Organic transistor, manufacturing method of semiconductor device and organic transistor
a manufacturing method and organic technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, basic electric elements, electric devices, etc., can solve problems such as high tunnel leakage current, difficult to use plastic or film as a substrate, and concern about reliability degradation, so as to reduce the tunnel leakage current, reduce the cost, and improve the effect of quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment mode 1
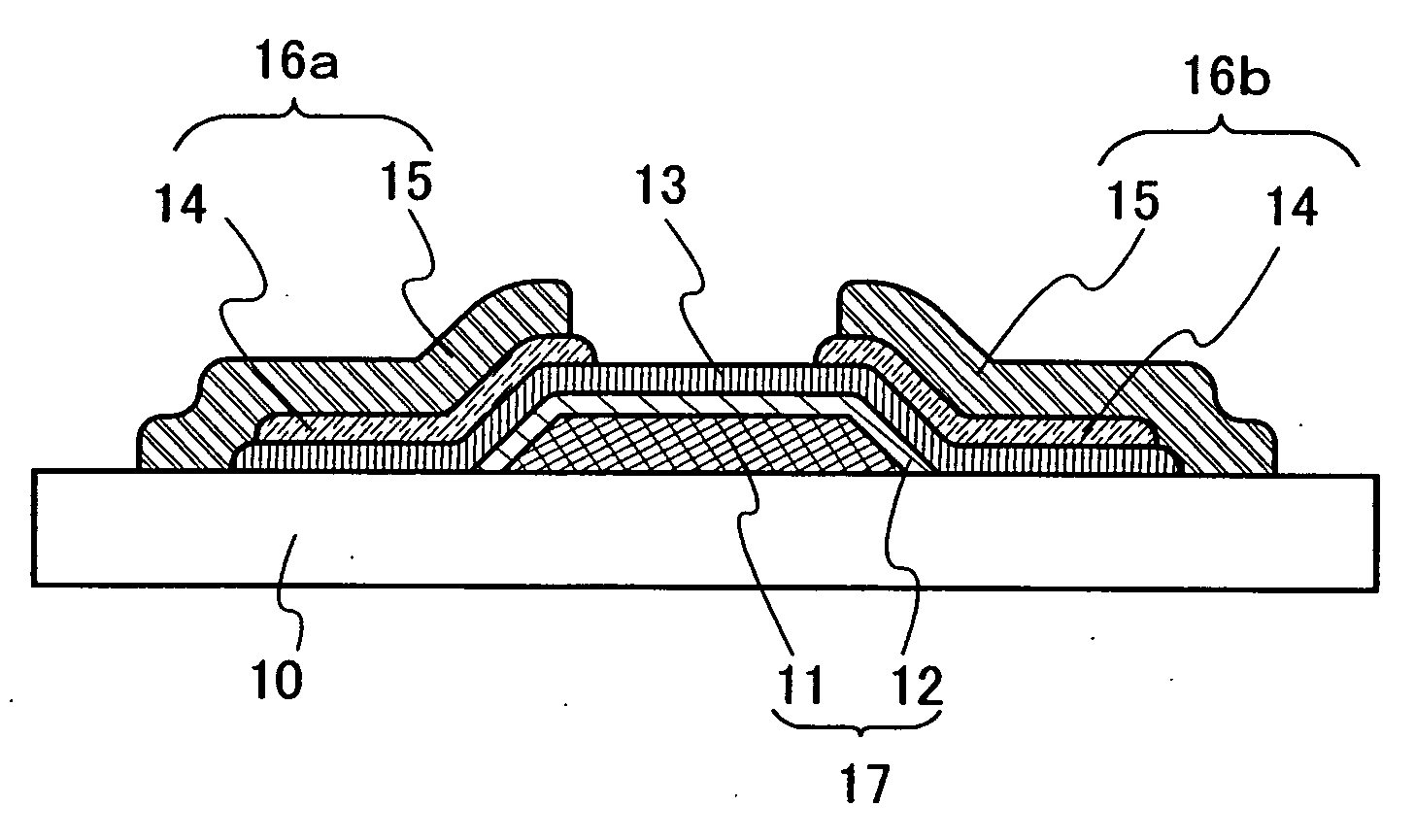
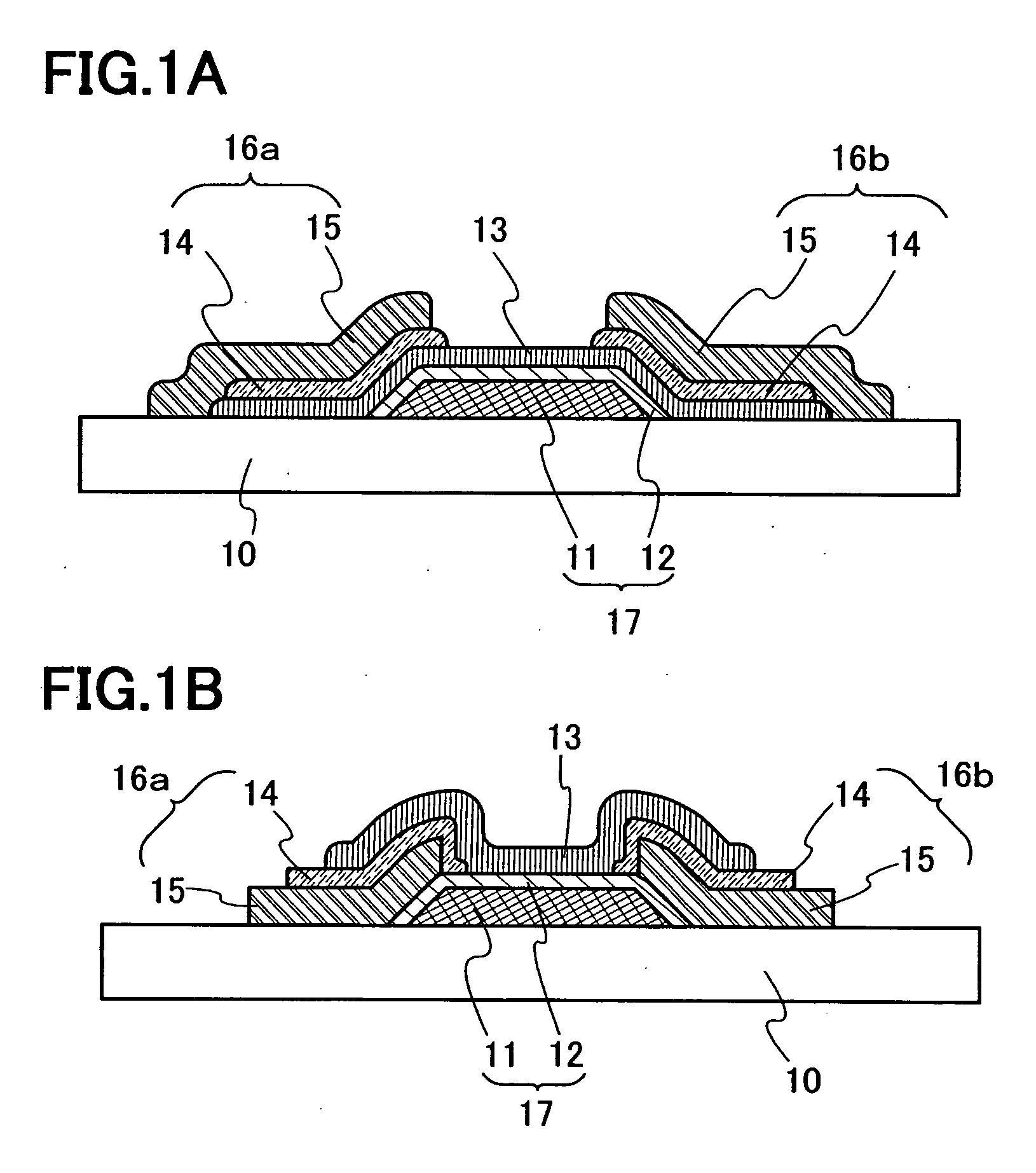
[0036] A configuration of an organic transistor structure of the present invention is shown in FIGS. 1A and 1B. Note that reference numeral 10 is a substrate, 11 is a gate electrode, 12 is a gate insulating film, 13 is a semiconductor layer including an organic semiconductor material, 14 is a composite layer having an organic compound and a metal oxide, 15 is a conductive layer, and a source and a drain electrodes 16a and 16b have a composite layer 14 and a conductive layer 15. Arrangement of each layer and electrode can be selected suitably depending of the use of the element. In addition, the composite layer 14 is formed to be in contact with the semiconductor layer 13 in FIGS. 1A and 1B; however, without being limited to this, the composite layer may be included in a portion of a source electrode and / or a drain electrode.
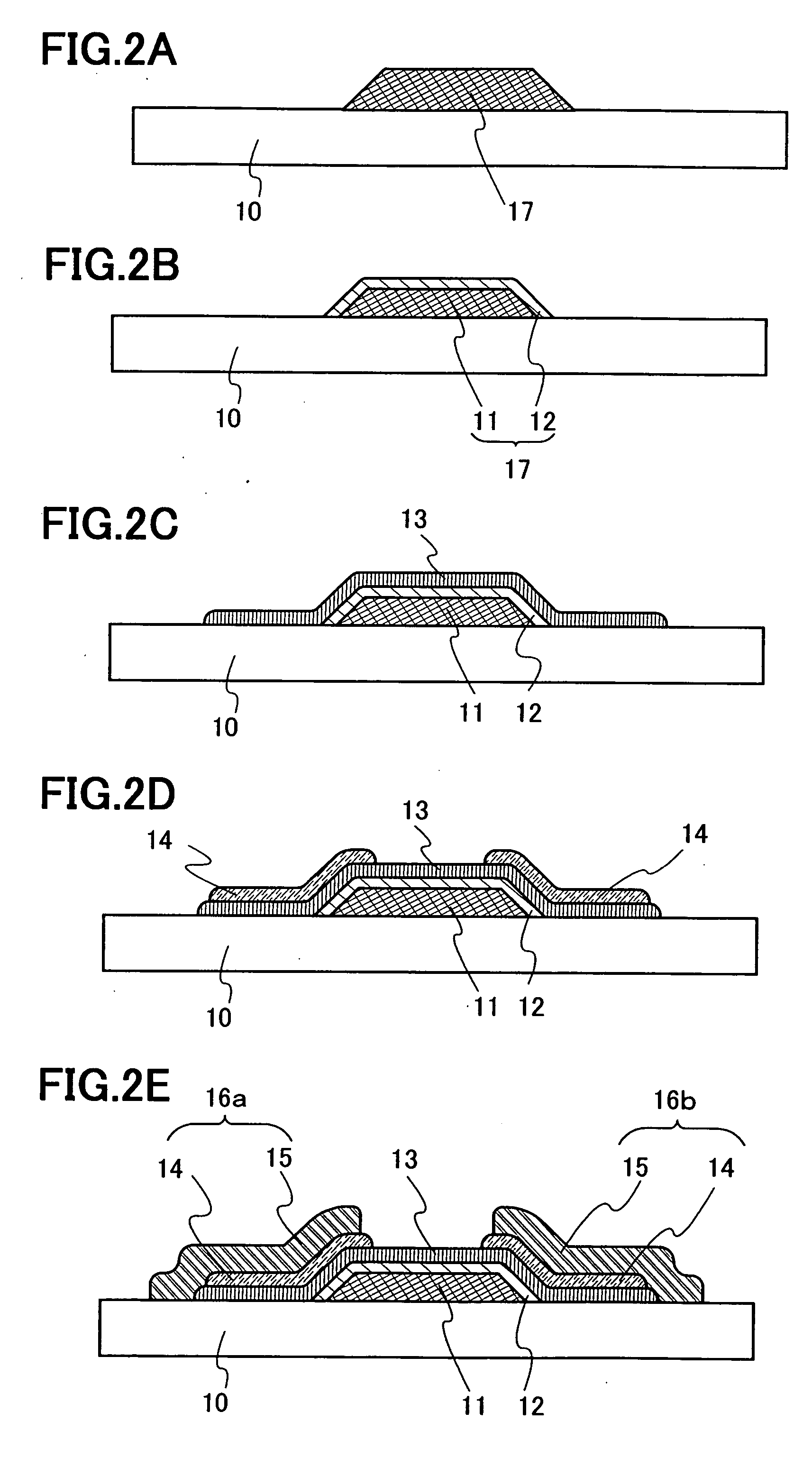
[0037] A structure of FIG. 1A is explained along manufacturing methods of FIGS. 2A to 2E. As the substrate 10, an insulating property substrate such as a glass ...
embodiment mode 2
[0061] The organic transistor as shown in embodiment mode 1 uses the insulating film formed by performing dense plasma treatment to the conductive layer which becomes the gate electrode as the gate insulating film; however, in this embodiment mode, a gate insulating film is formed by nitriding or oxygenizing with dense plasma additionally to the insulating film formed previously like FIGS. 3A and 3B. Since, elements except the gate insulating film and the gate electrode are similar to those of Embodiment Mode 1, they are denoted by the same reference numerals and the description thereof is omitted.
[0062] A gate electrode 31 is formed over a substrate 10. A material using for the gate electrode 31 is not limited particularly. For example, a metal such as gold, platinum, aluminum, tungsten, titanium, copper, molybdenum, tantalum, niobium, chromium, nickel, cobalt, magnesium and an alloy including them, a conductive high molecular compound such as polyaniline, polypyrrole, polythiophe...
embodiment mode 3
[0074] In this embodiment mode, an organic transistor having a structure which is different from the structure denoted in Embodiment Modes 1 and 2 is explained using FIGS. 4A and 4B. The organic transistor of the embodiment modes 1 and 2 is the bottom gate type transistor; however, the transistor of this embodiment mode is a top gate type transistor. Portions similar to those of Embodiment Mode 1 are denoted by the common reference numerals and the description thereof is omitted.
[0075] A structure of FIG. 4A is explained. The semiconductor layer 13 is formed over the substrate 10. Further, the source and drain electrodes 16a and 16b having the composite layer 14 and the conductive layer 15 are formed over the semiconductor layer 13.
[0076] Next, an insulating film 42 covering the semiconductor layer 13 and the source and drain electrodes 16a and 16b is formed. An inorganic material such as silicon oxide, silicon nitride or silicon oxynitride is used for the insulating film 42. Thes...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com