Application of human platelet apoptosis microvesicles
A technology of microvesicles and platelets, applied in blood/immune system cells, medical science, animal cells, etc., can solve problems such as unsatisfactory results, avoid ethical issues and immune issues, rapid detection, and broad clinical application prospects Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
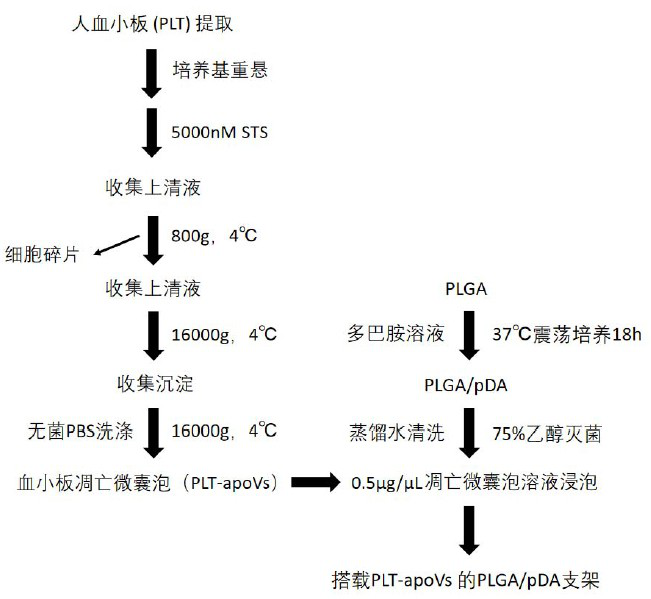
[0057] Example 1 Efficient extraction of apoVs derived from human platelets
[0058] Human platelets were isolated and purified in vitro, resuspended in culture medium, and 5000 nM STS was added to induce apoptosis. Platelet-derived apoVs were obtained by gradient centrifugation, and their concentration was detected by nanoparticle tracking analysis, and their protein content was detected by BCA method. Optimized extraction conditions and established a standard extraction process.
[0059] details as follows:
[0060] a) Centrifuge the supernatant of the cell culture liquid at 4° C. at 800 g for 10 min to remove cell debris in the supernatant of the culture liquid, and take the supernatant to obtain the first centrifugation supernatant;
[0061] b) centrifuging the first centrifugation supernatant at 4°C and 16000g for 30min, and taking the precipitate to obtain crude apoptotic microvesicles;
[0062] c) The crude apoptotic microvesicles were washed with sterile PBS, and the...
Embodiment 2
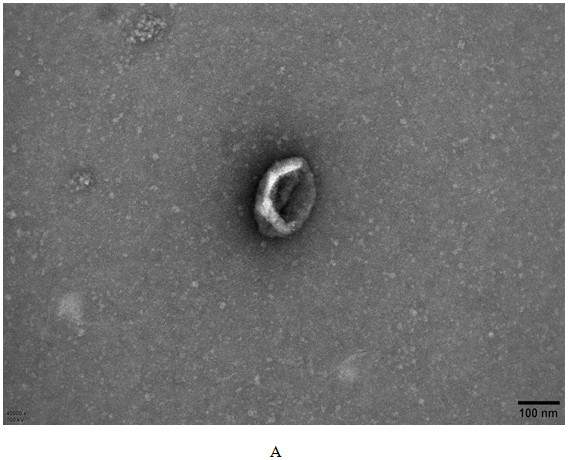
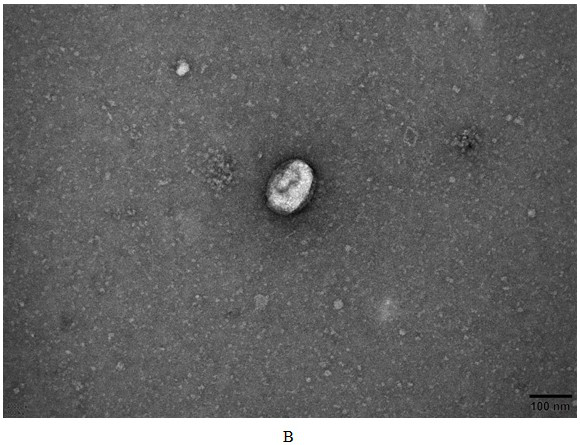
[0063] Example 2 Characteristic analysis of apoVs derived from human platelets
[0064] The morphology, particle size, and concentration of platelet-derived apoVs were detected by cryo-TEM and nanoparticle tracking analysis.
[0065] Cryo-TEM:
[0066] (1) Pipette 5 μl of apoptotic microvesicle suspension onto the copper grid, and let stand at room temperature for 1 min;
[0067] (2) Use filter paper to absorb excess liquid along the outside of the copper grid, absorb 5 μl of 2% uranyl acetate and drop it on the copper grid, and let it stand at room temperature for 30 seconds;
[0068] (3) Use filter paper to absorb excess liquid along the outside of the copper mesh, and let it dry at room temperature;
[0069] (4) Images were taken under a transmission electron microscope, and the voltage was set to 120kV.
[0070] Nanoparticle size tracking analysis detection:
[0071] (1) Use a nanoparticle tracking analyzer to record the trajectory of apoptotic microvesicles under Brow...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Example 3 In vitro experiments to detect the effect of human platelet-derived apoVs on the differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteogenesis in vitro
[0076] Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells were cultured under the following three culture conditions:
[0077] 1) Proliferation medium (PM): MEMα medium containing 10% FBS and 1% penicillin-streptomycin double antibody.
[0078] 2) Osteogenic induction (OM): Contains 10% FBS, 1% penicillin-streptomycin double antibody, 10mM β-sodium glycerophosphate (β-Sodium Glycerophosphate), 0.2mM L-ascorbic acid (Ascorbic Acid) and 100nM dexamethasone (dexamethasone) MEMα medium.
[0079] 3) Add 0.225 μg / mL human platelet-derived apoVs (OM+ 0.225 μg / mL PLT-apoVs) to the osteogenic induction medium.
[0080] After 10 days of osteogenic induction, the effect of osteogenic differentiation of cells was examined by alizarin red staining.
[0082] To prepare the dye solu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com