Method for modifying carbide of austenitic heat-resistant steel
A technology of austenitic heat-resistant steel and carbide, which is applied in the field of iron and steel metallurgy, can solve the problems of decreased impact toughness, easy nozzle accumulation, serious splashing, etc., achieve plasticity and strength improvement, reduce production cost, and wire feeding process stable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
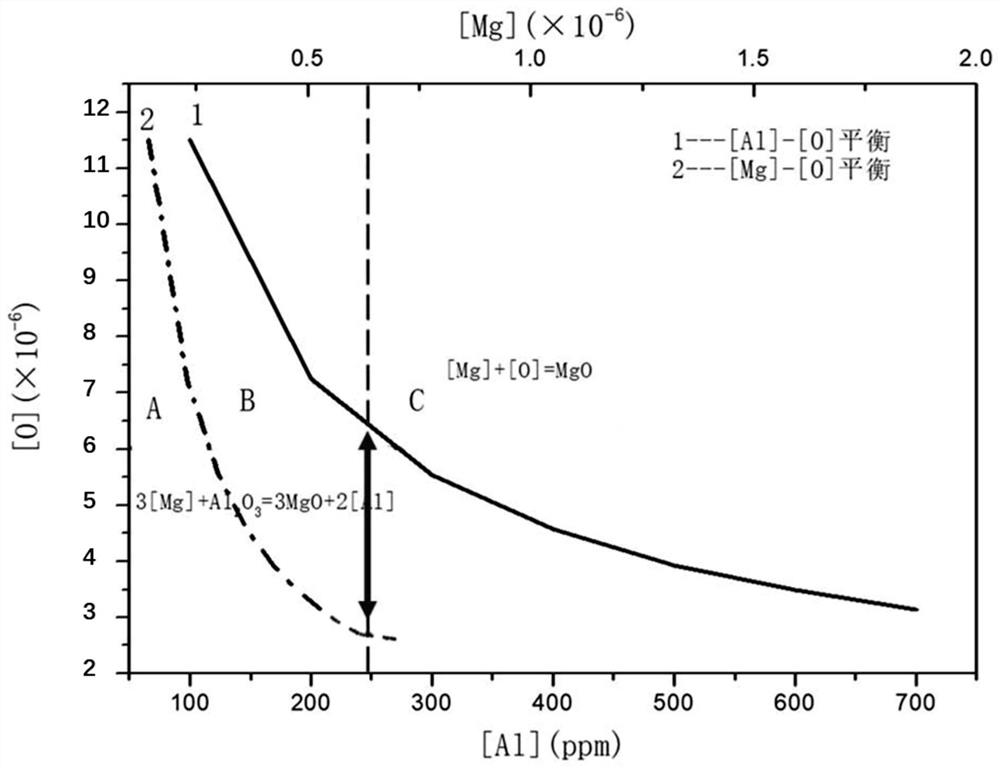
[0065]This embodiment provides a method for modifying carbides of austenitic heat-resistant steel, which includes sequentially smelting magnesium-containing austenitic heat-resistant steel raw materials through a 40t steel electric furnace, AOD furnace smelting, LF furnace refining, and feeding Nickel-magnesium cored wire, continuous casting, rolling, total solution and aging solution to obtain modified austenitic heat-resistant steel; among them, at the end of LF furnace refining, under the condition of bottom blowing argon, intermittently multiple times Feed nickel-magnesium cored wire. When feeding nickel-magnesium cored wire, the basicity value of the molten steel slag layer in the LF furnace is 5.5. The amount is 1.6 tons, and the amount of slag is controlled to be no more than 1.6 tons. The temperature of the molten steel is controlled at 1450±5°C while preventing the oxidation of the molten steel while reducing the volatilization of magnesium vapor. The mass percentage o...
Embodiment 2
[0070] This embodiment provides a method for modifying carbides of austenitic heat-resistant steel, which includes sequentially smelting magnesium-containing austenitic heat-resistant steel raw materials through a 40t steel electric furnace, AOD furnace smelting, LF furnace refining, and feeding Nickel-magnesium cored wire, die casting, blooming, rolling, full solution and aging solution to obtain modified austenitic heat-resistant steel; among them, at the end of LF furnace refining, under the condition of bottom blowing argon , Feed the nickel-magnesium cored wire intermittently multiple times, compared with the embodiment, more than 20% of the nickel-magnesium cored wire is fed into the nickel-magnesium cored wire, the molten steel slag layer alkalinity value in the LF furnace is 5.5, The amount of slag in molten steel is greater than 4% of the amount of molten steel, the refining time of white slag is greater than 25 minutes, the amount of slag is 1.6 tons, the temperature ...
Embodiment 3
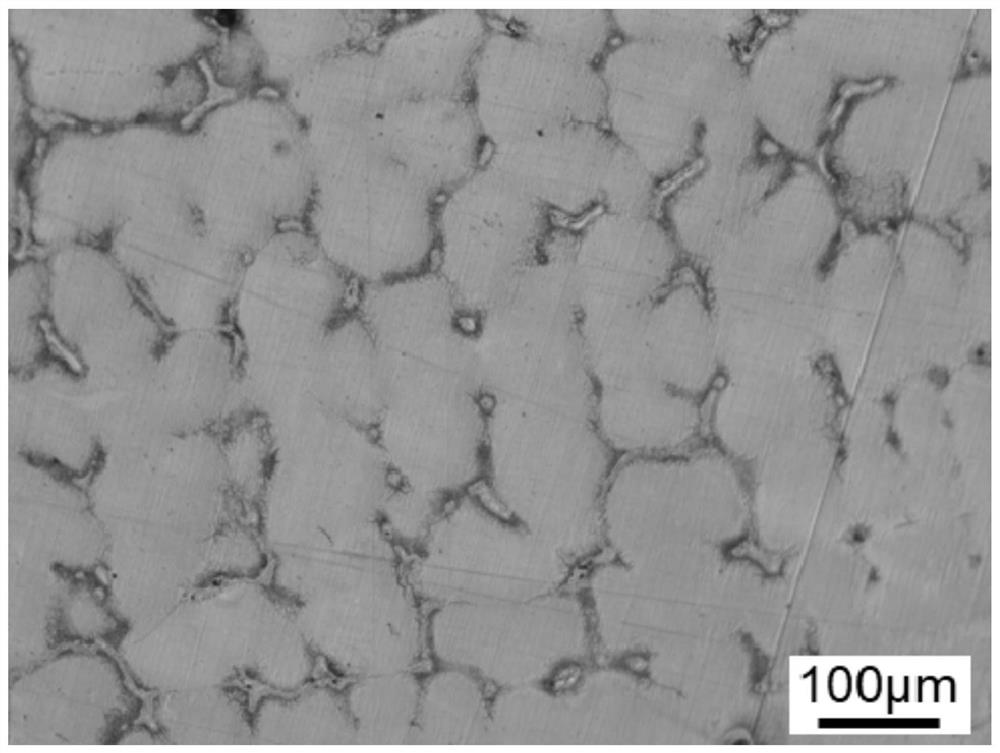
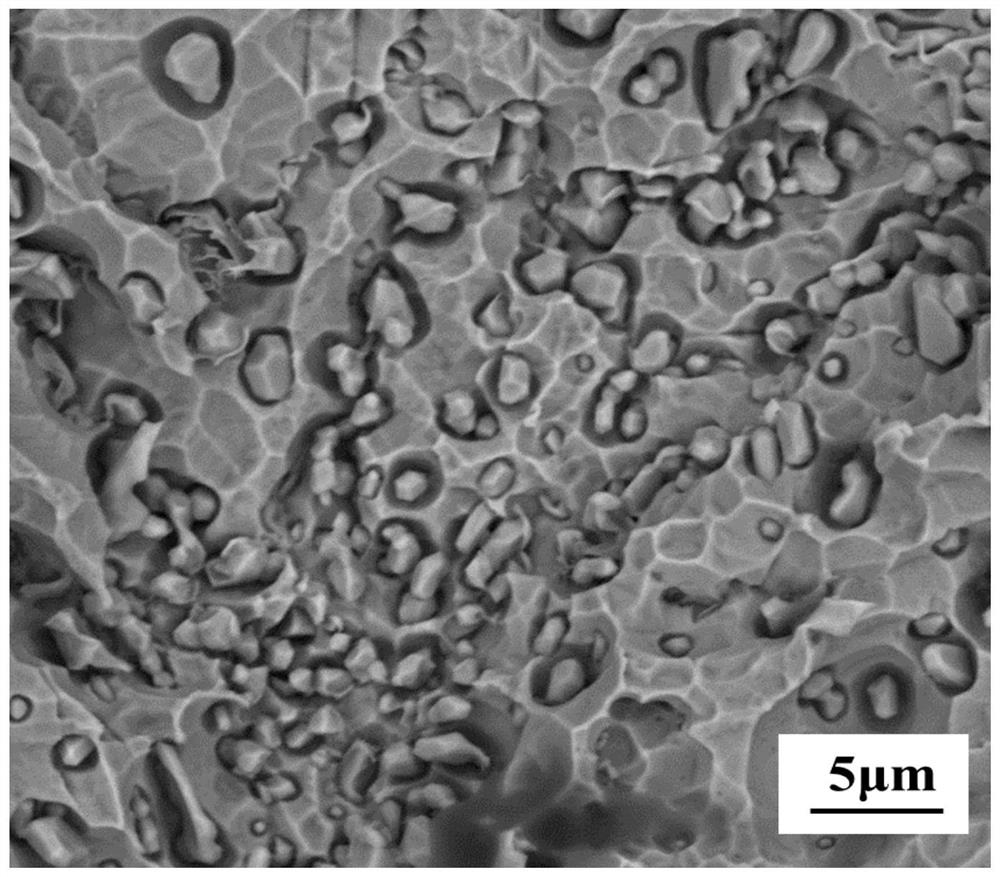
[0075] Compared with Example 1, the method for modifying austenitic heat-resistant steel carbide in this example is different in that the composition of the magnesium-containing cored wire fed is different, and the composition of the magnesium-containing cored wire core material used is based on mass percentage It is calculated as Mg 15%, Ni 15%, Cr 25%, N 0.6%, and the balance is Fe and unavoidable impurity elements. In the on-site production of this embodiment, the wire feeding process is stable, the reaction is gentle, and there is no violent splashing.
[0076] The modified austenitic heat-resistant steel prepared in this example has a magnesium content of 16 ppm as measured by ICP, and the magnesium yield calculated according to the added amount is 29%. It can be seen from calculation and verification that the composition of the magnesium-containing austenitic heat-resistant steel prepared in this example is by mass percentage: C 0.5%, Si 0.31%, Mn 8.75%, P 0.02%, S 0.01%...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com