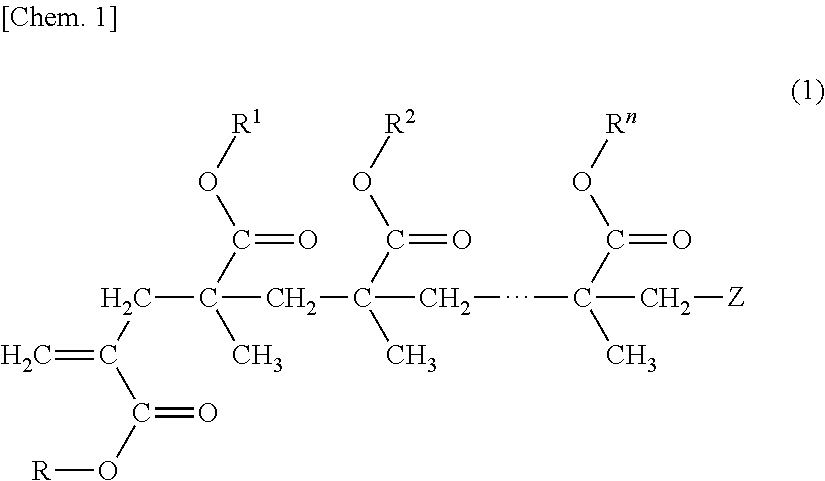
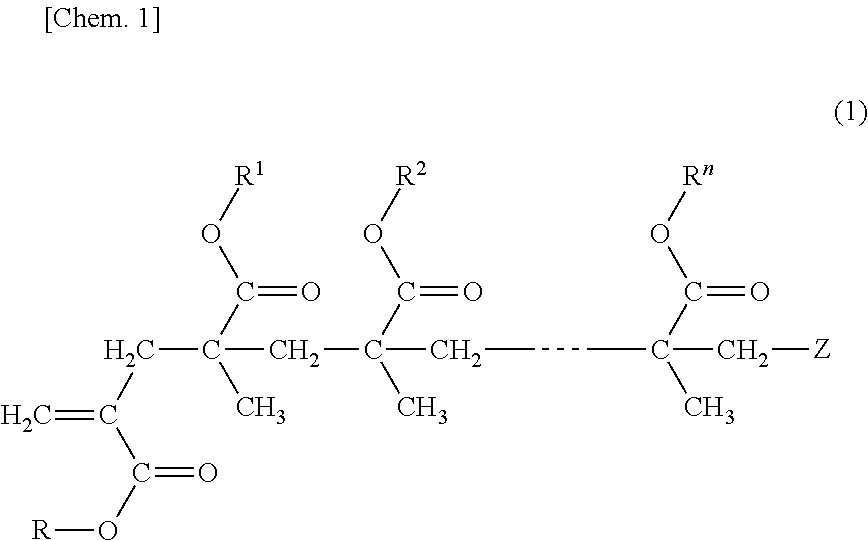
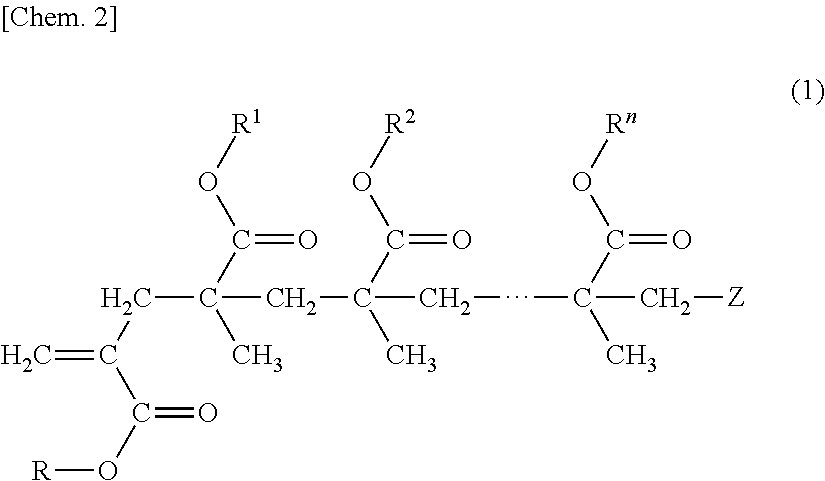
Polymer Composition and Porous Membrane
a technology of porous membrane and polymer composition, which is applied in the direction of water/sewage treatment, osmosis/dialysis, electrical equipment, etc., can solve the problems that the fractionation performance of porous membrane cannot be said to be sufficient for ultrafiltration applications, and the cost-effectiveness of porous membrane cannot be said to be high, so as to achieve favorable fractionation performance and high water permeability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0160]Hereinafter, the invention will be described in detail with reference to Examples. Incidentally, in the following, the composition and structure of the macromonomer (b1) and the polymer, the Mw of the polymer, the Mn and Mw / Mn of the macromonomer (b1) and the polymer were evaluated by the following methods.
[0161]In addition, in the following, the “parts” and the “%” indicate the “parts by mass” and the “% by mass”, respectively.
[0162](1) Composition and Structure of Macromonomer (b1) and Polymer
[0163]The composition and structure of the macromonomer (b1) and the polymer were analyzed by 1H-NMR (product name: JNM-EX270 manufactured by JEOL Ltd.).
[0164](2) Mw of Membrane Forming Polymer (A)
[0165]The Mw of the membrane forming polymer (A) was determined using a GPC (“HLC-8020” (trade name) manufactured by TOSOH CORPORATION) under the following conditions.
[0166]Column: TSK GUARD COLUMN a (7.8 mm×40 mm) and three TSK-GEL α-M (7.8×300 mm) are connected in series
[0167]Eluent: DMF 20 ...
synthesis example 2
(Synthesis Example 2) Synthesis of Dispersant 1
[0189]Into a reactor equipped with a stirrer, a cooling tube, and a thermometer, 61.6 parts of 17% aqueous solution of potassium hydroxide, 19.1 parts of methyl methacrylate (trade name: ACRYESTER M manufactured by Mitsubishi Rayon Co., Ltd.), and 19.3 parts of deionized water were introduced. Subsequently, the liquid in the reactor was stirred at room temperature, the exothermic peak thereof was confirmed, and then the liquid was further stirred for 4 hours. Thereafter, the reaction mixture in the reactor was cooled to room temperature, thereby obtaining an aqueous solution of potassium methacrylate.
[0190]Subsequently, 900 parts of deionized water, 70 parts of a 42% aqueous solution of sodium 2-sulfoethyl methacrylate (trade name: ACRYESTER SEM-Na manufactured by Mitsubishi Rayon Co., Ltd.), 16 parts of the above aqueous solution of potassium methacrylate, and 7 parts of methyl methacrylate (trade name: ACRYESTER M manufactured by Mits...
example 1
[0201]In a glass container, 16 parts of Kynar 761A (manufactured by Arkema Inc., PVDF homopolymer, trade names, Mw=550,000) as the membrane forming polymer (A), 12 parts of the polymer (B-1) as the polymer (B), and 72 parts of NMP (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., Wako special grade) as the solvent (C3) were blended and stirred for 10 hours at 50° C. using a stirrer, thereby preparing the membrane forming solution.
[0202]The membrane forming solution thus obtained was allowed to stand for one day at room temperature, subsequently coated on a glass substrate using a bar coater so as to have a thickness of 125 μm, thereby obtaining a coating film layered body. The coating film layered body was immersed in a coagulating bath containing 70 parts of deionized water and 30 parts of NMP as the coagulating bath solvent at room temperature.
[0203]The coating film layered body was allowed to stand in the coagulating bath for 5 minutes, and the coagulated product of coating f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com