Plasma treatment apparatus and method
A plasma and equipment technology, applied in the field of fiber materials, which can solve problems such as economical infeasibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
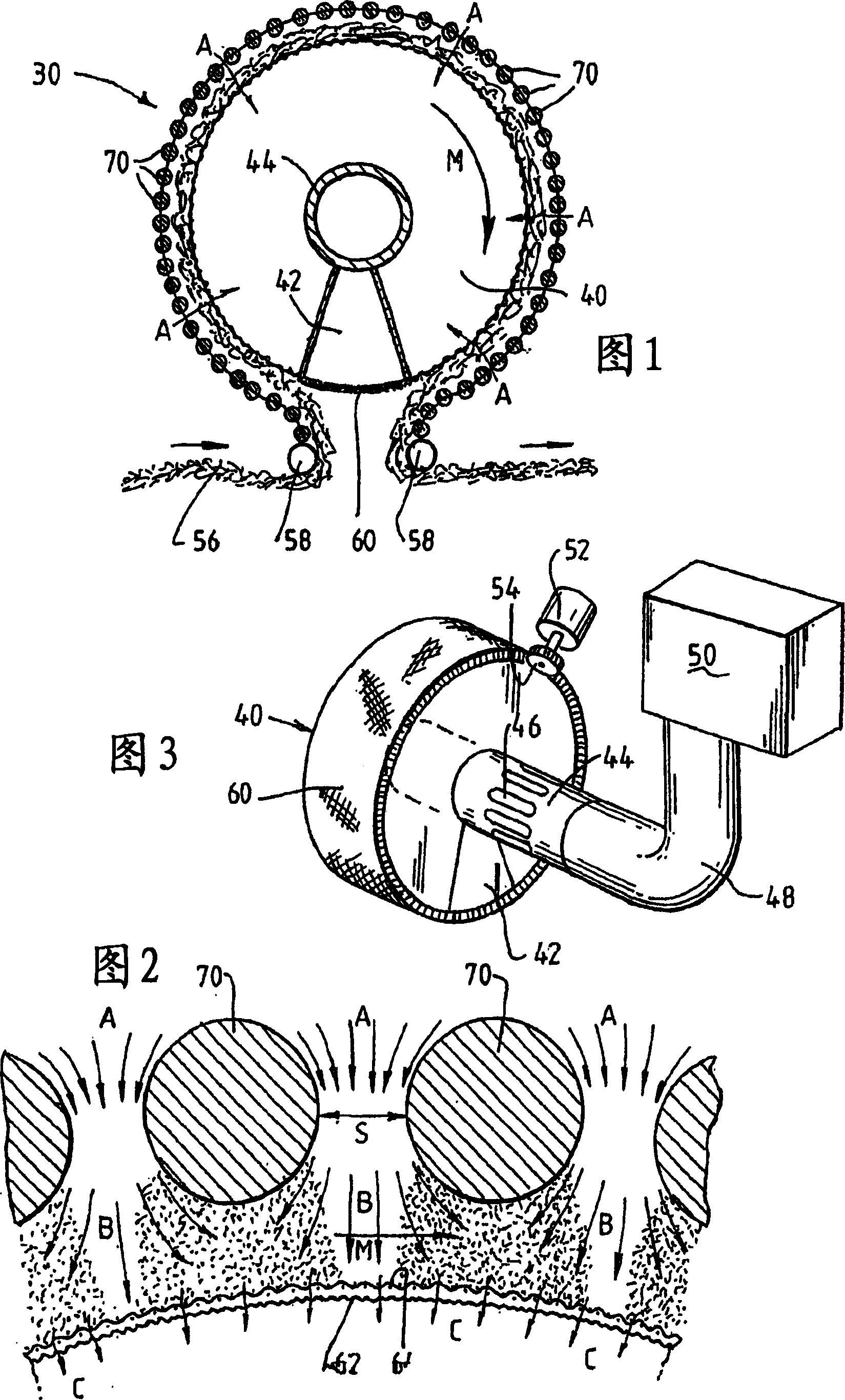
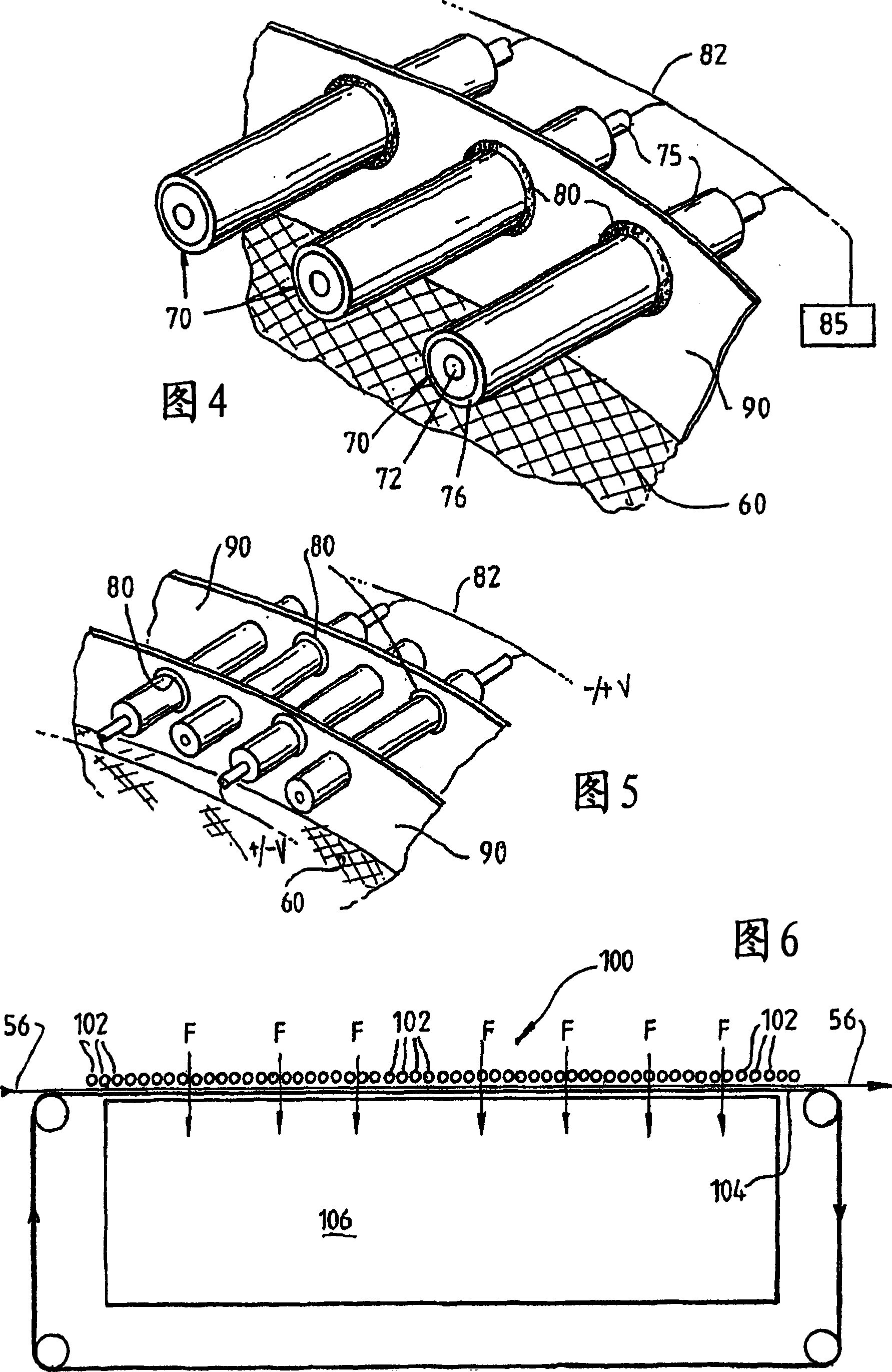
[0055] Referring first to Figures 1 and 2, it can be seen that the plasma processing apparatus 30 includes a hollow, rotatable drum 40 having a first electrode formed on the curved outer surface of the drum 40 in the form of a mesh electrode 60 thereon. The device 30 further includes a second electrode formed as a plurality of rod electrodes 70 spaced radially outward from the mesh electrode 60 .
[0056] The mesh electrode 60 includes a coarse mesh 62 that supports an overlying fine mesh 64 . The fine mesh 64 prevents the localization of the plasma microdischarge by providing a large array of potential plasma formation sites, where a reduced number of potential plasma formation locations will generally result in plasma microdischarge compared to the coarse mesh 62. Electrical localization.
[0057] As shown in FIGS. 1 and 3 , the drum 40 has a tubular core 44 and wedge-shaped baffles 42 extending from the core to the periphery of the drum 40 . The core 44 extends through th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com