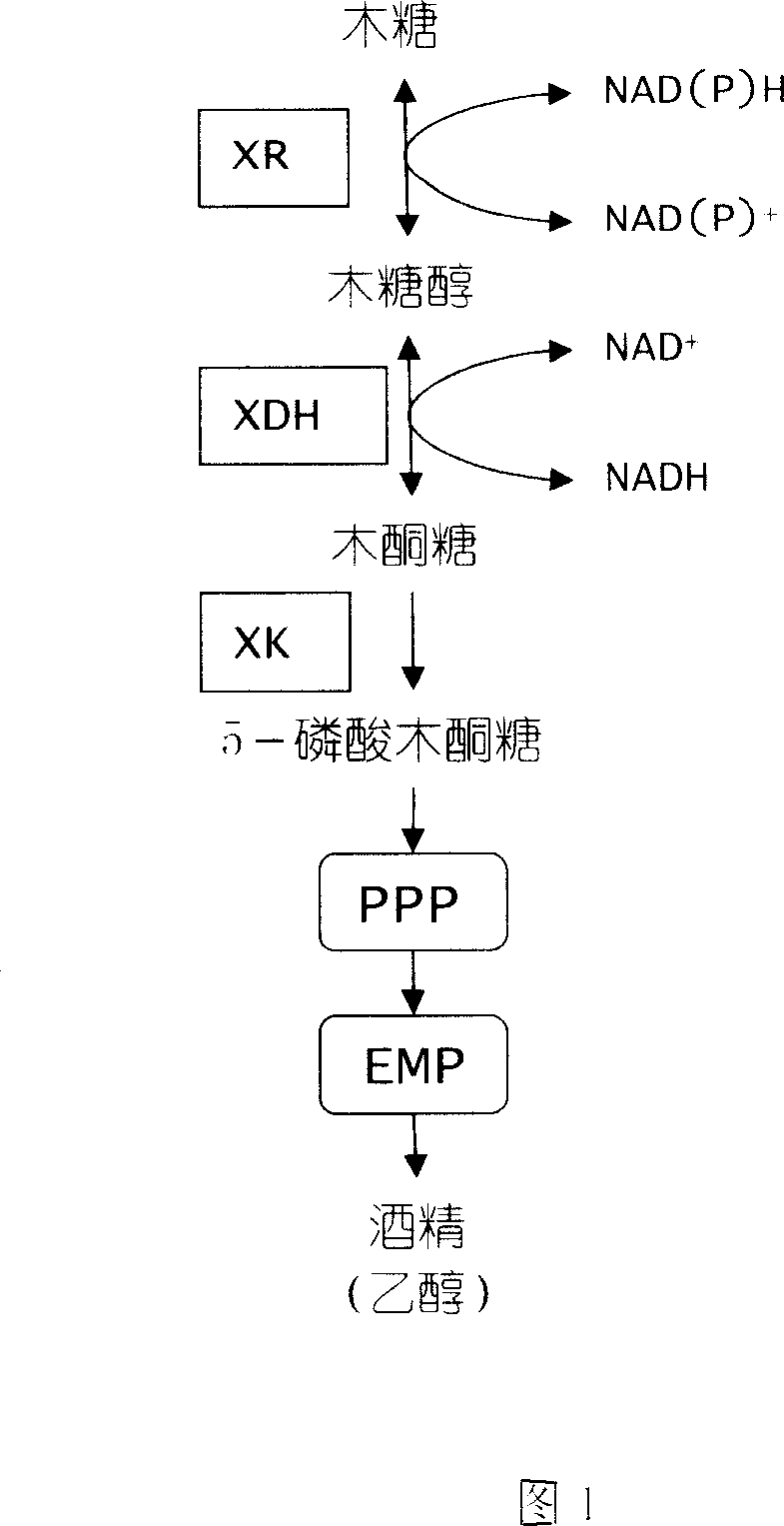
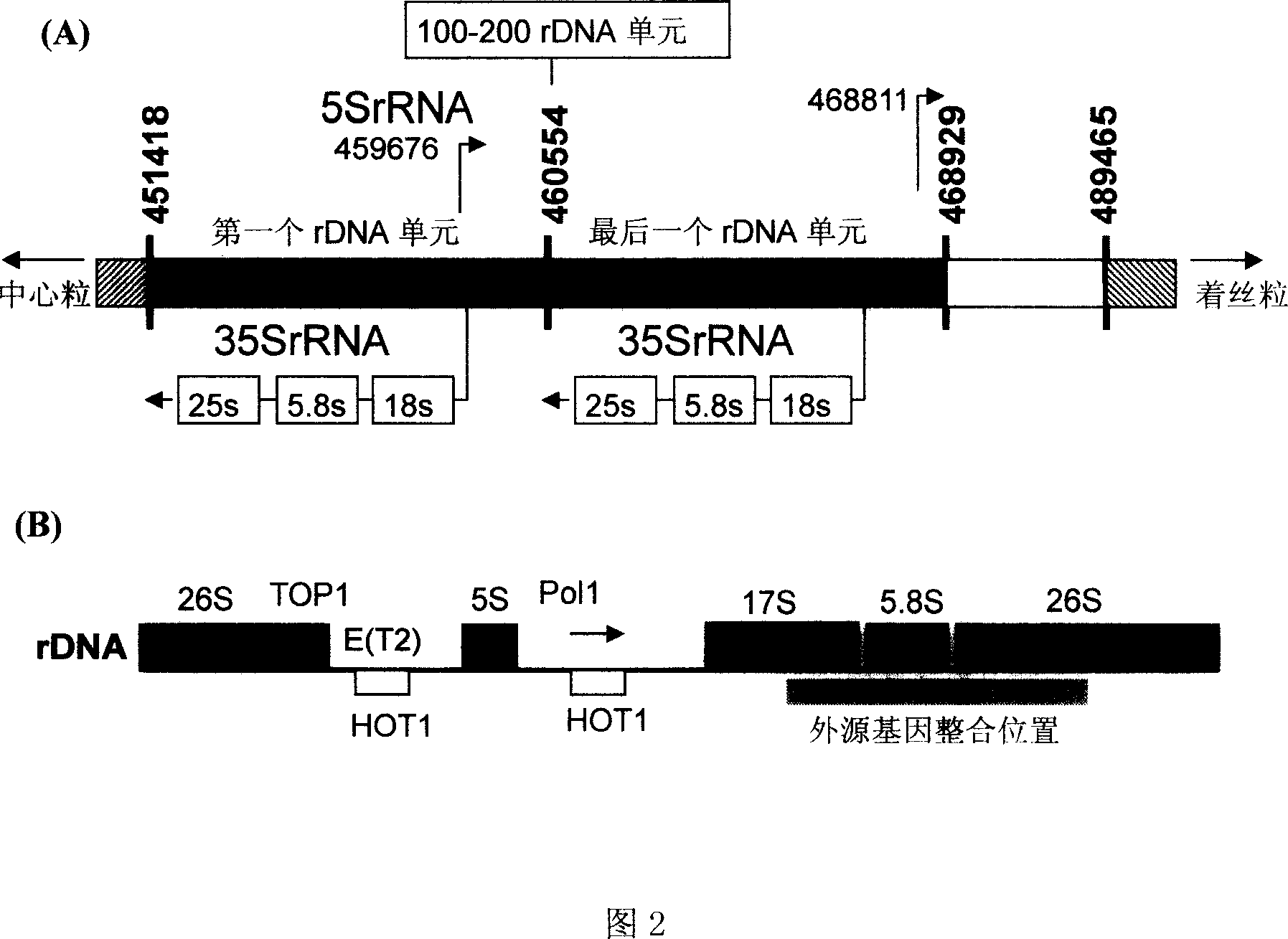
Process for producing alcohol by co-fermentation of glucose and xylose
A technology of co-fermentation of glucose and co-fermentation, which is applied in the field of co-fermentation of glucose and xylose to produce alcohol, can solve the problems of insufficient stability of recombinant strains in alcohol production, and the problem of integration area is not considered, and achieve stable properties of strains, simple fermentation process and high expression level high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1 The construction method of the recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae NAN127 of the present invention:
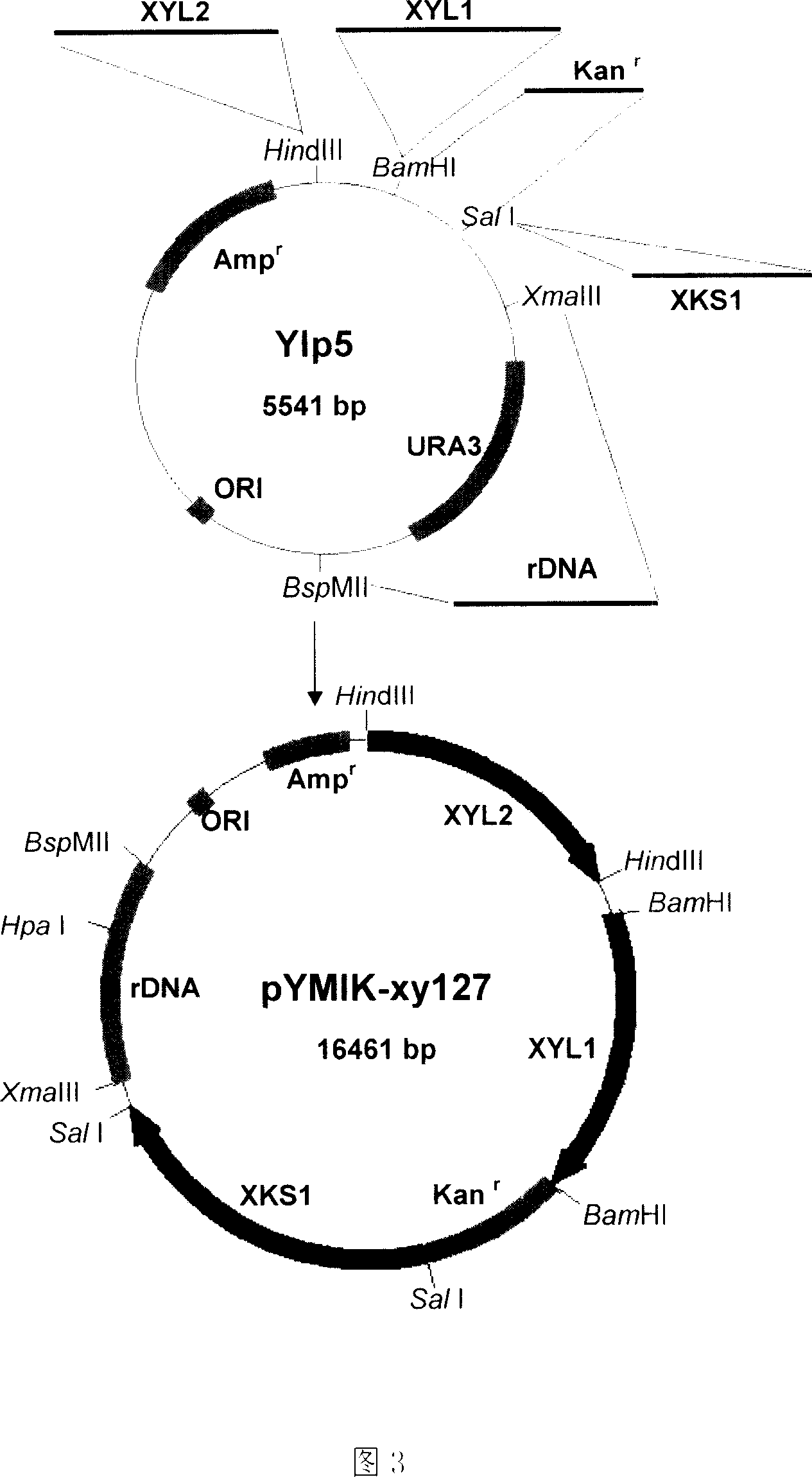
[0037] (1) Construct the recombinant plasmid pYMIK-127 with the yeast universal single-copy integration vector YIp5 as the basic backbone (Figure 2).
[0038] (2) Linearize the recombinant plasmid pYMIK-127 at the 5232bp restriction site with restriction endonuclease HpaI.
[0039] (3) The industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain NAN27 was transformed by the universal lithium acetate transformation method, and the recombinant strain NAN127 was obtained by screening with the YEPD plate added G418.
[0040] Among them, the PGK promoter and terminator (PGK promoter and terminator) in the recombinant plasmid vector pYMIK-127 in step (1) are cloned into the yeast chromosomal DNA, and inserted between the promoter and the terminator into the Pichia stipitis chromosomal DNA The xylitol dehydrogenase gene XYL2 of, the entire fragment is connected to the HindIII (32bp) ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2 Using recombinant engineering bacteria to simultaneously ferment glucose and xylose to produce alcohol, the method is as follows
[0049] (1) Selection of strains: select Saccharomyces cerevisiae NAN127, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.1848;
[0050] (2) Slant culture: Connect 1-2 loops of the above-mentioned recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain NAN127 to a YEPD medium slant containing 2% agar (w / v), and cultivate at 30°C for 24 hours;
[0051] (3) Seed culture: Connect NAN127 to 50mL YEPD liquid medium in the step 1~2 step (2), 30℃, 150~180r / min shaking culture for 24 hours;
[0052] (4) Expanded culture: Transfer the NAN127 in step (3) to 500mL YEPD liquid medium at a volume percentage of 10% of the inoculum, and culture at 30°C with a shaker of 150~180r / min for 24 hours;
[0053] (5) Alcohol fermentation: Transfer the NAN127 in step (4) to the fermenter for fermentation at a volume percentage of 10% inoculum. The fermentation conditions are at 30...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3: Using recombinant engineering bacteria to simultaneously ferment glucose and xylose to produce alcohol, the method is as follows
[0058] (1) Selection of strains: select Saccharomyces cerevisiae NAN127, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.1848;
[0059] (2) Slant culture: Connect 1-2 loops of the above-mentioned recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain NAN127 to a YEPD medium slant containing 2% agar (w / v), and cultivate at 26°C for 36 hours;
[0060] (3) Seed culture: Connect NAN127 to 50mL YEPD liquid medium in step 1 to 2 in step (2), culture at 26°C, 150~180r / min shaking for 36 hours;
[0061] (4) Expanded culture: Transfer the NAN127 in step (3) to 500mLYEPD liquid medium at 5% of the inoculum amount by volume percentage, and culture for 36 hours at 26°C with a shaker of 150-180r / min;
[0062] (5) Alcohol fermentation: According to the volume percentage of 5% of the inoculum, transfer the NAN127 in step (4) to the fermenter for fermentation, the ferm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com