Microbial solid-state fermentation method for improving eating quality of brown rice and application of microbial solid-state fermentation method
A solid-state fermentation and microbial technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems affecting fermentation effects, achieve easy cooking, high moisture content, and improve cooking characteristics and sensory quality.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] The solid-state fermentation process of embodiment 1 brown rice
[0041] The method includes the following steps: activation and expansion of strains → brown rice cleaning and impurity removal → washing and soaking → high-pressure sterilization → inoculation → fermentation → regular material turning → drying → packaging and refrigeration.
[0042] Add the frozen lactic acid bacteria seed solution with an inoculum of 1% by volume to 100mL of MRS broth medium; add the frozen yeast seed solution with an inoculum of 1% by volume to In 100 mL of YPD medium; add the frozen Rhizopus oryzae seed solution to 1% inoculum volume in 100 mL of potato dextrose broth medium PDB. Then place the three kinds of bacterial suspensions in a shaker at 28-37°C and 150r / min for 10-30 hours; then take 1 mL from the bacterial suspensions and add them to 100 mL of the corresponding culture medium for the second-generation culture , cultivated for 10-12 hours. Finally, the bacterial solution in ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The mensuration of embodiment 2 immersing water absorption rate
[0047] Take 3.0g of brown rice and 30.0mL of distilled water and place them in a centrifuge tube. After soaking at room temperature for a certain period of time, drain the water on the surface of the brown rice and measure its quality. The formula for calculating the soaking water absorption rate is as follows.
[0048]
[0049] In the formula, W 1 is the weight of brown rice before soaking, g; W 2 is the weight of brown rice after soaking, g.
[0050] Effects of solid-state fermentation of different microorganisms on soaking water absorption of brown rice as follows: figure 1 shown. After soaking for 0-0.5h, the soaking water absorption rate of brown rice increased rapidly. After soaking for 1 hour, the soaking water absorption rate of different solid-state fermented brown rice slowed down and even stabilized, while the soaking water absorption rate of unfermented brown rice still increased gradu...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The mensuration of embodiment 3pH
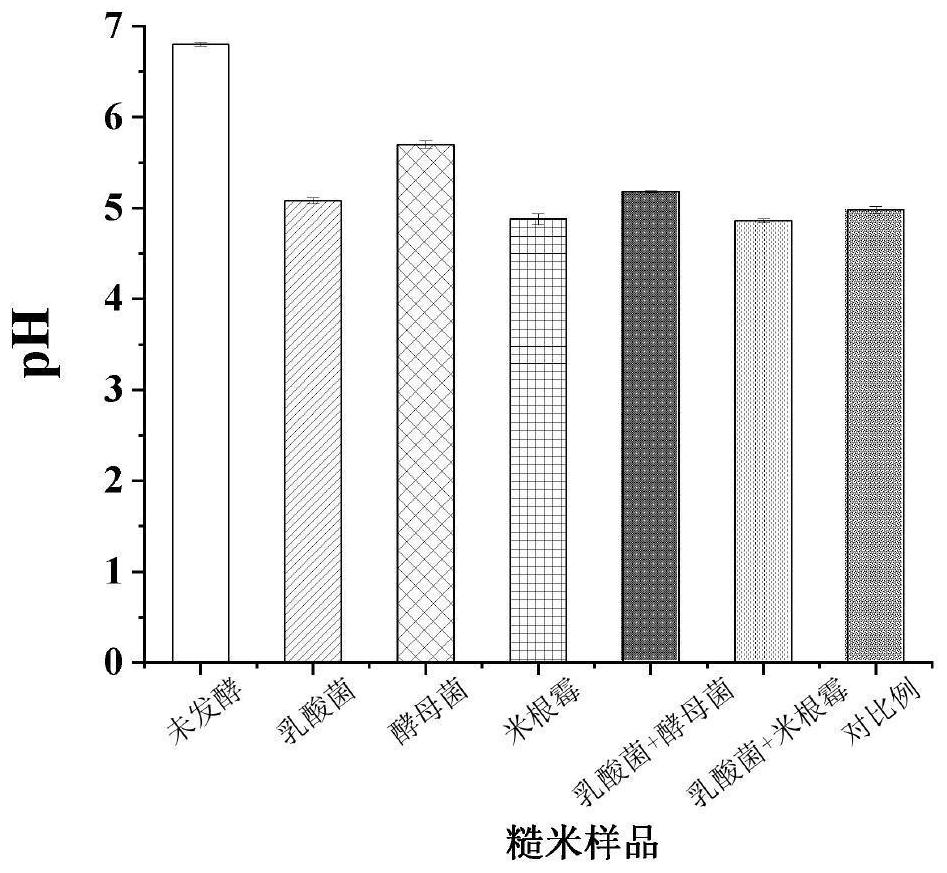
[0053] Weigh 10.0 g of brown rice and 20 mL of boiling water and mix thoroughly for 1 h. After the mixture is cooled, centrifuge at 3000 r / min for 20 min, and measure the pH of the supernatant.
[0054] Effects of solid-state fermentation of different microorganisms on the pH of brown rice such as figure 2 shown. The pH of unfermented brown rice is 6.80, while the pH of lactic acid bacteria, saccharomyces, rhizopus oryzae, lactic acid bacteria + yeast, lactic acid bacteria + rhizopus oryzae, and the fermented brown rice of the comparative example are 5.08, 5.70, 4.88, 5.18, 4.86, 4.98, respectively. During the fermentation process, yeast can produce lactic acid; lactic acid bacteria mainly produce lactic acid, and also produce organic acids such as acetic acid and propionic acid. The accumulation of organic acids reduces the pH of the system. During the metabolic process, Rhizopus oryzae can produce organic acids such as lactic aci...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Enthalpy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com