Method for regulating and controlling polymer injection cell structure by utilizing 3D printing and product
A 3D printing and polymer technology, used in manufacturing auxiliary devices, processing data acquisition/processing, additive processing, etc., can solve problems such as deformation and failure of 3D printing parts, achieve good consistency, solve poor interface performance, Small product warpage effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
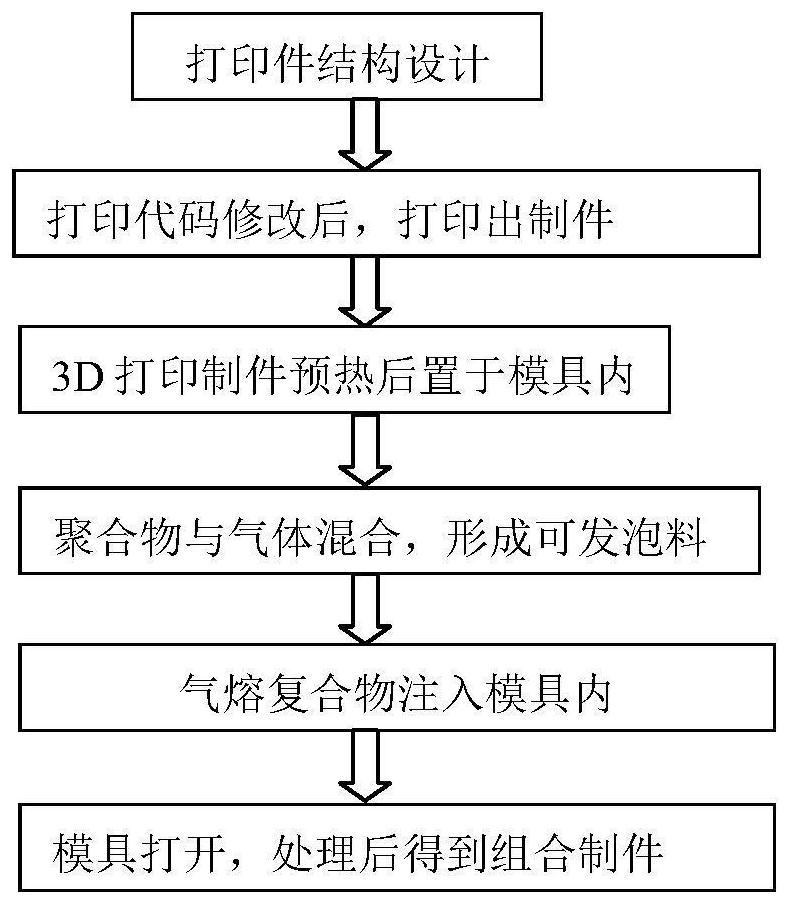
[0035] The cell structure control method described in this embodiment mainly involves a combined manufacturing technology of injection foam molding and 3D printing. In terms of equipment, an ordinary injection machine and 3D printer are required. The cavity shape of the mold used is the dog-bone shape used for standard tensile splines, and the raw and auxiliary materials used are all commercially available. The material used is thermoplastic resin: PP, its tensile strength is 27.5MPA, the heat deformation temperature is 100 degrees, and the melting point is 165 degrees. The FDM process used in 3D printing, the material selected is PLA, and the heat deformation temperature is 80 degrees. The tensile strength is 42.6MPA, and the foamed gas comes from the self-made foaming masterbatch. The process route diagram of the present invention is as follows figure 1 shown.
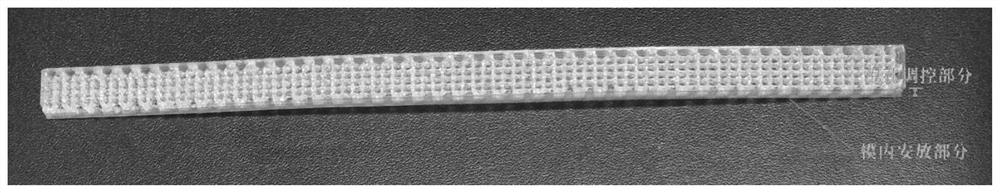
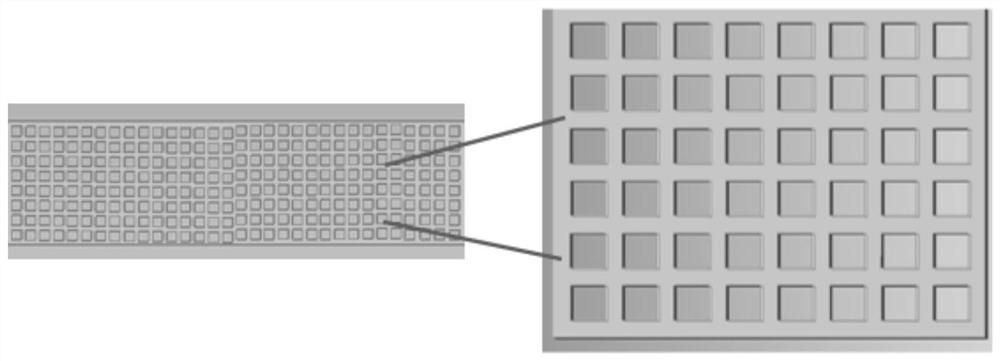
[0036] First, according to the shape of the mold cavity, the structure of the 3D printed part is designed, which...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Example 2 is similar to Example 1, except that supercritical carbon dioxide is introduced into the barrel of the injection machine, so that the foaming raw material used is a foamable raw material containing supercritical carbon dioxide. Similarly, an integrated composite product is obtained, the cross-sectional results of which are as follows Figure 8 , from which it can be seen that the cell distribution of the post-injection material after foaming is characterized by a vertical orientation along the direction of the 3D printed parts, which is closely combined with the 3D printed parts. The mechanical properties of the article were tested, and its tensile strength was 34.5MPA.
Embodiment 3
[0064] Embodiment 3 is similar to Embodiment 1, except that variable speed printing is not used in the printing process. Similarly, an integrated composite article is obtained. The mechanical properties of the article were tested, and its tensile strength was 32.8MPA.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com