Charge pump circuit and working method using its non-volatile storage
A charge pump and circuit technology, applied in the field of non-volatile memory, can solve the problems of not being able to get negative high voltage output, not being able to get high voltage output, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
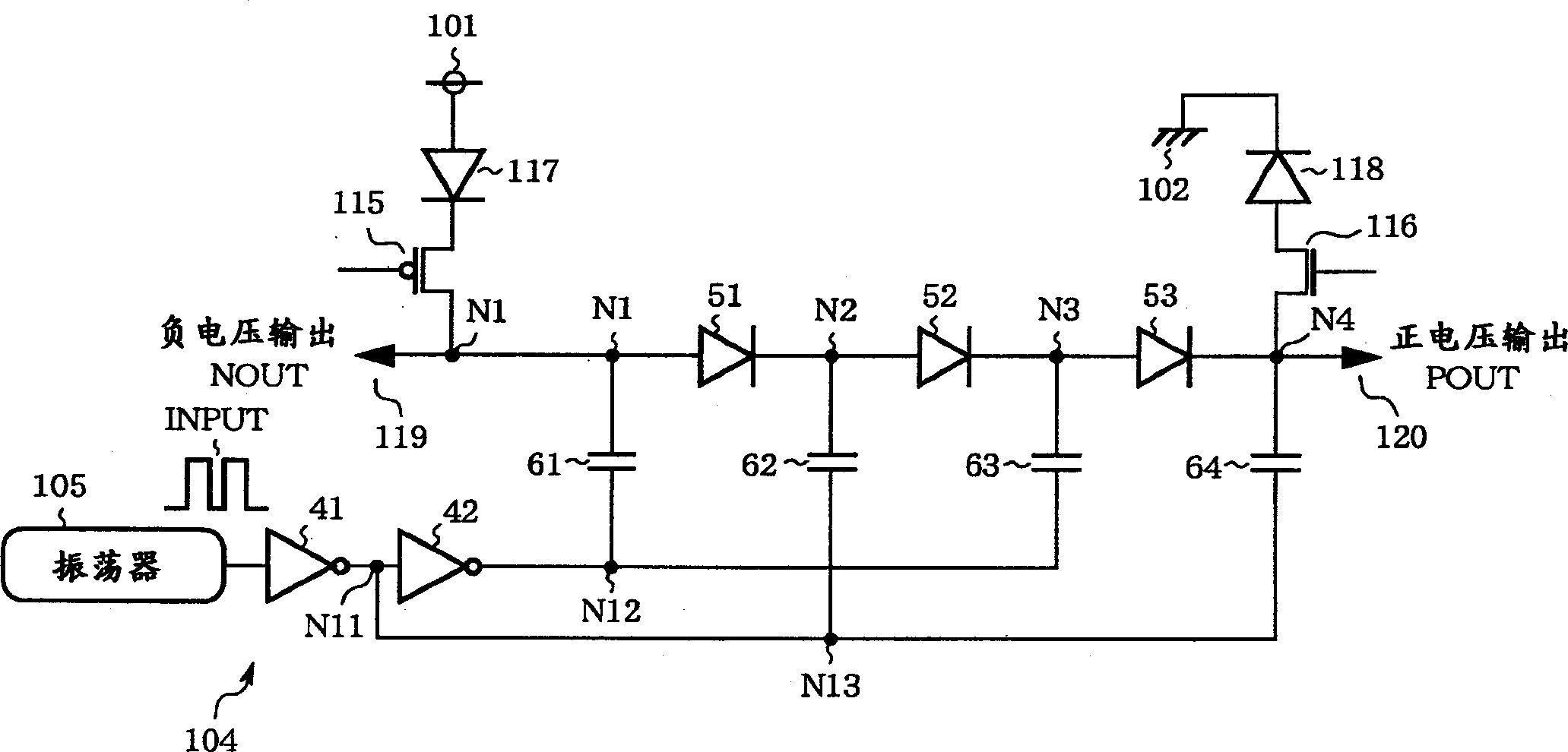
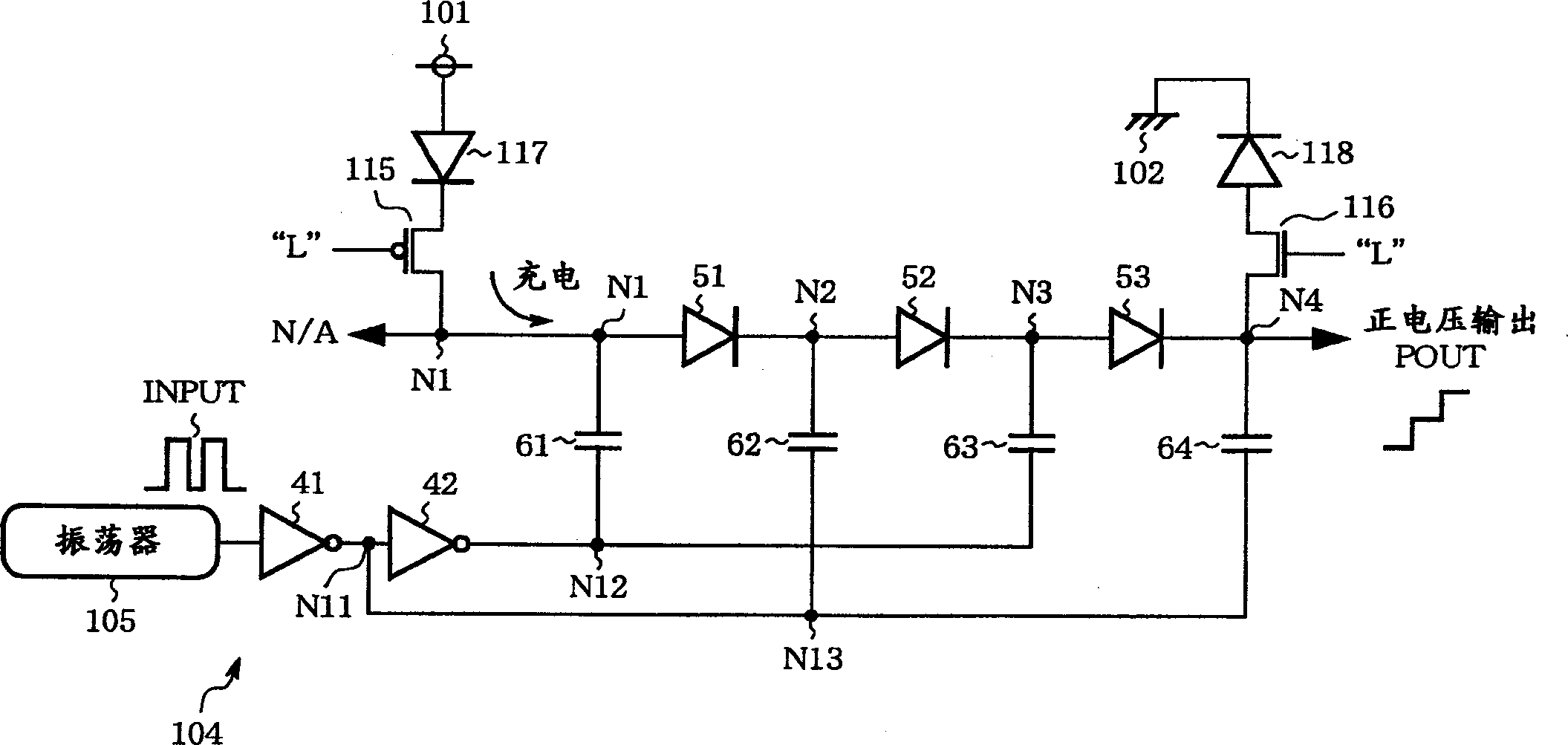
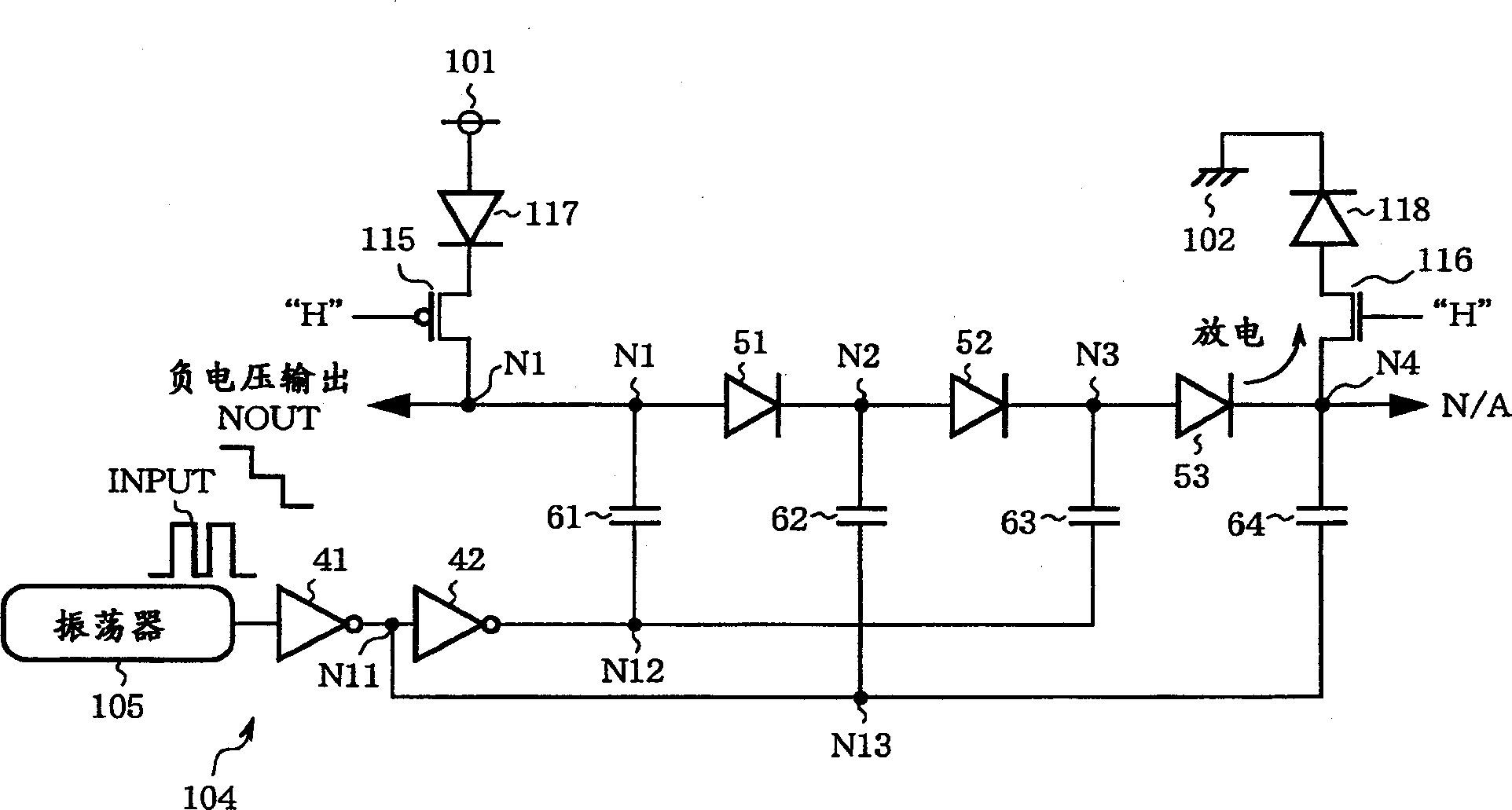
[0055] figure 1 It is a circuit diagram showing the structure of the charge pump circuit in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. In the figure, 41 and 42 are inverters, constituting the actuator 104, 51-53, 117, and 118 are diodes, 61-64 are capacitors, and 101 is a An external power supply supplying Vdd potential (first power supply potential), 102 is a ground wire supplying GND potential (second power supply potential), 105 is an oscillator, 115 is a PMOS transistor (P channel MOS transistor), and 116 is an NMOS transistor ( N-channel MOS transistor), N1-N4, N11-N13 are nodes. Diodes 51 to 53 are connected in series to form a voltage generating circuit (voltage generating unit). Nodes N1 and N4 serve as first and fourth internal nodes, respectively, connecting negative voltage output NOUT and positive voltage output POUT of the voltage generating circuit.
[0056] Here, the external power supply 101 is a power supply for the user to use the semiconductor integrated circu...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Figure 4 is a circuit diagram for illustrating problems to be considered in Embodiment 2 of the present invention, using Figure 1 ~ Figure 3 The charge pump circuit of the above-mentioned embodiment 1 is shown. in addition, Figure 5 and Image 6 These are a schematic sectional view of the first backflow prevention circuit on the external power supply 101 side and a schematic sectional view of the second backflow prevention circuit on the ground 102 side, respectively.
[0068] In the figure, 21 is an N well, 31 is a P well, 23 and 33 are gates, 22a and 22b are P+ diffusion layers, 32a and 32b are N+ diffusion layers, and other structures are the same as those in Embodiment 1 above, so the repeated illustrate. For convenience of description, DVth represents the thresholds of the diodes 117 and 118, and Vth represents the thresholds of the PN junctions between the P+ diffusion layer and the N well and between the N+ diffusion layer and the P well.
[0069]In the s...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Figure 8 is a schematic diagram for explaining problems to be considered in Embodiment 3 of the present invention, Figure 9 It is a circuit diagram showing the configuration of the charge pump circuit of the third embodiment. In the figure, Q0 is the charge amount (several pF) supplied each time, Q1 is the charge amount of the load capacitor (several pF), ΔQ is the remaining charge amount, and SW1, SW2, and SW3 are switches (the first to third switching units ), N21 is a node, 125 is a minimum unit, and other structures are the same as in the above-mentioned embodiment 1, so the repeated description thereof is omitted.
[0078] Usually, a capacitor and a diode of a charge pump circuit are the smallest unit 125, and a high voltage is generated by connecting a plurality of them in series. The larger the number of connections, the higher the voltage can be generated, and the larger the supply current can be. However, the required voltages may be different between the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com