Method for extracorporeal carbon dioxide removal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Capacity of Solutions Comprising One or More Buffering Agents
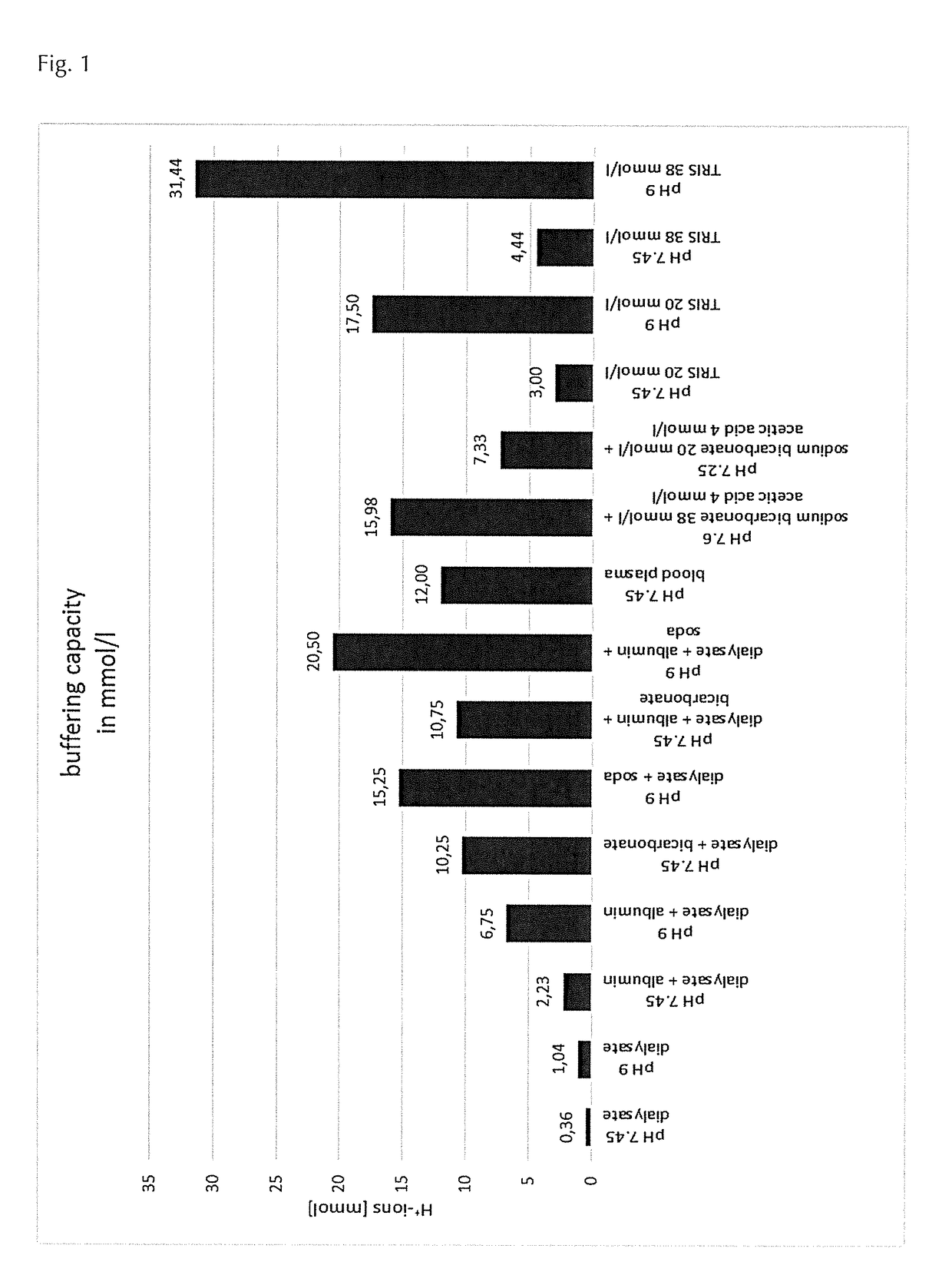
[0290]The buffering capacity of various aqueous solutions comprising one or more buffering agents was experimentally tested. These aqueous solutions are exemplary liquids. Exemplary liquids 1 and 2 refer to dialysis liquids (dialysates without buffering agents). Exemplary liquids 3 to 8 of table 1 refer to dialysis liquids (dialysates with various buffering agents exemplary liquids). Dialysis liquids 9 and 10 of table 1 refer to dialysis liquids (dialysates) as described in the prior art. Exemplary liquids 11 to 14 refer to Tris solution only. The buffering capacity of exemplary dialysis liquids (dialysates 5 to 8) correspond to dialysis liquids (dialysates) according to the present invention.
[0291]1A: Preparation of Liquids
[0292]These exemplary liquids were generally prepared as follows:
[0293]For the preparation of exemplary liquids according to the present invention and of exemplary liquids as outlined in table 1, pure w...
example 2
n of the Process According to the Present Invention to a Reference Process
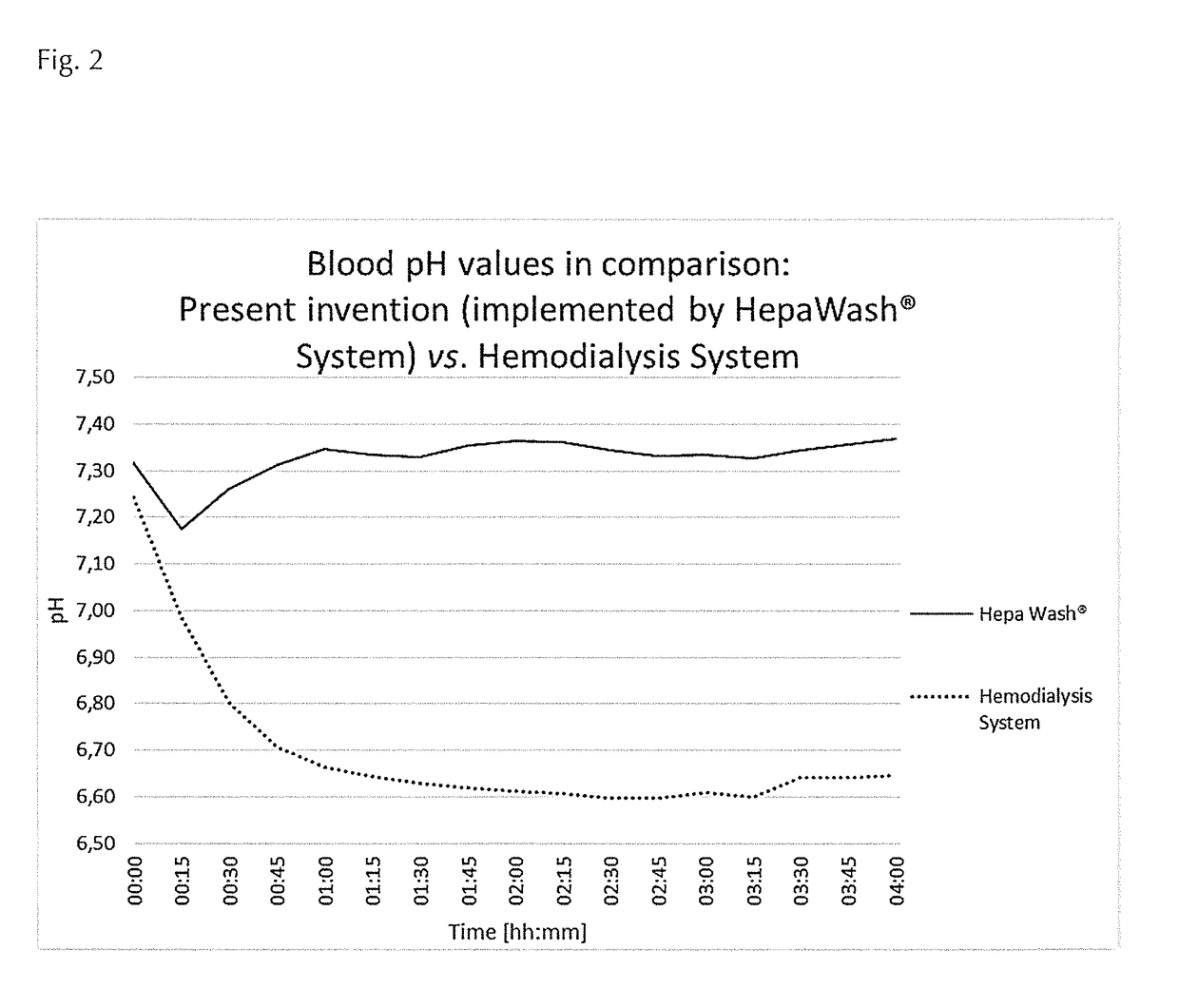
[0311]A dialysis liquid according to the present invention was tested by using a HepaWash® (Munich, Germany) dialysis device (Hepa Wash LK2001 dialysis device). As a reference device, a dialysis device (Nikkiso DBB-03 dialysis device) commercially offered by Nikkiso (Japan) was used.
[0312]The HepaWash® dialysis device was described previously, but not in combination with the process according to the present invention, nor in combination with the purpose of carbon dioxide removal from blood.
[0313]The reference device commercially offered by Nikkiso is a conventional hemodialysis system. That device uses a counter-current and is thus specifically designed to provide a renal support (hemodialysis), and to remove the undesired substance urea from the blood. The device is connected directly to osmosis apparatus for supply of osmosis water. The dialysis liquid is used in a single pass process; i.e. after a single pa...
example 3
oncentrations
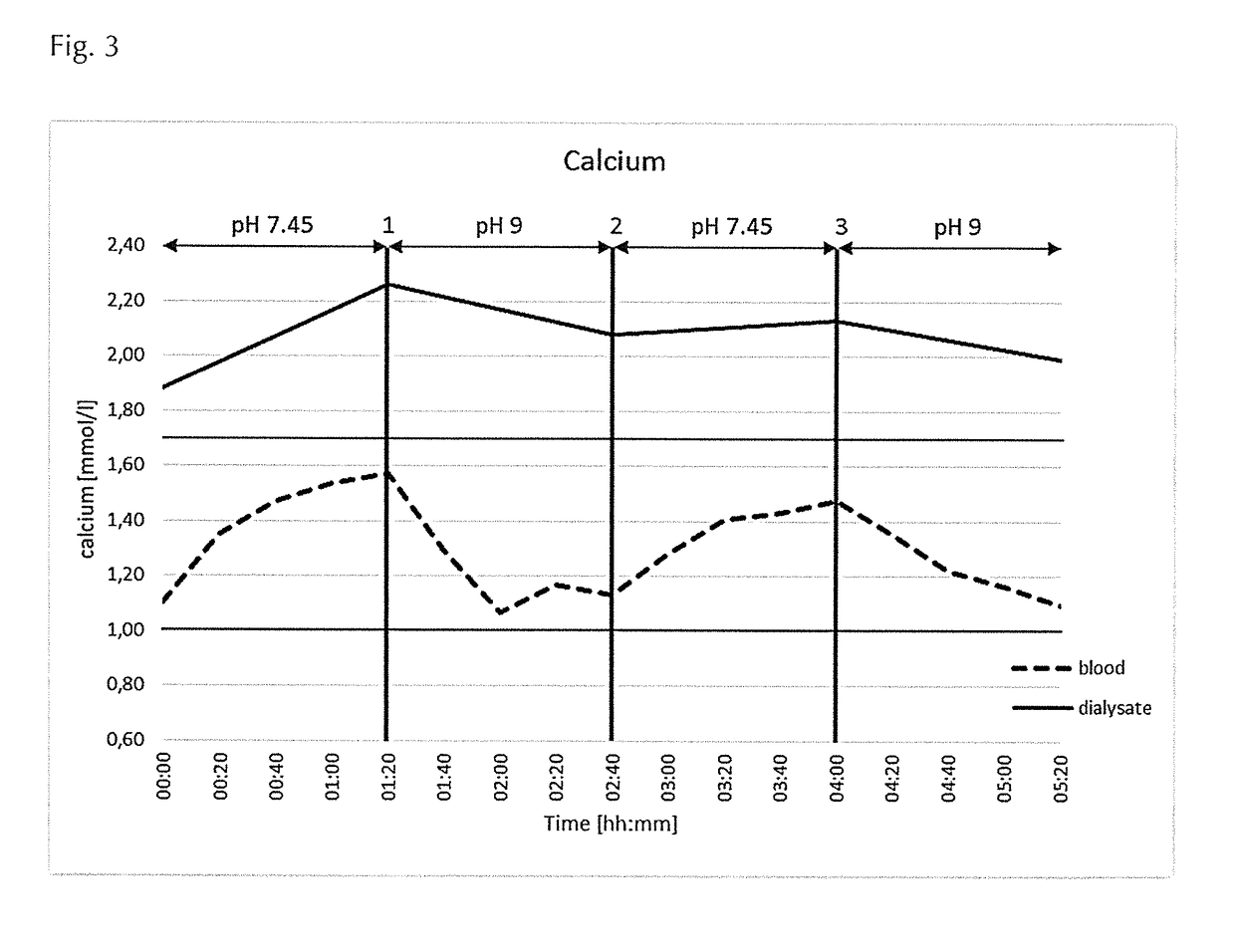
[0330]Dialysis liquid comprising calcium (Ca2+ ions) was used, and the pH of the dialysis liquid was altered in the range of pH 7.45 to pH 9 (see FIG. 3). The dialysis liquid was in contact with blood via a semipermeable membrane. The calcium concentration in blood was determined. As can be taken from FIG. 3, even in the case of a calcium concentration above 1.70 mmol / l in the dialysis liquid, the calcium ion concentration in the blood remains within the desired range of 1.00-1.70 mmol / l. This demonstrates that the calcium ion concentration in the dialysis liquid according to the present invention is suitably in a range above 1.70 mmol / l.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com