Beverage manufacture, processing, packaging and dispensing using electrochemically activated water
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
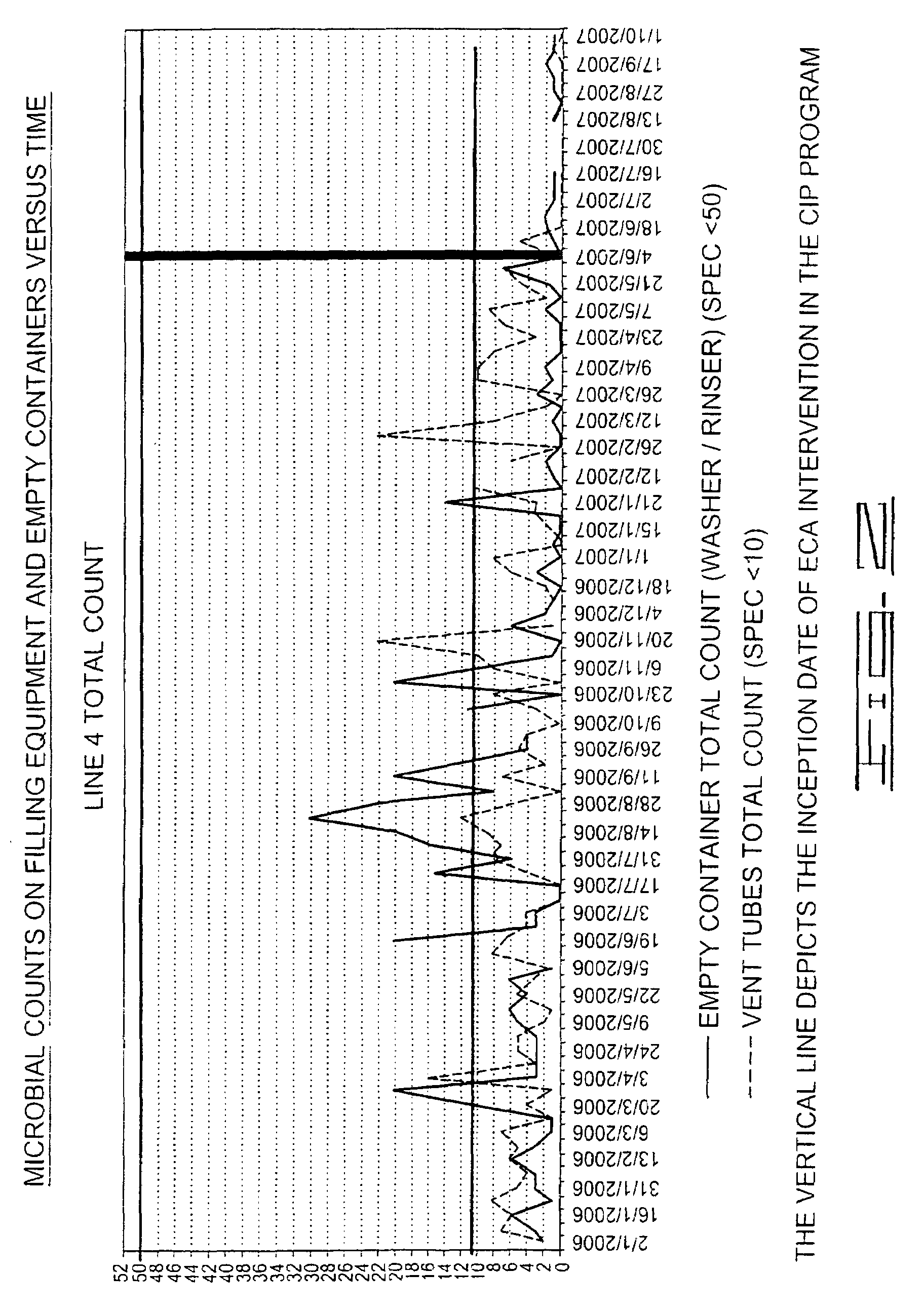
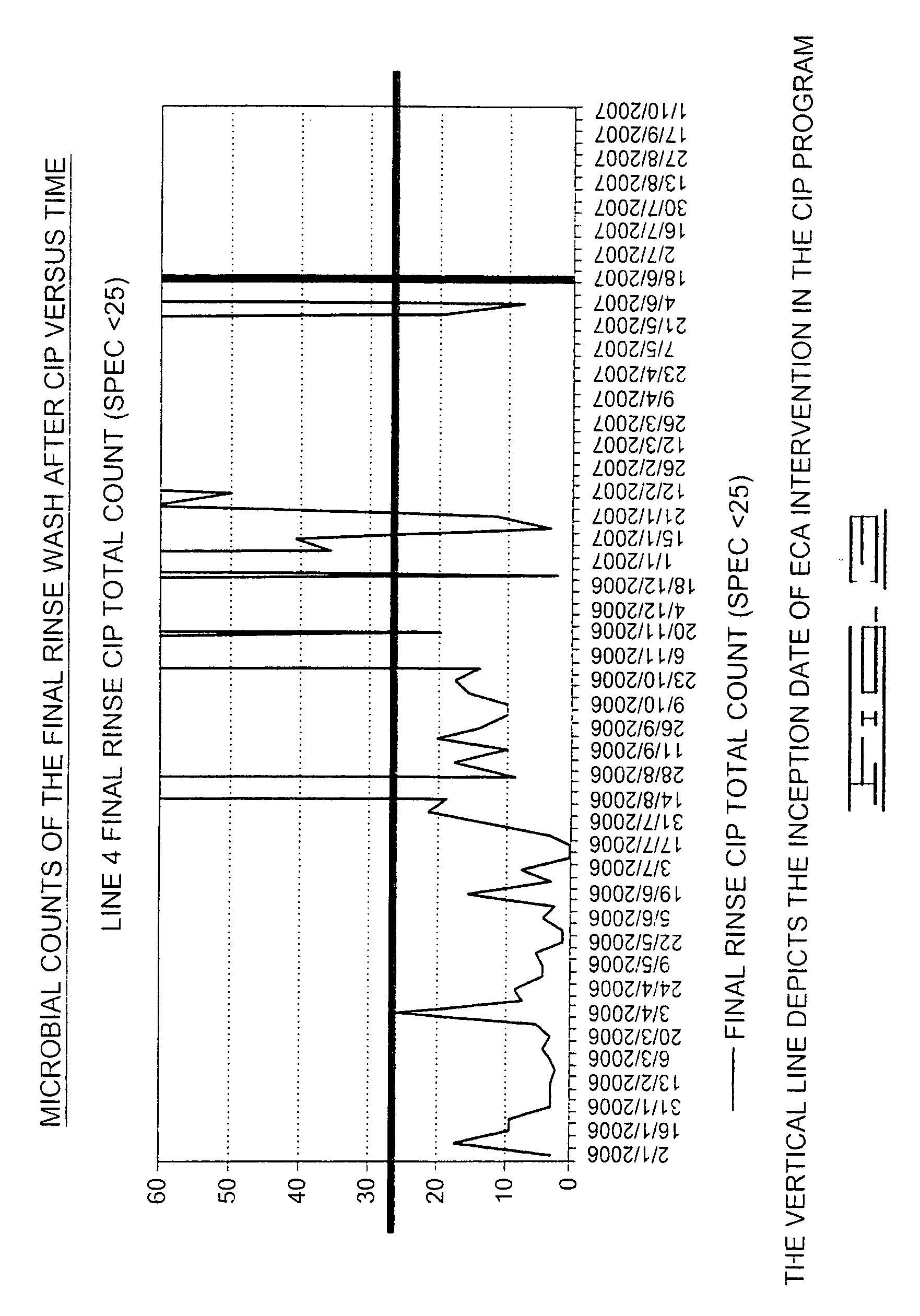
[0123]This was a comparative test involving the use of ECAW solutions to replace the existing chemical agents used in conventional Cleaning-in-Place (CIP) protocols. As shown below, the inventive method provided enhanced microbial control, reduced water usage, and shorter cleaning and disinfection cycles in a carbonated beverage plant.
[0124]Conventional cleaning and disinfection of systems and equipment in carbonated beverage packaging plants has typically comprised two protocols—either a three step (only disinfection) or a five step process (cleaning, rinsing and disinfection).
[0125]Antioxidant catholyte and oxidant anolyte were added to process water used for the cleaning and disinfection of production and packaging systems and equipment for diverse beverage types as a complete substitution for existing conventional chemical products. The measured characteristics of the diluted aqueous treatment solutions used were as follows:
Solution*EC**pHORPFAO 5% Anolyte0.676.674030% Catholyte...
example 2
Carbonation of ECA Solutions
[0131]Carbonation of predetermined, diluted ECA solutions was conducted to establish the changes in the physiochemical characteristics that resulted from the addition and presence of gaseous Carbon Dioxide (CO2).
[0132]Standard dilutions of freshly generated ECA anolyte and catholyte were prepared using untreated potable process water. The physiochemical attributes of each solution were recorded both before and after carbonation in order to detail the changes effected by the introduction of CO2.
[0133]As will be understood by those in the art, the various solutions tested in this example were carbonated by the application of 2.5 volumes (5 gm / 500 ml) of CO2 to 500 ml of the sample at ambient temperature for 30 seconds.
TABLE 3Physiochemical parameters of the ECA solutionbefore and after carbonation.Catholyte @ 30%ParameterBeforeAfterConcentrate CatholyteEC (mS)3.382.539.93pH11.35.411.6ORP (mV)15441−110Anolyte @ 30%BeforeAfterConcentrate AnolyteEC (mS)2.82.63...
example 3
Residue Neutralization
[0137]The breakdown of pesticide and fungicide residues by an oxidant ECA anolyte solution was evaluated as follows.
[0138]The oxidant anolyte solution was diluted using a 10 fold dilution series. As a control for this test, the potential for non-ECA based hydrolysis or chemical breakdown was assessed using two untreated control solutions, one being the tap water used as the diluent in the anolyte dilution series and the other being the non-activated brine solution that was used as the electrolysis feed solution prior to electro-activation.
[0139]The experiment was performed to contrast the difference in degree of recovery of a variety of pesticide and fungicide active ingredients (AI's) after the tap water and the various diluted anolyte solutions were ‘spiked’ with the same AI's at fixed inclusion rates. In each case, a one ppm cocktail of the active ingredients was added to a 100 ml aliquot of the test or control solution sample. The test samples were agitated...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com