Method for improving low-temperature toughness of medium carbon steel rail welding joint
A technology of welded joints and low temperature toughness, applied in the field of railway rail manufacturing, can solve problems such as brittle fracture, and achieve the effect of improving hardness and toughness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
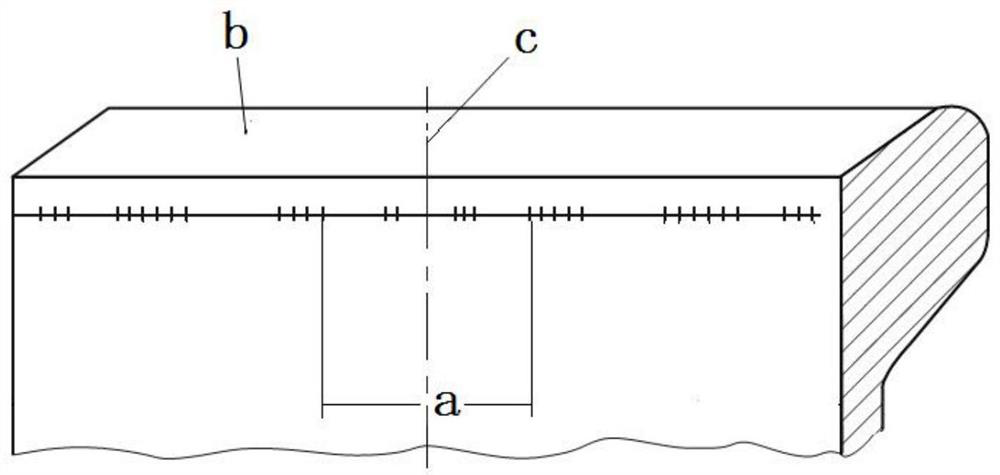
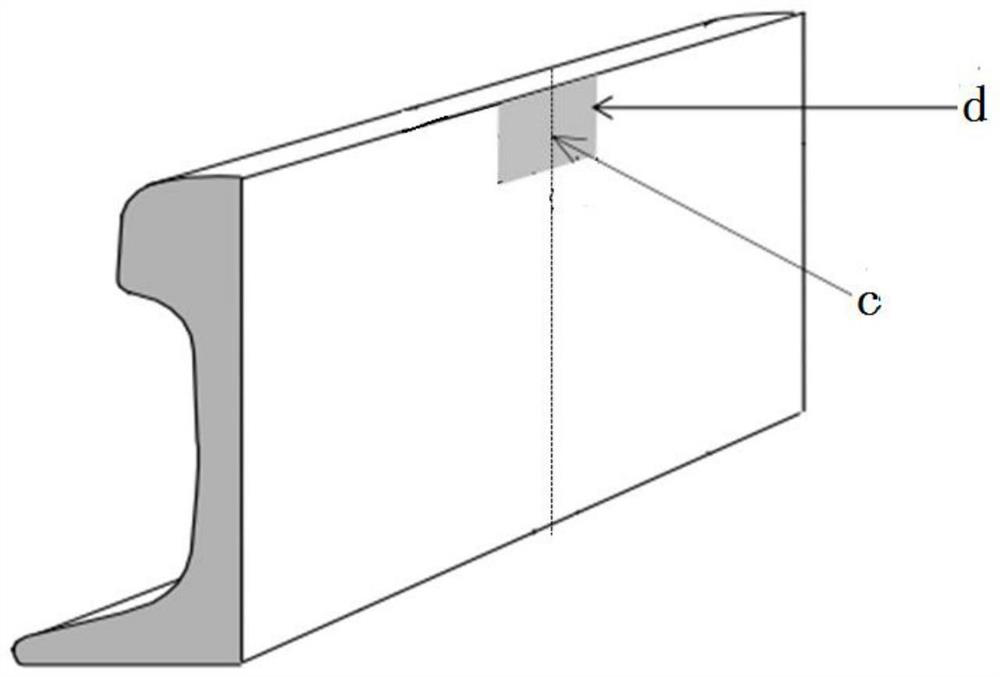
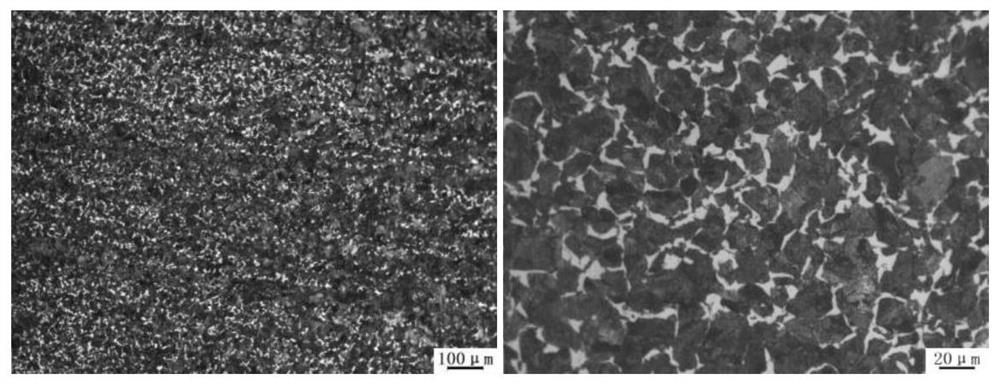
[0037] The microstructure of the rail base metal is controlled to be 80% pearlite and 20% proeutectoid ferrite. The tensile strength of the rail parent material at room temperature (20-25°C) is 1080MPa, the elongation is 17%, and the U-shaped impact energy is 35J. Under the condition of -20℃, the U-shaped impact energy of the base metal of the rail is 29J. The chemical composition of the rail steel to obtain this microstructure needs to meet the following conditions: 0.50% content of C, 0.30% content of Si, 0.70% content of Mn, 0.1% content of Cr, 0.04% content of V, and the balance is Fe and unavoidable impurities. The heat treatment process of rail steel to obtain this microstructure needs to meet the following conditions: after the billet is heated and rolled into a rail with a single weight of 60kg / m, it is left to stand and cooled in the air. When the temperature at the center of the top surface of the rail head drops to 790°C Spray cooling medium to the top surface of ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The microstructure of the control rail base metal is 88% pearlite and 12% proeutectoid ferrite. The tensile strength of the rail parent material at room temperature (20-25°C) is 1080MPa, the elongation is 17%, and the U-shaped impact energy is 32J. Under the condition of -20°C, the U-shaped impact energy of the base metal of the rail is 27J. The chemical composition of the rail steel to obtain this microstructure needs to meet the following conditions: 0.58% content of C, 0.45% content of Si, 0.90% content of Mn, 0.3% content of Cr, 0.045% content of V, and the balance is Fe and unavoidable impurities. The heat treatment process of rail steel to obtain this microstructure needs to meet the following conditions: after the steel billet is heated and rolled into a rail with a single weight of 60kg / m, it is left standing and cooled in the air. When the temperature at the center of the top surface of the rail head drops to 840°C Spray cooling medium to the top surface of t...
Embodiment 3
[0047] The microstructure of the rail base metal is controlled to be 90% pearlite and 10% proeutectoid ferrite. The tensile strength of the rail base material at room temperature (20-25°C) is 1100MPa, the elongation is 16%, and the U-shaped impact energy is 32J; at -20°C, the U-shaped impact energy of the rail base material is 28J. The chemical composition of the rail steel to obtain this microstructure needs to meet the following conditions: 0.58% content of C, 0.50% content of Si, 0.92% content of Mn, 0.35% content of Cr, 0.05% content of V, and the balance is Fe and unavoidable impurities. The heat treatment process of the rail steel to obtain this microstructure needs to meet the following conditions: the billet is heated and rolled into a rail with a single weight of 60kg / m, and then cooled in the air. When the temperature at the center of the top surface of the rail head drops to 800°C Spray a cooling medium with a cooling rate of 5.0°C / s to the top surface of the rail ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Impact energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com