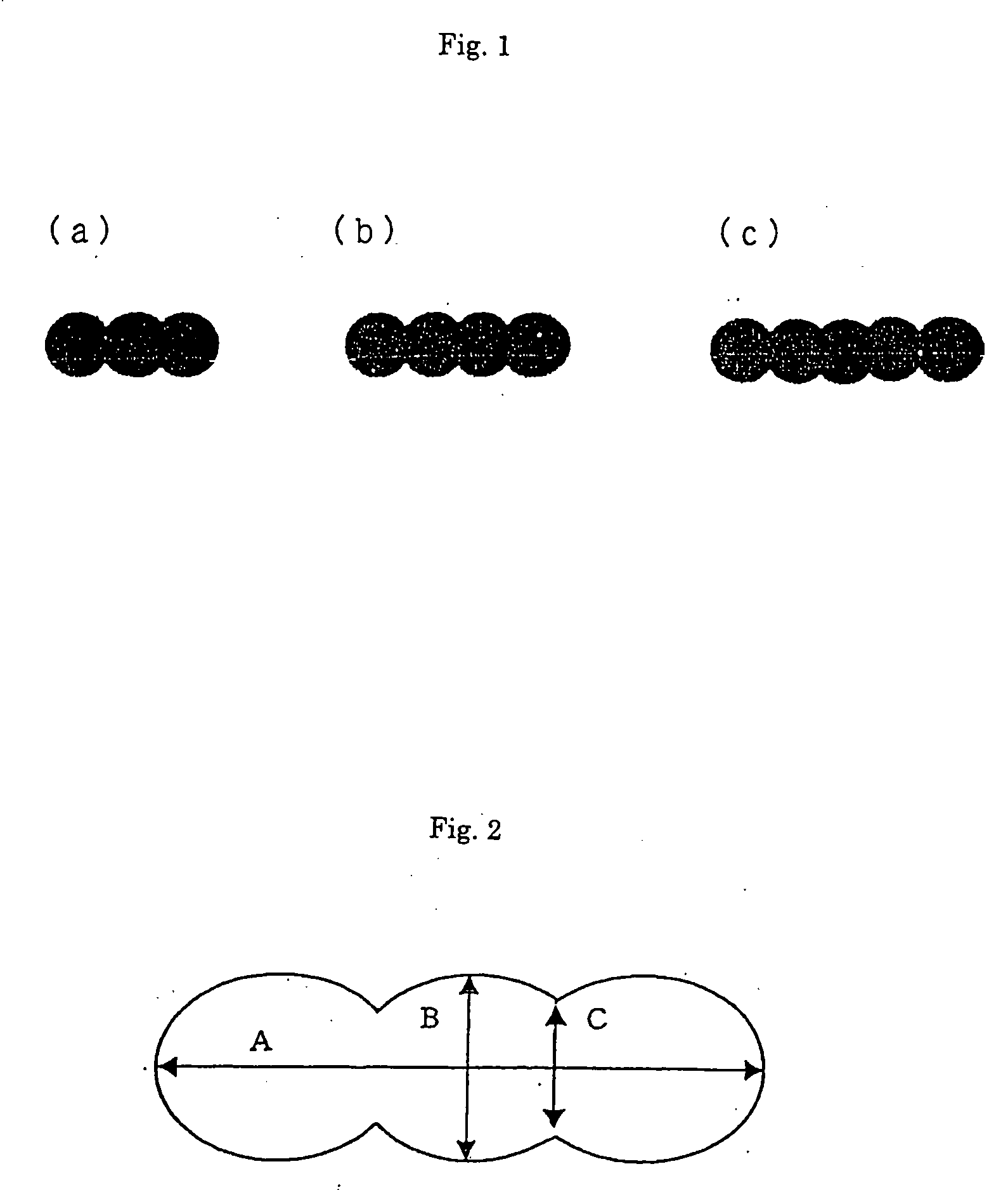
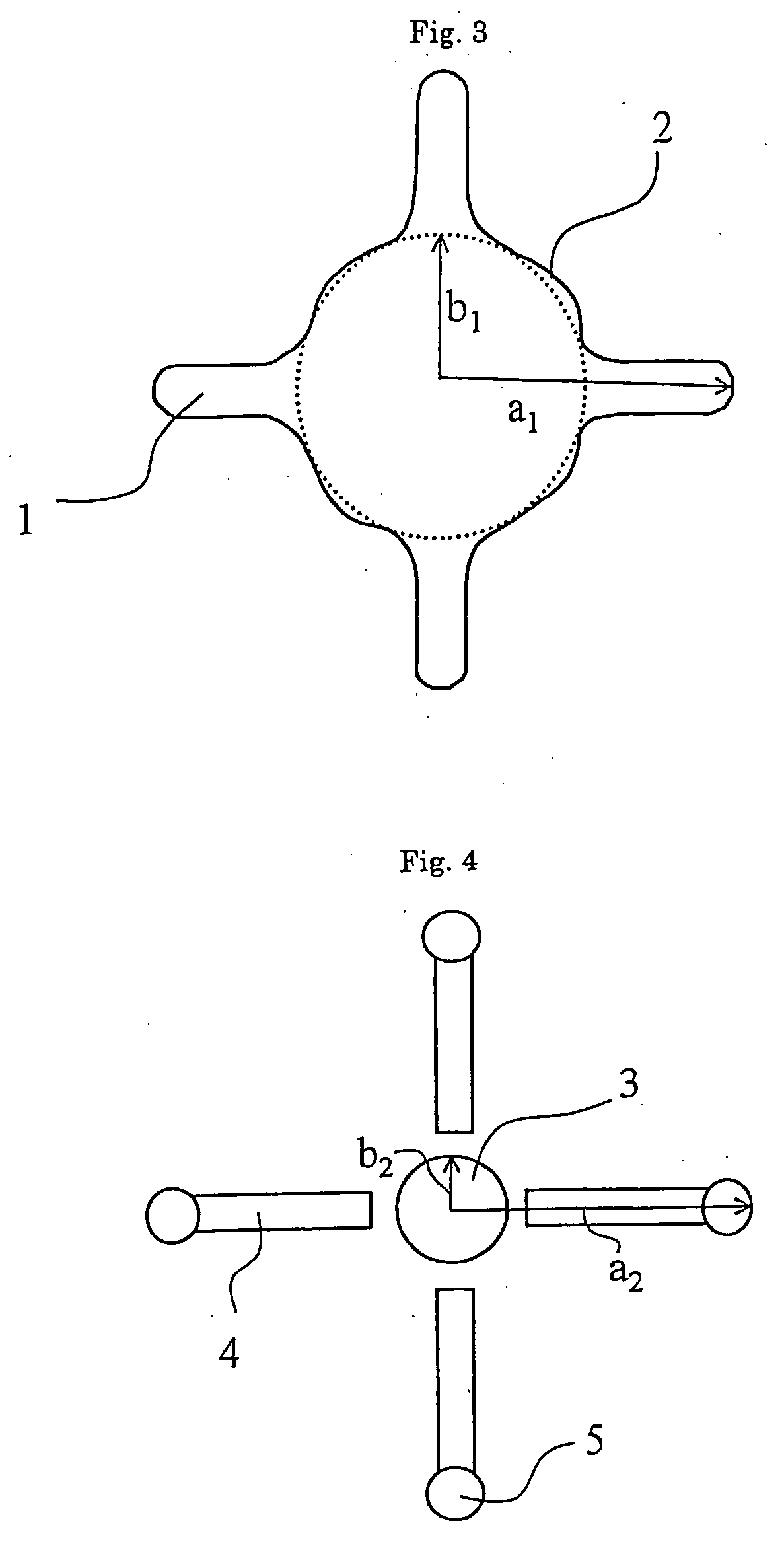
Modified cross-section polyester fibers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Titanium Compound:
[0199] A 2 L three-necked flask equipped with a function allowing mixing and stirring of the contents was prepared, 919 g of ethylene glycol and 10 g of acetic acid were placed therein, and after stirring and mixing, 71 g of titanium tetrabutoxide was slowly added to obtain a (transparent) solution of a titanium compound in ethylene glycol. This solution will hereinafter be abbreviated as “TB solution”. The titanium atom concentration of the solution was 1.02%.
Preparation of Phosphorus Compound:
[0200] A 2 L three-necked flask equipped with a function allowing heating, mixing and stirring of the contents was prepared, and 656 g of ethylene glycol was placed therein and heated to 100° C. while stirring. Upon reaching 100° C., 34.5 g of monolauryl phosphate was added, and the mixture was heated, mixed and stirred to dissolution to obtain a transparent solution. This solution will hereinafter be abbreviated as “P1 solution”.
Preparation of Catalyst...
example 4
[0210] After charging 0.009 part by mass of tetra-n-butyl titanate (TBT) into a mixture of 100 parts by mass of dimethyl terephthalate and 70 parts by mass of ethylene glycol in a pressure reaction-capable stainless steel reactor, pressurization was conducted at 0.07 MPa for transesterification reaction while increasing the temperature from 140° C. to 240° C., and then 0.035 part by mass of triethyl phosphonoacetate (TEPA) was added to terminate the transesterification reaction.
[0211] The reaction product was then transferred to a polymerization reactor, the temperature was raised to 290° C., and polycondensation reaction was conducted in a high vacuum of no greater than 26.67 Pa to obtain polyethylene terephthalate. During the reaction, titanium dioxide was added as a delustering agent at 2.5 wt % based on the total weight of the polyester. The intrinsic viscosity of the polyethylene terephthalate was 0.62 and the diethylene glycol content was 1.5%. The obtained polyethylene terep...
examples 7-9
[0243] Preparation of a titanium compound, phosphorus compound and catalyst and production of an oligomer were carried out in the same manner as Example 1.
[0244] After transferring 225 parts by mass of the obtained oligomer to a polycondensation reactor, 3.34 parts by mass of the “TP1-2.0 catalyst” produced earlier was charged in as the polycondensation catalyst. The reaction temperature in the system was then raised from 255° C. to 280° C. and the reaction pressure was lowered from atmospheric pressure to 60 Pa in stages, for polycondensation reaction while removing out of the system the water and ethylene glycol generated by the reaction.
[0245] The extent of the polycondensation reaction was confirmed while monitoring the load on the stirring blade in the system, and the reaction was suspended when the desired degree of polymerization was reached. The reaction product in the system was then continuously extruded into a strand from the discharge port and then cooled and cut to ob...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com