Preparation method of Nicodil
A nicorandil and molar ratio technology, applied in the field of preparation of nicorandil, can solve the problems of large consumption of reagents, low production efficiency, many reaction steps, etc., and achieve the effects of good product quality, low cost and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
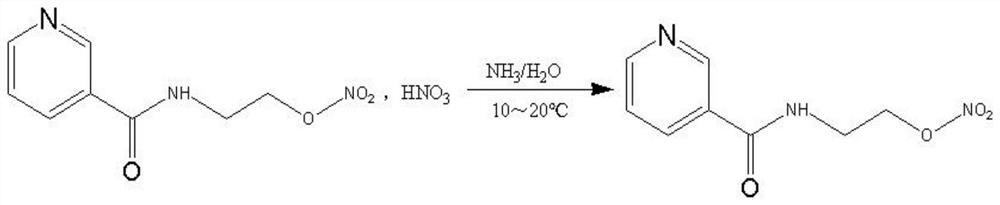
[0040] For ease of understanding, see Figure 1~2 , a preparation method of nicorandil, comprising the following steps:
[0041] Step (1): Add nicotinamide, ethanolamine and catalyst into the reaction kettle, heat to 120-180°C, preferably to 150-160°C, stir for 4-10 hours, and the molar ratio of ethanolamine to nicotinamide is 1.0-2.0 : 1, preferably the molar ratio of ethanolamine to nicotinamide is 1.4-1.6. Catalysts include boric acid, borate salts or borate esters, preferably boric acid, to make the reaction milder. The molar ratio of catalyst to nicotinamide is 0.01-0.3:1. The specific chemical reaction formula is as follows:
[0042]
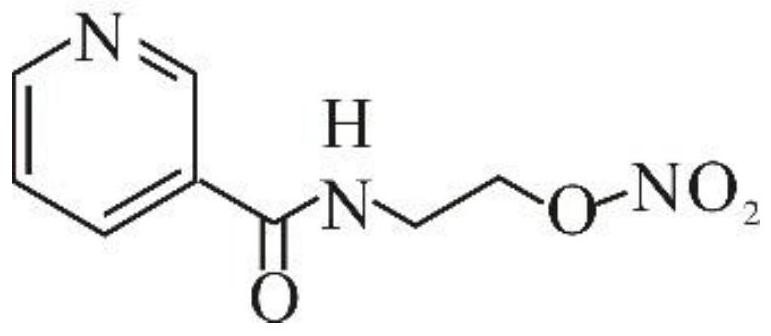
[0043] After the reaction is over, distill under reduced pressure at 120-180°C, and control the vacuum degree ≤ -0.08Mpa until no obvious liquid is distilled out, then stop the distillation; cool the concentrate to 60-80°C, add glacial acetic acid to dissolve under stirring, and cool to room temperature. The obtained N-(2-hydroxyethyl...
Embodiment 1
[0051] One embodiment of the preparation method of a kind of nicorandil provided by the invention, comprises the following steps:
[0052] Step (1): Take 122g of nicotinamide, the catalyst boric acid and ethanolamine, and add them to the reaction kettle respectively. The molar ratio of boric acid and nicotinamide is 0.1:1, and the molar ratio of ethanolamine and nicotinamide is 1.6:1. The temperature was 140°C, and the reaction was stirred for 10h. After the reaction, carry out vacuum distillation to remove excess ethanolamine, the temperature is 140°C, turn on the vacuum, control the vacuum degree ≤ -0.08Mpa, and stop the distillation when almost no liquid flows out again. The product distilled under reduced pressure was cooled to 60°C, 122 g of glacial acetic acid was added with stirring to dissolve, and cooled to room temperature to obtain N-(2-hydroxyethyl)nicotinamide solution. The N-(2-hydroxyethyl)nicotinamide content in the N-(2-hydroxyethyl)nicotinamide solution was ...
Embodiment 2
[0058] The present embodiment provides a kind of preparation method of nicorandil, comprises the following steps:
[0059] Step (1): Take 122g of nicotinamide, the catalyst boric acid and ethanolamine, and add them to the reaction kettle respectively. The molar ratio of boric acid and nicotinamide is 0.1:1, and the molar ratio of ethanolamine and nicotinamide is 1.6:1. At 155°C, the reaction was stirred for 8h. After the reaction is over, excess ethanolamine is distilled off under reduced pressure. The temperature is 155° C., the vacuum is turned on, and the vacuum degree is controlled to be ≤ -0.08 Mpa. When almost no liquid flows out again, the distillation is stopped. The concentrated product distilled under reduced pressure was cooled to 65°C, 122 g of glacial acetic acid was added under stirring to dissolve, and cooled to room temperature to obtain N-(2-hydroxyethyl)nicotinamide solution. The N-(2-hydroxyethyl)nicotinamide content in the N-(2-hydroxyethyl)nicotinamide so...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com