Poylmeric composition for use as a temporary support material in extrusion based additive manufacturing
a technology of polymeric composition and additive manufacturing, which is applied in the direction of additive manufacturing processes, manufacturing tools, yarns, etc., can solve the problems of poor impact strength and low softening temperature, difficulty in extrusion and printing quality, and less suitable options for desktop 3d printers. , to achieve the effect of simple mechanical means, easy removal and less labor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
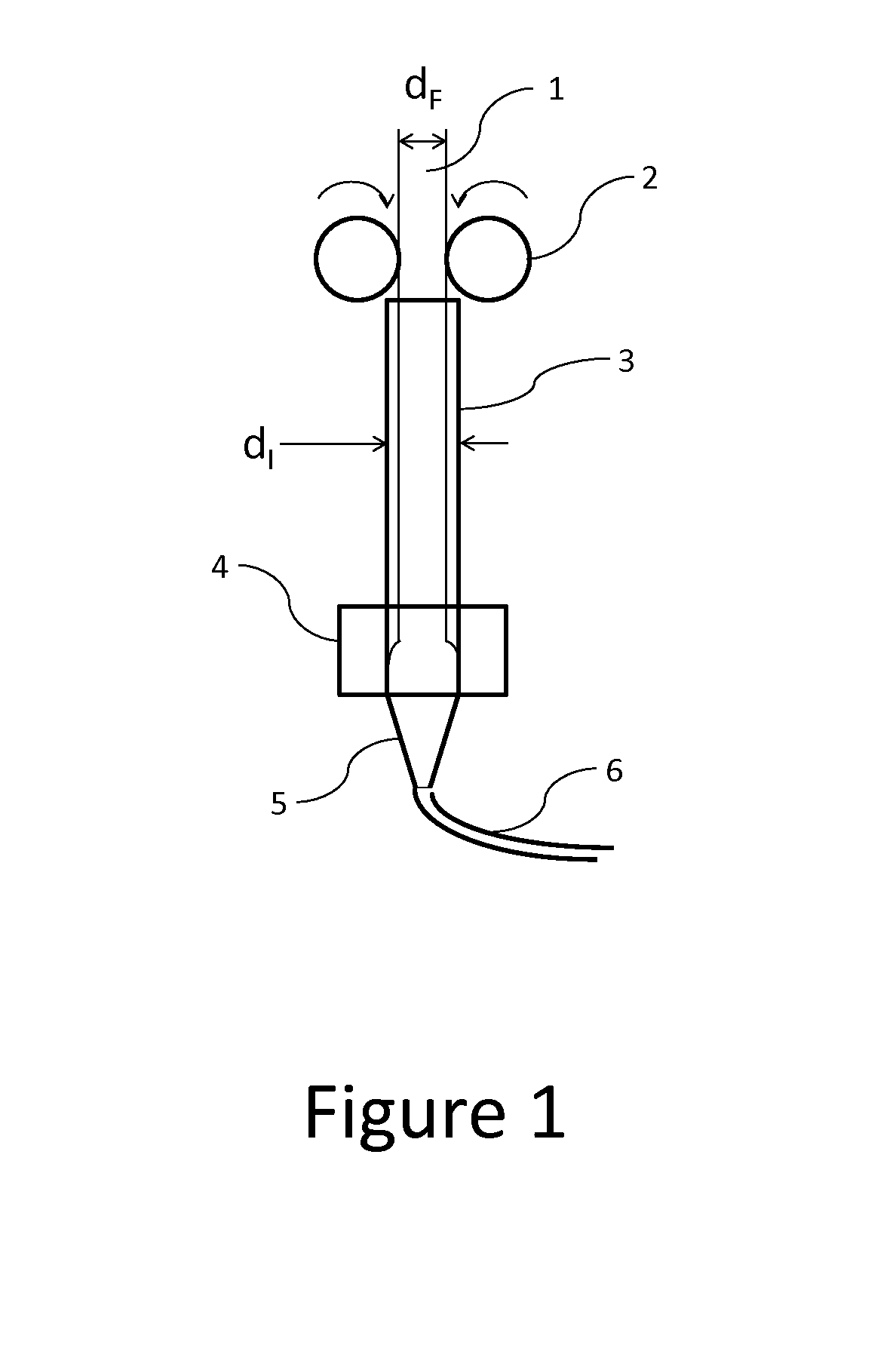
[0043]A poly(lactic acid) (PLA) (4043D from NatureWorks, LLC) and a thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) (Estane TPU S375D from Lubrizol) in the mass ratio of PLA:TPU=25:75 were fed into a 20 mm single-screw extruder with a cylindrical die with a diameter of 3 mm to manufacture a filament with a targeted diameter of 1.75 mm. The processing conditions are as follows:
231(compression(metering4Screw(feed zone)zone)zone)(die)(rpm)120° C.190° C.215° C.190° C.30
[0044]The manufactured filament exhibits an average diameter of 1.75 mm with <±0.05 mm in variation. The TPU has a phase-separated morphology, with TPU and PLA forming the continuous matrix and dispersed phase, respectively.
[0045]The produced material was heated and sandwiched between a glass slide and a cover slip for observation by optical microscopy. The micrograph showed that PLA forms spherical particles, with diameters ranging from several microns to 20 microns, evenly dispersed in a continuous matrix of TPU.
example 2
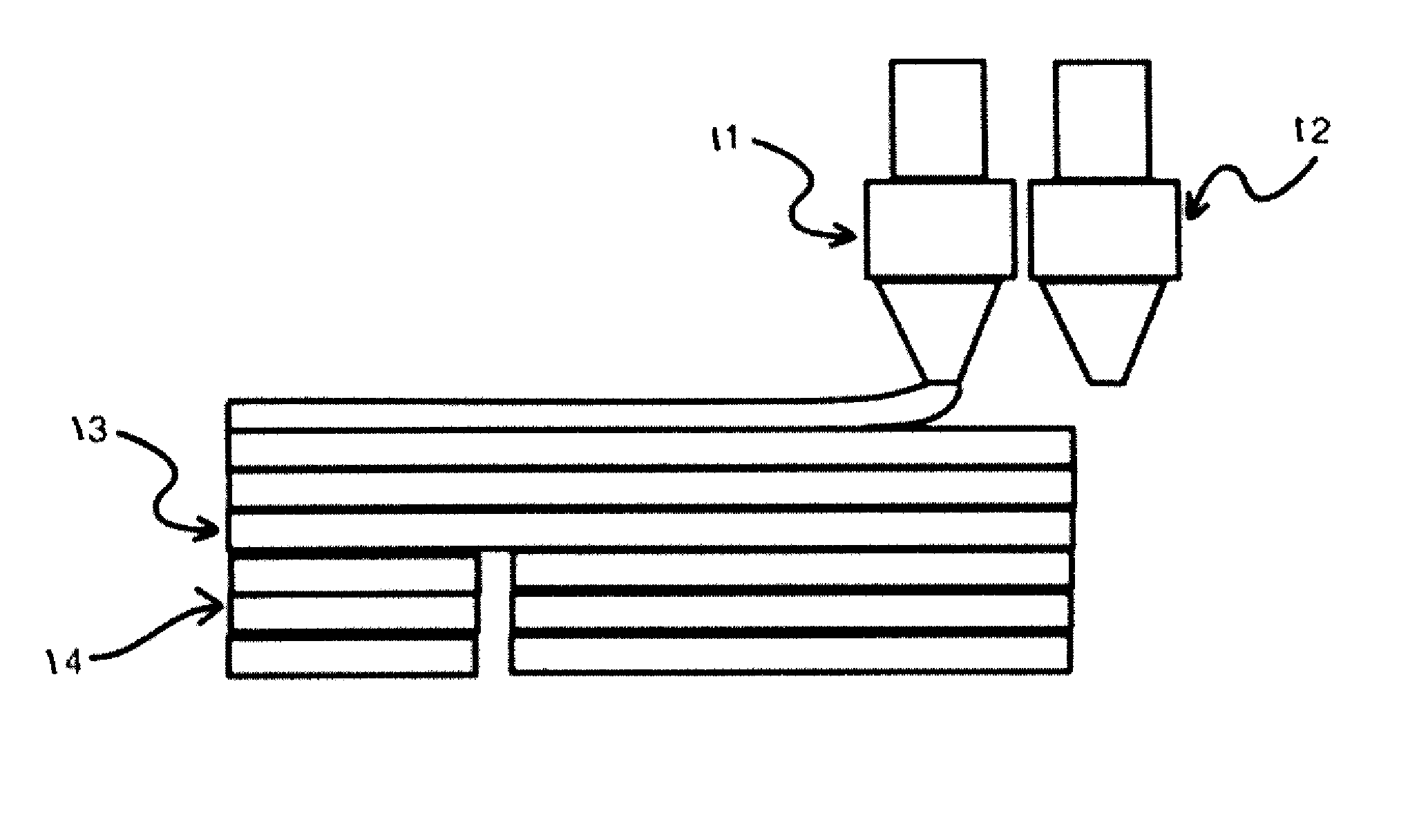
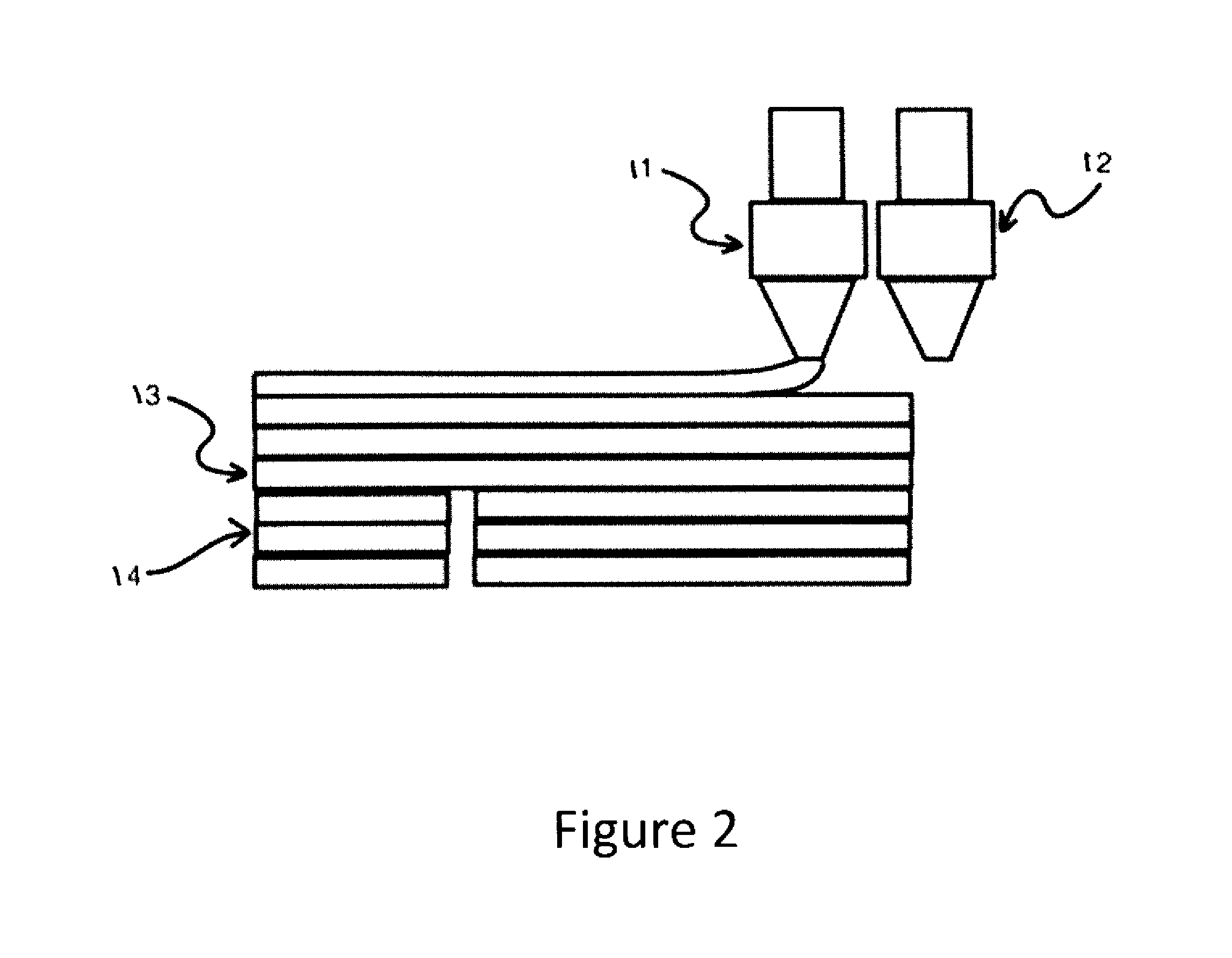
[0046]The manufactured filament as described in Example 1 was loaded onto a dual-extruder desktop FDM / FFF 3D printer (Replicator 2X from MakerBot Industries, LLC). Several models with large overhang portions were used to test the support performance as well as the ease of support removal. The basic printing conditions are as follows:[0047]Modeling material: PolyPlus™ PLA (manufactured by JF Polymers (Suzhou) Co. Ltd.), printed at 195° C.[0048]Support material: printed at 220° C.[0049]Build plate temperature: 60° C.
[0050]The printing speed used was 90 mm / s. For all models tested, the support structure was adequate in supporting the overhang portions, and can be afterwards removed with simple pulling and tearing actions. In most cases the support can be removed by hand or with simple tools such as tweezers. No residue support material is visible on the printed model, meaning that the fracture always occurs at the support-model interface, as designed. In average it takes 1-2 minutes to...
example 3
[0051]The manufactured filament as described in Example 1 was loaded onto a single-extruder desktop FDM / FFF 3D printer (Up! Plus 2nd Generation from Beijing Tier Times Technology Co., Ltd.). In this case the material is used both as the modeling material as well as the support material. It was found that, once a relatively large model infill density (>50%) is used, the support can be removed easily without breaking the model.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com