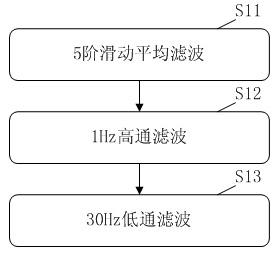
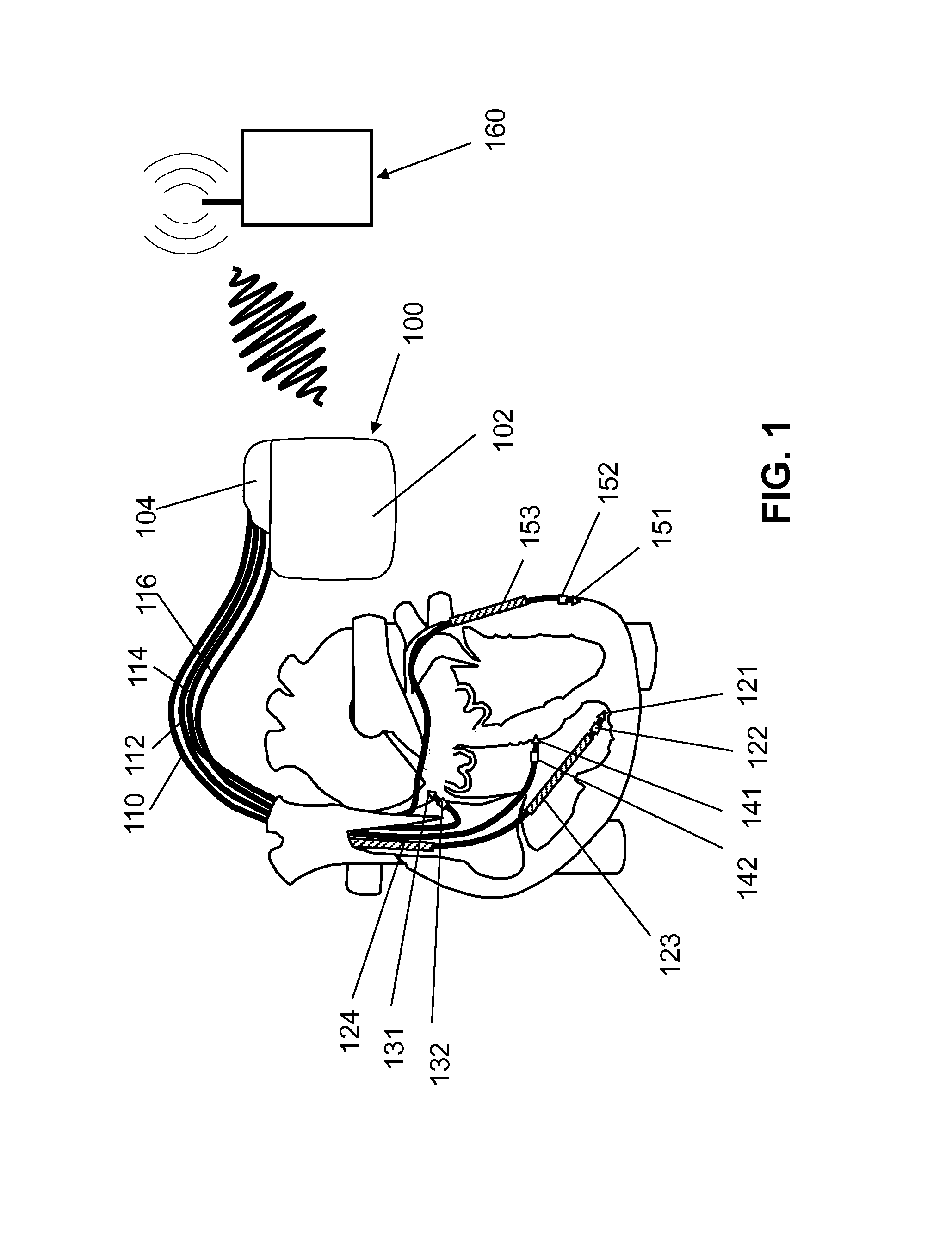
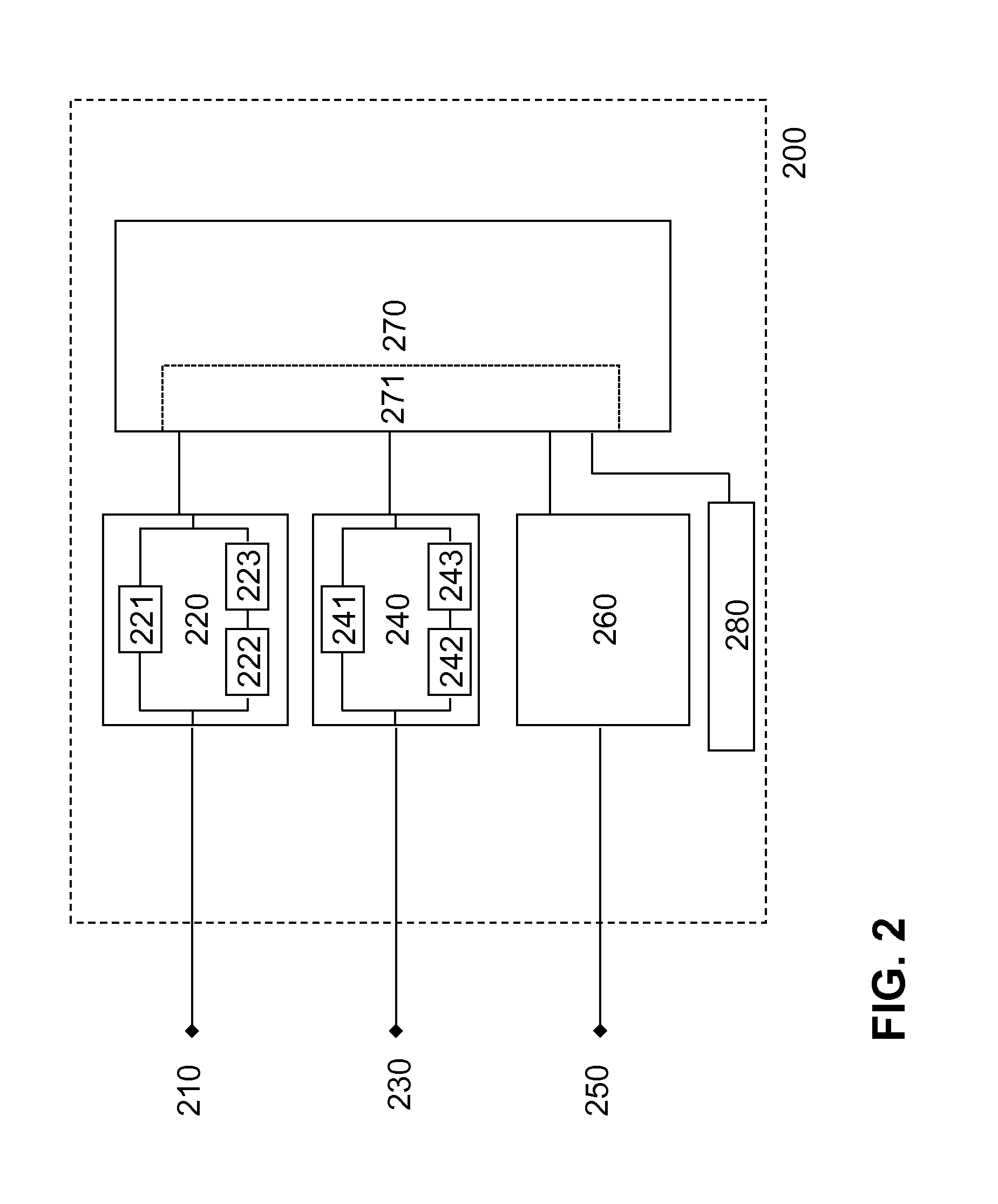
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "ATRIAL RHYTHMS" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
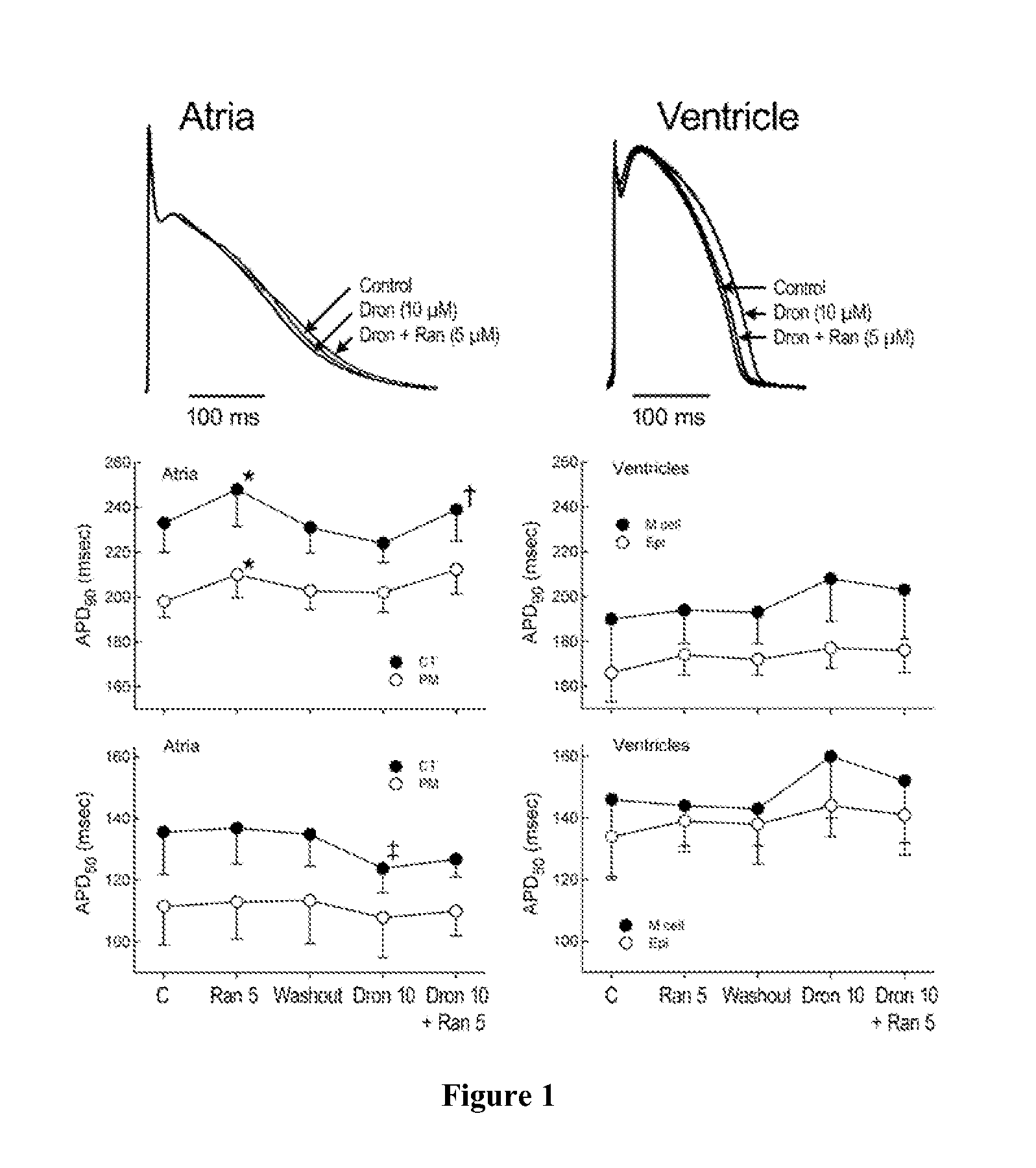
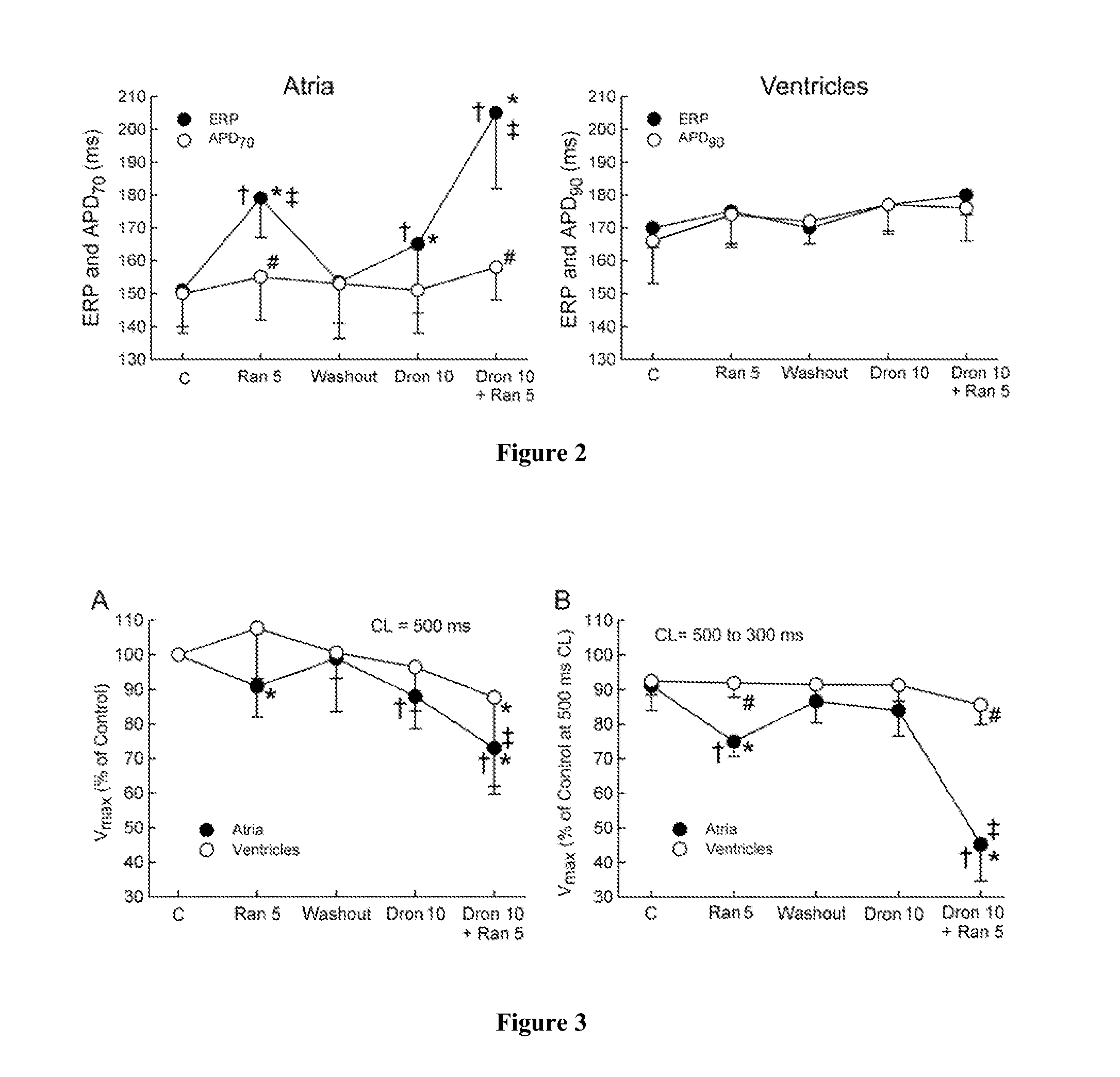
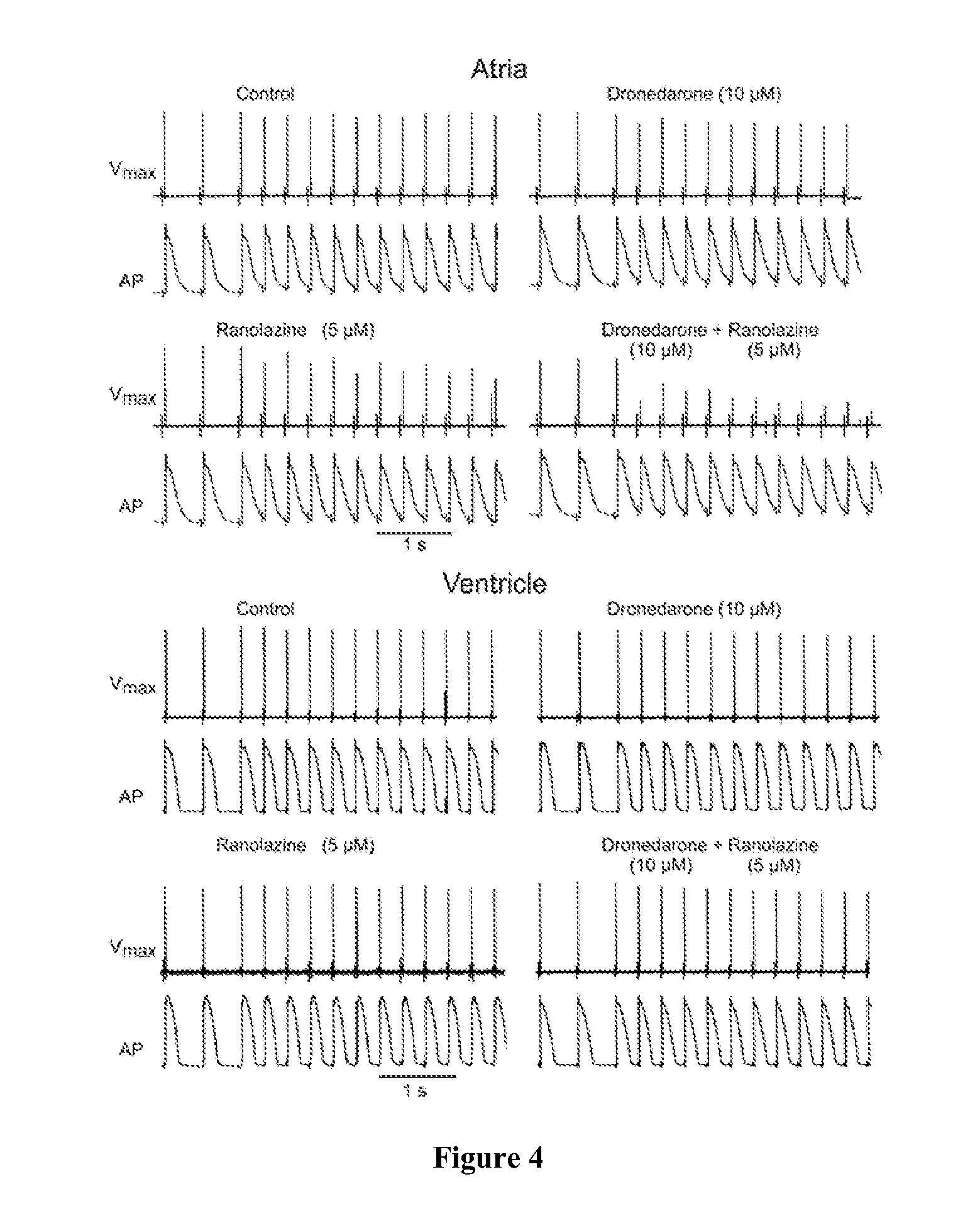
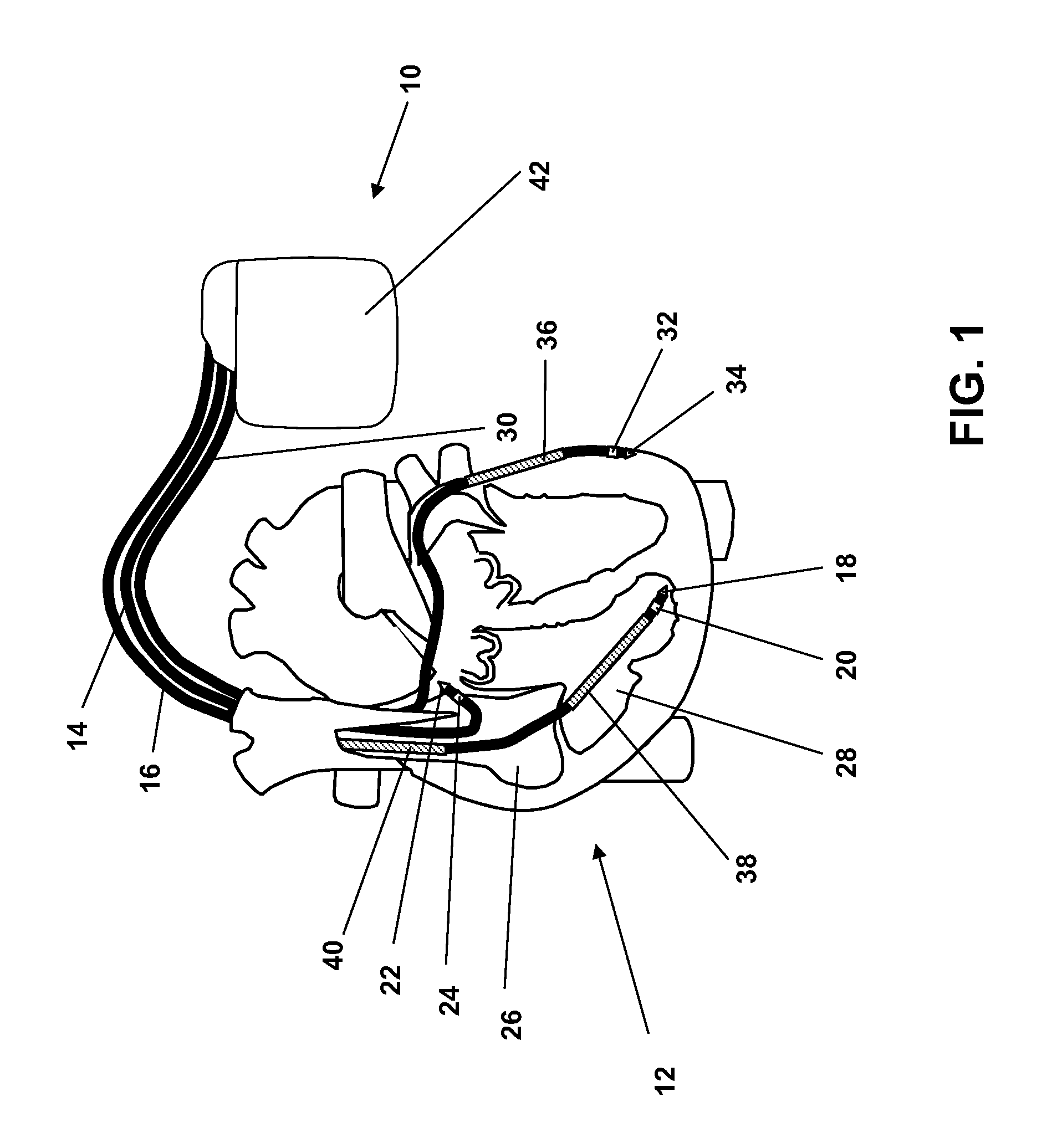
Method of treating atrial fibrillation
InactiveUS20110183990A1Reduce the amplitudeReduce adverse side effectsBiocideAnimal repellantsDronedaroneRanolazine
The present invention relates to a method for the treatment or prevention of atrial fibrillation and / or atrial flutter comprising coadministration of a synergistically therapeutic amount of dronedarone or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or salts thereof and a synergistically therapeutic amount of ranolazine or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or salts thereof. Also provided are methods for modulating ventricular and atrial rhythm and rate. This invention also relates to pharmaceutical formulations that are suitable for such combined administration.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
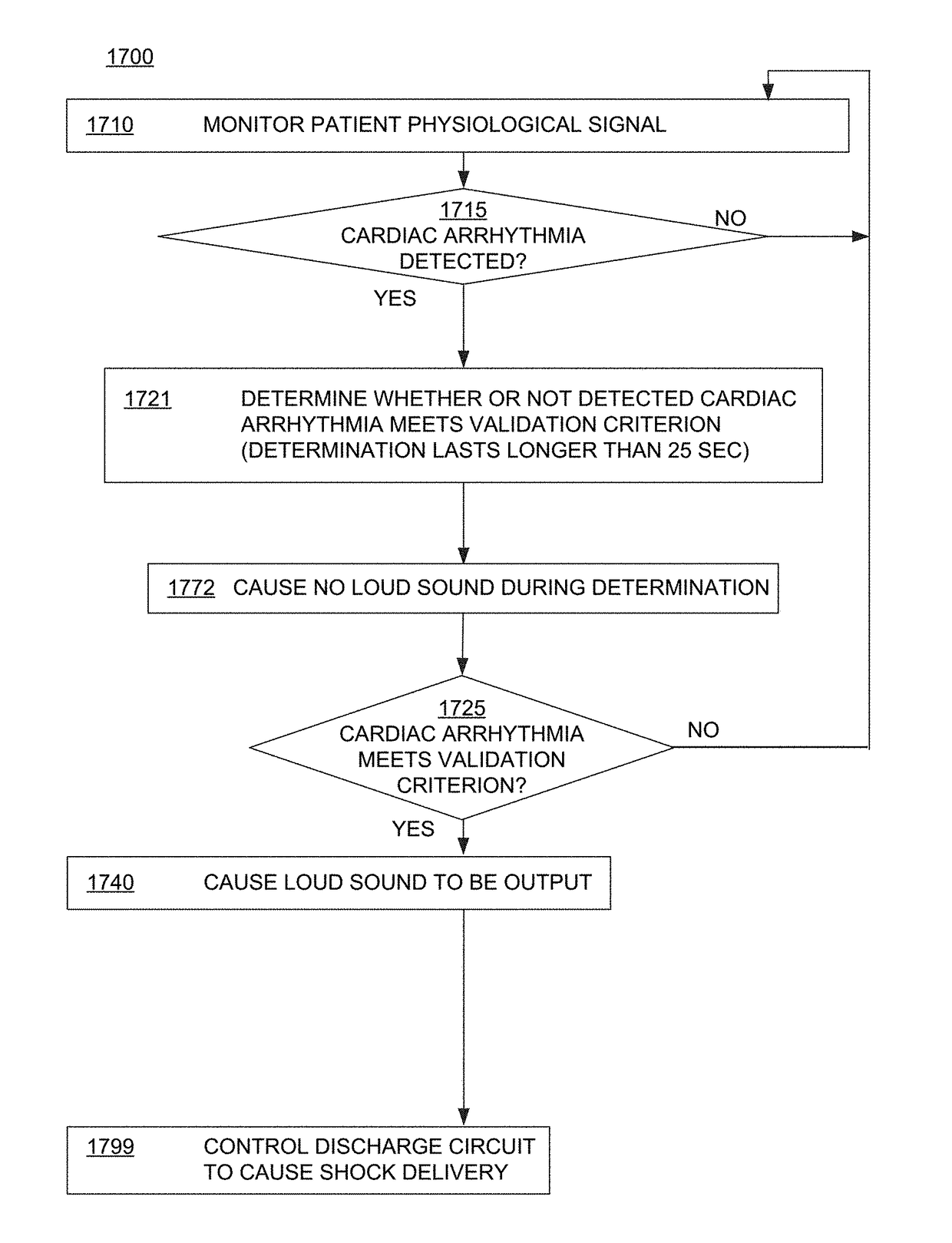
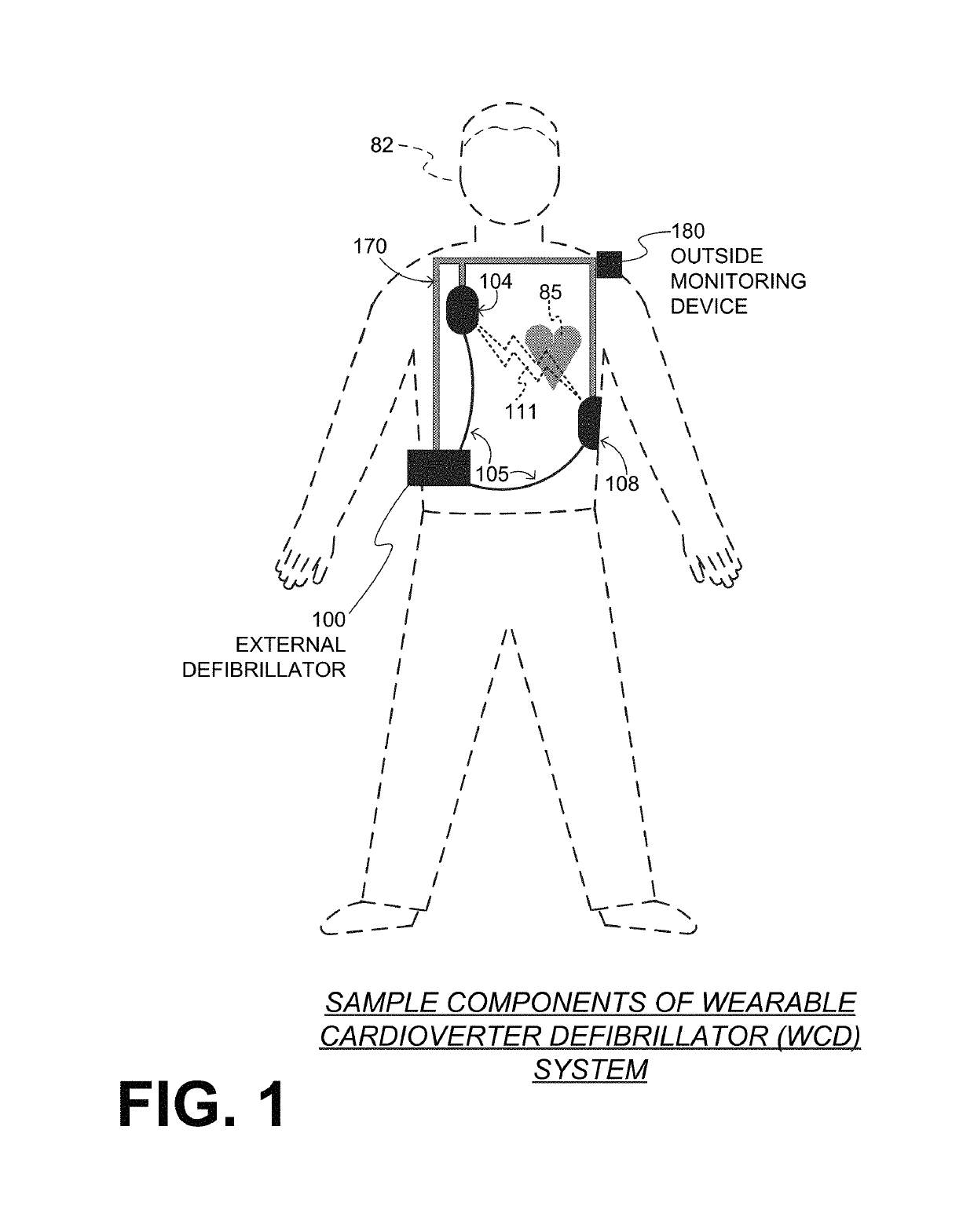
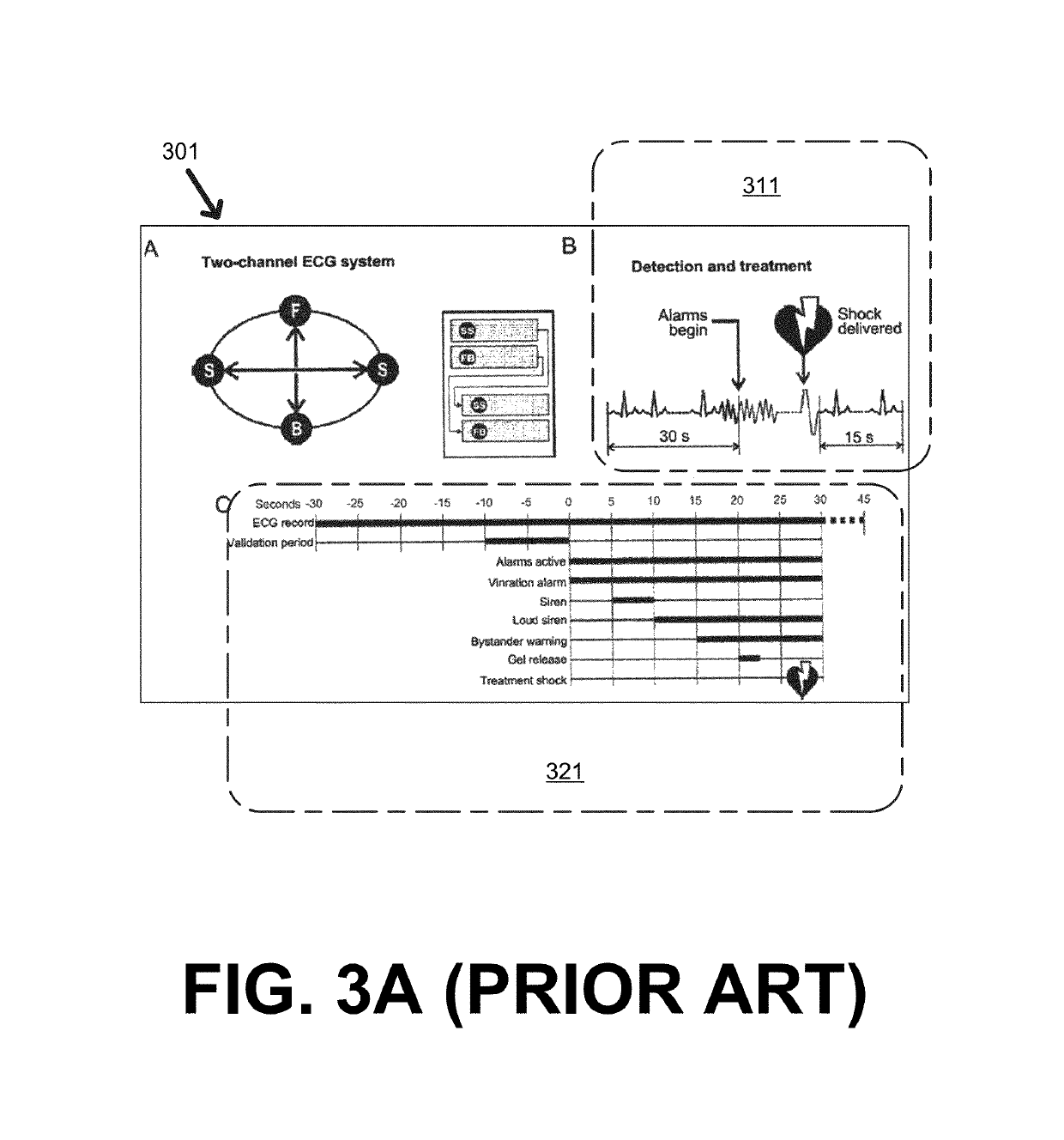
Wcd system validating detected cardiac arrhythmias thoroughly so as to not sound loudly due to some quickly self-terminating cardiac arrhythmias
ActiveUS20170319862A1Heart defibrillatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringWearable cardioverter defibrillatorCardiac arrhythmia
A wearable cardioverter defibrillator (“WCD”) system may output a loud sound after detecting and validating a shockable cardiac arrhythmia. In such embodiments, however, the WCD system might not sound a loud alarm before validating the arrhythmia thoroughly, i.e. for a longer time, thus giving the arrhythmia a further chance to self-terminate. The WCD system may thus detect more robustly the cardiac arrhythmias that do not self-terminate quickly. Such arrhythmias that self-terminate quickly may occur from likely harmless events occurring multiple times in the daily life of the patient, such as the patient becoming “winded” from climbing stairs. In embodiments the WCD system may notify the patient only discreetly, or even not at all. The lack of sounding such a loud alarm responsive to such events reduces the overall number of times in which the patient experiences unwanted attention by others, embarrassment, loss of privacy and dignity, and so on.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG DAC
Automated reapplication of atrial pacing therapies
InactiveUS6876880B2Good curative effectReducing atrial tachyarrhythmia burdenHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsAtrial pacingMedical device
The invention relates to the use of atrial pacing therapies to treat atrial tachycardia (AT). When an AT episode is detected, an implantable medical device applies an ATP therapy. If the AT episode persists, the ATP therapy may be automatically reapplied at a later time during the course of the same AT episode. In particular, previously used ATP therapies are reapplied when episodic conditions, such as cycle length or cycle regularity, change. Although a particular ATP therapy initially may be unsuccessful in terminating the AT, it may prove successful when the cycle length or regularity of the atrial rhythm changes. As the rhythm slows down, the AT may be more responsive to ATP therapies that were previously unsuccessful. As a result, potentially efficacious ATP therapies can be reapplied to terminate AT episodes, and reduce the number of episodes that require more aggressive termination by painful, atrial shocks.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
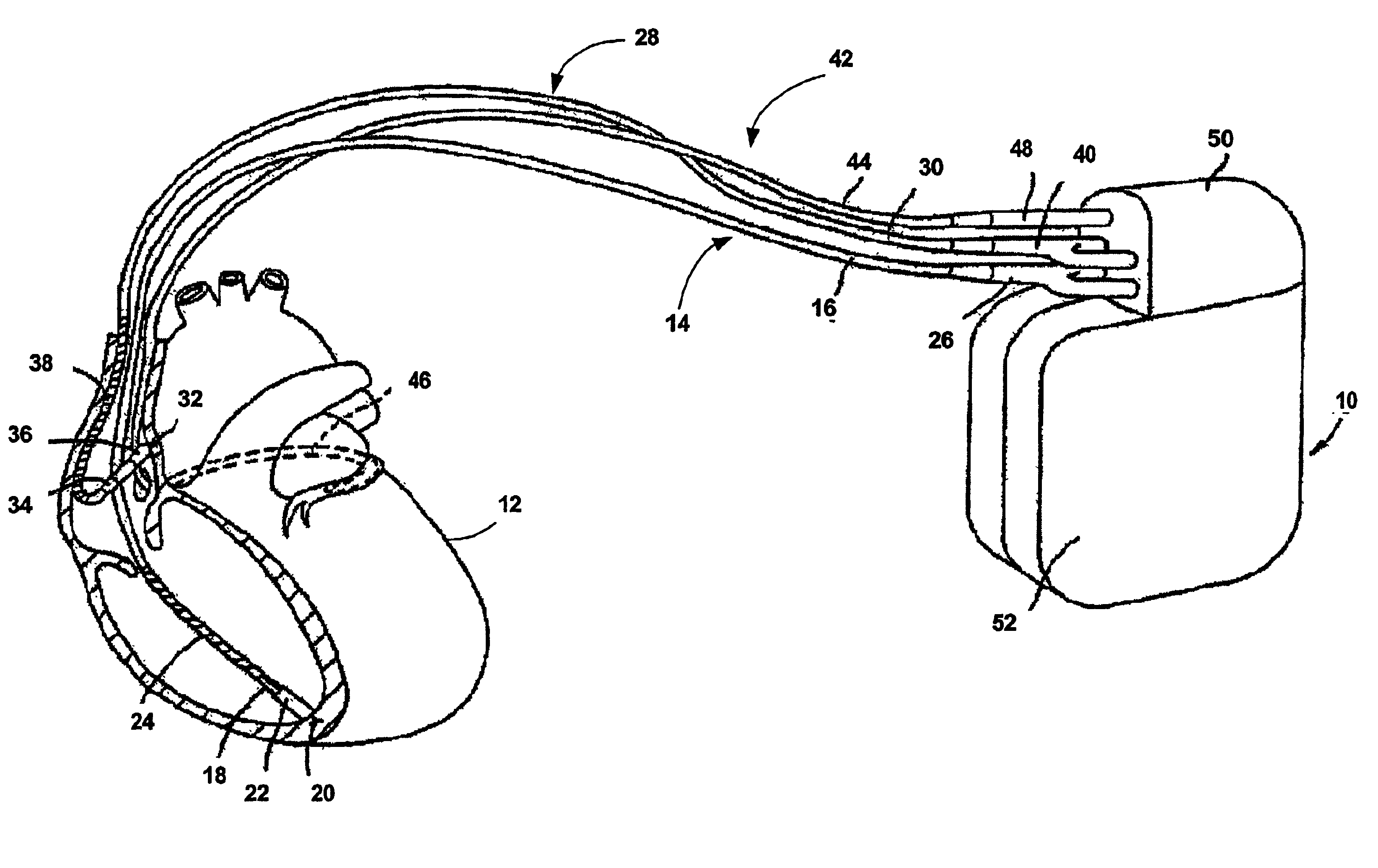
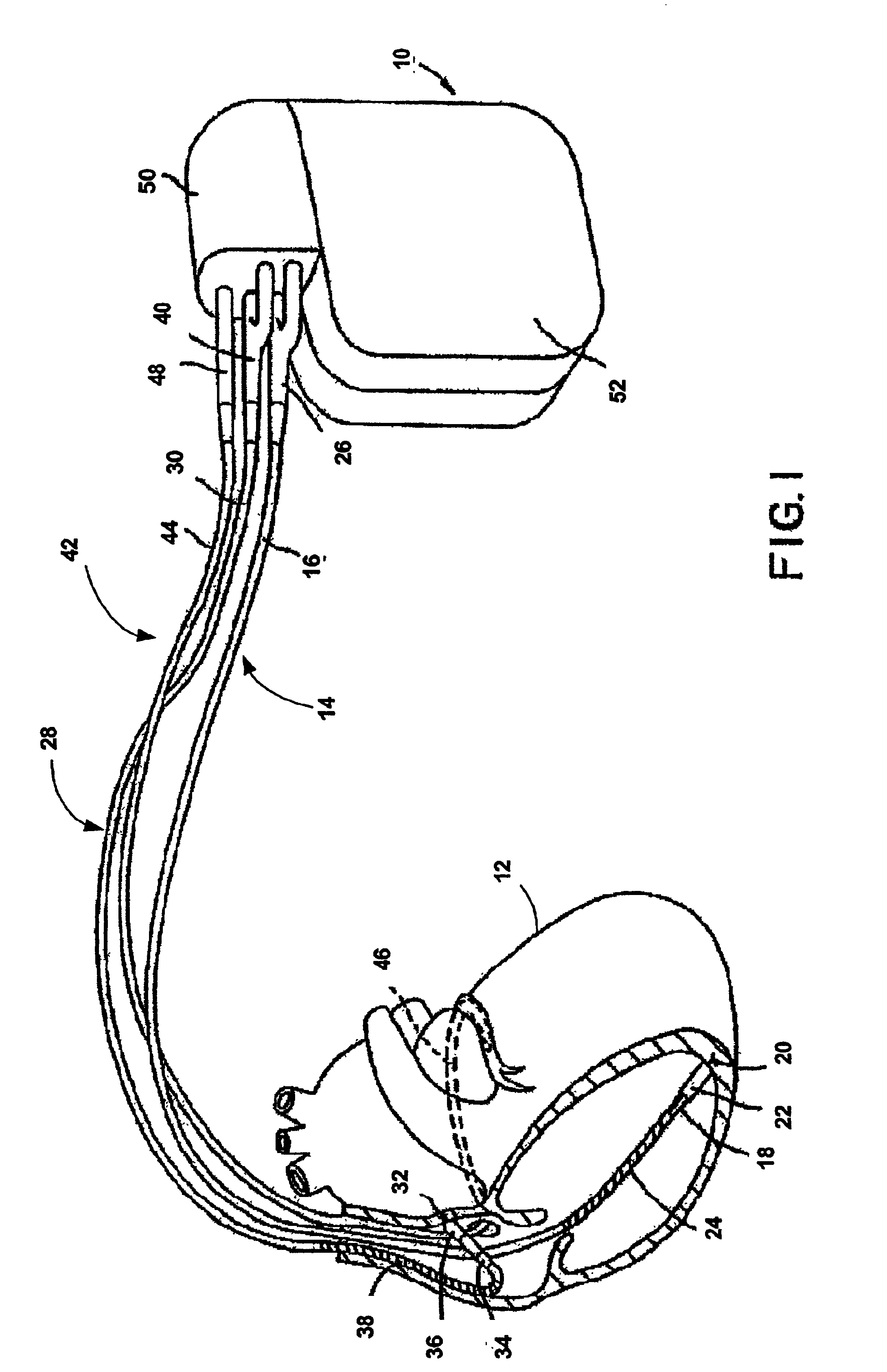
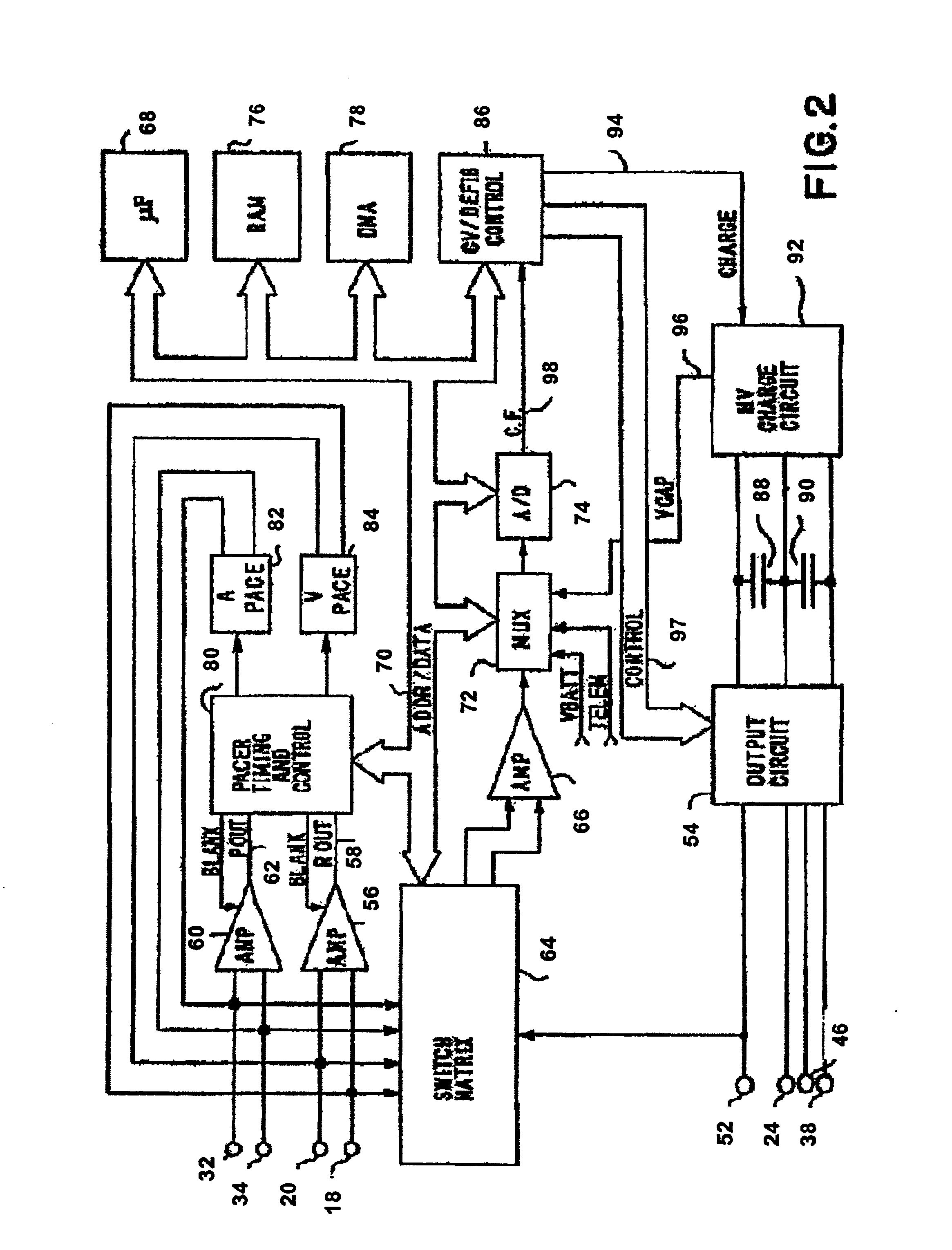
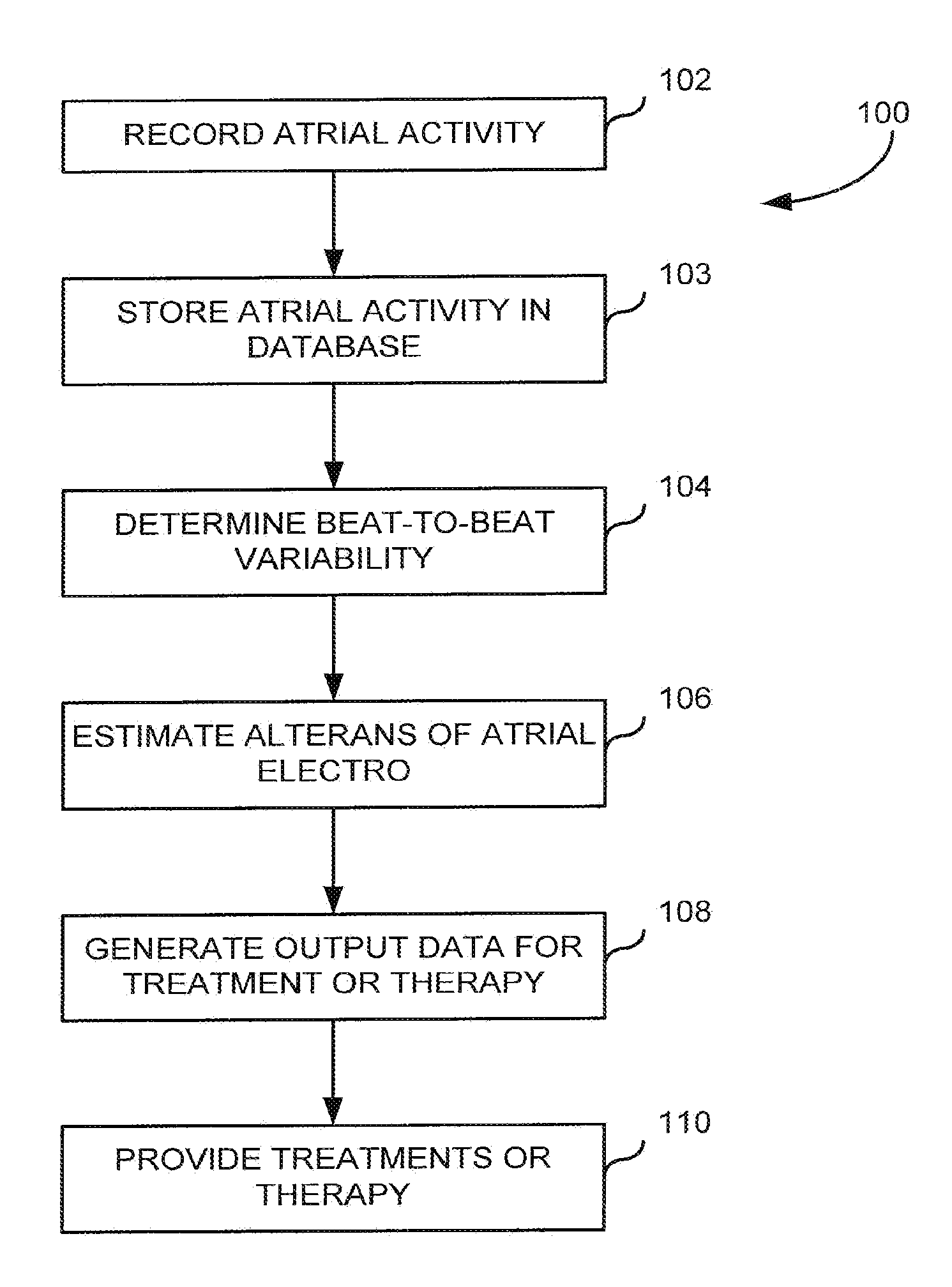
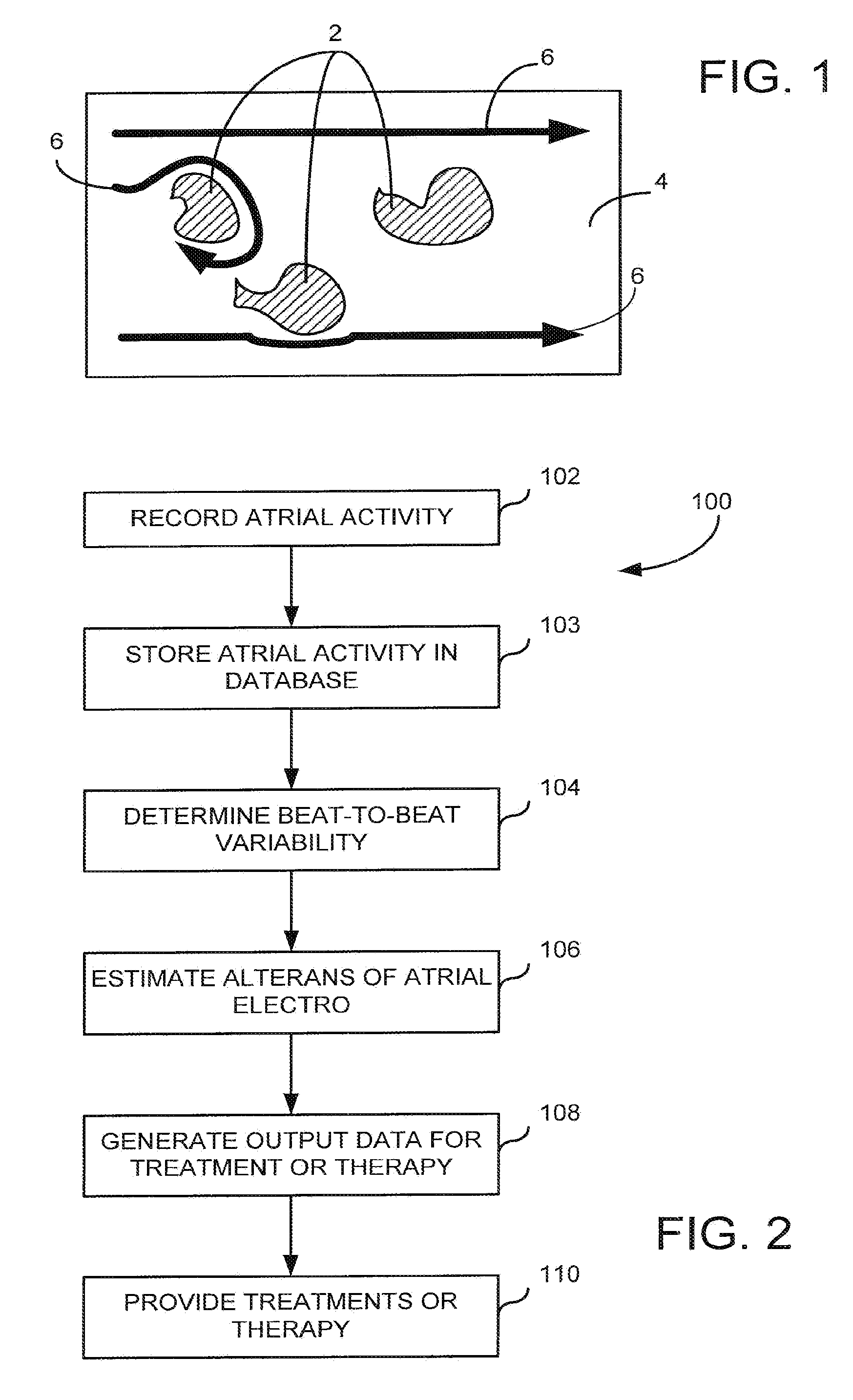
System and method for assessing atrial electrical stability
A method for identifying a susceptibility of a subject to atrial-rhythm disturbances includes a) placing a plurality of sensors on the subject to measure a physiologic signal of the subject, and b) recording the physiologic signal from the sensor. The physiologic signal includes an atrial electrical activity of the subject. The method includes c) determining a beat-to-beat variability in the atrial electrical activity of the subject. The beat-to-beat variability includes alternans of electrocardiographic waveforms of a predetermined number of a sequence of heart beats. The method includes d) determining a susceptibility to atrial-rhythm disturbances of the subject using the beat-to-beat variability in the atrial electrical activity determined in step c), and e) generating a report of the susceptibility to atrial-rhythm disturbances of the subject.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
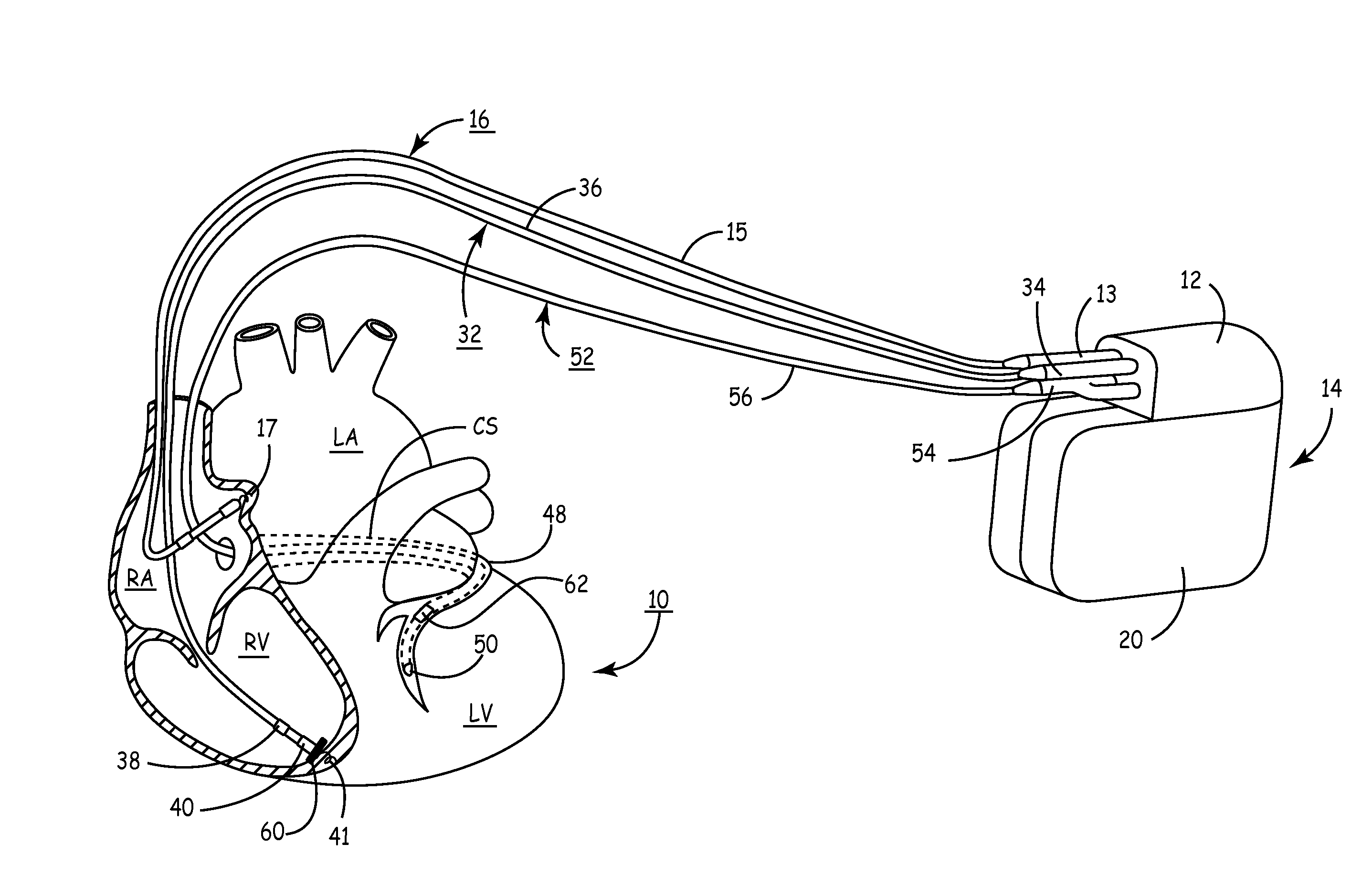
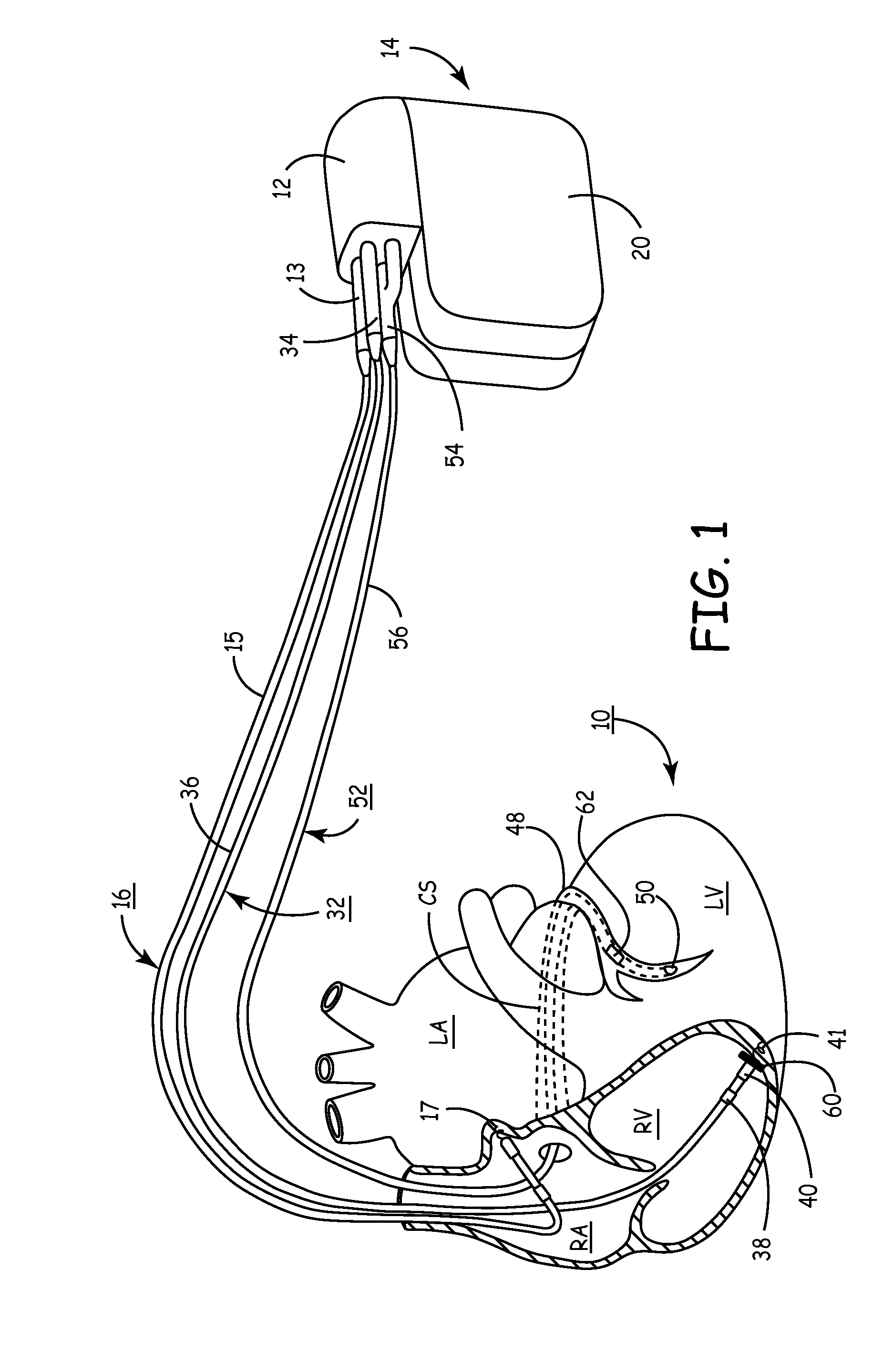
System providing ventricular pacing and biventricular coordination
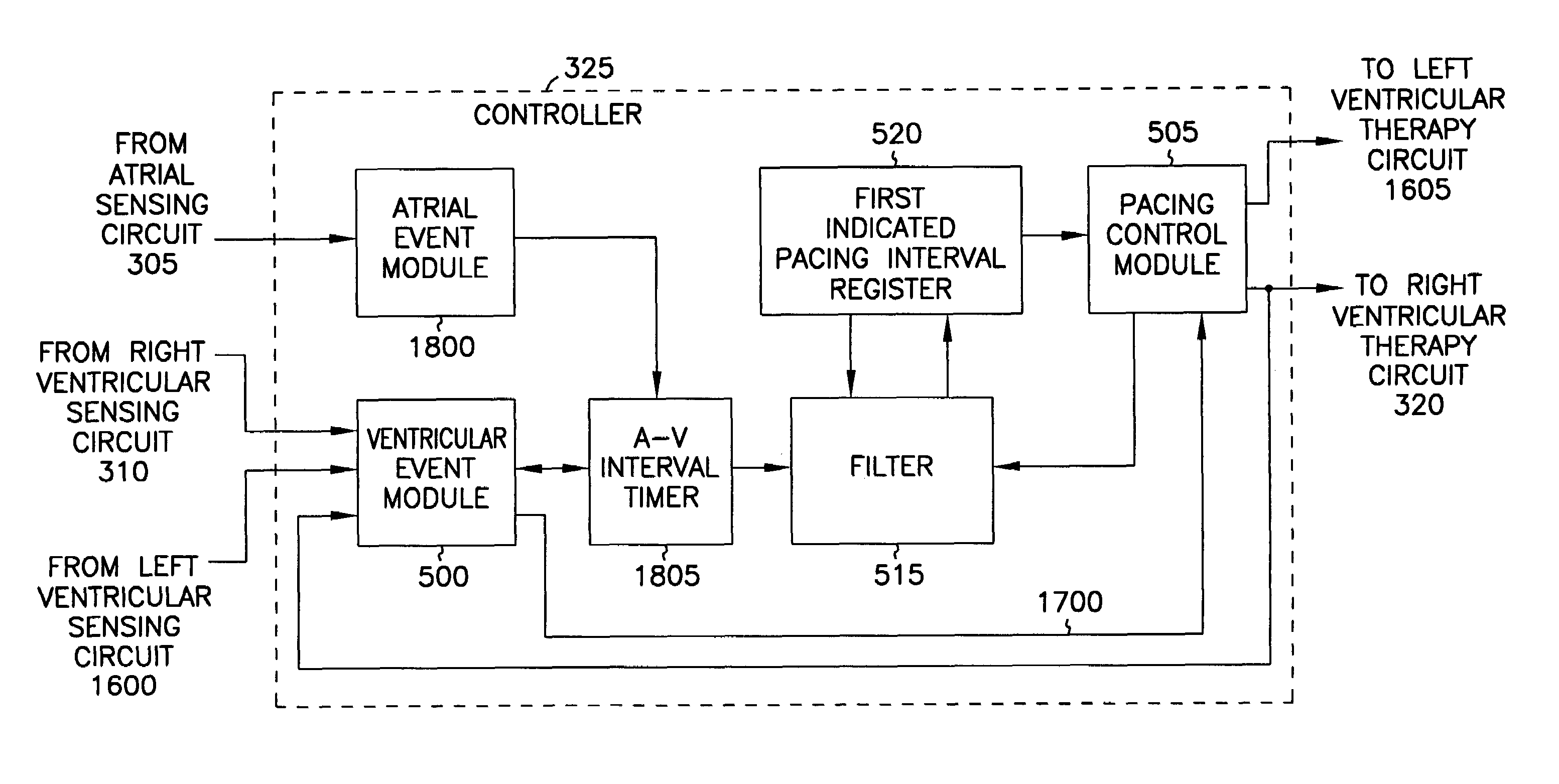
A cardiac rhythm management system includes techniques for computing an indicated pacing interval, AV delay, or other timing interval. In one embodiment, a variable indicated pacing interval is computed based at least in part on an underlying intrinsic heart rate. The indicated pacing interval is used to time the delivery of biventricular coordination therapy even when ventricular heart rates are irregular, such as in the presence of atrial fibrillation. In another embodiment, a variable filter indicated AV interval is computed based at least in part on an underlying intrinsic AV interval. The indicated AV interval is used to time the delivery of atrial tracking biventricular coordination therapy when atrial heart rhythms are not arrhythmic. Other indicated timing intervals may be similarly determined. The indicated pacing interval, AV delay, or other timing interval can also be used in combination with a sensor indicated rate indicator.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
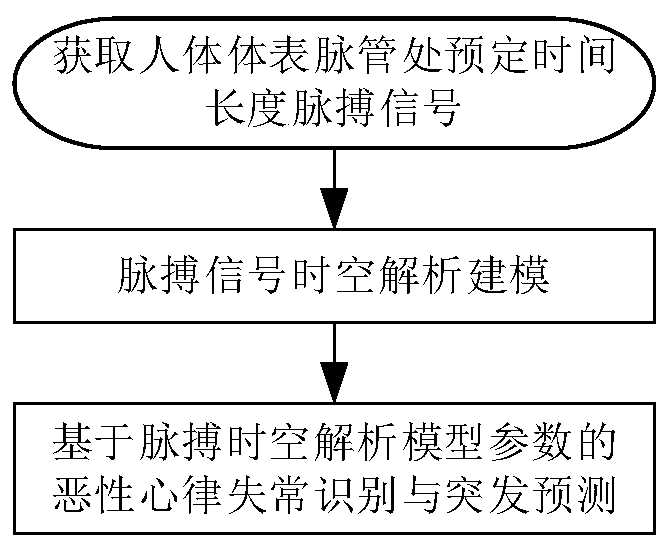
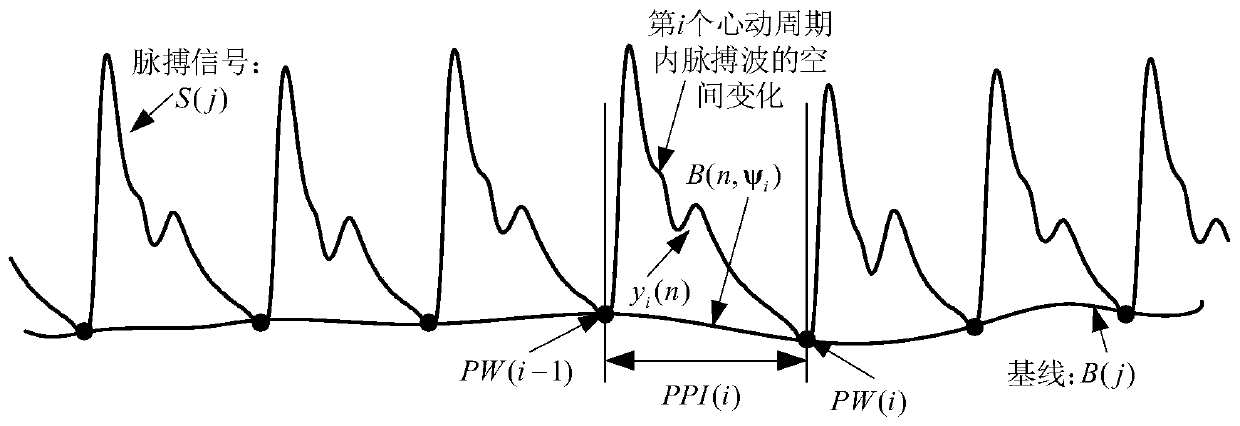
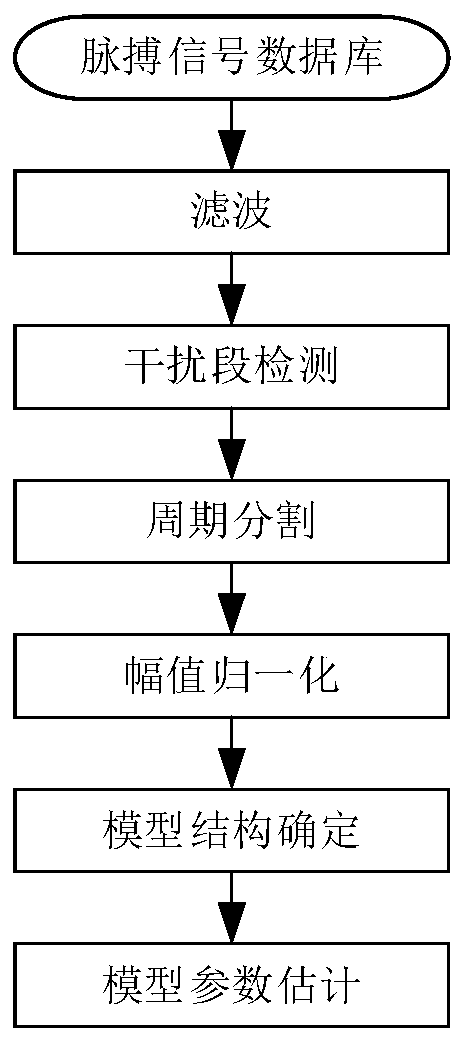
System for judging age and health status and identifying malignant arrhythmia by pulse signal time-space domain combination model
ActiveCN110037668ASuitable for remote monitoringHigh precisionCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringModel parametersDomain combination
The invention discloses a system for judging age and health status and identifying malignant arrhythmia by a pulse signal time-space domain combination model. The system comprises the following steps:acquiring pulse signals at a vessel part of the body surface of a human body for a preset time length; performing pulse signal time-space resolution modeling; and performing malignant arrhythmia identification and outbreak prediction based on the parameters of the pulse time-space analytical model. The invention proposes use of the pulse time-space analytical model to quantitatively describe pulse signal periods and waveform change, can judge age and rhythm of the heart, and can realize intelligent identification of malignant arrhythmia and outbreak early warning.
Owner:JIANGSU SAIKANG MEDICAL EQUIP
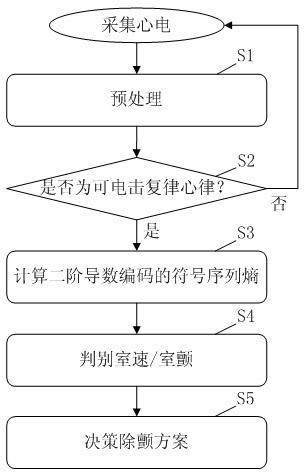
External defibrillator for automatic identification of ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation based on symbolic sequence entropy of second-order derivative coding
InactiveCN102284138AAccurate identificationIncreased sensitivityHeart defibrillatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringMedical equipmentVentricular tachycardia
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical equipment, and particularly relates to an in-vitro defibrillator for distinguishing ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation automatically on the basis of a symbol sequence entropy of second derivative codes. In the in-vitro defibrillator, shockable rhythms are distinguished automatically to be the ventricular tachycardia or the ventricular fibrillation by calculating the symbol sequence entropy of second derivative codes of a signal, so that the appropriate defibrillation scheme is determined on the basis of the ventricular tachycardia or the ventricular fibrillation, wherein the scheme comprises the following steps of: preprocessing, namely filtering the collected electrocardiosignal; identifying if the electrocardiosignal is the shockable rhythms or not; calculating the symbol sequence entropy of the second derivative codes of the shockable rhythms; distinguishing the ventricular tachycardia / the ventricular fibrillation according to the symbol sequence entropy; and deciding the defibrillation scheme according to the ventricular tachycardia / the ventricular fibrillation. The in-vitro defibrillator can reduce the injury on mind and bodies of patients and improve the pertinence and success rate of defibrillation.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
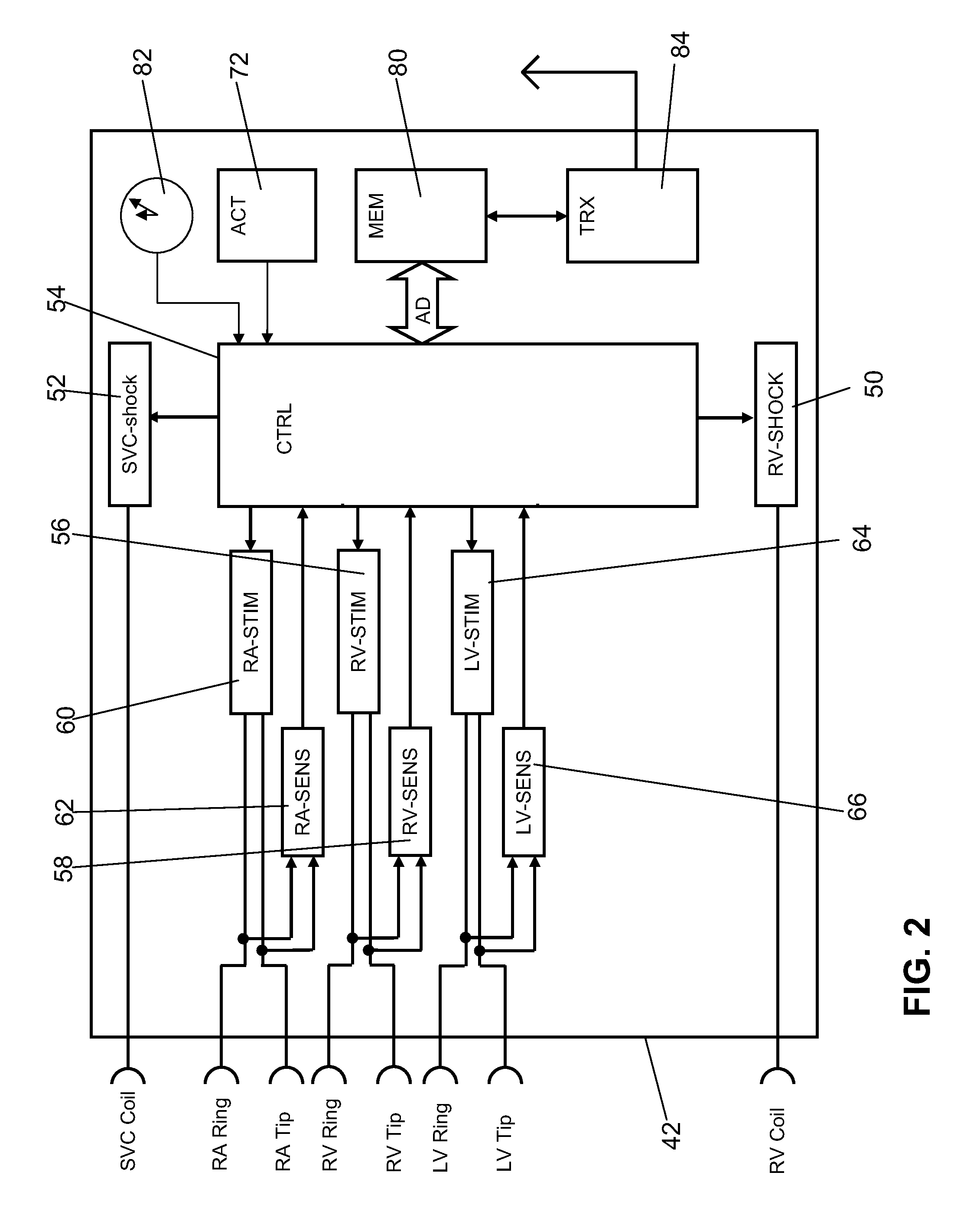
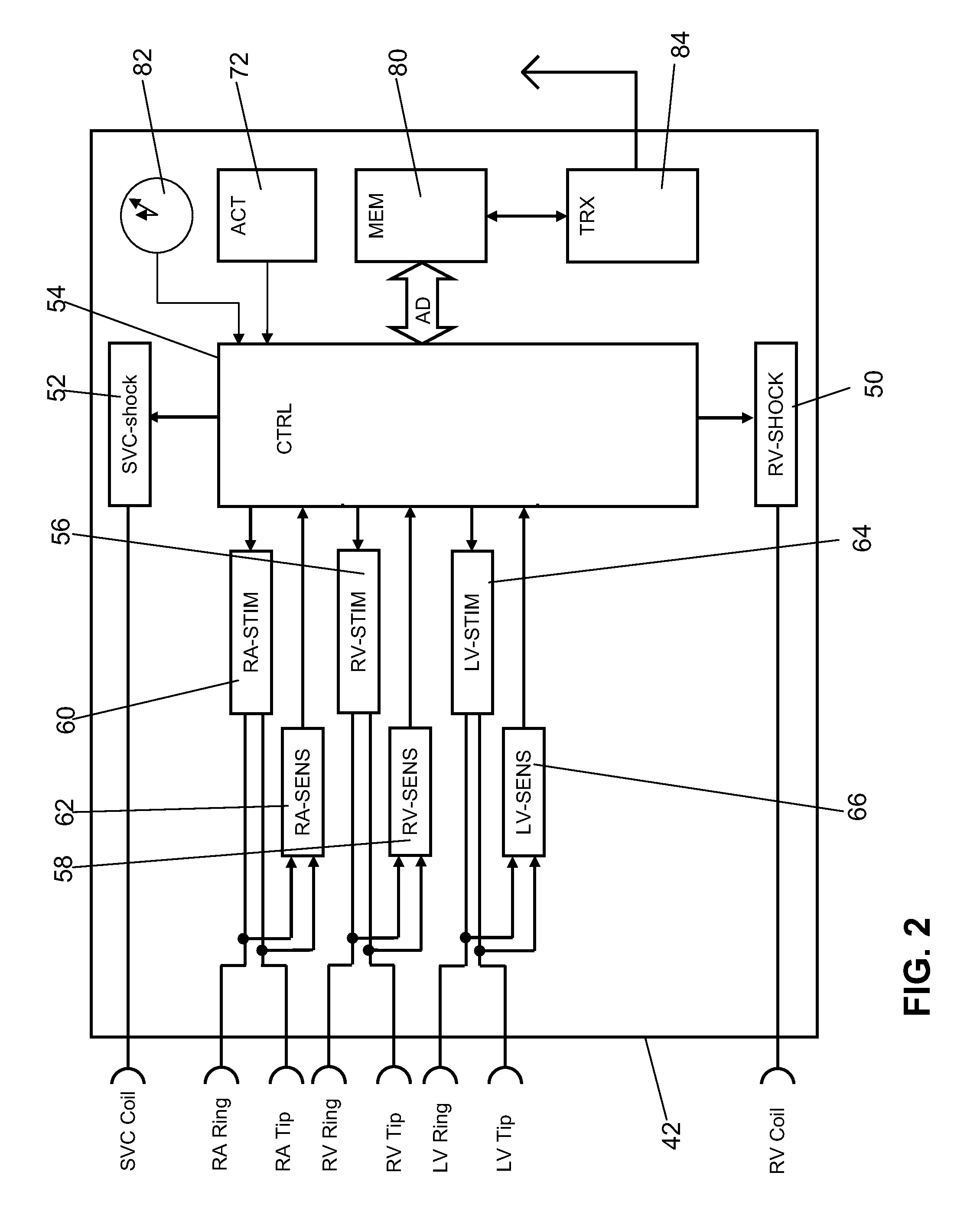
Cardiac stimulator for delivery of cardiac contractility modulation therapy
ActiveUS20130006319A1Immense clinical benefitGreat therapeutic benefitHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsCardiac muscleContractility
A combination cardiac stimulator for CRT stimulation and CCM stimulation, which is connected to a rhythm evaluation unit which can either detect a sinus rhythm that is present, or classify an atrial arrhythmia, and which comprises an additional therapy selection unit, wherein the therapy selection unit selects the delivery of either CRT therapy or CCM therapy on the basis of the classification of the atrial rhythm such that CRT therapy is preferred in the case of sinus rhythm, and CCM therapy is delivered in the case of atrial arrhythmia.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
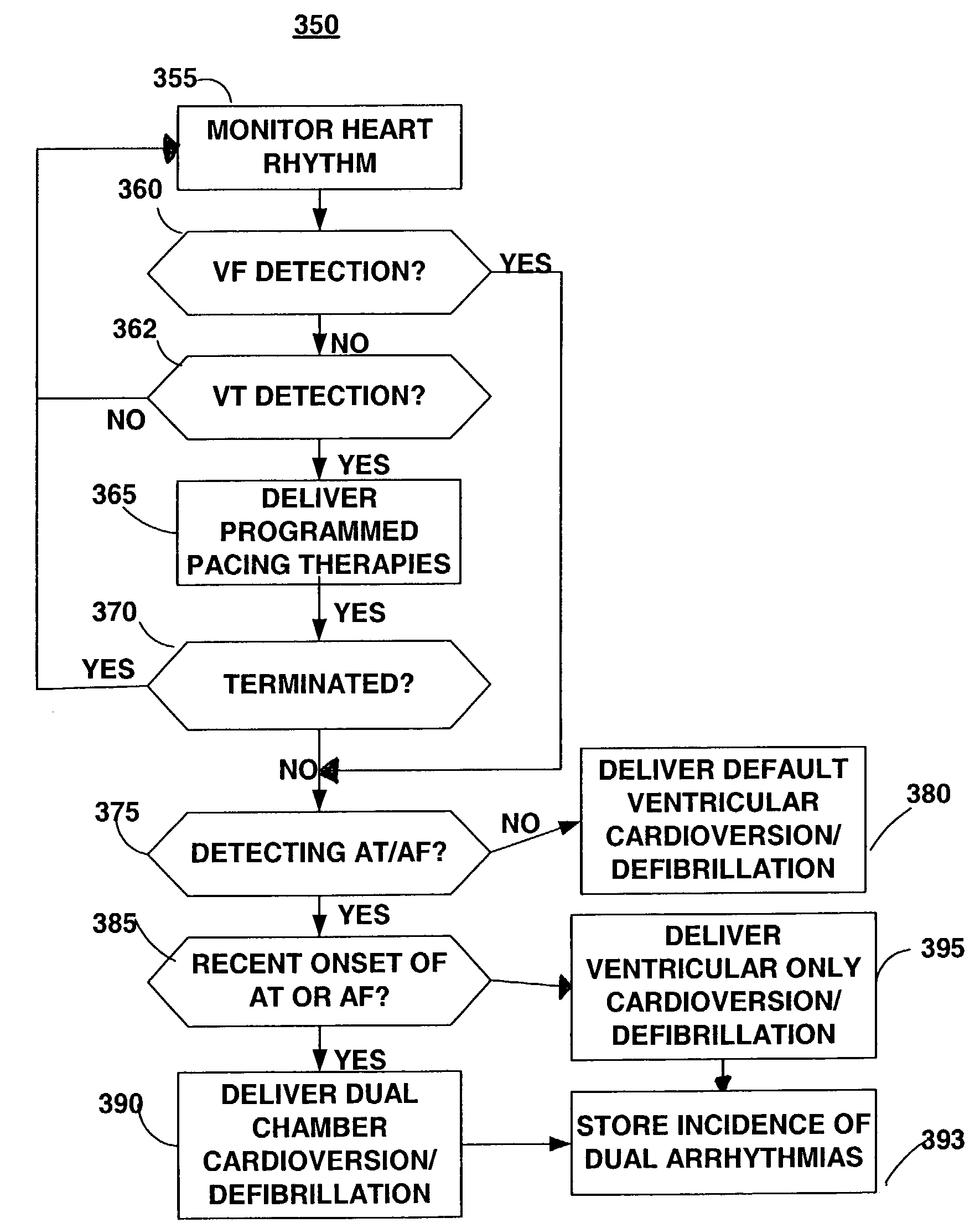
Configurable cardioversion and defibrillation therapies in the presence of coexisting atrial and ventricular arrhythmia
InactiveUS7313436B2Reduce riskProvide goodHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsVentricular dysrhythmiaAtrial cavity
An implantable cardioverter defibrillator system and method are provided having configurable shock therapies selected based on an evaluation of the atrial rhythm status following a ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation detection. A dual chamber shock configuration is selected if the ventricular arrhythmia is co-existing with an atrial arrhythmia of recent onset. A ventricular only shock configuration is selected if the ventricular arrhythmia is co-existing with a sustained atrial arrhythmia.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and method for conditional biventricular pacing
An implantable pacing system with single, double and triple chamber pacing capabilities, provided individually or in concert on a conditional or continuous basis depending upon ongoing analyses of atrial rhythm status, atrioventricular conduction status and ventricular rate. A mode is selected to reduce the occurrence of any ventricular pacing in favor of intrinsic atrioventricular and ventricular conduction. If excessively long PR intervals are occurring too frequently or atrioventricular conduction is unreliable or absent, the implantable pulse generator is operated in a conditional triple chamber pacing mode that provides atrial-synchronous biventricular pacing in every cardiac cycle for a period of time as necessary to restore and maintain AV synchrony, while minimizing ventricular asynchrony otherwise associated with monochamber RV pacing as in conventional dual chamber pacing systems. Similarly, biventricular pacing is provided in every cardiac cycle when ventricular rates are undesirably slow during atrial fibrillation, where AV synchronization is excluded.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
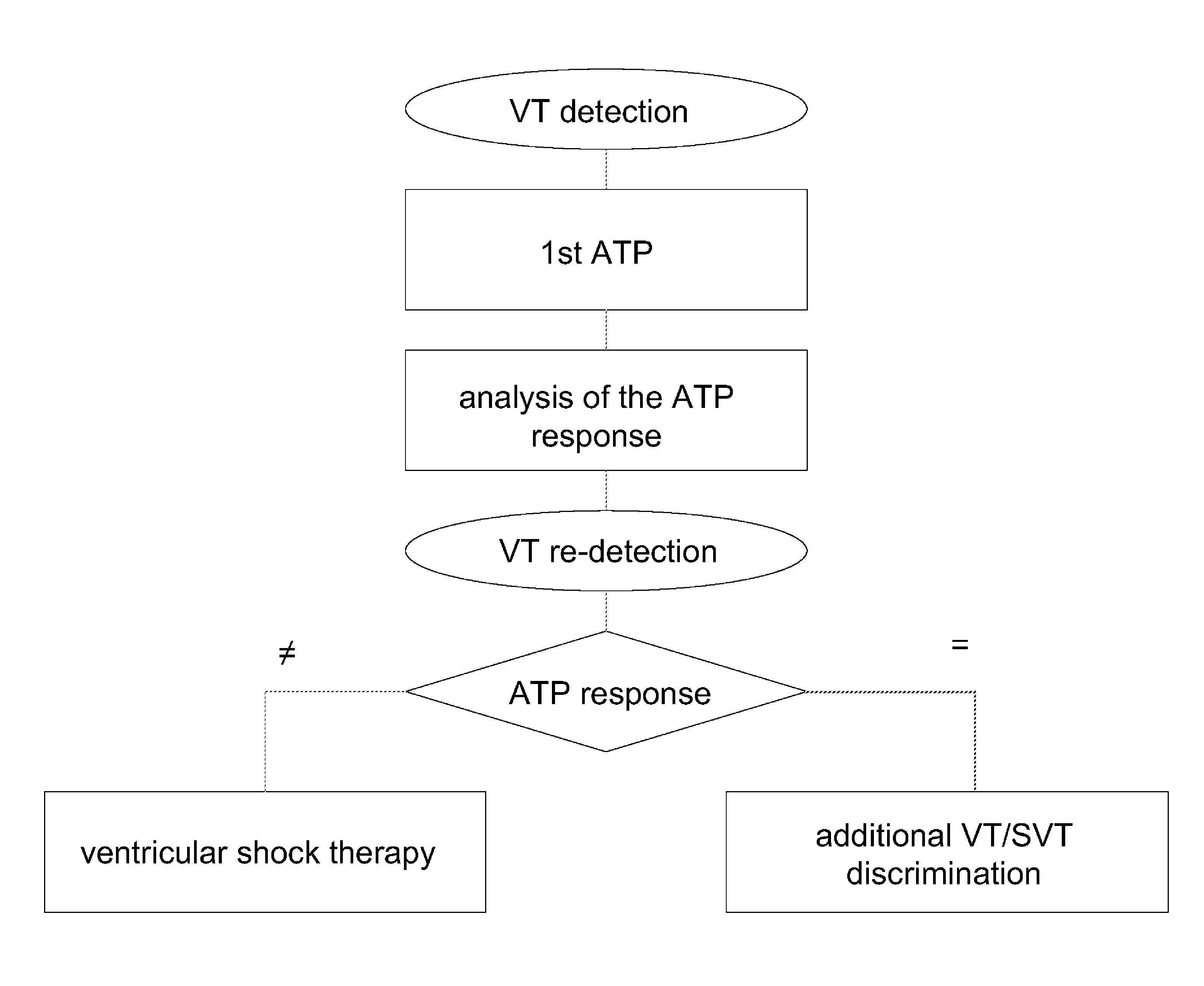
Antitachycardiac stimulator
ActiveUS20090264947A1Prevent inadequate shock therapyExtend detection timeHeart defibrillatorsInternal electrodesNodal rhythmSupraventricular tachycardia
Implantable cardiac stimulator, with chamber stimulation unit connectable to left / right ventricular stimulation electrode to generate / deliver chamber stimulation pulses for stimulation of ventricle; ventricular sensing unit (VSU) to detect respective chamber contraction and deliver ventricular sensing signal when chamber contraction detected; optional atrial stimulation unit, connectable to atrial stimulation electrode to generate atrial stimulation pulses to stimulate atrium; atrial sensing unit, to detect atrial contraction, deliver atrial sensing signal indicating respective atrial event; tachycardia detection unit, connected to VSU to detect and categorize ventricular / supraventricular tachycardia; treatment control unit (TCU), triggers chamber stimulation unit to deliver antitachycardiac stimulation (ATP); analyzer unit, connected to atrial sensing unit and TCU. Analyzes atrial events from sensing unit before / during / after delivering antitachycardiac stimulation for atrial rhythm pattern during ventricular ATP by comparison atrial rhythm pattern immediately before ATP and to trigger TCU as function of ATP response signal representing comparison result for selection of the following antitachycardiac treatment.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
In-vitro defibrillator for distinguishing ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation automatically on basis of symbol sequence entropy of second derivative codes
InactiveCN102284138BAccurate identificationIncreased sensitivityHeart defibrillatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringEcg signalMedical equipment
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical equipment, and particularly relates to an in-vitro defibrillator for distinguishing ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation automatically on the basis of a symbol sequence entropy of second derivative codes. In the in-vitro defibrillator, shockable rhythms are distinguished automatically to be the ventricular tachycardia or the ventricular fibrillation by calculating the symbol sequence entropy of second derivative codes of a signal, so that the appropriate defibrillation scheme is determined on the basis of the ventricular tachycardia or the ventricular fibrillation, wherein the scheme comprises the following steps of: preprocessing, namely filtering the collected electrocardiosignal; identifying if the electrocardiosignal is the shockable rhythms or not; calculating the symbol sequence entropy of the second derivative codes of the shockable rhythms; distinguishing the ventricular tachycardia / the ventricular fibrillation according to the symbol sequence entropy; and deciding the defibrillation scheme according to the ventricular tachycardia / the ventricular fibrillation. The in-vitro defibrillator can reduce the injury on mind and bodies of patients and improve the pertinence and success rate of defibrillation.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Antitachycardiac stimulator
InactiveUS7983752B2Extend detection timeStrong specificityHeart stimulatorsNodal rhythmSupraventricular tachycardia
Implantable cardiac stimulator, with chamber stimulation unit connectable to left / right ventricular stimulation electrode to generate / deliver chamber stimulation pulses for stimulation of ventricle; ventricular sensing unit (VSU) to detect respective chamber contraction and deliver ventricular sensing signal when chamber contraction detected; optional atrial stimulation unit, connectable to atrial stimulation electrode to generate atrial stimulation pulses to stimulate atrium; atrial sensing unit, to detect atrial contraction, deliver atrial sensing signal indicating respective atrial event; tachycardia detection unit, connected to VSU to detect and categorize ventricular / supraventricular tachycardia; treatment control unit (TCU), triggers chamber stimulation unit to deliver antitachycardiac stimulation (ATP); analyzer unit, connected to atrial sensing unit and TCU. Analyzes atrial events from sensing unit before / during / after delivering antitachycardiac stimulation for atrial rhythm pattern during ventricular ATP by comparison atrial rhythm pattern immediately before ATP and to trigger TCU as function of ATP response signal representing comparison result for selection of the following antitachycardiac treatment.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
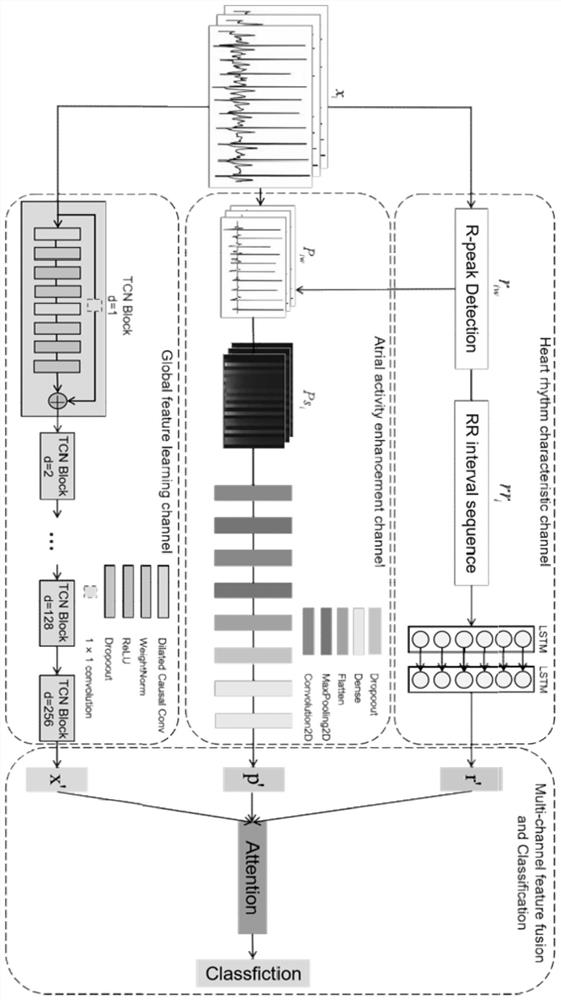
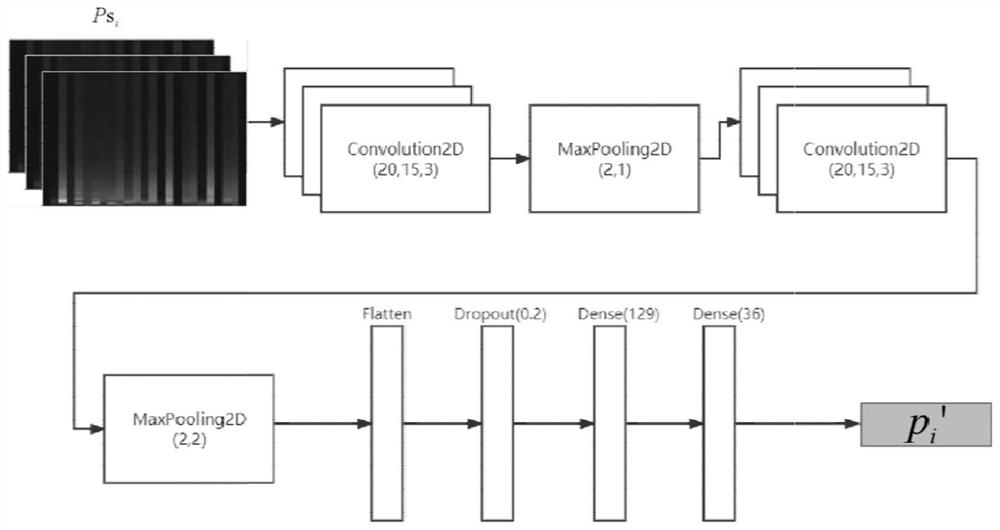
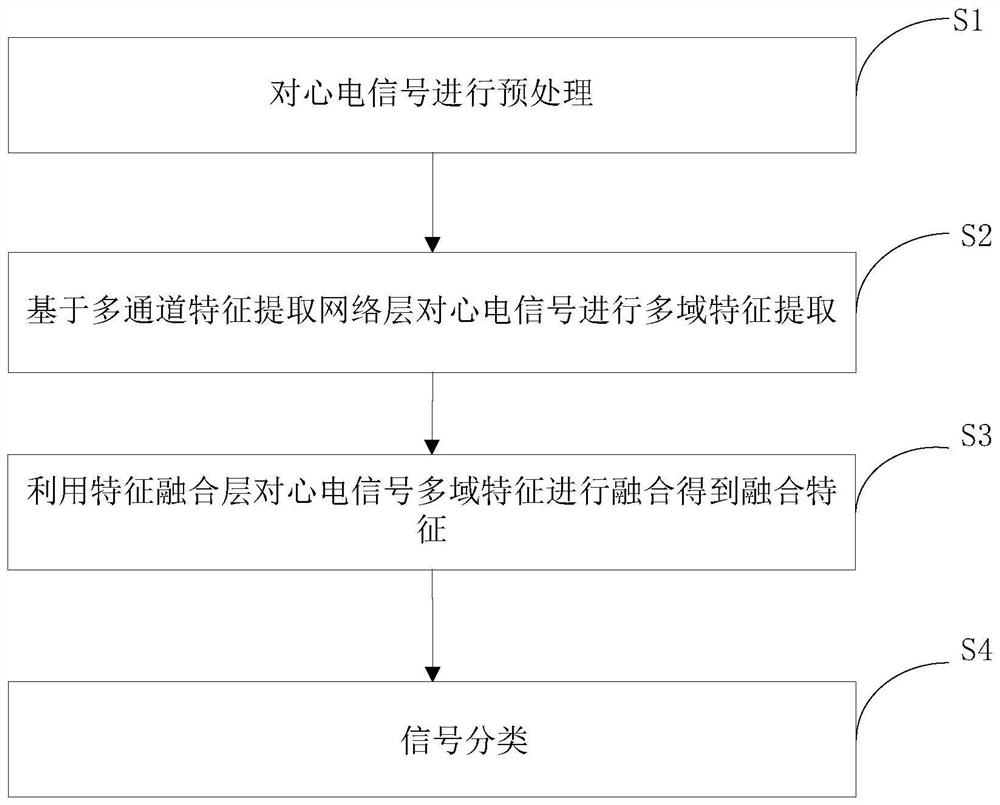
Electrocardiosignal classification method and system based on multi-domain feature learning
PendingCN114652322AImplement extractionImprove effectivenessDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRR intervalFrequency conversion
The invention discloses an electrocardiosignal classification method and system based on multi-domain feature learning, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the preprocessing of an original electrocardiosignal, i.e., extracting an RR interval sequence and P-wave region data of the electrocardiosignal, and carrying out the time-frequency conversion of the P-wave region data, and obtaining a P-wave region time-frequency graph; performing multi-domain feature extraction on the electrocardiosignals to obtain heart rhythm feature representation, atrial activity feature representation and global spatial-temporal feature representation of the electrocardiosignals; and fusing the heart rhythm feature representation, the atrial activity feature representation and the global spatio-temporal feature representation to obtain fused features of the electrocardiosignals, and inputting the fused features into a classification layer to obtain a classification result of the electrocardiosignals. According to the method, collection and fusion of multi-domain features are achieved, local features and global features are combined, more complete patient representation is obtained, and then the precision of a model classification result is improved. Particularly, when the method is applied to atrial fibrillation classification, the classification result is of great significance for clinically assisting doctors to make decisions.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method of treating atrial fibrillation
The present invention relates to a method for the treatment or prevention of atrial fibrillation and / or atrial flutter comprising coadministration of a synergistically therapeutic amount of dronedarone or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or salts thereof and a synergistically therapeutic amount of ranolazine or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or salts thereof. Also provided are methods for modulating ventricular and atrial rhythm and rate. This invention also relates to pharmaceutical formulations that are suitable for such combined administration.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
System and method for conditional biventricular pacing
An implantable pacing system with single, double and triple chamber pacing capabilities, provided individually or in concert on a conditional or continuous basis depending upon ongoing analyses of atrial rhythm status, atrioventricular conduction status and ventricular rate. A mode is selected to reduce the occurrence of any ventricular pacing in favor of intrinsic atrioventricular and ventricular conduction. If excessively long PR intervals are occurring too frequently or atrioventricular conduction is unreliable or absent, the implantable pulse generator is operated in a conditional triple chamber pacing mode that provides atrial-synchronous biventricular pacing in every cardiac cycle for a period of time as necessary to restore and maintain AV synchrony, while minimizing ventricular asynchrony otherwise associated with monochamber RV pacing as in conventional dual chamber pacing systems. Similarly, biventricular pacing is provided in every cardiac cycle when ventricular rates are undesirably slow during atrial fibrillation, where AV synchronization is excluded.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and method for conditional biventricular pacing
An implantable pacing system with single, double and triple chamber pacing capabilities, provided individually or in concert on a conditional or continuous basis depending upon ongoing analyses of atrial rhythm status, atrioventricular conduction status and ventricular rate. A mode is selected to reduce the occurrence of any ventricular pacing in favor of intrinsic atrioventricular and ventricular conduction. If excessively long PR intervals are occurring too frequently or atrioventricular conduction is unreliable or absent, the implantable pulse generator is operated in a conditional triple chamber pacing mode that provides atrial-synchronous biventricular pacing in every cardiac cycle for a period of time as necessary to restore and maintain AV synchrony, while minimizing ventricular asynchrony otherwise associated with monochamber RV pacing as in conventional dual chamber pacing systems. Similarly, biventricular pacing is provided in every cardiac cycle when ventricular rates are undesirably slow during atrial fibrillation, where AV synchronization is excluded.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Cardiac stimulator for delivery of cardiac contractility modulation therapy
ActiveUS8538518B2Significant comprehensive benefitsGood benefitHeart stimulatorsCardiac muscleContractility
A combination cardiac stimulator for CRT stimulation and CCM stimulation, which is connected to a rhythm evaluation unit which can either detect a sinus rhythm that is present, or classify an atrial arrhythmia, and which comprises an additional therapy selection unit, wherein the therapy selection unit selects the delivery of either CRT therapy or CCM therapy on the basis of the classification of the atrial rhythm such that CRT therapy is preferred in the case of sinus rhythm, and CCM therapy is delivered in the case of atrial arrhythmia.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
System and method for conditional biventricular pacing
An implantable pacing system with single, double and triple chamber pacing capabilities, provided individually or in concert on a conditional or continuous basis depending upon ongoing analyses of atrial rhythm status, atrioventricular conduction status and ventricular rate. A mode is selected to reduce the occurrence of any ventricular pacing in favor of intrinsic atrioventricular and ventricular conduction. If excessively long PR intervals are occurring too frequently or atrioventricular conduction is unreliable or absent, the implantable pulse generator is operated in a conditional triple chamber pacing mode that provides atrial-synchronous biventricular pacing in every cardiac cycle for a period of time as necessary to restore and maintain AV synchrony, while minimizing ventricular asynchrony otherwise associated with monochamber RV pacing as in conventional dual chamber pacing systems. Similarly, biventricular pacing is provided in every cardiac cycle when ventricular rates are undesirably slow during atrial fibrillation, where AV synchronization is excluded.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
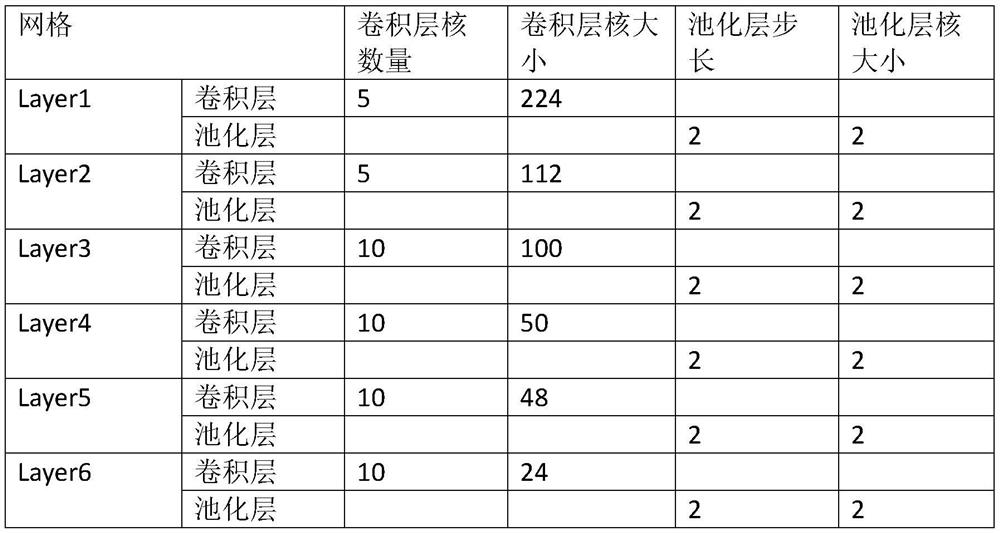
Improved Convolutional Neural Network and Its Training Method for Identifying Heart Rhythm Types
ActiveCN110037683BGuaranteed accuracyReduce missed detection rateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMedicineNeural network nn
Owner:SHANGHAI SID MEDICAL CO LTD
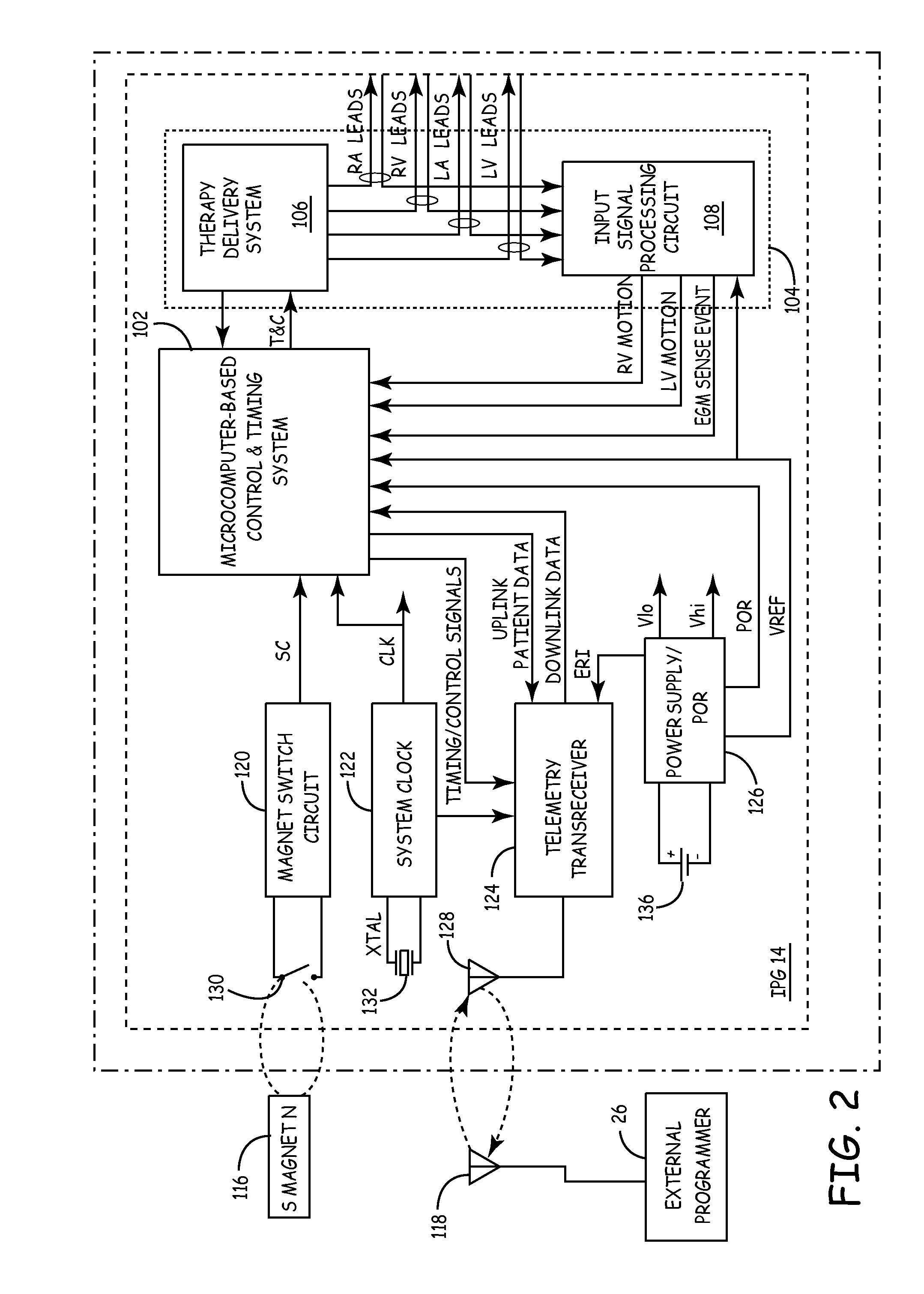
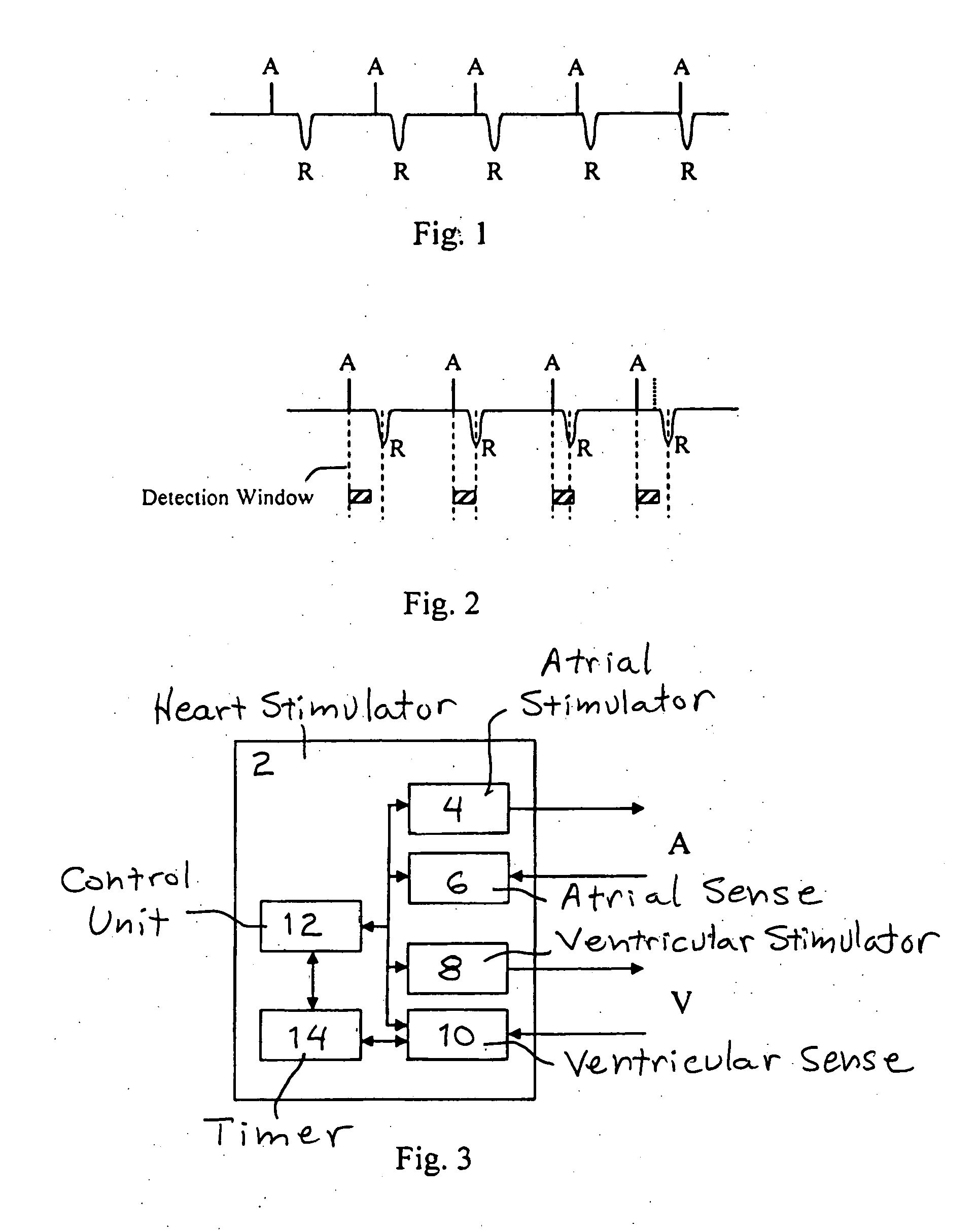
Implantable Heart Stimulator for Enabling Normal Atrio-Ventricular Stimulation Sequence in the Presence of Av-Nodal Interference
InactiveUS20080234775A1Increase atrial stimulation rateLess-optimal hemodynamicsHeart stimulatorsNODALAtrial cavity
A heart stimulator for enhancing cardiac performance of a patient suffering from ventricular rhythms that tend to overdrive the patient's atrial rhythm, has sensing circuitry that detects atrial events and ventricular events, and an atrial stimulator that generates and supplies stimulation pulses to the atrium. A timer generates a detection window having a predetermined duration for the ventricular sensing, the detection window starting upon detection of an intrinsic or stimulated atrial event. If an R-wave is sensed from the ventricle during the detection window, a control unit determines that a focus, that pre-depolarizes the ventricles, exists, and the control unit operates the atrial stimulator to increase the atrial stimulation rate for a predetermined number of consecutive heart cycles.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Electrocardiogram-based processing method and processing system
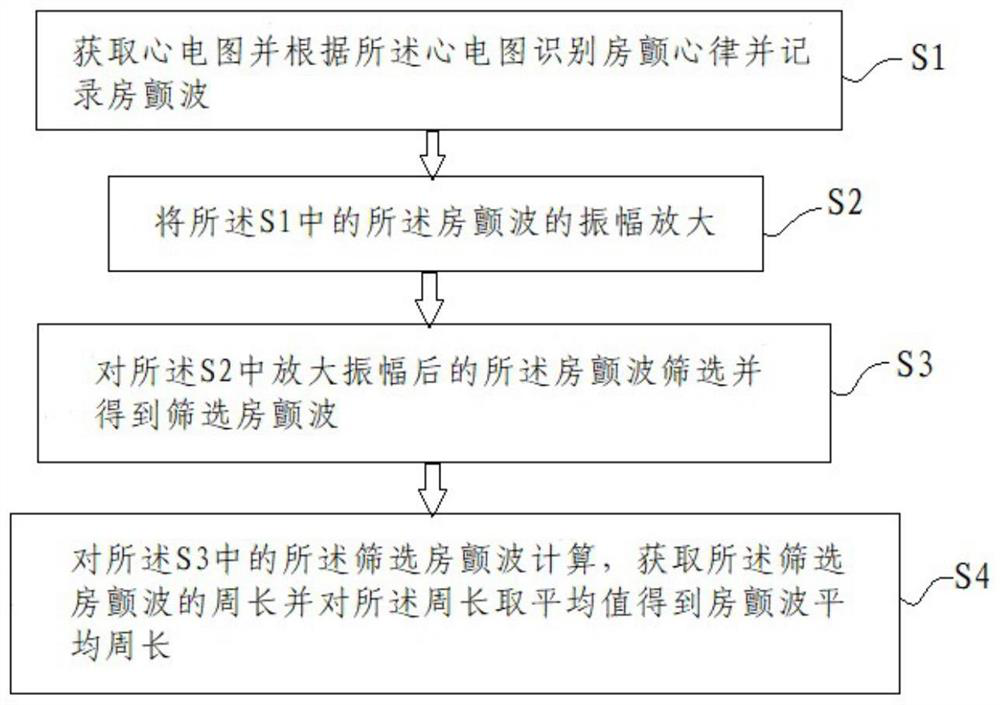
PendingCN111739631AIncrease valueImprove calculation accuracyMedical data miningHealth-index calculationAtrial cavityBiomedical engineering
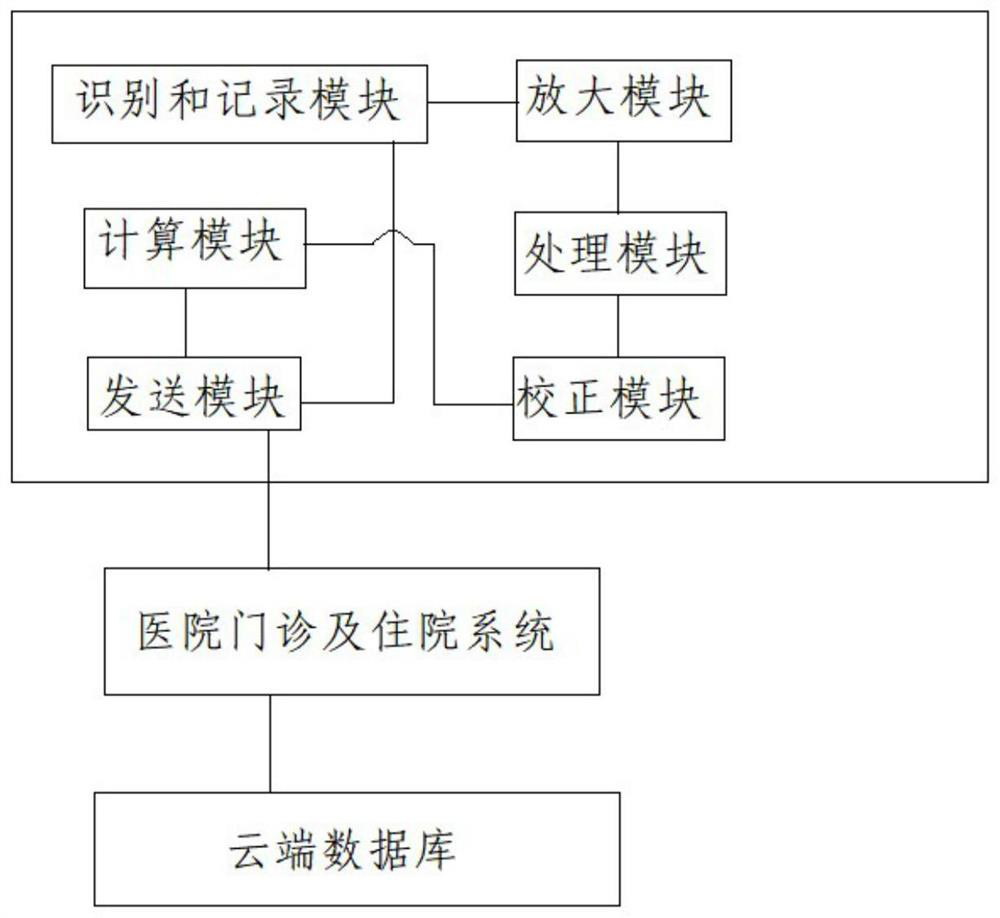
The invention relates to the technical field of medical treatment, and discloses an electrocardiogram-based processing method and processing system. The method comprises the steps of obtaining an electrocardiogram, recognizing atrial fibrillation rhythm according to the electrocardiogram, and recording atrial fibrillation waves; amplifying the amplitude of the atrial fibrillation wave; screening to obtain screened atrial fibrillation waves; and calculating the average perimeter of the atrial fibrillation waves for screening the atrial fibrillation waves. The system comprises an identificationand recording module, an amplification module, a processing module and a calculation module which are electrically connected in sequence. The algorithm program module is integrated in the electrocardiograph to process the atrial fibrillation waves, the algorithm is used for replacing a manual measuring and calculating mode, the measuring and calculating accuracy can be improved, and time and laborare saved; according to the embodiment of the invention, the key information of the atrial fibrillation electrocardiogram is analyzed through the electrocardiogram, the perimeter of the atrial fibrillation wave provided by the electrocardiogram has higher value for atrial matrix evaluation and atrial fibrillation research, and the value of electrocardiogram examination is improved.
Owner:首都医科大学附属北京潞河医院
Atrial fibrillation classification method, device and system based on RR interval spatial features
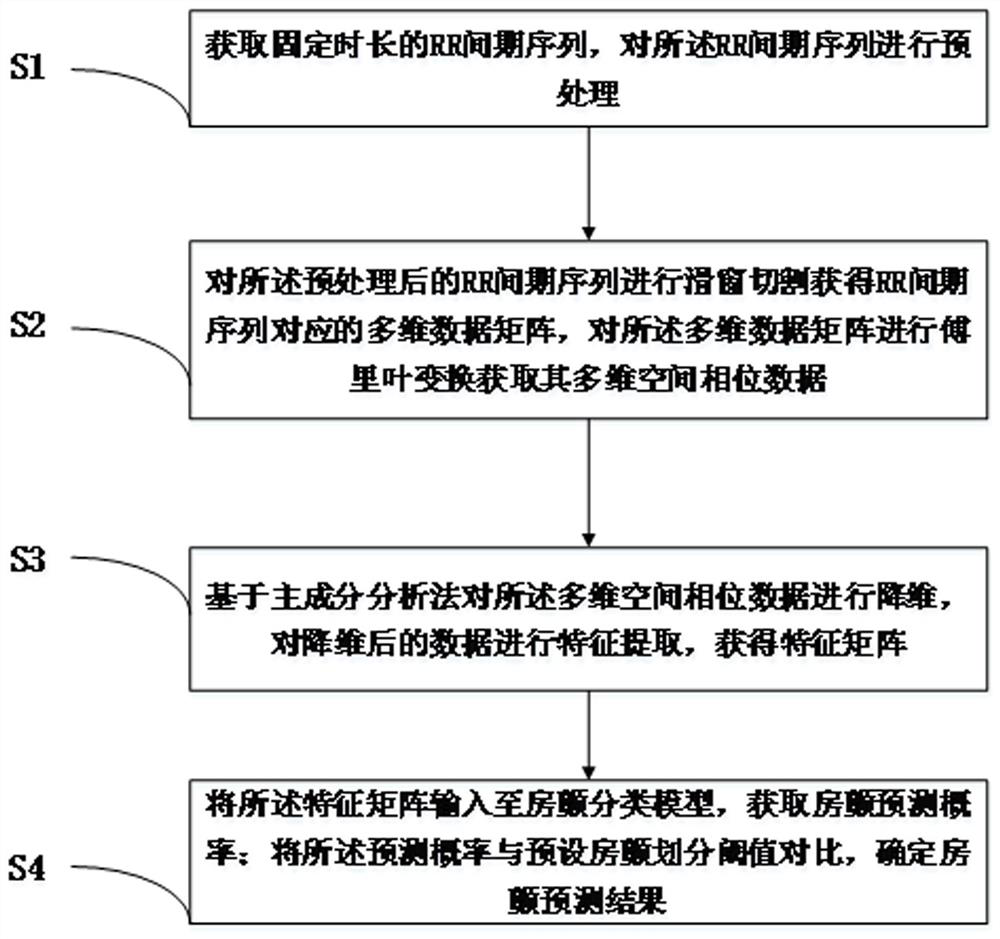
ActiveCN114764581AImprove accuracyReduce complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringPrincipal component analysisDimensionality reduction
The invention discloses an atrial fibrillation classification method, device and system based on RR interval spatial features, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining an RR interval sequence with a fixed time length, and carrying out the preprocessing of the RR interval sequence; performing sliding window cutting on the preprocessed RR interval sequence to obtain a multi-dimensional data matrix corresponding to the RR interval sequence, and performing Fourier transform on the multi-dimensional data matrix to obtain multi-dimensional space phase data of the multi-dimensional data matrix; dimension reduction is carried out on the multi-dimensional space phase data based on a principal component analysis method, feature extraction is carried out on the data after dimension reduction, and a feature matrix is obtained; inputting the feature matrix into an atrial fibrillation classification model to obtain an atrial fibrillation prediction probability; comparing the prediction probability with a preset atrial fibrillation division threshold, and determining an atrial fibrillation prediction result; according to the method, the difference between the atrial fibrillation rhythm and other types of rhythms in RR interval spatial features is effectively obtained, and atrial fibrillation recognition is effectively achieved.
Owner:HEFEI HEART VOICE HEALTH TECH CO LTD
WCD system validating detected cardiac arrhythmias thoroughly so as to not sound loudly due to some quickly self-terminating cardiac arrhythmias
ActiveUS10500403B2ElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsWearable cardioverter defibrillatorCardiac arrhythmia
A wearable cardioverter defibrillator (“WCD”) system may output a loud sound after detecting and validating a shockable cardiac arrhythmia. In such embodiments, however, the WCD system might not sound a loud alarm before validating the arrhythmia thoroughly, i.e. for a longer time, thus giving the arrhythmia a further chance to self-terminate. The WCD system may thus detect more robustly the cardiac arrhythmias that do not self-terminate quickly. Such arrhythmias that self-terminate quickly may occur from likely harmless events occurring multiple times in the daily life of the patient, such as the patient becoming “winded” from climbing stairs. In embodiments the WCD system may notify the patient only discreetly, or even not at all. The lack of sounding such a loud alarm responsive to such events reduces the overall number of times in which the patient experiences unwanted attention by others, embarrassment, loss of privacy and dignity, and so on.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG DAC
System and method for conditional biventricular pacing
An implantable pacing system with single, double and triple chamber pacing capabilities, provided individually or in concert on a conditional or continuous basis depending upon ongoing analyses of atrial rhythm status, atrioventricular conduction status and ventricular rate. A mode is selected to reduce the occurrence of any ventricular pacing in favor of intrinsic atrioventricular and ventricular conduction. If excessively long PR intervals are occurring too frequently or atrioventricular conduction is unreliable or absent, the implantable pulse generator is operated in a conditional triple chamber pacing mode that provides atrial-synchronous biventricular pacing in every cardiac cycle for a period of time as necessary to restore and maintain AV synchrony, while minimizing ventricular asynchrony otherwise associated with monochamber RV pacing as in conventional dual chamber pacing systems. Similarly, biventricular pacing is provided in every cardiac cycle when ventricular rates are undesirably slow during atrial fibrillation, where AV synchronization is excluded.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and system for detecting arrhythmias in cardiac activity
PendingUS20210290140A1Reduce sensitivityHigh sensitivityHealth-index calculationDiagnostic recording/measuringATRIAL RHYTHMSBiomedical engineering
Systems and methods for detecting arrhythmias in cardiac activity are provided and include memory to store specific executable instructions. One or more processors are configured to execute the specific executable instructions for obtaining first and second far field cardiac activity (CA) data sets over primary and secondary sensing channels, respectively, in connection with a series of beats. The system detects candidate atrial features from the second CA data set, identifies ventricular features from the first CA data set and utilizes the ventricular features to separate beat segments within the second CA data set. The system automatically iteratively analyzes the beat segments by overlaying an atrial activity search window with the second CA data set and determines whether one or more of the candidate atrial features occur within the atrial activity search window. The system adjusts an atrial sensitivity profile based on whether the atrial activity search window includes the one or more of the candidate atrial features and detects atrial events based on the atrial sensitivity profile.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Health state trends for a consistent patient situation
PendingCN112545469AHealth-index calculationDiagnostic recording/measuringSpinal columnEmergency medicine
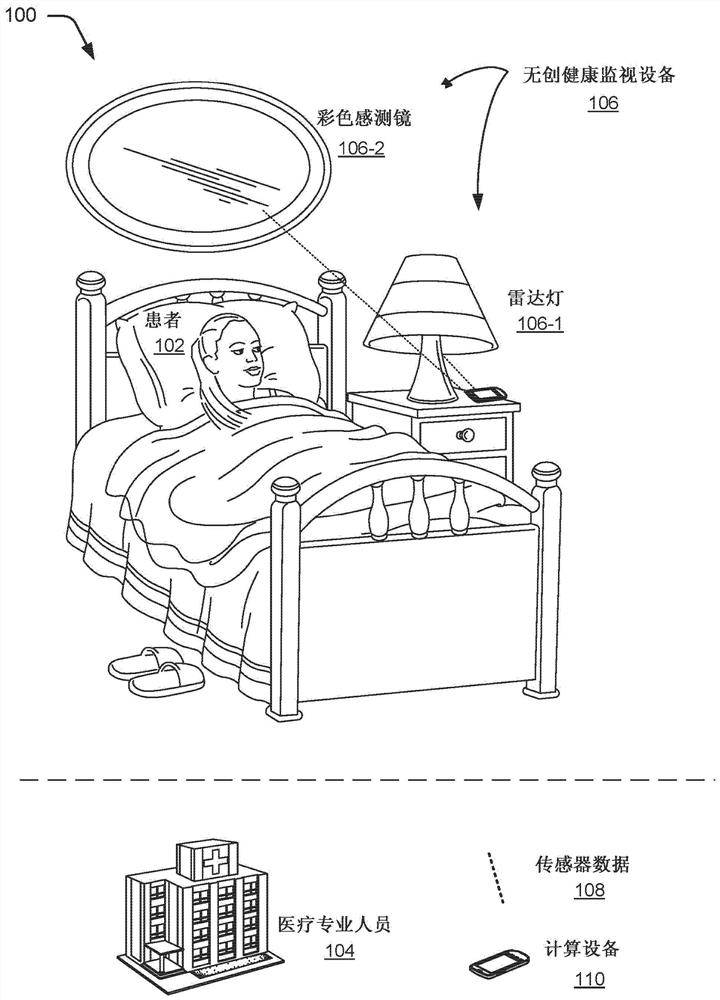
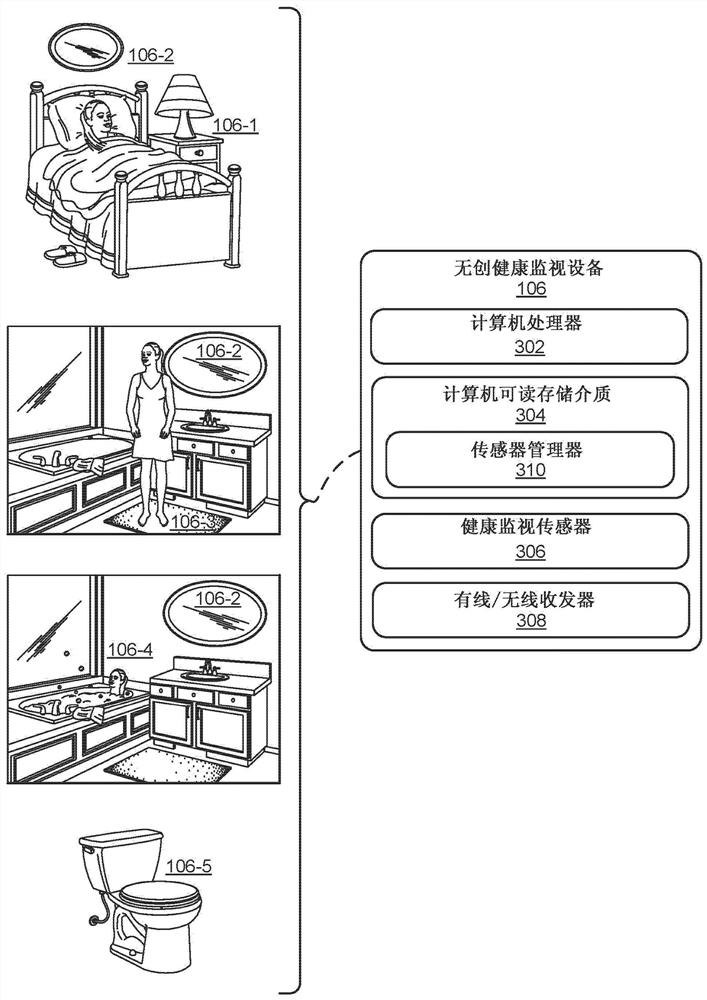
Health state trends for a consistent patient situation. Various noninvasive health monitors can be used to sense a patient's situation and health states, including disease progression, at those states. These noninvasive health monitors may also act passively and in a patient's normal course of life, which enhances many patient's desire to submit to monitoring, as well as increase consistency of use, as in many cases the patient does little or nothing to cause his or her health monitoring and health-trend determination. With health states determined for a consistent patient situation, more accurate and more robust health trends can be determined. In particular, parameters like cardiac rhythm, respiration rate or the spine curvature can be determined using a radar based motion sensing systemlocated in the vicinity of a patient's bed.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Optimization calculation method for atrial fibrillation blood pressure based on principle of oscillometry
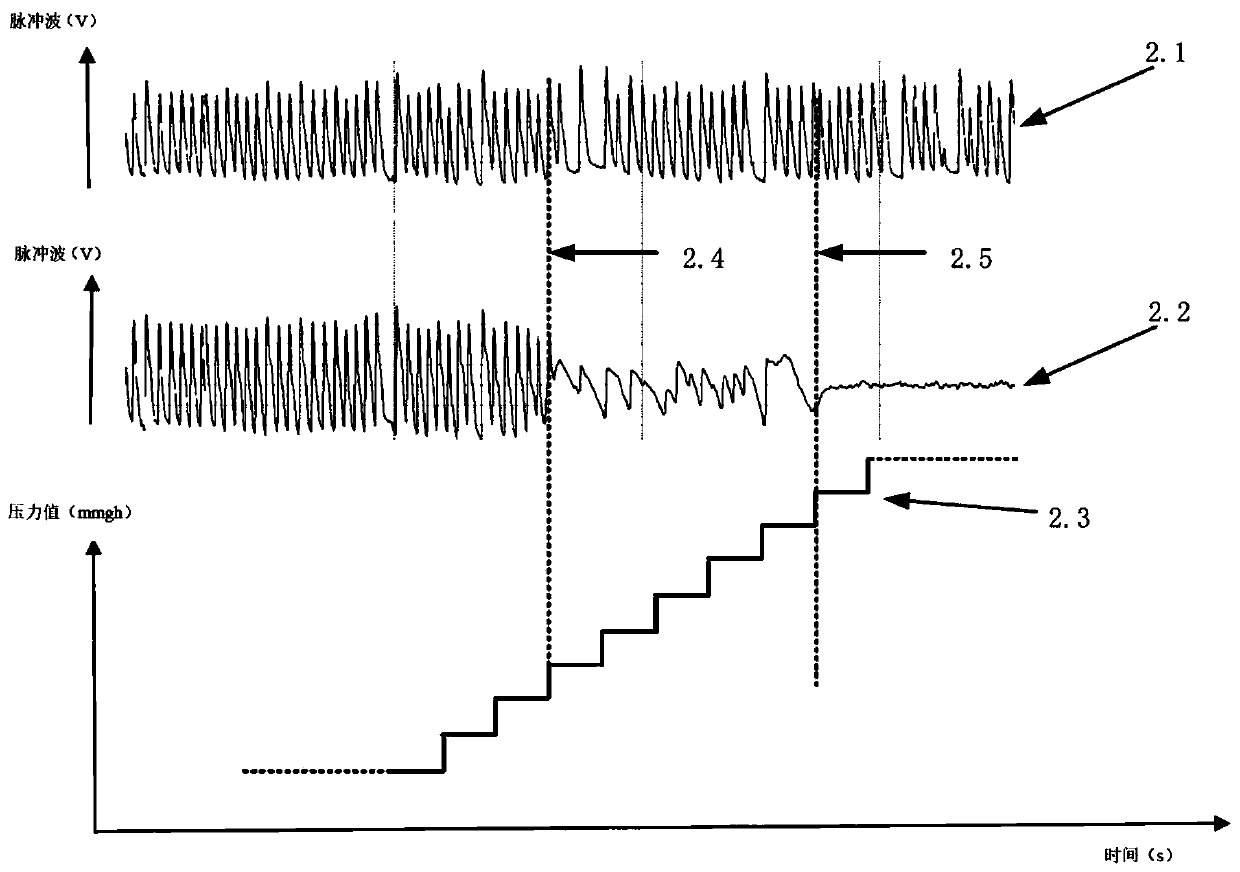
InactiveCN110772243AAvoid the problem of fluctuating blood pressure measurement resultsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsOscillometrySphygmomanometer
The invention discloses an optimization calculation method for atrial fibrillation blood pressure based on the principle of oscillometry. According to the method, the working principle of blood pressure measurement through the oscillometry is adopted, through three cuffs, pulse wave signals of the two hands in the acting process of the pressure cuff are collected, and then the pulse wave signals are processed through the optimization calculation method for blood pressure. According to the optimization calculation method, in the measurement process of a patient with atrial fibrillation and arrhythmia, through the static pressure measured by the pressure cuff and the characteristics of pulse waves sensed by the other cuffs, the optimization result of the blood pressure is calculated by comparing two sets of data, the frequent problem of inaccurate blood pressure measurement result caused by irregularity of pulse waves in existing oscillometry sphygmomanometer measurement is solved, and thus the accuracy of blood pressure measurement of the patient with arrhythmia is improved. Therefore, the method is of great significance for blood pressure measurement of the patient with arrhythmia.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
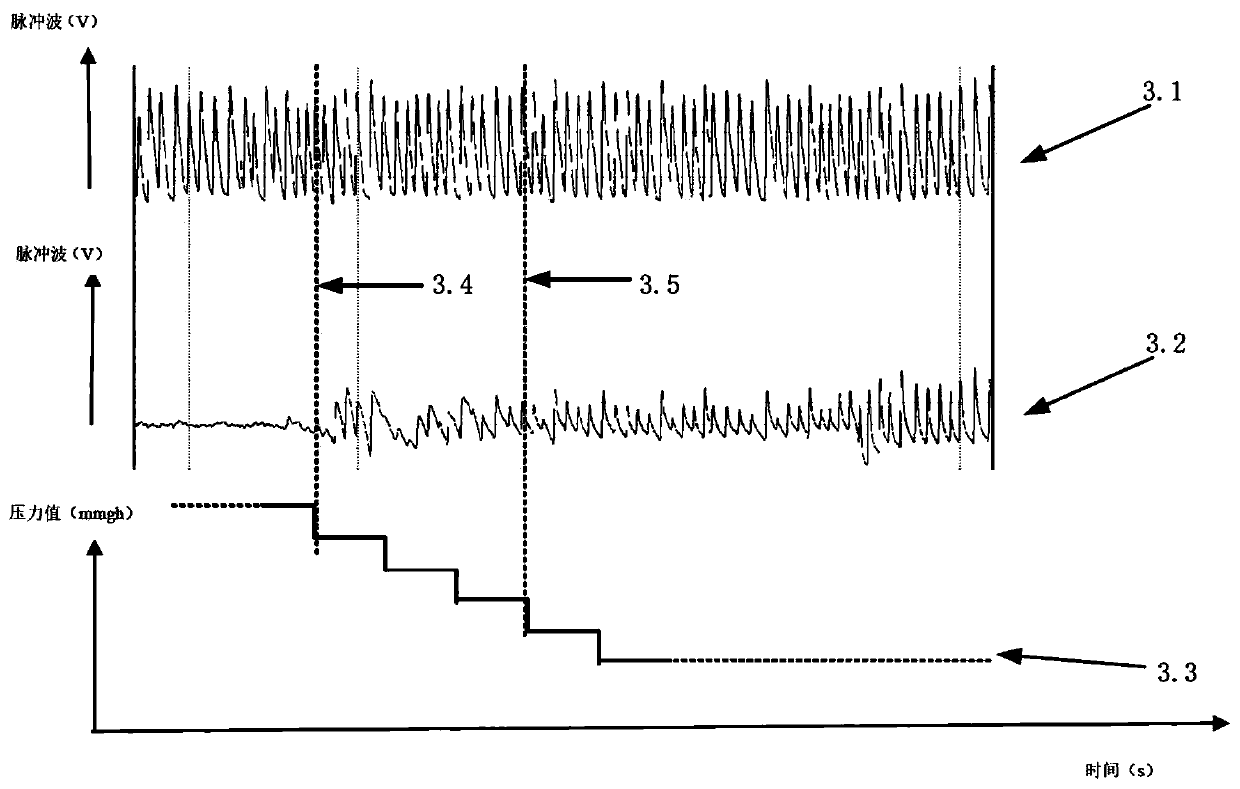
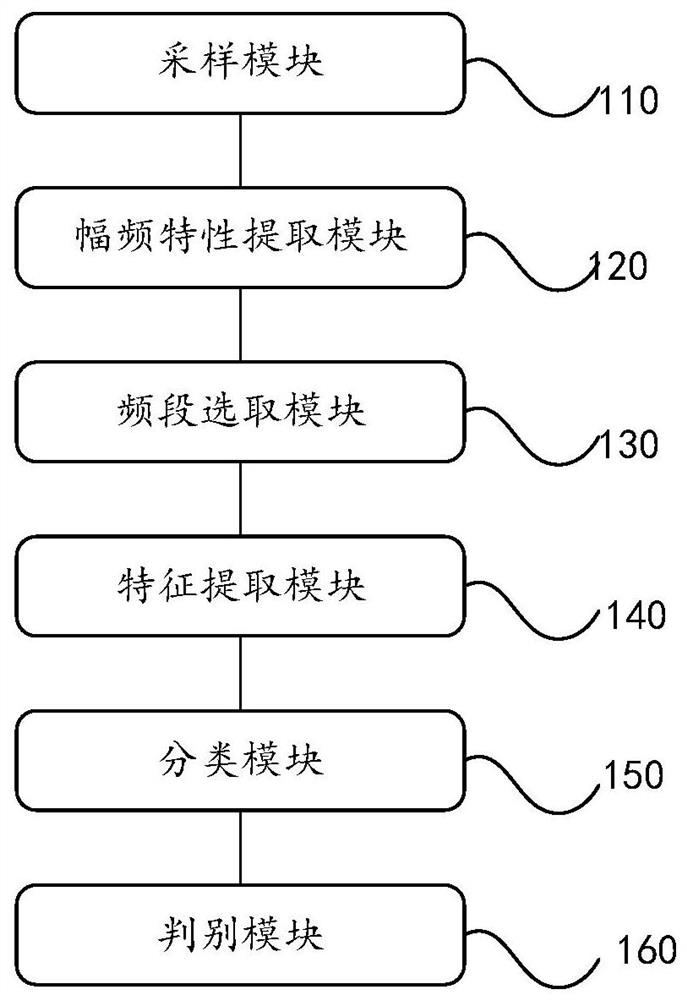
Distinguishing device and equipment for malignant ventricular arrhythmia
ActiveCN108615026BSmall amount of calculationShorten the timeCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringEcg signalPhysical therapy
The invention discloses a device for discriminating malignant ventricular arrhythmia. After the sampling module discretely samples the continuous ECG signal; the amplitude-frequency characteristic extraction module extracts the amplitude-frequency characteristic of the signal and obtains a matrix; then the frequency band selection module Select the vector of the preset frequency band from the matrix to obtain a new matrix; then the feature extraction module will select the column vector of the preset number with the largest variance from the new matrix as the feature vector of the signal; the classification module will then The feature vector is input into a pre-trained classifier to obtain a classification result; finally, the discrimination module judges whether the electrocardiographic signal is a malignant ventricular rhythm according to the classification result. It can be seen that the device can select a preset number of vectors with the largest variance from the vectors of the preset frequency band as feature vectors, which effectively reduces the amount of calculation of the classifier and saves the time spent on discrimination. The present invention also provides a device for judging malignant ventricular rhythm, the function of which is corresponding to that of the above-mentioned device.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
System and method for conditional biventricular pacing
An implantable pacing system with single, double and triple chamber pacing capabilities, provided individually or in concert on a conditional or continuous basis depending upon ongoing analyses of atrial rhythm status, atrioventricular conduction status and ventricular rate. A mode is selected to reduce the occurrence of any ventricular pacing in favor of intrinsic atrioventricular and ventricular conduction. If excessively long PR intervals are occurring too frequently or atrioventricular conduction is unreliable or absent, the implantable pulse generator is operated in a conditional triple chamber pacing mode that provides atrial-synchronous biventricular pacing in every cardiac cycle for a period of time as necessary to restore and maintain AV synchrony, while minimizing ventricular asynchrony otherwise associated with monochamber RV pacing as in conventional dual chamber pacing systems. Similarly, biventricular pacing is provided in every cardiac cycle when ventricular rates are undesirably slow during atrial fibrillation, where AV synchronization is excluded.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com