Formulation of immunopotentiators
a technology of immunopotentiators and forms, which is applied in the field of formulating immunopotentiators, can solve the problems of smips typically lacking suitable functional groups, and achieve the effects of improving the immunopotentiator's pharmacological properties, reducing the general activation of b cells, and improving immunostimulating activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example compound 102
[0526 includes a phosphate group attached to compound O's phenyl ring. The phosphate provides a group which could undergo ligand exchange with an aluminium salt. Compound 102 is synthesised as disclosed in reference 10.
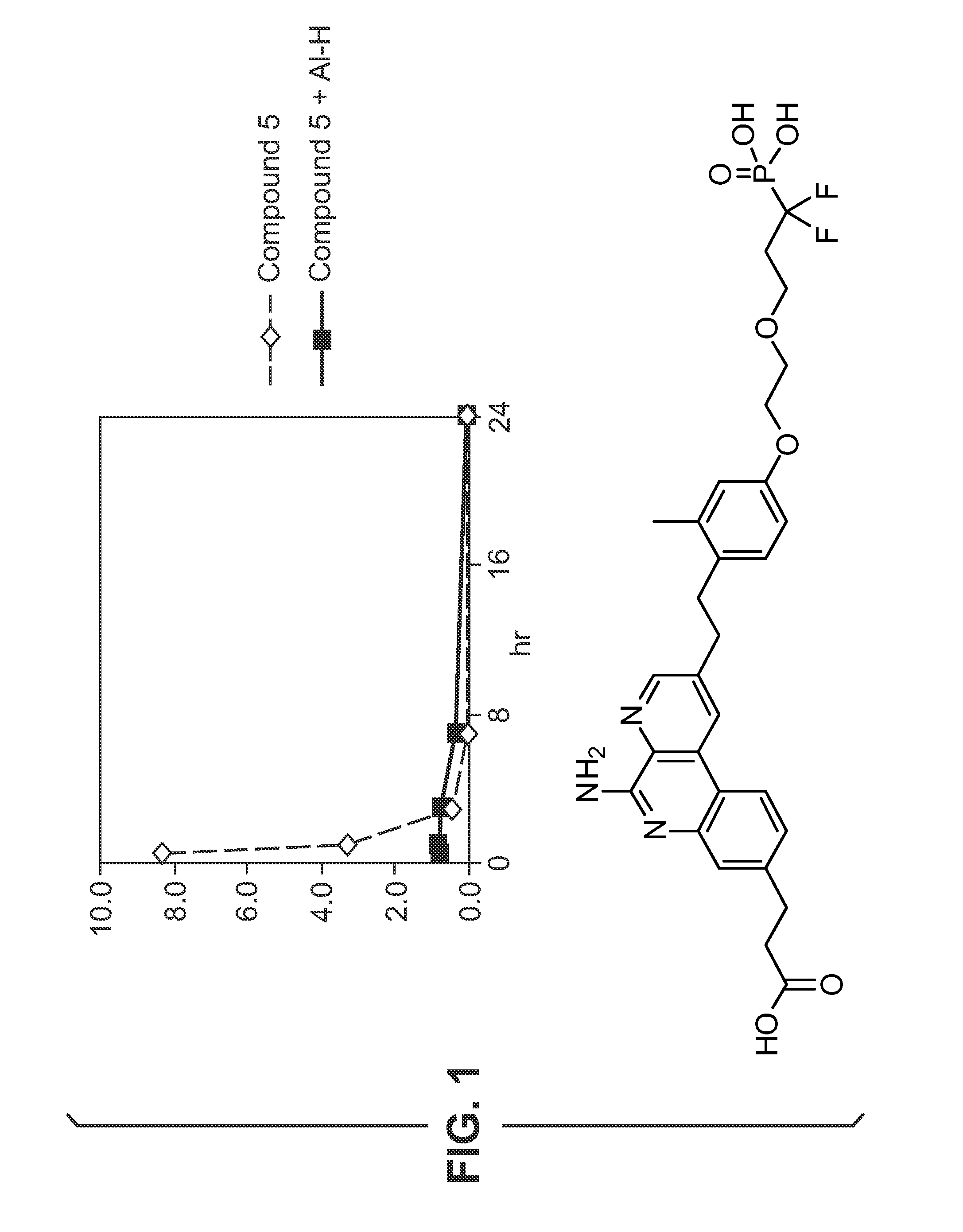
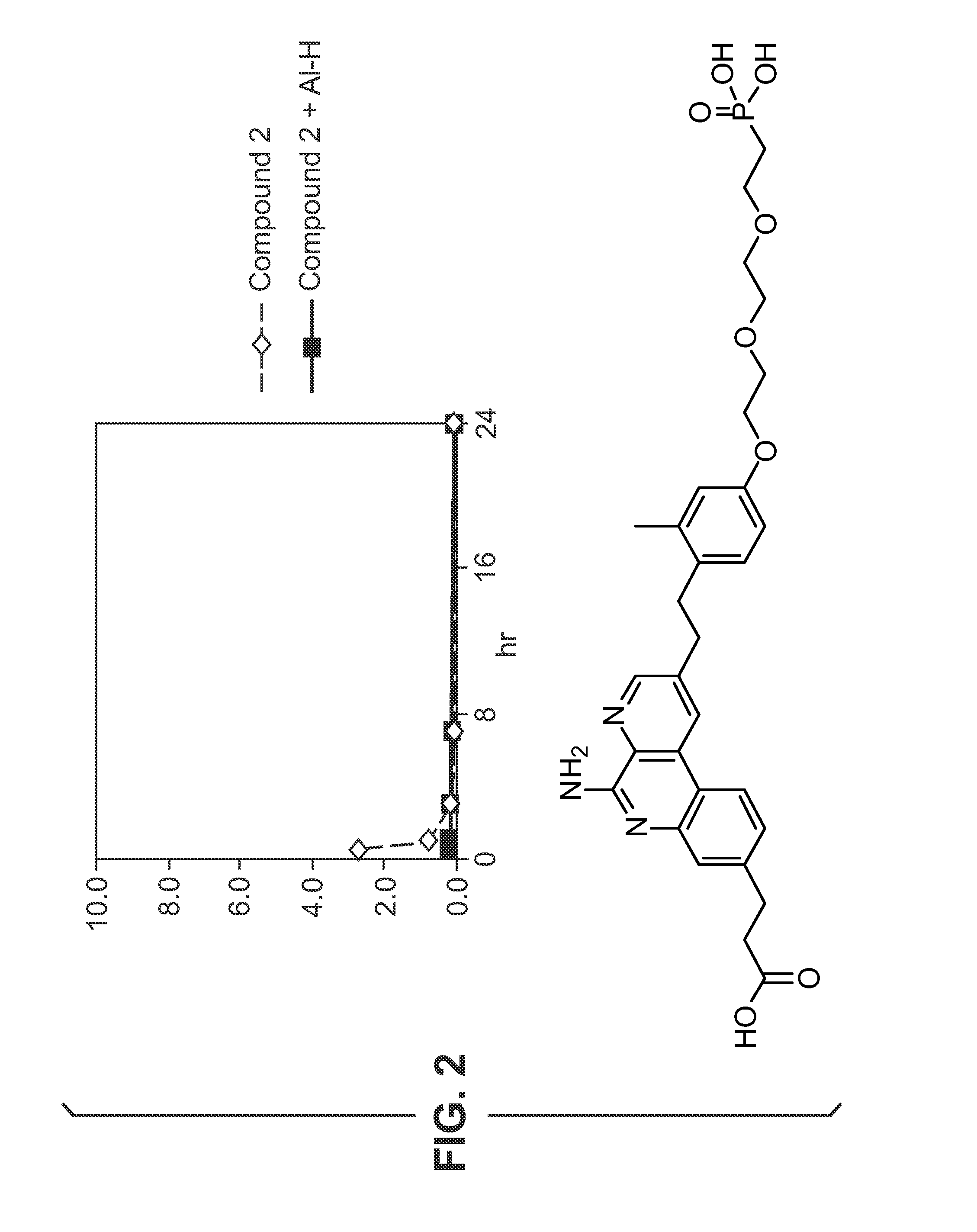
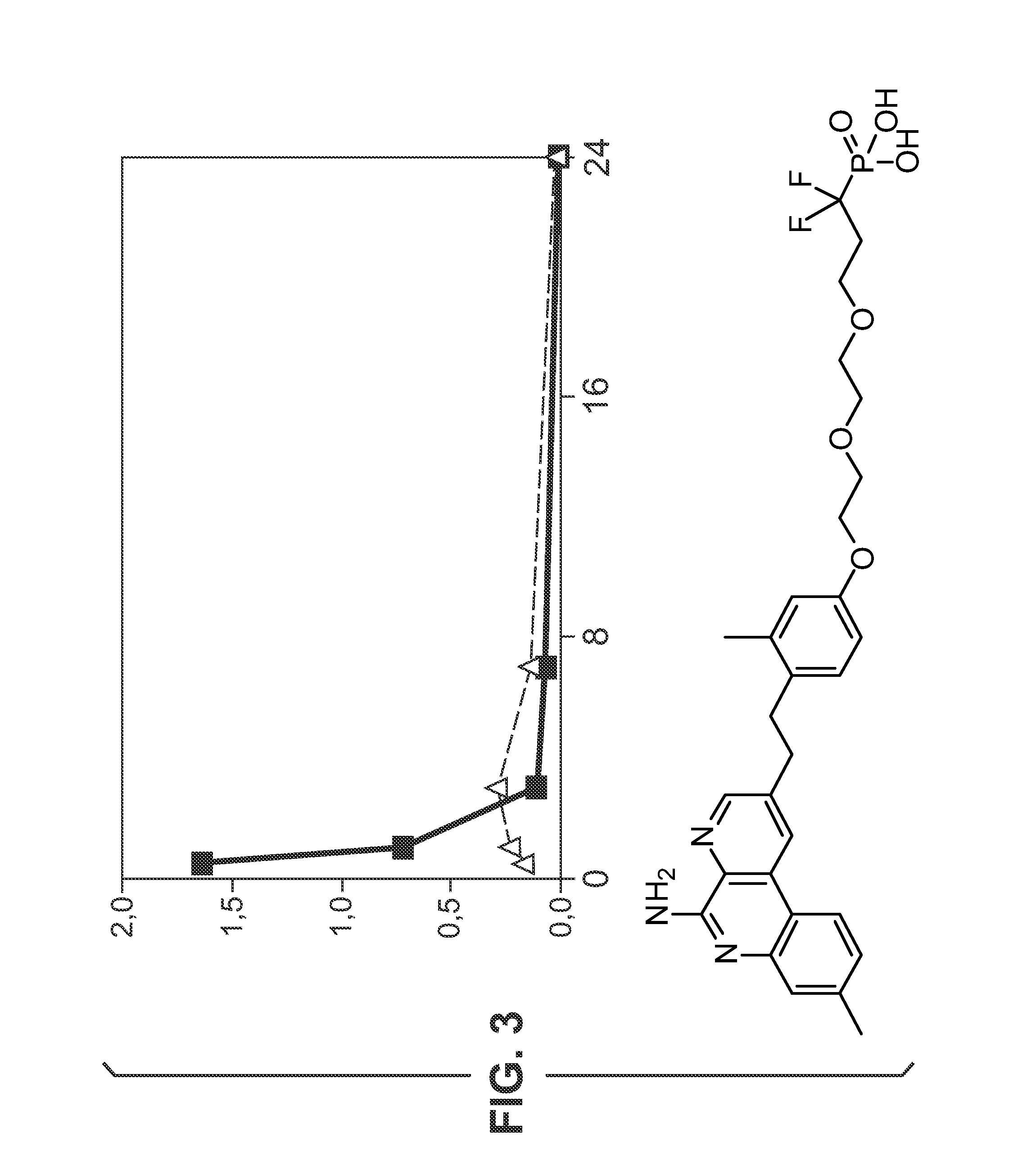
Adsorption Studies—Aluminium Hydroxide
[0527]Adsorption of compounds to aluminium hydroxide (Al—H) is studied at various pH.
[0528]Compound 13 (0.5 mg / mL) is dissolved in 10 mM NaOH (pH 6.5 or pH 9) and added to aluminium hydroxide adjuvant (2 mg / mL) resulting in a 100 μg / dose formulation. The supernatant is evaluated with HPLC using a ballistic gradient (from 10% CH3CN-0.1% TFA to 100% CH3CN-0.1% TFA in 2.5 minutes) on a C18 (50 cm×4.6 mm) ACE column at 45° C. To evaluate the effect of supernatant temperature and incubation time on binding, the supernatant is evaluated at room temperature and at 37° C. after 1 hour, 5 hours and 24 hours. A control without aluminium hydroxide is also evaluated. HPLC chromatograms for compound 1 formulations with and without aluminium hy...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com