Method for constructing mammalian esophageal squamous epithelial immortalized cell line, constructed cell line and organoid thereof
A technology of immortalized cell lines and construction methods, which is applied in the field of construction of esophageal organoids and esophageal squamous epithelial immortalized cell lines, which can solve problems such as unfavorable research, cell cycle, and genome stability defects of apoptosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
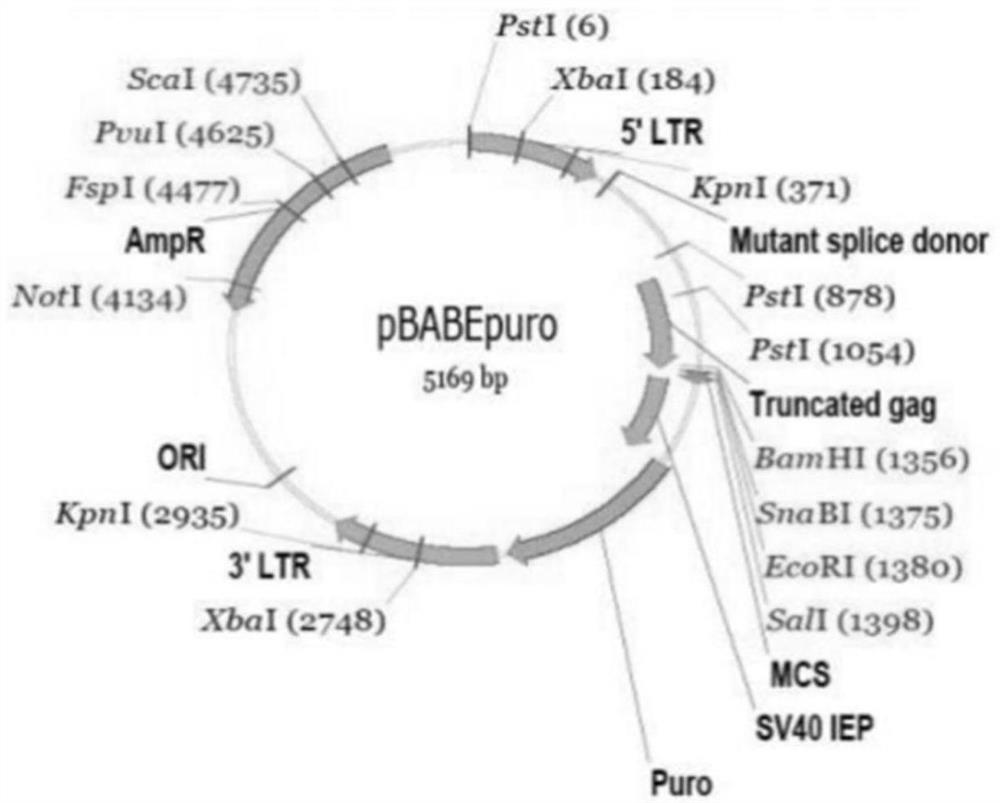
[0051] Example 1 Establishment of Esophageal Squamous Epithelial Immortalized Cell Line
[0052] 1. Preparation of primary rat squamous epithelial cells
[0053] Anesthetize the rats with 10% chloral hydrate anesthesia at a dose of 0.3ml / 100g intraperitoneally, perform routine surgical disinfection, and prepare instruments; remove the esophagus after sacrificing the rats, rinse in PBS to remove blood stains, and then remove the esophagus along the long axis of the esophagus. The esophagus was cut open; the esophageal muscular layer and esophageal mucosa were torn apart with forceps, and the esophageal epithelial tissue was preserved; in the ultra-clean workbench, the esophageal epithelial tissue was rinsed with sterile PBS, and then transferred to a medium containing 5× double antibody (final concentration 500U / mL penicillin, 500μg / mL streptomycin) in DMEM medium for 10min, and then washed with sterile PBS; put the esophageal epithelial tissue in a petri dish, add 3ml 2.4U / ml ...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Example 2 Characteristics of Immortalized Esophageal Squamous Cell Line
[0068] 1. Cell morphology and origin
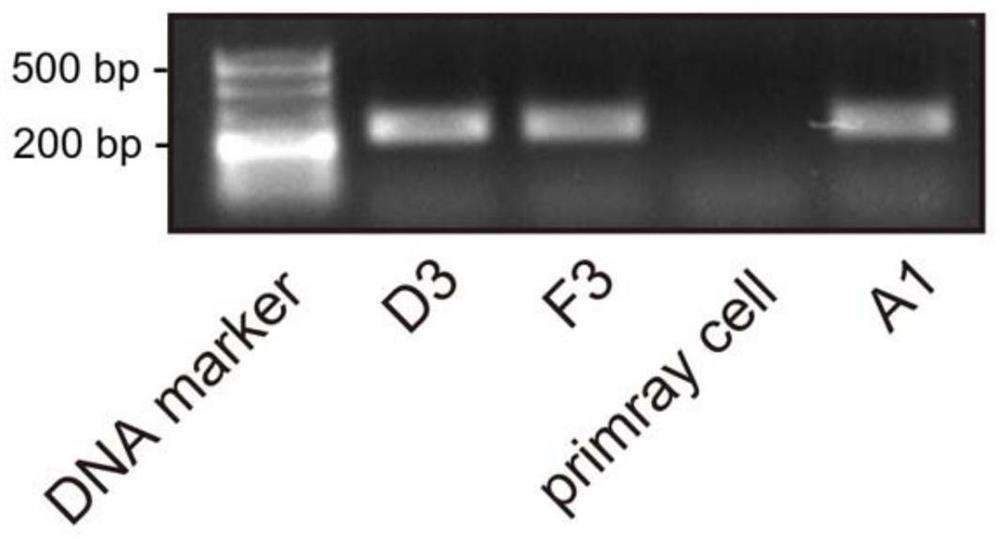
[0069] D3, F3 and A1 single-cell clones were further cultured to establish "normal" immortalized rat esophageal epithelial cell lines, and the cell lines formed by D3, F3 and A1 were observed with an optical microscope. The experimental results are as follows: Figure 4 Shown; karyotype analysis as Figure 5 Shown; Immunofluorescent staining results of the suprabasal layer marker CK13 and the basal layer marker CK14 are shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7 as shown, Figure 6 The results of immunofluorescence staining of CK13 and CK14 in normal esophageal tissue, Figure 7 It is the results of immunofluorescence staining of CK13 and CK14 in D3, F3 and A1 cells. From Figure 4 It can be seen that the D3, F3 and A1 cell lines are all typical polygonal stone step-shaped squamous cells, which are the same shape as normal esophageal squamous epithelial cells.
...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Example 3 Organoids
[0089] D3, F3, and A1 cells can all be cultured into organoids, and D3 cells are taken as an example for illustration.
[0090] D3 cells were digested by TrypLE into a single cell suspension, and every 5000 cells were mixed with 55ul Matrigel to form a suspension and added to a 24-well culture plate, and the organoid medium was added after solidification. The fresh organoid medium was replaced every two days, and cultured for 12-15 days, during which the growth of the spheroids was recorded. After the organoid matures, discard the organoid medium, add 500 μl of pre-cooled cell recovery solution, incubate on ice for 45 min~1 h, centrifuge at 1000 g for 5 min, and discard the supernatant. Then add PBS to wash once, discard the PBS washing solution by centrifugation, and add 4% paraformaldehyde solution to fix at room temperature for 1 h. Afterwards, the supernatant was discarded by centrifugation, followed by adding 20% sucrose solution for dehyd...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com