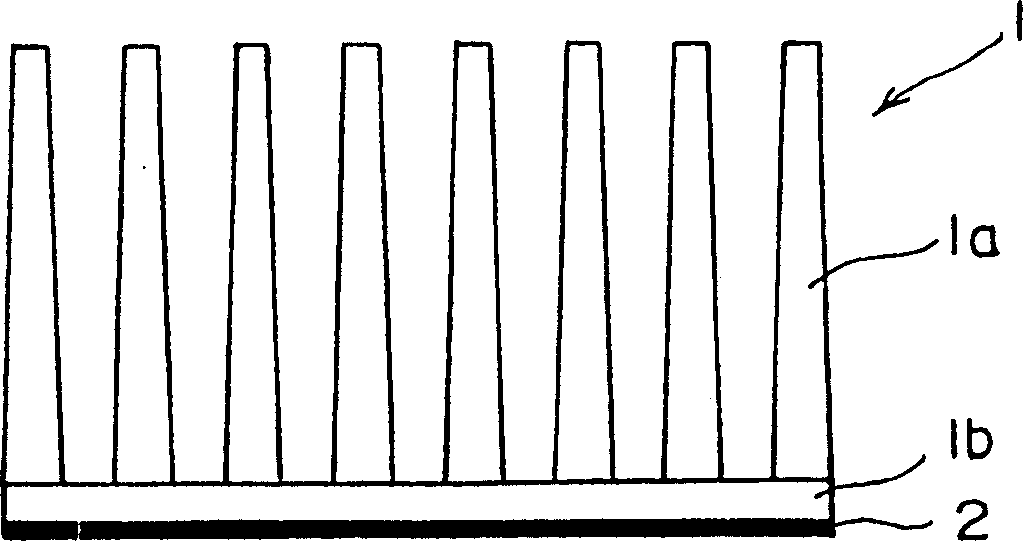
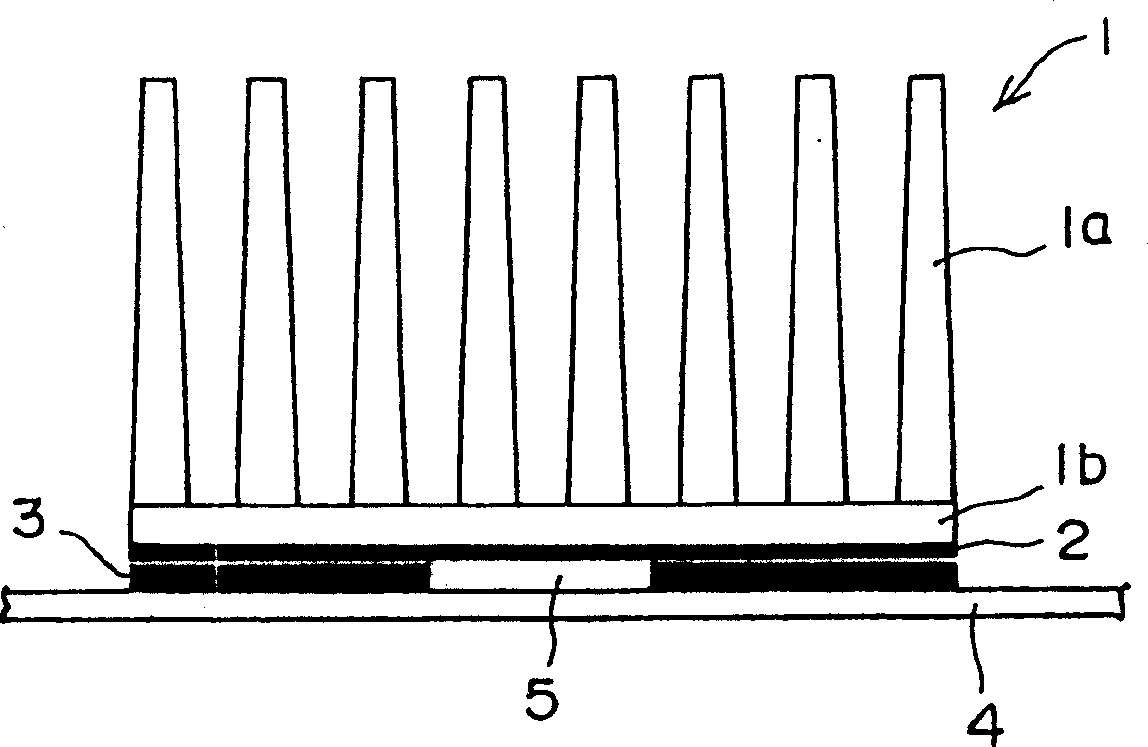
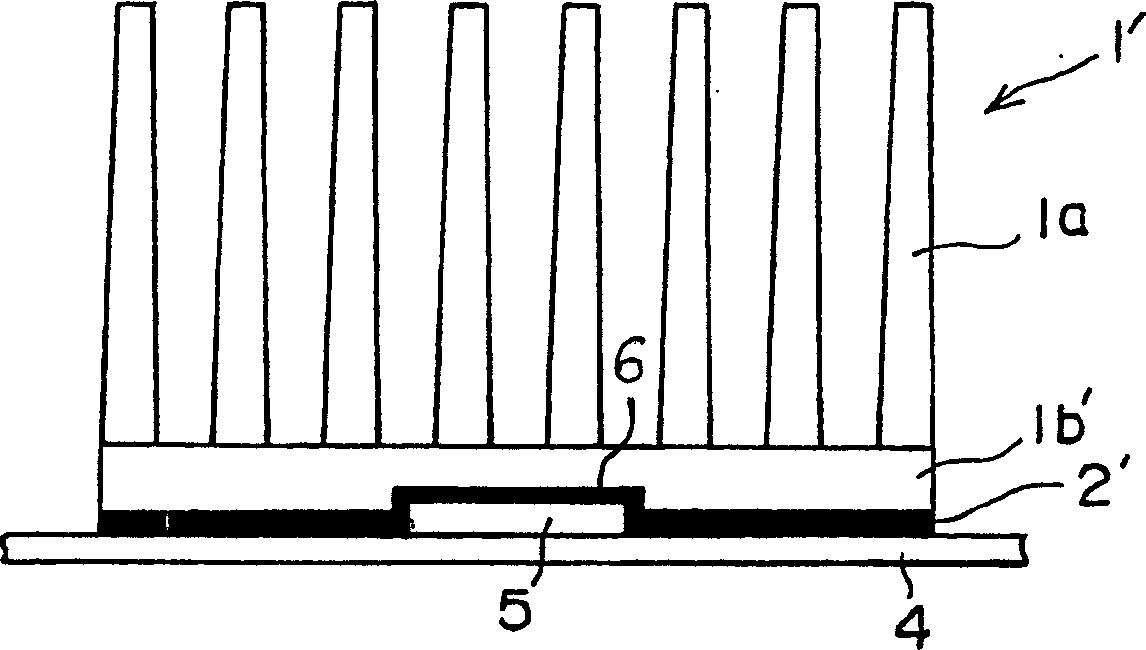
Radiator capable of notable controlling high frequency current passing through electronic element
A technology of electronic components and high-frequency current, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, electric solid devices, circuits, etc., and can solve problems such as insufficient consideration of high-frequency current prevention measures and difficulties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0058] use Figure 6A The sputtering device shown in Table 1 was used to produce thin films of M-X-Y magnetic composites on glass plates according to the sputtering conditions in Table 1.
[0059] Vacuum before sputtering
-6 torr
Ar gas
RF
target plating
Fe (diameter 100mm) and Al 2 o 3
Chip (120 pieces) (chip size: 5mm
×5mm×2mm)
[0060] The prepared thin film sample 1 was analyzed by means of a fluorescent X-ray spectrometer, and was confirmed to be a synthetic Fe 72 Al 11 o 17 film. Film sample 1 with a thickness of 2.0 micrometers (μm), a DC specific resistance of 530 microohm centimeters (μΩcm), an anisotropic magnetic field (Hk) of 18 Oersteds (Oe), and a saturation magnetization (Ms) of 16,800 Gauss .
[0061] The percentage {Ms(M-X-Y) / Ms(M)}×100 of the saturation magnetization of the thin film sample 1 to the metallic magnetic material M itself is 72.2%.
[0062] I...
example 2
[0064] Similar to Example 1 except that 150 Al 2 o 3 Thin film sample 2 was formed on a glass plate under chip conditions.
[0065] The prepared thin film sample 2 was analyzed by means of a fluorescent X-ray spectrometer, and was confirmed to be a synthetic Fe 44 Al 22 o 34 film. Film sample 2 has a thickness of 1.2 micrometers (μm), a DC specific resistance of 2400 microohm centimeters (μΩcm), an anisotropic magnetic field (Hk) of 120 Oe, and a saturation magnetization (Ms) of 9600 Gauss. It should be noted that the specific resistance of film sample 2 is higher than that of film sample 1.
[0066] The percentage {Ms(M-X-Y) / Ms(M)}×100 of the saturation magnetization of the thin film sample 2 to the magnetization of the metal magnetic material M itself was 44.5%.
[0067] The μ”-f response characteristic of film sample 2 is also obtained in a similar way to sample 1, such as Figure 8 shown. It is to be noted that, similar to the case in film sample 1, this peak also ...
example 4
[0078] use Figure 6A According to the sputtering conditions in Table 2, a M-X-Y magnetic composite thin film was formed on a glass plate by a reactive sputtering method. N 2 The partial pressure ratio is 20%. The film was heat-treated at 300° C. for two hours under a vacuum and a magnetic field to obtain a film sample 4 .
[0079] Vacuum before sputtering
-6 Torr
Ar+N 2 the gas
RF
target plating
Fe (100mm diameter) and Al cores
Chips (150 pieces) (chip size: 5mm×
5mm×2mm)
[0080] The properties of Film Sample 4 are shown in Table 3.
[0081] membrane thickness
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com