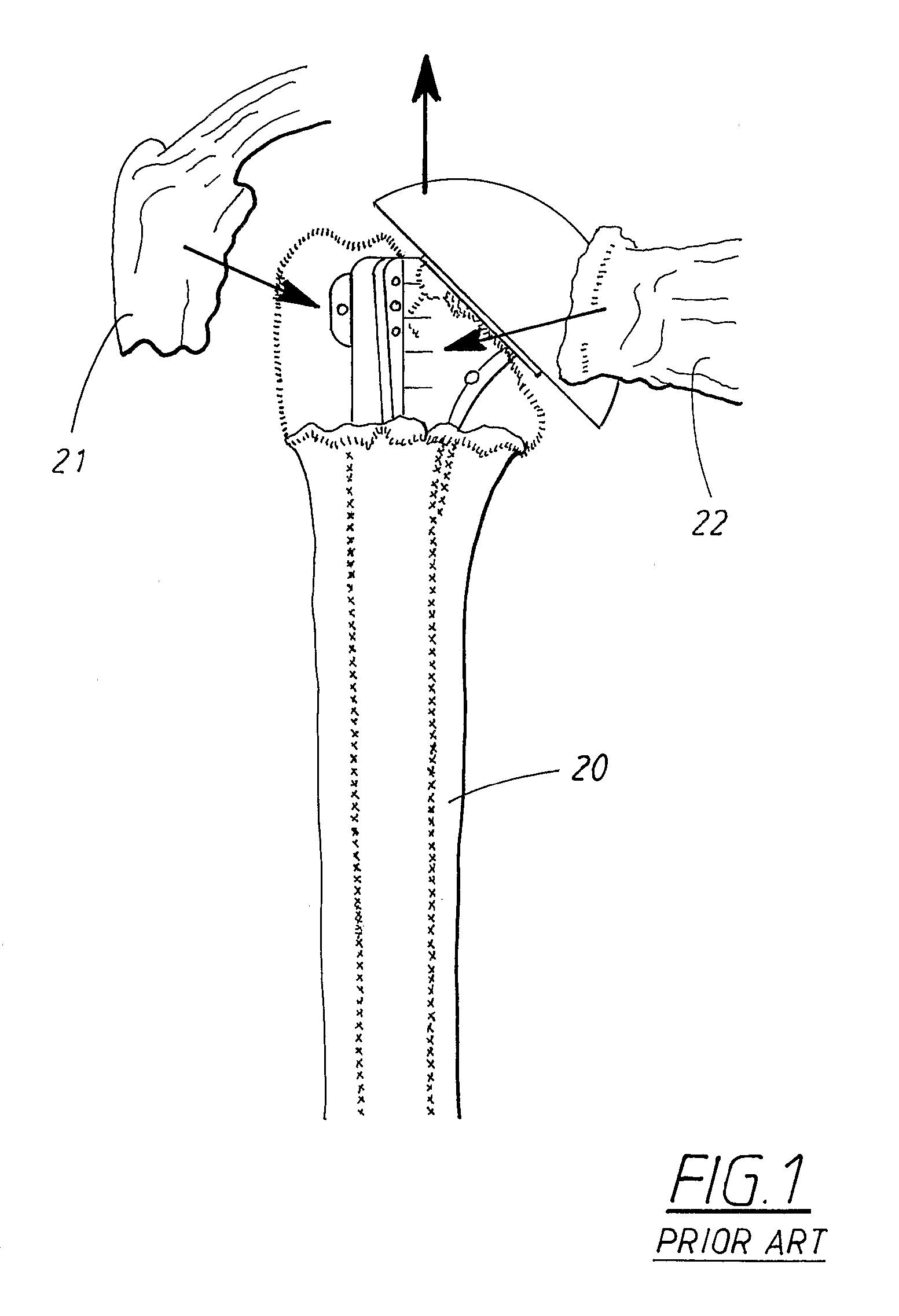
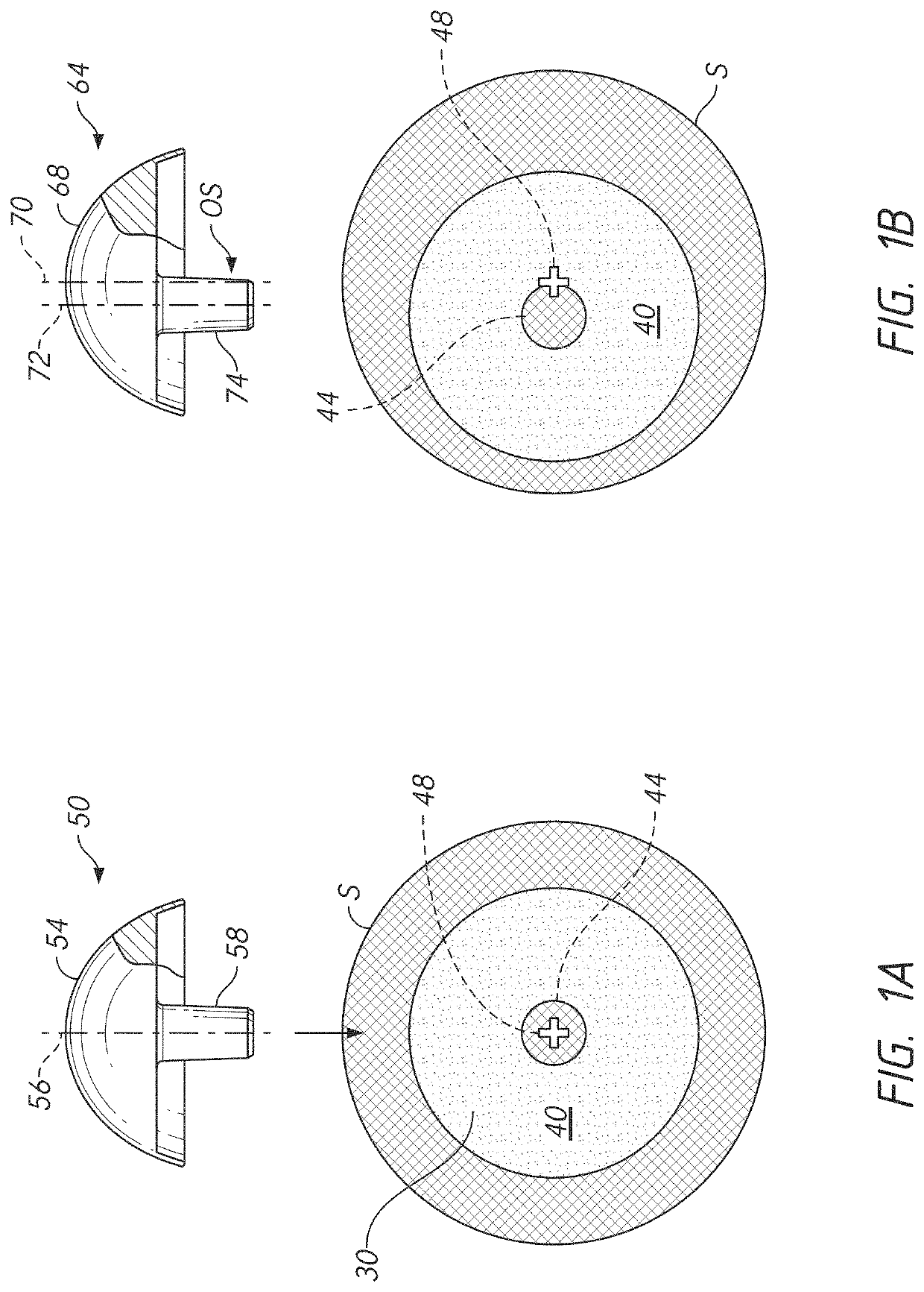
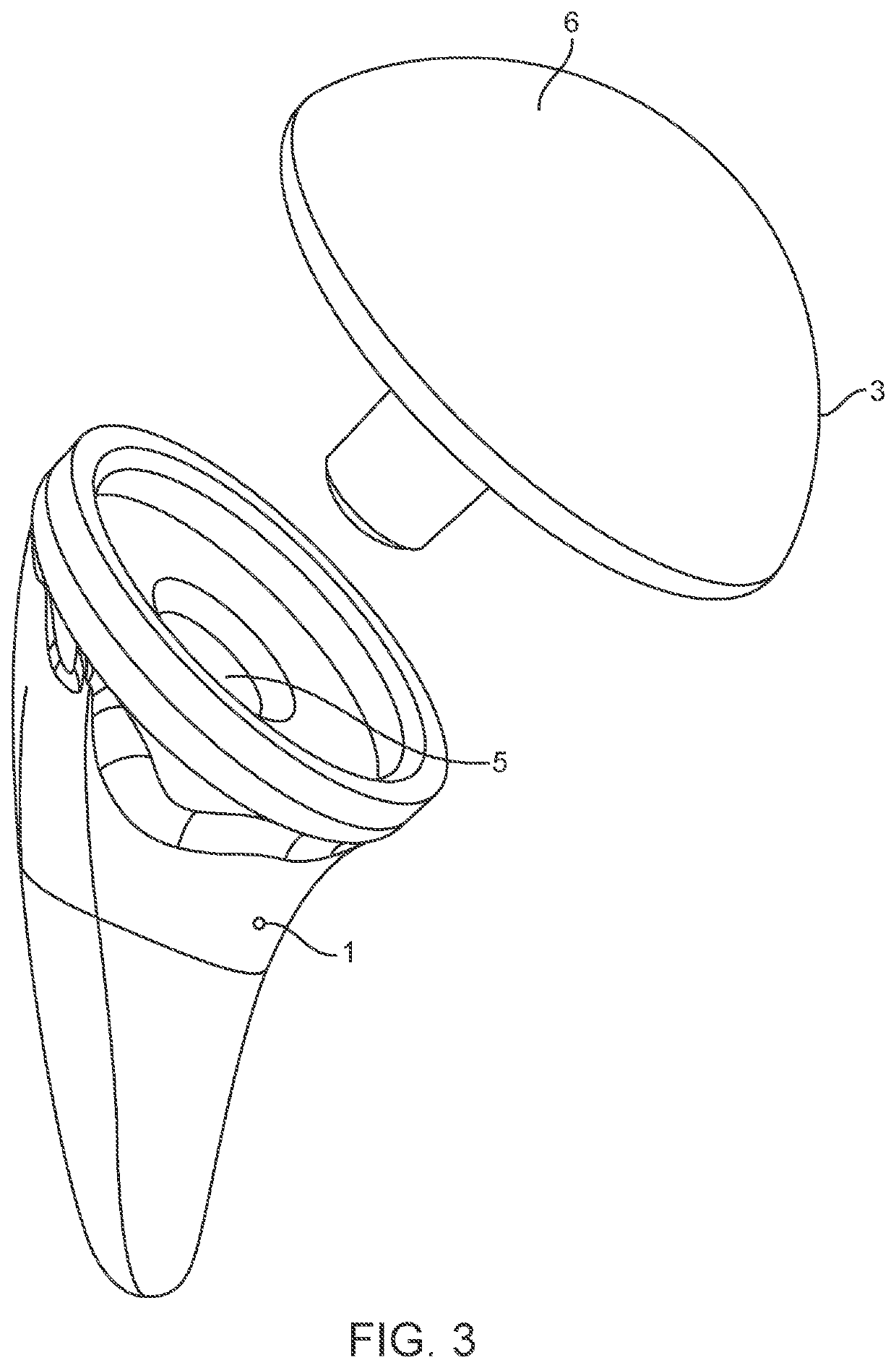
Bone resection apparatus
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
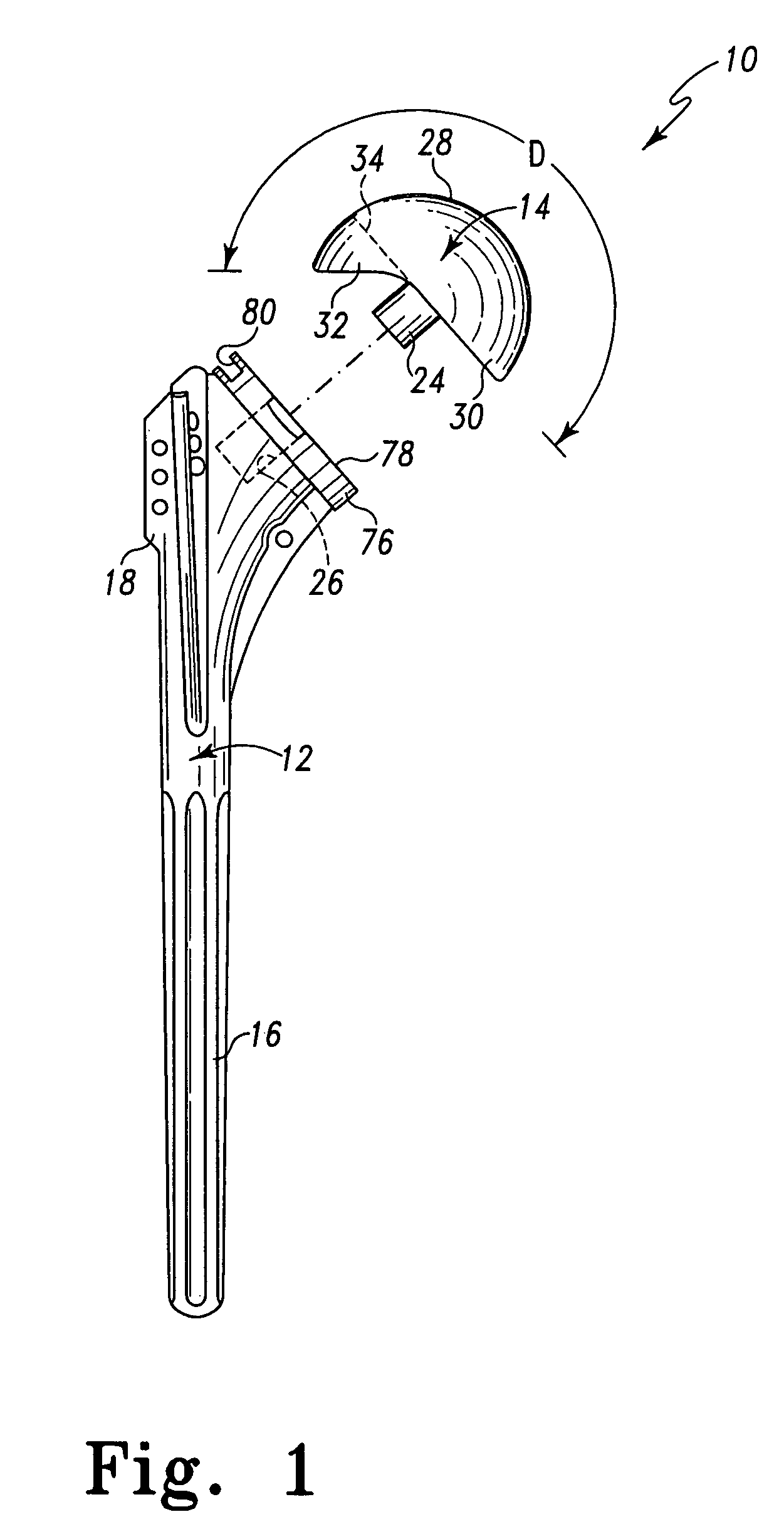
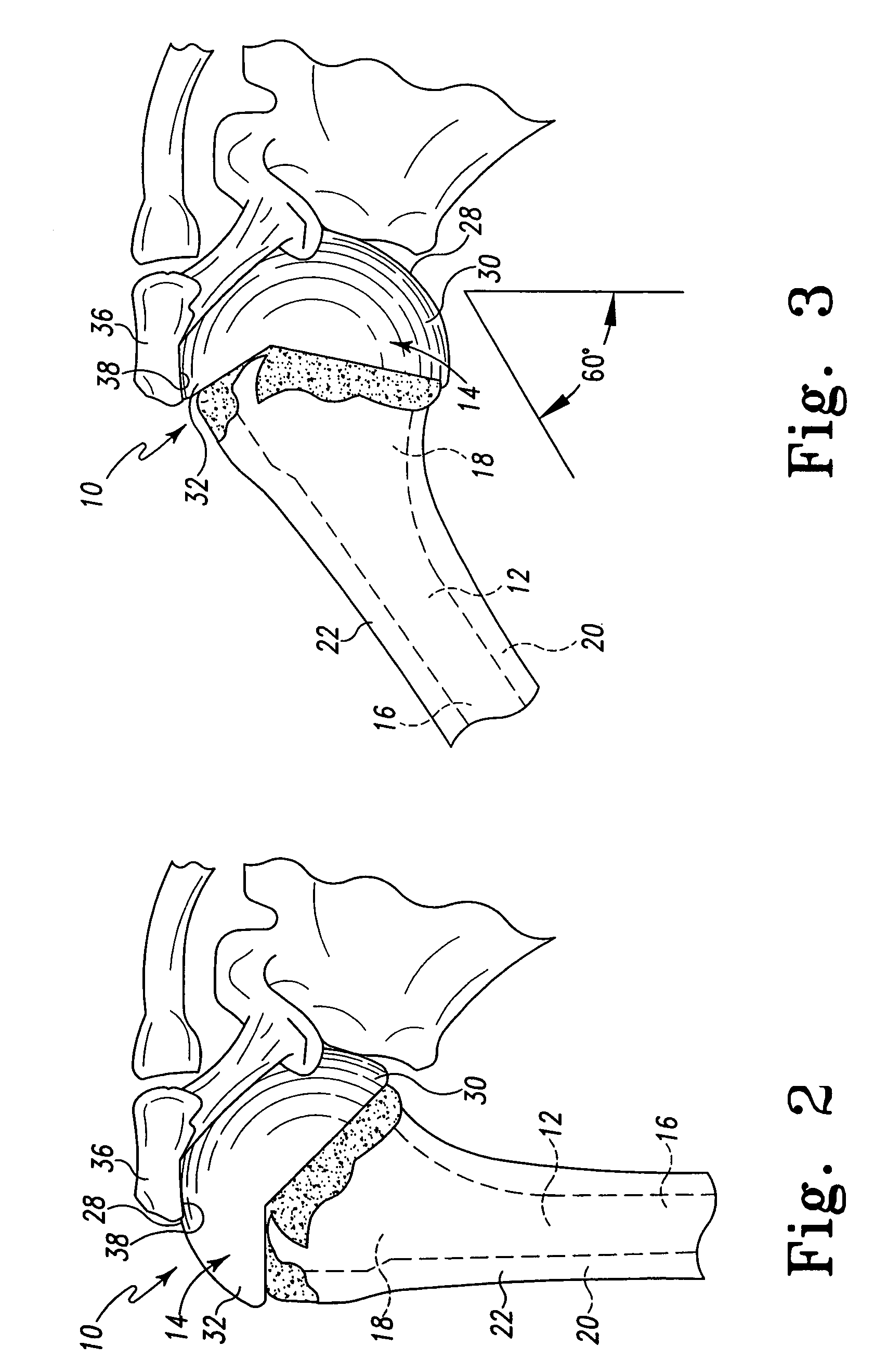
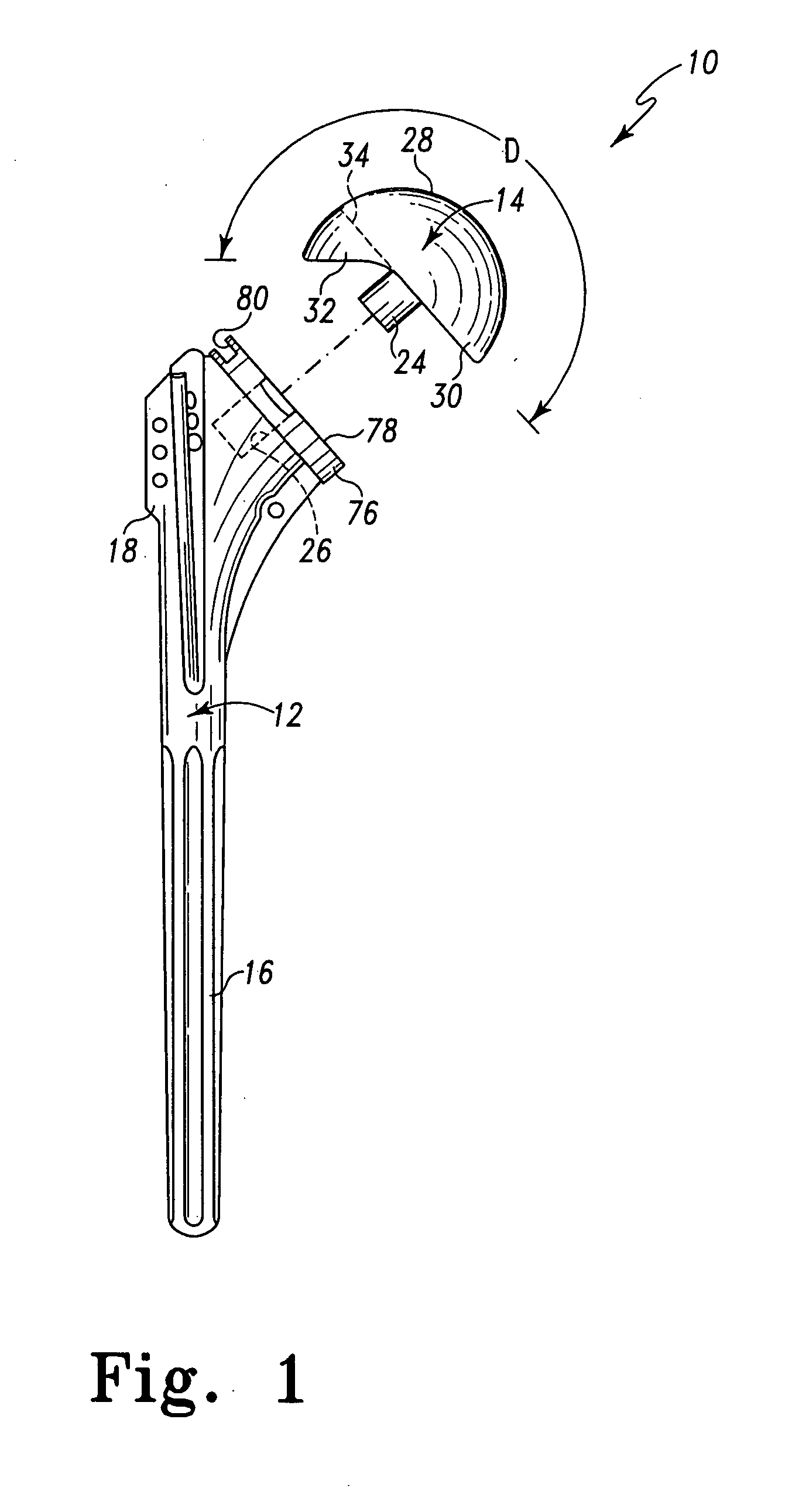
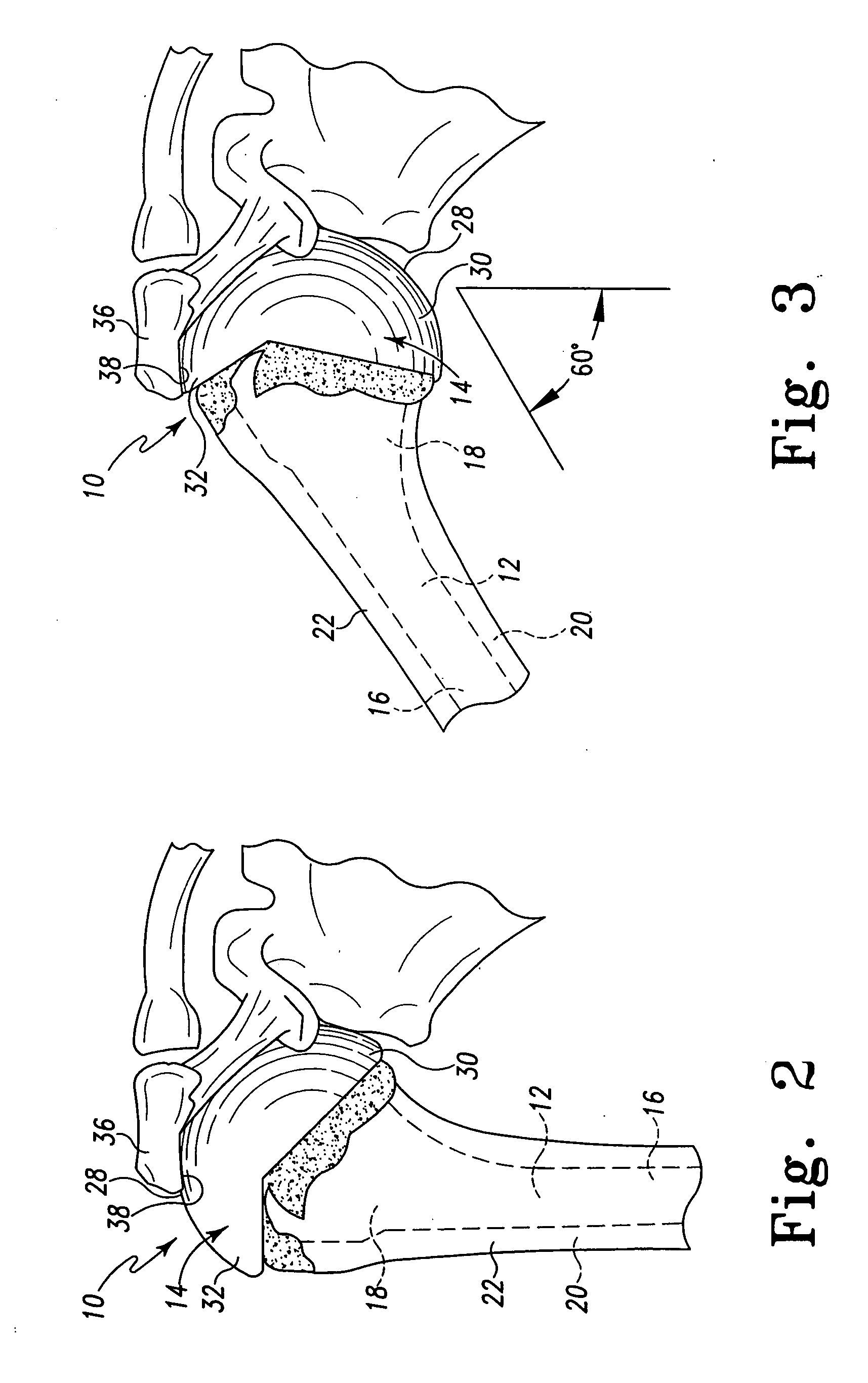
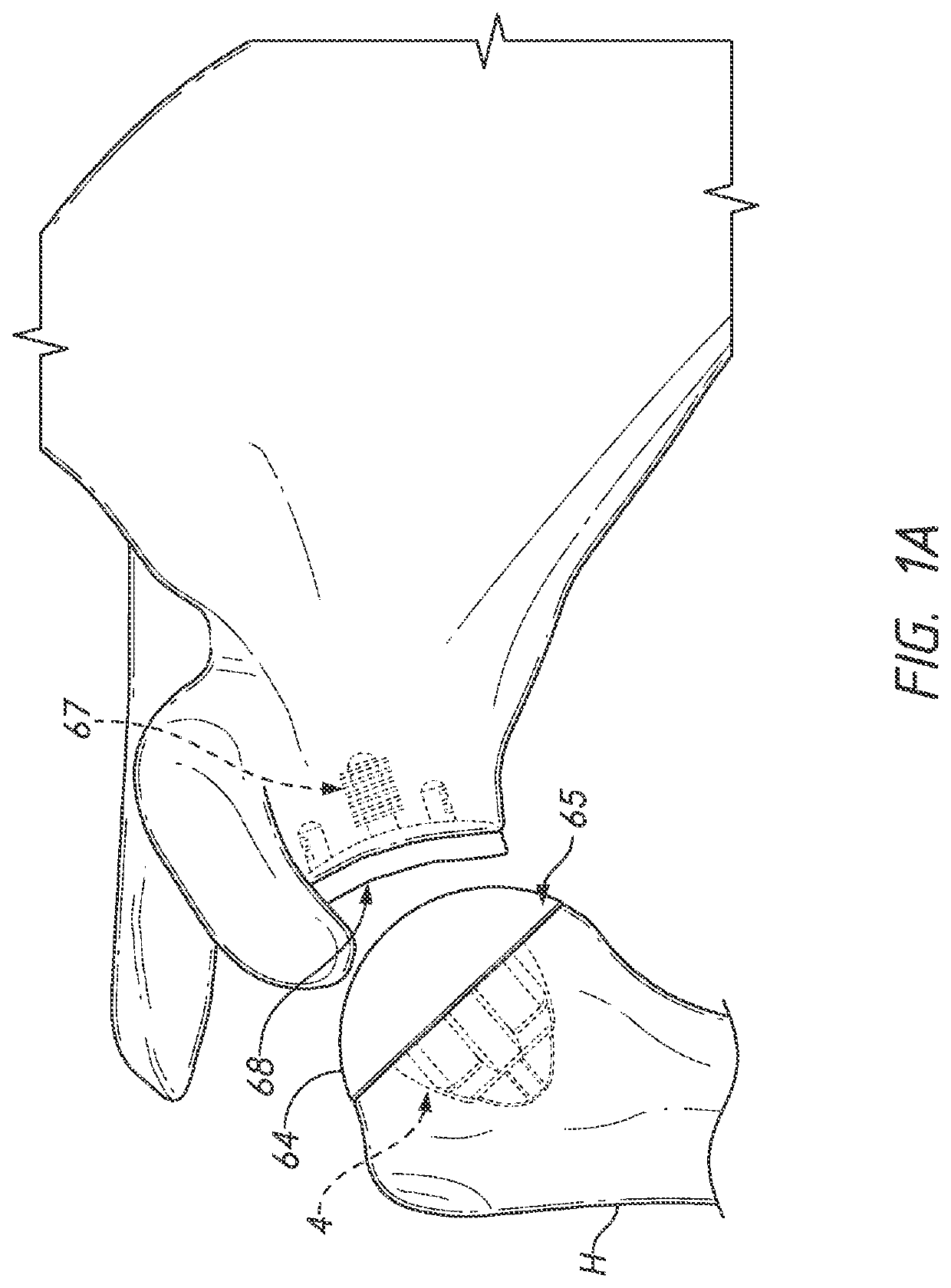
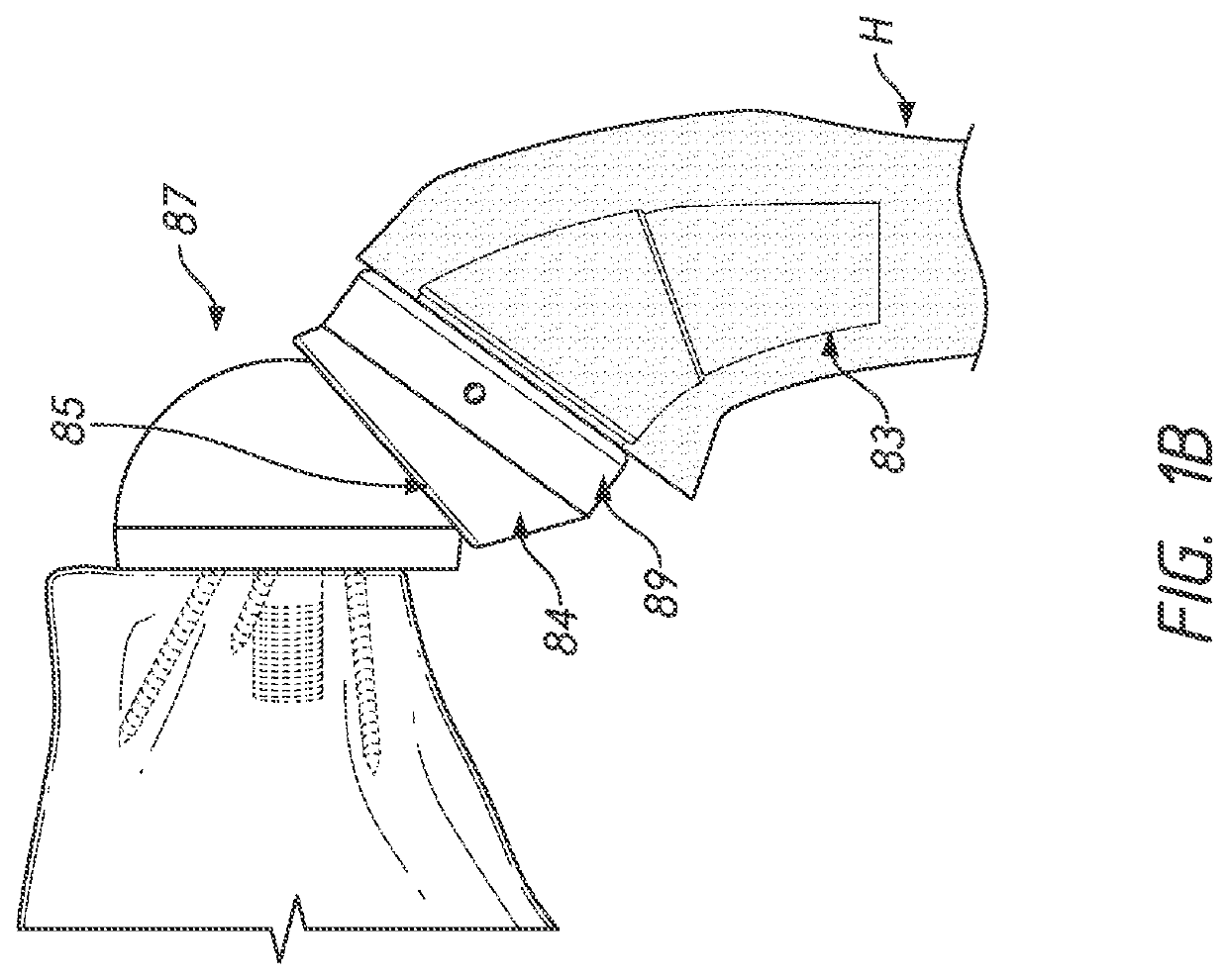
Humeral shoulder prosthesis
The humeral portion of a shoulder prosthesis includes a diaphyseal component configured for fixation within the humerus, a metaphyseal component, configured for removable implantation within the metaphysis of the humerus, and an engagement mechanism for removably engaging the two components. The metaphyseal component can initially include a convex articulating surface that can be replaced with a concave surface during the shoulder arthroplasty procedure or in a subsequent revision surgery. The metaphyseal component can also include a feature to facilitate removal of the component from the bone once it has been disengaged from the diaphyseal component.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Shoulder prosthesis having infinitely adjustable humeral head
InactiveUS6986790B2Joint implantsShoulder jointsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationThree-dimensional space
A humeral prosthesis allows a surgeon to adjust humeral head position thereof in three-dimensional space with respect to a humeral component of the humeral prosthesis that has been either previously implanted into a humerus of a patient or not. The humeral prosthesis includes a conjoining component that is configured to releasably mate with the humeral component and to releasably mate with a humeral head. The conjoining component allows the humeral head to be selectively positionable from continuously infinite positions about two orthographic axes with respect to the conjoining component. The selected spatial position of the head is locked by a locking member of the conjoining component. The conjoining component allows the use of various sized heads, allow in vivo head trialing and / or exchange, and retrofit of heads for previously implanted shoulder prosthesis in need of revision.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Device and method for positioning an eccentric humeral head of a humerus prosthesis for a shoulder arthroplasty
A kit and associated method is for implanting a prosthetic device in a resected bone such as a humerus. The kit includes a trial assembly including a trial body portion having a trial bore defined therein, and a trial head portion having (i) a trail head member which includes a trial offset indicia, and (ii) an eccentrically located trial stem extending from the trial head member, the trial head stem being configured to be received within the trial bore. The kit also includes a final prosthesis assembly including a final body portion having a final bore defined therein, and a final head portion having (i) a final head member which includes a final offset indicia, and (ii) an eccentrically located final head stem extending from the final head portion, the final head stem being configured to be received within the final bore.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Glenoid extension block
ActiveUS20130238099A1Easy maintenanceReliable toolJoint implantsShoulder jointsPlastic materialsHumerus
A glenoid implant has an anatomically formed body including of metal and / or plastic materials. It further has a contact surface adapted to extend the surface of a glenoid and to bear a humerus. In the implant body, there is at least one hole with a screw head seating area for holding the head of a screw, which may be screwed into a glenoid for fixedly attaching the glenoid implant.
Owner:ARTHREX
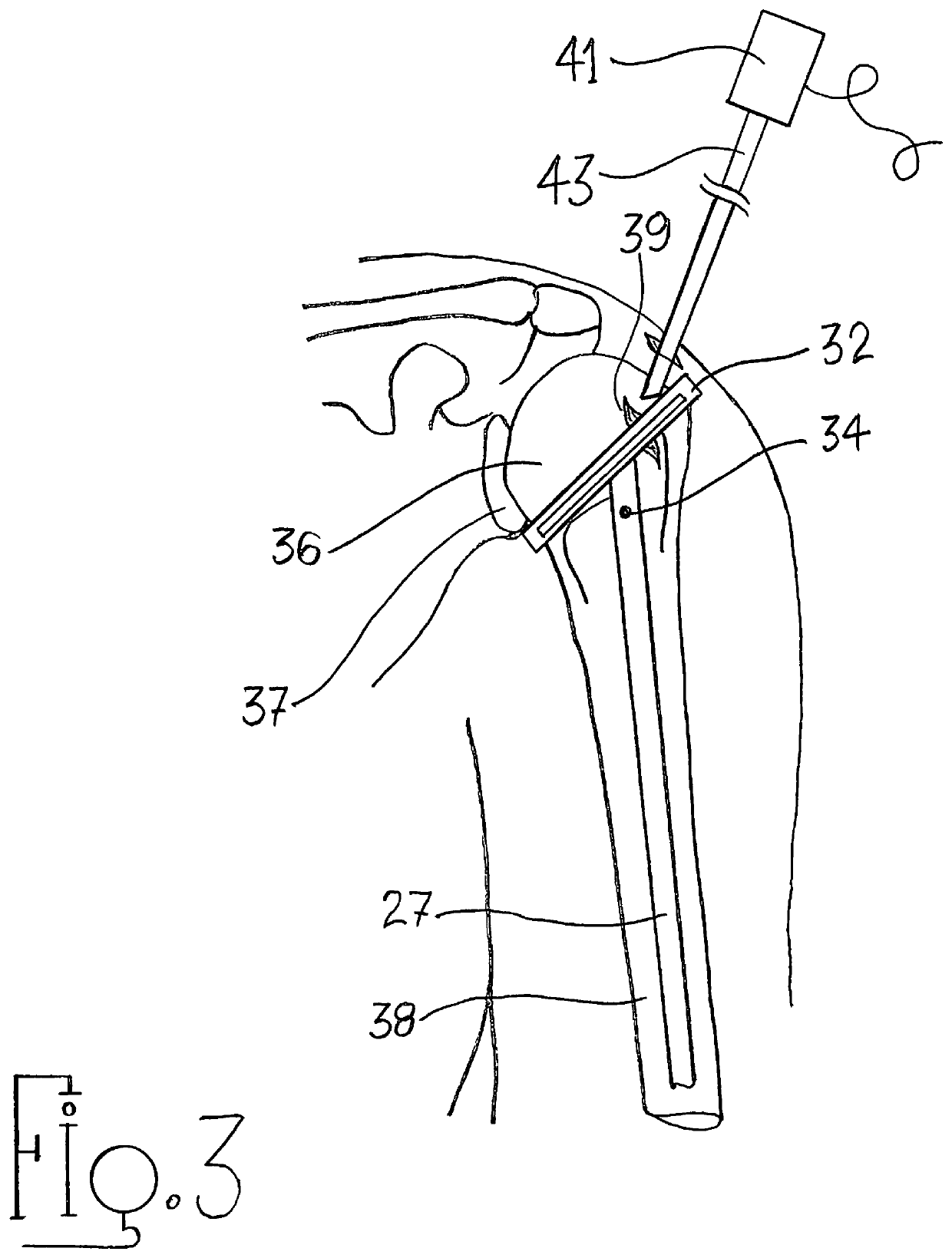
Stemless shoulder implant
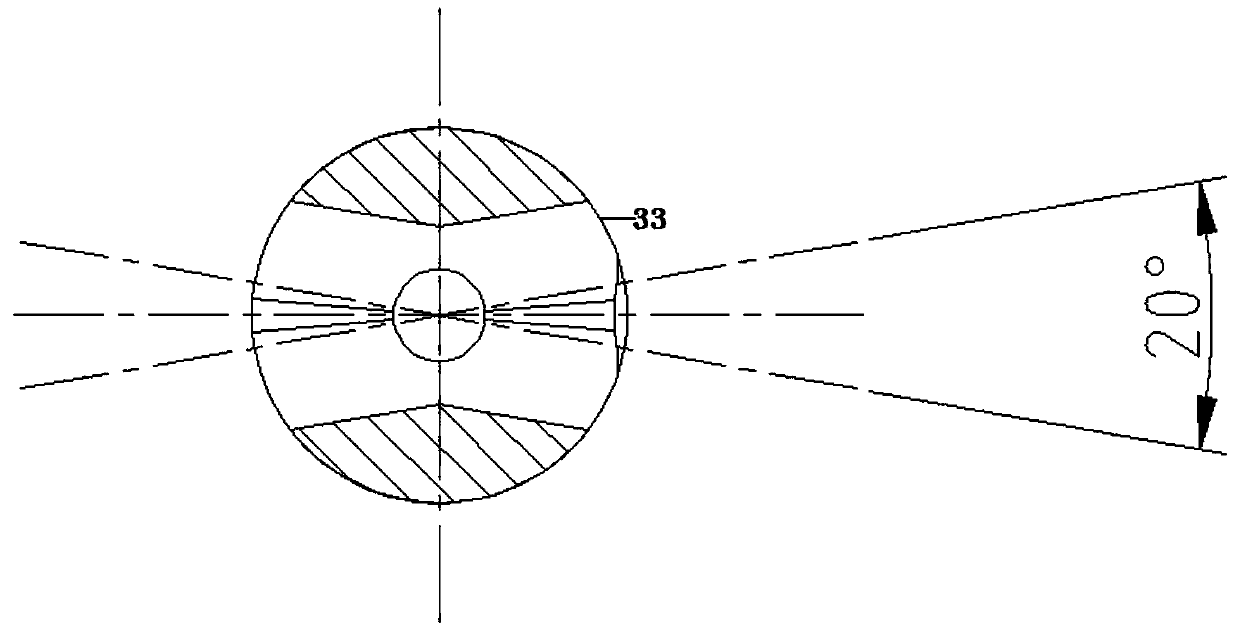
ActiveUS8512410B2Improve pullout forceInsertion torque is minimizedJoint implantsShoulder jointsAnatomyBone humerus
Owner:ARTHREX
Bone resection apparatus
ActiveUS20050021038A1Simple methodEliminates articulationJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesShoulder joint prosthesisShoulder replacement
A surgical assembly for resecting a greater tubercle from a humerus of a patient during performance of a shoulder replacement procedure. The surgical assembly includes a cutting tool for resecting the greater tubercle from the humerus. The surgical assembly also includes a tool guide member having a tool guide surface defined therein. The tool guide surface is configured to position the cutting tool in a predetermined position relative to the greater tubercle of the humerus.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
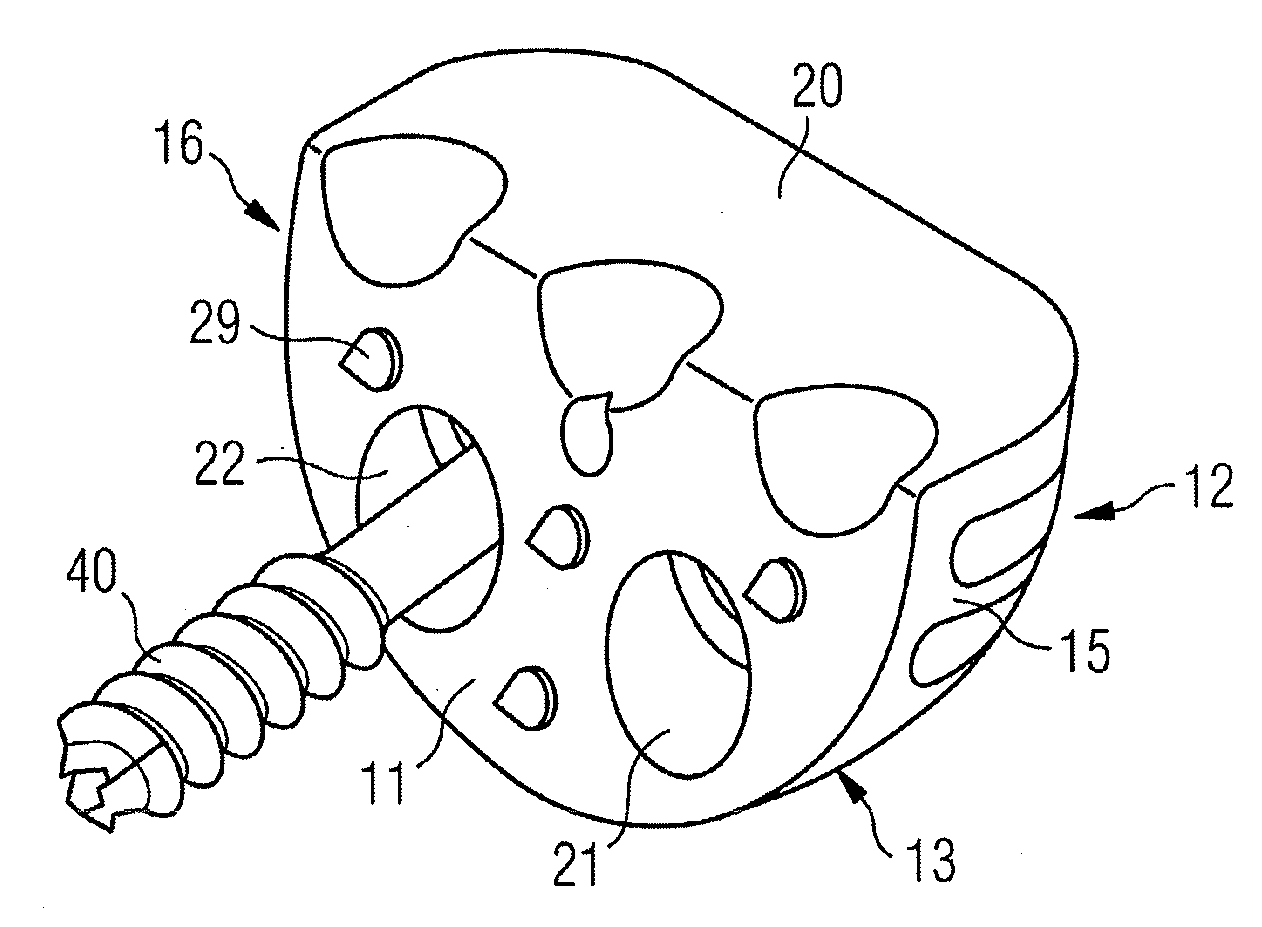
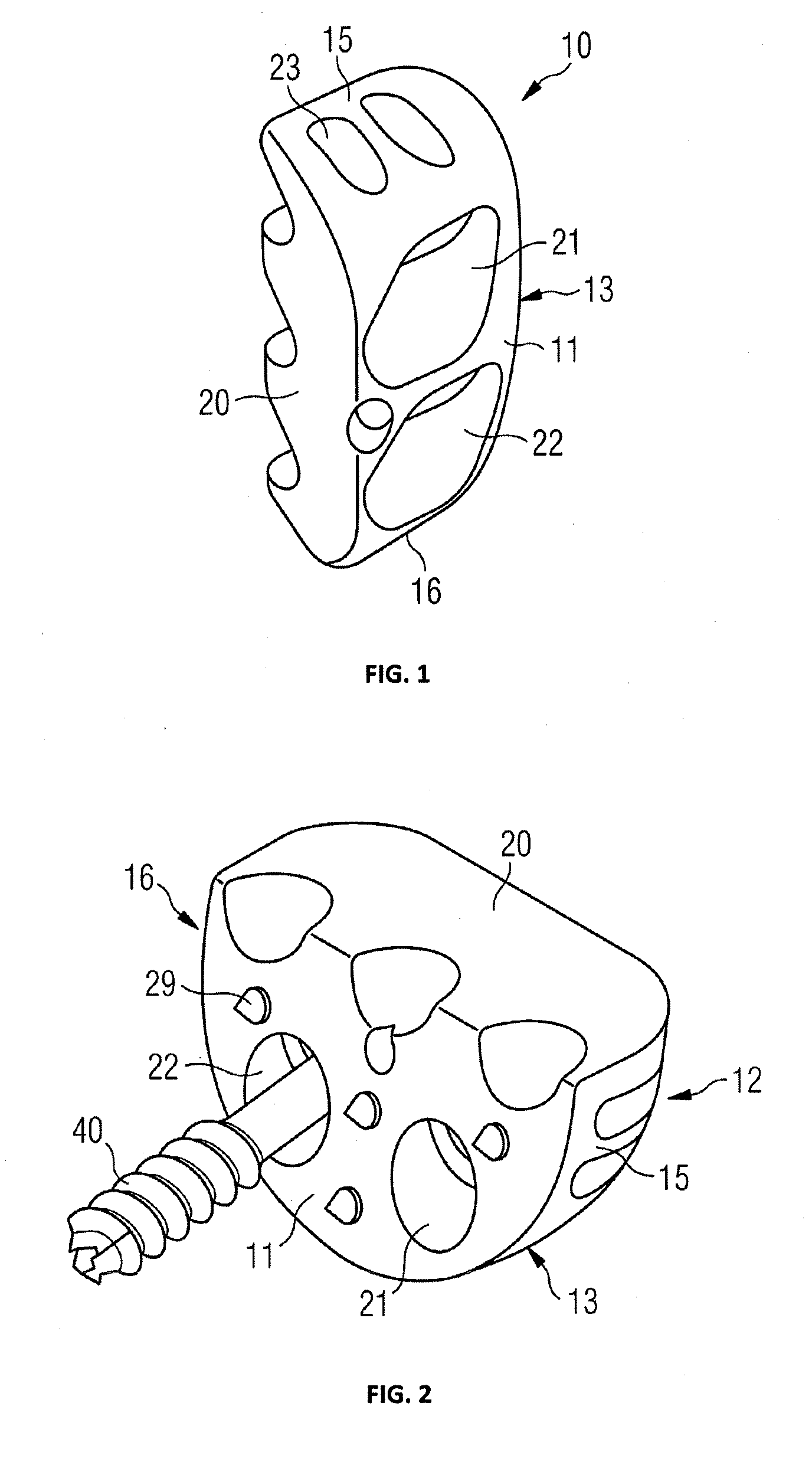
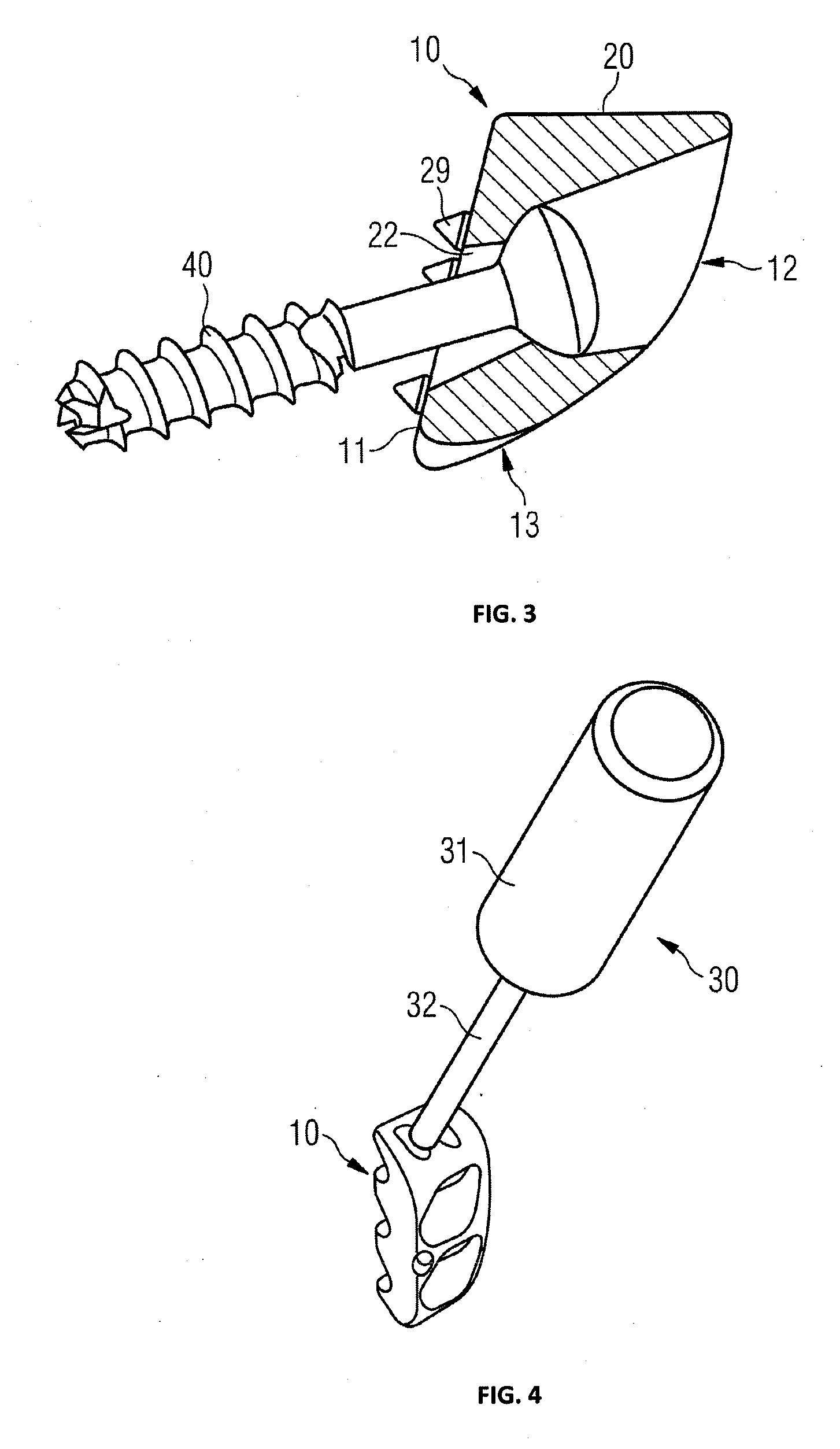
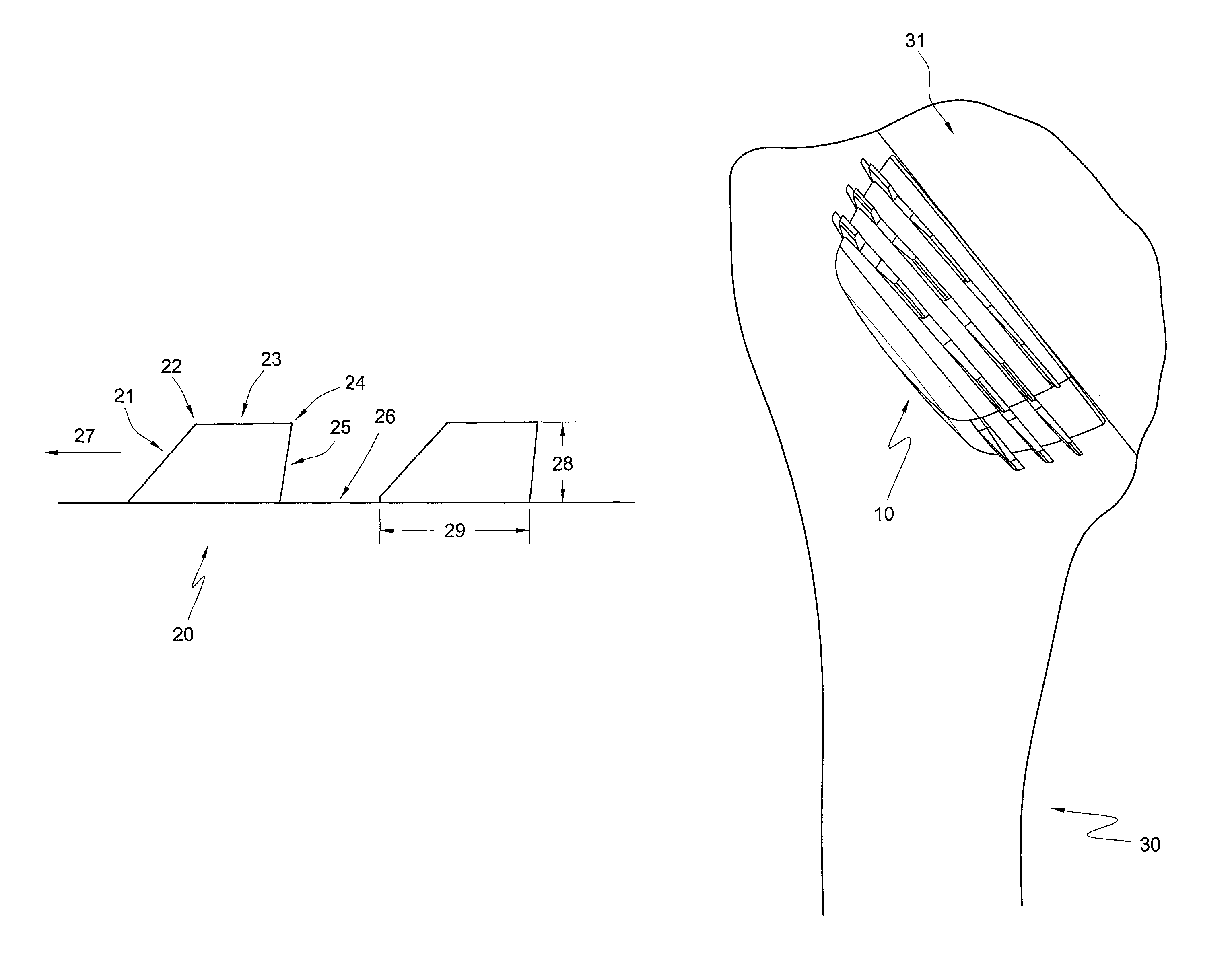
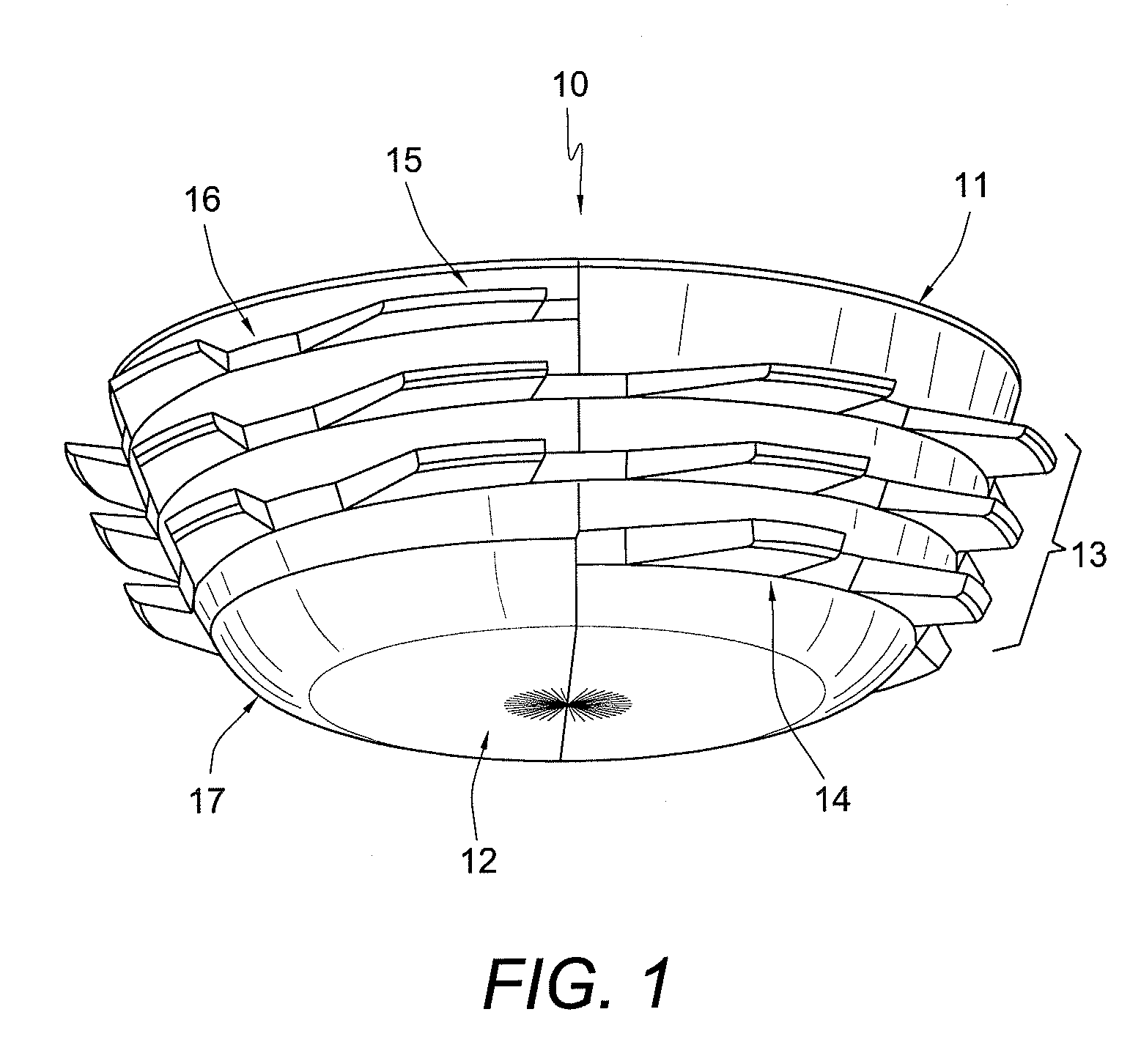
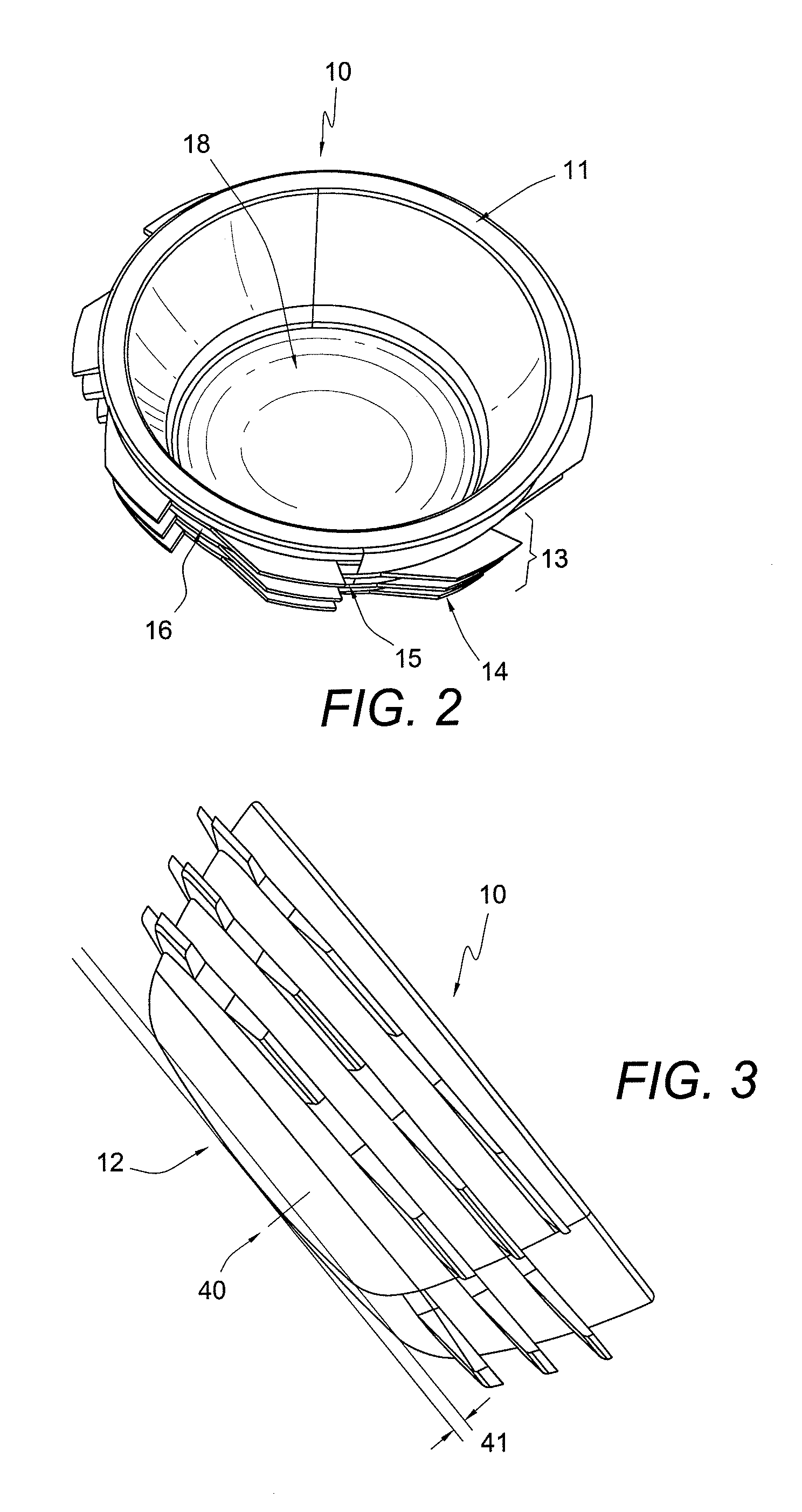
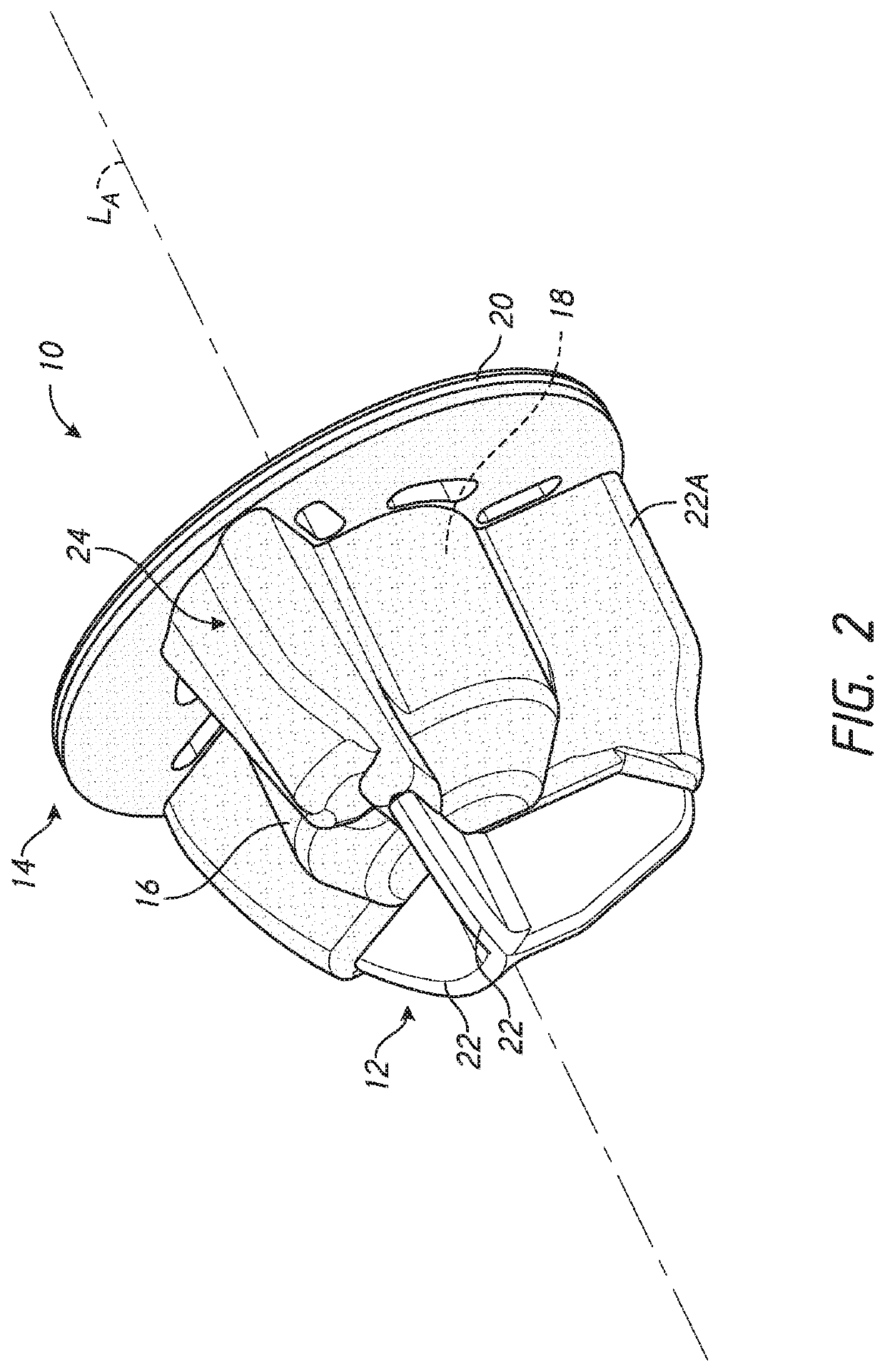
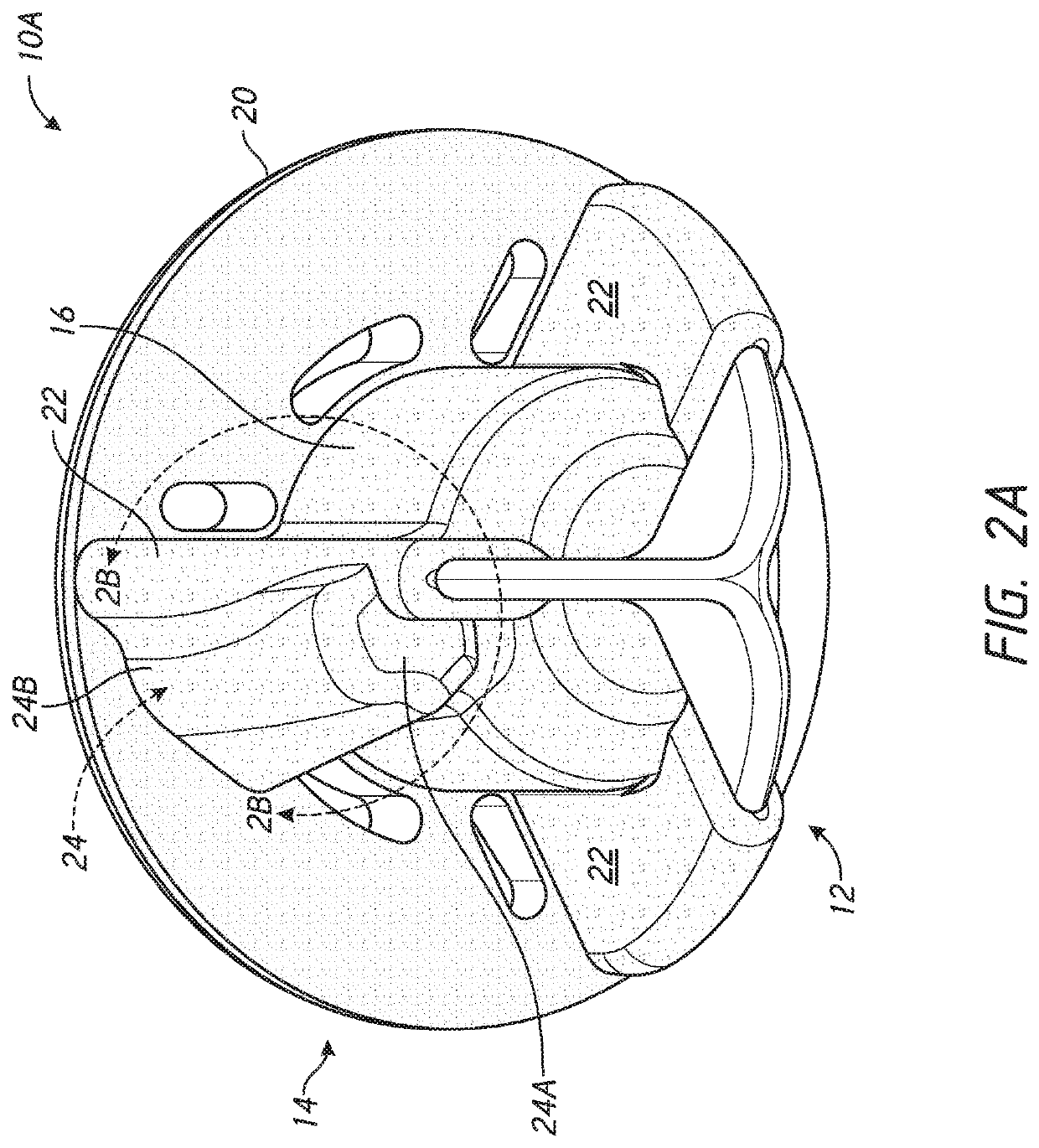
Patient specific stemless prosthesis anchor components
PendingUS20200214845A1Reduce bone erosionReduce degradationJoint implantsShoulder jointsAnatomyBone humerus
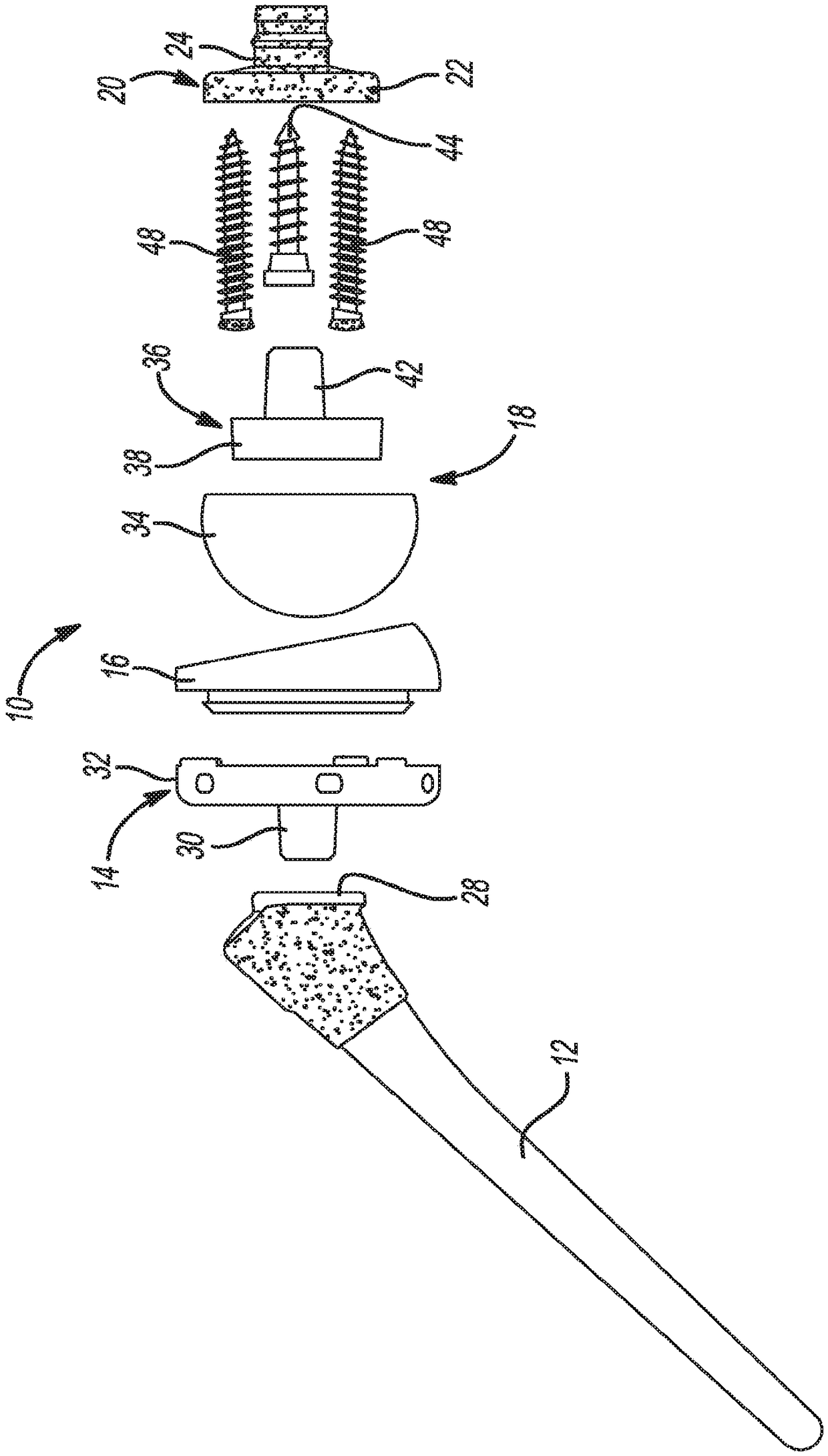
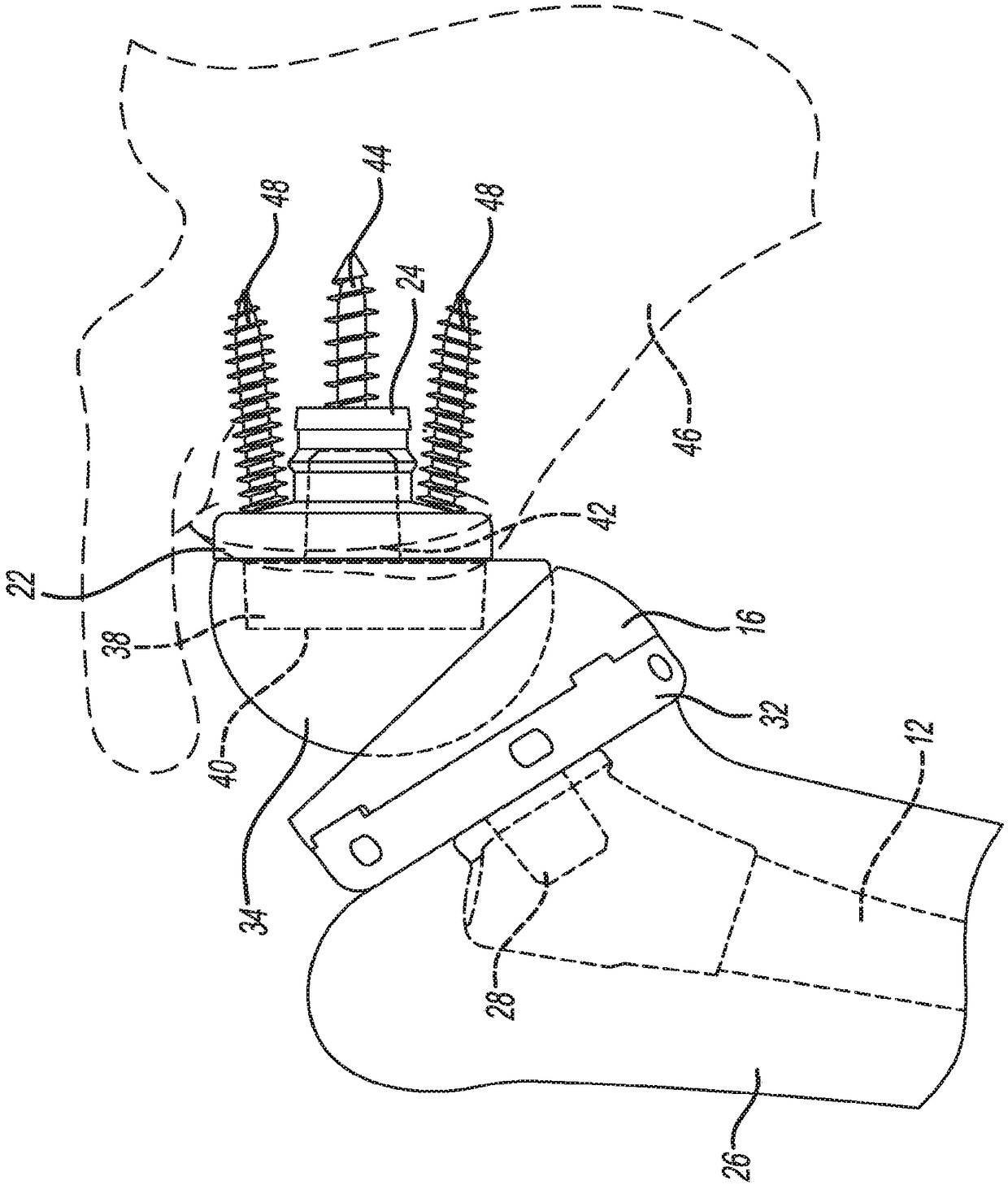
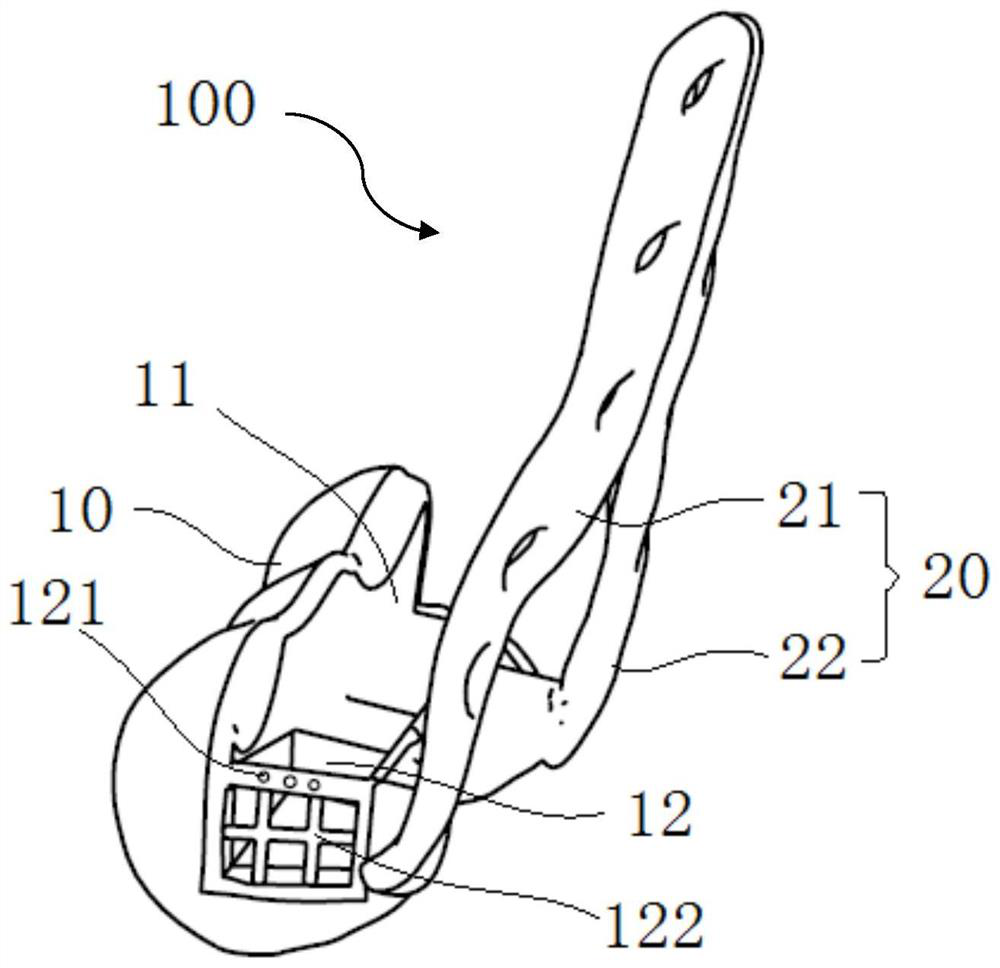
A stemless humeral anchor (10) includes a first end (12) configured to be embedded in a proximal portion of a humerus and a second end (14); a mating portion (16) for an articular component; a transversely extending collar (20); and a rotation control feature (22, 22A) for resisting rotation when the stemless humeral anchor is implanted. A void filling protrusion (24) can extend circumferentially from rotation control feature and can include a porous shell (26), in which a void filling component (28) can be disposed. The rotation control feature can comprise arms. One or more arms (22A) can have a larger radial extent than the others (22). A prosthesis assembly includes a base member (104) that has a helical structure (224) and one or more pathways (300). The pathway is accessible from a proximal end and is directed distally through the helical structure. The pathway is located inward of an outer periphery of the helical structure. The pathway extends in a space between successive portions of the helical structure. The prosthesis assembly includes a locking device (108) that has a support member (132) and an arm (110) that projects away from the support member. The arm is disposed in the pathway when the support member is disposed adjacent to the proximal end of the base member. The arm is disposed through bone in the space between successive portions of the helical structure when the prosthesis assembly is implanted.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
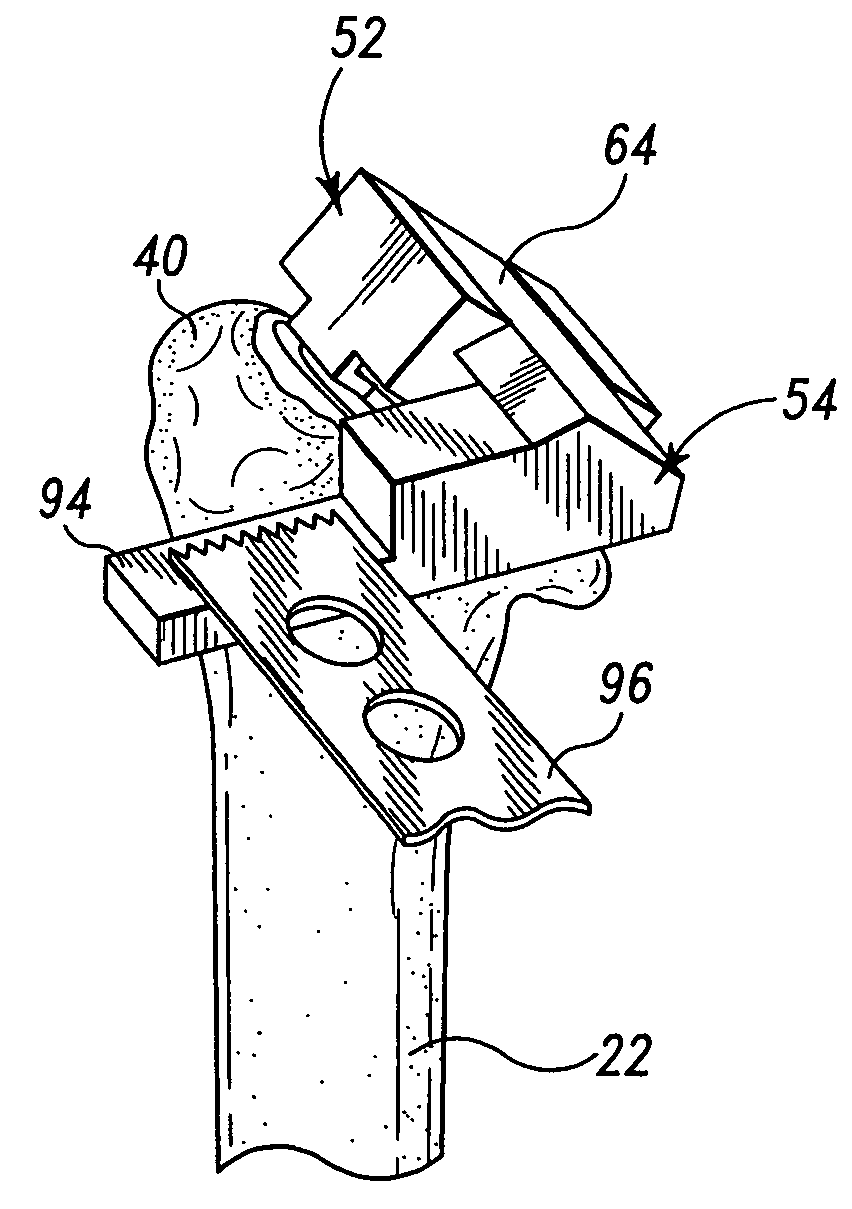
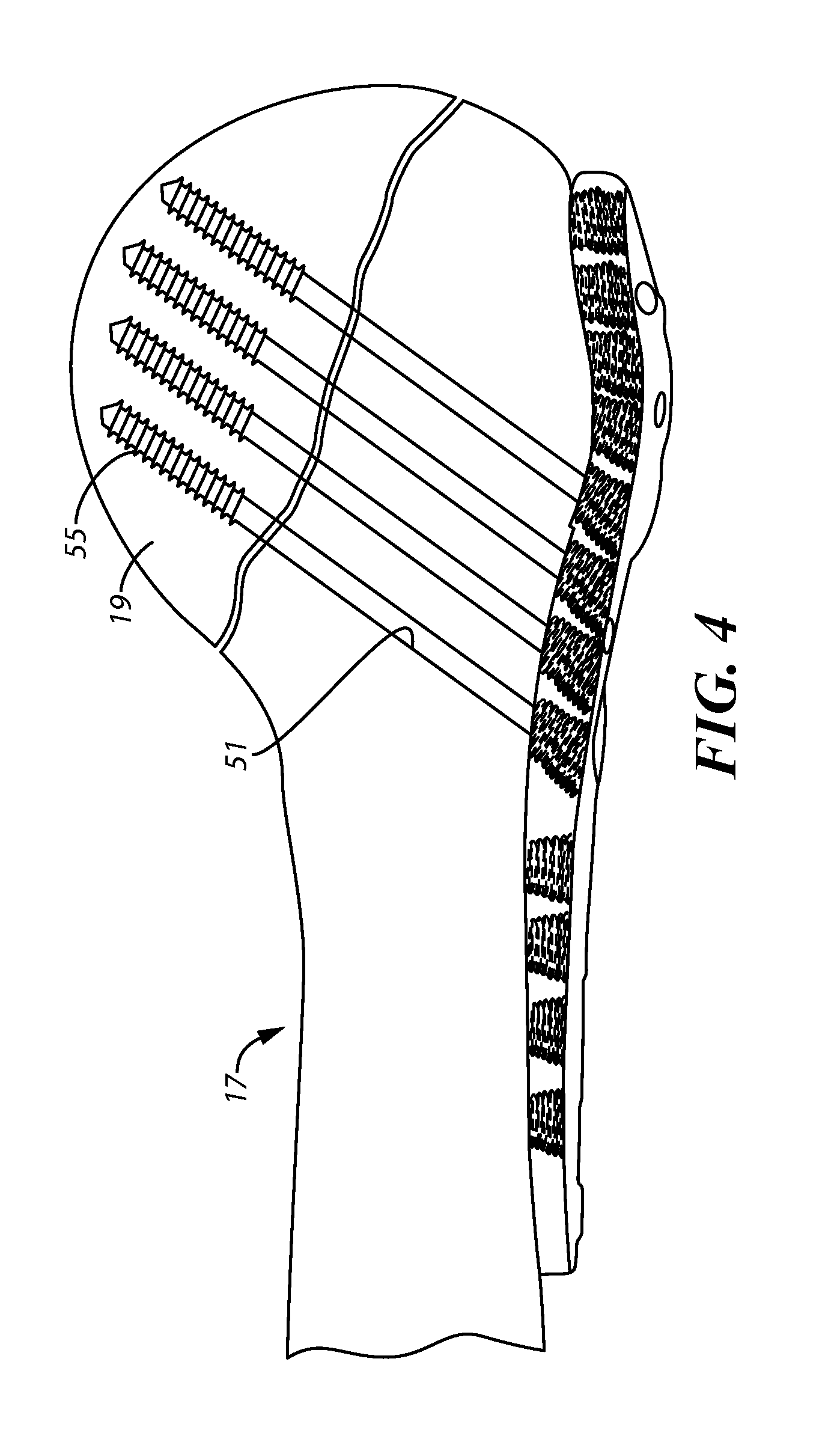
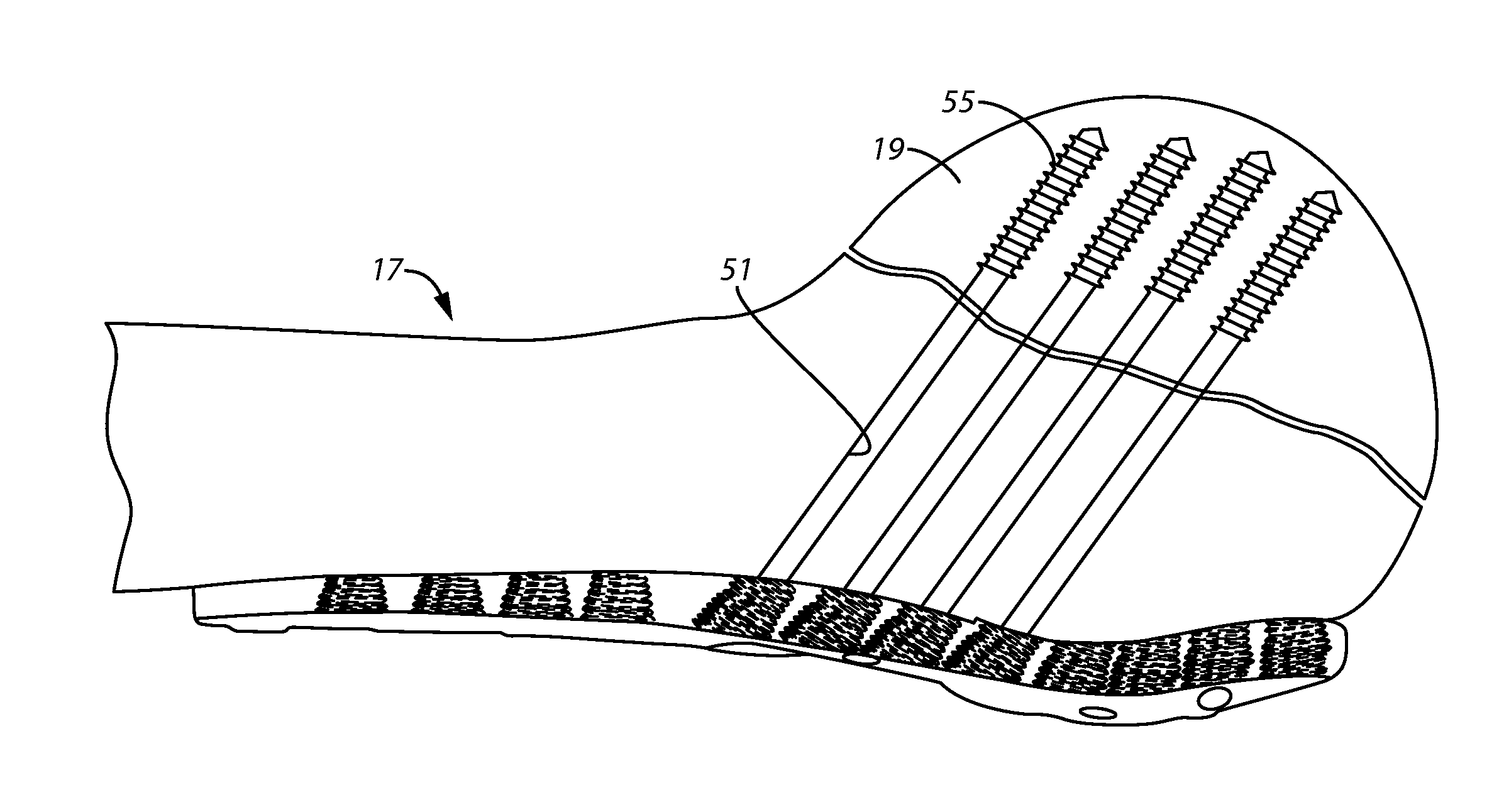
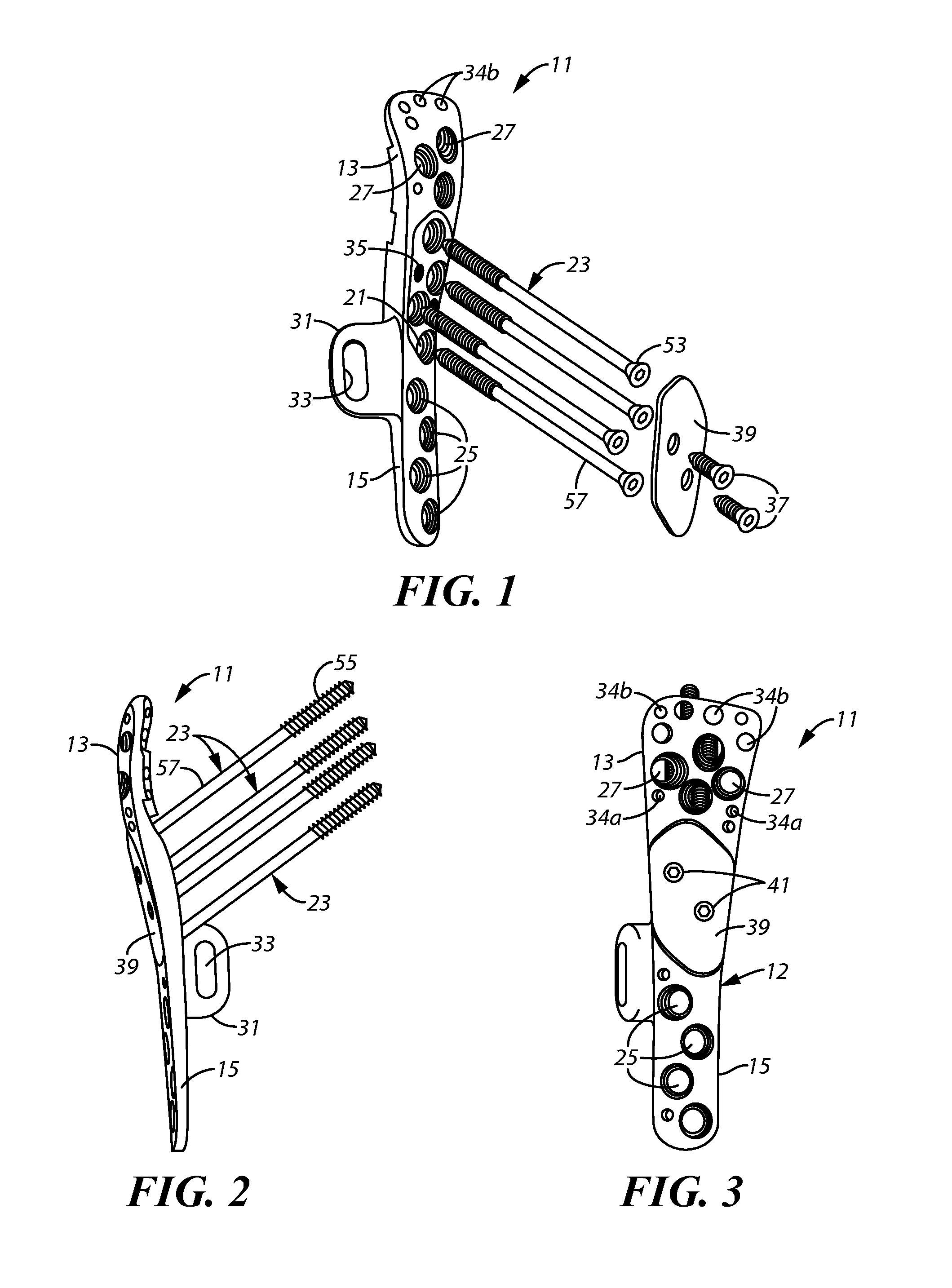
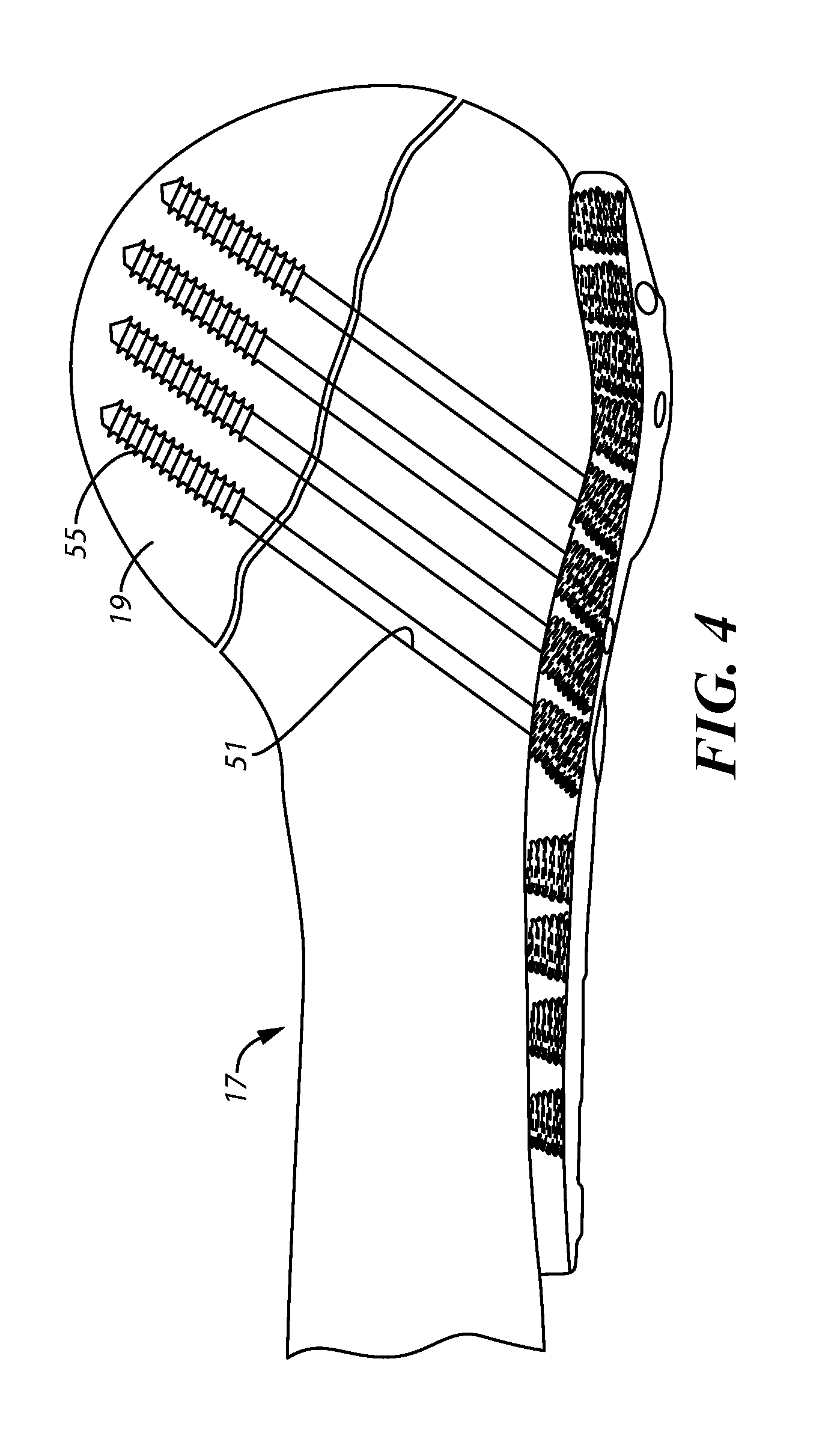
Bone plate system for repair of proximal humeral fracture
A bone plate system for repair of a proximal humeral head fracture, which includes a fixation plate having a main body and a depending alignment flange, a plurality of elongated compression screws to extend through the intact humeral head into the cortical bone of the fractured portion and a cover plate. With the fixation plate in place, fastened to the humerus, the cover plate is in turn fastened to the fixation plate and provides a defined amount of clearance in a region adjacent the heads of the compression screws to allow measured back-out of the screws upon settling of the fractured bone portion at the fracture site.
Owner:ASCENSION ORTHOPEDICS
Bone plate system for repair of proximal humeral fracture
A bone plate system for repair of a proximal humeral head fracture, which includes a fixation plate having a main body and a depending alignment flange, a plurality of elongated compression screws to extend through the intact humeral head into the cortical bone of the fractured portion and a cover plate. With the fixation plate in place, fastened to the humerus, the cover plate is in turn fastened to the fixation plate and provides a defined amount of clearance in a region adjacent the heads of the compression screws to allow measured back-out of the screws upon settling of the fractured bone portion at the fracture site.
Owner:ASCENSION ORTHOPEDICS
Shoulder prosthesis and a system for implanting a shoulder prosthesis
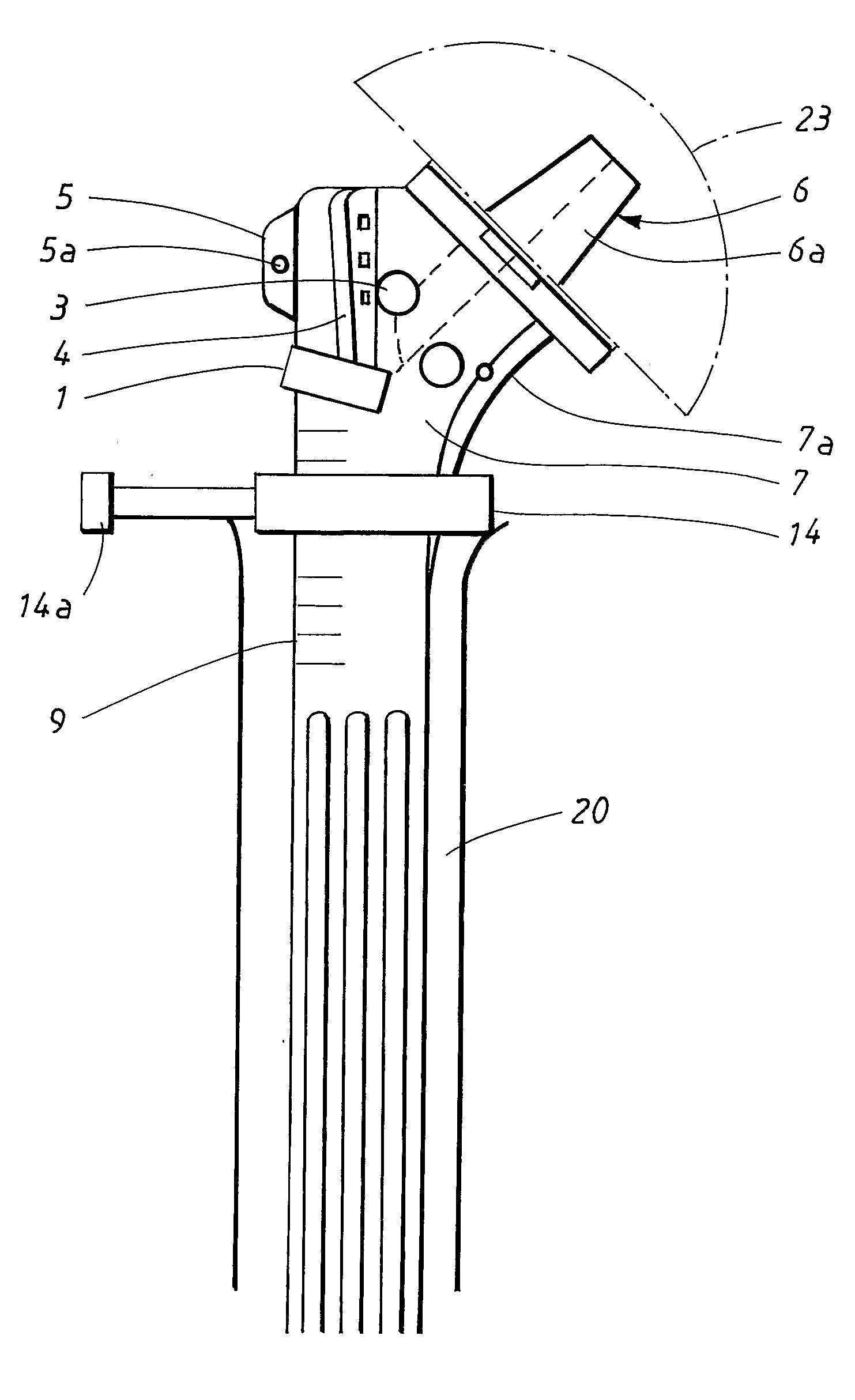
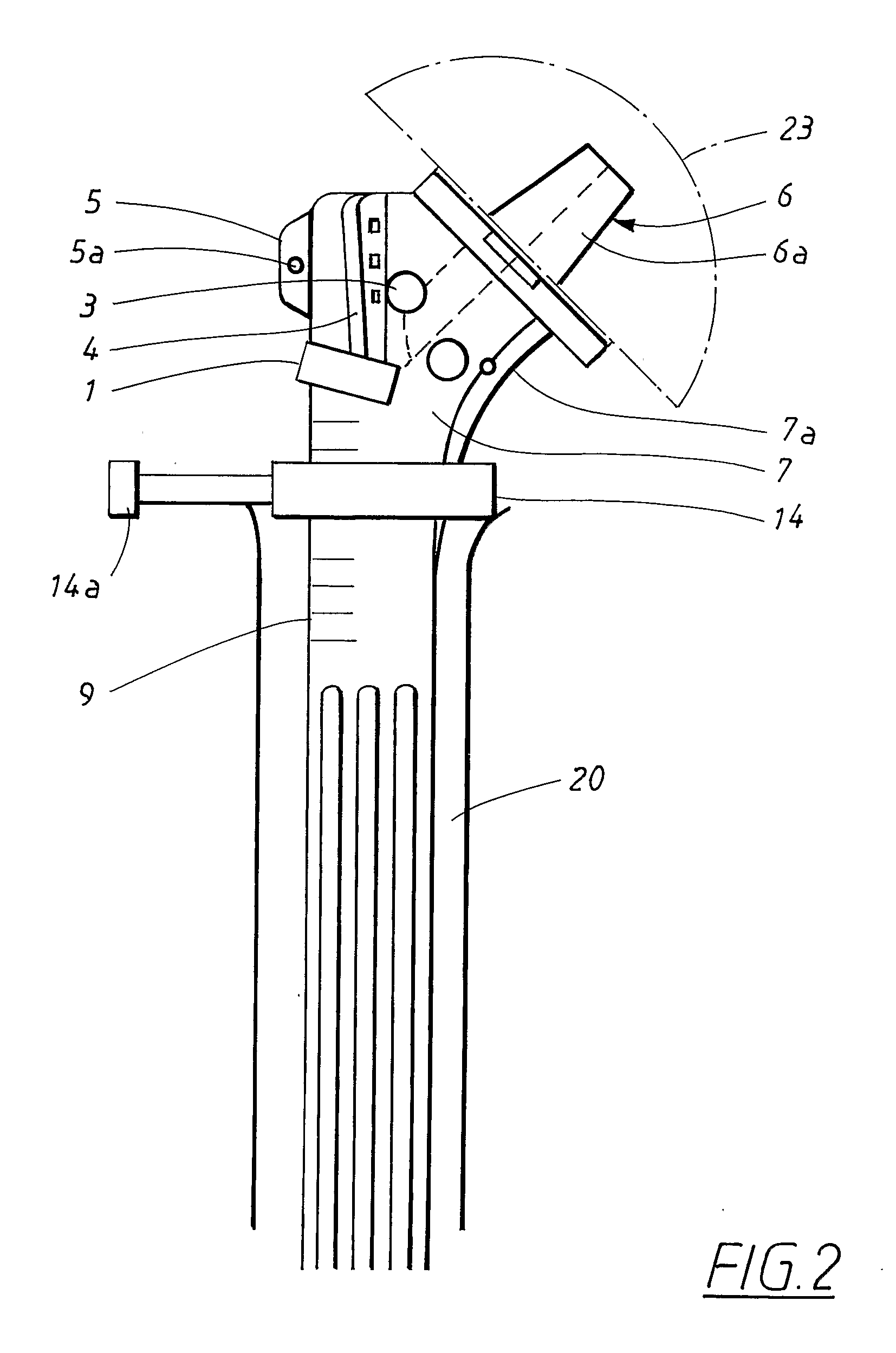
Shoulder prosthesis, including a stem provided to be inserted into a canal of the humerus shaft, a neck and a head supported by the neck. The neck is provided with two holes (1, 2) for anchoring screws (1a, 2a), namely a first hole (1) for a lateral anchoring screw (1a) and a second hole (2) for an anterior anchoring screw (2a). The lateral anchoring screw is provided to attach a first tubercle laterally to the neck and the anterior anchoring screw is provided to attach a second tubercle anterior to the neck. A system for implanting a shoulder prosthesis, comprises a targeting arm attachable to the neck of the prosthesis and is provided with guide means for guiding anchoring screws (1a, 2a) to be screwed into at least a lateral hole (1) and an anterior hole (2) in the neck. The targeting arm is also provided for holding a trial prosthesis.
Owner:EKHOLM CARL +1
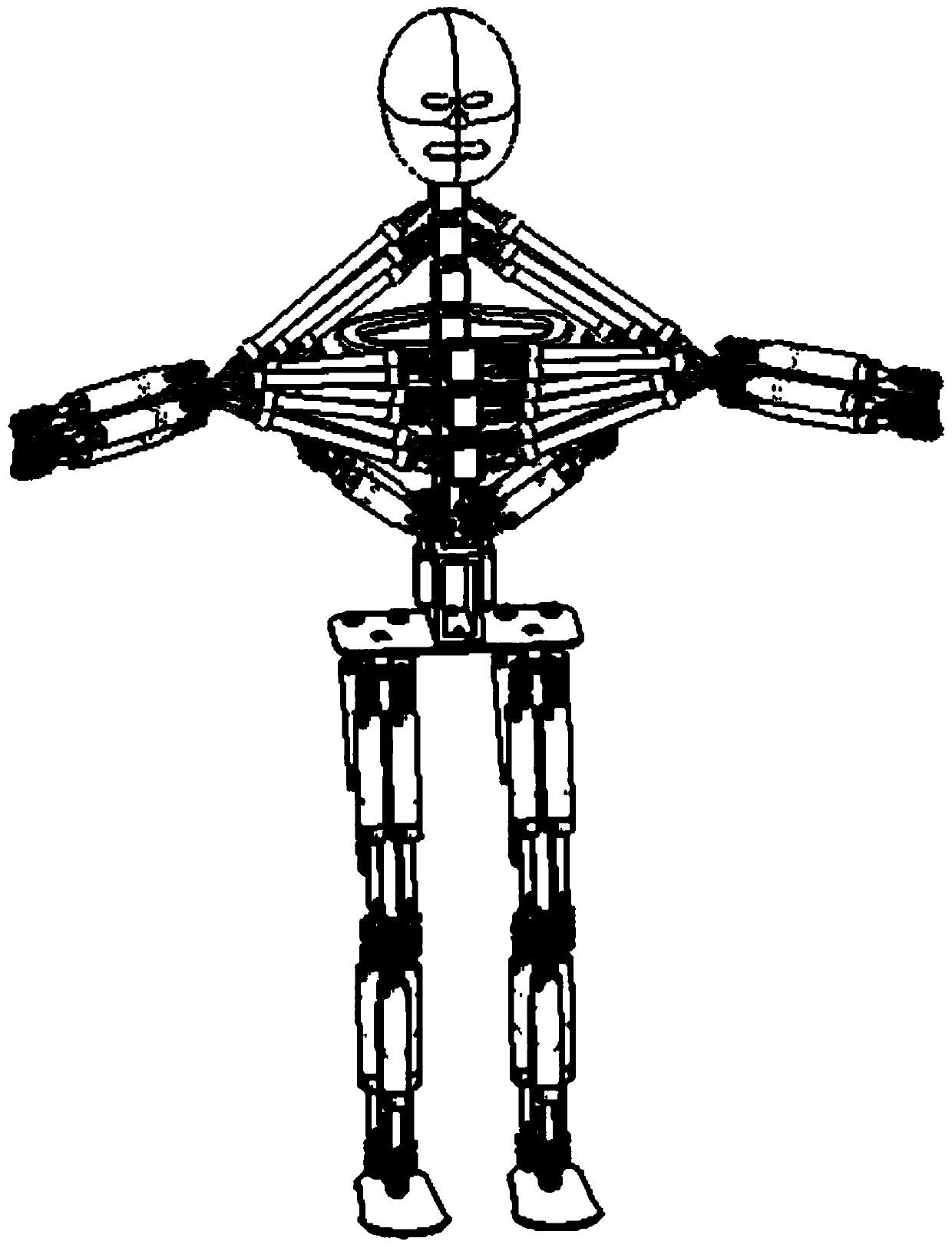
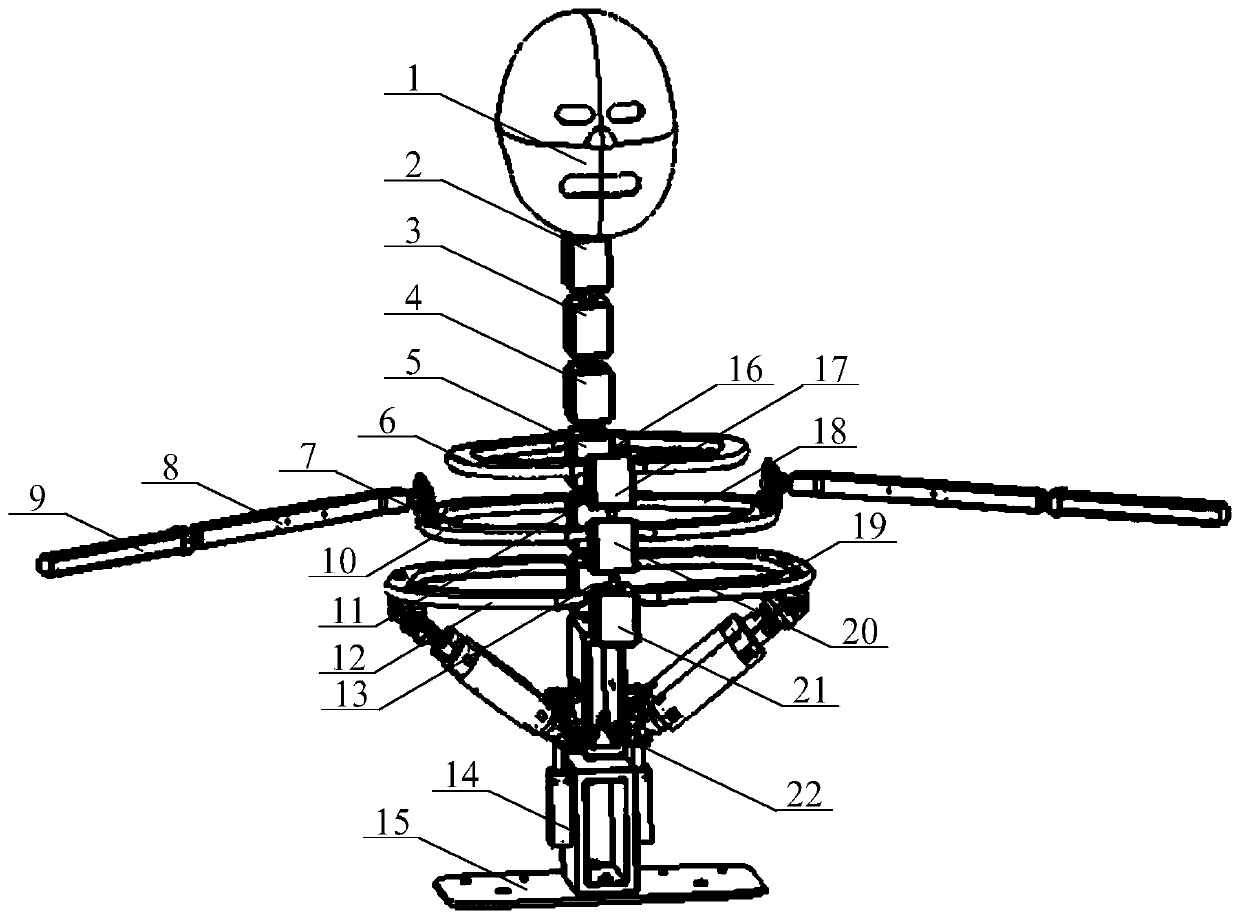
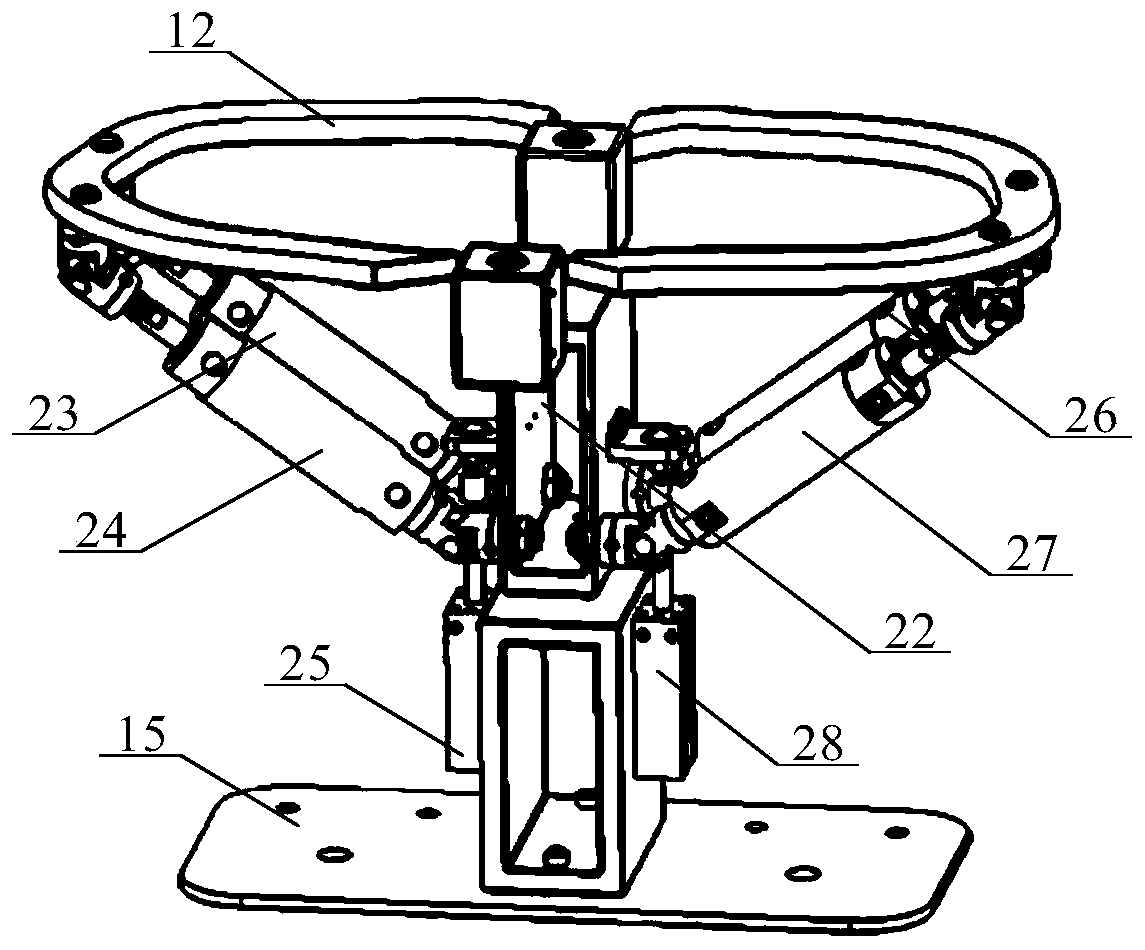
A Humanoid Robot System Based on Pneumatic Muscle and Cylinder
InactiveCN108466256BHigh power/mass ratioImprove flexibilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorVehiclesBone humerusEngineering
The invention discloses a humanoid robot system based on pneumatic muscles and air cylinders. The pneumatic muscles and the air cylinders are used for driving shoulder joints, elbow joints, a waist joint, a hip joint, knee joints and ankle joints of a humanoid robot to move. The robot is mainly composed of a skull, vertebrae, ribs, humeri, radii, fixed parts, thighbones, fibulae, the pneumatic muscles, the air cylinders and feet. The shoulder joints, the elbow joints, the waist joint, the hip joint, the knee joints and the ankle joints respectively have three, three, four, three, three and four degrees of freedom, the whole system has 34 degrees of freedom, the shoulder joints are distributed and driven in a flexible redundant form by nine pneumatic muscles from the vertebrae, and talocrural joints are formed by a parallel mechanism which is supported by the middle air cylinder of three air cylinders uniformly distributed on the periphery, so that the free switching of rotation and movement is realized. The humanoid robot system is driven by the pneumatic muscles and the air cylinders at the same time and has the advantages of compact structure, cleanness and good explosion-proof performance and can be used for exhibition, meeting and teaching demonstration.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
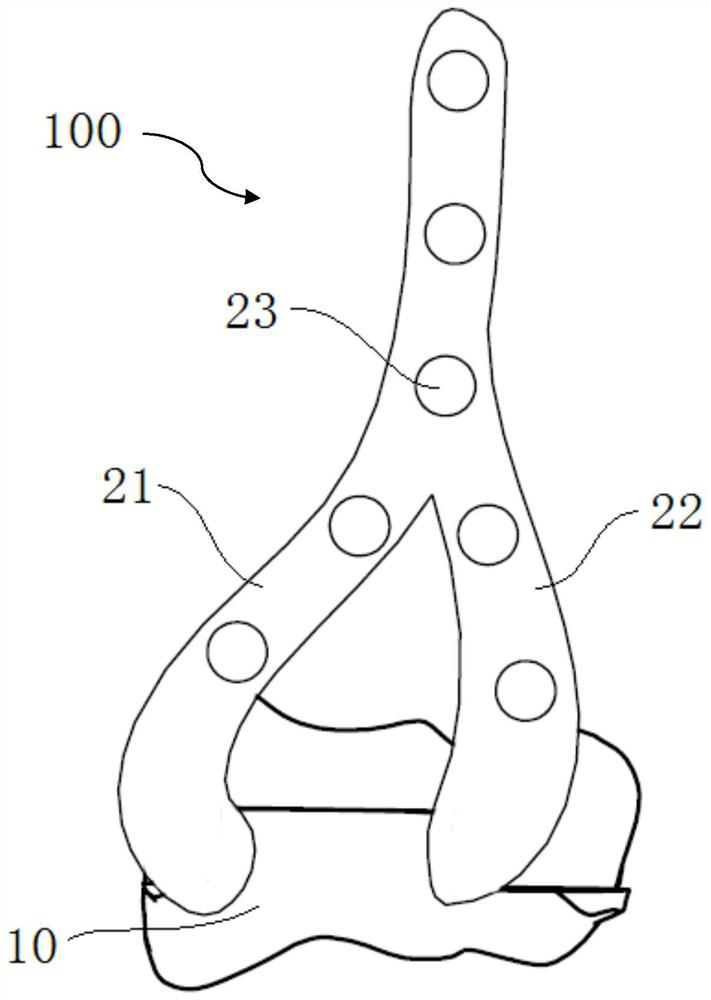
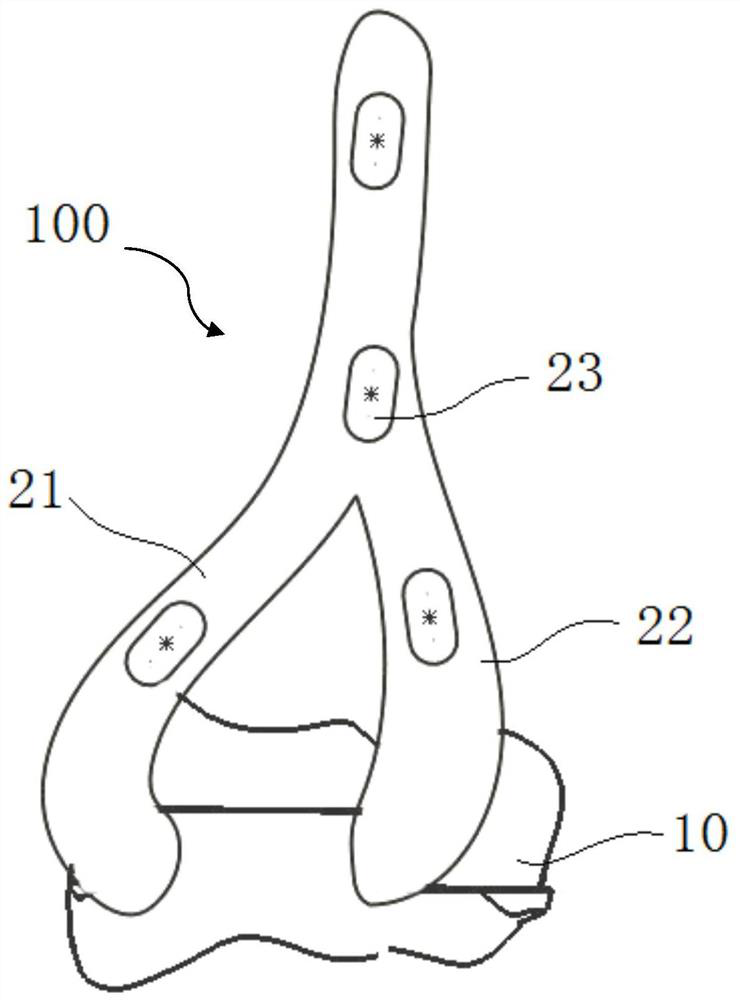
Proximal humerus greater tuberosity hook-arm clip
InactiveUS20130060251A1Stabilizing a fractured greater tuberosityStabilizing the fractured greater tuberosityJoint implantsBone platesAnatomyBone humerus
The invention relates to a bone plate for stabilizing a fractured greater tuberosity, wherein the bone plate comprises one or more apertures for fixing the bone plate to bone; one or more hook-arm receivers; one or more attachable hook-arms comprising one or more prongs and a device for attachment to the bone plate. The invention also relates to methods for stabilizing a fractured greater tuberosity using the bone plates of the invention and kits comprising the same.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
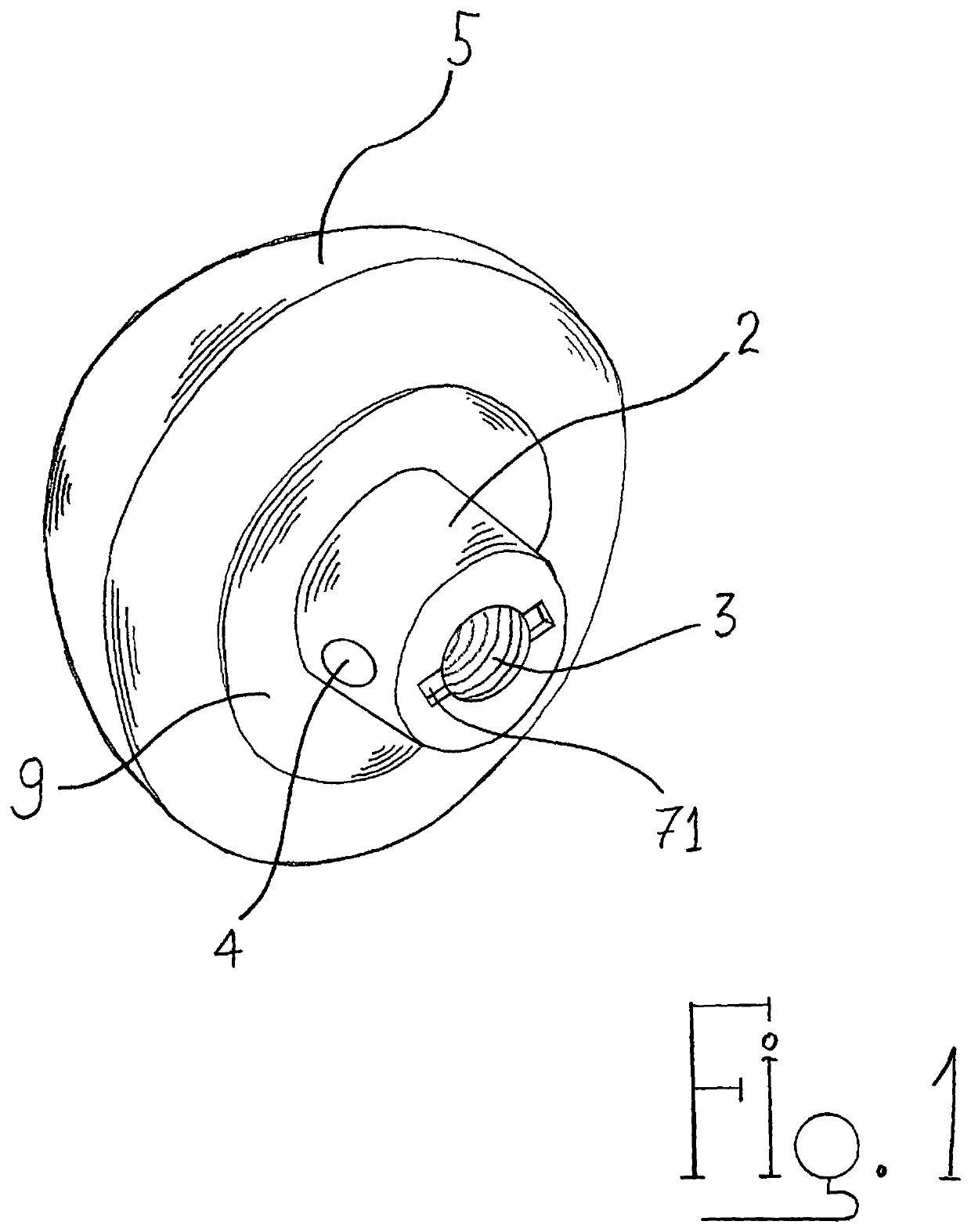
Composite shoulder prosthesis
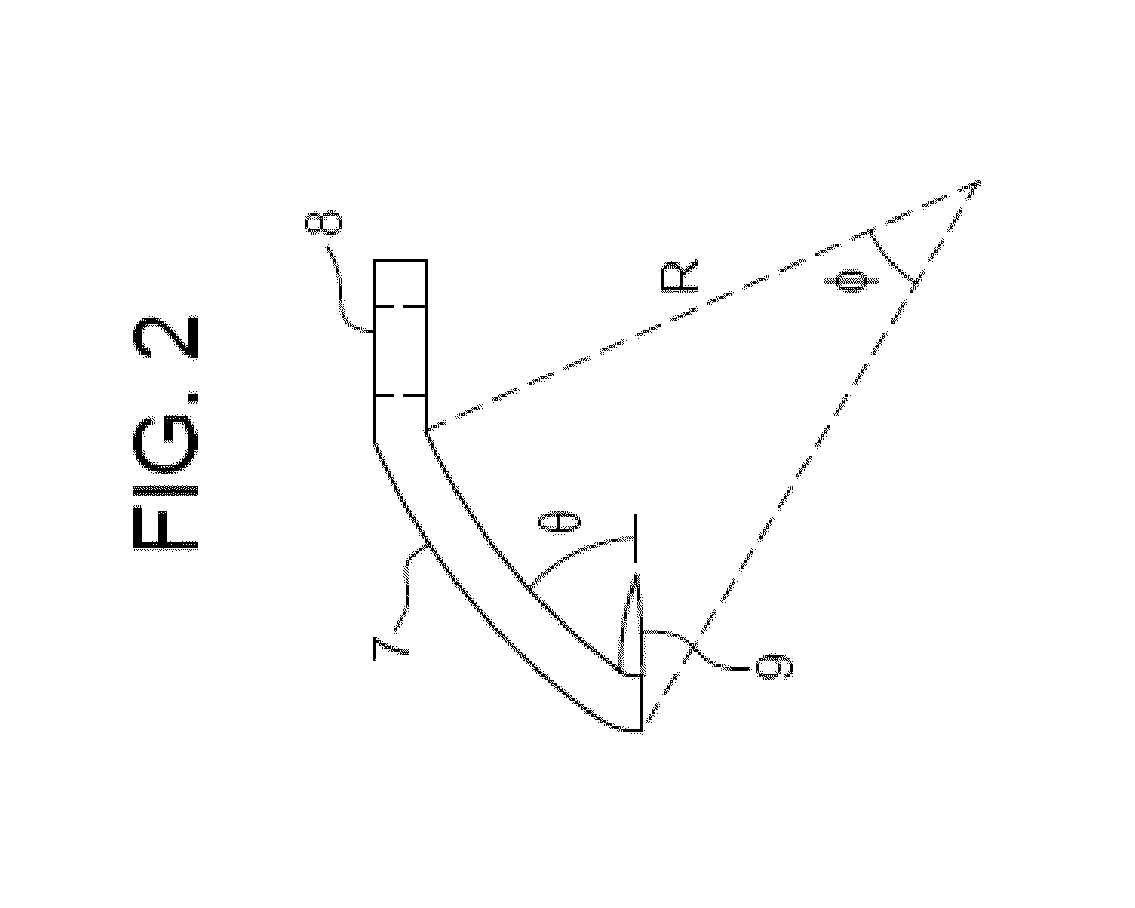
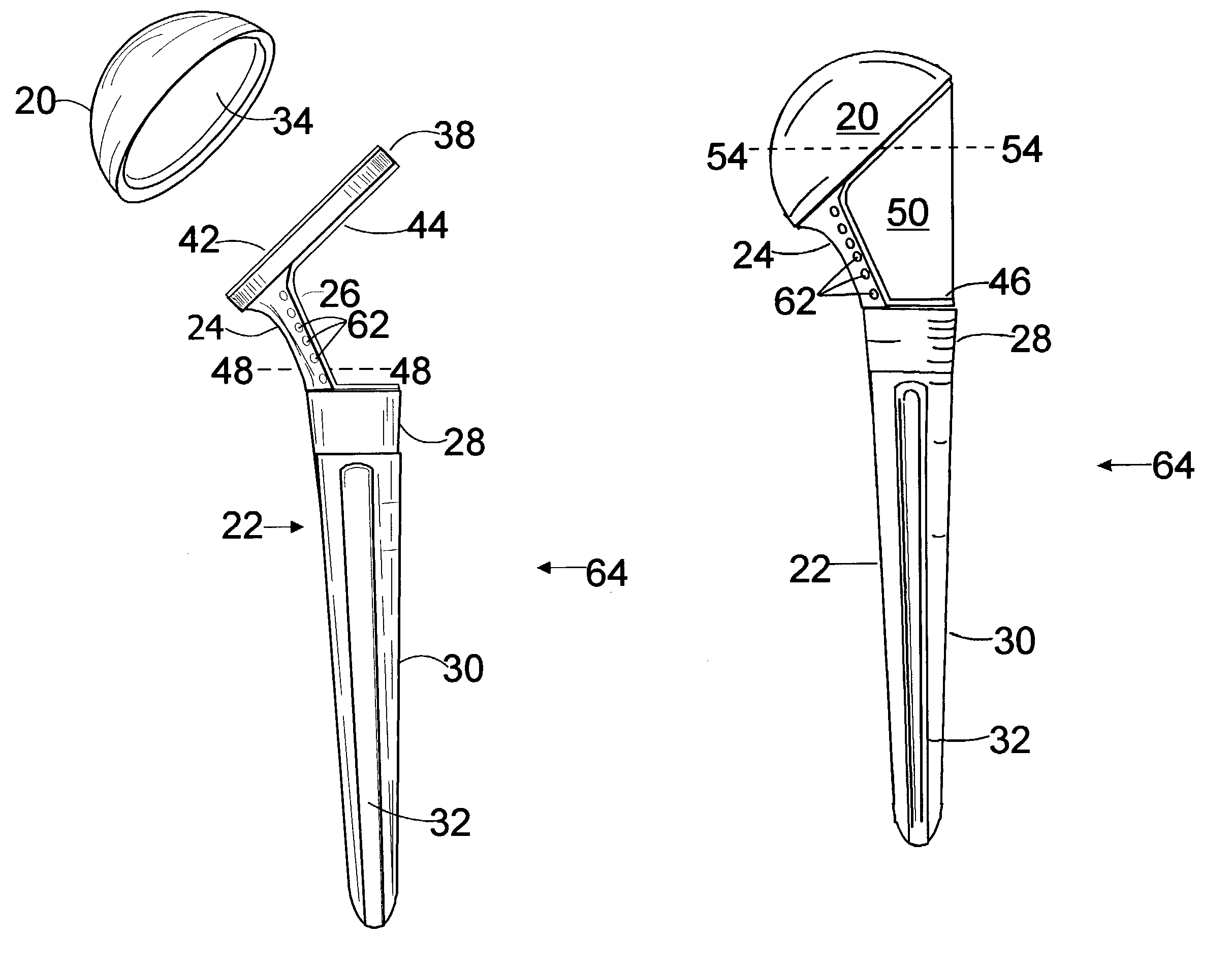
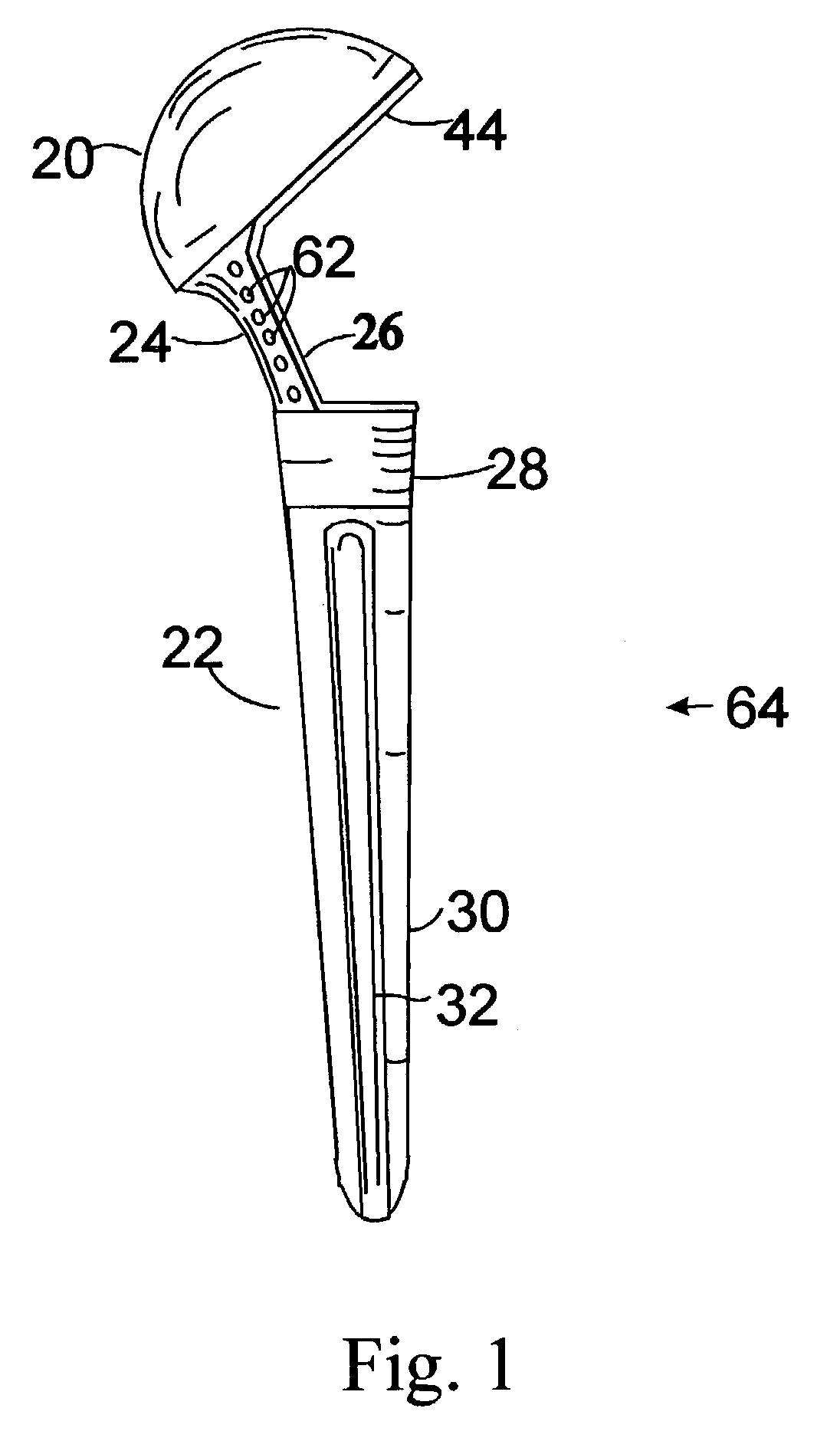
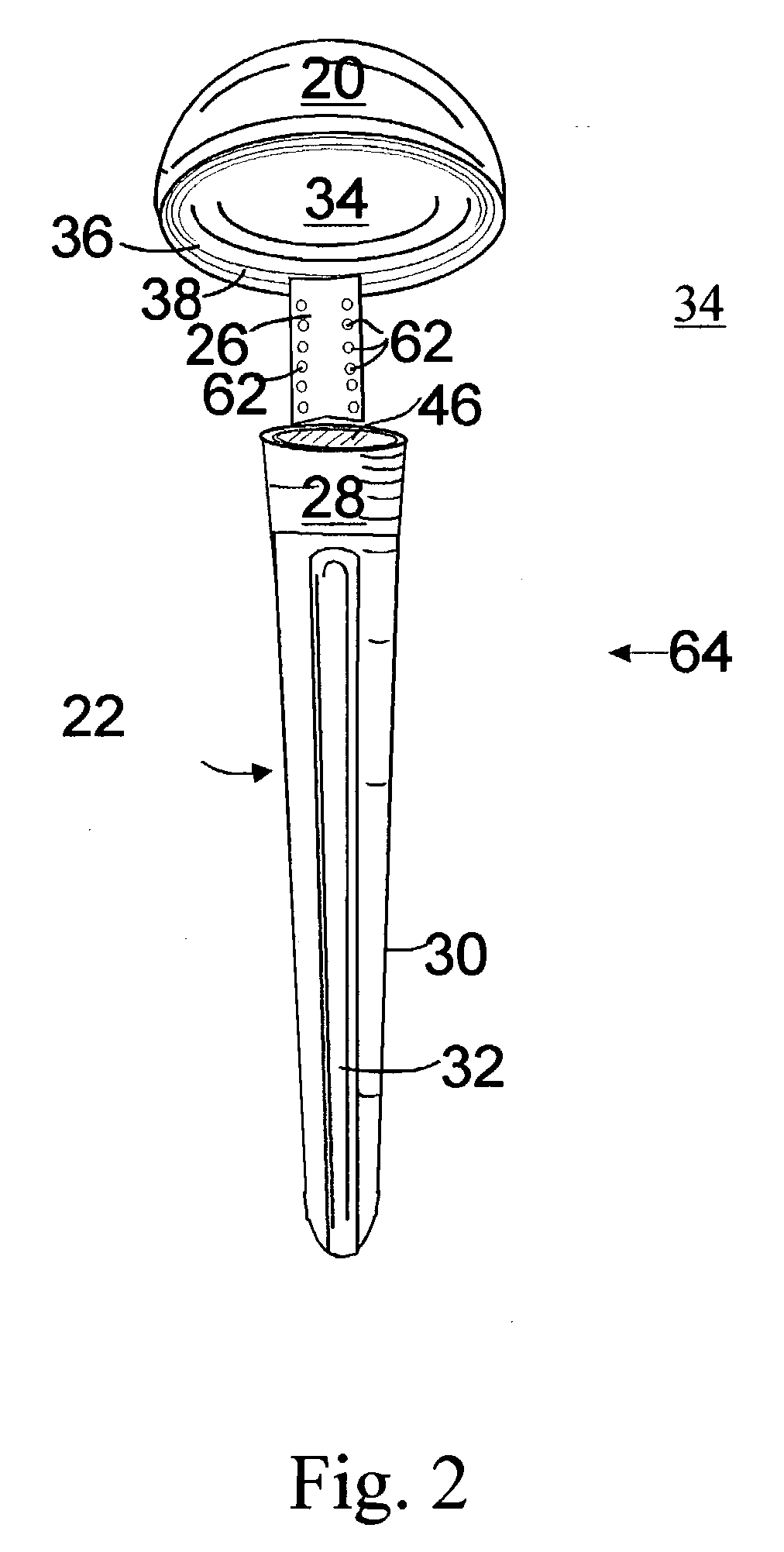
The invention is a modular composite shoulder prosthesis 64, whose construct incorporates a solid autogenous bone graft 50 to be used to replace the upper humerus in certain fracture types. The prosthesis comprises a stem 22 to be inserted in the canal of the humerus, an intermediary part reduced to a medial pillar 24 and a head which is a generally spherical cap 20 that is hollow. The head of the prosthesis being hollow and coated with an osteoconductive material, the lateral aspect of the medial pillar as well as the upper part of the stem being also coated with the same material, an epiphyso-metaphyseal space is delineated in which a solid autogenous bone graft is fitted. Union can be achieved between the coated parts of the prosthesis, the bone graft 50 and the tuberosities reattached to the humerus shaft, secured to holes 62 of the medial pillar and between themselves.
Owner:CYPRIEN JEAN MAXWELL +4
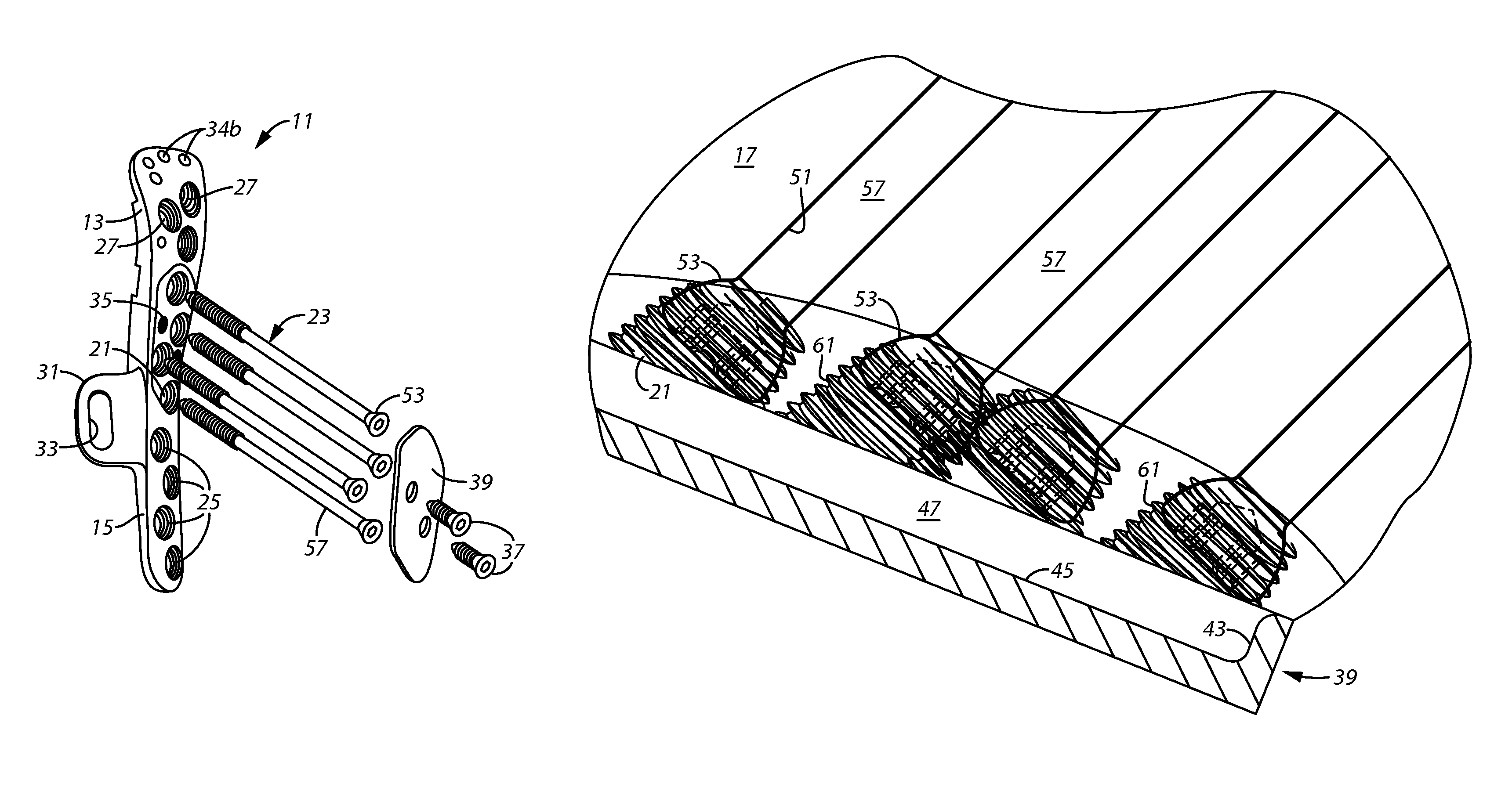
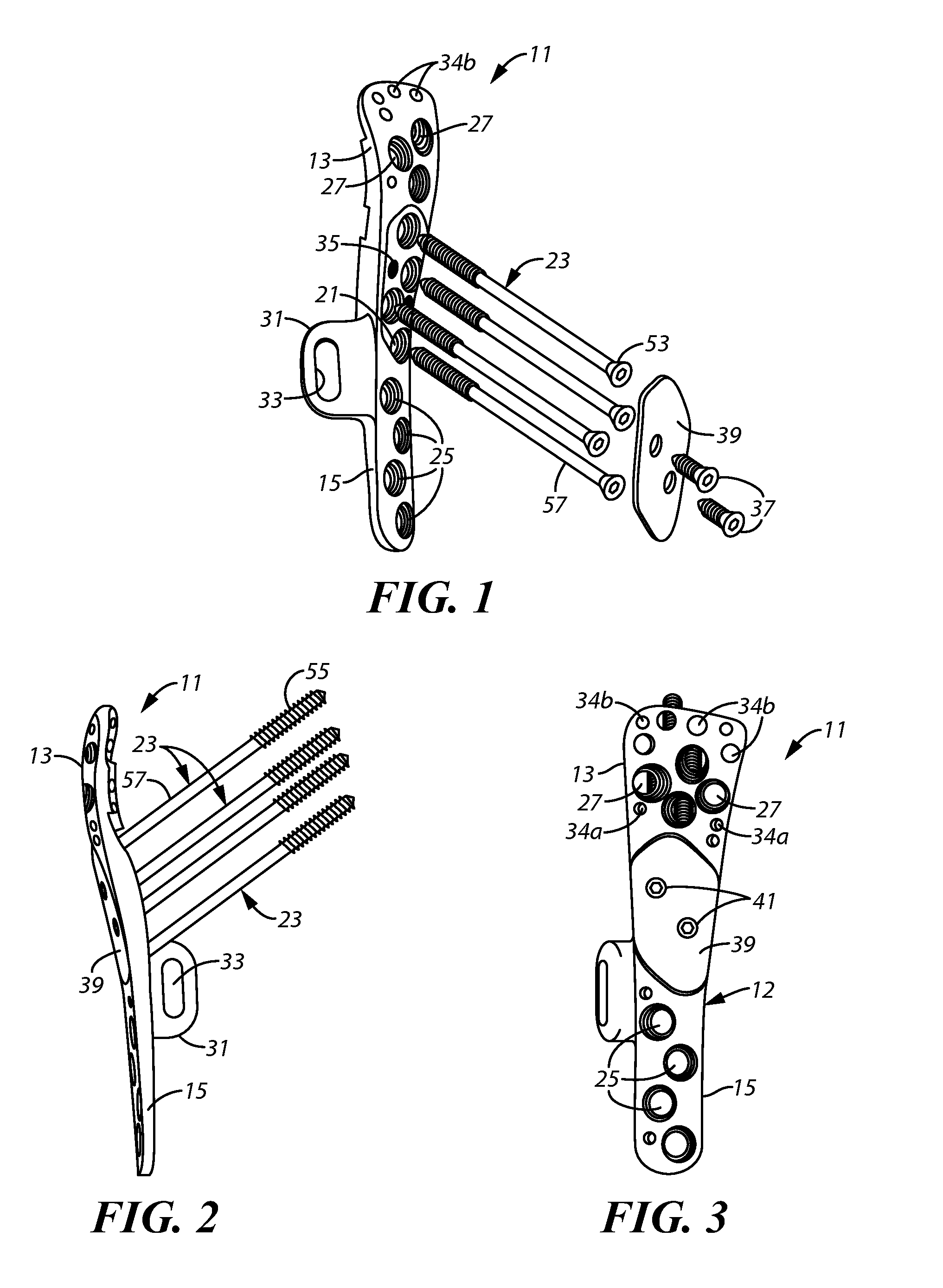
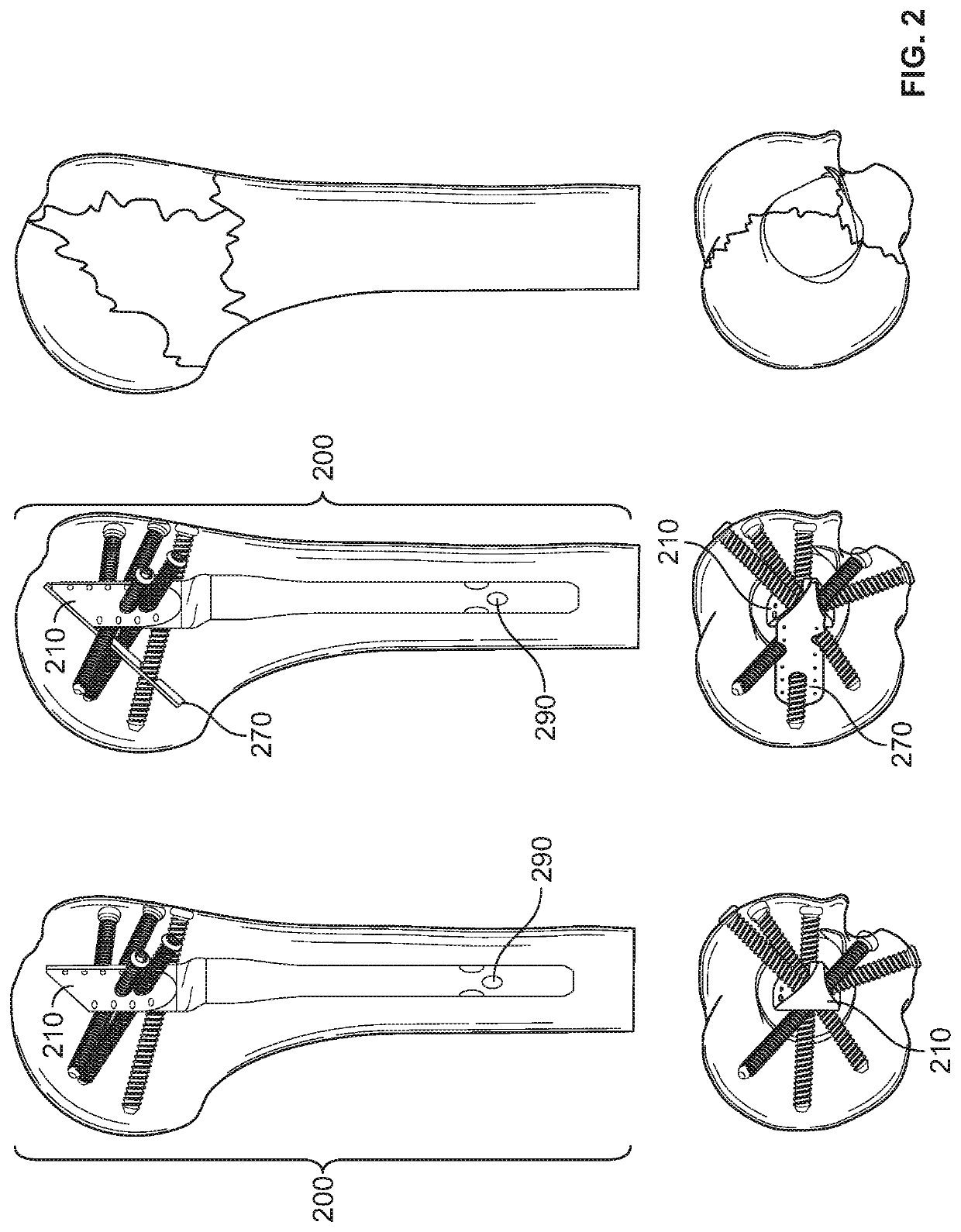
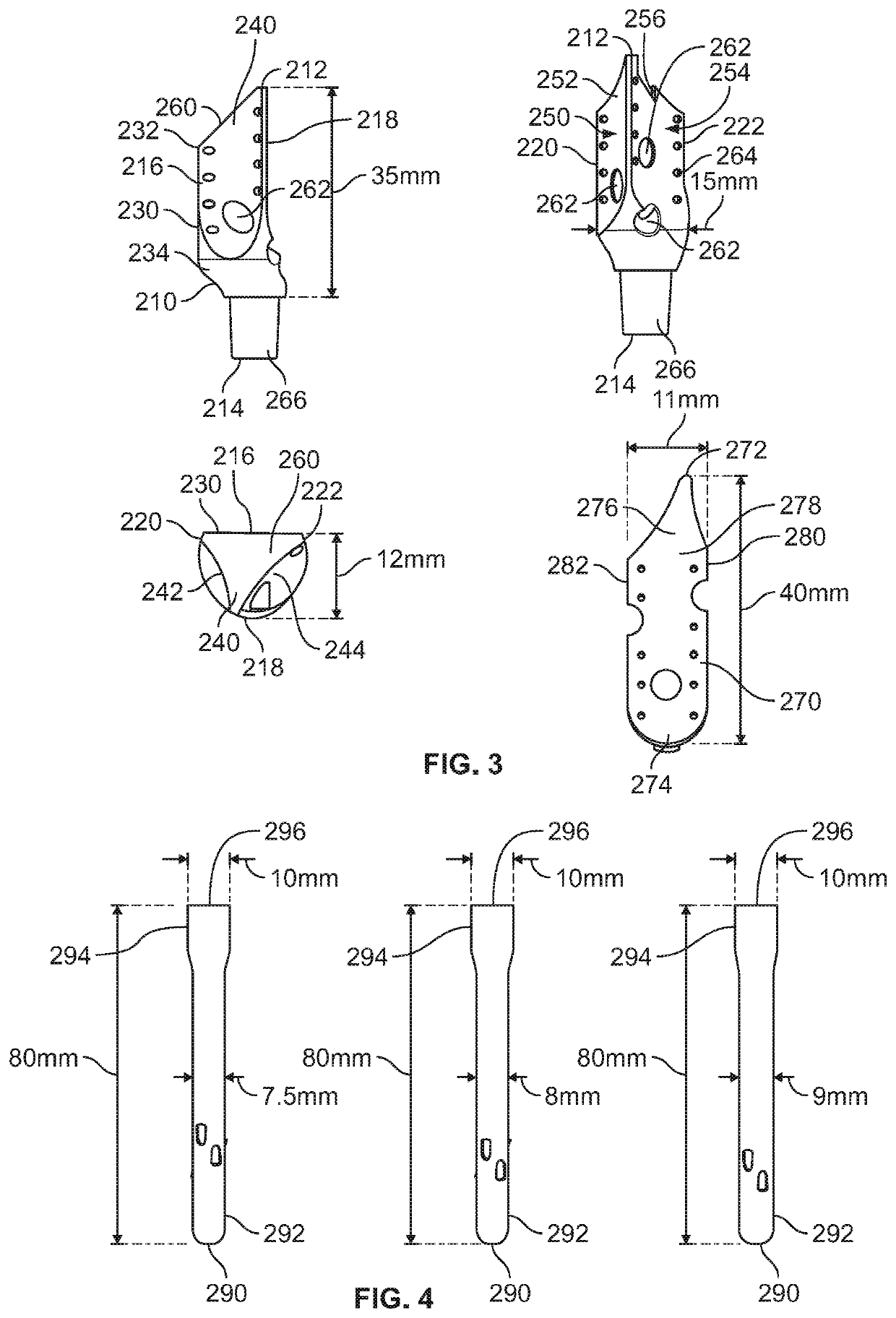
Proximal humerus fracture repair plate and system
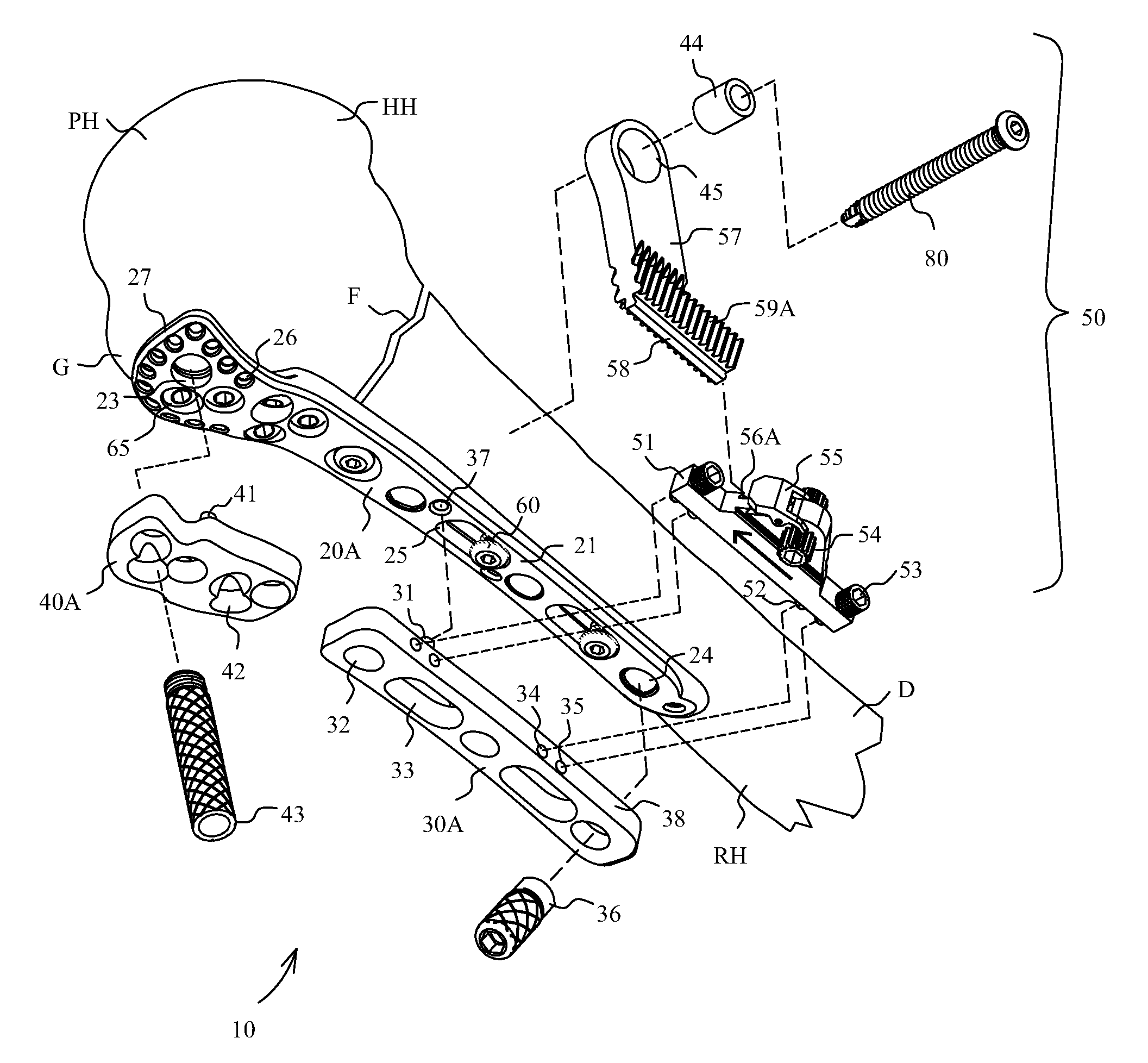
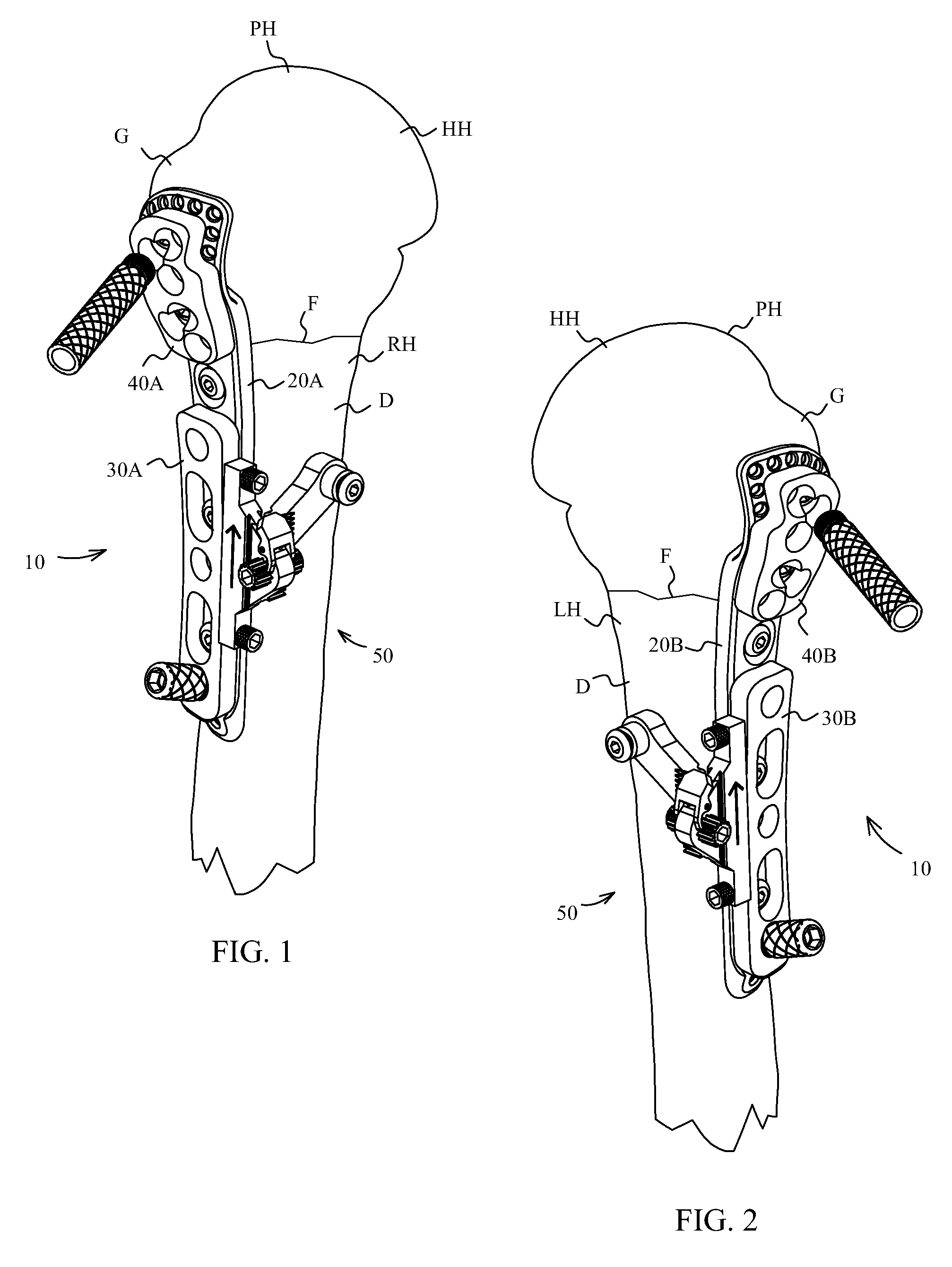
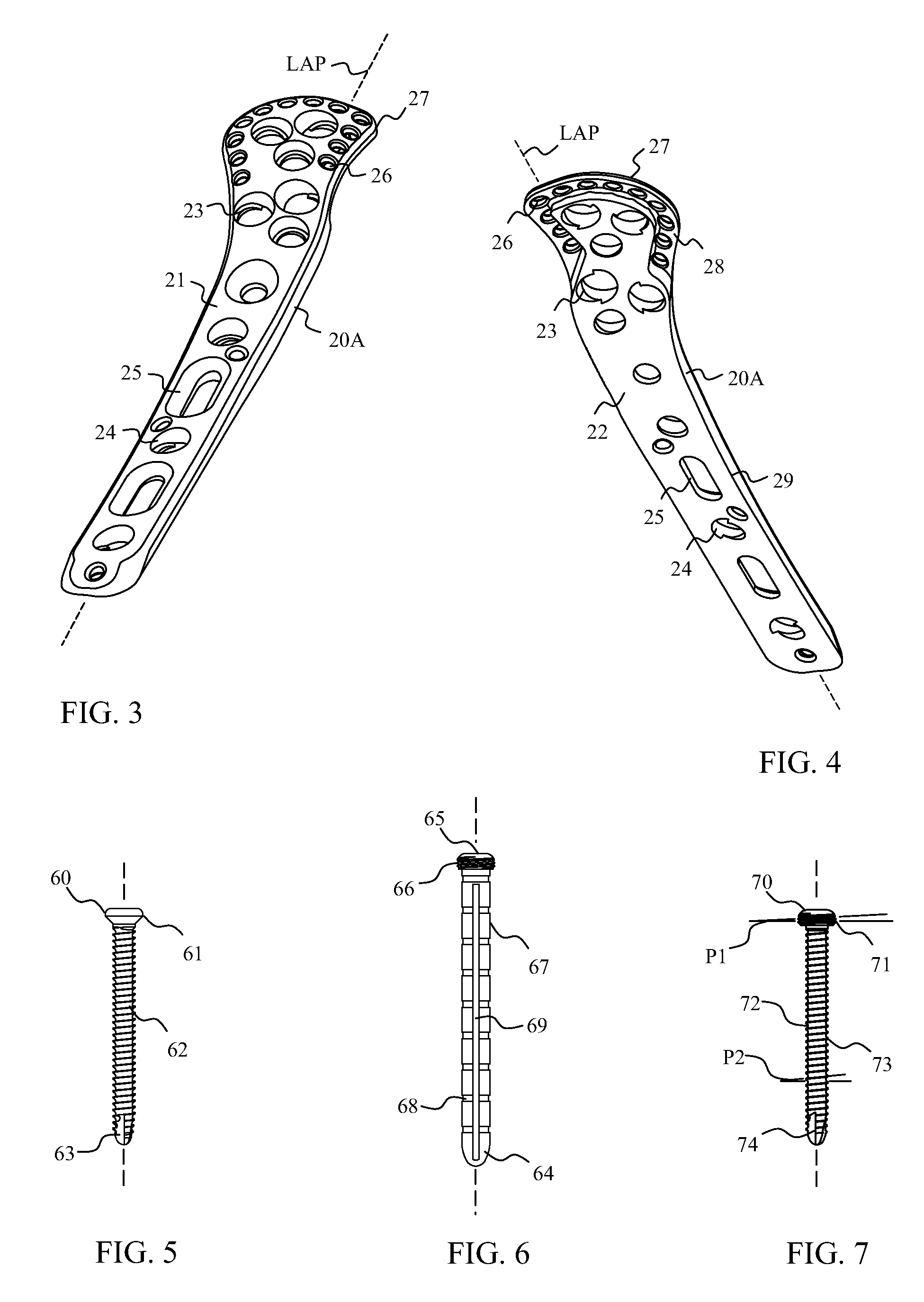
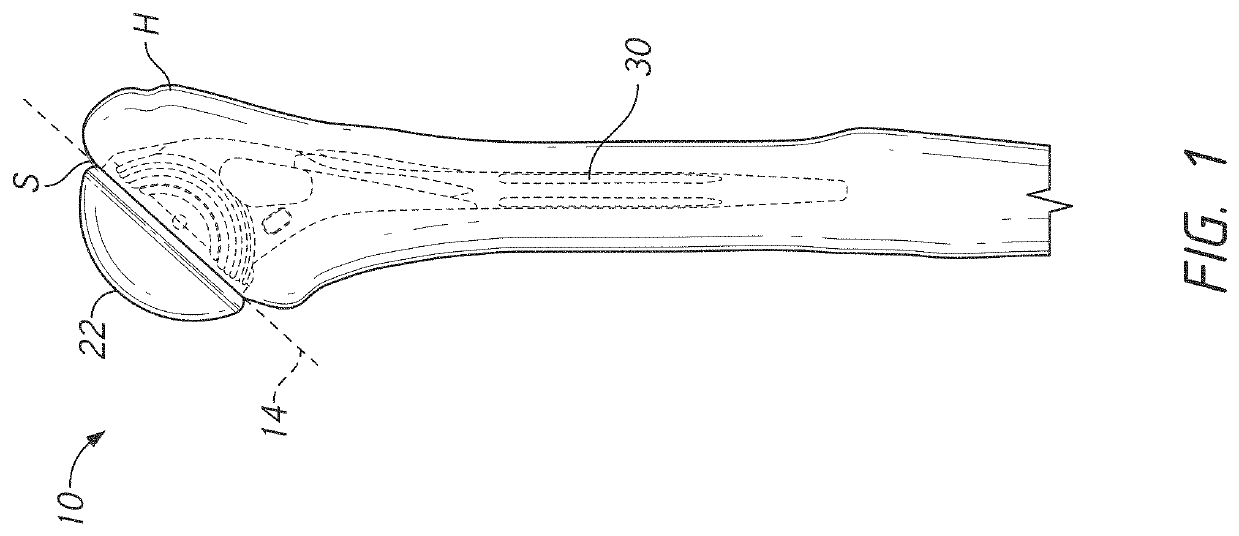
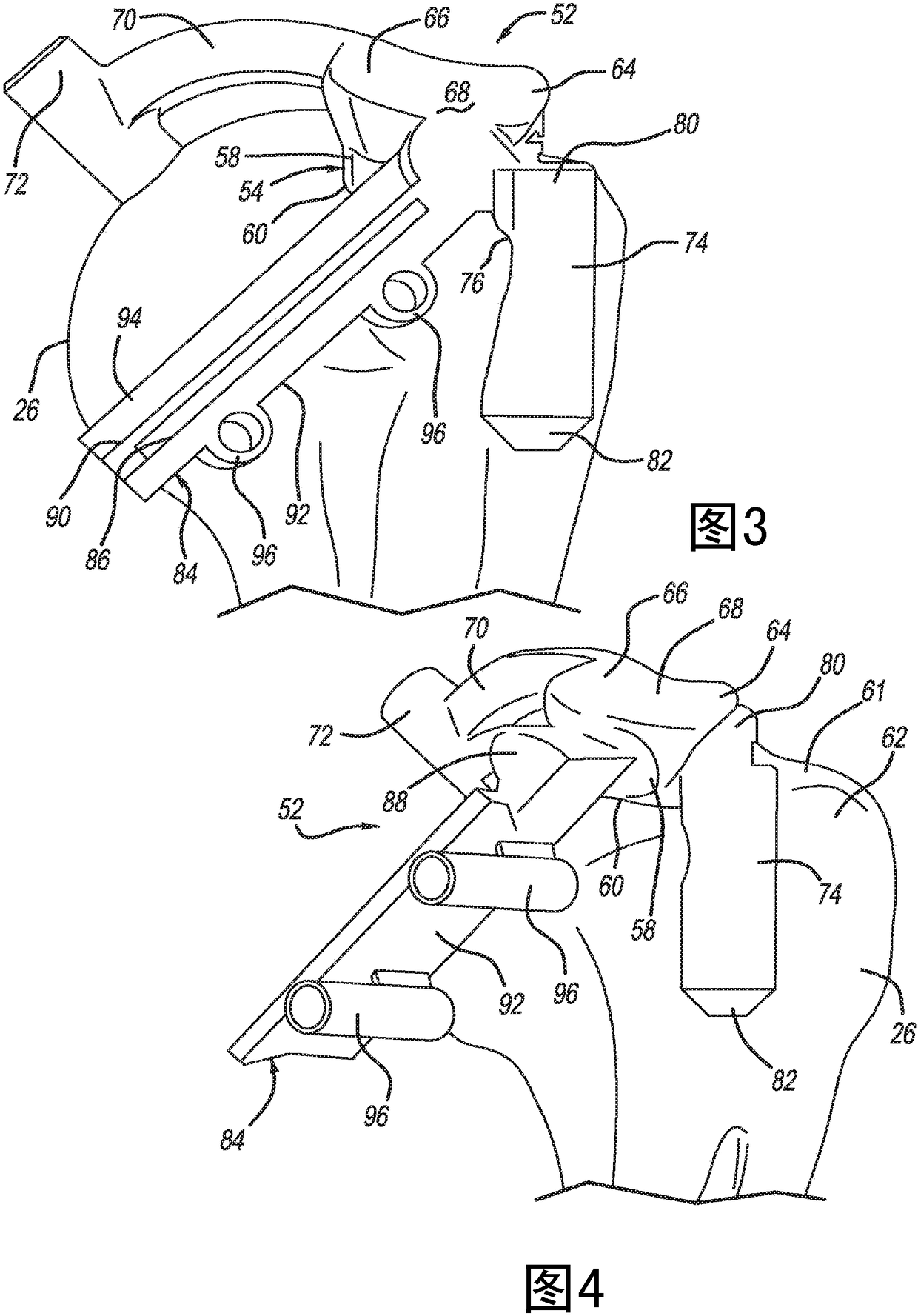
InactiveUS8968371B2Small surface areaGood for bone healthFastenersBone drill guidesMetaphysisFracture reduction
Devices and systems for repairing bone fractures and more specifically a fracture repair plate that provides for fixation of a metaphysis to the diaphysis of a long bone, for instance a fracture between the proximal humerus and the diaphysis of the humerus. The fracture repair system includes an implantable repair fracture repair plate and a bone anchor for fixing the fracture repair plate to a bone. In one embodiment, the fracture repair plate may also be adapted to serve as an anchor for a suture. The fracture repair system may also include a fracture reduction mechanism attachable to the fracture repair plate for imparting a controlled translational movement between two bone segments along a plane that lies substantially parallel to the surface of the bone to which the fracture repair plate is attached and substantially parallel to the longitudinal axis of the bone shaft.
Owner:SHOULDER OPTIONS
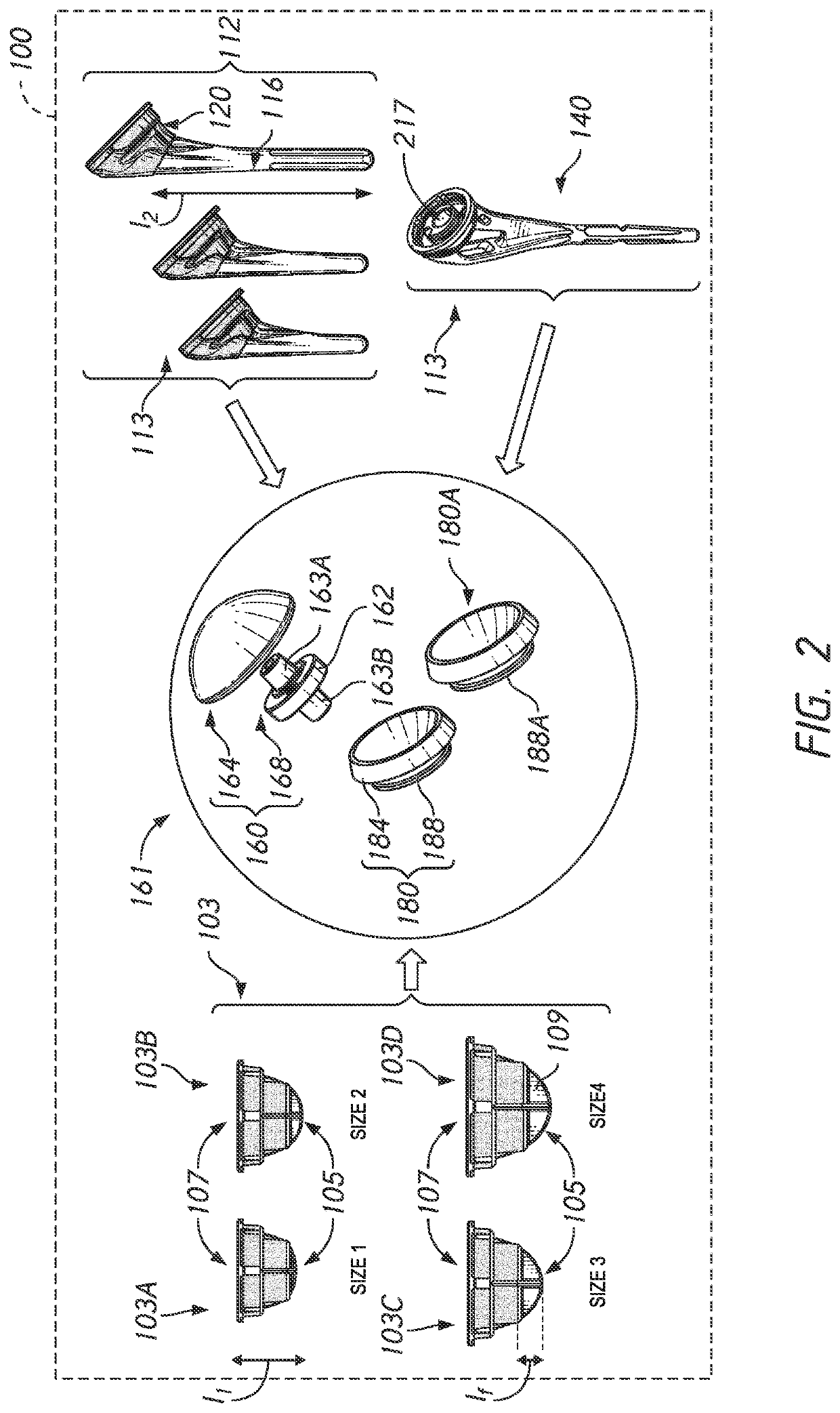
Modular humeral head
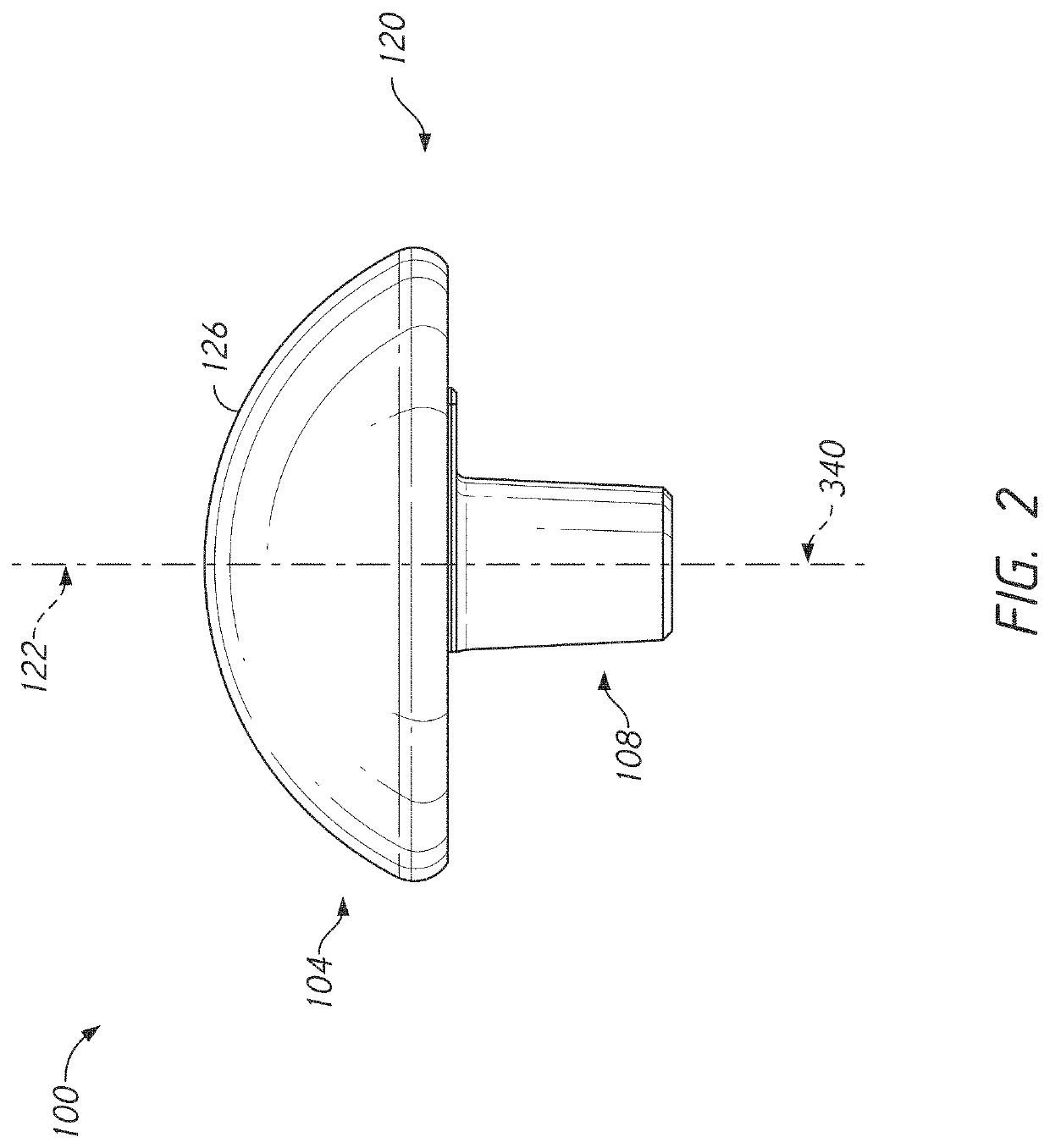
ActiveUS11197764B2Good flexibilityPrevent rotationJoint implantsKnee jointsArticular surfacesArticular surface
A humeral head assembly is provided that includes an articular body and a coupler. The articular body includes a coupling portion disposed on a side of the articular body opposite an articular surface. The coupling portion includes a continuous zone of eccentricity adjustment. The coupler portion optionally includes one or more than one discrete position site. The coupler includes a first portion and a second portion opposite the first portion. The first portion is configured to mate with the coupling portion and the second portion is configured to mate with another member of a joint prosthesis. A coupling portion with the continuous range of eccentricity adjustment can be provided on a bone anchor and the eccentricity of another component can be selected by motion of a coupler, such as a tray for reverse humeral assemblies, along the coupling portion of the anchor.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Implants, systems and methods of using the same
ActiveUS10722373B2Joint implantsShoulder jointsArticular surfacesPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Owner:IGNITE ORTHOPEDICS LLC
Assembly type shoulder joint prosthesis and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN111374805ASolve the errorAvoid printing errorsJoint implantsTomographyBone humerusBone cement
The invention provides an assembly type shoulder joint prosthesis and a manufacturing method thereof. The assembly type shoulder joint prosthesis comprises a scapula prosthesis, a glenoid cavity prosthesis and a humerus prosthesis, wherein the free end of a glenoid cavity supporting rod of the glenoid cavity prosthesis is in movable pivot connection with a glenoid cavity part of the scapula prosthesis; a glenoid cavity bone inner sleeve of the glenoid cavity prosthesis is arranged in a humeral head hinging groove of the humerus prosthesis; and a bone trabecula structure is arranged on the outer wall of a humerus handle in a coating manner. Through the adoption of the assembly type shoulder joint prosthesis disclosed by the invention, a set of the scapula prosthesis, the glenoid cavity prosthesis and the humerus prosthesis which are assembled in a cooperating manner and are mutually connected and in cooperation is provided, so that the prosthetic replacement requirements of a patient ofwhich the humerus, the glenoid cavity and the scapula are damaged can be met, and relative moving relationship between the scapula and the glenoid cavity of the human body is also practically simulated; and the bone trabecula structure is arranged on the outer wall of the humerus handle in a coating manner, so that the human organism can be quickly and firmly adhered to the prosthesis, and the problem that prosthesis loosening is easy to generate through bone cement, and during polymerization of the bone cement monomer, a large amount of heat is released, and periphery tissue damages are generated are solved.
Owner:BEIJING CHUNLIZHENGDA MEDICAL INSTR
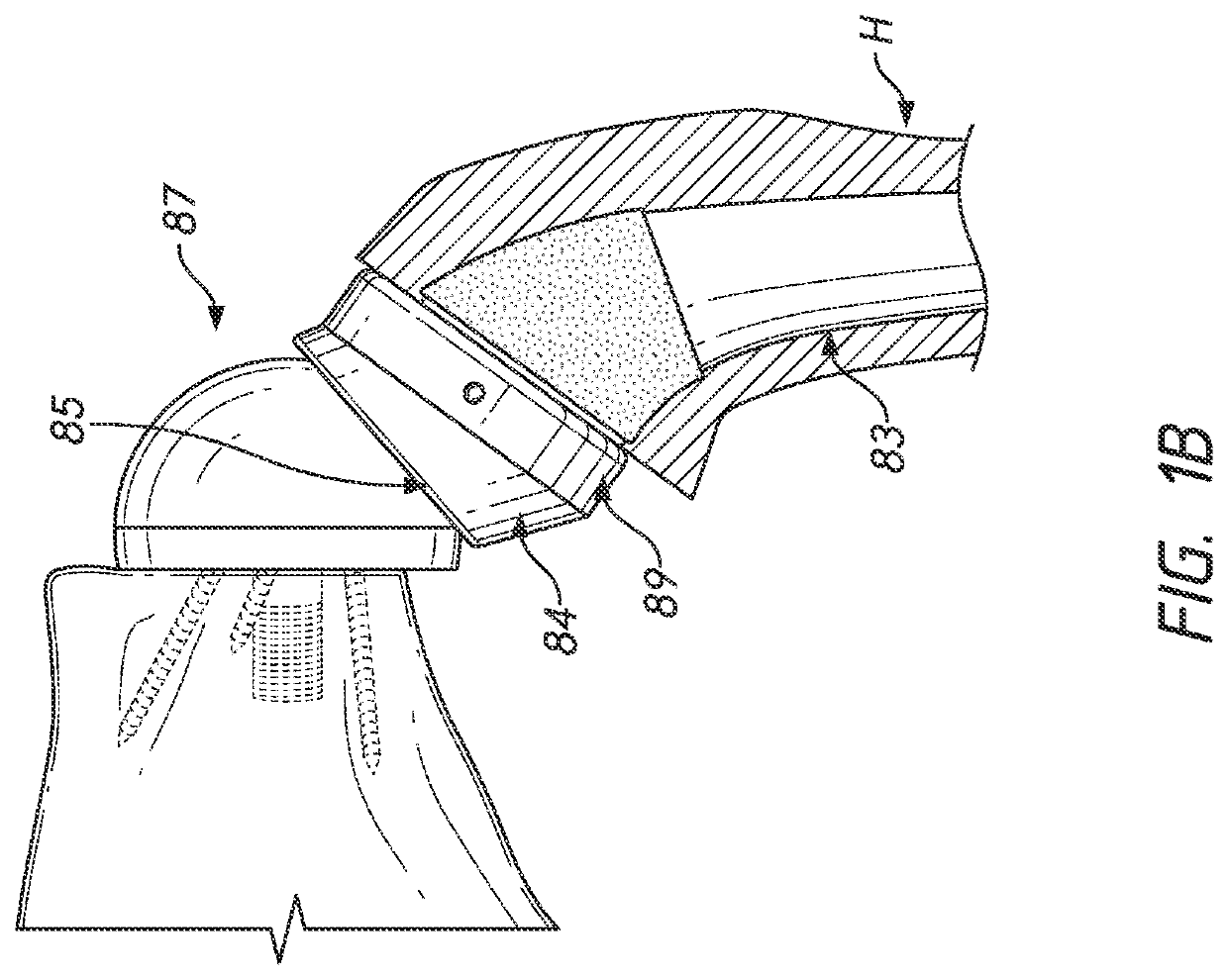
Patient-specific humeral guide designs
A humeral cut guide member for a humeral head that can comprise: a bone-engagement member including a first patient-specific bone-engagement surface that is complementary and made to substantially mate and nest in only one position on a specific patient's humeral head; a registration member connected to the bone-engagement member including a second patient-specific bone engagement surface that issized and made to substantially mate and nest in only one position with the specific patient's bicipital groove; and a cut guide plate connected to and extending away from the bone-engagement member such that, upon the bone-engagement member mating and nesting with the specific patient's humeral head, the cut guide plate is spaced apart from the humeral head, wherein cut guide plate defines an elongated slot.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Multi-angle locking and fixing humerus straight type interlocking intramedullary pin
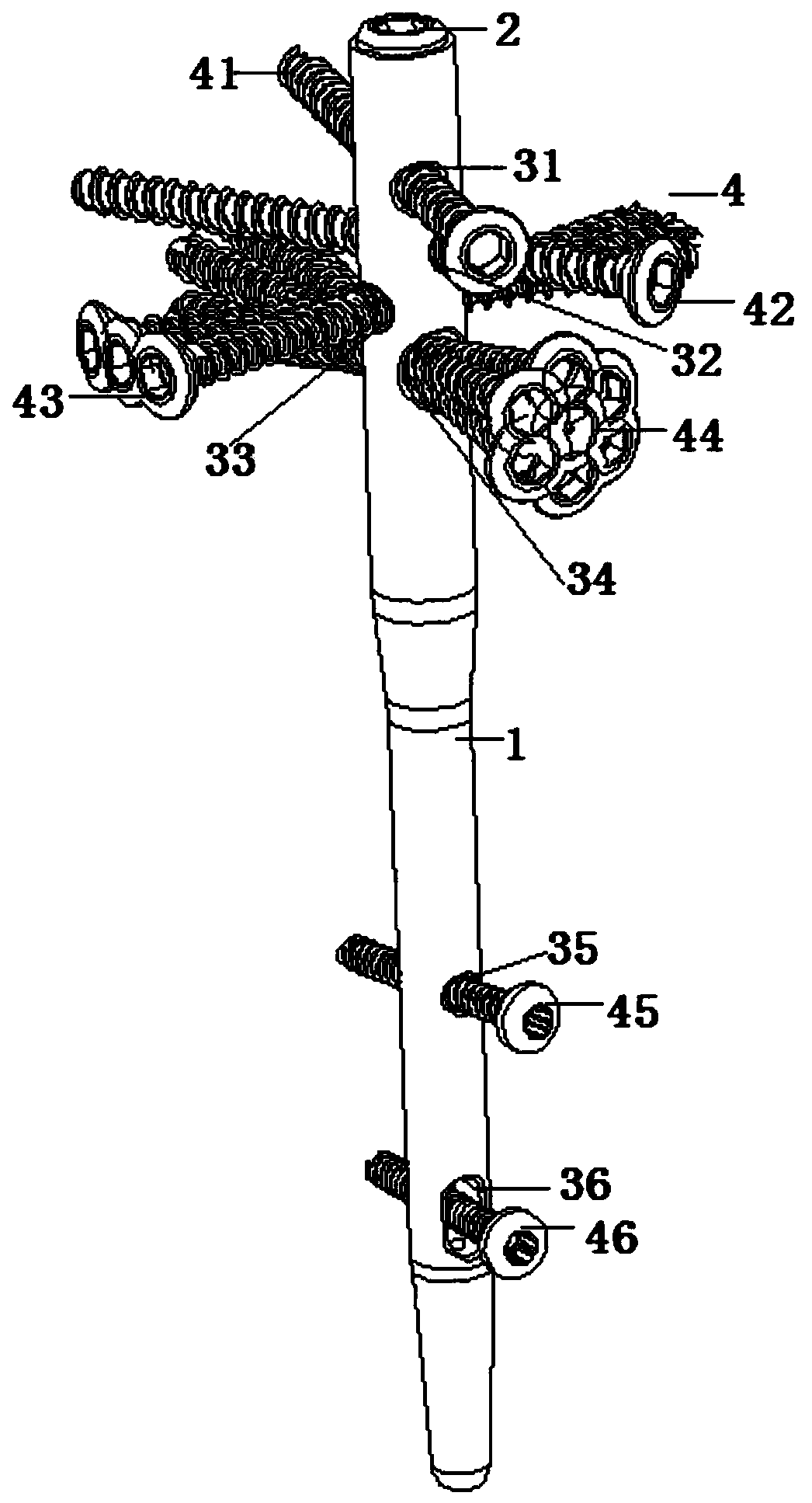
PendingCN110934630AHigh strengthAvoid slight misalignmentInternal osteosythesisSurgical riskBone humerus
The invention discloses a multi-angle locking and fixing humerus straight type interlocking intramedullary pin. The multi-angle locking and fixing humerus straight type interlocking intramedullary pincomprises a humerus intramedullary pin main pin, wherein the humerus intramedullary pin main pin adopts a hollow structure, and comprises a near end intramedullary pin, a far end intramedullary pin and a connecting section; the diameter of the near end intramedullary pin is greater than that of the far end intramedullary pin; one end of the near end intramedullary pin is in transition connectionwith the far end intramedullary pin through the connecting section, and the inner part of the other end of the near end intramedullary pin is connected with a terminal cap; the near end intramedullarypin, the far end intramedullary pin and the connecting section adopt an integrated structure; the diameter of the near end intramedullary pin is 9mm, a plurality of pin holes are formed in the near end intramedullary pin and the far end intramedullary pin; bone screws are arranged in the pin holes; and the bone screws in the near end intramedullary pin are multi-angle screws. According to the multi-angle locking and fixing humerus straight type interlocking intramedullary pin disclosed by the invention, the opportunity of selecting appropriate humerus intramedullary pin main pin according tohumerus individual dissection differences is increased, and the operation risk of generating fracture of humeral head and injury of axillary nerve caused by that an opening in the humerus head part islarge is reduced.
Owner:上海伯塔医疗器械有限公司
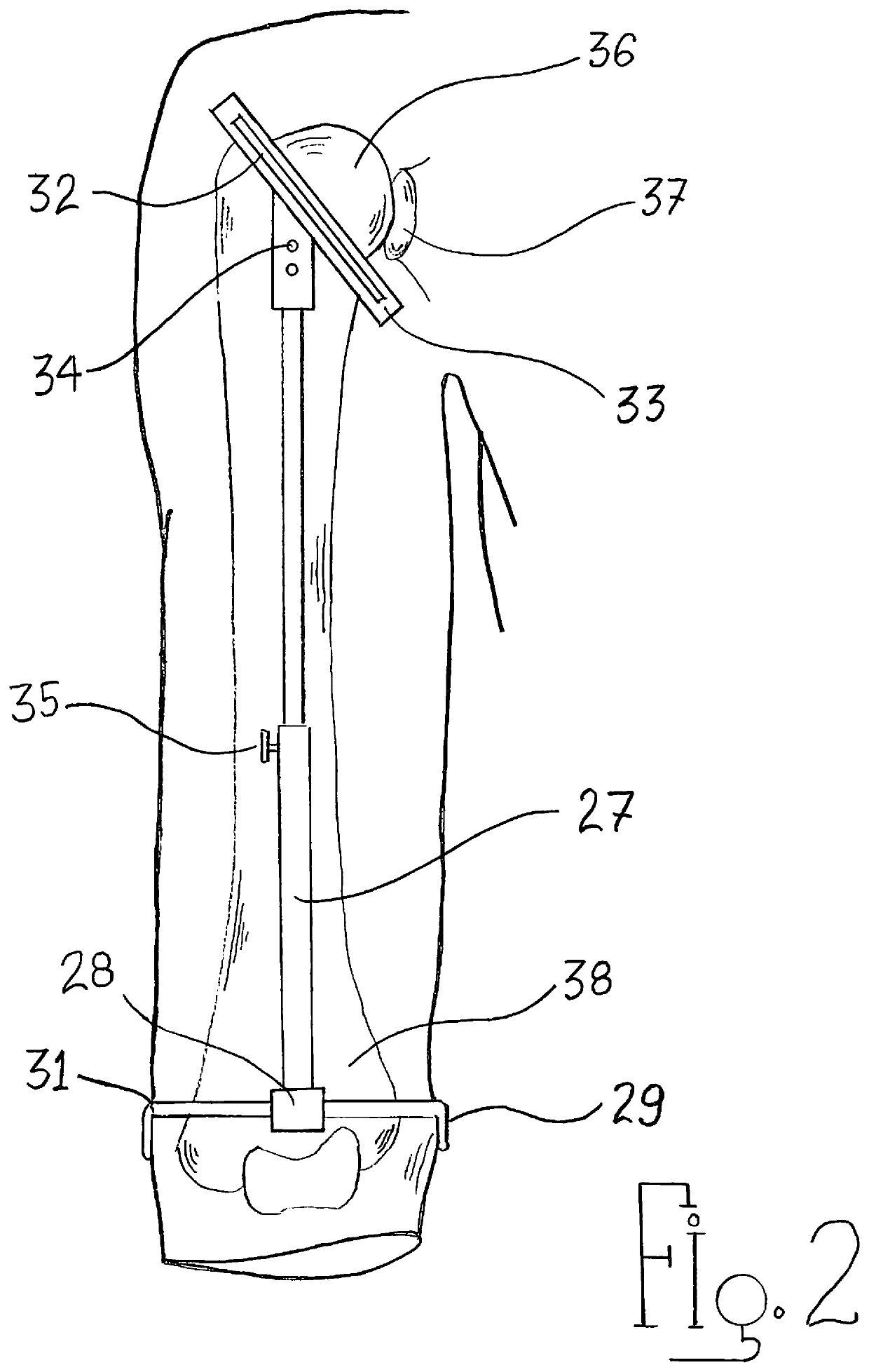
Functional shoulder support brace with cabling system
ActiveUS10646366B2Easy to placeFunctional movementBreast bandagesFractureFunctional movementBone humerus
The present invention relates to a shoulder brace for the rehabilitation of patients that suffer from shoulder instability. The shoulder brace uses a novel elevation and compression cabling system to stabilize and approximate the humerus to glenoid fossa. More specifically, the present invention allows an individual that suffers from shoulder instability to easily put on and, while wearing the device, adjust all forces that approximate their shoulder without the assistance of another individual. The design will also allow the individual the ability to have functional movement. This will give someone who has become dependent on others to regain a greater degree of independence.
Owner:PIMENTEL SILAS EFRAIM BEZERRA DE ARAUJO +2
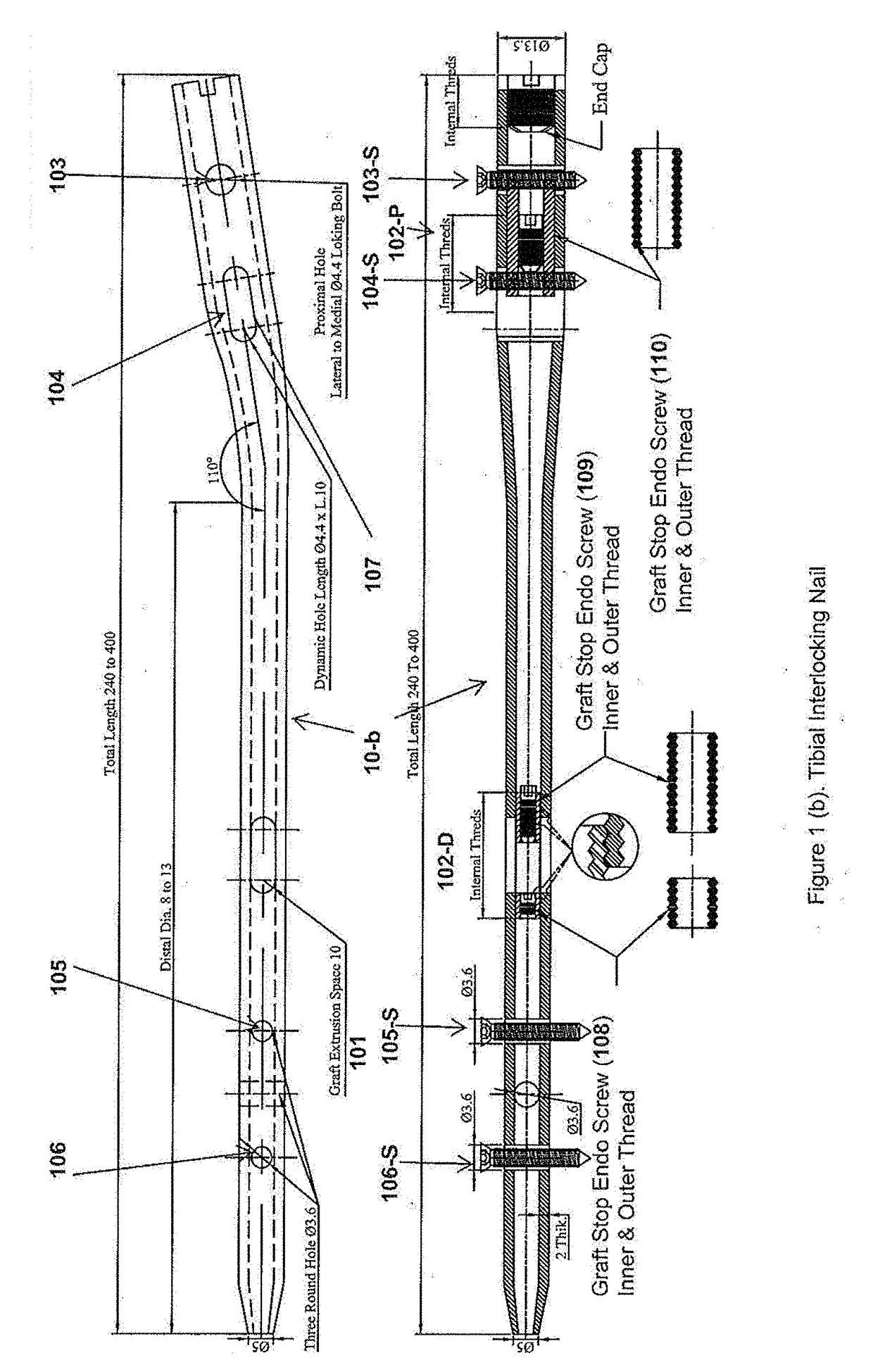
Interlocking Nail
InactiveUS20170224394A1Maintain strengthEnhanced bone healingInternal osteosythesisNailing toolsTibiaWound healing
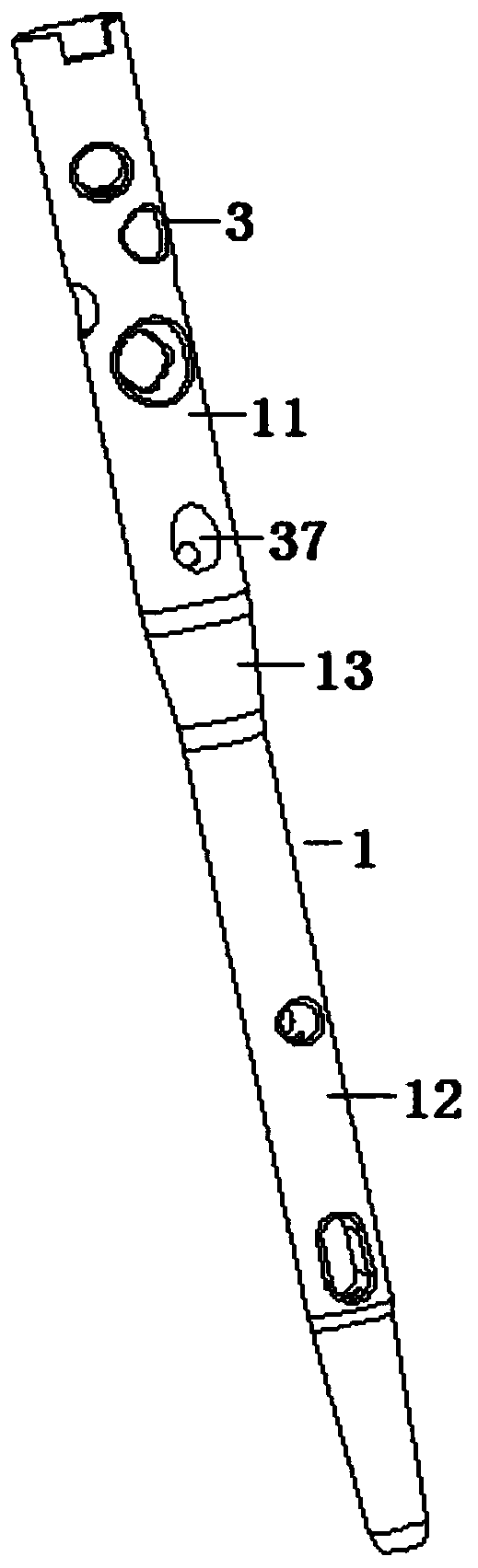
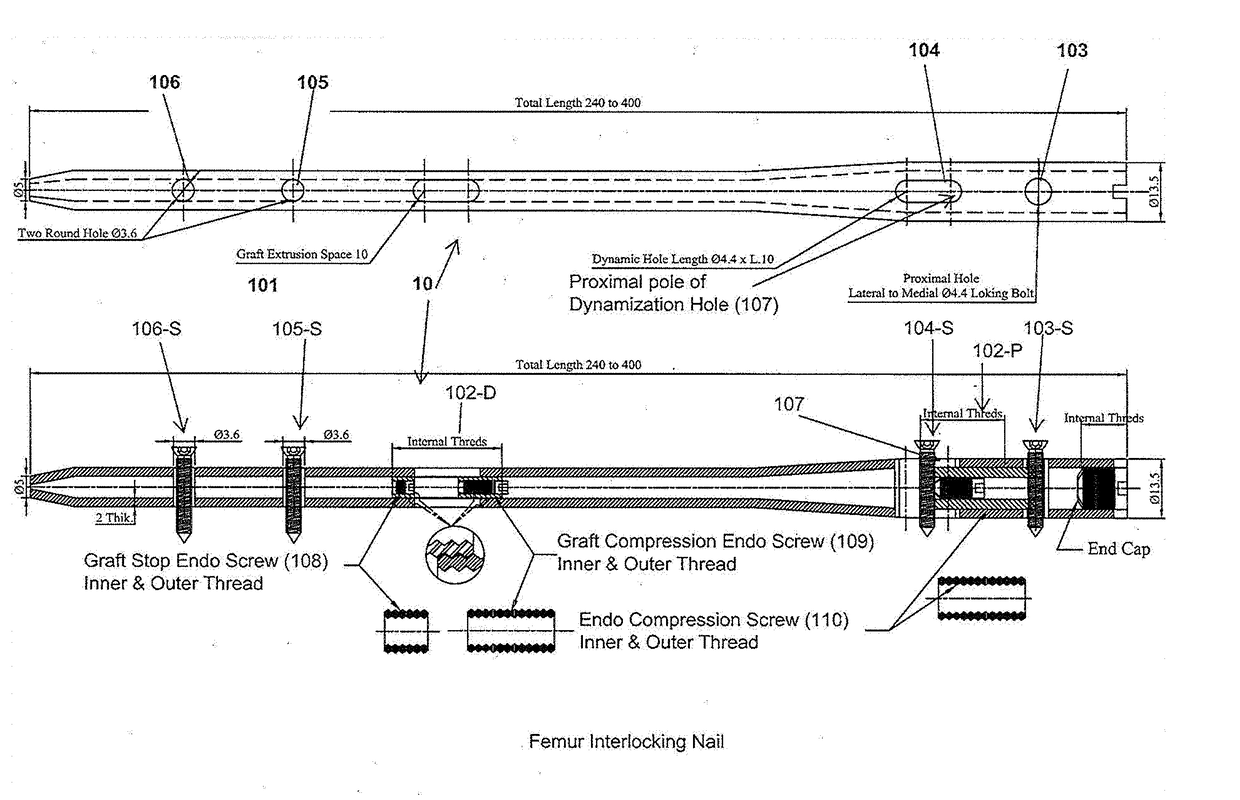
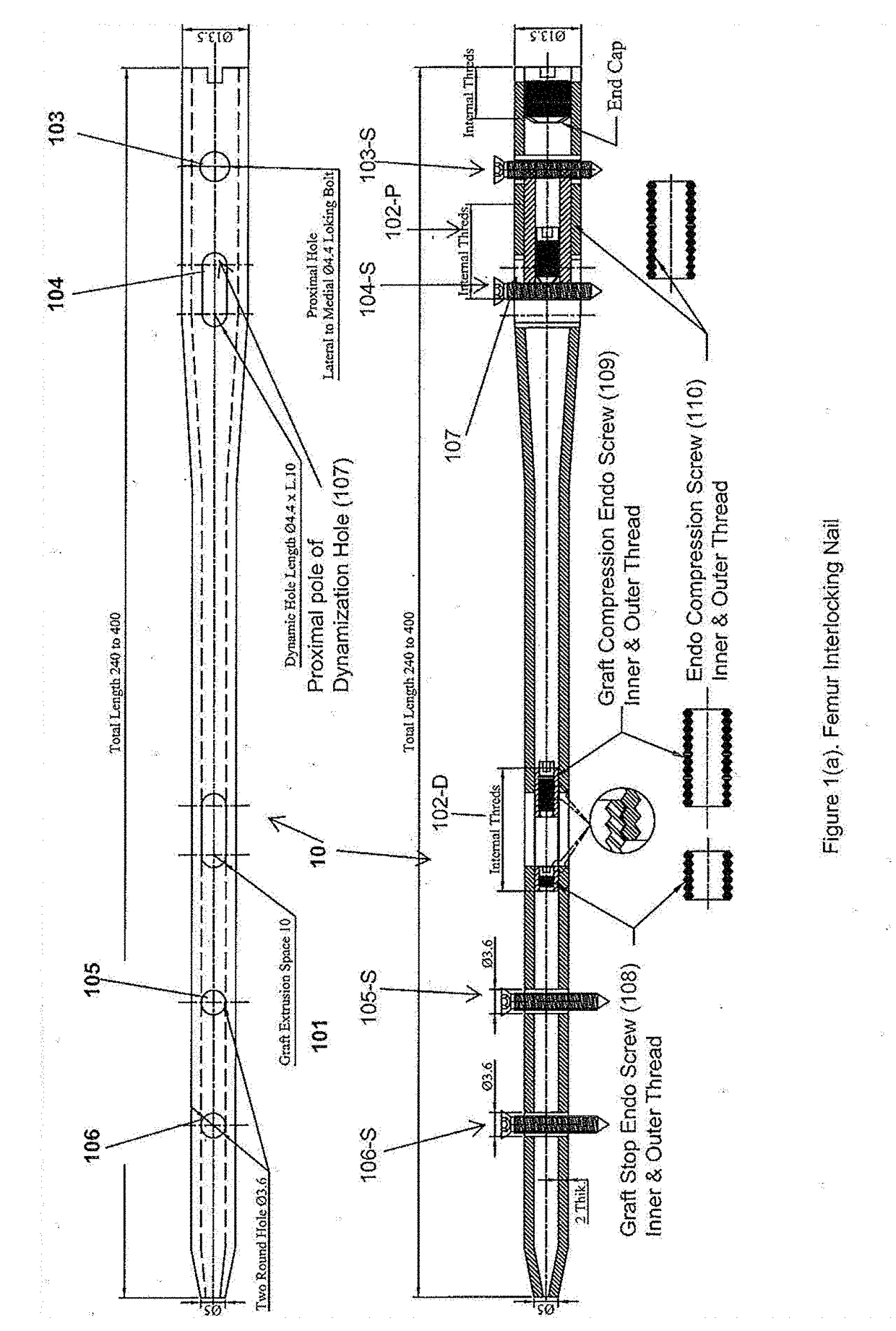
The invention relates to an interlocking nail (10) for fixation of transverse and short spiral fractures of, long bone, particularly shaft of the femur, tibia and humerus, having Graft extrusion space / slot (101) for holding stem cells graft and 4 or 5 holes for putting interlocking bolts from lateral to medial direction. Constant compression achieved (irrespective of weight bearing cycle) at the fracture site by tightening of the Endo-Compression Screws (108, 109 and 110) results in stimulation of stem cells and reduction in bone gap, thus enhances bone healing and union manifolds.
Owner:TANDIYA NITESH KUMAR
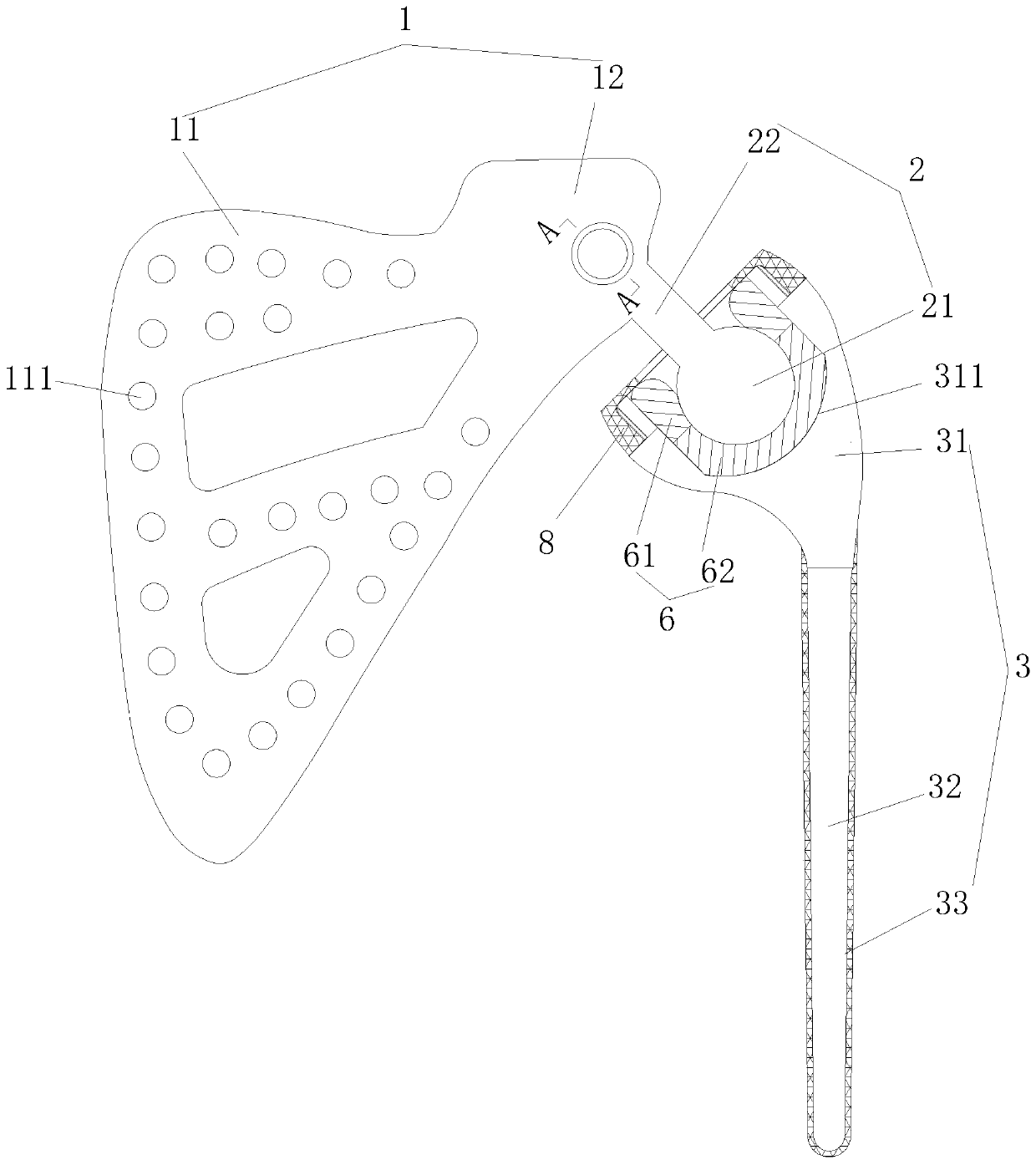
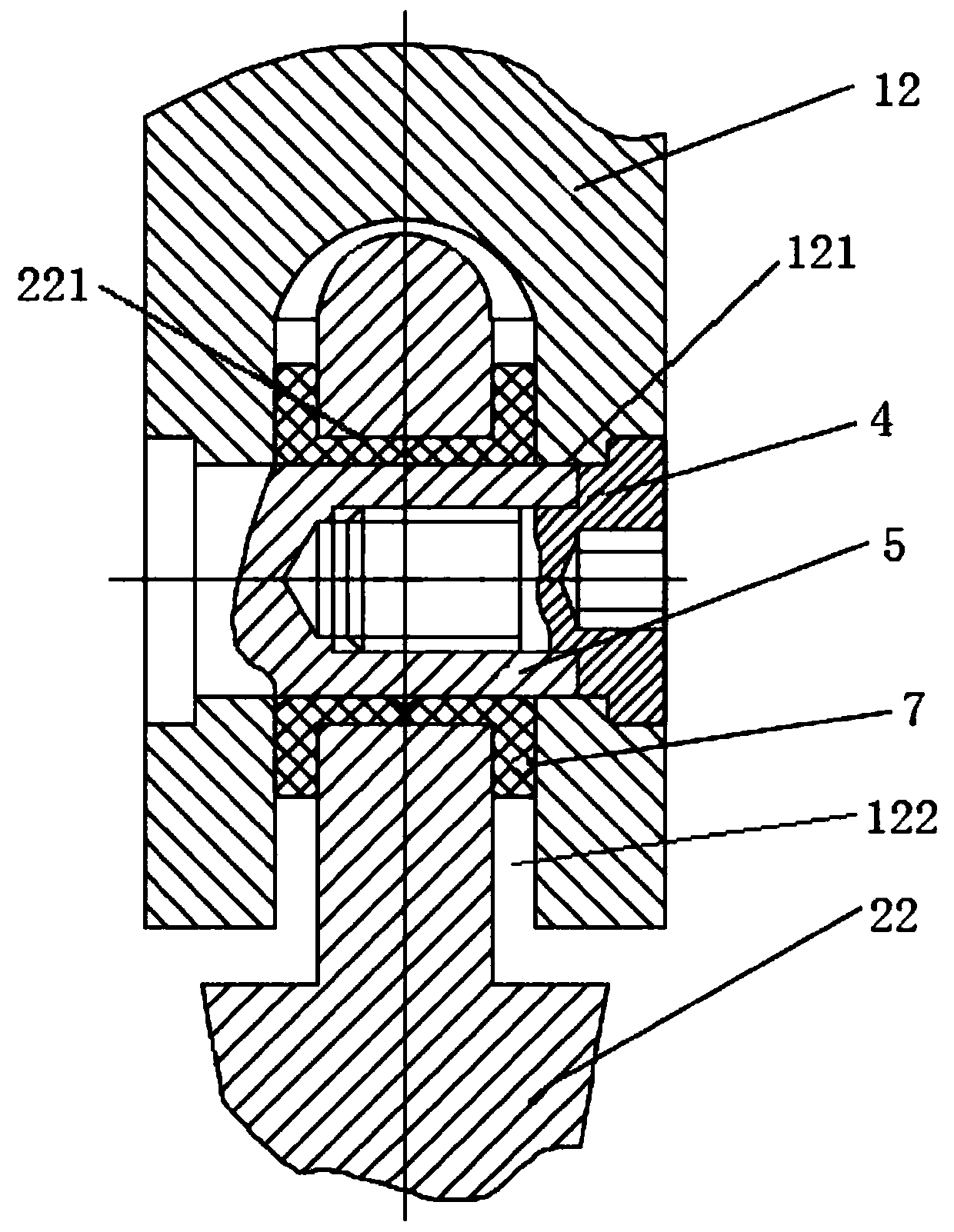
Platform fracture fixation implants
A proximal portion of an implant for repairing a multipart fracture of a proximal humerus includes an asymmetric body having a proximal end, a distal end, a medial side, a lateral side, an anterior edge, and a posterior edge a medial surface extending along at least a portion of the medial side and having a proximal end and a distal end; a protrusion forming the lateral side of the asymmetric body, offset in an anterior direction, and pointing toward a bicipital groove of the humerus when the proximal portion is implanted in the humerus, an anterior support surface configured to support a lesser tuberosity; a posterior support surface configured to support a greater tuberosity; an angled surface having a first side defined by the medial surface, a second side defined by the anterior support surface, and a third side defined by the posterior support surface; and an anchoring point.
Owner:EXACTECH INC
Shoulder prosthesis components and assemblies
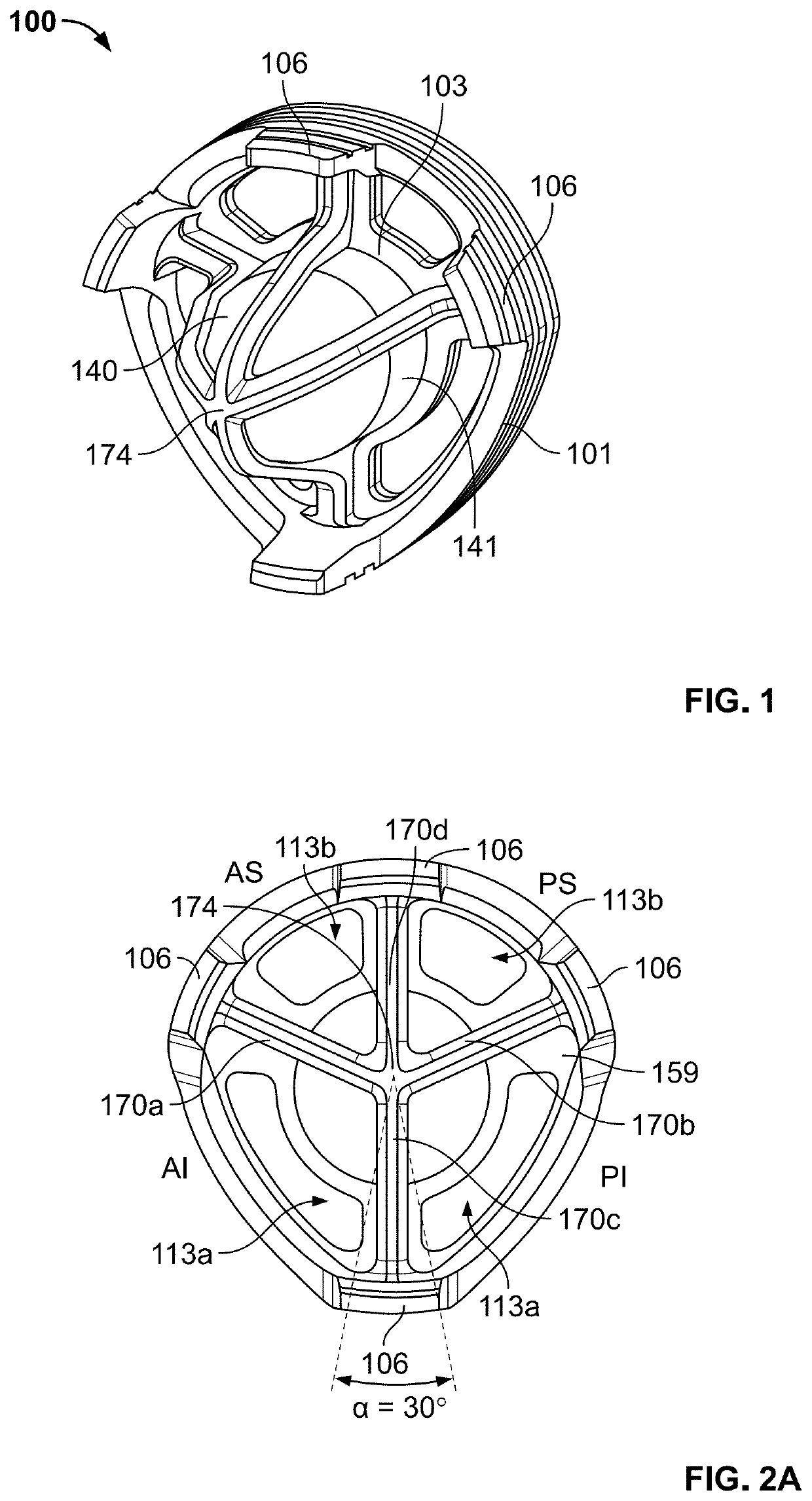
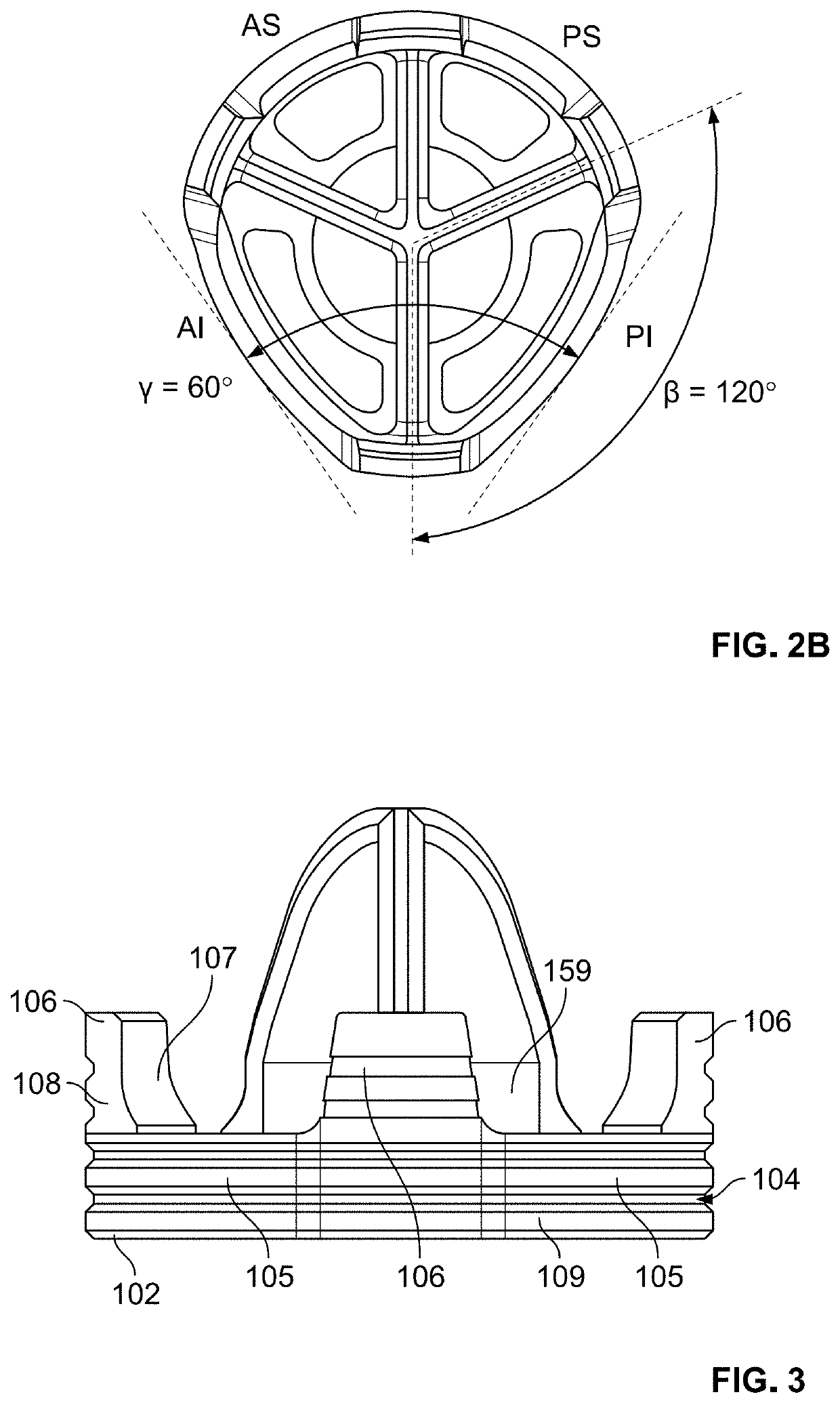
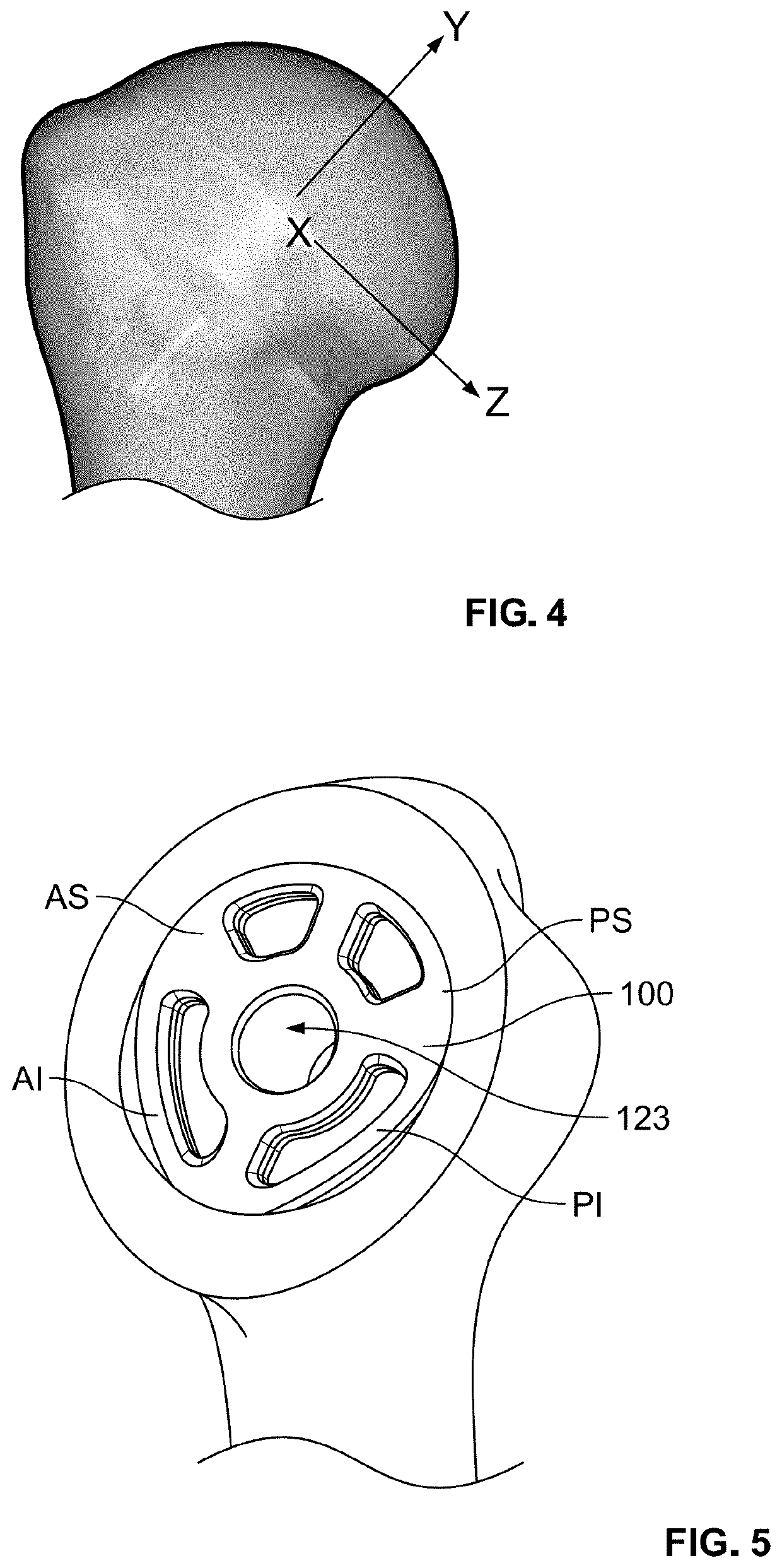
PendingUS20210401584A1Reduce and minimize and eliminate rotationJoint implantsShoulder jointsBone humerusMechanical engineering
Various embodiments disclosed herein relate to stemmed and stemless humeral anchors for use in shoulder arthroplasty procedures. For example, the humeral anchor can include a first end, a second end, and an interior surface extending between the first end and the second end. The interior surface can be disposed about a recess disposed between the first end and the second end. The recess can be configured to secure a coupling of a shoulder articular body directly to the interior surface.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Superficial replacement prosthesis for elbow joint
PendingCN113244025AUnrestricted degrees of freedomFlexible activitiesJoint implantsKnee jointsArticular headBone humerus
The invention relates to the technical field of artificial prosthesis and particularly relates to a superficial replacement prosthesis for an elbow joint. The superficial replacement prosthesis for the elbow joint comprises a prosthetic elbow joint head, wherein a mounting groove is formed in the prosthetic elbow joint head and is mounted at a distal end of a humerus; a connecting part, wherein one end of the connecting part is connected with the prosthetic elbow joint head, and the other end of the connecting part stretches along a proximal end of the humerus; and a bone grafting groove, which is arranged in the mounting groove and is used for accommodating grafted bone scraps. According to the superficial replacement prosthesis for the elbow joint, provided by the invention, the degree of freedom of the elbow joint of a sufferer is not restricted, and the traditional problem that the movement of the elbow joint is restricted is solved; by using the superficial replacement prosthesis for the elbow joint, the mass of bone section of the elbow joint of the sufferer is little, and the recovery and later-stage reconditioning of the elbow joint of the sufferer are facilitated; and furthermore, the bone grafting groove is further arranged and is used for being implanted with bone so as to supplement bone mass of the sufferer, the reducing of the weight of the elbow joint part is facilitated, the degree of comfort of the sufferer is increased, and the bone in the bone grafting groove after long-term recovery can be ankylosed with the humerus, so that the normal form and function of the humerus are restored.
Owner:WUHAN UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE SURGICAL TECH CO LTD
Shoulder arthroplasty implant system
PendingUS20220023054A1Less over-tensioningImprove stabilityInternal osteosythesisBone implantMetaphysisDiaphysis
A stemless implant for shoulder arthroplasty includes a body having a proximal portion, distal portion, and an outer surface. A cylindrical extrusion is substantially perpendicular to and adjacent the proximal portion. At least a portion of the outer surface is configured to contact bone, the outer bone contacting surface comprising a concave taper. The stemless implant can be sized and shaped for insertion into a metaphysis of a humerus bone without penetrating a diaphysis of the humerus bone. The implant optionally comprises a medial fin, a lateral fin, an anterior fin, and a posterior fin. The medial fin and lateral fin may be thicker than the anterior fin. The fins may taper from the proximal portion to the distal portion.
Owner:INTEGRATED SHOULDER COLLABORATION INC
Platform fracture fixation implants
A proximal portion of an implant for repairing a multipart fracture of a proximal humerus includes an asymmetric body having a proximal end, a distal end, a medial side, a lateral side, an anterior edge, and a posterior edge a medial surface extending along at least a portion of the medial side and having a proximal end and a distal end; a protrusion forming the lateral side of the asymmetric body, offset in an anterior direction, and pointing toward a bicipital groove of the humerus when the proximal portion is implanted in the humerus, an anterior support surface configured to support a lesser tuberosity; a posterior support surface configured to support a greater tuberosity; an angled surface having a first side defined by the medial surface, a second side defined by the anterior support surface, and a third side defmed by the posterior support surface; and an anchoring point.
Owner:EXACTECH INC
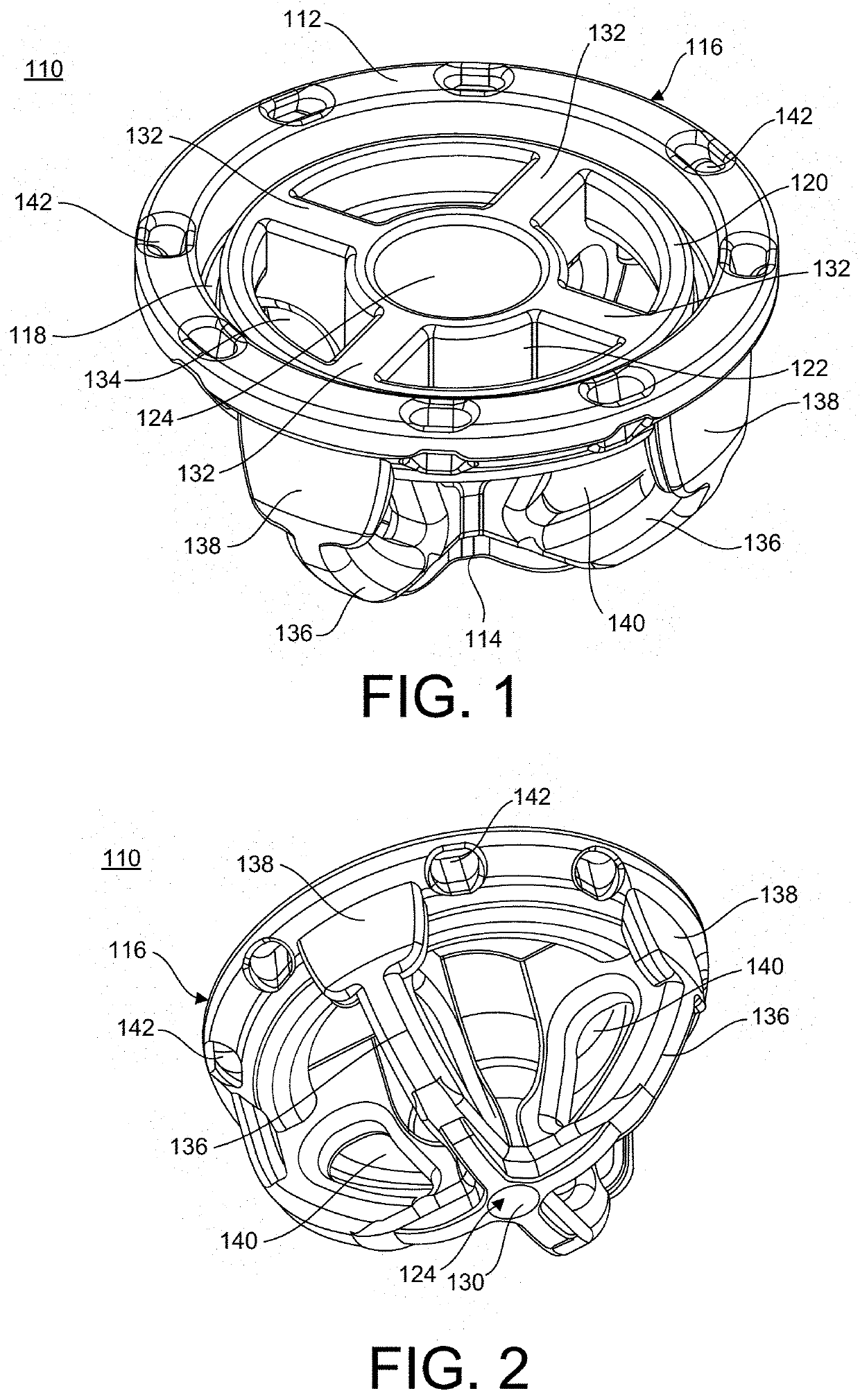
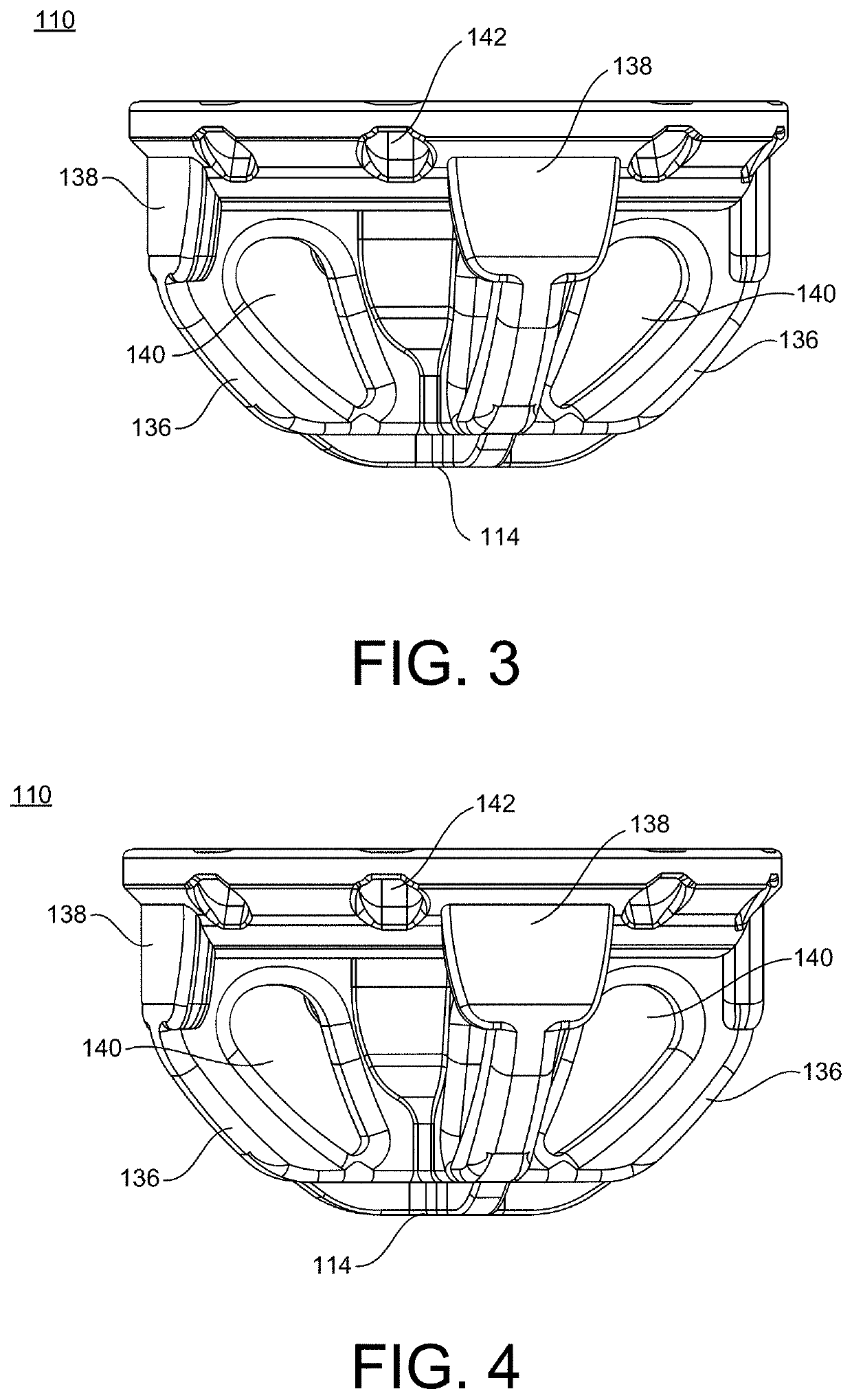
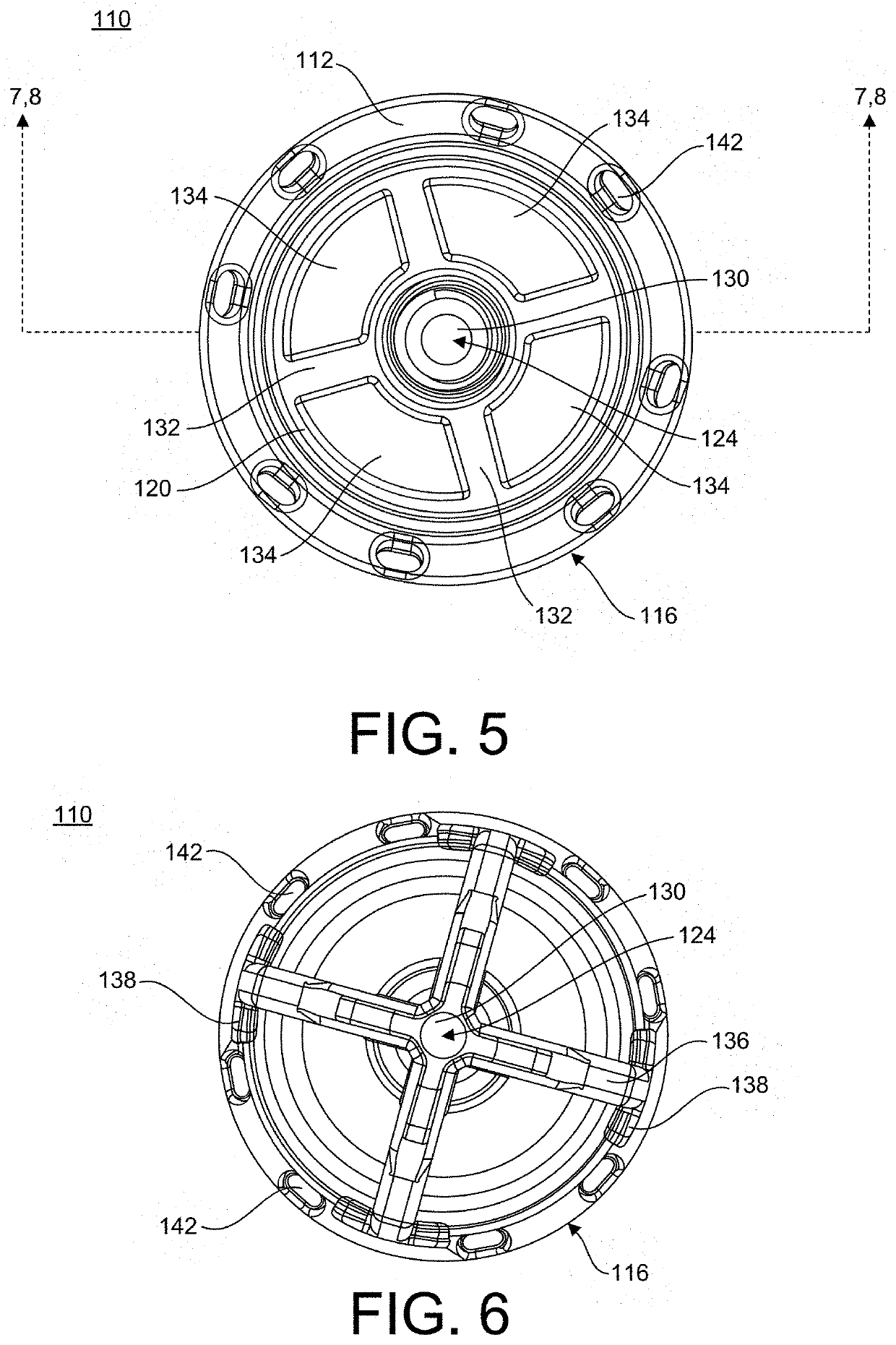
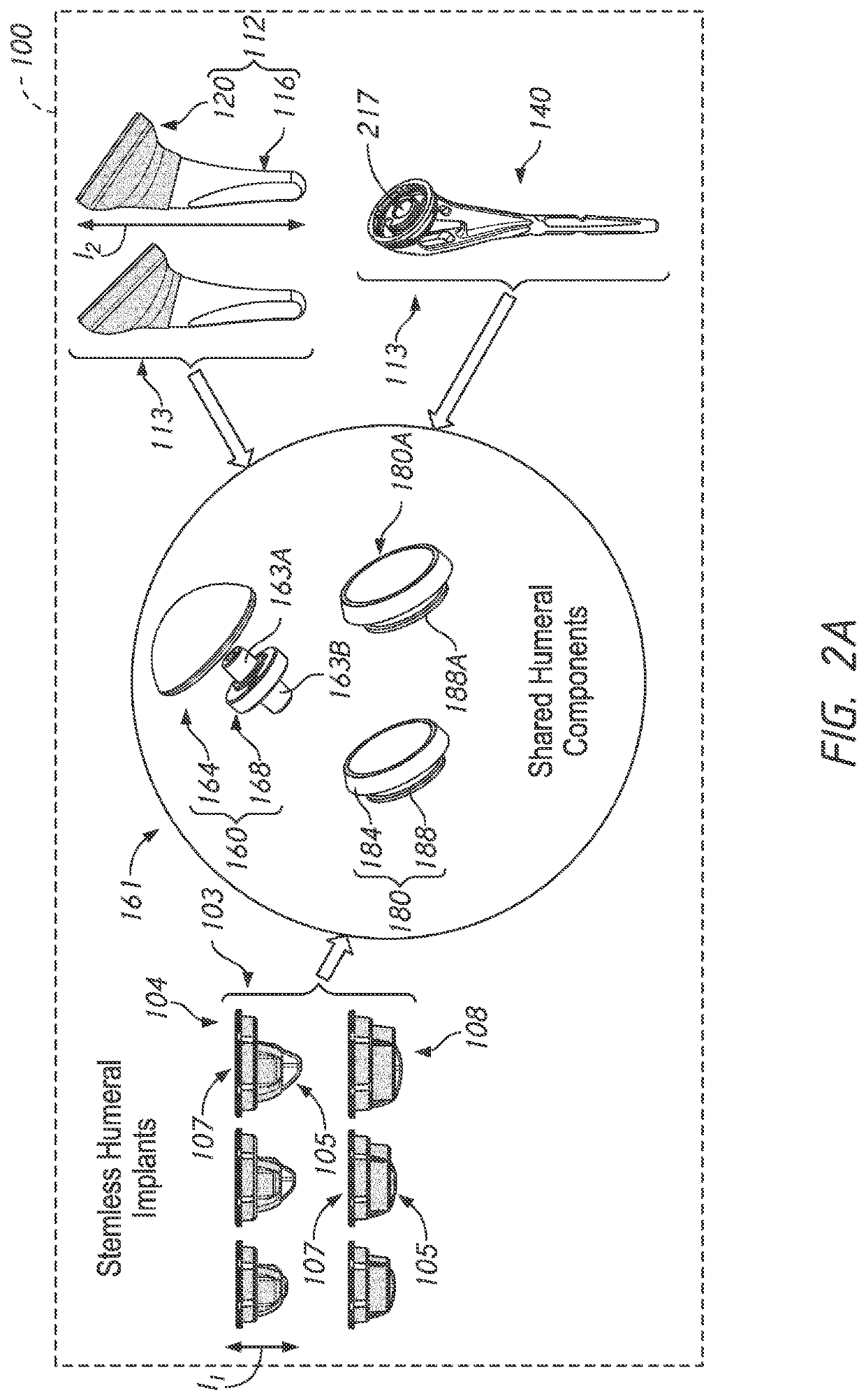
Stemless Metaphyseal Humeral Implant
A stemless prosthetic shoulder joint may include a prosthetic humeral head and a stemless base. The stemless base may include a collar and an anchor extending from the collar intended to anchor the base into the proximal humerus. The base may include a proximal collar having a proximal surface and a bone-engaging surface opposite the proximal surface. The collar may have a superior portion and an inferior portion, the superior portion defining an arc shape and the inferior portion defining a substantially triangular shape.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Shoulder prosthesis components and assemblies
PendingUS20220354658A1Reduce in quantityFacilitate placement and retentionJoint implantsSurgical sawsMedicineBone humerus
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Arthroscopic shoulder arthroplasty and method thereof
ActiveUS10595886B2Minimizing damageEasy extractionJoint implantsSurgical sawsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationBone humerus
A novel method and instrumentation for insertion of humeral and glenoid total shoulder implant using arthroscopic visualization for bony preparation as well as insertion of components through small incisions. Mini instruments and cannulated guides and reamers are used in order to perform the procedure under direct arthroscopic visualization. For ease of insertion, the components are inserted separately and assembled in situ. Securing the humeral components in place is accomplished with bicortical screw transfixing the central peg of component.
Owner:JOINT INNOVATION TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com