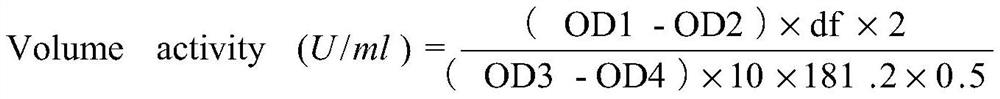Protease K heat-resistant mutant
A protease and mutant technology, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering, can solve the problems of poor stability and high cost of cross-border low-temperature long-distance transportation, and achieve good thermal stability, stability and specific activity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0164] Embodiment 1: Determination of protease mutation site
[0165] According to the three-dimensional crystal structure of proteinase K, the 350th amino acid in the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2 was determined as the key site through rational design. Specifically, a single-point mutant of proteinase K was designed through the structure-assisted Consensus Concept method, and a proteinase K mutant with significantly improved thermal stability was obtained. Consensus Concept is an emerging theoretical system for improving protein thermal stability in rational protein design. Different from rational design based on information such as precise protein structure-function relationship and catalytic mechanism, this method is based on the sequence information of homologous proteins, and explores factors that may lead to improved thermal stability from an evolutionary perspective, thereby improving thermal stability. Combine the existing proteinase K structural informatio...
Embodiment 2
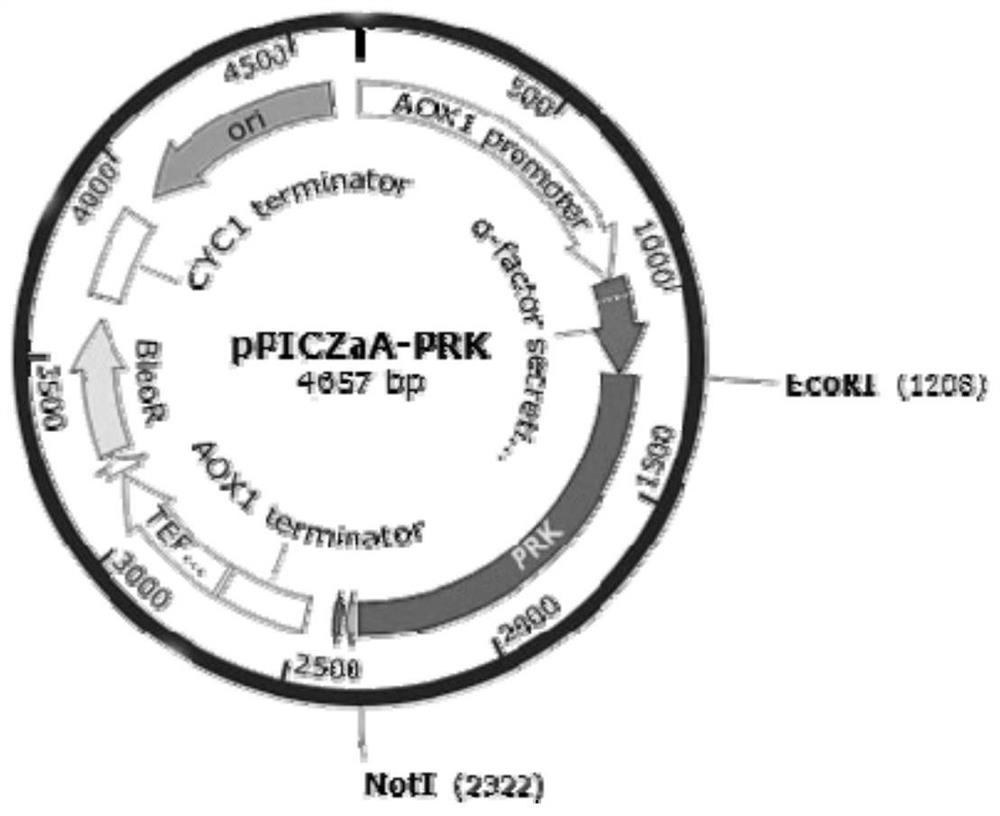
[0174] Embodiment 2: Construction of the recombinant expression vector carrying the nucleotide sequence encoding proteinase K mutant
[0175] As described in Example 1, it is determined that the 350th amino acid of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2 is used as the key site, and the mutants shown in SEQ ID NO.3 and SEQ ID NO.4 are designed, that is: single Mutant D350V, combined mutant Y151A / K208H / S273T / G293A / K332R / S337N / D350V. Specific steps are as follows:
[0176] The amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO.2 was reverse-transcribed and optimized according to the codons of Pichia pastoris to obtain the nucleotide sequence SEQ ID NO.5; the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO.3 was reverse-transcribed according to the Pichia The yeast codon was optimized to obtain the nucleotide sequence SEQ ID NO.6; the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO.4 was reverse-transcribed and then optimized according to the Pichia pastoris codon to obtain the nucleotide sequence SEQ ID NO.7; respective...
Embodiment 3
[0178] The construction of the recombinant microorganism cell of embodiment 3 expression proteinase K mutants
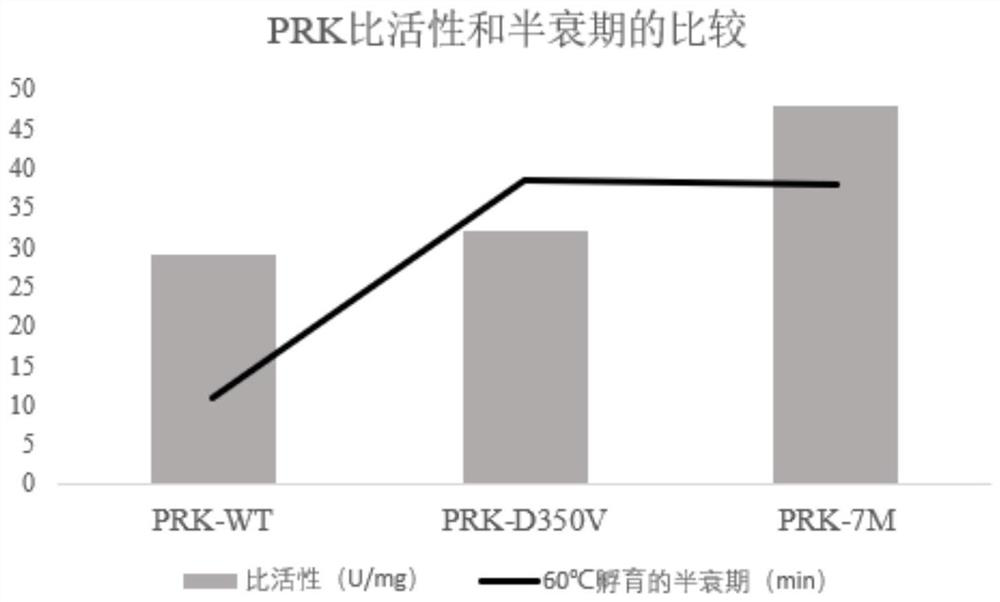
[0179] After the recombinant expression vector constructed in Example 2 was linearized with BglII, it was transformed into Pichia pastoris X33 competent cells by electroporation to obtain recombinant strains expressing proteinase K wild type and mutant, respectively named PRK-WT (for expression of wild-type proteinase K), PRK-D350V (for expression of mutant D350V), PRK-7M (for expression of combined mutant Y151A / K208H / S273T / G293A / K332R / S337N / D350V). The protein sequences of the expressed proteinase K correspond to the amino acid sequences shown in SEQ ID NO.2, SEQ ID NO.3 and SEQ ID NO.4 respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com