Staphylococcus aureus phage and bacteriostatic application thereof
A staphylococcus, golden yellow technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of narrow host spectrum, poor temperature and pH stability, etc., and achieve the effect of good pH stability, good temperature stability and high potency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1 Isolation, preparation and purification of phage
[0046] 1.1. Source of the strain
[0047] The host bacteria came from Staphylococcus aureus (107) isolated from milk samples submitted for mastitis in dairy cows in Shandong Province;
[0048] 1.2. Sewage source:
[0049] Staphylococcus aureus was detected in a mixed sample of fecal sewage and milking pond sewage around a dairy farm in Qufu;
[0050] 1.3. Main reagents:
[0051] LB broth, LB semi-solid medium, LB solid medium, SM buffer solution;
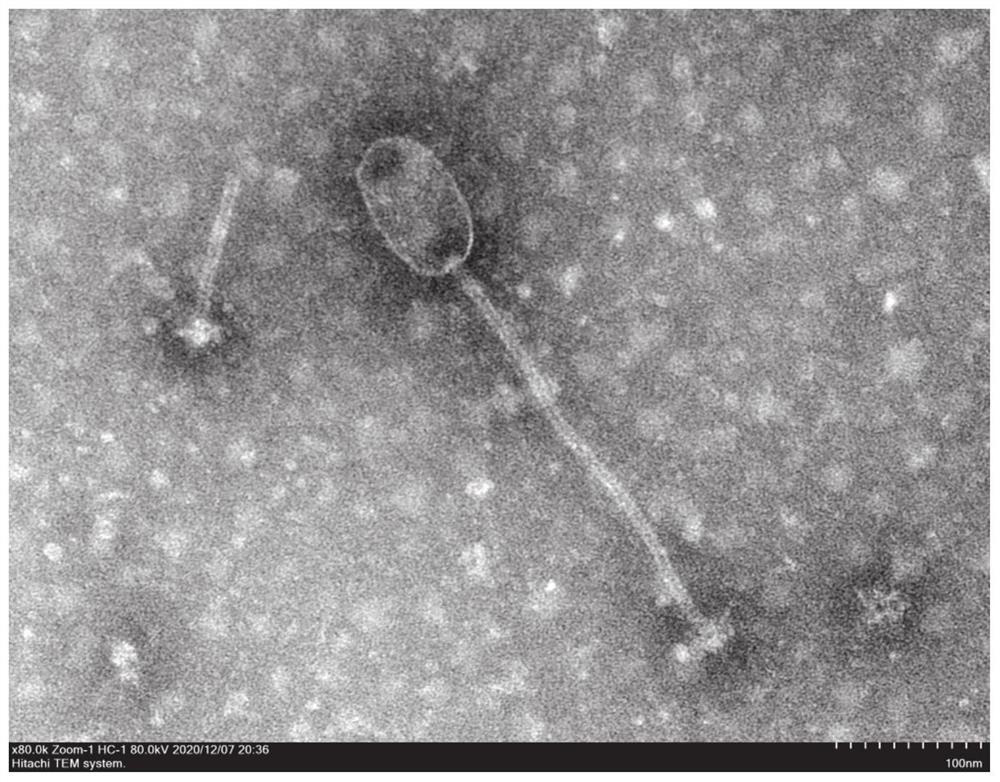
[0052] Main instruments: biological safety cabinet, electric heating incubator, constant temperature shaker, low temperature high-speed centrifuge, JEM-2100Plus transmission electron microscope, dynamic microplate reader.
[0053] 2. Method
[0054] 2.1. Enrichment of phage
[0055] The collected mixed sewage was centrifuged at 12000rpm for 15min to remove impurities, and the supernatant was drawn with a syringe. If the collected sewage contains a large amoun...
Embodiment 2
[0070] 2.7. Determination of phage titer
[0071] The purified phages were serially diluted 10 times, and 100 μl of each gradient concentration was taken, and the double-layer plate was coated according to the method in 2.2, and the appropriate concentration gradient plate was selected to calculate the number of phage plaques. Each concentration gradient was repeated three times, and the average value was finally calculated to calculate the phage titer.
[0072] Phage titer (PFU / mL) = average number of plaques × dilution factor × 10
[0073] The purified phages were serially diluted 10 times, and the number of plaques in each concentration gradient was calculated by the double-layer plate method. After multiple parallel experiments, the titer of s107 phage was 2.31×10 10 PFU / mL.
Embodiment 3
[0075] 2.8. Lysis ability of bacteriophage
[0076] The microplate phage virulence test was used to evaluate the lytic activity of phage on the host, that is, the lytic ability. Cultivate the host bacteria to the logarithmic growth phase (approximately 1×10 8 CFU / mL), dilute with broth, so that the final concentration of inoculated bacteria is 1×10 6 CFU / mL. The phage liquid was serially diluted 10 times, and each dilution concentration was co-inoculated with 100 μl of the host bacteria into a 96-microwell plate, and the multiplicity of infection was 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100, and 1000. Culture in air at 37°C 6-10h. Visually inspect the turbidity of the microwells and measure the absorbance at OD600, and record the highest dilution that completely dissolves the bacteria.
[0077] The MOI calculation method of phage-host experiment: the number of phage per well / the number of bacteria per well. Phage sensitivity is divided into: very sensitive (10 -6 ≤MOI-2 ); highly su...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com