Method for remediation of aquifers
a technology for aquifers and water bodies, applied in the field of methods, can solve the problems of high operation and maintenance costs, significant capital expense associated with the installation of required tanks, pumps, mixers, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing the mobility of emulsions through the aquifer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preliminary Studies
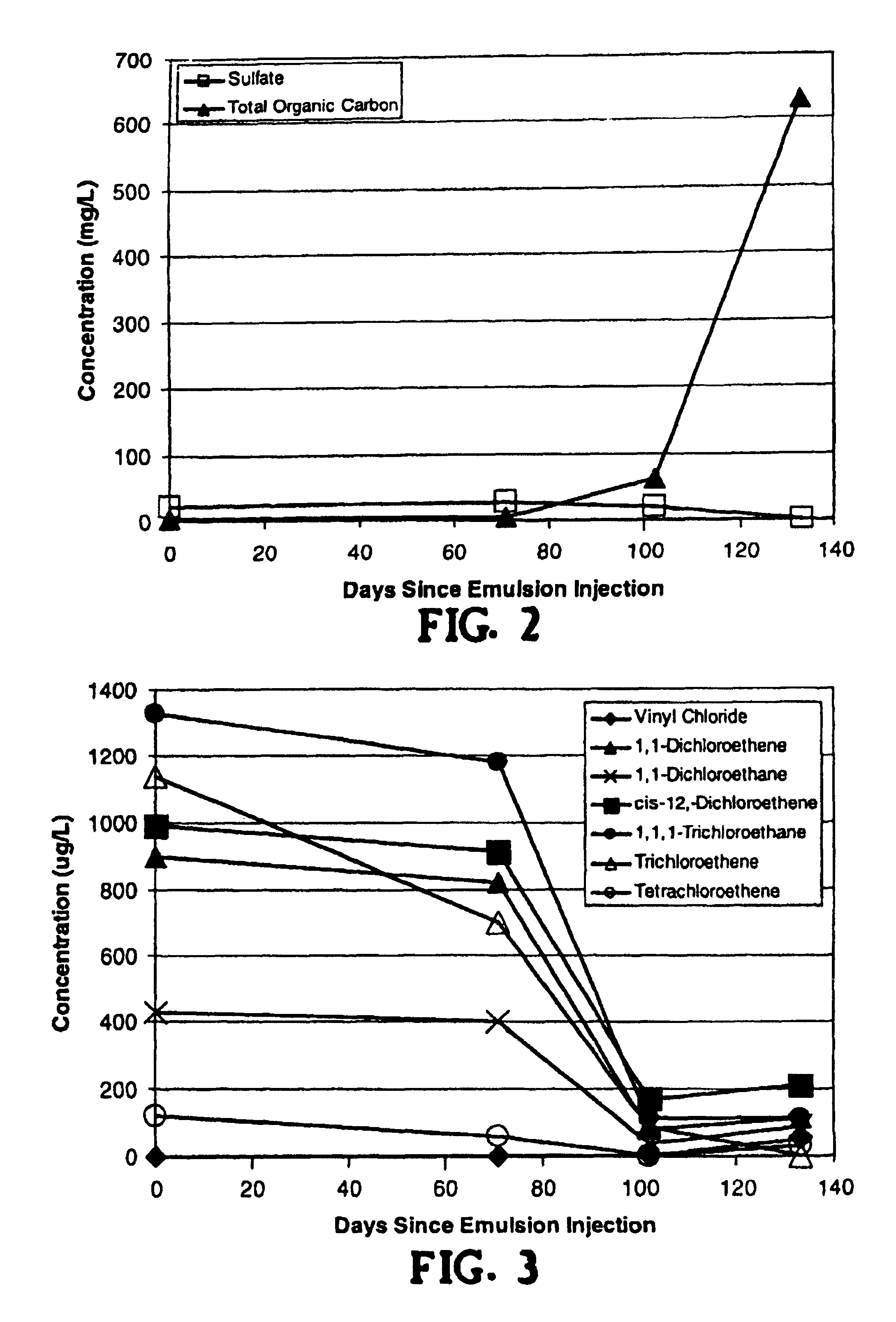
[0064]Preliminary biodegradability screening studies were first conducted to evaluate edible oils (liquid soybean oil and semi-solid soybean oil, as compared to molasses) for their potential use in a biologically active barrier system. Laboratory microcosm experiments showed that reductive dehalogenation was most rapid in the microcosm amended with semi-solid soybean oil. TCE and DCE were reduced to below detection within two months with concurrent production of vinyl chloride and ethene. After 130 days of incubation, vinyl chloride in the headspace was reduced to near the analytical detection limit with essentially complete conversion of TCE to ethene. Molasses and liquid soybean oil also stimulated reductive dehalogenation; however ethene production was slower than for the semi-solid soybean oil.
example 2
Pilot Test
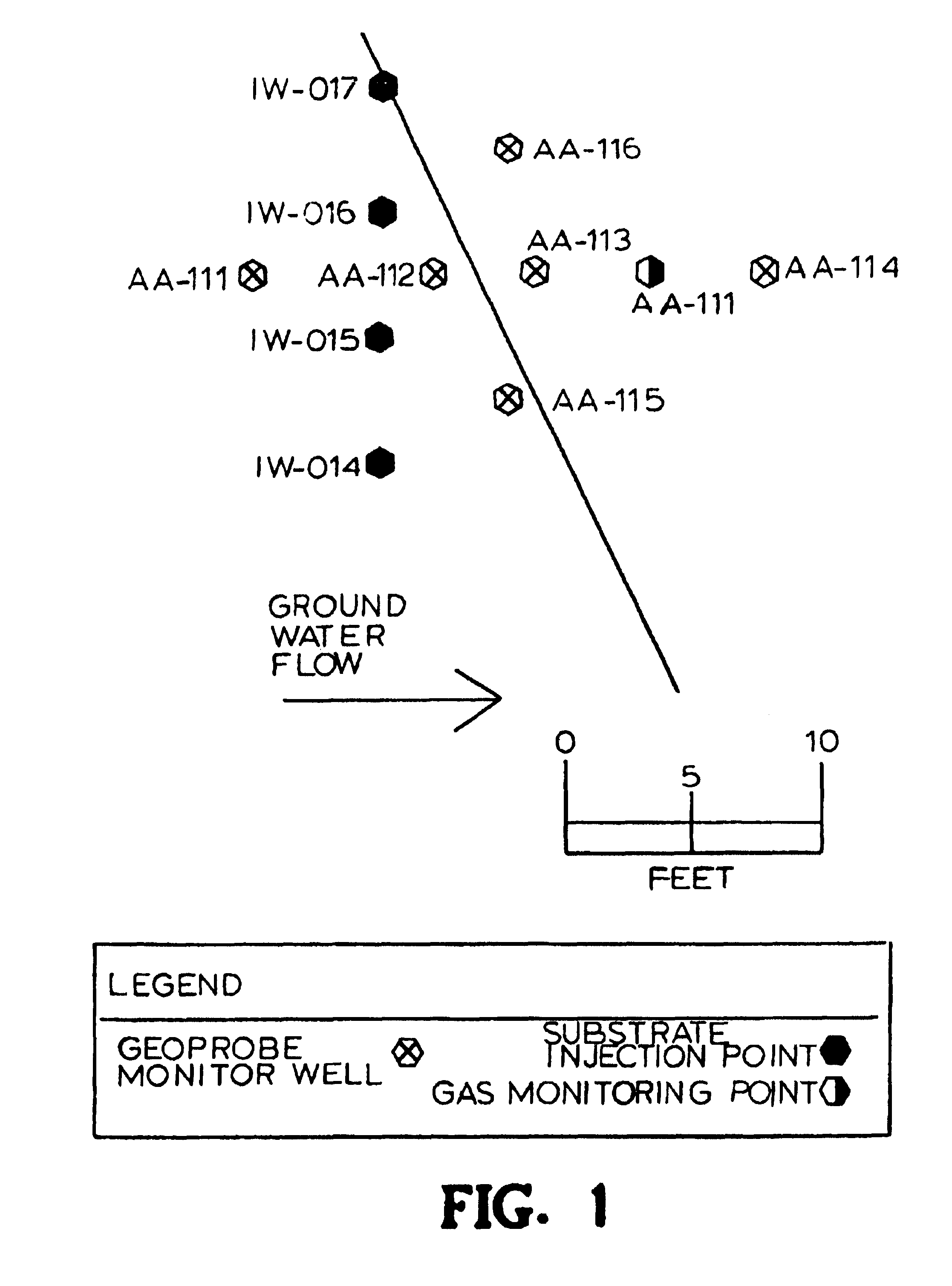
[0065]An extensive pilot test of this process is being conducted in a chlorinated solvent plume at Dover Air Force Base near Dover, Del. The primary contaminants at this site include tetrachloroethene (PCE), trichloroethene (TCE) and dichloroethene (DCE). Two different barrier configurations are being evaluated: 1) injection of liquid soybean oil in closely spaced wells; and 2) injection of a soybean and lecithin oil-in-water emulsion in moderately spaced wells (see FIG. 1). Each barrier is constructed with 1-inch diameter continuously screened direct push wells.
[0066]In Barrier 1, about 20 gallons of liquid soybean oil were injected into each well followed by about 100 gallons of groundwater resulting in 18 to 24 inch cylindrical plugs of oil spaced 24-inches on center (OC).
[0067]In Barrier 2, a soybean oil-in-water emulsion was injected into wells spaced 5 ft. OC followed by 1,000 gallons of groundwater to distribute the oil resulting in 6 to 8 ft.-diameter cylindrical c...
example 3
Site Remediate Process
[0069]Planning for Treatment. A food-grade edible oil is distributed at two locations at the subsurface at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. to treat soil and groundwater contaminants utilizing the invention. At the first location, the primary contaminant is trichloroethylene (TCE). At the second site, the primary contaminant is perchlorate (ClO4−). The injection procedure is similar at the two sites. At the TCE site, the groundwater table occurs at 45 to 50 ft. below ground surface and flows down-gradient at an average groundwater velocity of 40 feet per year. The objective of this process is to construct a barrier to contaminant migration by installing a series of wells in a row generally perpendicular to the groundwater flow direction. A low solubility edible oil microemulsion is injected into the wells and distributed throughout the surrounding aquifer. Sufficient oil is distributed throughout the aquifer to enhance the biotransformation of TCE entering the ba...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com