Molecularly imprinted polymer for targeted degradation of emerging pollutants based on advanced oxidation system as well as preparation method and application of molecularly imprinted polymer
A technology of molecular imprinting and advanced oxidation, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, water treatment of special compounds, oxidized water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of low degradation efficiency of emerging pollutants, unstable effect of activated materials, and large influence of pH value, etc. problems, to achieve broad practical application prospects, short catalytic time, and good durability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] A method for preparing a functionalized molecularly imprinted polymer MIP-AA material applied to emerging pollutants of sulfonamides, the specific operation steps are as follows:
[0045] (1) Add 40mL of acetonitrile, 1mmoLSMX and 4mmol of acrylic acid (AA) to a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask in sequence, stir evenly and let stand for 12h for pre-assembly, then add 0.3gNH 2 - MIL-53 (Fe), 6 mmoL divinylbenzene (DVB) and 0.065 g azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN). At the same time, nitrogen was passed through for 15 minutes to remove oxygen, and then sealed and placed in a water bath at 65° C. for 12 hours. Finally, the reacted mixture was centrifuged, washed, and dried in a vacuum oven at 80° C. for 12 hours to obtain a black powder, which was a molecularly imprinted polymer, marked as MIP-AA.
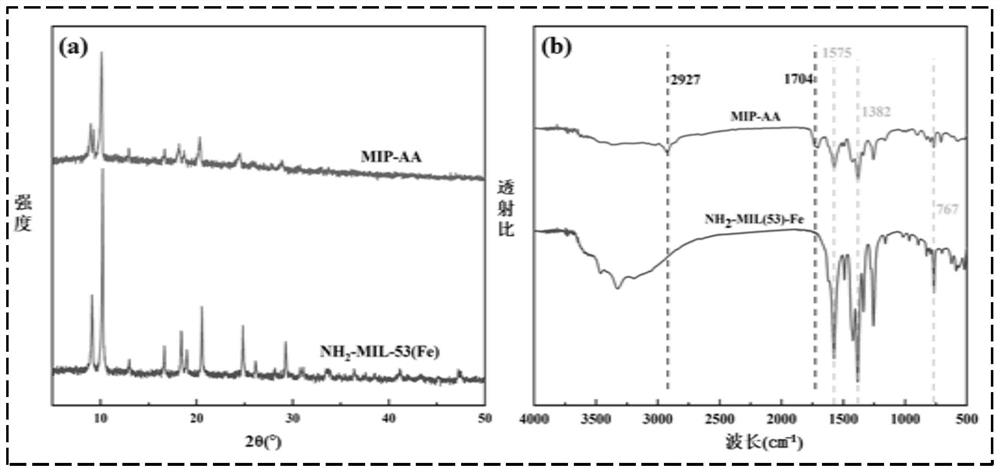
[0046] figure 1 NH prepared for Example 1 2 -X-ray crystallography (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared absorption spectrum (FTIR) of MIL-53(Fe) and MIP-AA;
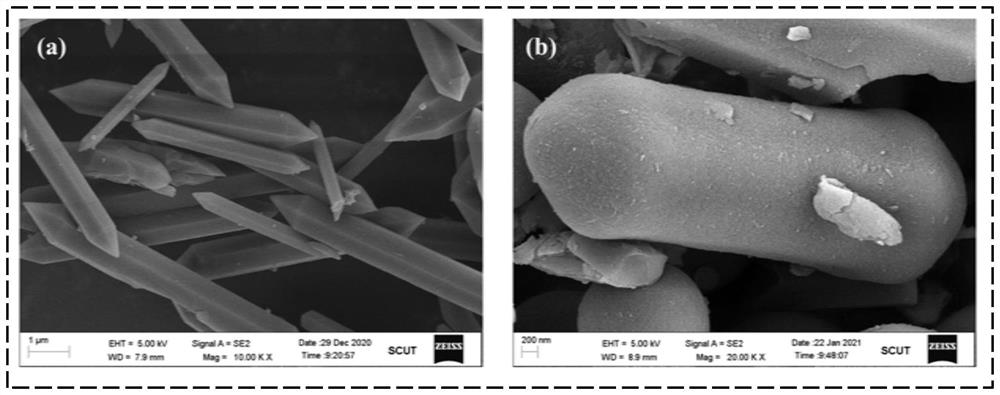
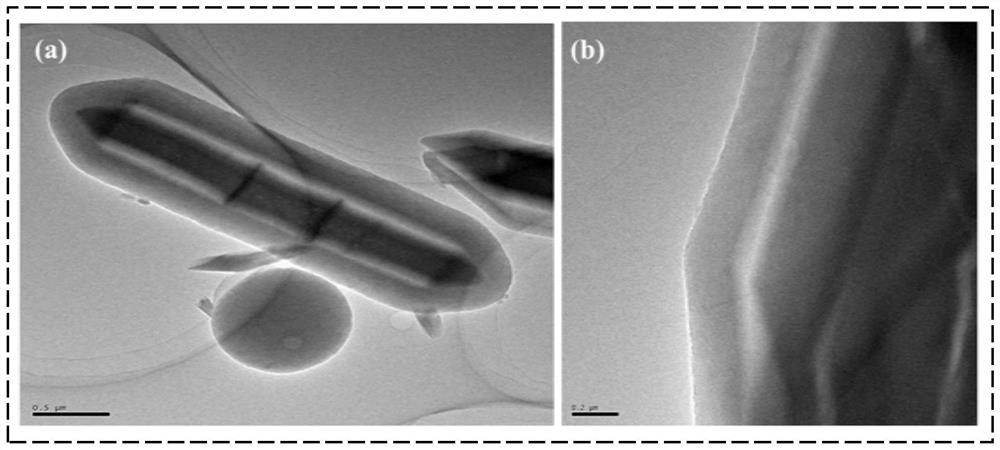
[0047] figure 2 NH prepar...
Embodiment 2
[0059] This example compares NH 2 -MIL-53(Fe) and NH 2 - MIP-AA synthesized with MIL-53(Fe) as the substrate catalyzes the difference in the degradation effect of oxidant PS in degrading SMX.
[0060] (1) The preparation method of MIP-AA is the same as step (1) in Example 1;
[0061] (2) Using the MIP-AA prepared in Example 1 as a catalyst, Na 2 S 2 o 8 As the oxidant, four groups of SMX simulated organic wastewater with initial SMX concentration of 0.04mmol / L were prepared. The pH of the waste water is not adjusted, and the conical flask is used as the reactor, and four treatment groups are set up, which are: (1) only 0.6g / L NH 2 -MIL-53(Fe); (2) Add only 0.6g / L of MIP-AA; (3) Add 8mmol / L of Na 2 S 2 o 8 and 0.6g / L NH 2 -MIL-53(Fe); (4) Add 8mmol / L of Na 2 S 2 o 8 and 0.6g / L of MIP-AA. Add the above four groups of reaction solutions to the Erlenmeyer flask in turn, stir at room temperature to make the reaction uniform, place the Erlenmeyer flask in a shaker at 18...
Embodiment 3
[0066] This embodiment compares the influence of different molar ratios of oxidant and SMX (oxidant: SMX=50, 150, 200, 250, 300) on the targeted degradation reaction of MIP-AA.
[0067] (1) The preparation method of MIP-AA is the same as step (1) in Example 1;
[0068] (2) Using the MIP-AA prepared in Example 1 as a catalyst, Na 2 S 2 o 8 、H 2 o 2 As an oxidant, five groups of SMX simulated organic wastewater with an initial SMX concentration of 0.04mmol / L were prepared. The pH of the waste water is not adjusted, the conical flask is used as the reactor, and five treatment groups are set up for the reaction, which are: (1) adding 2mmol / L oxidant; (2) adding 6mmol / L oxidant; (3) adding 8mmol / L (4) add oxidant of 10mmol / L; (5) add oxidant of 12mmol / L. Add the above five groups of reaction solutions and 0.6g / L MIP-AA to the Erlenmeyer flask in turn, stir at room temperature to make the reaction uniform, place the Erlenmeyer flask on a shaker at 180rpm, and proceed at room t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com